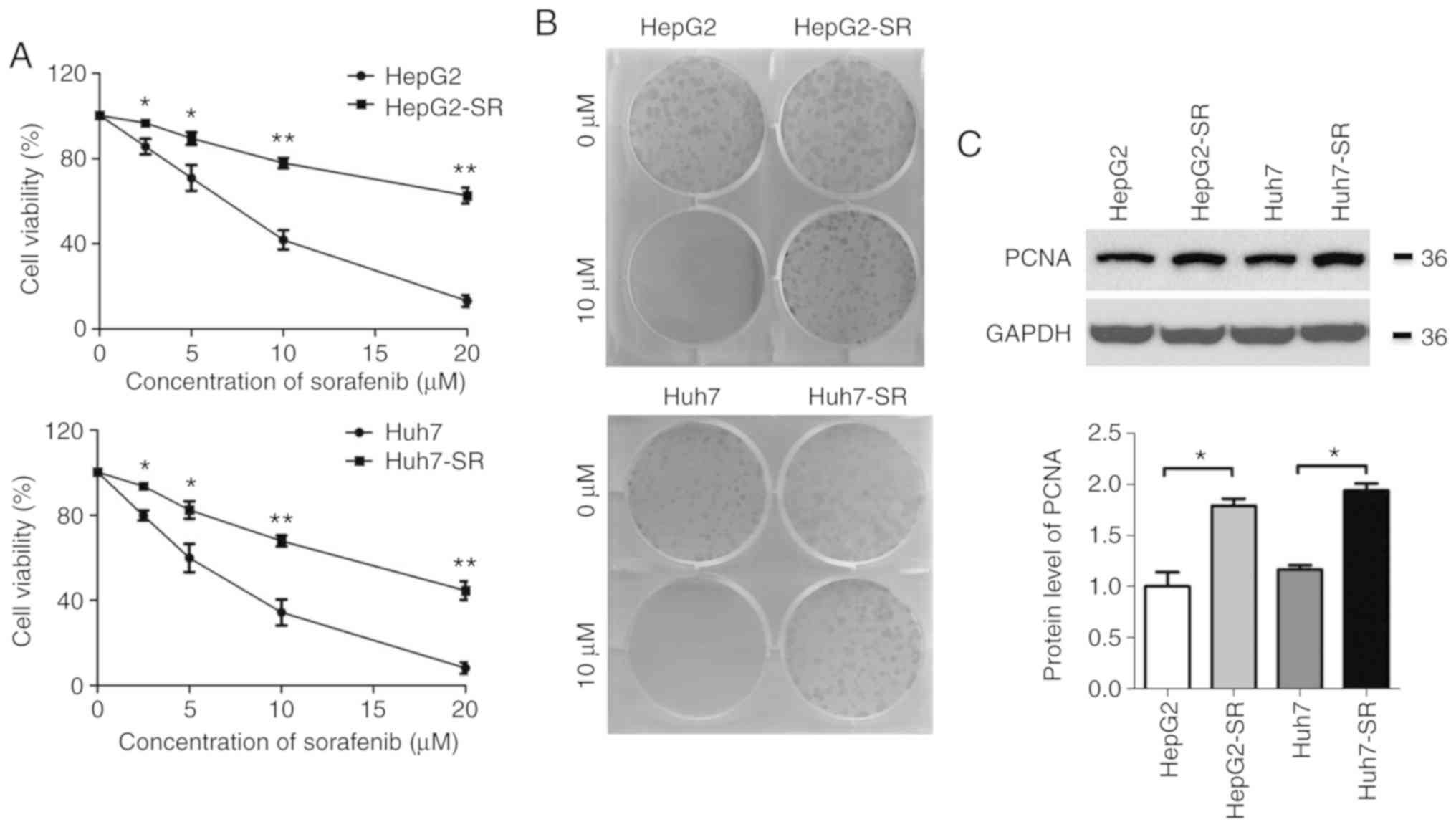
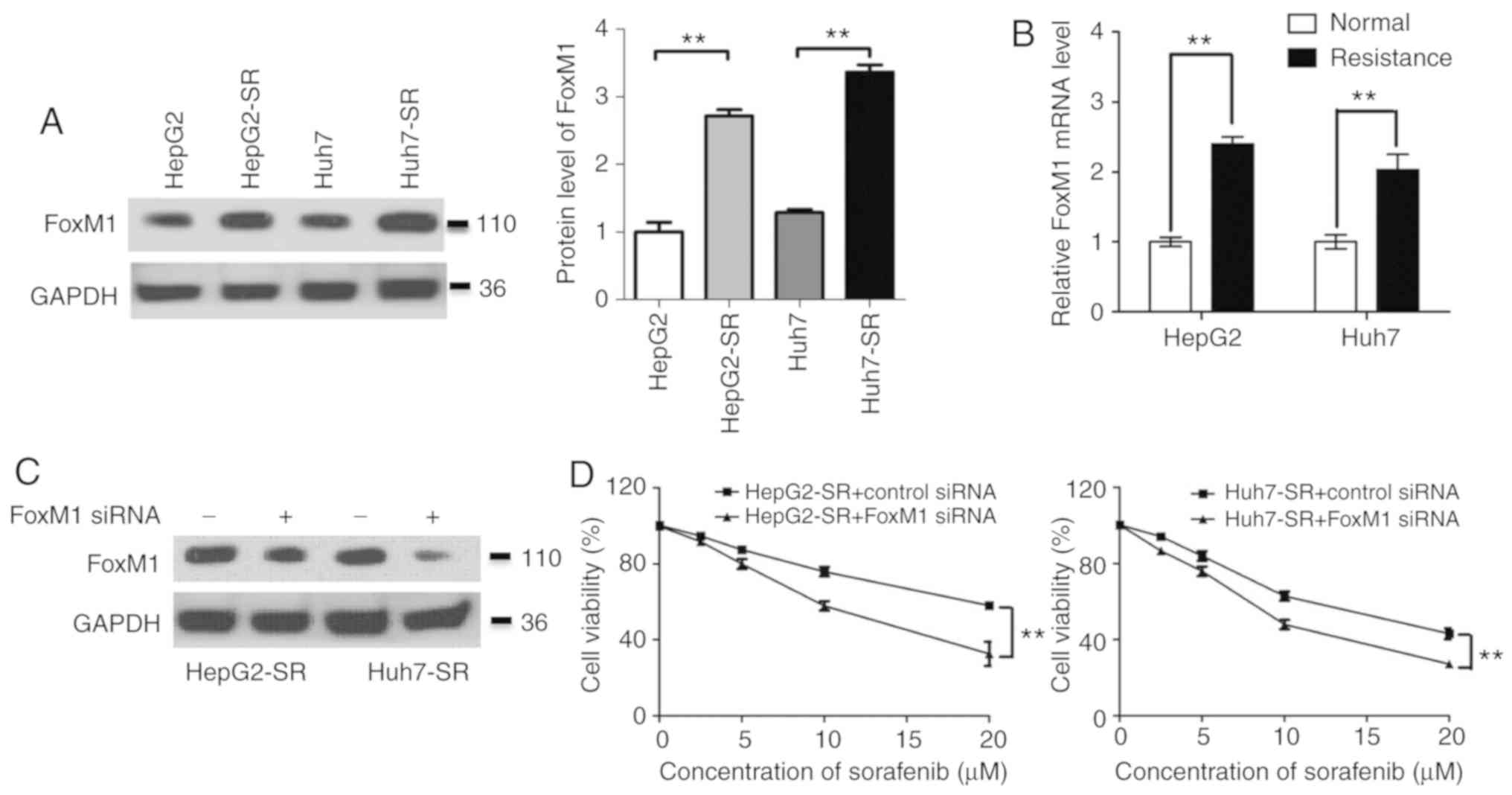
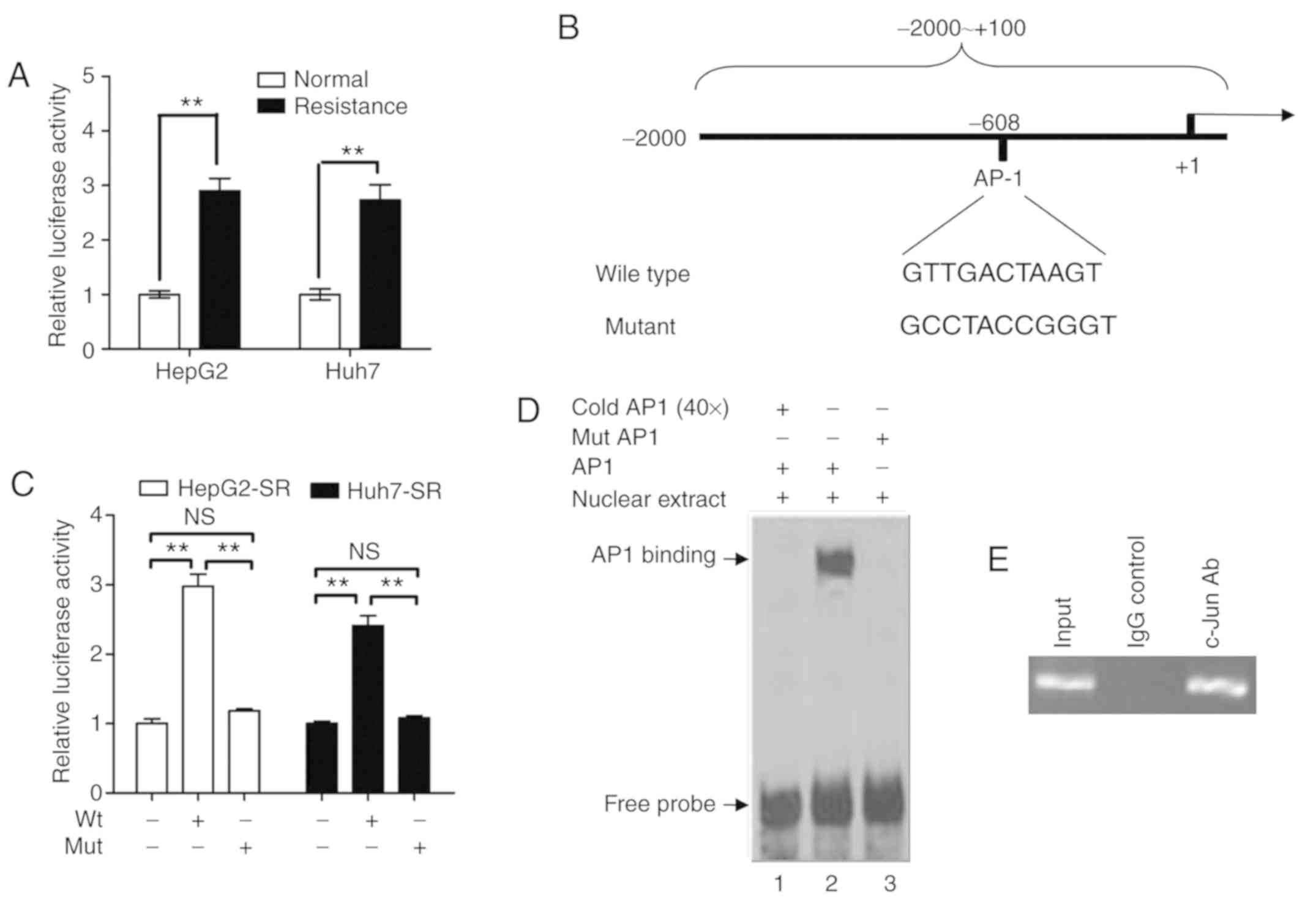
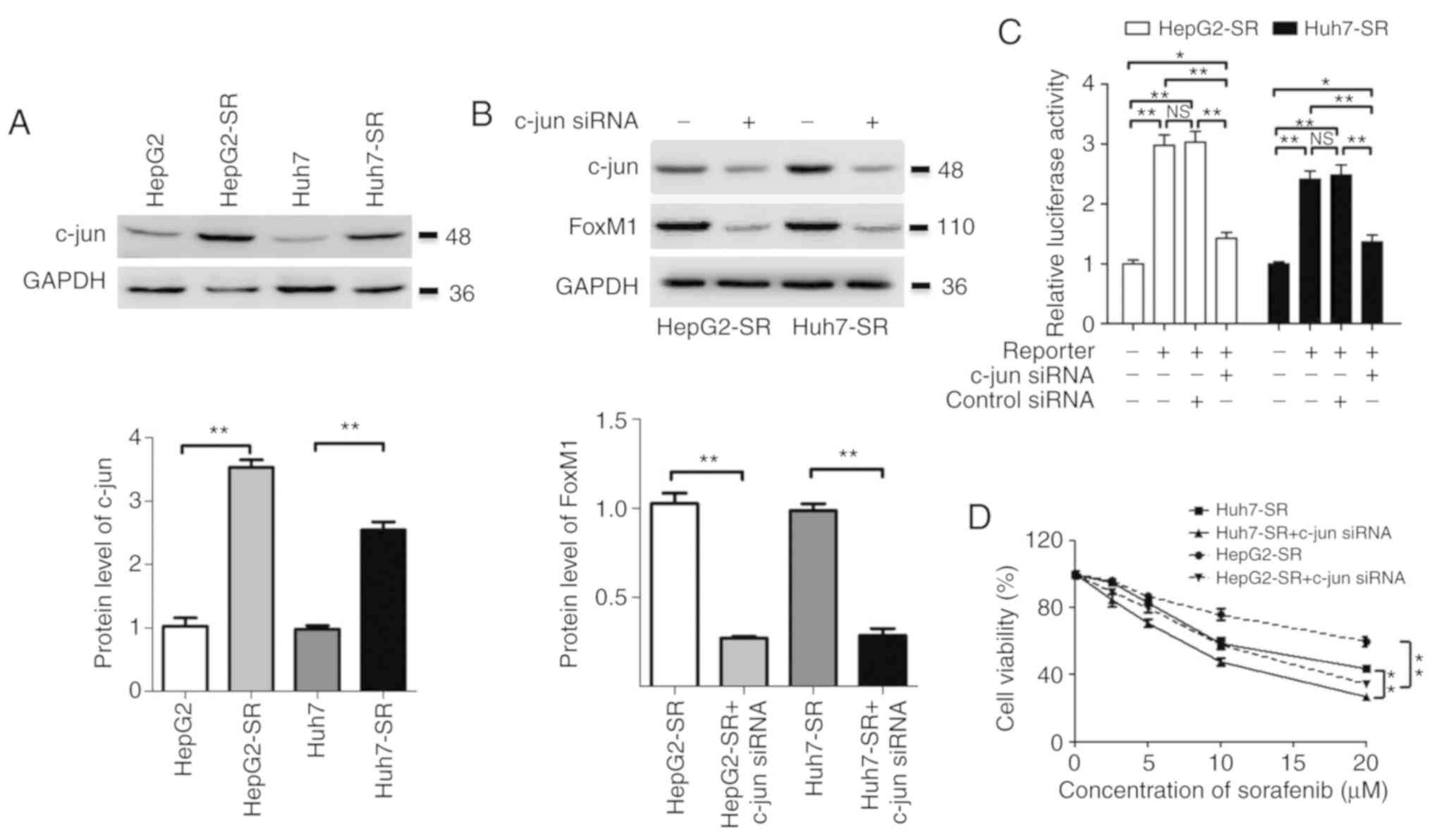
|
1
|
Khemlina G, Ikeda S and Kurzrock R: The
biology of Hepatocellular carcinoma: Implications for genomic and
immune therapies. Mol Cancer. 16:1492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee DH and Lee JM: Primary malignant
tumours in the non-cirrhotic liver. Eur J Radiol. 95:349–361. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eso Y and Marusawa H: Novel approaches for
molecular targeted therapy against hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatol Res. 48:597–607. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ray EM and Sanoff HK: Optimal therapy for
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and resistance or
intolerance to sorafenib: Challenges and solutions. J Hepatocell
Carcinoma. 4:131–138. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yao S, Fan LY and Lam EW: The FOXO3-FOXM1
axis: A key cancer drug target and a modulator of cancer drug
resistance. Semin Cancer Biol. 50:77–89. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Frau M, Feo F and Pascale RM: Pleiotropic
effects of methionine adenosyltransferases deregulation as
determinants of liver cancer progression and prognosis. J Hepatol.
59:830–841. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang IC, Chen YJ, Hughes D, Petrovic V,
Major ML, Park HJ, Tan Y, Ackerson T and Costa RH: Forkhead box M1
regulates the transcriptional network of genes essential for
mitotic progression and genes encoding the SCF (Skp2-Cks1)
ubiquitin ligase. Mol Cell Biol. 25:10875–10894. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Z, Ahmad A, Li Y, Banerjee S, Kong D
and Sarkar FH: Forkhead box M1 transcription factor: A novel target
for cancer therapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 36:151–156. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Laoukili J, Stahl M and Medema RH: FoxM1:
At the crossroads of ageing and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1775:92–102. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma RY, Tong TH, Leung WY and Yao KM:
Raf/MEK/MAPK signaling stimulates the nuclear translocation and
transactivating activity of FOXM1. Methods Mol Biol. 647:113–123.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Balli D, Zhang Y, Snyder J, Kalinichenko
VV and Kalin TV: Endothelial cell-specific deletion of
transcription factor FoxM1 increases urethane-induced lung
carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 71:40–50. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Y, Zhang N, Dai B, Liu M, Sawaya R,
Xie K and Huang S: FoxM1B transcriptionally regulates vascular
endothelial growth factor expression and promotes the angiogenesis
and growth of glioma cells. Cancer Res. 68:8733–8742. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Z, Banerjee S, Kong D, Li Y and
Sarkar FH: Down-regulation of Forkhead Box M1 transcription factor
leads to the inhibition of invasion and angiogenesis of pancreatic
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 67:8293–8300. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan Y, Raychaudhuri P and Costa RH: Chk2
mediates stabilization of the FoxM1 transcription factor to
stimulate expression of DNA repair genes. Mol Cell Biol.
27:1007–1016. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Myatt SS and Lam EW: The emerging roles of
forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:847–859.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kwok JM, Peck B, Monteiro LJ, Schwenen HD,
Millour J, Coombes RC, Myatt SS and Lam EW: FOXM1 confers acquired
cisplatin resistance in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res.
8:24–34. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Carr JR, Park HJ, Wang Z, Kiefer MM and
Raychaudhuri P: FoxM1 mediates resistance to herceptin and
paclitaxel. Cancer Res. 70:5054–5063. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sebaugh JL: Guidelines for accurate
EC50/IC50 estimation. Pharm Stat. 10:128–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang F, Wu Q, Zhang Y, Xiong H, Li X, Li
B, Xie W, Zhang L, Xu M, Zhang K and He F: LncRNA LOC653786
promotes growth of RCC cells via upregulating FOXM1. Oncotarget.
9:12101–12111. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhai B, Hu F, Jiang X, Xu J, Zhao D, Liu
B, Pan S, Dong X, Tan G, Wei Z, et al: Inhibition of Akt reverses
the acquired resistance to sorafenib by switching protective
autophagy to autophagic cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol
Cancer Ther. 13:1589–1598. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
da Motta Girardi D, Correa TS, Crosara
Teixeira M and Dos Santos Fernandes G: Hepatocellular carcinoma:
Review of targeted and immune therapies. J Gastrointest Cancer.
49:227–236. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu QF, Liu C, Tai MH, Liu D, Lei L, Wang
RT, Tian M and Lü Y: Knockdown of FoxM1 by siRNA interference
decreases cell proliferation, induces cell cycle arrest and
inhibits cell invasion in MHCC-97H cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 31:361–366. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qu K, Xu X, Liu C, Wu Q, Wei J, Meng F,
Zhou L, Wang Z, Lei L and Liu P: Negative regulation of
transcription factor FoxM1 by p53 enhances oxaliplatin-induced
senescence in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 331:105–114.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun H, Teng M, Liu J, Jin D, Wu J, Yan D,
Fan J, Qin X, Tang H and Peng Z: FOXM1 expression predicts the
prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients after orthotopic
liver transplantation combined with the Milan criteria. Cancer
Lett. 306:214–222. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wei JC, Meng FD, Qu K, Wang ZX, Wu QF,
Zhang LQ, Pang Q and Liu C: Sorafenib inhibits proliferation and
invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via up-regulation
of p53 and suppressing FoxM1. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 36:241–251. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tian C, Wu H, Li C, Tian X, Sun Y, Liu E,
Liao X and Song W: Downreguation of FoxM1 by miR-214 inhibits
proliferation and migration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gene Ther.
25:312–319. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hu Q, Du K, Mao X and Ning S: miR-197 is
downregulated in cervical carcinogenesis and suppresses cell
proliferation and invasion through targeting forkhead box M1. Oncol
Lett. 15:10063–10069. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Segal NH, He AR, Doi T, Levy R, Bhatia S,
Pishvaian MJ, Cesari R, Chen Y, Davis CB, Huang B, et al: Phase I
study of single-agent utomilumab (PF-05082566), a 4-1BB/CD137
agonist, in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
24:1816–1823. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tian L, Zhao Z, Xie L and Zhu J:
MiR-361-5p suppresses chemoresistance of gastric cancer cells by
targeting FOXM1 via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncotarget.
9:4886–4896. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cao S, Lin L, Xia X and Wu H: MicroRNA-761
promotes the sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to
5-Fluorouracil through targeting FOXM1. Oncotarget. 9:321–331.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
He S, Liao B, Deng Y, Su C, Tuo J, Liu J,
Yao S and Xu L: MiR-216b inhibits cell proliferation by targeting
FOXM1 in cervical cancer cells and is associated with better
prognosis. BMC Cancer. 17:6732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yuan Y, Haiying G, Zhuo L, Ying L and Xin
H: Long non-coding RNA LINC00339 facilitates the tumorigenesis of
non-small cell lung cancer by sponging miR-145 through targeting
FOXM1. Biomed Pharmacother. 105:707–713. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li XY, Wu HY, Mao XF, Jiang LX and Wang
YX: USP5 promotes tumorigenesis and progression of pancreatic
cancer by stabilizing FoxM1 protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
492:48–54. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Guo L, Ding Z, Huang N, Huang Z, Zhang N
and Xia Z: Forkhead Box M1 positively regulates UBE2C and protects
glioma cells from autophagic death. Cell Cycle. 16:1705–1718. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kongsema M, Zona S, Karunarathna U,
Cabrera E, Man EP, Yao S, Shibakawa A, Khoo US, Medema RH, Freire R
and Lam EW: RNF168 cooperates with RNF8 to mediate FOXM1
ubiquitination and degradation in breast cancer epirubicin
treatment. Oncogenesis. 5:e2522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pan H, Zhu Y, Wei W, Shao S and Rui X:
Transcription factor FoxM1 is the downstream target of c-Myc and
contributes to the development of prostate cancer. World J Surg
Oncol. 16:592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qi W, Li X, Zhang Y, Yao R, Qiu W, Tang D
and Liang J: Overexpression of Her-2 upregulates FoxM1 in gastric
cancer. Int J Mol Med. 33:1531–1538. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bai C, Liu X, Qiu C and Zheng J: FoxM1 is
regulated by both HIF-1α and HIF-2α and contributes to
gastrointestinal stromal tumor progression. Gastric Cancer.
22:91–103. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Eferl R and Wagner EF: AP-1: A
double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:859–868.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fuest M, Willim K, Macnelly S, Fellner N,
Resch GP, Blum HE and Hasselblatt P: The transcription factor c-Jun
protects against sustained hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress
thereby promoting hepatocyte survival. Hepatology. 55:408–418.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Min L, Ji Y, Bakiri L, Qiu Z, Cen J, Chen
X, Chen L, Scheuch H, Zheng H, Qin L, et al: Liver cancer
initiation is controlled by AP-1 through SIRT6-dependent inhibition
of survivin. Nat Cell Biol. 14:1203–1211. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Haga Y, Kanda T, Nakamura M, Nakamoto S,
Sasaki R, Takahashi K, Wu S and Yokosuka O: Overexpression of c-Jun
contributes to sorafenib resistance in human hepatoma cell lines.
PLoS One. 12:e01741532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kunter I, Erdal E, Nart D, Yilmaz F,
Karademir S, Sagol O and Atabey N: Active form of AKT controls cell
proliferation and response to apoptosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 31:573–580. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dong J, Zhai B, Sun W, Hu F, Cheng H and
Xu J: Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/snail
signaling pathway contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal
transition-induced multi-drug resistance to sorafenib in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 12:e01850882017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang PF, Li KS, Shen YH, Gao PT, Dong ZR,
Cai JB, Zhang C, Huang XY, Tian MX, Hu ZQ, et al: Galectin-1
induces hepatocellular carcinoma EMT and sorafenib resistance by
activating FAK/PI3K/AKT signaling. Cell Death Dis. 7:e22012016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gedaly R, Angulo P, Chen C, Creasy KT,
Spear BT, Hundley J, Daily MF, Shah M and Evers BM: The role of
PI3K/mTOR inhibition in combination with sorafenib in
hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. Anticancer Res. 32:2531–2536.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang H, Wang Q, Liu J and Cao H:
Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway reverses
sorafenib-derived chemo-resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncol Lett. 15:9377–9384. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kumar D, Tewari-Singh N, Agarwal C, Jain
AK, Inturi S, Kant R, White CW and Agarwal R: Nitrogen mustard
exposure of murine skin induces DNA damage, oxidative stress and
activation of MAPK/Akt-AP1 pathway leading to induction of
inflammatory and proteolytic mediators. Toxicol Lett. 235:161–71.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|