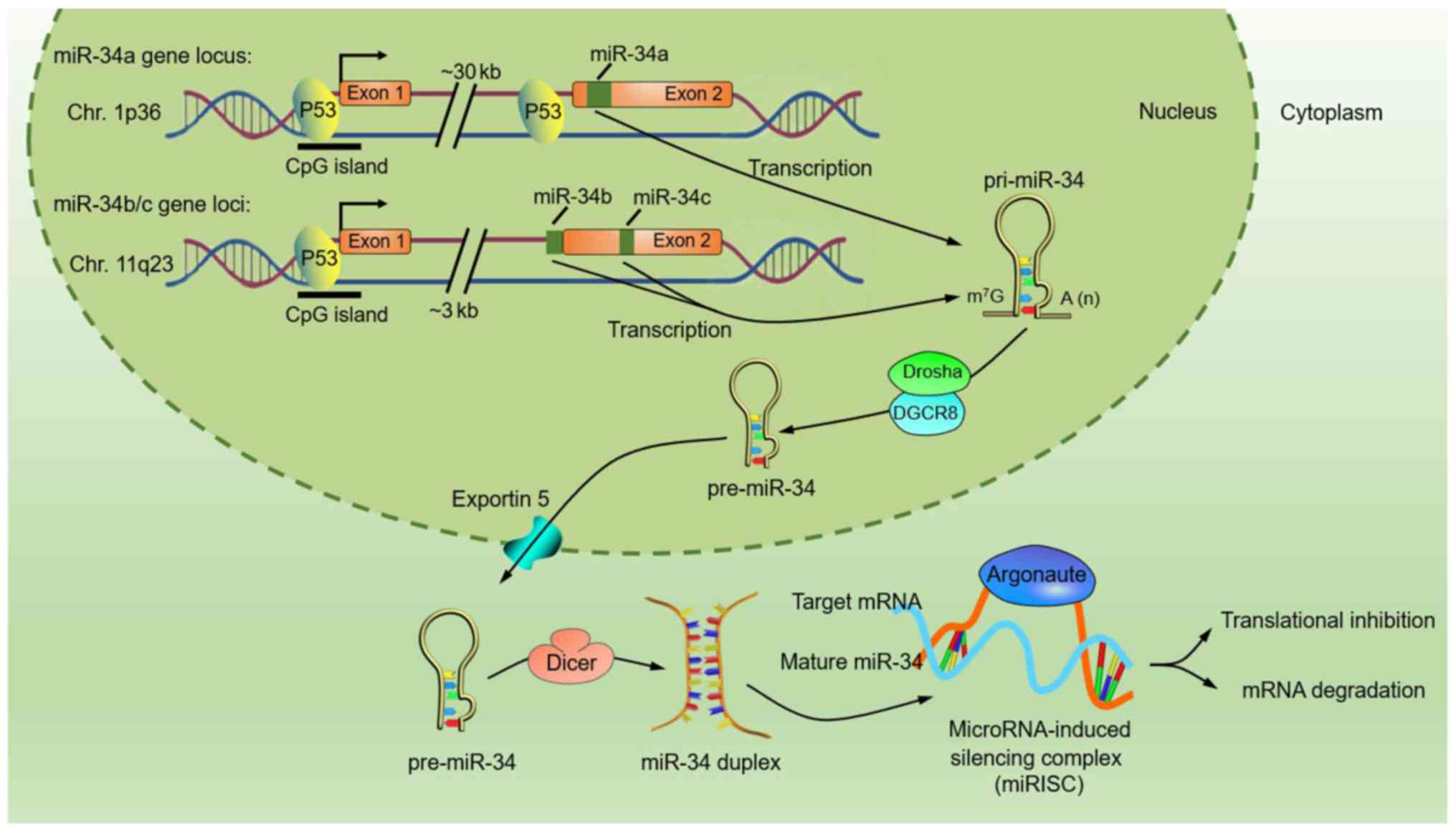
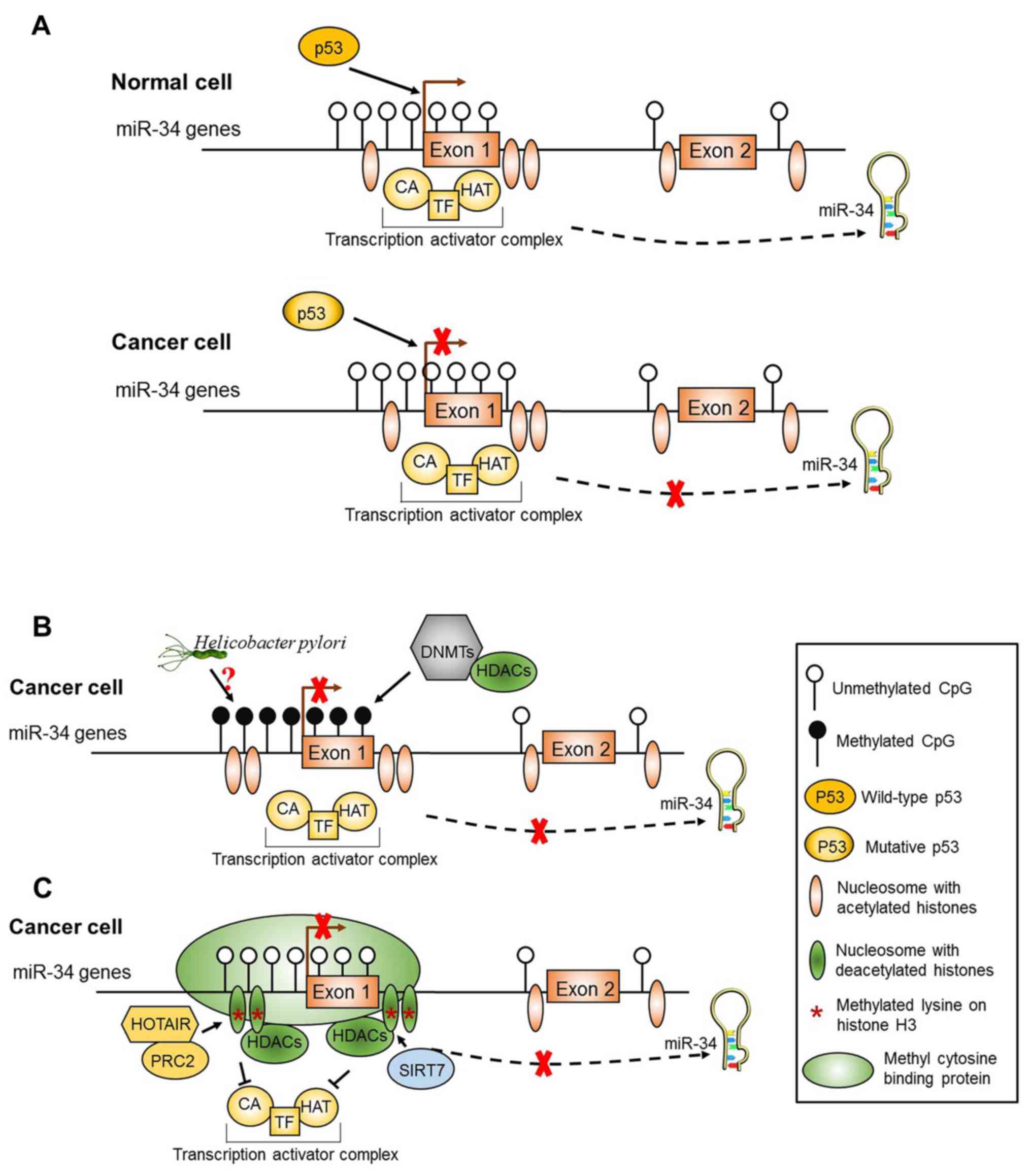
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Plummer M, Franceschi S, Vignat J, Forman
D and Martel C: Global burden of gastric cancer attributable to
Helicobacter pylori. Int J Cancer. 136:487–490. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tsugane S and Sasazuki S: Diet and the
risk of gastric cancer: Review of epidemiological evidence. Gastric
Cancer. 10:75–83. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pasquinelli AE: MicroRNAs and their
targets: Recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal
relationship. Nat Rev Genet. 13:271–282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hayes J, Peruzzi PP and Lawler S:
MicroRNAs in cancer: Biomarkers, functions and therapy. Trends Mol
Med. 20:460–469. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bommer GT, Gerin I, Feng Y, Kaczorowski
AJ, Kuick R, Love RE, Zhai Y, Giordano TJ, Qin ZS, Moore BB, et al:
p53-mediated activation of miRNA34 candidate tumor-suppressor
genes. Curr Biol. 17:1298–1307. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dingli D and Michor F: Successful therapy
must eradicate cancer stem cells. Stem Cells. 24:2603–2610. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dontu G, Al-Hajj M, Abdallah WM, Clarke MF
and Wicha MS: Stem cells in normal breast development and breast
cancer. Cell Prolif. 36 (Suppl 1):S59–S72. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ji Q, Hao X, Meng Y, Zhang M, Desano J,
Fan D and Xu L: Restoration of tumor suppressor miR-34 inhibits
human p53-mutant gastric cancer tumorspheres. BMC Cancer.
8:2662008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Versteeg R, Caron H, Cheng NC, van der
Drift P, Slater R, Westerveld A, Voûte PA, Delattre O, Laureys G,
Van Roy N, et al: 1p36: every subband a suppressor? Eur J Cancer
31A. 538–541. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rodriguez A, Griffiths-Jones S, Ashurst JL
and Bradley A: Identification of mammalian microRNA host genes and
transcription units. Genome Res. 14:1902–1910. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan
Z, Liang Y, Xue W, Zender L, Magnus J, Ridzon D, et al: A microRNA
component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature.
447:1130–1134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Krawetz SA, Kruger A, Lalancette C, Tagett
R, Anton E, Draghici S and Diamond MP: A survey of small RNAs in
human sperm. Hum Reprod. 26:3401–3412. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jafari N and Abediankenari S: MicroRNA-34
dysregulation in gastric cancer and gastric cancer stem cell.
Tumour Biol. 39:10104283177016522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Riley T, Sontag E, Chen P and Levine A:
Transcriptional control of human p53-regulated genes. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:402–412. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tarasov V, Jung P, Verdoodt B, Lodygin D,
Epanchintsev A, Menssen A, Meister G and Hermeking H: Differential
regulation of microRNAs by p53 revealed by massively parallel
sequencing: miR-34a is a p53 target that induces apoptosis and
G1-arrest. Cell Cycle. 6:1586–1593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chang TC, Wentzel EA, Kent OA,
Ramachandran K, Mullendore M, Lee KH, Feldmann G, Yamakuchi M,
Ferlito M, Lowenstein CJ, et al: Transactivation of miR-34a by p53
broadly influences gene expression and promotes apoptosis. Mol
Cell. 26:745–752. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M and Lowenstein CJ:
miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:13421–13426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Menssen A, Hydbring P, Kapelle K,
Vervoorts J, Diebold J, Lüscher B, Larsson LG and Hermeking H: The
c-MYC oncoprotein, the NAMPT enzyme, the SIRT1-inhibitor DBC1, and
the SIRT1 deacetylase form a positive feedback loop. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 109:E187–E196. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mandke P, Wyatt N, Fraser J, Bates B,
Berberich SJ and Markey MP: MicroRNA-34a modulates MDM4 expression
via a target site in the open reading frame. PLoS One.
7:e420342012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Christoffersen NR, Shalgi R, Frankel LB,
Leucci E, Lees M, Klausen M, Pilpel Y, Nielsen FC, Oren M and Lund
AH: p53-independent upregulation of miR-34a during oncogene-induced
senescence represses MYC. Cell Death Differ. 17:236–245. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Welch C, Chen Y and Stallings RL:
MicroRNA-34a functions as a potential tumor suppressor by inducing
apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene. 26:5017–5022. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Raver-Shapira N, Marciano E, Meiri E,
Spector Y, Rosenfeld N, Moskovits N, Bentwich Z and Oren M:
Transcriptional activation of miR-34a contributes to p53-mediated
apoptosis. Mol Cell. 26:731–743. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rokavec M, Li H, Jiang L and Hermeking H:
The p53/miR-34 axis in development and disease. J Mol Cell Biol.
6:214–230. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun F, Fu H, Liu Q, Tie Y, Zhu J, Xing R,
Sun Z and Zheng X: Downregulation of CCND1 and CDK6 by miR-34a
induces cell cycle arrest. FEBS Lett. 582:1564–1568. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mudduluru G, Ceppi P, Kumarswamy R,
Scagliotti GV, Papotti M and Allgayer H: Regulation of Axl receptor
tyrosine kinase expression by miR-34a and miR-199a/b in solid
cancer. Oncogene. 30:2888–2899. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang B, Li D, Kovalchuk I, Apel IJ,
Chinnaiyan AM, Wóycicki RK, Cantor CR and Kovalchuk O: miR-34a
directly targets tRNAiMet precursors and affects cellular
proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
115:7392–7397. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Grammatikakis I, Gorospe M and Abdelmohsen
K: Modulation of cancer traits by tumor suppressor microRNAs. Int J
Mol Sci. 14:1822–1842. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou Y, Huang T, Siu HL, Wong CC, Dong Y,
Wu F, Zhang B, Wu WK, Cheng AS, Yu J, et al: IGF2BP3 functions as a
potential oncogene and is a crucial target of miR-34a in gastric
carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer. 16:772017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang AM, Huang TT, Hsu KW, Huang KH, Fang
WL, Yang MH, Lo SS, Chi CW, Lin JJ and Yeh TS: Yin Yang 1 is a
target of microRNA-34 family and contributes to gastric
carcinogenesis. Oncotarget. 5:5002–5016. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mert U, Ozgür E, Tiryakioglu D, Dalay N
and Gezer U: Induction of p53-inducible microRNA miR-34 by gamma
radiation and bleomycin are different. Front Genet. 3:2202012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Polyak K, Xia Y, Zweier JL, Kinzler KW and
Vogelstein B: A model for p53-induced apoptosis. Nature.
389:300–305. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shen Z, Zhan G, Ye D, Ren Y, Cheng L, Wu Z
and Guo J: MicroRNA-34a affects the occurrence of laryngeal
squamous cell carcinoma by targeting the antiapoptotic gene
survivin. Med Oncol. 29:2473–2480. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Deng X, Zheng H, Li D, Xue Y, Wang Q, Yan
S, Zhu Y and Deng M: MicroRNA-34a regulates proliferation and
apoptosis of gastric cancer cells by targeting silent information
regulator 1. Exp Ther Med. 15:3705–3714. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lin L, Jiang H, Huang M, Hou X, Sun X,
Jiang X, Dong X, Sun X, Zhou B and Qiao H: Depletion of histone
deacetylase 1 inhibits metastatic abilities of gastric cancer cells
by regulating the miR-34a/CD44 pathway. Oncol Rep. 34:663–672.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ha SY, Lee J, Kang SY, Do IG, Ahn S, Park
JO, Kang WK, Choi MG, Sohn TS, Bae JM, et al: MET overexpression
assessed by new interpretation method predicts gene amplification
and poor survival in advanced gastric carcinomas. Mod Pathol.
26:1632–1641. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Takaishi S, Okumura T, Tu S, Wang SS,
Shibata W, Vigneshwaran R, Gordon SA, Shimada Y and Wang TC:
Identification of gastric cancer stem cells using the cell surface
marker CD44. Stem Cells. 27:1006–1020. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pu Y, Zhao F, Wang H and Cai S: miR-34a-5p
promotes multi-chemoresistance of osteosarcoma through
down-regulation of the DLL1 gene. Sci Rep. 7:442182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Krause CJ, Popp O, Thirunarayanan N,
Dittmar G, Lipp M and Müller G: MicroRNA-34a promotes genomic
instability by a broad suppression of genome maintenance mechanisms
downstream of the oncogene KSHV-vGPCR. Oncotarget. 7:10414–10432.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dutta KK, Zhong Y, Liu YT, Yamada T,
Akatsuka S, Hu Q, Yoshihara M, Ohara H, Takehashi M, Shinohara T,
et al: Association of microRNA-34a overexpression with
proliferation is cell type-dependent. Cancer Sci. 98:1845–1852.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hao Q, Lu X, Liu N, Xue X, Li M, Zhang C,
Qin X, Li W, Shu Z, Song B, et al: Posttranscriptional deregulation
of Src due to aberrant miR34a and miR203 contributes to gastric
cancer development. BMB Rep. 46:316–321. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu G, Jiang C, Li D, Wang R and Wang W:
miRNA-34a inhibits EGFR-signaling-dependent MMP7 activation in
gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:9801–9806. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cao W, Fan R, Wang L, Cheng S, Li H, Jiang
J, Geng M, Jin Y and Wu Y: Expression and regulatory function of
miRNA-34a in targeting survivin in gastric cancer cells. Tumor
Biol. 34:963–971. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Cao W, Yang W, Fan R, Li H, Jiang J, Geng
M, Jin Y and Wu Y: miR-34a regulates cisplatin-induce gastric
cancer cell death by modulating PI3K/AKT/survivin pathway. Tumour
Biol. 35:1287–1295. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Peng Y, Guo JJ, Liu YM and Wu XL:
MicroRNA-34A inhibits the growth, invasion and metastasis of
gastric cancer by targeting PDGFR and MET expression. Biosci Rep.
34(pii): e001122014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
He M, Gao L, Zhang S, Tao L, Wang J, Yang
J and Zhu M: Prognostic significance of miR-34a and its target
proteins of FOXP1, p53, and BCL2 in gastric MALT lymphoma and
DLBCL. Gastric Cancer. 17:431–441. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wei B, Huang QY, Huang SR, Mai W and Zhong
XG: MicroRNA-34a attenuates the proliferation, invasion and
metastasis of gastric cancer cells via downregulation of MET. Mol
Med Rep. 12:5255–5261. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang Z, Kong Y, Yang W, Ma F, Zhang Y, Ji
S, Ma EM, Liu H, Chen Y and Hua Y: Upregulation of microRNA-34a
enhances the DDP sensitivity of gastric cancer cells by modulating
proliferation and apoptosis via targeting MET. Oncol Rep.
36:2391–2397. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu YW, Sun M, Xia R, Zhang EB, Liu XH,
Zhang ZH, Xu TP, De W, Liu BR and Wang ZX: LincHOTAIR
epigenetically silences miR34a by binding to PRC2 to promote the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human gastric cancer. Cell
Death. 6:e18022015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Hu Y, Pu Q, Cui B and Lin J: MicroRNA-34a
inhibits tumor invasion and metastasis in gastric cancer by
targeting Tgif2. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:8921–8928.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jang E, Kim E, Son HY, Lim EK, Lee H, Choi
Y, Park K, Han S, Suh JS, Huh YM and Haam S: Nanovesicle-mediated
systemic delivery of microRNA-34a for CD44 overexpressing gastric
cancer stem cell therapy. Biomaterials. 105:12–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kim S-M, Hur DY, Hong SW and Kim JH:
EBV-encoded EBNA1 regulates cell viability by modulating
miR34a-NOX2-ROS signaling in gastric cancer cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 494:550–555. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bader AG: miR-34-a microRNA replacement
therapy is headed to the clinic. Front Genet. 3:1202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hui WT, Ma XB, Zan Y, Wang XJ and Dong L:
Prognostic significance of miR-34a expression in patients with
gastric cancer after radical gastrectomy. Chin Med J (Engl).
128:2632–2637. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kim CH, Kim HK, Rettig RL, Kim J, Lee ET,
Aprelikova O, Choi IJ, Munroe DJ and Green JE: miRNA signature
associated with outcome of gastric cancer patients following
chemotherapy. BMC Med Genomics. 4:792011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Suzuki H, Yamamoto E, Nojima M, Kai M,
Yamano HO, Yoshikawa K, Kimura T, Kudo T, Harada E, Sugai T, et al:
Methylation-associated silencing of microRNA-34b/c in gastric
cancer and its involvement in an epigenetic field defect.
Carcinogenesis. 31:2066–2073. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Stánitz E, Juhász K, Tóth C, Gombos K,
Natali PG and Ember I: Evaluation of MicroRNA expression pattern of
gastric adenocarcinoma associated with socioeconomic, environmental
and lifestyle factors in northwestern Hungary. Anticancer Res.
33:3195–3200. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Katada T, Ishiguro H, Kuwabara Y, Kimura
M, Mitui A, Mori Y, Ogawa R, Harata K and Fujii Y: microRNA
expression profile in undifferentiated gastric cancer. Int J Oncol.
34:537–542. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yao Y, Suo AL, Li ZF, Liu LY, Tian T, Ni
L, Zhang WG, Nan KJ, Song TS and Huang C: MicroRNA profiling of
human gastric cancer. Mol Med Rep. 2:963–970. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Osawa S, Shimada Y, Sekine S, Okumura T,
Nagata T, Fukuoka J and Tsukada K: MicroRNA profiling of gastric
cancer patients from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples.
Oncol Lett. 2:613–619. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Su Y, Ni Z, Wang G, Cui J, Wei C, Wang J,
Yang Q, Xu Y and Li F: Aberrant expression of microRNAs in gastric
cancer and biological significance of miR-574-3p. Int
Immunopharmacol. 13:468–475. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Tsukamoto Y, Nakada C, Noguchi T, Tanigawa
M, Nguyen LT, Uchida T, Hijiya N, Matsuura K, Fujioka T, Seto M and
Moriyama M: MicroRNA-375 is downregulated in gastric carcinomas and
regulates cell survival by targeting PDK1 and 14-3-3zeta. Cancer
Res. 70:2339–2349. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Tsai KW, Wu CW, Hu LY, Li SC, Liao YL, Lai
CH, Kao HW, Fang WL, Huang KH, Chan WC and Lin WC: Epigenetic
regulation of miR-34b and miR-129 expression in gastric cancer. Int
J Cancer. 129:2600–2610. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Liu D, Hu X, Zhou H, Shi G and Wu J:
Identification of aberrantly expressed miRNAs in gastric cancer.
Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014:4738172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhang H, Li S, Yang J, Liu S, Gong X and
Yu X: The prognostic value of miR-34a expression in completely
resected gastric cancer: Tumor recurrence and overall survival. Int
J Clin Exp Med. 8:2635–2641. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yang B, Huang J, Liu H, Guo W and Li G:
miR-335 directly, while miR-34a indirectly modulate survivin
expression and regulate growth, apoptosis, and invasion of gastric
cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 37:1771–1779. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wang L, Yu J, Xu J, Zheng C, Li X and Du
J: The analysis of microRNA-34 family expression in human cancer
studies comparing cancer tissues with corresponding pericarcinous
tissues. Gene. 554:1–8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Hanazono K, Natsugoe S, Stein HJ, Aikou T,
Hoefler H and Siewert JR: Distribution of p53 mutations in
esophageal and gastric carcinomas and the relationship with p53
expression. Oncol Rep. 15:821–824. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Corney DC, Hwang CI, Matoso A, Vogt M,
Flesken-Nikitin A, Godwin AK, Kamat AA, Sood AK, Ellenson LH and
Hermeking H: Nikitin AYFrequent downregulation of miR-34 family in
human ovarian cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 16:1119–1128. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Lodygin D, Tarasov V, Epanchintsev A,
Berking C, Knyazeva T, Körner H, Knyazev P, Diebold J and Hermeking
H: Inactivation of miR-34a by aberrant CpG methylation in multiple
types of cancer. Cell Cycle. 7:2591–2600. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Gal-Yam EN, Saito Y, Egger G and Jones PA:
Cancer epigenetics: Modifications, screening, and therapy. Annu Rev
Med. 59:267–280. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Jones PA and Baylin SB: The fundamental
role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 3:415–428.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hermeking H: The miR-34 family in cancer
and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 17:193–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zhang S, Chen P, Huang Z, Hu X, Chen M, Hu
S, Hu Y and Cai T: Sirt7 promotes gastric cancer growth and
inhibits apoptosis by epigenetically inhibiting miR-34a. Sci Rep.
5:97872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Noto JM and Peek RM: The role of microRNAs
in Helicobacter pylori pathogenesis and gastric
carcinogenesis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 1:212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chang H, Kim N, Park JH, Nam RH, Choi YJ,
Lee HS, Yoon H, Shin CM, Park YS, Kim JM and Lee DH: Different
microRNA expression levels in gastric cancer depending on
Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut Liver. 9:188–196. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Liu P, Cheng H, Roberts TM and Zhao JJ:
Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 8:627–644. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wang G, Liu G, Ye Y, Fu Y and Zhang X:
Upregulation of miR-34a by diallyl disulfide suppresses invasion
and induces apoptosis in SGC-7901 cells through inhibition of the
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 11:2661–2667. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Sun XP, Dong X, Lin L, Jiang X, Wei Z,
Zhai B, Sun B, Zhang Q, Wang X, Jiang H, et al: Up-regulation of
survivin by AKT and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α contributes to
cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer. FEBS J. 281:115–128. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Tang T, Su R, Wang B and Zhang Y: An
integrated approach of predicted miR-34a targets identifies a
signature for gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 10:653–660. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Suzuki R, Yamamoto E, Nojima M, Maruyama
R, Yamano HO, Yoshikawa K, Kimura T, Harada T, Ashida M, Niinuma T,
et al: Aberrant methylation of microRNA-34b/c is a predictive
marker of metachronous gastric cancer risk. J Gastroenterol.
49:1135–1144. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Saunders MA, Liang H and Li WH: Human
polymorphism at microRNAs and microRNA target sites. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 104:3300–3305. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Cai M, Zhang Y, Ma Y, Li W, Min P, Qiu J,
Xu W, Zhang M, Li M, Li L, et al: Association between microRNA-499
polymorphism and gastric cancer risk in Chinese population. Bull
Cancer. 102:973–978. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Jiang J, Jia ZF, Cao DH, Wu YH, Sun ZW and
Cao XY: Association of the miR-146a rs2910164 polymorphism with
gastric cancer susceptibility and prognosis. Future Oncol.
12:2215–2226. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Xu Y, Liu L, Liu J, Zhang Y, Zhu J, Chen
J, Liu S, Liu Z, Shi H, Shen H and Hu Z: A potentially functional
polymorphism in the promoter region of miR-34b/c is associated with
an increased risk for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 128:412–417. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Yang C, Ma X, Liu D, Wang Y, Tang R, Zhu
Y, Xu Z and Yang L: Promoter polymorphisms of miR-34b/c are
associated with risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population.
Tumour Biol. 35:12545–12554. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Pan XM, Sun RF, Li ZH, Guo XM, Qin HJ and
Gao LB: Pri-miR-34b/c rs4938723 polymorphism is associated with a
decreased risk of gastric cancer. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers.
19:198–202. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Li H, Diao S, Li J, Ma B and Yuan S: An
updated meta-analysis of 23 case-control studies on the association
between miR-34b/c polymorphism and cancer risk. Oncotarget.
8:28888–28896. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Wang X, Li J, Dong K, Lin F, Long M,
Ouyang Y, Wei J, Chen X, Weng Y, He T and Zhang H: Tumor suppressor
miR-34a targets PD-L1 and functions as a potential
immunotherapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Signal.
27:443–452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Cortez MA, Ivan C, Valdecanas D, Wang X,
Peltier HJ, Ye Y, Araujo L, Carbone DP, Shilo K, Giri DK, et al:
PDL1 Regulation by p53 via miR-34. J Natl Cancer Inst. 108(pii):
djv3032015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Di Martino MT, Leone E, Amodio N, Foresta
U, Lionetti M, Pitari MR, Cantafio ME, Gullà A, Conforti F, Morelli
E, et al: Synthetic miR-34a mimics as a novel therapeutic agent for
multiple myeloma: In vitro and in vivo evidence. Clin Cancer Res.
18:6260–6270. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, Chen X,
Calhoun-Davis T, Li H, Patrawala L, Yan H, Jeter C, Honorio S, et
al: The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and
metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med. 17:211–215. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Di Martino MT, Campani V, Misso G, Gallo
Cantafio ME, Gullà A, Foresta U, Guzzi PH, Castellano M, Grimaldi
A, Gigantino V, et al: In vivo activity of miR-34a mimics delivered
by stable nucleic acid lipid particles (SNALPs) against multiple
myeloma. PLoS One. 9:e900052014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Daige CL, Wiggins JF, Priddy L,
Nelligan-Davis T, Zhao J and Brown D: Systemic delivery of a miR34a
mimic as a potential therapeutic for liver cancer. Mol Cancer Ther.
13:2352–2360. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Beg MS, Brenner AJ, Sachdev J, Borad M,
Kang YK, Stoudemire J, Smith S, Bader AG, Kim S and Hong DS: Phase
I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice
weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs.
35:180–188. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Shi L, Lin H, Li G, Sun Y, Shen J, Xu J,
Lin C, Yeh S, Cai X and Chang C: Cisplatin enhances NK cells
immunotherapy efficacy to suppress HCC progression via altering the
androgen receptor (AR)-ULBP2 signals. Cancer Lett. 373:45–56. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Yan LH, Chen ZN, Li L, Chen J, Mo XW, Qin
YZ, Wei WE, Qin HQ, Lin Y and Chen JS: E2F-1 promotes DAPK2-induced
anti-tumor immunity of gastric cancer cells by targeting miR-34a.
Tumor Biol. Oct 4–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|