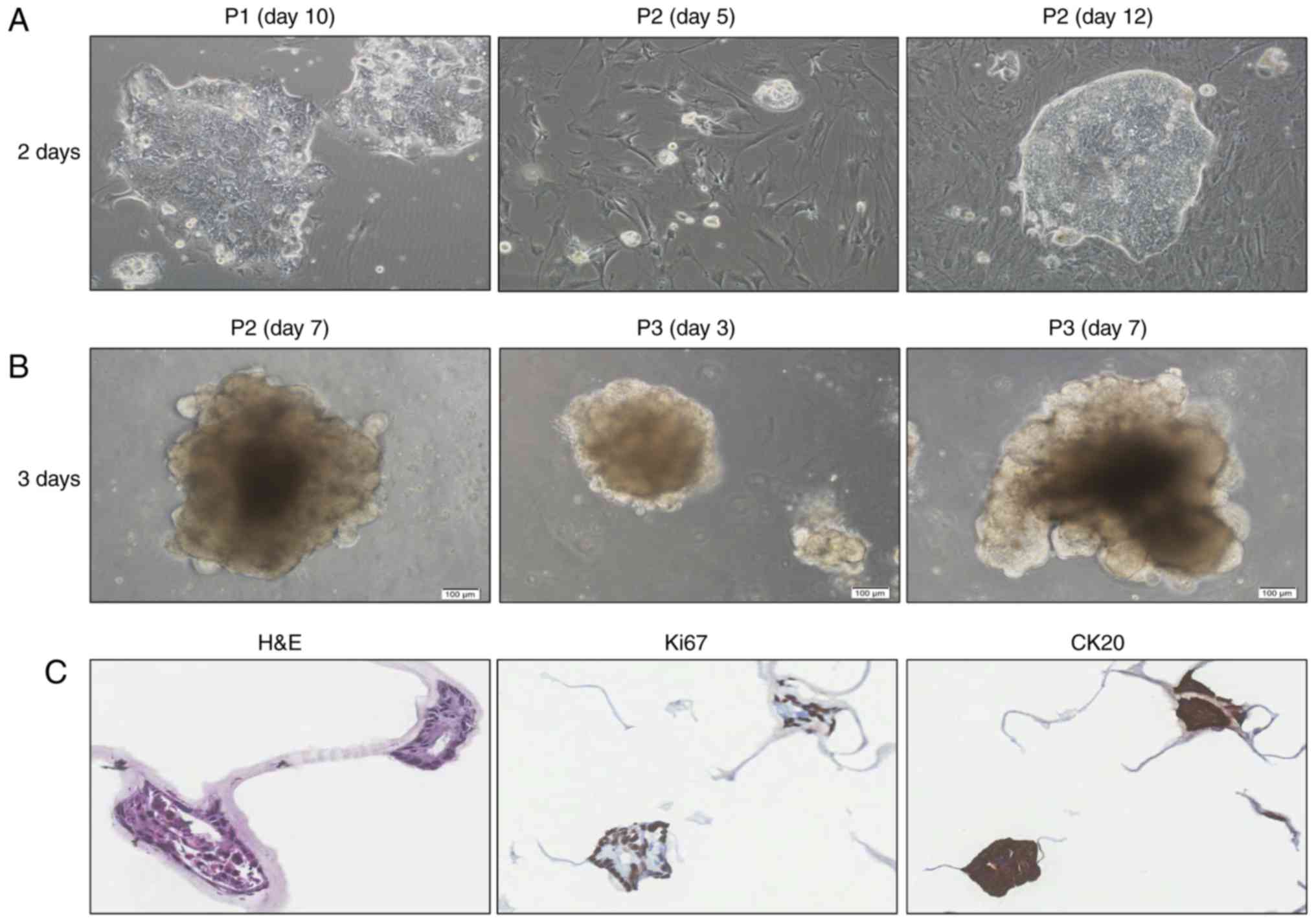
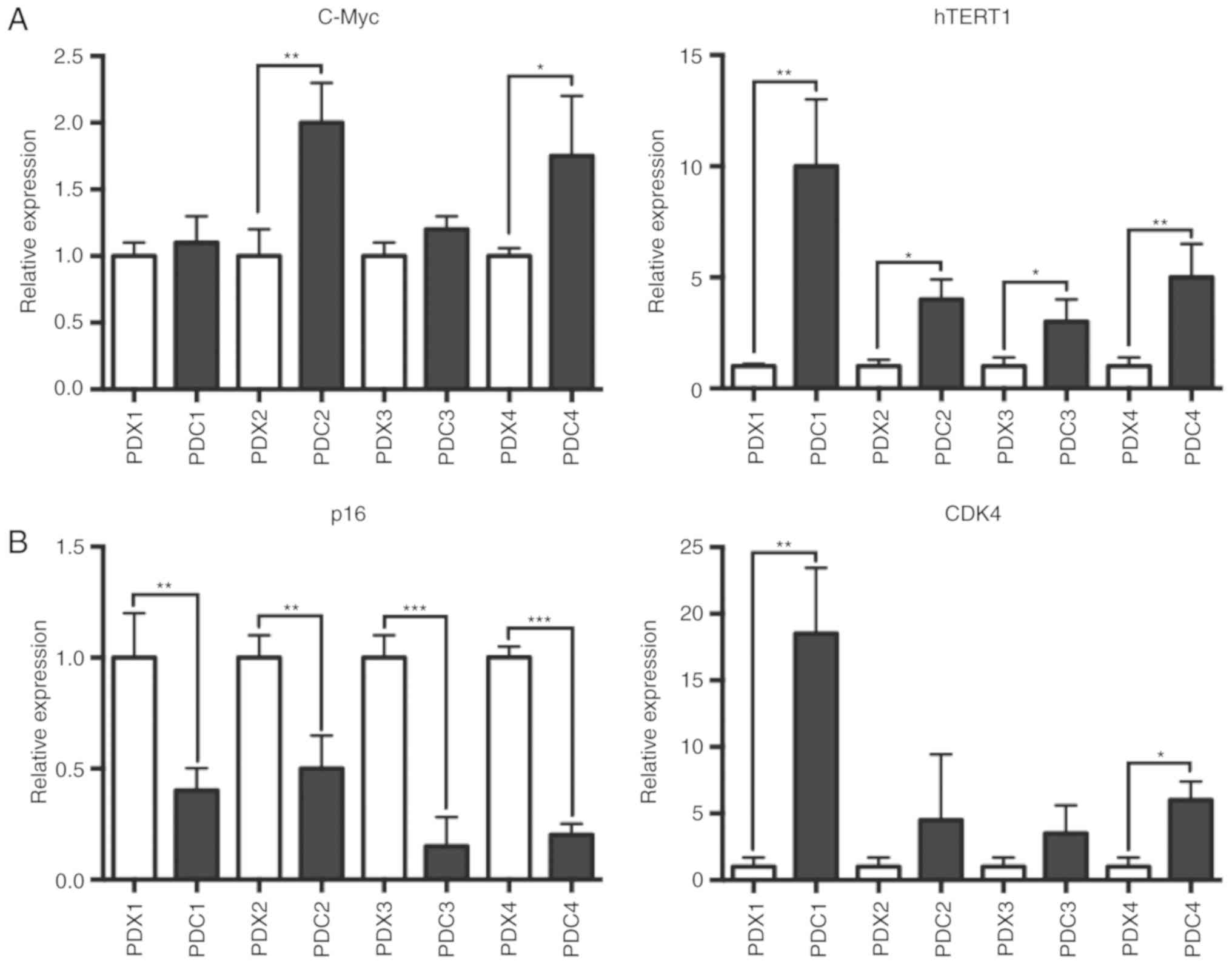
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jeppesen M, Hagel G, Glenthoj A, Vainer B,
Ibsen P, Harling H, Thastrup O, Jørgensen LN and Thastrup J:
Short-term spheroid culture of primary colorectal cancer cells as
an in vitro model for personalizing cancer medicine. PLoS One.
12:e01830742017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Riedl A, Schlederer M, Pudelko K, Stadler
M, Walter S, Unterleuthner D, Unger C, Kramer N, Hengstschläger M,
Kenner L, et al: Comparison of cancer cells in 2D vs 3D culture
reveals differences in AKT-mTOR-S6K signaling and drug responses. J
Cell Sci. 130:203–218. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dolznig H, Rupp C, Puri C, Haslinger C,
Schweifer N, Wieser E, Kerjaschki D and Garin-Chesa P: Modeling
colon adenocarcinomas in vitro a 3D co-culture system induces
cancer-relevant pathways upon tumor cell and stromal fibroblast
interaction. Am J Pathol. 179:487–501. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Katt ME, Placone AL, Wong AD, Xu ZS and
Searson PC: In vitro tumor models: Advantages, disadvantages,
variables, and selecting the right platform. Front Bioeng
Biotechnol. 4:122016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hidalgo M, Amant F, Biankin AV, Budinská
E, Byrne AT, Caldas C, Clarke RB, de Jong S, Jonkers J, Maelandsmo
GM, et al: Patient-derived xenograft models: An emerging platform
for translational cancer research. Cancer Discov. 4:998–1013. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gillet JP, Varma S and Gottesman MM: The
clinical relevance of cancer cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst.
105:452–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Voskoglou-Nomikos T, Pater JL and Seymour
L: Clinical predictive value of the in vitro cell line, human
xenograft, and mouse allograft preclinical cancer models. Clin
Cancer Res. 9:4227–4239. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu X, Krawczyk E, Suprynowicz FA,
Palechor-Ceron N, Yuan H, Dakic A, Simic V, Zheng YL, Sripadhan P,
Chen C, et al: Conditional reprogramming and long-term expansion of
normal and tumor cells from human biospecimens. Nat Protoc.
12:439–451. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Suprynowicz FA, Upadhyay G, Krawczyk E,
Kramer SC, Hebert JD, Liu X, Yuan H, Cheluvaraju C, Clapp PW,
Boucher RC Jr, et al: Conditionally reprogrammed cells represent a
stem-like state of adult epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:20035–20040. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu X, Ory V, Chapman S, Yuan H, Albanese
C, Kallakury B, Timofeeva OA, Nealon C, Dakic A, Simic V, et al:
ROCK inhibitor and feeder cells induce the conditional
reprogramming of epithelial cells. Am J Pathol. 180:599–607. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chapman S, Liu X, Meyers C, Schlegel R and
McBride AA: Human keratinocytes are efficiently immortalized by a
Rho kinase inhibitor. J Clin Invest. 120:2619–2626. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Clevers H: Modeling development and
disease with organoids. Cell. 165:1586–1597. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cho YB, Hong HK, Choi YL, Oh E, Joo KM,
Jin J, Nam DH, Ko YH and Lee WY: Colorectal cancer patient-derived
xenografted tumors maintain characteristic features of the original
tumors. J Surg Res. 187:502–509. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee JK, Liu Z, Sa JK, Shin S, Wang J,
Bordyuh M, Cho HJ, Elliott O, Chu T, Choi SW, et al:
Pharmacogenomic landscape of patient-derived tumor cells informs
precision oncology therapy. Nat Genet. 50:1399–1411. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oh BY, Lee WY, Jung S, Hong HK, Nam DH,
Park YA, Huh JW, Yun SH, Kim HC, Chun HK and Cho YB: Correlation
between tumor engraftment in patient-derived xenograft models and
clinical outcomes in colorectal cancer patients. Oncotarget.
6:16059–16068. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chopra DP, Yeh K and Brockman RW:
Isolation and characterization of epithelial cell types from the
normal rat colon. Cancer Res. 41:168–175. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McCallum HM and Lowther GW: Long-term
culture of primary breast cancer in defined medium. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 39:247–259. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Castell JV and Gómez-Lechón MJ: Liver cell
culture techniques. Methods Mol Biol. 481:35–46. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mitra A, Mishra L and Li S: Technologies
for deriving primary tumor cells for use in personalized cancer
therapy. Trends Biotechnol. 31:347–354. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sugimoto H, Mundel TM, Kieran MW and
Kalluri R: Identification of fibroblast heterogeneity in the tumor
microenvironment. Cancer Biol Ther. 5:1640–1646. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dakic A, DiVito K, Fang S, Suprynowicz F,
Gaur A, Li X, Palechor-Ceron N, Simic V, Choudhury S, Yu S, et al:
ROCK inhibitor reduces Myc-induced apoptosis and mediates
immortalization of human keratinocytes. Oncotarget. 7:66740–66753.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
André T, Boni C, Navarro M, Tabernero J,
Hickish T, Topham C, Bonetti A, Clingan P, Bridgewater J, Rivera F
and de Gramont A: Improved overall survival with oxaliplatin,
fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment in stage II or
III colon cancer in the MOSAIC trial. J Clin Oncol. 27:3109–3116.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Janik K, Popeda M, Peciak J, Rosiak K,
Smolarz M, Treda C, Rieske P, Stoczynska-Fidelus E and Ksiazkiewicz
M: Efficient and simple approach to in vitro culture of primary
epithelial cancer cells. Biosci Rep. 36(pii): e004232016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ali MY, Anand SV, Tangella K, Ramkumar D
and Saif TA: Isolation of primary human colon tumor cells from
surgical tissues and culturing them directly on soft elastic
substrates for traction cytometry. J Vis Exp. 2015:e525322015.
|
|
27
|
Liu X, Dakic A, Chen R, Disbrow GL, Zhang
Y, Dai Y and Schlegel R: Cell-restricted immortalization by human
papillomavirus correlates with telomerase activation and engagement
of the hTERT promoter by Myc. J Virol. 82:11568–11576. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Van der Haegen BA and Shay JW:
Immortalization of human mammary epithelial cells by SV40 large
T-antigen involves a two step mechanism. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol
29A. 180–182. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hudson JB, Bedell MA, McCance DJ and
Laiminis LA: Immortalization and altered differentiation of human
keratinocytes in vitro by the E6 and E7 open reading frames of
human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 64:519–526. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Münger K, Phelps WC, Bubb V, Howley PM and
Schlegel R: The E6 and E7 genes of the human papillomavirus type 16
together are necessary and sufficient for transformation of primary
human keratinocytes. J Virol. 63:4417–4421. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hawley-Nelson P, Vousden KH, Hubbert NL,
Lowy DR and Schiller JT: HPV16 E6 and E7 proteins cooperate to
immortalize human foreskin keratinocytes. EMBO J. 8:3905–3910.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schlegel R, Phelps WC, Zhang YL and
Barbosa M: Quantitative keratinocyte assay detects two biological
activities of human papillomavirus DNA and identifies viral types
associated with cervical carcinoma. EMBO J. 7:3181–3187. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang L, Valdez JM, Zhang B, Wei L, Chang
J and Xin L: ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 suppresses dissociation-induced
apoptosis of murine prostate stem/progenitor cells and increases
their cloning efficiency. PLoS One. 6:e182712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Terunuma A, Limgala RP, Park CJ, Choudhary
I and Vogel JC: Efficient procurement of epithelial stem cells from
human tissue specimens using a Rho-associated protein kinase
inhibitor Y-27632. Tissue Eng Part A. 16:1363–1368. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hanna JH, Saha K and Jaenisch R:
Pluripotency and cellular reprogramming: Facts, hypotheses,
unresolved issues. Cell. 143:508–525. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Takehara T, Teramura T, Onodera Y,
Kakegawa R, Fukunaga N, Takenoshita M, Sagawa N, Fukuda K and Hosoi
Y: Rho-associated kinase inhibitor Y-27632 promotes survival of
cynomolgus monkey embryonic stem cells. Mol Hum Reprod. 14:627–634.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li X, Meng G, Krawetz R, Liu S and
Rancourt DE: The ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 enhances the survival rate
of human embryonic stem cells following cryopreservation. Stem
Cells Dev. 17:1079–1085. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li X, Krawetz R, Liu S, Meng G and
Rancourt DE: ROCK inhibitor improves survival of cryopreserved
serum/feeder-free single human embryonic stem cells. Hum Reprod.
24:580–589. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Watanabe K, Ueno M, Kamiya D, Nishiyama A,
Matsumura M, Wataya T, Takahashi JB, Nishikawa S, Nishikawa S,
Muguruma K and Sasai Y: A ROCK inhibitor permits survival of
dissociated human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 25:681–686.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lièvre A, Bachet JB, Le Corre D, Boige V,
Landi B, Emile JF, Côté JF, Tomasic G, Penna C, Ducreux M, et al:
KRAS mutation status is predictive of response to cetuximab therapy
in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 66:3992–3995. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bardelli A and Jänne PA: The road to
resistance: EGFR mutation and cetuximab. Nat Med. 18:199–200. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Schütte M, Risch T, Abdavi-Azar N, Boehnke
K, Schumacher D, Keil M, Yildiriman R, Jandrasits C, Borodina T,
Amstislavskiy V, et al: Molecular dissection of colorectal cancer
in pre-clinical models identifies biomarkers predicting sensitivity
to EGFR inhibitors. Nat Commun. 8:142622017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
McGranahan N and Swanton C: Clonal
heterogeneity and tumor evolution: Past, present, and the future.
Cell. 168:613–628. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dangles-Marie V, Pocard M, Richon S,
Weiswald LB, Assayag F, Saulnier P, Judde JG, Janneau JL, Auger N,
Validire P, et al: Establishment of human colon cancer cell lines
from fresh tumors versus xenografts: Comparison of success rate and
cell line features. Cancer Res. 67:398–407. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sachs N and Clevers H: Organoid cultures
for the analysis of cancer phenotypes. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
24:68–73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American Joint
Committee On Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|