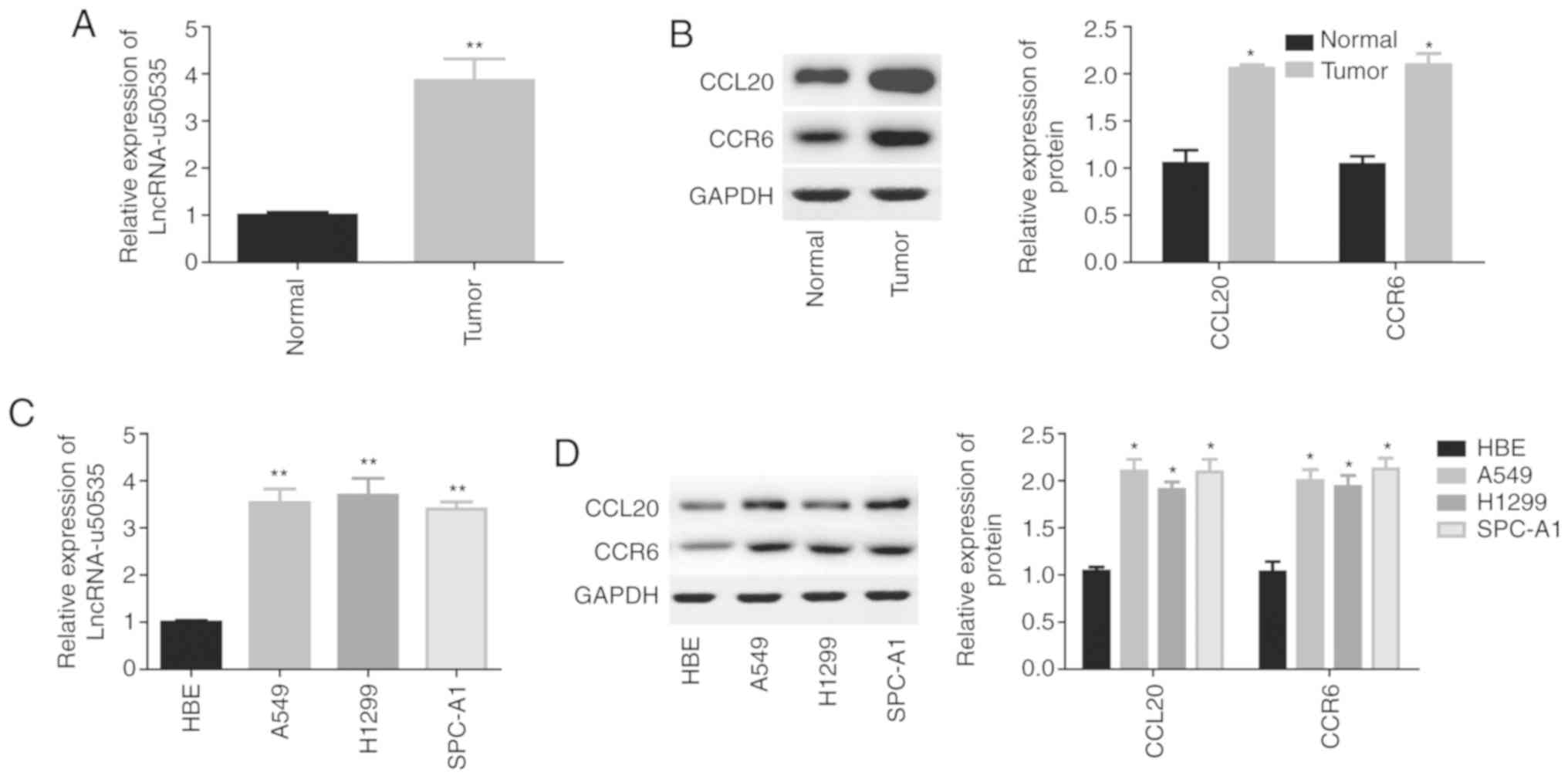
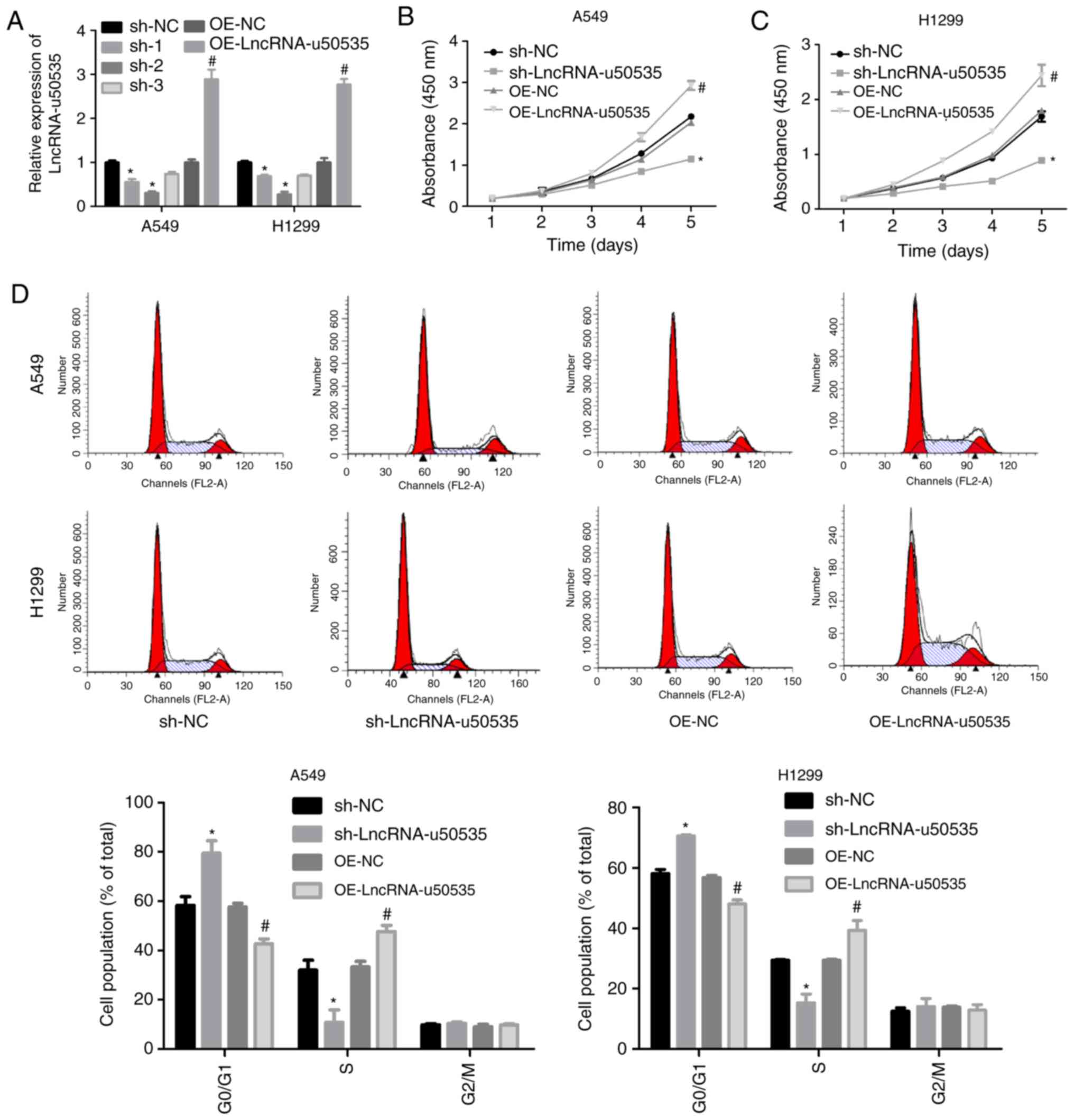
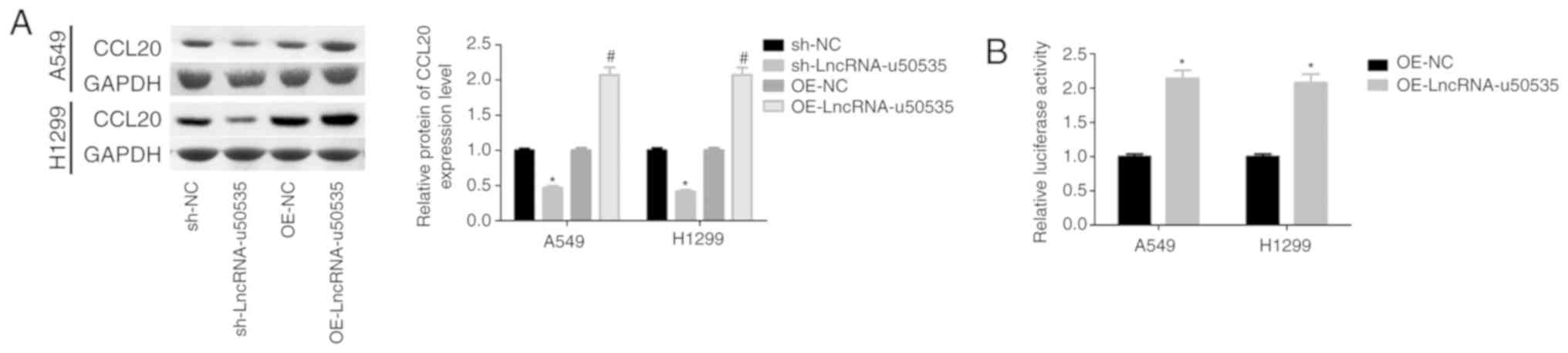
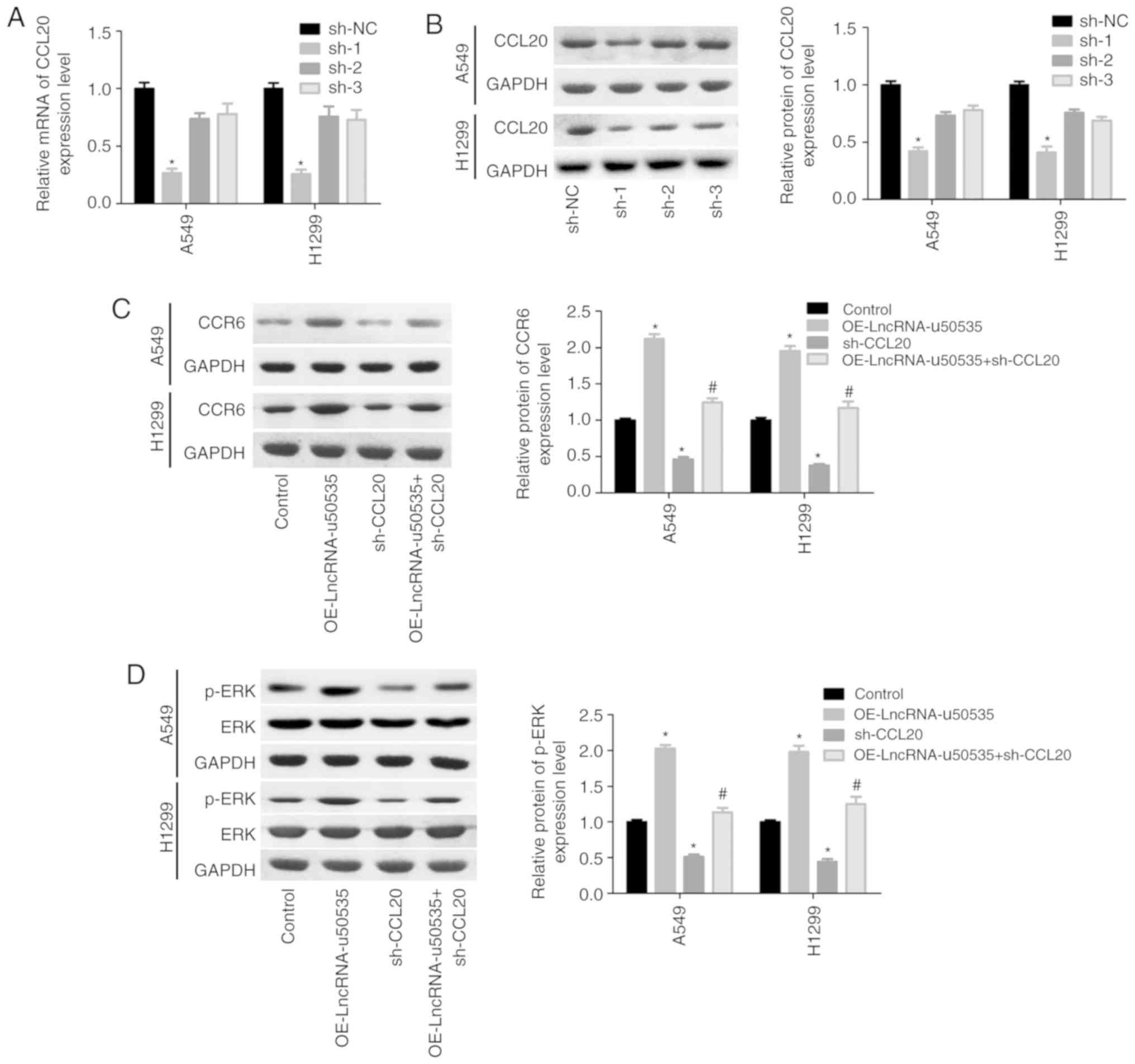
|
1
|
McGuire S: World Cancer Report 2014.
Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, International
agency for research on cancer, WHO press, 2015. Adv Nutr.
7:418–419. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nagarsheth N, Wicha MS and Zou W:
Chemokines in the cancer microenvironment and their relevance in
cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 17:559–572. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cao Y, Huang H, Wang Z and Zhang G: The
inflammatory CXC chemokines, GROαhigh,
IP-10low, and MIGlow, in tumor
microenvironment can be used as new indicators for non-small cell
lung cancer progression. Immunol Invest. 46:361–374. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Murphy PM, Baggiolini M, Charo IF, Hébert
CA, Horuk R, Matsushima K, Miller LH, Oppenheim JJ and Power CA:
International union of pharmacology. XXII. Nomenclature for
chemokine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 52:145–176. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mantovani A: Chemokines in neoplastic
progression. Semin Cancer Biol. 14:147–148. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Beider K, Abraham M, Begin M, Wald H,
Weiss ID, Wald O, Pikarsky E, Abramovitch R, Zeira E, Galun E, et
al: Interaction between CXCR4 and CCL20 pathways regulates tumor
growth. PLoS One. 4:e51252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schutyser E, Struyf S and Van Damme J: The
CC chemokine CCL20 and its receptor CCR6. Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 14:409–426. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang XP, Hu ZJ, Meng AH, Duan GC, Zhao QT
and Yang J: Role of CCL20/CCR6 and the ERK signaling pathway in
lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol Lett. 14:8183–8189. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang B, Shi L, Sun X, Wang L, Wang X and
Chen C: Production of CCL20 from lung cancer cells induces the cell
migration and proliferation through PI3K pathway. J Cell Mol Med.
20:920–929. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang G, Lu X and Yuan L: LncRNA: A link
between RNA and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1839:1097–1109. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huarte M: The emerging role of lncRNAs in
cancer. Nat Med. 21:1253–1261. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Batista PJ and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell.
152:1298–1307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wei L, Wu T, He P, Zhang JL and Wu W:
LncRNA ATB promotes the proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer
via activation of the p38 signaling pathway. Oncol Lett.
16:3907–3912. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu X, Yuan Z, Yang Z, Chen D, Kim T, Cui
Y, Luo Q, Liu Z, Yang Z, Fan X, et al: The novel long noncoding RNA
u50535 promotes colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by
regulating CCL20. Cell Death Dis. 9:7512018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen S, Wu H, Lv N, Wang H, Wang Y, Tang
Q, Shao H and Sun C: LncRNA CCAT2 predicts poor prognosis and
regulates growth and metastasis in small cell lung cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 82:583–588. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
She K, Huang J, Zhou H, Huang T, Chen G
and He J: lncRNA-SNHG7 promotes the proliferation, migration and
invasion and inhibits apoptosis of lung cancer cells by enhancing
the FAIM2 expression. Oncol Rep. 36:2673–2680. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao QS, Li L, Zhang L, Meng XW, Li LL, Ge
XF and Li ZP: Over-expression of lncRNA SBF2-AS1 is associated with
advanced tumor progression and poor prognosis in patients with
non-small cell lung cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
20:3031–3034. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu M, Sun W, Liu Y and Dong X: The role
of lncRNA MALAT1 in bone metastasis in patients with non-small cell
lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 36:1679–1685. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen J, Hu L, Wang J, Zhang F, Chen J, Xu
G, Wang Y and Pan Q: Low expression LncRNA TUBA4B is a poor
predictor of prognosis and regulates cell proliferation in
non-small cell lung cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 23:265–270. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dong Y, Huo X, Sun R, Liu Z, Huang M and
Yang S: LncRNA Gm15290 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in
non-small cell lung cancer through directly interacting with and
suppressing the tumor suppressor miR-615-5p. Oncol Res. May
5–2017.(Epub ahead of print) doi: 10.3727/096504017X14930316817366.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Lei T, Lv ZY, Fu JF, Wang Z, Fan Z and
Wang Y: LncRNA NBAT-1 is down-regulated in lung cancer and
influences cell proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:1958–1962. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Edwards SM, Evans DG, Hope Q, Norman AR,
Barbachano Y, Bullock S, Kote-Jarai Z, Meitz J, Falconer A, Osin P,
et al: Prostate cancer in BRCA2 germline mutation carriers is
associated with poorer prognosis. Br J Cancer. 103:918–924. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Maitra A, Kern SE and Hruban RH: Molecular
pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer. Best Pract Res Clin
Gastroenterol. 20:211–226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Anifantaki F, Boutas I, Kalampokas T,
Kalampokas E, Sofoudis C and Salakos N: Association of
endometriosis and breast cancer: Mini review of the literature.
Arch Gynecol Obstet. 293:5–10. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Amoh Y, Yang M, Li L, Reynoso J, Bouvet M,
Moossa AR, Katsuoka K and Hoffman RM: Nestin-linked green
fluorescent protein transgenic nude mouse for imaging human tumor
angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 65:5352–5357. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Adcock IM, Caramori G and Barnes PJ:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and lung cancer: New
molecular insights. Respiration. 81:265–284. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Winkler AE, Brotman JJ, Pittman ME, Judd
NP, Lewis JS Jr, Schreiber RD and Uppaluri R: CXCR3 enhances a
T-cell-dependent epidermal proliferative response and promotes skin
tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 71:5707–5716. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang CY, Qi Y, Li XN, Yang Y, Liu DL,
Zhao J, Zhu DY, Wu K, Zhou XD and Zhao S: The role of CCL20/CCR6
axis in recruiting Treg cells to tumor sites of NSCLC patients.
Biomed Pharmacother. 69:242–248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brand S, Olszak T, Beigel F, Diebold J,
Otte JM, Eichhorst ST, Göke B and Dambacher J: Cell differentiation
dependent expressed CCR6 mediates ERK-1/2, SAPK/JNK, and Akt
signaling resulting in proliferation and migration of colorectal
cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 97:709–723. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Roberts PJ and Der CJ: Targeting the
Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the
treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 26:3291–3310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|