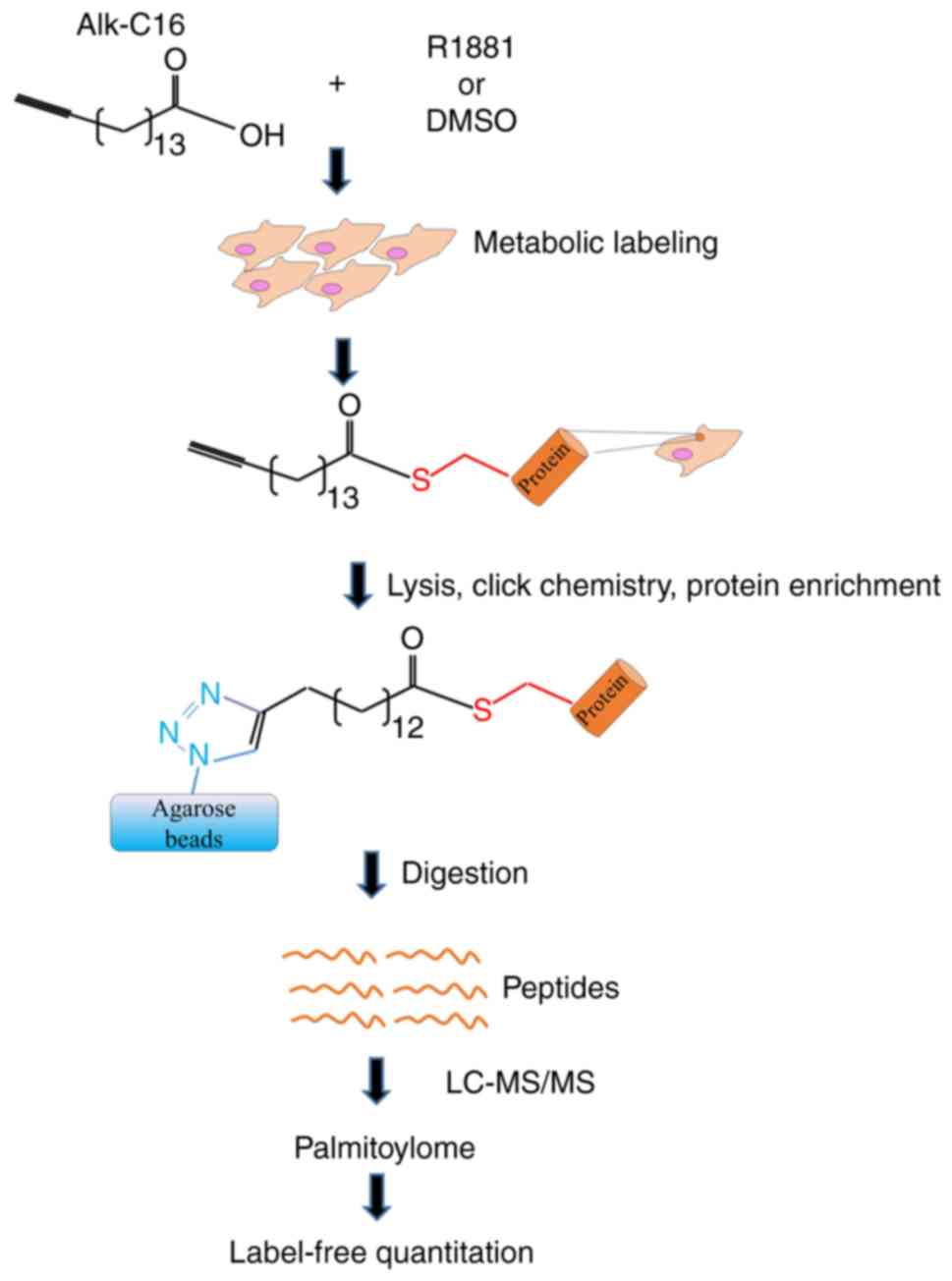
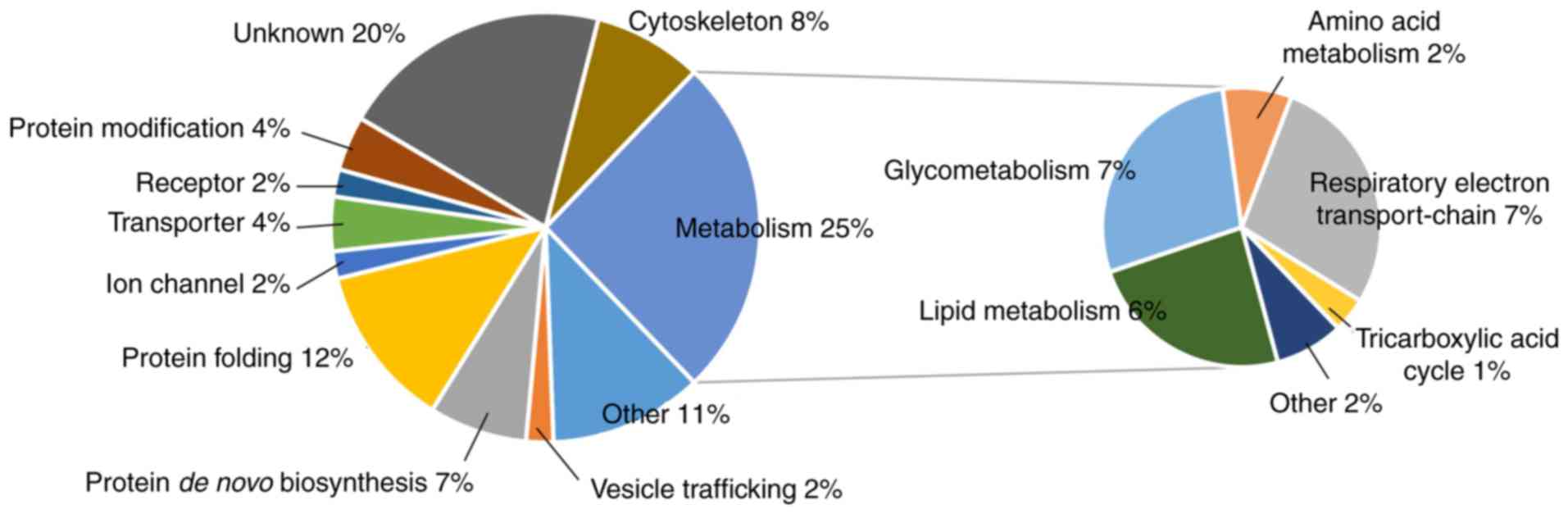
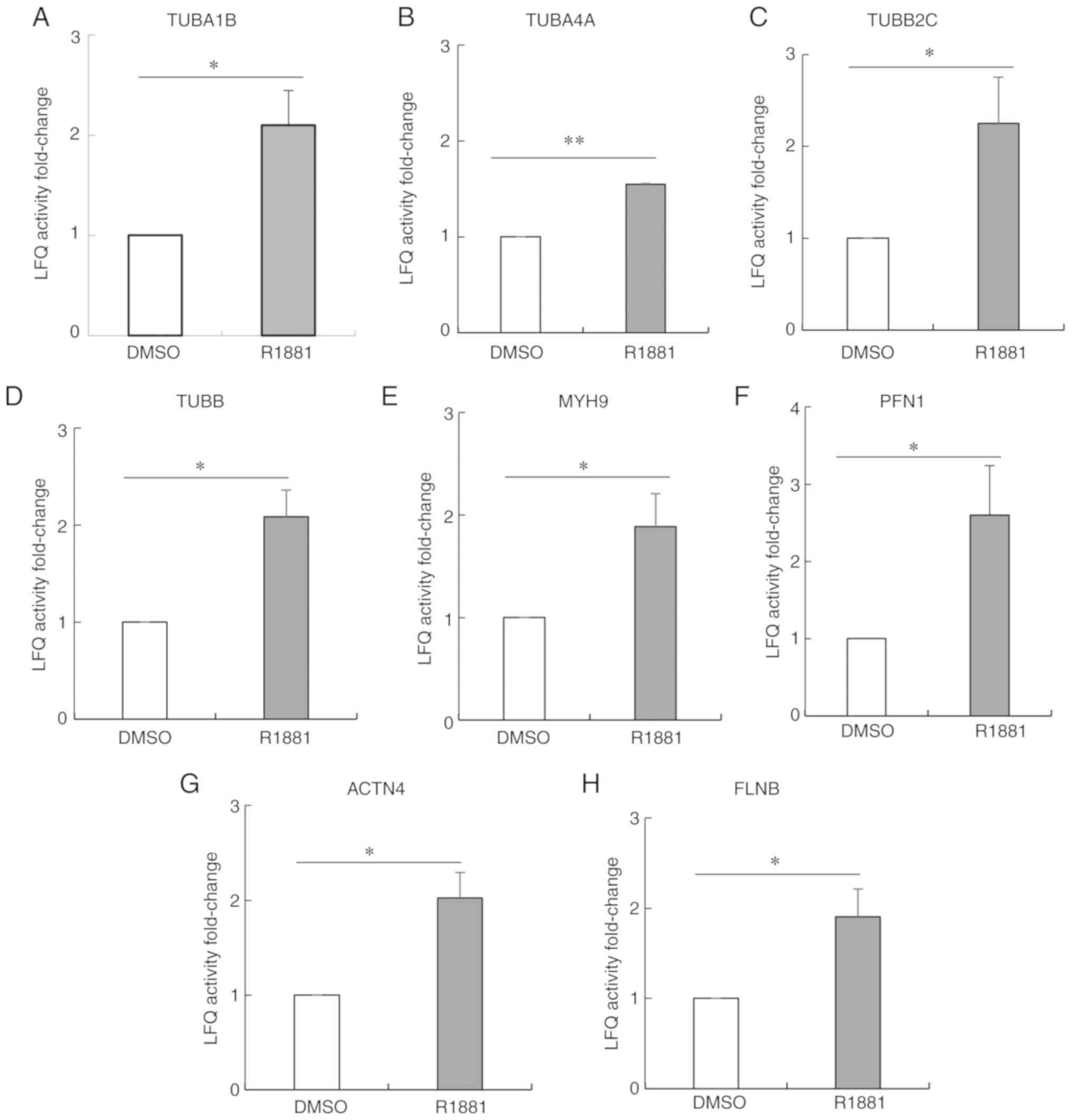
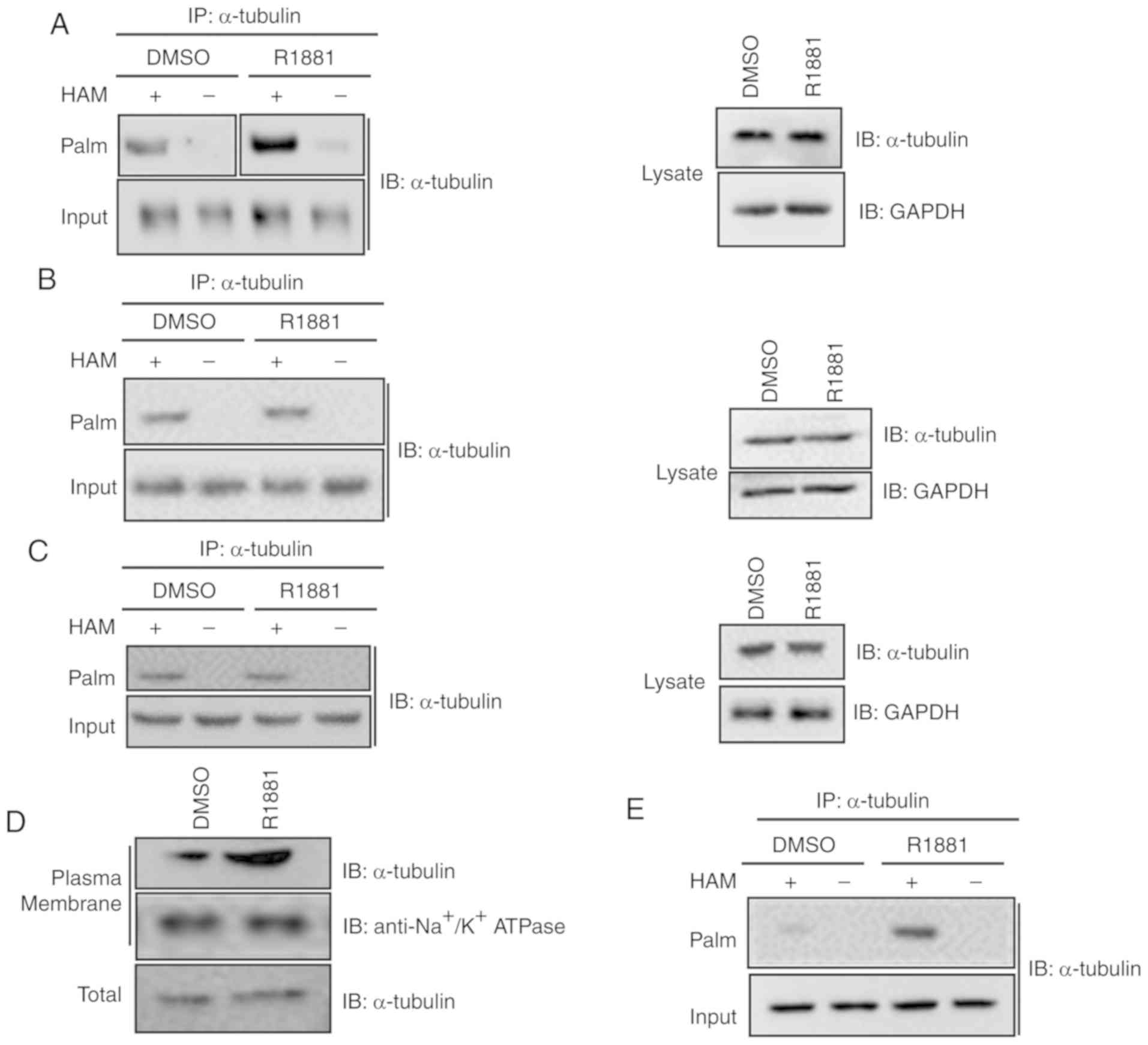
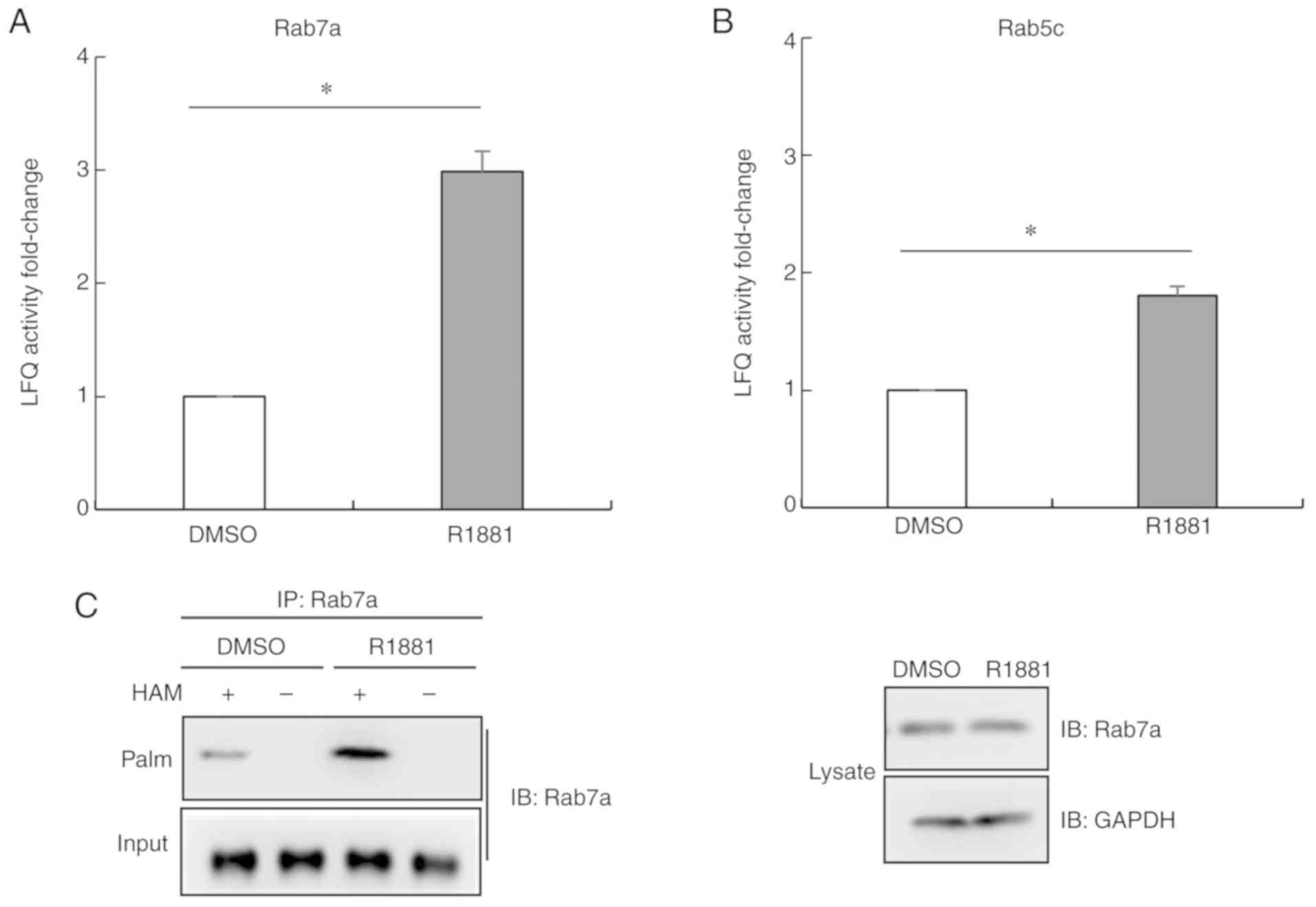
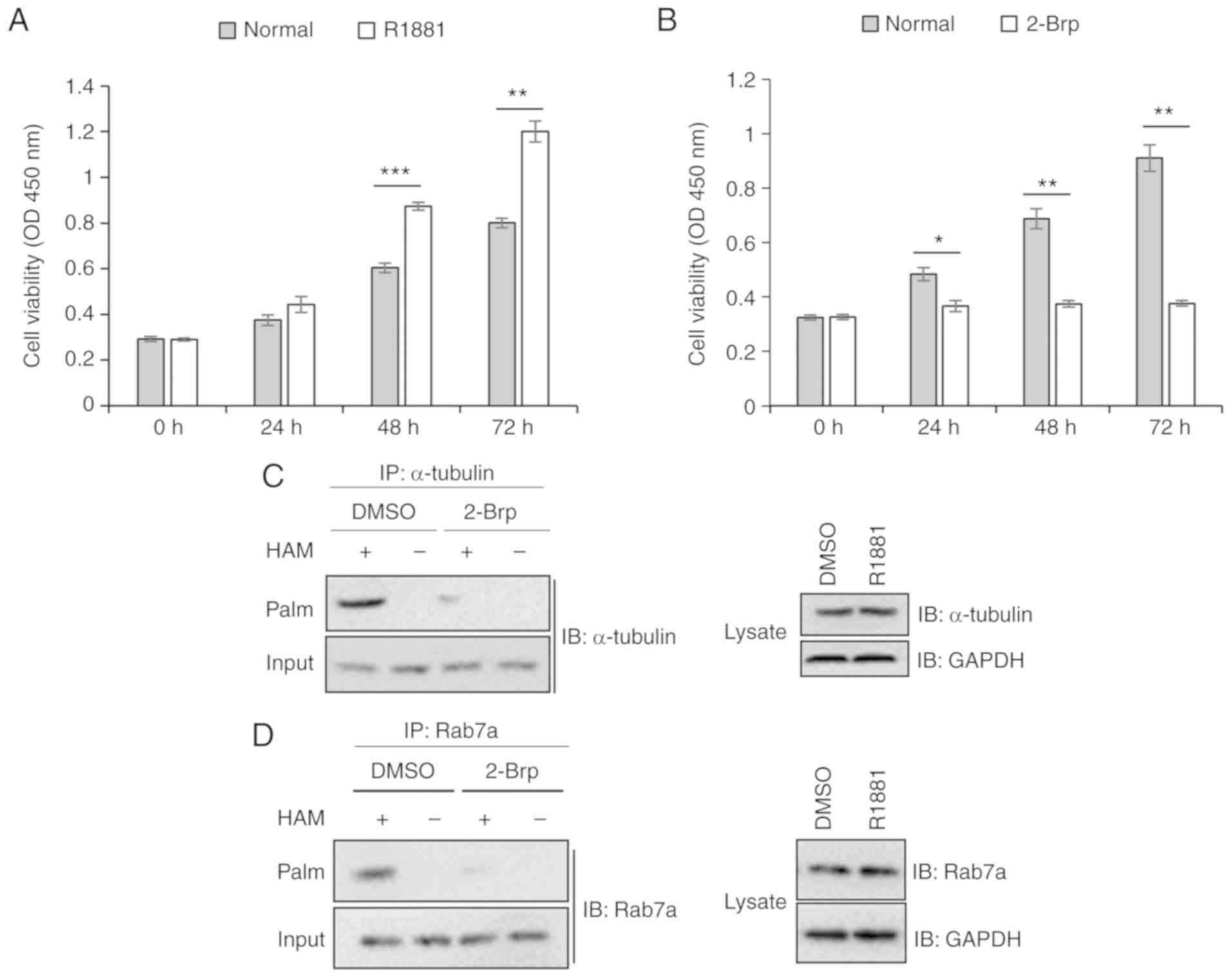
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lonergan PE and Tindall DJ: Androgen
receptor signaling in prostate cancer development and progression.
J Carcinog. 10:202011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Klein EA, Ciezki J, Kupelian PA and
Mahadevan A: Outcomes for intermediate risk prostate cancer: Are
there advantages for surgery, external radiation, or brachytherapy?
Urol Oncol. 27:67–71. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Loblaw DA, Virgo KS, Nam R, Somerfield MR,
Ben-Josef E, Mendelson DS, Middleton R, Sharp SA, Smith TJ, Talcott
J, et al: Initial hormonal management of androgen-sensitive
metastatic, recurrent, or progressive prostate cancer: 2006 update
of an American Society of Clinical Oncology Practice Guideline. J
clin Oncol. 25:1596–1605. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tilki D, Schaeffer EM and Evans CP:
Understanding mechanisms of resistance in metastatic
castration-resistant prostate cancer: The role of the androgen
receptor. Eur Urol Focus. 2:499–505. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aicart-Ramos C, Valero RA and
Rodriguez-Crespo I: Protein palmitoylation and subcellular
trafficking. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1808:2981–2994. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thinon E and Hang HC: Chemical reporters
for exploring protein acylation. Biochem Soc Trans. 43:253–261.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mitchell DA, Vasudevan A, Linder ME and
Deschenes RJ: Protein palmitoylation by a family of DHHC protein
S-acyltransferases. J Lipid Res. 47:1118–1127. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gao X and Hannoush RN: Single-cell imaging
of Wnt palmitoylation by the acyltransferase porcupine. Nat Chem
Biol. 10:61–68. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pepinsky RB, Zeng C, Wen D, Rayhorn P,
Baker DP, Williams KP, Bixler SA, Ambrose CM, Garber EA, Miatkowski
K, et al: Identification of a palmitic acid-modified form of human
sonic hedgehog. J Biol Chem. 273:14037–14045. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hofmann K: A superfamily of membrane-bound
O-acyltransferases with implications for wnt signaling. Trends
Biochem Sci. 25:111–112. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Smotrys JE and Linder ME: Palmitoylation
of intracellular signaling proteins: Regulation and function. Ann
Rev Biochem. 73:559–587. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Resh MD: Targeting protein lipidation in
disease. Trends Mol Med. 18:206–214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Heakal Y, Woll MP, Fox T, Seaton K,
Levenson R and Kester M: Neurotensin receptor-1 inducible
palmitoylation is required for efficient receptor-mediated
mitogenic-signaling within structured membrane microdomains. Cancer
Biol Ther. 12:427–435. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hannoush RN and Sun J: The chemical
toolbox for monitoring protein fatty acylation and prenylation. Nat
Chem Biol. 6:498–506. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hernandez JL, Davda D, Majmudar JD, Won
SJ, Prakash A, Choi AI and Martin BR: Correlated S-palmitoylation
profiling of snail-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition.
Mol Biosyst. 12:1799–17808. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Greaves J, Munro KR, Davidson SC, Riviere
M, Wojno J, Smith TK, Tomkinson NC and Chamberlain LH: Molecular
basis of fatty acid selectivity in the zDHHC family of
S-acyltransferases revealed by click chemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci
U S A. 114:E1365–E1374. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li W, Li W, Zou L, Ji S, Li C, Liu K,
Zhang G, Sun Q, Xiao F and Chen D: Membrane targeting of inhibitory
Smads through palmitoylation controls TG-β/BMP signaling. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 114:13206–132011. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hannoush RN and Arenas-Ramirez N: Imaging
the lipidome: Omega-alkynyl fatty acids for detection and cellular
visualization of lipid-modified proteins. ACS Chem Biol. 4:581–587.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu NQ, Braakman RB, Stingl C, Luider TM,
Martens JW, Foekens JA and Umar A: Proteomics pipeline for
biomarker discovery of laser capture microdissected breast cancer
tissue. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 17:155–164. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shen LF, Chen YJ, Liu KM, Haddad ANS, Song
IW, Roan HY, Chen LY, Yen JJY, Chen YJ, Wu JY and Chen YT: Role of
S-palmitoylation by ZDHHC13 in mitochondrial function and
metabolism in liver. Sci Rep. 7:21822017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Caron JM: Posttranslational modification
of tubulin by palmitoylation: I. In vivo and cell-free studies. Mol
Biol Cell. 8:621–636. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Niu Y, Altuwaijri S, Lai KP, Wu CT, Ricke
WA, Messing EM, Yao J, Yeh S and Chang C: Androgen receptor is a
tumor suppressor and proliferator in prostate cancer. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 105:12182–12187. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Caron JM, Vega LR, Fleming J, Bishop R and
Solomon F: Single site alpha-tubulin mutation affects astral
microtubules and nuclear positioning during anaphase in
Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Possible role for palmitoylation of
alpha-tubulin. Mol Biol Cell. 12:2672–2687. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Caron JM and Herwood M: Vinblastine, a
chemotherapeutic drug, inhibits palmitoylation of tubulin in human
leukemic lymphocytes. Chemotherapy. 53:51–58. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Heuer TS, Ventura R, Mordec K, Lai J,
Fridlib M, Buckley D and Kemble G: FASN inhibition and taxane
treatment combine to enhance anti-tumor efficacy in diverse
xenograft tumor models through disruption of tubulin palmitoylation
and microtubule organization and FASN inhibition-mediated effects
on oncogenic signaling and gene expression. EBioMedicine. 16:51–62.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ng EL, Gan BQ, Ng F and Tang BL: Rab
GTPases regulating receptor trafficking at the late
endosome-lysosome membranes. Cell Biochem Function. 30:515–523.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Rink J, Ghigo E, Kalaidzidis Y and Zerial
M: Rab conversion as a mechanism of progression from early to late
endosomes. Cell. 122:735–749. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bucci C, Thomsen P, Nicoziani P, McCarthy
J and van Deurs B: Rab7: A key to lysosome biogenesis. Mol Biol
Cell. 11:467–480. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Modica G, Skorobogata O, Sauvageau E,
Vissa A, Yip CM, Kim PK, Wurtele H and Lefrancois S: Rab7
palmitoylation is required for efficient endosome-to-TGN
trafficking. J Cell Sci. 130:2579–2590. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guerra F and Bucci C: Multiple roles of
the small GTPase Rab7. Cells. 5(pii): E342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|