|
1
|
Roshan MH, Tambo A and Pace NP: The role
of testosterone in colorectal carcinoma: Pathomechanisms and open
questions. EPMA J. 7:222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Amos-Landgraf JM, Heijmans J, Wielenga MC,
Dunkin E, Krentz KJ, Clipson L, Ederveen AG, Groothuis PG,
Mosselman S, Muncan V, et al: Sex disparity in colonic
adenomagenesis involves promotion by male hormones, not protection
by female hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:16514–16519. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Docea AO, Goumenou M, Calina D, Arsene AL,
Dragoi CM, Gofita E, Pisoschi CG, Zlatian O, Stivaktakis PD,
Nikolouzakis TK, et al: Adverse and hormetic effects in rats
exposed for 12 months to low dose mixture of 13 chemicals: RLRS
part III. Toxicol Lett. 310:70–91. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tsatsakis AM, Docea AO, Calina D, Buga AM,
Zlatian O, Gutnikov S, Kostoff RN and Aschner M: Hormetic
Neurobehavioral effects of low dose toxic chemical mixtures in
real-life risk simulation (RLRS) in rats. Food Chem Toxicol.
125:141–149. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tsatsakis AM, Kouretas D, Tzatzarakis MN,
Stivaktakis P, Tsarouhas K, Golokhvast KS, Rakitskii VN, Tutelyan
VA, Hernandez AF, Rezaee R, et al: Simulating real-life exposures
to uncover possible risks to human health: A proposed consensus for
a novel methodological approach. Hum Exp Toxicol. 36:554–564. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fearon ER and Vogelstein B: A genetic
model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 61:759–767. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B: Lessons from
hereditary colorectal cancer. Cell. 87:159–170. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW: Cancer genes
and the pathways they control. Nat Med. 10:789–799. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nikolouzakis TK, Vassilopoulou L,
Fragkiadaki P, Mariolis Sapsakos T, Papadakis GZ, Spandidos DA,
Tsatsakis AM and Tsiaoussis J: Improving diagnosis, prognosis and
prediction by using biomarkers in CRC patients (Review). Oncol Rep.
39:2455–2472. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Terzic J, Grivennikov S, Karin E and Karin
M: Inflammation and colon cancer. Gastroenterology.
138:2101–2114.e5. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Greten FR, Eckmann L, Greten TF, Park JM,
Li ZW, Egan LJ, Kagnoff MF and Karin M: IKKbeta links inflammation
and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer.
Cell. 118:285–296. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, Mucida
D, Yu GY, Vallabhapurapu S, Scheller J, Rose-John S, Cheroutre H,
Eckmann L, et al: IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of
intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated
cancer. Cancer Cell. 15:103–113. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chlebowski RT, Wactawski-Wende J,
Ritenbaugh C, Hubbell FA, Ascensao J, Rodabough RJ, Rosenberg CA,
Taylor VM, Harris R, Chen C, et al Women's Health Initiative
Investigators, : Estrogen plus progestin and colorectal cancer in
postmenopausal women. N Engl J Med. 350:991–1004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tsoukalas D, Fragkiadaki P, Docea AO,
Alegakis AK, Sarandi E, Thanasoula M, Spandidos DA, Tsatsakis A,
Razgonova MP and Calina D: Discovery of potent telomerase
activators: Unfolding new therapeutic and anti-aging perspectives.
Mol Med Rep. 20:3701–3708. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tsatsakis AM, Docea AO and Tsitsimpikou C:
New challenges in risk assessment of chemicals when simulating real
exposure scenarios; simultaneous multi-chemicals' low dose
exposure. Food Chem Toxicol. 96:174–176. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Potter JD and McMichael AJ: Large bowel
cancer in women in relation to reproductive and hormonal factors: A
case-control study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 71:703–709. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
McMichael AJ and Potter JD: Reproduction,
endogenous and exogenous sex hormones, and colon cancer: A review
and hypothesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 65:1201–1207. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Young JL Jr, Asire AJ and Polalack ES:
SEER Program: Cancer incidence and mortality in the United States:
1973–1976. US Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, NCI.
671978.
|
|
19
|
Burbank F: Patterns in cancer mortality in
the United States: 1950–1967. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 71:1–594.
1971.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Haenszel W and Correa P: Cancer of the
colon and rectum and adenomatous polyps. A review of epidemiologic
findings. Cancer. 28:14–24. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Howell MA: The association between
colorectal cancer and breast cancer. J Chronic Dis. 29:243–261.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Izbicki JR, Wambach G, Hamilton SR,
Harnisch E, Hogenschurz R, Izbicki W and Kusche J: Androgen
receptors in experimentally induced colon carcinogenesis. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 112:39–46. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nikolouzakis TK, Stivaktakis PD, Apalaki
P, Kalliantasi K, Sapsakos TM, Spandidos DA, Tsatsakis A, Souglakos
J and Tsiaoussis J: Effect of systemic treatment on the micronuclei
frequency in the peripheral blood of patients with metastatic
colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 17:2703–2712. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qiu S, Jiang C and Zhou L: Physical
activity and mortality in patients with colorectal cancer: a
meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Eur J Cancer Prev.
April 5–2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gabrielsen JS, Najari BB, Alukal JP and
Eisenberg ML: Trends in Testosterone Prescription and Public Health
Concerns. Urol Clin North Am. 43:261–271. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Georgiadis N, Tsarouhas K, Tsitsimpikou C,
Vardavas A, Rezaee R, Germanakis I, Tsatsakis A, Stagos D and
Kouretas D: Pesticides and cardiotoxicity. Where do we stand?
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 353:1–14. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Margina D, Nițulescu G, Ungurianu A,
Mesnage R, Goumenou M, Sarigiannis DA, Aschner M, Spandidos DA,
Renieri EA, Hernández AF and Tsatsakis A: Overview of the effects
of chemical mixtures with endocrine disrupting activity in the
context of real life risk simulation (RLRS): an integrative
approach (Review). World Acad Sci J (In press).
|
|
28
|
Veremchuk LV, Tsarouhas K, Vitkina TI,
Mineeva EE, Gvozdenko TA, Antonyuk MV, Rakitskii VN, Sidletskaya
KA, Tsatsakis AM and Golokhvast KS: Impact evaluation of
environmental factors on respiratory function of asthma patients
living in urban territory. Environ Pollut. 235:489–496. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zafiropoulos A, Tsarouhas K, Tsitsimpikou
C, Fragkiadaki P, Germanakis I, Tsardi M, Maravgakis G,
Goutzourelas N, Vasilaki F, Kouretas D, et al: Cardiotoxicity in
rabbits after a low-level exposure to diazinon, propoxur, and
chlorpyrifos. Hum Exp Toxicol. 33:1241–1252. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tsatsakis A, Docea AO, Constantin C,
Calina D, Zlatian O, Nikolouzakis TK, Stivaktakis PD, Kalogeraki A,
Liesivuori J, Tzanakakis G, et al: Genotoxic, cytotoxic, and
cytopathological effects in rats exposed for 18 months to a mixture
of 13 chemicals in doses below NOAEL levels. Toxicol Lett. Sep
12–2019.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Ozcagli E, Kara M, Kotil T, Fragkiadaki P,
Tzatzarakis MN, Tsitsimpikou C, Stivaktakis PD, Tsoukalas D,
Spandidos DA, Tsatsakis AM, et al: Stanozolol administration
combined with exercise leads to decreased telomerase activity
possibly associated with liver aging. Int J Mol Med. 42:405–413.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kadıoğlu E, Taçoy G, Özçağlı E, Okyay K,
Akboğa MK, Çengel A and Şardaş S: The role of oxidative DNA damage
and GSTM1, GSTT1, and hOGG1 gene polymorphisms in coronary artery
disease risk. Anatol J Cardiol. 16:931–938. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McClendon JE, Appleby D, Claudon DB,
Donegan WL and DeCosse JJ: Colonic neoplasms: Tissue estrogen
receptor and carcinoembryonic antigen. Arch Surg. 112:240–241.
1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Alford TC, Do HM, Geelhoed GW, Tsangaris
NT and Lippman ME: Steroid hormone receptors in human colon
cancers. Cancer. 43:980–984. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sica V, Contieri E, Nola E, Bova R,
Papaleo G and Puca GA: Estrogen and progesterone binding proteins
in human colorectal cancer. A preliminary characterization of
estradiol receptor. Tumori. 67:307–314. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Odagiri E, Jibiki K, Demura R, Shinozaki
H, Nakamura S, Demura H and Suzuki H: Steroid receptors and the
distribution of IR-carcinoembryonic antigen in colonic cancer. Dis
Colon Rectum. 27:787–791. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jacobson HL: Present status of steroid
hormone receptor in large bowel cancer. Prog Cancer Res Ther.
29:3671984.
|
|
38
|
Izbicki JR, Schmitz R, Hoppen HO, Izbicki
W and Troidl H: Effects of steroid hormone therapy on primarily
xenotransplanted human colorectal adenocarcinomas. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 108:345–350. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wobbes T, Beex LVAM and Koenders AMJ:
Estrogen and progestin receptors in colonic cancer? Dis Colon
Rectum. 27:591–592. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bucci L, Salfi R, Meraviglia F and Delric
G: Hormonal receptors in colorectal cancers (abstract). Second
European Conference on Clinical Oncology and Cancer Nursing.
8:41–98. 1983.
|
|
41
|
Handelsman DJ: Androgen Physiology,
Pharmacology and AbuseEndotext [Internet]. Feingold KR, Anawalt B,
Boyce A, et al: MDText.com, Inc.; South Dartmouth, MA: 2000
|
|
42
|
Hiort O, Holterhus PM and Nitsche EM:
Physiology and pathophysiology of androgen action. Baillieres Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 12:115–132. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Guyton AC and Hall JE: Textbook of medical
physiology11th. Elsevier Saunders; Philladelphia, PA: 2006
|
|
44
|
Brenu EW, McNaughton L and
Marshall-Gradisnik SM: Is there a potential immune dysfunction with
anabolic androgenic steroid use?: A review. Mini Rev Med Chem.
11:438–445. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tsarouhas K, Kioukia-Fougia N, Papalexis
P, Tsatsakis A, Kouretas D, Bacopoulou F and Tsitsimpikou C: Use of
nutritional supplements contaminated with banned doping substances
by recreational adolescent athletes in Athens, Greece. Food Chem
Toxicol. 115:447–450. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tsitsimpikou C, Chrisostomou N, Papalexis
P, Tsarouhas K, Tsatsakis A and Jamurtas A: The use of nutritional
supplements among recreational athletes in Athens, Greece. Int J
Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 21:377–384. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Vasilaki F, Tsitsimpikou C, Tsarouhas K,
Germanakis I, Tzardi M, Kavvalakis M, Ozcagli E, Kouretas D and
Tsatsakis AM: Cardiotoxicity in rabbits after long-term nandrolone
decanoate administration. Toxicol Lett. 241:143–151. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Baggish AL, Weiner RB, Kanayama G, Hudson
JI, Picard MH, Hutter AM Jr and Pope HG Jr: Long-term
anabolic-androgenic steroid use is associated with left ventricular
dysfunction. Circ Heart Fail. 3:472–476. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tsitsimpikou C, Tsarouhas K, Spandidos DA
and Tsatsakis AM: Detection of stanozolol in the urine of athletes
at a pg level: The possibility of passive exposure. Biomed Rep.
5:665–666. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sattler FR, Jaque SV, Schroeder ET, Olson
C, Dube MP, Martinez C, Briggs W, Horton R and Azen S: Effects of
pharmacological doses of nandrolone decanoate and progressive
resistance training in immunodeficient patients infected with human
immunodeficiency virus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 84:1268–1276.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Santos MA, Oliveira CV and Silva AS:
Adverse cardiovascular effects from the use of anabolic-androgenic
steroids as ergogenic resources. Subst Use Misuse. 49:1132–1137.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bonetti A, Tirelli F, Catapano A, Dazzi D,
Dei Cas A, Solito F, Ceda G, Reverberi C, Monica C, Pipitone S, et
al: Side effects of anabolic androgenic steroids abuse. Int J
Sports Med. 29:679–687. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gould DC and Petty R: The male menopause:
does it exist? For: Some men need investigation and testosterone
treatment. West J Med. 173:76–78. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gillessen S, Templeton A, Marra G, Kuo YF,
Valtorta E and Shahinian VB: Risk of colorectal cancer in men on
long-term androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 102:1760–1770. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Izbicki JR, Schmitz R, Kamran D and
Izbicki W: Androgens as promoters of colon carcinogenesis. Cancer
Detect Prev. 6:355–362. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mehta RG, Fricks CM and Moon RC: Androgen
receptors in chemically-induced colon carcinogenesis. Cancer. 45
(Suppl):1085–1089. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Moon RC and Fricks CM: Influence of
gonadal hormones and age on 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colon
carcinogenesis. Cancer. 40 (Suppl):2502–2508. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hyde Z, Flicker L, McCaul KA, Almeida OP,
Hankey GJ, Chubb SA and Yeap BB: Associations between testosterone
levels and incident prostate, lung, and colorectal cancer. A
population-based study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
21:1319–1329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Orsted DD, Nordestgaard BG and Bojesen SE:
Plasma testosterone in the general population, cancer prognosis and
cancer risk: A prospective cohort study. Ann Oncol. 25:712–718.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Koliarakis I, Psaroulaki A, Nikolouzakis
TK, Kokkinakis M, Sgantzos MN, Goulielmos G, Androutsopoulos VP,
Tsatsakis A and Tsiaoussis J: Intestinal microbiota and colorectal
cancer: a new aspect of research. J BUON. 23:1216–1234.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Alberg AJ, Gordon GB, Hoffman SC, Comstock
GW and Helzlsouer KJ: Serum dehydroepiandrosterone and
dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate and the subsequent risk of
developing colon cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
9:517–521. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Anagnostopoulou V, Pediaditakis I,
Alkahtani S, Alarifi SA, Schmidt EM, Lang F, Gravanis A,
Charalampopoulos I and Stournaras C: Differential effects of
dehydroepiandrosterone and testosterone in prostate and colon
cancer cell apoptosis: The role of nerve growth factor (NGF)
receptors. Endocrinology. 154:2446–2456. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ferro P, Catalano MG, Raineri M, Reato G,
dell'Eva R, Risio M, Foà R, Fortunati N and Pfeffer U: Somatic
alterations of the androgen receptor CAG repeat in human colon
cancer delineate a novel mutation pathway independent of
microsatellite instability. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 123:35–40.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Slattery ML, Sweeney C, Murtaugh M, Ma KN,
Wolff RK, Potter JD, Caan BJ and Samowitz W: Associations between
ERalpha, ERbeta, and AR genotypes and colon and rectal cancer.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 14:2936–2942. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hoque A, Albanes D, Lippman SM, Spitz MR,
Taylor PR, Klein EA, Thompson IM, Goodman P, Stanford JL, Crowley
JJ, et al: Molecular epidemiologic studies within the Selenium and
Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial (SELECT). Cancer Causes Control.
12:627–633. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Krithivas K, Yurgalevitch SM, Mohr BA,
Wilcox CJ, Batter SJ, Brown M, Longcope C, McKinlay JB and Kantoff
PW: Evidence that the CAG repeat in the androgen receptor gene is
associated with the age-related decline in serum androgen levels in
men. J Endocrinol. 162:137–142. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ding D, Xu L, Menon M, Reddy GP and
Barrack ER: Effect of a short CAG (glutamine) repeat on human
androgen receptor function. Prostate. 58:23–32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Westberg L, Baghaei F, Rosmond R,
Hellstrand M, Landén M, Jansson M, Holm G, Björntorp P and Eriksson
E: Polymorphisms of the androgen receptor gene and the estrogen
receptor beta gene are associated with androgen levels in women. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 86:2562–2568. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Rudolph A, Shi H, Försti A, Hoffmeister M,
Sainz J, Jansen L, Hemminki K, Brenner H and Chang-Claude J: Repeat
polymorphisms in ESR2 and AR and colorectal cancer risk and
prognosis: Results from a German population-based case-control
study. BMC Cancer. 14:8172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Bonin A, Bellemain E, Bronken Eidesen P,
Pompanon F, Brochmann C and Taberlet P: How to track and assess
genotyping errors in population genetics studies. Mol Ecol.
13:3261–3273. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Pompanon F, Bonin A, Bellemain E and
Taberlet P: Genotyping errors: Causes, consequences and solutions.
Nat Rev Genet. 6:847–859. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Huang R, Wang G, Song Y, Wang F, Zhu B,
Tang Q, Liu Z, Chen Y, Zhang Q, Muhammad S, et al: Polymorphic CAG
Repeat and Protein Expression of Androgen Receptor Gene in
Colorectal Cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:1066–1074. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Chamberlain NL, Driver ED and Miesfeld RL:
The length and location of CAG trinucleotide repeats in the
androgen receptor N-terminal domain affect transactivation
function. Nucleic Acids Res. 22:3181–3186. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Choong CS, Kemppainen JA, Zhou ZX and
Wilson EM: Reduced androgen receptor gene expression with first
exon CAG repeat expansion. Mol Endocrinol. 10:1527–1535. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Ferro P, Catalano MG, Dell'Eva R,
Fortunati N and Pfeffer U: The androgen receptor CAG repeat: A
modifier of carcinogenesis? Mol Cell Endocrinol. 193:109–120. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Catalano MG, Pfeffer U, Raineri M, Ferro
P, Curto A, Capuzzi P, Corno F, Berta L and Fortunati N: Altered
expression of androgen-receptor isoforms in human colon-cancer
tissues. Int J Cancer. 86:325–330. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Gu S, Papadopoulou N, Nasir O, Föller M,
Alevizopoulos K, Lang F and Stournaras C: Activation of membrane
androgen receptors in colon cancer inhibits the prosurvival signals
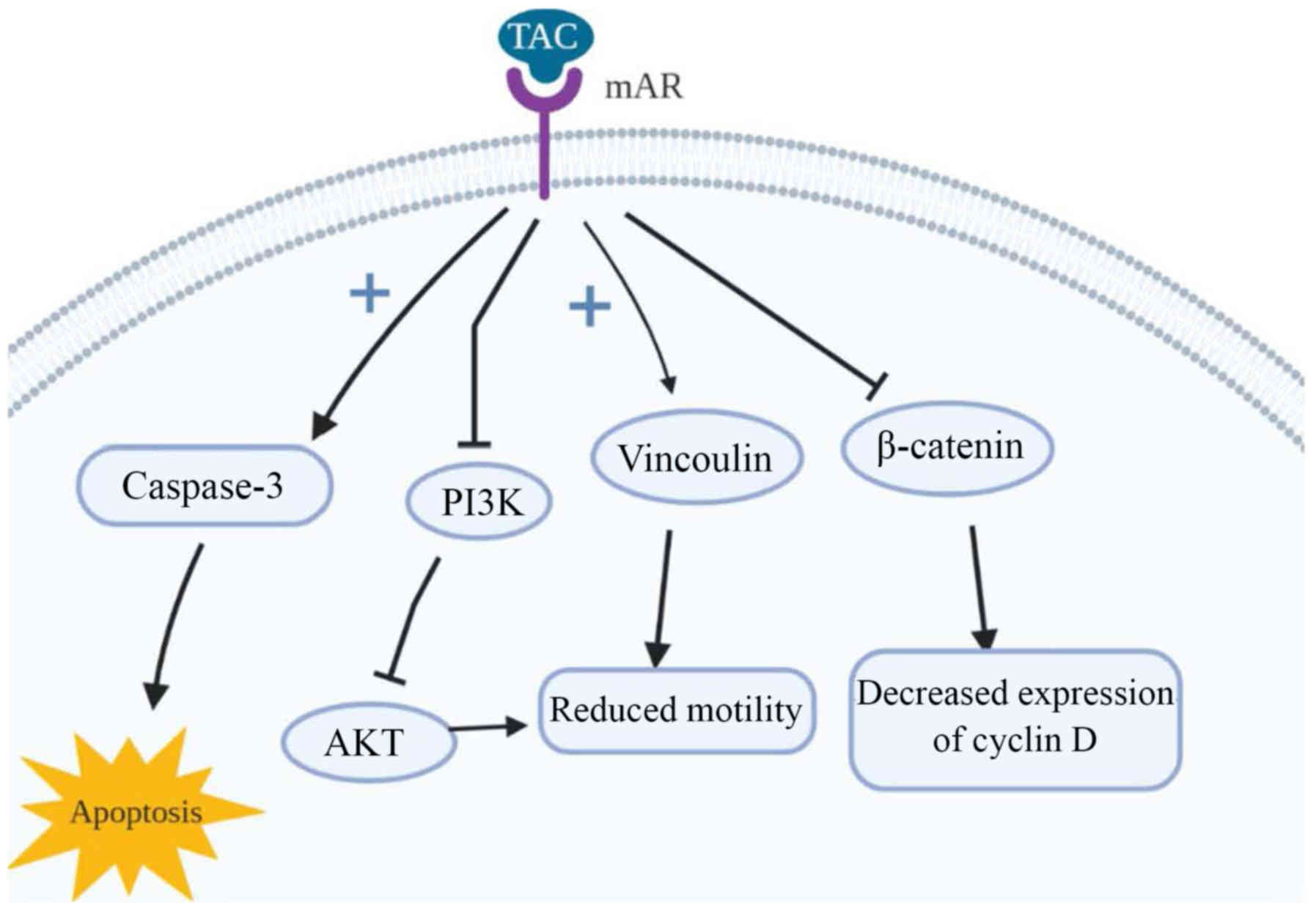
Akt/bad in vitro and in vivo and blocks migration via
vinculin/actin signaling. Mol Med. 17:48–58. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Gu S, Papadopoulou N, Gehring EM, Nasir O,
Dimas K, Bhavsar SK, Föller M, Alevizopoulos K, Lang F and
Stournaras C: Functional membrane androgen receptors in colon
tumors trigger pro-apoptotic responses in vitro and reduce
drastically tumor incidence in vivo. Mol Cancer. 8:1142009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chesire DR and Isaacs WB: Ligand-dependent
inhibition of beta-catenin/TCF signaling by androgen receptor.
Oncogene. 21:8453–8469. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yoshioka T, Nishikawa Y, Ito R, Kawamata
M, Doi Y, Yamamoto Y, Yoshida M, Omori Y, Kotanagi H, Masuko T, et
al: Significance of integrin αvβ5 and erbB3 in enhanced cell
migration and liver metastasis of colon carcinomas stimulated by
hepatocyte-derived heregulin. Cancer Sci. 101:2011–2018. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Holgren C, Dougherty U, Edwin F, Cerasi D,
Taylor I, Fichera A, Joseph L, Bissonnette M and Khare S: Sprouty-2
controls c-Met expression and metastatic potential of colon cancer
cells: Sprouty/c-Met upregulation in human colonic adenocarcinomas.
Oncogene. 29:5241–5253. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Huynh N, Liu KH, Baldwin GS and He H:
P21-activated kinase 1 stimulates colon cancer cell growth and
migration/invasion via ERK- and AKT-dependent pathways. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1803:1106–1113. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Teyssier C, Ou CY, Khetchoumian K, Losson
R and Stallcup MR: Transcriptional intermediary factor 1alpha
mediates physical interaction and functional synergy between the
coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1 and
glucocorticoid receptor-interacting protein 1 nuclear receptor
coactivators. Mol Endocrinol. 20:1276–1286. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Chen D, Ma H, Hong H, Koh SS, Huang SM,
Schurter BT, Aswad DW and Stallcup MR: Regulation of transcription
by a protein methyltransferase. Science. 284:2174–2177. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Koh SS, Li H, Lee YH, Widelitz RB, Chuong
CM and Stallcup MR: Synergistic coactivator function by
coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase (CARM) 1 and
beta-catenin with two different classes of DNA-binding
transcriptional activators. J Biol Chem. 277:26031–26035. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
El Messaoudi S, Fabbrizio E, Rodriguez C,
Chuchana P, Fauquier L, Cheng D, Theillet C, Vandel L, Bedford MT
and Sardet C: Coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1
(CARM1) is a positive regulator of the Cyclin E1 gene. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 103:13351–13356. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Kim YR, Lee BK, Park RY, Nguyen NT, Bae
JA, Kwon DD and Jung C: Differential CARM1 expression in prostate
and colorectal cancers. BMC Cancer. 10:1972010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Ilboudo S, Fouche E, Rizzati V, Toé AM,
Gamet-Payrastre L and Guissou PI: In vitro impact of five
pesticides alone or in combination on human intestinal cell line
Caco-2. Toxicol Rep. 1:474–489. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Carroll RE, Goodlad RA, Poole AJ, Tyner
AL, Robey RB, Swanson SM and Unterman TG: Reduced susceptibility to
azoxymethane-induced aberrant crypt foci formation and colon cancer
in growth hormone deficient rats. Growth Horm IGF Res. 19:447–456.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Chuang KH, Altuwaijri S, Li G, Lai JJ, Chu
CY, Lai KP, Lin HY, Hsu JW, Keng P, Wu MC, et al: Neutropenia with
impaired host defense against microbial infection in mice lacking
androgen receptor. J Exp Med. 206:1181–1199. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Mårin P, Krotkiewski M and Björntorp P:
Androgen treatment of middle-aged, obese men: Effects on
metabolism, muscle and adipose tissues. Eur J Med. 1:329–336.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Lin JH and Giovannucci E: Sex hormones and
colorectal cancer: What have we learned so far? J Natl Cancer Inst.
102:1746–1747. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Thevis M and Schänzer W: Synthetic
anabolic agents: Steroids and nonsteroidal selective androgen
receptor modulatorsDoping in Sports: Biochemical Principles,
Effects and Analysis. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Thieme
D and Hemmersbach P: 195. Springer; Berlin, Heidelberg: pp. 99–126.
2010, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Joseph JF and Parr MK: Synthetic androgens
as designer supplements. Curr Neuropharmacol. 13:89–100. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Watanabe S and Kobayashi Y: Exogenous
hormones and human cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 23:1–13.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Rosner F and Khan MT: Renal cell carcinoma
following prolonged testosterone therapy. Arch Intern Med.
152:426–429. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Martorana G, Concetti S, Manferrari F and
Creti S: Anabolic steroid abuse and renal cell carcinoma. J Urol.
162:2089. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Bryden AAG, Rothwell PJN and O'Reilly PH:
Anabolic steroid abuse and renal-cell carcinoma. Lancet.
346:1306–1307. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Zahm SH and Fraumeni JF Jr: The
epidemiology of soft tissue sarcoma. Semin Oncol. 24:504–514.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Nourbakhsh M, Golestani A, Zahrai M,
Modarressi MH, Malekpour Z and Karami-Tehrani F: Androgens
stimulate telomerase expression, activity and phosphorylation in
ovarian adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 330:10–16. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
McKeown-Eyssen G: Epidemiology of
colorectal cancer revisited: Are serum triglycerides and/or plasma
glucose associated with risk? Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
3:687–695. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Bronson FH and Matherne CM: Exposure to
anabolic-androgenic steroids shortens life span of male mice. Med
Sci Sports Exerc. 29:615–619. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Froehner M, Fischer R, Leike S, Hakenberg
OW, Noack B and Wirth MP: Intratesticular leiomyosarcoma in a young
man after high dose doping with oral-turinabol: A case report.
Cancer. 86:1571–1575. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Chacon A and Monga M: Medical management
of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Geriatr Nephrol Urol. 9:39–48.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Dimitriadis G, Mitrou P, Lambadiari V,
Maratou E and Raptis SA: Insulin effects in muscle and adipose
tissue. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 93 (Suppl 1):S52–S59. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Giovannucci E and Michaud D: The role of
obesity and related metabolic disturbances in cancers of the colon,
prostate, and pancreas. Gastroenterology. 132:2208–2225. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Yang YX, Hennessy S and Lewis JD: Insulin
therapy and colorectal cancer risk among type 2 diabetes mellitus
patients. Gastroenterology. 127:1044–1050. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Larsson SC, Orsini N, Brismar K and Wolk
A: Diabetes mellitus and risk of bladder cancer: A meta-analysis.
Diabetologia. 49:2819–2823. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Flood A, Mai V, Pfeiffer R, Kahle L,
Remaley AT, Lanza E and Schatzkin A: Elevated serum concentrations
of insulin and glucose increase risk of recurrent colorectal
adenomas. Gastroenterology. 133:1423–1429. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Polednak AP: Comorbid diabetes mellitus
and risk of death after diagnosis of colorectal cancer: A
population-based study. Cancer Detect Prev. 30:466–472. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Jullumstrø E, Kollind M, Lydersen S and
Edna TH: Diabetes mellitus and outcomes of colorectal cancer. Acta
Oncol. 48:361–367. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Schoen RE, Weissfeld JL, Kuller LH, Thaete
FL, Evans RW, Hayes RB and Rosen CJ: Insulin-like growth factor-I
and insulin are associated with the presence and advancement of
adenomatous polyps. Gastroenterology. 129:464–475. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
LeRoith D, Baserga R, Helman L and Roberts
CT Jr: Insulin-like growth factors and cancer. Ann Intern Med.
122:54–59. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Sandhu MS, Dunger DB and Giovannucci EL:
Insulin, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), IGF binding
proteins, their biologic interactions, and colorectal cancer. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 94:972–980. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Siddle K: Signalling by insulin and IGF
receptors: Supporting acts and new players. J Mol Endocrinol.
47:R1–R10. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Mosthaf L, Grako K, Dull TJ, Coussens L,
Ullrich A and McClain DA: Functionally distinct insulin receptors
generated by tissue-specific alternative splicing. EMBO J.
9:2409–2413. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Abbruzzese C, Diodoro MG, Sperduti I,
Mileo AM, Pattaro G, De Salvo L, Cosimelli M, Perrotti N and Paggi
MG: Detection of phosphorylated insulin receptor in colorectal
adenoma and adenocarcinoma: Implications for prognosis and clinical
outcome. J Cell Physiol. 230:562–567. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Frasca F, Pandini G, Scalia P, Sciacca L,
Mineo R, Costantino A, Goldfine ID, Belfiore A and Vigneri R:
Insulin receptor isoform A, a newly recognized, high-affinity
insulin-like growth factor II receptor in fetal and cancer cells.
Mol Cell Biol. 19:3278–3288. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Kosaki A and Webster NJ: Effect of
dexamethasone on the alternative splicing of the insulin receptor
mRNA and insulin action in HepG2 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem.
268:21990–21996. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Heckl SM, Pellinghaus M, Krüger S,
Bosselmann C, Wilhelm F, Behrens HM, Schreiber S and Röcken C:
Epithelial insulin receptor expression-prognostic relevance in
colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 9:37497–37508. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Morcavallo A, Genua M, Palummo A,
Kletvikova E, Jiracek J, Brzozowski AM, Iozzo RV, Belfiore A and
Morrione A: Insulin and insulin-like growth factor II
differentially regulate endocytic sorting and stability of insulin
receptor isoform A. J Biol Chem. 287:11422–11436. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Wang X, Häring MF, Rathjen T, Lockhart SM,
Sørensen D, Ussar S, Rasmussen LM, Bertagnolli MM, Kahn CR and
Rask-Madsen C: Insulin resistance in vascular endothelial cells
promotes intestinal tumour formation. Oncogene. 36:4987–4996. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Laakso M, Edelman SV, Brechtel G and Baron
AD: Impaired insulin-mediated skeletal muscle blood flow in
patients with NIDDM. Diabetes. 41:1076–1083. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Steinberg HO, Chaker H, Leaming R, Johnson
A, Brechtel G and Baron AD: Obesity/insulin resistance is
associated with endothelial dysfunction. Implications for the
syndrome of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 97:2601–2610. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Rask-Madsen C, Ihlemann N, Krarup T,
Christiansen E, Kober L, Nervil Kistorp C and Torp-Pedersen C:
Insulin therapy improves insulin-stimulated endothelial function in
patients with type 2 diabetes and ischemic heart disease. Diabetes.
50:2611–2618. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Tabit CE, Shenouda SM, Holbrook M,
Fetterman JL, Kiani S, Frame AA, Kluge MA, Held A, Dohadwala MM,
Gokce N, et al: Protein kinase C-β contributes to impaired
endothelial insulin signaling in humans with diabetes mellitus.
Circulation. 127:86–95. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Simpson RJ, Lim JW, Moritz RL and
Mathivanan S: Exosomes: Proteomic insights and diagnostic
potential. Expert Rev Proteomics. 6:267–283. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Gangoda L and Mathivanan S: Cortactin
enhances exosome secretion without altering cargo. J Cell Biol.
214:129–131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Gangoda L, Boukouris S, Liem M, Kalra H
and Mathivanan S: Extracellular vesicles including exosomes are
mediators of signal transduction: Are they protective or
pathogenic? Proteomics. 15:260–271. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Silantyev AS, Falzone L, Libra M, Gurina
OI, Kardashova KS, Nikolouzakis TK, Nosyrev AE, Sutton CW, Mitsias
PD and Tsatsakis A: Current and Future Trends on Diagnosis and
Prognosis of Glioblastoma: From Molecular Biology to Proteomics.
Cells. 8:82019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Taniguchi CM, Emanuelli B and Kahn CR:
Critical nodes in signalling pathways: Insights into insulin
action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:85–96. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Huang XF and Chen JZ: Obesity, the
PI3K/Akt signal pathway and colon cancer. Obes Rev. 10:610–616.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Matsuzaki H, Daitoku H, Hatta M, Tanaka K
and Fukamizu A: Insulin-induced phosphorylation of FKHR (Foxo1)
targets to proteasomal degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:11285–11290. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Liem M, Ang CS and Mathivanan S: Insulin
Mediated Activation of PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Modifies the
Proteomic Cargo of Extracellular Vesicles. Proteomics. 17:172017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Baserga R: The insulin-like growth factor
I receptor: A key to tumor growth? Cancer Res. 55:249–252.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Párrizas M and LeRoith D: Insulin-like
growth factor-1 inhibition of apoptosis is associated with
increased expression of the bcl-xL gene product. Endocrinology.
138:1355–1358. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Wang L, Ma W, Markovich R, Lee WL and Wang
PH: Insulin-like growth factor I modulates induction of apoptotic
signaling in H9C2 cardiac muscle cells. Endocrinology.
139:1354–1360. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Remacle-Bonnet MM, Garrouste FL, Heller S,
André F, Marvaldi JL and Pommier GJ: Insulin-like growth factor-I
protects colon cancer cells from death factor-induced apoptosis by
potentiating tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced mitogen-activated
protein kinase and nuclear factor kappaB signaling pathways. Cancer
Res. 60:2007–2017. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Liu B, Fang M, Lu Y, Mendelsohn J and Fan
Z: Fibroblast growth factor and insulin-like growth factor
differentially modulate the apoptosis and G1 arrest induced by
anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody.
Oncogene. 20:1913–1922. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Ryan PD and Goss PE: The emerging role of
the insulin-like growth factor pathway as a therapeutic target in
cancer. Oncologist. 13:16–24. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Pollak M: The insulin and insulin-like
growth factor receptor family in neoplasia: An update. Nat Rev
Cancer. 12:159–169. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Islam MA, Hooiveld GJEJ, van den Berg JHJ,
van der Velpen V, Murk AJ, Rietjens IMCM and van Leeuwen FXR: Soy
supplementation: Impact on gene expression in different tissues of
ovariectomized rats and evaluation of the rat model to predict
(post)menopausal health effect. Toxicol Rep. 5:1087–1097. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Ma J, Pollak MN, Giovannucci E, Chan JM,
Tao Y, Hennekens CH and Stampfer MJ: Prospective study of
colorectal cancer risk in men and plasma levels of insulin-like
growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 91:620–625. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Lahm H, Suardet L, Laurent PL, Fischer JR,
Ceyhan A, Givel JC and Odartchenko N: Growth regulation and
co-stimulation of human colorectal cancer cell lines by
insulin-like growth factor I, II and transforming growth factor
alpha. Br J Cancer. 65:341–346. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Guo YS, Narayan S, Yallampalli C and Singh
P: Characterization of insulinlike growth factor I receptors in
human colon cancer. Gastroenterology. 102:1101–1108. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Freier S, Weiss O, Eran M, Flyvbjerg A,
Dahan R, Nephesh I, Safra T, Shiloni E and Raz I: Expression of the
insulin-like growth factors and their receptors in adenocarcinoma
of the colon. Gut. 44:704–708. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Hakam A, Yeatman TJ, Lu L, Mora L, Marcet
G, Nicosia SV, Karl RC and Coppola D: Expression of insulin-like
growth factor-1 receptor in human colorectal cancer. Hum Pathol.
30:1128–1133. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Lee J, Jain A, Kim P, Lee T, Kuller A,
Princen F, In-GuDo, Kim SH, Park JO, Park YS, et al: Activated cMET
and IGF1R-driven PI3K signaling predicts poor survival in
colorectal cancers independent of KRAS mutational status. PLoS One.
9:e1035512014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Soubry A, Il'yasova D, Sedjo R, Wang F,
Byers T, Rosen C, Yashin A, Ukraintseva S, Haffner S and D'Agostino
R Jr: Increase in circulating levels of IGF-1 and IGF-1/IGFBP-3
molar ratio over a decade is associated with colorectal adenomatous
polyps. Int J Cancer. 131:512–517. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Ollberding NJ, Cheng I, Wilkens LR,
Henderson BE, Pollak MN, Kolonel LN and Le Marchand L: Genetic
variants, prediagnostic circulating levels of insulin-like growth
factors, insulin, and glucose and the risk of colorectal cancer:
The Multiethnic Cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
21:810–820. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Giovannucci E: Insulin, insulin-like
growth factors and colon cancer: A review of the evidence. J Nutr.
131 (Suppl):3109S–3120S. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Shiratsuchi I, Akagi Y, Kawahara A,
Kinugasa T, Romeo K, Yoshida T, Ryu Y, Gotanda Y, Kage M and
Shirouzu K: Expression of IGF-1 and IGF-1R and their relation to
clinicopathological factors in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res.
31:2541–2545. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Peters G, Gongoll S, Langner C, Mengel M,
Piso P, Klempnauer J, Rüschoff J, Kreipe H and von Wasielewski R:
IGF-1R, IGF-1 and IGF-2 expression as potential prognostic and
predictive markers in colorectal-cancer. Virchows Arch.
443:139–145. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Furlanetto RW, Harwell SE and Frick KK:
Insulin-like growth factor-I induces cyclin-D1 expression in MG63
human osteosarcoma cells in vitro. Mol Endocrinol. 8:510–517. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Sahin AA, Ro JY, Brown RW, Ordonez NG,
Cleary KR, el-Naggar AK, Wilson P and Ayala AG: Assessment of
Ki-67-derived tumor proliferative activity in colorectal
adenocarcinomas. Mod Pathol. 7:17–22. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Kubota Y, Petras RE, Easley KA, Bauer TW,
Tubbs RR and Fazio VW: Ki-67-determined growth fraction versus
standard staging and grading parameters in colorectal carcinoma. A
multivariate analysis. Cancer. 70:2602–2609. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Cascinu S, Del Ferro E, Grianti C, Ligi M,
Ghiselli R, Foglietti G, Saba V, Lungarotti F and Catalano G:
Inhibition of tumor cell kinetics and serum insulin growth factor I
levels by octreotide in colorectal cancer patients.
Gastroenterology. 113:767–772. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Bowers LW, Rossi EL, O'Flanagan CH,
deGraffenried LA and Hursting SD: The Role of the Insulin/IGF
System in Cancer: Lessons Learned from Clinical Trials and the
Energy Balance-Cancer Link. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 6:772015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Firth SM and Baxter RC: Cellular actions
of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr Rev.
23:824–854. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Liou JM, Shun CT, Liang JT, Chiu HM, Chen
MJ, Chen CC, Wang HP, Wu MS and Lin JT: Plasma insulin-like growth
factor-binding protein-2 levels as diagnostic and prognostic
biomarker of colorectal cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
95:1717–1725. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Jones JI and Clemmons DR: Insulin-like
growth factors and their binding proteins: Biological actions.
Endocr Rev. 16:3–34. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Héron-Milhavet L and LeRoith D:
Insulin-like growth factor I induces MDM2-dependent degradation of
p53 via the p38 MAPK pathway in response to DNA damage. J Biol
Chem. 277:15600–15606. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Peretz S, Jensen R, Baserga R and Glazer
PM: ATM-dependent expression of the insulin-like growth factor-I
receptor in a pathway regulating radiation response. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 98:1676–1681. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Huang F, Xu LA and Khambata-Ford S:
Correlation between gene expression of IGF-1R pathway markers and
cetuximab benefit in metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
18:1156–1166. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Jones HE, Goddard L, Gee JM, Hiscox S,
Rubini M, Barrow D, Knowlden JM, Williams S, Wakeling AE and
Nicholson RI: Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signalling and
acquired resistance to gefitinib (ZD1839; Iressa) in human breast
and prostate cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer. 11:793–814. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Albanell J and Baselga J: Unraveling
resistance to trastuzumab (Herceptin): Insulin-like growth factor-I
receptor, a new suspect. J Natl Cancer Inst. 93:1830–1832. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Shen K, Cui D, Sun L, Lu Y, Han M and Liu
J: Inhibition of IGF-IR increases chemosensitivity in human
colorectal cancer cells through MRP-2 promoter suppression. J Cell
Biochem. 113:2086–2097. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Warren RS, Yuan H, Matli MR, Ferrara N and
Donner DB: Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor by
insulin-like growth factor 1 in colorectal carcinoma. J Biol Chem.
271:29483–29488. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Akagi Y, Liu W, Zebrowski B, Xie K and
Ellis LM: Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor
expression in human colon cancer by insulin-like growth factor-I.
Cancer Res. 58:4008–4014. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Sekharam M, Zhao H, Sun M, Fang Q, Zhang
Q, Yuan Z, Dan HC, Boulware D, Cheng JQ and Coppola D: Insulin-like
growth factor 1 receptor enhances invasion and induces resistance
to apoptosis of colon cancer cells through the Akt/Bcl-x(L)
pathway. Cancer Res. 63:7708–7716. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Zhang QY, Wang L, Song ZY and Qu XJ:
Knockdown of type I insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibits
human colorectal cancer cell growth and downstream PI3K/Akt,
WNT/β-catenin signal pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 73:12–18. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Nahor I, Abramovitch S, Engeland K and
Werner H: The p53-family members p63 and p73 inhibit insulin-like
growth factor-I receptor gene expression in colon cancer cells.
Growth Horm IGF Res. 15:388–396. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Ramocki NM, Wilkins HR, Magness ST,
Simmons JG, Scull BP, Lee GH, McNaughton KK and Lund PK: Insulin
receptor substrate-1 deficiency promotes apoptosis in the putative
intestinal crypt stem cell region, limits Apcmin/+ tumors, and
regulates Sox9. Endocrinology. 149:261–267. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Chan BT and Lee AV: Insulin receptor
substrates (IRSs) and breast tumorigenesis. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 13:415–422. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Esposito DL, Aru F, Lattanzio R, Morgano
A, Abbondanza M, Malekzadeh R, Bishehsari F, Valanzano R, Russo A,
Piantelli M, et al: The insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) in
intestinal epithelial differentiation and in colorectal cancer.
PLoS One. 7:e361902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Day E, Poulogiannis G, McCaughan F,
Mulholland S, Arends MJ, Ibrahim AE and Dear PH: IRS2 is a
candidate driver oncogene on 13q34 in colorectal cancer. Int J Exp
Pathol. 94:203–211. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Slattery ML, Samowitz W, Curtin K, Ma KN,
Hoffman M, Caan B and Neuhausen S: Associations among IRS1, IRS2,
IGF1, and IGFBP3 genetic polymorphisms and colorectal cancer.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 13:1206–1214. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Sanchez-Lopez E, Flashner-Abramson E,
Shalapour S, Zhong Z, Taniguchi K, Levitzki A and Karin M:
Targeting colorectal cancer via its microenvironment by inhibiting
IGF-1 receptor-insulin receptor substrate and STAT3 signaling.
Oncogene. 35:2634–2644. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Krajewski W, Dzięgała M, Kołodziej A,
Dembowski J and Zdrojowy R: Vitamin D and urological cancers. Cent
European J Urol. 69:139–147. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Lefkowitz ES and Garland CF: Sunlight,
vitamin D, and ovarian cancer mortality rates in US women. Int J
Epidemiol. 23:1133–1136. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Uitterlinden AG, Fang Y, Van Meurs JB,
Pols HA and Van Leeuwen JP: Genetics and biology of vitamin D
receptor polymorphisms. Gene. 338:143–156. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Boscoe FP and Schymura MJ: Solar
ultraviolet-B exposure and cancer incidence and mortality in the
United States, 1993–2002. BMC Cancer. 6:2642006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Bishop JE, Collins ED, Okamura WH and
Norman AW: Profile of ligand specificity of the vitamin D binding
protein for 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its analogs. J Bone
Miner Res. 9:1277–1288. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Bikle D: Vitamin D: Production,
Metabolism, and Mechanisms of ActionEndotext [Internet]. Feingold
KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, et al: MDText.com, Inc.; South Dartmouth,
MA: 2000
|
|
185
|
Feskanich D, Ma J, Fuchs CS, Kirkner GJ,
Hankinson SE, Hollis BW and Giovannucci EL: Plasma vitamin D
metabolites and risk of colorectal cancer in women. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 13:1502–1508. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Braun MM, Helzlsouer KJ, Hollis BW and
Comstock GW: Colon cancer and serum vitamin D metabolite levels
10–17 years prior to diagnosis. Am J Epidemiol. 142:608–611. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Gorham ED, Garland CF, Garland FC, Grant
WB, Mohr SB, Lipkin M, Newmark HL, Giovannucci E, Wei M and Holick
MF: Vitamin D and prevention of colorectal cancer. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 97:179–194. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Garland C, Shekelle RB, Barrett-Connor E,
Criqui MH, Rossof AH and Paul O: Dietary vitamin D and calcium and
risk of colorectal cancer: A 19-year prospective study in men.
Lancet. 1:307–309. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Garland CF and Garland FC: Do sunlight and
vitamin D reduce the likelihood of colon cancer? Int J Epidemiol.
9:227–231. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Belleli A, Shany S, Levy J, Guberman R and
Lamprecht SA: A protective role of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in
chemically induced rat colon carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis.
13:2293–2298. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Comer PF, Clark TD and Glauert HP: Effect
of dietary vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) on colon carcinogenesis
induced by 1,2-dimethylhydrazine in male Fischer 344 rats. Nutr
Cancer. 19:113–124. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Thomas MG, Tebbutt S and Williamson RC:
Vitamin D and its metabolites inhibit cell proliferation in human
rectal mucosa and a colon cancer cell line. Gut. 33:1660–1663.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Brehier A and Thomasset M: Human colon
cell line HT-29: Characterisation of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3
receptor and induction of differentiation by the hormone. J Steroid
Biochem. 29:265–270. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Cross HS, Farsoudi KH and Peterlik M:
Growth inhibition of human colon adenocarcinoma-derived Caco-2
cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and two synthetic analogs:
Relation to in vitro hypercalcemic potential. Naunyn Schmiedebergs
Arch Pharmacol. 347:105–110. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Vandewalle B, Adenis A, Hornez L,
Revillion F and Lefebvre J: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptors in
normal and malignant human colorectal tissues. Cancer Lett.
86:67–73. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Zhao X and Feldman D: Regulation of
vitamin D receptor abundance and responsiveness during
differentiation of HT-29 human colon cancer cells. Endocrinology.
132:1808–1814. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Carlberg C and Dunlop TW: An integrated
biological approach to nuclear receptor signaling in physiological
control and disease. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 16:1–22. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Padi SK, Zhang Q, Rustum YM, Morrison C
and Guo B: MicroRNA-627 mediates the epigenetic mechanisms of
vitamin D to suppress proliferation of human colorectal cancer
cells and growth of xenograft tumors in mice. Gastroenterology.
145:437–446. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Fernandez-Garcia NI, Palmer HG, Garcia M,
Gonzalez-Martin A, del Rio M, Barettino D, Volpert O, Muñoz A and
Jimenez B: 1alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 regulates the expression
of Id1 and Id2 genes and the angiogenic phenotype of human colon
carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 24:6533–6544. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Pendás-Franco N, Aguilera O, Pereira F,
González-Sancho JM and Muñoz A: Vitamin D and Wnt/β-catenin pathway
in colon cancer: Role and regulation of DICKKOPF genes. Anticancer
Res 28 (5A). 2613–2623. 2008.
|
|
201
|
Ylikomi T, Laaksi I, Lou YR, Martikainen
P, Miettinen S, Pennanen P, Purmonen S, Syvälä H, Vienonen A and
Tuohimaa P: Antiproliferative action of vitamin D. Vitam Horm.
64:357–406. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Taghizadeh F, Tang MJ and Tai IT:
Synergism between vitamin D and secreted protein acidic and rich in
cysteine-induced apoptosis and growth inhibition results in
increased susceptibility of therapy-resistant colorectal cancer
cells to chemotherapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:309–317. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Pálmer HG, Sánchez-Carbayo M,
Ordóñez-Morán P, Larriba MJ, Cordón-Cardó C and Muñoz A: Genetic
signatures of differentiation induced by 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin
D3 in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 63:7799–7806.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Jensen SS, Madsen MW, Lukas J, Binderup L
and Bartek J: Inhibitory effects of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3)
on the G(1)-S phase-controlling machinery. Mol Endocrinol.
15:1370–1380. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Scaglione-Sewell BA, Bissonnette M,
Skarosi S, Abraham C and Brasitus TA: A vitamin D3 analog induces a
G1-phase arrest in CaCo-2 cells by inhibiting cdk2 and cdk6: Roles
of cyclin E, p21Waf1, and p27Kip1. Endocrinology. 141:3931–3939.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Liu W, Chen Y, Golan MA, Annunziata ML, Du
J, Dougherty U, Kong J, Musch M, Huang Y, Pekow J, et al:
Intestinal epithelial vitamin D receptor signaling inhibits
experimental colitis. J Clin Invest. 123:3983–3996. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Murillo G, Nagpal V, Tiwari N, Benya RV
and Mehta RG: Actions of vitamin D are mediated by the TLR4 pathway
in inflammation-induced colon cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
121:403–407. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Kim KE and Brasitus TA: The role of
vitamin D in normal and pathologic processes in the colon. Curr
Opin Gastroenterol. 17:72–77. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Revelli A, Massobrio M and Tesarik J:
Nongenomic effects of 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3). Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 9:419–427. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Norman AW, Song X, Zanello L, Bula C and
Okamura WH: Rapid and genomic biological responses are mediated by
different shapes of the agonist steroid hormone, 1α,25(OH)2vitamin
D3. Steroids. 64:120–128. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Sitrin MD, Bissonnette M, Bolt MJ, Wali R,
Khare S, Scaglione-Sewell B, Skarosi S and Brasitus TA: Rapid
effects of 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 on signal transduction systems in
colonic cells. Steroids. 64:137–142. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Nelson WJ and Nusse R: Convergence of Wnt,
beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science. 303:1483–1487. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Jeanes A, Gottardi CJ and Yap AS:
Cadherins and cancer: How does cadherin dysfunction promote tumor
progression? Oncogene. 27:6920–6929. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Rozen F, Yang XF, Huynh H and Pollak M:
Antiproliferative action of vitamin D-related compounds and
insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 accumulation. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 89:652–656. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Kaler P, Augenlicht L and Klampfer L:
Macrophage-derived IL-1beta stimulates Wnt signaling and growth of
colon cancer cells: A crosstalk interrupted by vitamin D3.
Oncogene. 28:3892–3902. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Kaler P, Galea V, Augenlicht L and
Klampfer L: Tumor associated macrophages protect colon cancer cells
from TRAIL-induced apoptosis through IL-1beta-dependent
stabilization of Snail in tumor cells. PLoS One. 5:e117002010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Chen A, Davis BH, Sitrin MD, Brasitus TA
and Bissonnette M: Transforming growth factor-beta 1 signaling
contributes to Caco-2 cell growth inhibition induced by
1,25(OH)(2)D(3). Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
283:G864–G874. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Yanagisawa J, Yanagi Y, Masuhiro Y, Suzawa
M, Watanabe M, Kashiwagi K, Toriyabe T, Kawabata M, Miyazono K and
Kato S: Convergence of transforming growth factor-beta and vitamin
D signaling pathways on SMAD transcriptional coactivators. Science.
283:1317–1321. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Deeb KK, Trump DL and Johnson CS: Vitamin
D signalling pathways in cancer: Potential for anticancer
therapeutics. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:684–700. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Tong WM, Hofer H, Ellinger A, Peterlik M
and Cross HS: Mechanism of antimitogenic action of vitamin D in
human colon carcinoma cells: Relevance for suppression of epidermal
growth factor-stimulated cell growth. Oncol Res. 11:77–84.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Ben-Shoshan M, Amir S, Dang DT, Dang LH,
Weisman Y and Mabjeesh NJ: 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3
(Calcitriol) inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1/vascular
endothelial growth factor pathway in human cancer cells. Mol Cancer
Ther. 6:1433–1439. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Harris DM and Go VL: Vitamin D and colon
carcinogenesis. J Nutr. 134 (Suppl):3463S–3471S. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Lappe JM, Travers-Gustafson D, Davies KM,
Recker RR and Heaney RP: Vitamin D and calcium supplementation
reduces cancer risk: Results of a randomized trial. Am J Clin Nutr.
85:1586–1591. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Binder G, Wittekindt N and Ranke MB:
Noonan Syndrome: Genetics and Responsiveness to Growth Hormone
Therapy. Horm Res Paediatr. 67:45–49. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
225
|
Campbell GS: Growth-hormone signal
transduction. J Pediatr. 131:S42–S44. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Savage MO, Blum WF, Ranke MB, Postel-Vinay
MC, Cotterill AM, Hall K, Chatelain PG, Preece MA and Rosenfeld RG:
Clinical features and endocrine status in patients with growth
hormone insensitivity (Laron syndrome). J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
77:1465–1471. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Gunawardane K, Hansen TK, Muller N,
Christiansen JS and Jorgensen JOL: Normal Physiology of Growth
Hormone in AdultsEndotext [Internet]. Feingold KR, Anawalt B and
Boyce A: MDText.com, Inc.; South Dartmouth, MA: 2000
|
|
228
|
Slater MD and Murphy CR: Co-expression of
interleukin-6 and human growth hormone in apparently normal
prostate biopsies that ultimately progress to prostate cancer using
low pH, high temperature antigen retrieval. J Mol Histol. 37:37–41.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Waters MJ and Conway-Campbell BL: The
oncogenic potential of autocrine human growth hormone in breast
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:14992–14993. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Brooks AJ and Waters MJ: The growth
hormone receptor: Mechanism of activation and clinical
implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 6:515–525. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Brown-Borg HM and Bartke A: GH and IGF1:
Roles in energy metabolism of long-living GH mutant mice. J
Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 67:652–660. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Chesnokova V, Zonis S, Zhou C, Recouvreux
MV, Ben-Shlomo A, Araki T, Barrett R, Workman M, Wawrowsky K,
Ljubimov VA, et al: Growth hormone is permissive for neoplastic
colon growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:E3250–E3259. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Morin PJ, Sparks AB, Korinek V, Barker N,
Clevers H, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW: Activation of
beta-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in
beta-catenin or APC. Science. 275:1787–1790. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Koliarakis I, Messaritakis I, Nikolouzakis
TK, Hamilos G, Souglakos J and Tsiaoussis J: Oral Bacteria and
Intestinal Dysbiosis in Colorectal Cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
20:41462019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|