|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. Ca Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
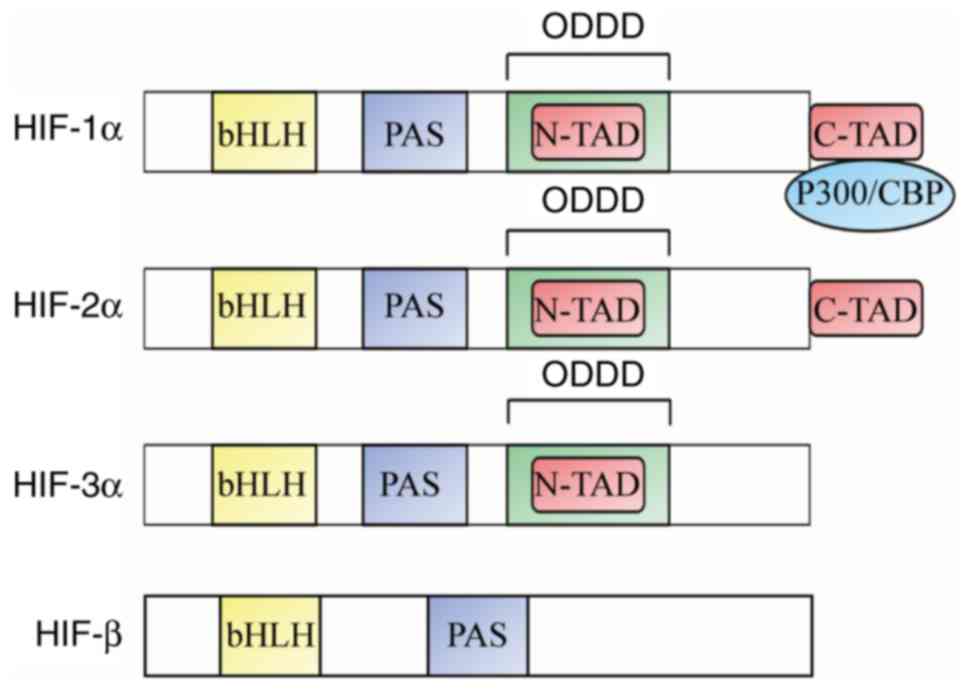
|
2
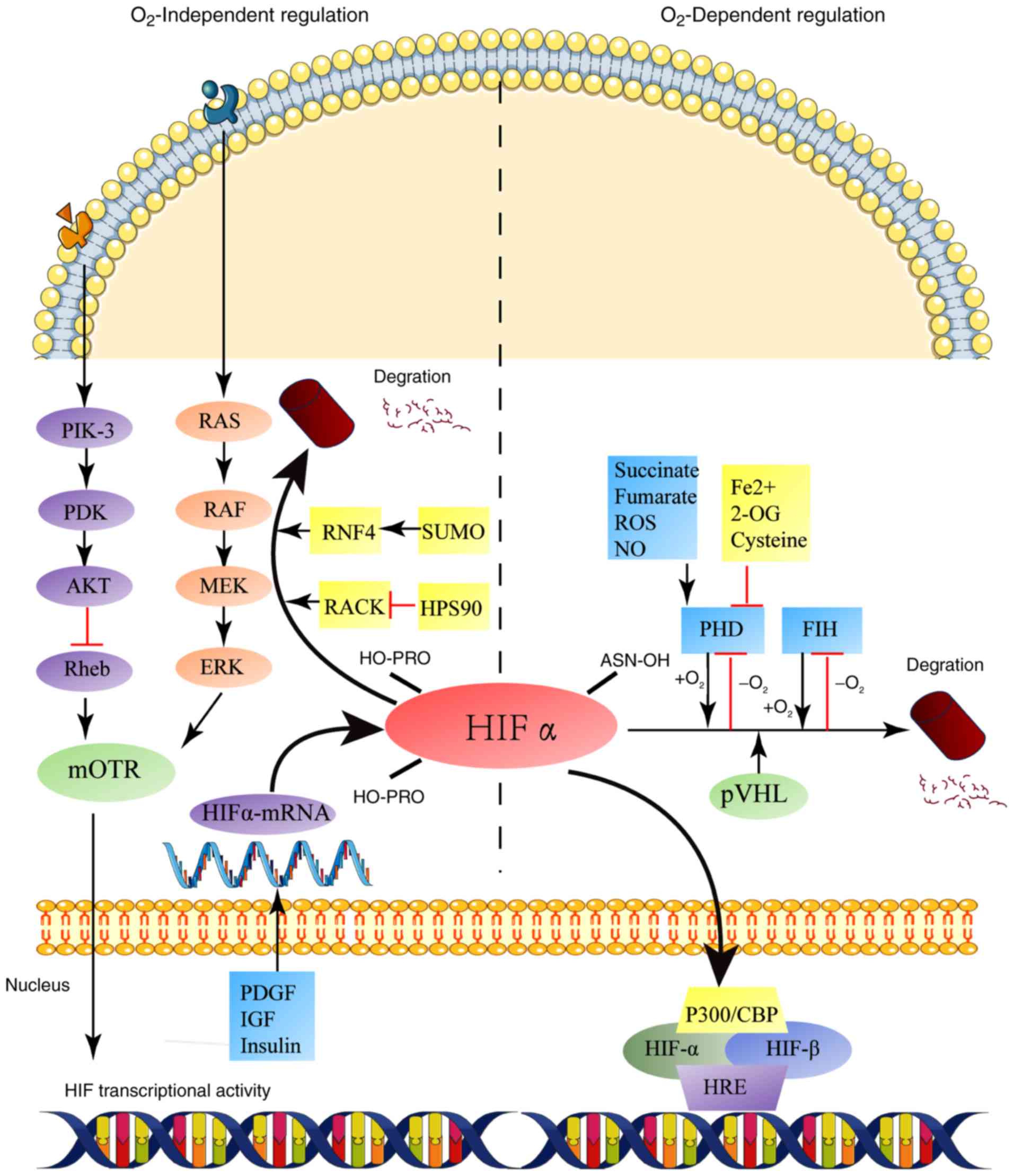
|
Mckeown SR: Defining normoxia, physoxia
and hypoxia in tumours-implications for treatment response. Br J
Radiol. 87:201306762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cui CP, Wong CC, Kai AK, Ho DW, Lau EY,
Tsui YM, Chan LK, Cheung TT, Chok KS, Chan ACY, et al: SENP1
promotes hypoxia-induced cancer stemness by HIF-1α deSUMOylation
and SENP1/HIF-1α positive feedback loop. Gut. 66:2149–2159. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang J, Ma Y, Jiang H, Zhu H, Liu L, Sun
B, Pan S, Krissansen GW and Sun X: Overexpression of von
Hippel-Lindau protein synergizes with doxorubicin to suppress
hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. J Hepatol. 55:359–368. 2011.
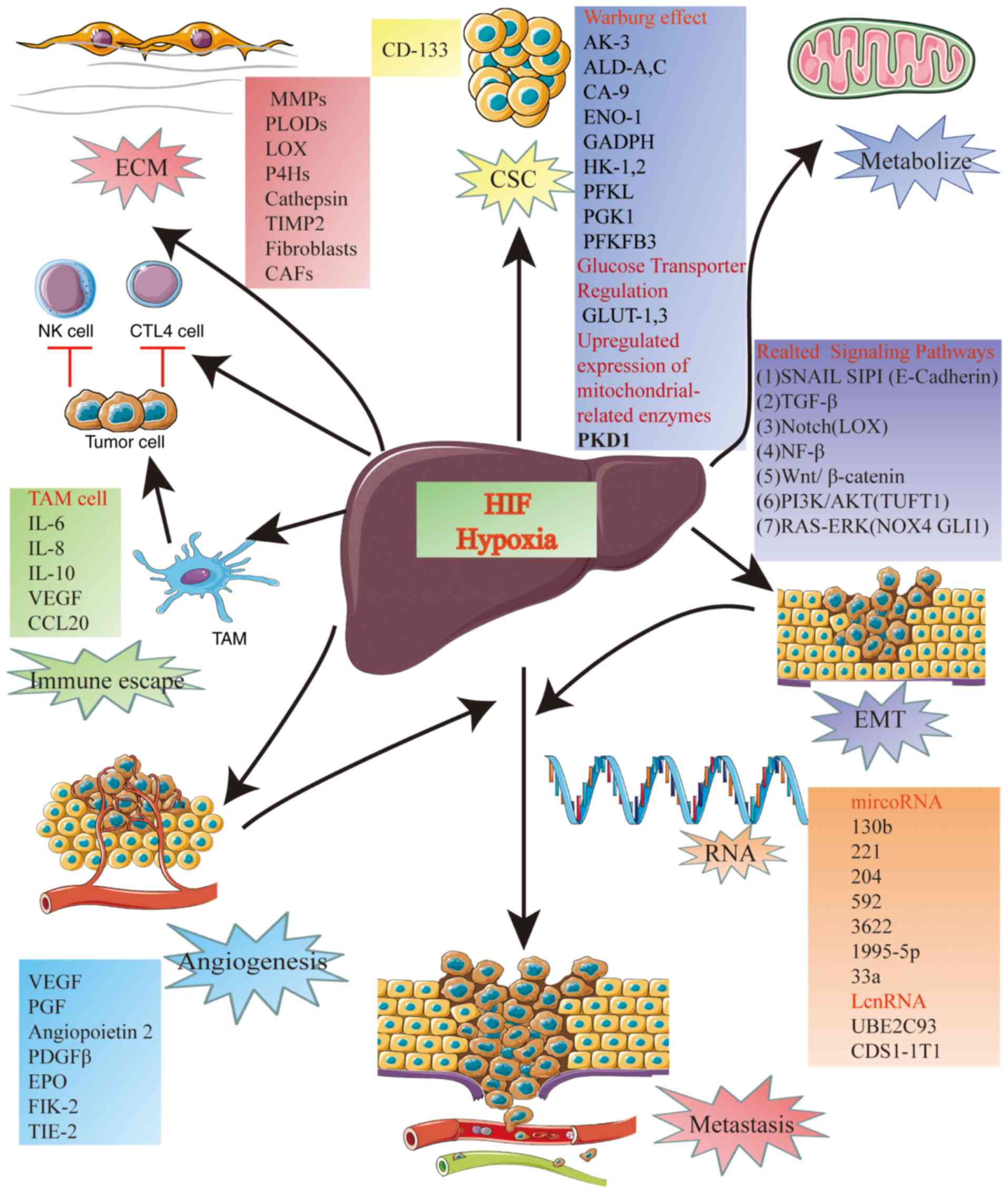
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Blagosklonny MV: Hypoxia-inducible factor:
Achilles' heel of antiangiogenic cancer therapy (Review). Int J
Oncol. 19:257–262. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dengler VL, Galbraith MD and Espinosa JM:
Transcriptional regulation by hypoxia inducible factors. Crit Rev
Biochem Mol Biol. 49:1–15. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hu CJ, Sataur A, Wang L, Chen H and Simon
MC: The N-terminal Transactivation domain confers target gene
specificity of hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha.
Mol Biol Cell. 18:4528–4542. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ohh M, Park CW, Ivan M, Hoffman MA, Kim
TY, Huang LE, Pavletich N, Chau V and Kaelin WG: Ubiquitination of
hypoxia-inducible factor requires direct binding to the beta-domain
of the von Hippel-Lindau protein. Nat Cell Biol. 2:423–427. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW,
Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME, Wykoff CC, Pugh CW, Maher ER and
Ratcliffe PJ: The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets
hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature.
399:271–275. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando
J, Ohh M, Salic A, Asara JM, Lane WS and Kaelin WG Jr: HIFalpha
targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation:
Implications for O2 sensing. Science. 292:464–468. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Garvalov BK and Acker T: Implications of
oxygen homeostasis for tumor biology and treatment. 903:169–185.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Benita Y, Kikuchi H, Smith AD, Zhang MQ,
Chung DC and Xavier RJ: An integrative genomics approach identifies
Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1 (HIF-1)-target genes that form the core
response to hypoxia. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:4587–4602. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Salminen A, Kauppinen A and Kaarniranta K:
2-Oxoglutarate- dependent dioxygenases are sensors of energy
metabolism, oxygen availability, and iron homeostasis: Potential
role in the regulation of aging process. Cell Mol Life Sci.
72:3897–3914. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Briggs KJ, Koivunen P, Cao S, Backus KM,
Olenchock BA, Patel H, Zhang Q, Signoretti S, Gerfen GJ, Richardson
AL, et al: Paracrine Induction of HIF by glutamate in breast
cancer: EglN1 senses cysteine. Cell. 166:126–139. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lau CK, Yang ZF, Ho DW, Ng MN, Yeoh GC,
Poon RT and Fan ST: An AKT/hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha/platelet-derived growth factor-BB autocrine loop
mediates hypoxia-induced chemoresistance in liver cancer cells and
tumorigenic hepatic progenitor cells. Clin Cancer Res.
15:3462–3471. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Akeno N, Robins J, Zhang M, Czyzyk-Krzeska
MF and Clemens TL: Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor
by IGF-I in osteoblast-like cells is mediated by the PI3K signaling
pathway through the hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha. Endocrinology.
143:420–425. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fukuda R, Hirota K, Fan F, Jung YD, Ellis
LM and Semenza GL: Insulin-like growth factor 1 induces
hypoxia-inducible factor 1-mediated vascular endothelial growth
factor expression, which is dependent on MAP kinase and
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling in colon cancer cells. J
Biol Chem. 277:38205–38211. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Biswas S, Mukherjee R, Tapryal N, Singh AK
and Mukhopadhyay CK: Insulin regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
transcription by reactive oxygen species sensitive activation of
Sp1 in 3T3-L1 preadipocyte. PLoS One. 8:e621282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Laughner E, Taghavi P, Chiles K, Mahon PC
and Semenza GL: HER2 (neu) signaling increases the rate of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) synthesis: Novel
mechanism for HIF-1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor
expression. Mol Cell Biol. 21:3995–4004. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nayak BK, Feliers D, Sudarshan S,
Friedrichs WE, Day RT, New DD, Fitzgerald JP, Eid A, Denapoli T,
Parekh DJ, et al: Stabilization of HIF-2α through redox regulation
of mTORC2 activation and initiation of mRNA translation. Oncogene.
32:3147–3155. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu LZ, Hu XW, Xia C, He J, Zhou Q, Shi X,
Fang J and Jiang BH: Reactive oxygen species regulate epidermal
growth factor-induced vascular endothelial growth factor and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression through activation of
AKT and P70S6K1 in human ovarian cancer cells. Free Radic Biol Med.
41:1521–1533. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang BH, Jiang G, Zheng JZ, Lu Z, Hunter
T and Vogt PK: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling controls
levels of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell Growth Differ.
12:363–369. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lim JH, Lee YM, Chun YS, Chen J, Kim JE
and Park JW: Sirtuin 1 modulates cellular responses to hypoxia by
deacetylating hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Mol Cell.
38:864–878. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu X, Chen S, Tu J, Cai W and Xu Q: HSP90
inhibits apoptosis and promotes growth by regulating HIF-1α
abundance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 37:825–835.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
van Hagen M, Overmeer RM, Abolvardi SS and
Vertegaal AC: RNF4 and VHL regulate the proteasomal degradation of
SUMO-conjugated Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2alpha. Nucleic Acids Res.
38:1922–1931. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Duan C: Hypoxia-inducible factor 3
biology: Complexities and emerging themes. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 310:C260–C269. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Makino Y, Kanopka A, Wilson WJ, Tanaka H
and Poellinger L: Inhibitory PAS domain protein (IPAS) is a
hypoxia-inducible splicing variant of the hypoxia-inducible
factor-3alpha locus. J Biol Chem. 277:32405–32408. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maynard MA, Qi H, Chung J, Lee EH, Kondo
Y, Hara S, Conaway RC, Conaway JW and Ohh M: Multiple splice
variants of the human HIF-3 alpha locus are targets of the von
Hippel-Lindau E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. J Biol Chem.
278:11032–11040. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Heikkilä M, Pasanen A, Kivirikko KI and
Myllyharju J: Roles of the human hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-3α
variants in the hypoxia response. Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:3885–3901.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen C and Lou T: Hypoxia inducible
factors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:46691–46703.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mucaj V, Shay JE and Simon MC: Effects of
hypoxia and HIFs on cancer metabolism. Int J Hematol. 95:464–470.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Warburg O, Wind F and Negelein E: The
metabolism of tumors in the body. J Gen Physiol. 8:519–530. 1927.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Alfarouk KO, Verduzco D, Rauch C,
Muddathir AK, Adil HH, Elhassan GO, Ibrahim ME, David Polo Orozco
J, Cardone RA, Reshkin SJ and Harguindey S: Glycolysis, tumor
metabolism, cancer growth and dissemination. A new pH-based
etiopathogenic perspective and therapeutic approach to an old
cancer question. Oncoscience. 1:777–802. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liberti MV and Locasale JW: The warburg
effect: How does it benefit cancer cells? Trends Biochem Sci.
41:211–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Denko NC: Hypoxia, HIF1 and glucose
metabolism in the solid tumour. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:705–713. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Semenza GL: Regulation of cancer cell
metabolism by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Semin Cancer Biol.
19:12–16. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Semenza GL: HIF-1: Upstream and downstream
of cancer metabolism. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 20:51–56. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ke Q and Costa M: Hypoxia-Inducible
Factor-1 (HIF-1). Mol Pharmacol. 70:1469–1480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Marín-Hernández A, Gallardo-Pérez JC,
Ralph SJ, Rodríguez-Enríquez S and Moreno-Sánchez R: HIF-1alpha
modulates energy metabolism in cancer cells by inducing
over-expression of specific glycolytic isoforms. Mini Rev Med Chem.
9:1084–1091. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kim JW, Tchernyshyov I, Semenza GL and
Dang CV: HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase
kinase: A metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to
hypoxia. Cell Metab. 3:177–185. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Weidemann A and Johnson RS: Biology of
HIF-1 alpha. Cell Death Differ. 15:621–627. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Graziano F, Ruzzo A, Giacomini E,
Ricciardi T, Aprile G, Loupakis F, Lorenzini P, Ongaro E, Zoratto
F, Catalano V, et al: Glycolysis gene expression analysis and
selective metabolic advantage in the clinical progression of
colorectal cancer. Pharmacogenomics J. 17:258–264. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Schito L and Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible
factors: Master regulators of cancer progression. Trends Cancer.
2:758–770. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Samanta D, Park Y, Ni X, Li H, Zahnow CA,
Gabrielson E, Pan F and Semenza GL: Chemotherapy induces enrichment
of CD47+/CD73+/PDL1+immune evasive
triple-negative breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
115:E1239–E1248. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Terry S, Buart S and Chouaib S: Hypoxic
stress-induced tumor and immune plasticity, suppression, and impact
on tumor heterogeneity. Front Immunol. 8:16252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Noman MZ, Janji B, Kaminska B, Moer KV,
Pierson S, Przanowski P, Buart S, Berchem G, Romero P, Mami-Chouaib
F and Chouaib S: Blocking hypoxia-induced autophagy in tumors
restores cytotoxic t-cell activity and promotes regression.
Autophagy. 71:5976–5986. 2012.
|
|
47
|
Hatfield SM and Sitkovsky M: A2A adenosine
receptor antagonists to weaken the hypoxia-HIF-1α driven
immunosuppression and improve immunotherapies of cancer. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 29:90–96. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Vinit K and Gabrilovich DI:
Hypoxia-inducible factors in regulation of immune responses in
tumour microenvironment. Immunology. 143:512–519. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fukuda K, Kobayashi A and Watabe K: The
role of tumor- associated macrophage in tumor progression. Front
Biosci. 4:787–798. 2012.
|
|
50
|
Zhu XD, Zhang JB, Zhuang PY, Zhu HG, Zhang
W, Xiong YQ, Wu WZ, Wang L, Tang ZY and Sun HC: High expression of
macrophage colony-stimulating factor in peritumoral liver tissue is
associated with poor survival after curative resection of
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 26:2707–2716. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wu Q, Zhou W, Yin S, Zhou Y, Chen T, Qian
J, Su R, Hong L, Lu H, Zhang F, et al: Blocking TREM-1
Tumor-associated macrophages induced by hypoxia reverses
immunosuppression and anti-PD-L1 resistance in liver cancer.
Hepatology. 70:198–214. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zeisberger SM, Odermatt B, Marty C,
Zehnder-Fjällman AH, Ballmer-Hofer K and Schwendener RA:
Clodronate-liposome- mediated depletion of tumour-associated
macrophages: A new and highly effective antiangiogenic therapy
approach. Br J Cancer. 95:272–281. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kuang DM, Peng C, Zhao Q, Wu Y, Chen MS
and Zheng L: Activated monocytes in peritumoral stroma of
hepatocellular carcinoma promote expansion of memory T helper 17
cells. Hepatology. 51:154–164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jiang J, Wang GZ, Wang Y, Huang HZ, Li WT
and Qu XD: Hypoxia-induced HMGB1 expression of HCC promotes tumor
invasiveness and metastasis via regulating macrophage-derived IL-6.
Exp Cell Res. 367:81–88. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ye LY, Chen W, Bai XL, Xu XY, Zhang Q, Xia
XF, Sun X, Li GG, Hu QD, Fu QH and Liang TB: Hypoxia-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma
induces an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment to promote
metastasis. Cancer Res. 76:818–830. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Payne SJ and Louise J: Influence of the
tumor microenvironment on angiogenesis. Future Oncol. 7:395–408.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Branco-Price C, Zhang N, Schnelle M, Evans
C, Katschinski DM, Liao D, Ellies L and Johnson RS: Endothelial
cell HIF-1α and HIF-2α differentially regulate metastatic success.
Cancer Cell. 21:52–65. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
De Francesco EM, Lappano R, Santolla MF,
Marsico S, Caruso A and Maggiolini M: HIF-1α/GPER signaling
mediates the expression of VEGF induced by hypoxia in breast cancer
associated fibroblasts (CAFs). Breast Cancer Res. 15:R642013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ahluwalia A and Tarnawski AS: Critical
role of hypoxia sensor-HIF-1α in VEGF gene activation. Implications
for angiogenesis and tissue injury healing. Curr Med Chem.
19:90–97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lee K, Zhang H, Qian DZ, Rey S, Liu JO and
Semenza GL: Acriflavine inhibits HIF-1 dimerization, tumor growth,
and vascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:17910–17915. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang W, Xu GL, Jia WD, Wang ZH, Li JS, Ma
JL, Ge YS, Xie SX and Yu JH: Expression and correlation of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, vascular endothelial growth factor
and microvessel density in experimental rat hepatocarcinogenesis. J
Int Med Res. 37:417–425. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Liu LP, Ho RL, Chen GG and Lai PB:
Sorafenib inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1α synthesis:
Implications for antiangiogenic activity in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 18:5662–5671. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Semenza GL: Defining the role of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics.
Oncogene. 29:625–634. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Li H, Ge C, Zhao F, Yan M, Hu C, Jia D,
Tian H, Zhu M, Chen T, Jiang G, et al: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1
alpha-activated angiopoietin-like protein 4 contributes to tumor
metastasis via vascular cell adhesion molecule-1/integrin β1
signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
54:910–919. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Tian H, McKnight SL and Russell DW:
Endothelial PAS domain protein 1 (EPAS1), a transcription factor
selectively expressed in endothelial cells. Genes Dev. 11:72–82.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Talks KL, Turley H, Gatter KC, Maxwell PH,
Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ and Harris AL: The expression and
distribution of the hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and
HIF-2alpha in normal human tissues, cancers, and tumor-associated
macrophages. Am J Pathol. 157:411–421. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wiesener MS, Jürgensen JS, Rosenberger C,
Scholze CK, Hörstrup JH, Warnecke C, Mandriota S, Bechmann I, Frei
UA, Pugh CW, et al: Widespread hypoxia-inducible expression of
HIF-2alpha in distinct cell populations of different organs. FASEB
J. 17:271–273. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhang T, Niu X, Liao L, Cho EA and Yang H:
The Contributions of HIF-Target Genes to Tumor Growth in RCC. PLoS
One. 8:e805442013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Feng N, Chen H, Fu S, Bian Z, Lin X, Yang
L, Gao Y, Fang J and Ge Z: HIF-1α and HIF-2α induced angiogenesis
in gastrointestinal vascular malformation and reversed by
thalidomide. Sci Rep. 6:272802016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Aprelikova O, Wood M, Tackett S,
Chandramouli GV and Barrett JC: Role of ETS transcription factors
in the hypoxia-inducible factor-2 target gene selection. Cancer
Res. 66:5641–5647. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Evans AJ, Russell RC, Roche O, Burry TN,
Fish JE, Chow VW, Kim WY, Saravanan A, Maynard MA, Gervais ML, et
al: VHL promotes E2 box-dependent E-cadherin transcription by
HIF-mediated regulation of SIP1 and snail. Mol Cell Biol.
27:157–169. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhang L, Huang G, Li X, Zhang Y, Jiang Y,
Shen J, Liu J, Wang Q, Zhu J, Feng X, et al: Hypoxia induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via activation of SNAI1 by
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in hepatocellular carcinoma. Bmc
Cancer. 13:1082013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Willis BC, Liebler JM, Luby-Phelps K,
Nicholson AG, Crandall ED, du Bois RM and Borok Z: Induction of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in alveolar epithelial cells by
transforming growth factor-beta1: Potential role in idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 166:1321–1332. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Copple BL: Hypoxia stimulates hepatocyte
epithelial to mesenchymal transition by hypoxia-inducible factor
and transforming growth factor-beta-dependent mechanisms. Liver
Int. 30:669–682. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wang XH, Liu MN, Sun X, Xu CH, Liu J, Chen
J, Xu RL and Li BX: TGF-β1 pathway affects the protein expression
of many signaling pathways, markers of liver cancer stem cells,
cytokeratins, and TERT in liver cancer HepG2 cells. Tumor Biol.
37:3675–3681. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Erler JT and Giaccia AJ: Lysyl oxidase
mediates hypoxic control of metastasis. Cancer Res. 66:10238–10241.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Sahlgren C, Gustafsson MV, Jin S,
Poellinger L and Lendahl U: Notch signaling mediates
hypoxia-induced tumor cell migration and invasion. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 105:6392–6397. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Gustafsson MV, Zheng X, Pereira T, Gradin
K, Jin S, Lundkvist J, Ruas JL, Poellinger L, Lendahl U and
Bondesson M: Hypoxia requires notch signaling to maintain the
undifferentiated cell state. Dev Cell. 9:617–628. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
D'Ignazio L, Batie M and Rocha S: Hypoxia
and inflammation in cancer, focus on HIF and NF-κB. Biomedicines.
5:E212017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Fitzpatrick SF, Tambuwala MM, Bruning U,
Schaible B, Scholz CC, Byrne A, O'Connor A, Gallagher WM, Lenihan
CR, Garvey JF, et al: An intact canonical NF-κB pathway is required
for inflammatory gene expression in response to hypoxia. J Immunol.
186:1091–1096. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Taylor CT and Cummins EP: The role of
NF-kappaB in hypoxia-induced gene expression. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1177:178–184. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Zhang L, Liu H, Mu X, Cui J and Peng Z:
Dysregulation of Fra1 expression by Wnt/β-catenin signalling
promotes glioma aggressiveness through epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Biosci Rep. 37:BSR201606432017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhang Q, Bai X, Chen W, Ma T, Hu Q, Liang
C, Xie S, Chen C, Hu L, Xu S and Liang T: Wnt/β-catenin signaling
enhances hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hepatocellular carcinoma via crosstalk with hif-1α signaling.
Carcinogenesis. 34:962–973. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Xu W, Zhou W, Cheng M, Wang J, Liu Z, He
S, Luo X, Huang W, Chen T, Yan W and Xiao J: Hypoxia activates
Wnt/β-catenin signaling by regulating the expression of BCL9 in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep. 7:404462017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Dou C, Zhou Z, Xu Q, Liu Z, Zeng Y, Wang
Y, Li Q, Wang L, Yang W, Liu Q and Tu K: Hypoxia-induced TUFT1
promotes the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by
activating the Ca2+/PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncogene.
38:1239–1255. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Liu Z, Tu K, Wang Y, Yao B, Li Q, Wang L,
Dou C, Liu Q and Zheng X: Hypoxia accelerates aggressiveness of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells involving oxidative stress,
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and non-canonical hedgehog
signaling. Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:1856–1868. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
An WG, Kanekal M, Simon MC, Maltepe E,
Blagosklonny MV and Neckers LM: Stabilization of wild-type p53 by
hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Nature. 392:405–408. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Hansson LO, Friedler A, Freund S, Rüdiger
S and Fersht AR: Two sequence motifs from HIF-1alpha bind to the
DNA-binding site of p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:10305–10309.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Amelio I, Inoue S, Markert EK, Levine AJ,
Knight RA, Mak TW and Melino G: TAp73 opposes tumor angiogenesis by
promoting hypoxia-inducible factor 1α degradation. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 112:226–231. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Liu Z, Wang J, Guo C and Fan X:
microRNA-21 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human
hepatocytes via PTEN/AKT pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 69:24–28.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Chang RM, Xu JF, Fang F, Yang H and Yang
LY: MicroRNA-130b promotes proliferation and EMT-induced metastasis
via PTEN/p-AKT/HIF-1α signaling. Tumor Biol. 37:10609–10619. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Liu Z, Wang Y, Dou C, Xu M, Sun L, Wang L,
Yao B, Li Q, Yang W, Tu K and Liu Q: Hypoxia-induced up-regulation
of VASP promotes invasiveness and metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Theranostics. 8:4649–4663. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Li B, He L, Zuo D, He W, Wang Y, Zhang Y,
Liu W and Yuan Y: Mutual Regulation of MiR-199a-5p and HIF-1α
modulates the warburg effect in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer.
8:940–949. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Jia YY, Zhao JY, Li BL, Gao K, Song Y, Liu
MY, Yang XJ, Xue Y, Wen AD and Shi L: miR-592/WSB1/HIF-1α axis
inhibits glycolytic metabolism to decrease hepatocellular carcinoma
growth. Oncotarget. 7:35257–35269. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Chen Z, Zuo X, Zhang Y, Han G, Zhang L, Wu
J and Wang X: MiR-3662 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth
through inhibition of HIF-1α-mediated Warburg effect. Cell Death
Dis. 9:5492018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Guo XF, Wang AY and Liu J:
HIFs-MiR-33a-Twsit1 axis can regulate invasiveness of
hepatocellular cancer cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
20:3011–3016. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Chai ZT, Kong J, Zhu XD, Zhang YY, Lu L,
Zhou JM, Wang LR, Zhang KZ, Zhang QB, Ao JY, et al: MicroRNA-26a
inhibits angiogenesis by down-regulating VEGFA through the
PIK3C2α/AKT/HIF-1α pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One.
8:e779572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Lin J, Cao S, Wang Y, Hu Y, Liu H, Li J,
Chen J, Li P, Liu J, Wang Q and Zheng L: Long non-coding RNA
UBE2CP3 enhances HCC cell secretion of VEGFA and promotes
angiogenesis by activating ERK1/2/HIF-1α/VEGFA signalling in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:1132018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Wang TH, Yu CC, Lin YS, Chen TC, Yeh CT,
Liang KH, Shieh TM, Chen CY and Hsueh C: Long noncoding RNA
CPS1-IT1 suppresses the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by
regulating HIF-1α activity and inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Oncotarget. 7:43588–43603. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Bonnans C, Chou J and Werb Z: Remodelling
the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 15:786–801. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Rankin EB and Giaccia AJ: Hypoxic control
of metastasis. Science. 352:175–180. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Kai AK, Chan LK, Lo RC, Lee JM, Wong CC,
Wong JC and Ng IO: Down-regulation of TIMP2 by
HIF-1α/miR-210/HIF-3α regulatory feedback circuit enhances cancer
metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 64:473–487.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Kalluri R: The biology and function of
fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:582–598. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Tse AP, Sze KM, Shea QT, Chiu EY, Tsang
FH, Chiu DK, Zhang MS, Lee D, Xu IM, Chan CY, et al: Hepatitis
transactivator protein X promotes extracellular matrix modification
through HIF/LOX pathway in liver cancer. Oncogenesis. 7:442018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Cheng ZC and Sadek HA: Hypoxia and
metabolic properties of hematopoietic stem cells. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 20:1891–1901. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Bao B, Azmi AS, Ali S, Ahmad A, Li Y,
Banerjee S, Kong D and Sarkar FH: The biological kinship of hypoxia
with CSC and EMT and their relationship with deregulated expression
of miRNAs and tumor aggressiveness. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1826:272–296. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Lai FB, Liu WT, Jing YY, Yu GF, Han ZP,
Yang X, Zeng JX, Zhang HJ, Shi RY, Li XY, et al: Lipopolysaccharide
supports maintaining the stemness of CD133(+) hepatoma cells
through activation of the NF-κB/HIF-1α pathway. Cancer Lett.
378:131–141. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Jing L, Ruan Z, Sun H, Li Q, Han L, Huang
L, Yu S, Wang Y, Guo H and Jiao M: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition induced cancer-stem-cell-like characteristics in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 234:18448–18458.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Cao Q, Lu W, Zhou T, Liu Y, Cai X, Zhu J
and Cao P: Analgesic-antitumor peptide inhibits angiogenesis by
suppressing AKT activation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell
Biochem. 455:119–125. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Tan Y, Du B, Zhan Y, Wang K, Wang X, Chen
B, Wei X and Xiao J: Antitumor effects of circ-EPHB4 in
hepatocellular carcinoma via inhibition of HIF-1α. Mol Carcinog.
58:875–886. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Qin Y, Liu HJ, Li M, Zhai DH, Tang YH,
Yang L, Qiao KL, Yang JH, Zhong WL, Zhang Q, et al: Salidroside
improves the hypoxic tumor microenvironment and reverses the drug
resistance of platinum drugs via HIF-1α signaling pathway.
EBioMedicine. 38:25–36. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Lei HW, Cai J, Li CM, Yang F, Shi WQ, Shi
WQ, Wang LP and Feng YY: Rapamycin combi with TAE on the growth,
metastasis, and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in rat
models. Ann Hepatol. 17:645–654. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Hua H, Zhu Y and Song YH: Ruscogenin
suppressed the hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 101:115–122.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Liu P, Atkinson SJ, Akbareian SE, Zhou Z,
Munsterberg A, Robinson SD and Bao Y: Sulforaphane exerts
anti-angiogenesis effects against hepatocellular carcinoma through
inhibition of STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF signalling. Sci Rep. 7:126512017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zhou QY, Tu CY, Shao CX, Wang WK, Zhu JD,
Cai Y, Mao JY and Chen W: GC7 blocks epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and reverses hypoxia-induced chemotherapy resistance in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Am J Transl Res. 9:2608–2617.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Chow AK, Yau TC, Ng L, Chu AC, Law WL,
Poon RT and Pang RW: A preclinical study on the combination therapy
of everolimus and transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 5:2376–2386. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Li C, Wu X, Zhang H, Yang G, Hao M, Sheng
S, Sun Y, Long J, Hu C, Sun X, et al: A Huaier polysaccharide
restrains hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis by
suppression angiogenesis. Int J Biol Macromol. 75:115–120. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Wu J, Contratto M, Shanbhogue KP, Manji
GA, O'Neil BH, Noonan A, Tudor R and Lee R: Evaluation of a locked
nucleic acid form of antisense oligo targeting HIF-1α in advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Clin Oncol. 10:149–160. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Rapisarda A, Uranchimeg B, Sordet O,
Pommier Y, Shoemaker RH and Melillo G: Topoisomerase I-mediated
inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor 1: Mechanism and therapeutic
implications. Cancer Res. 64:1475–1482. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Zhang C, Yang C, Feldman MJ, Wang H, Pang
Y, Maggio DM, Zhu D, Nesvick CL, Dmitriev P, Bullova P, et al:
Vorinostat suppresses hypoxia signaling by modulating nuclear
translocation of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha. Oncotarget.
8:56110–56125. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Li YL, Zhang NY, Hu X, Chen JL, Rao MJ, Wu
LW, Li QY, Zhang B, Yan W and Zhang C: Evodiamine induces apoptosis
and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell death induced by
vorinostat via downregulating HIF-1α under hypoxia. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 498:481–486. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Shao S, Duan W, Xu Q, Li X, Han L, Li W,
Zhang D, Wang Z and Lei J: Curcumin suppresses hepatic stellate
cell-induced hepatocarcinoma angiogenesis and invasion through
downregulating CTGF. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:81485102019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Xia Y, Choi HK and Lee K: Recent advances
in hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem.
49:24–40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Abu-Remaileh M, Khalaileh A, Pikarsky E
and Aqeilan RI: Author Correction: WWOX controls hepatic HIF1α to
suppress hepatocyte proliferation and neoplasia. Cell Death Dis.
9:11592018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Yang Q, Guo X and Yang L: Metformin
enhances the effect of regorafenib and inhibits recurrence and
metastasis of hepatic carcinoma after liver resection via
regulating expression of hypoxia inducible factors 2α (HIF-2α) and
30 kDa HIV tat-interacting protein (TIP30). Med Sci Monit.
24:2225–2234. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Wada H, Nagano H, Yamamoto H, Yang Y,
Kondo M, Ota H, Nakamura M, Yoshioka S, Kato H, Damdinsuren B, et
al: Expression pattern of angiogenic factors and prognosis after
hepatic resection in hepatocellular carcinoma: Importance of
angiopoietin-2 and hypoxia-induced factor-1 alpha. Liver Int.
26:414–423. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Dai CX, Gao Q, Qiu SJ, Ju MJ, Cai MY, Xu
YF, Zhou J, Zhang BH and Fan J: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha,
in association with inflammation, angiogenesis and MYC, is a
critical prognostic factor in patients with HCC after surgery. BMC
Cancer. 9:4182009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Xia L, Mo P, Huang W, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhu
H, Tian D, Liu J, Chen Z, Zhang Y, et al: The
TNF-α/ROS/HIF-1-induced upregulation of FoxMI expression promotes
HCC proliferation and resistance to apoptosis. Carcinogenesis.
33:2250–2259. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Xiang ZL, Zeng ZC, Fan J, Tang ZY, He J,
Zeng HY and Chang JY: The expression of HIF-1α in primary
hepatocellular carcinoma and its correlation with radiotherapy
response and clinical outcome. Mol Biol Rep. 39:2021–2029. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Zheng SS, Chen XH, Yin X and Zhang BH:
Prognostic significance of HIF-1α expression in hepatocellular
carcinoma: A meta-analysis. PLoS One. 8:e657532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Wang B, Ding YM, Fan P, Wang B, Xu JH and
Wang WX: Expression and significance of MMP2 and HIF-1α in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 8:539–546. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Cao S, Yang S, Wu C, Wang Y, Jiang J and
Lu Z: Protein expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and
hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review with meta-analysis.
Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 38:598–603. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Liu LP, Hu BG, Ye C, Ho RL, Chen GG and
Lai PB: HBx mutants differentially affect the activation of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J
Cancer. 110:1066–1073. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Wang D, Zhang X, Lu Y, Wang X and Zhu L:
Hypoxia inducible factor 1α in hepatocellular carcinoma with
cirrhosis: Association with prognosis. Pathol Res Pract.
214:1987–1992. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Bangoura G, Liu Z, Qian Q, Jiang C, Yang G
and Jing S: Prognostic significance of HIF-2alpha/EPAS1 expression
in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 13:3176–3182.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Sun HX, Xu Y, Yang XR, Wang WM, Bai H, Shi
RY, Nayar SK, Devbhandari RP, He YZ, Zhu QF, et al: Hypoxia
inducible factor 2 alpha inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth
through the transcription factor dimerization partner 3/E2F
transcription factor 1-dependent apoptotic pathway. Hepatology.
57:1088–1097. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Yao Q, Lv Y, Pan T, Liu Y, Ma J and Xu G:
Prognostic significance and clinicopathological features of hypoxic
inducible factor-2alpha expression in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Saudi Med J. 36:170–175. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Yang SL, Liu LP, Niu L, Sun YF, Yang XR,
Fan J, Ren JW, Chen GG and Lai PB: Downregulation and pro-apoptotic
effect of hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:34571–34581. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Jiang L, Liu QL, Liang QL, Zhang HJ, Ou WT
and Yuan GL: Association of PHD3 and HIF2α gene expression with
clinicopathological characteristics in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 15:545–551. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Liu P, Fang X, Song Y, Jiang JX, He QJ and
Liu XJ: Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 3α in hepatocellular
carcinoma and its association with other hypoxia-inducible factors.
Exp Ther Med. 11:2470–2476. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|