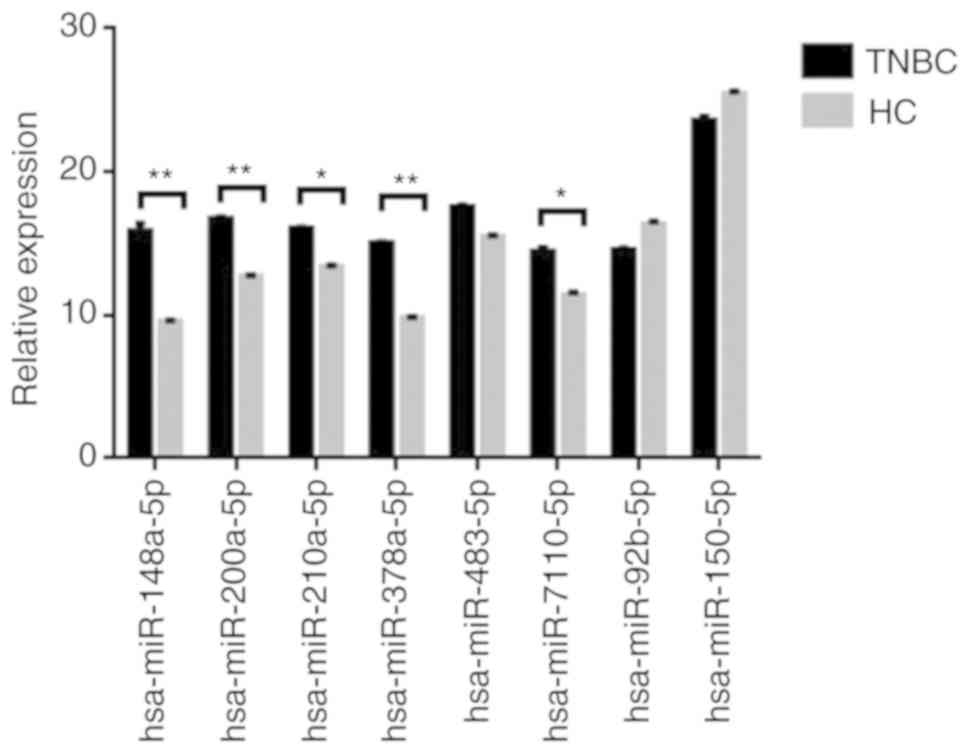
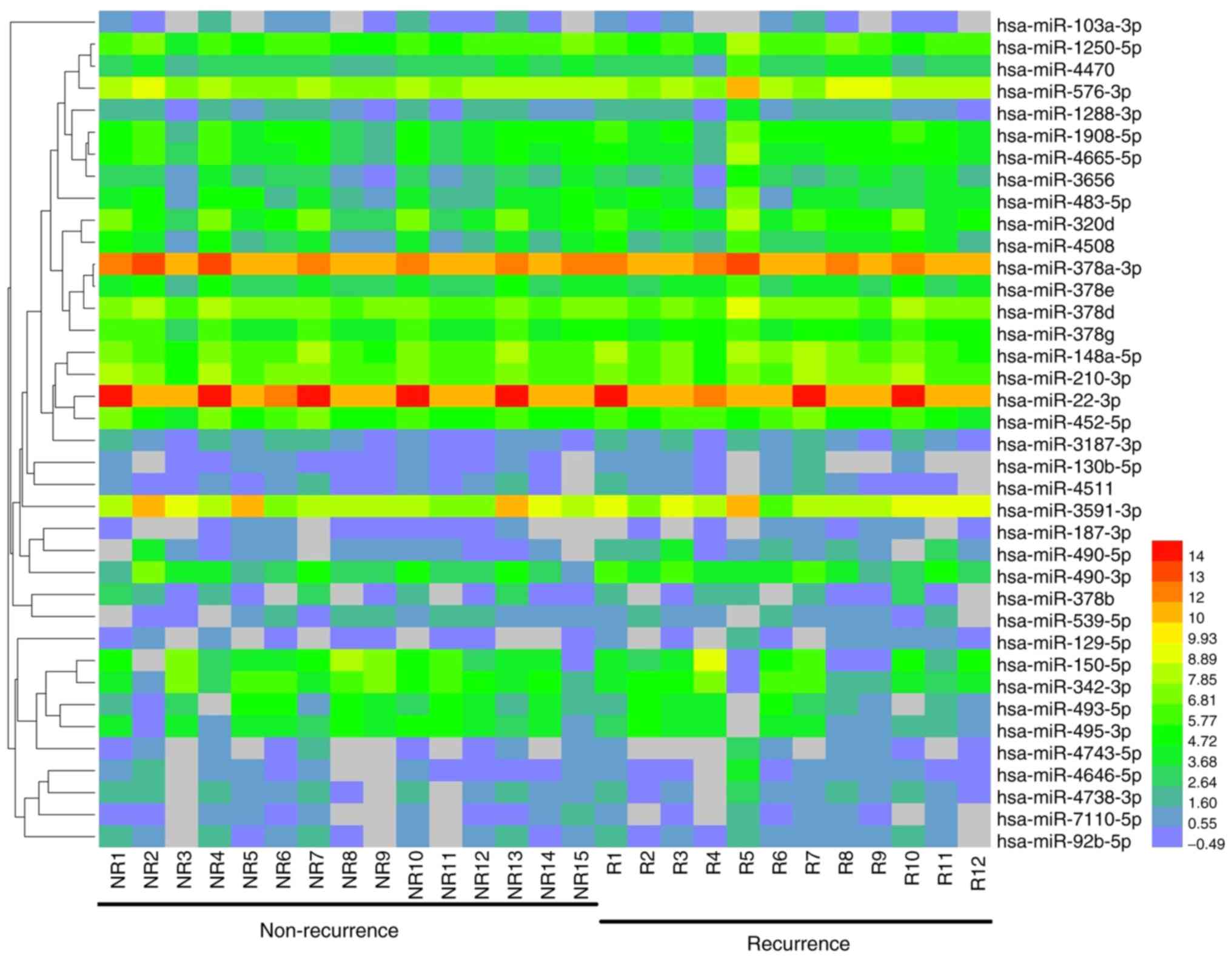
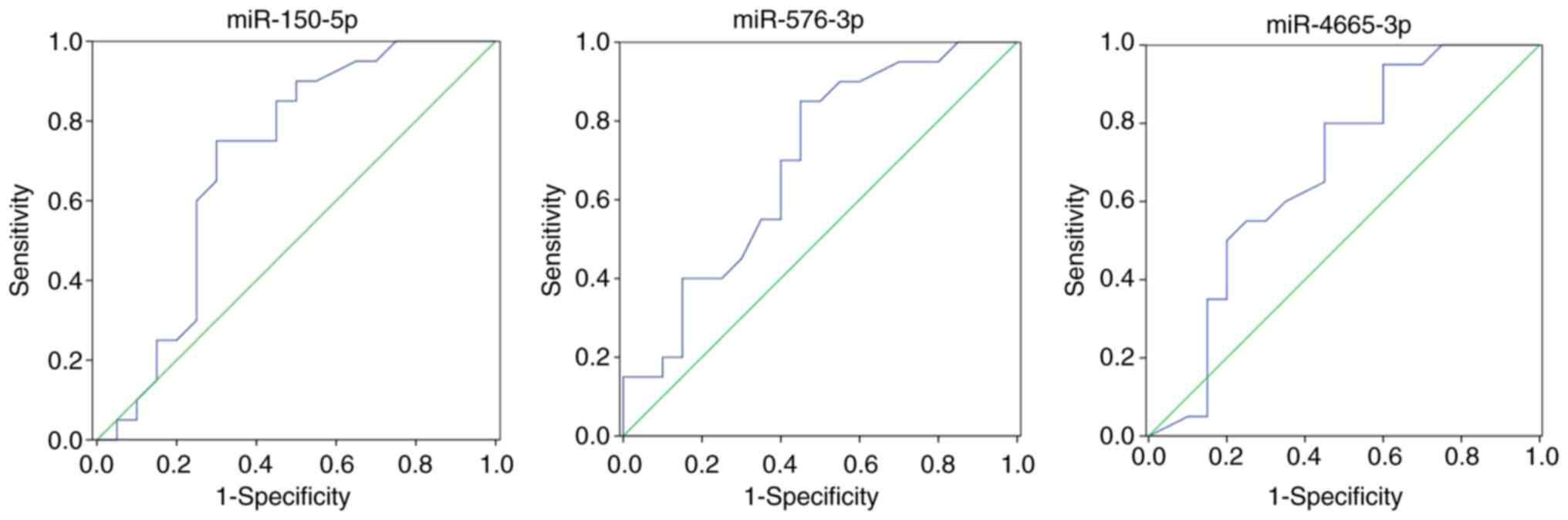
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L and Jemal A:
Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:52–62. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Unger-Saldaña K: Challenges to the early
diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer in developing countries.
World J Clin Onco. 5:465–477. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fan L, Strasser-Weippl K, Li JJ, St Louis
J, Finkelstein DM, Yu KD, Chen WQ, Shao ZM and Goss PE: Breast
cancer in China. Lancet Oncol. 15:e279–e289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wiechmann L, Sampson M, Stempel M, Jacks
LM, Patil SM, King T and Morrow M: Presenting features of breast
cancer differ by molecular subtype. Ann Surg Oncol. 16:2705–2710.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Parise CA, Bauer KR, Brown MM and Caggiano
V: Breast cancer subtypes as defined by the estrogen receptor (ER),
progesterone receptor (PR), and the human epidermal growth factor
receptor 2 (HER2) among women with invasive breast cancer in
California, 2004. Breast J. 15:593–602. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hugh J, Hanson J, Cheang MC, Nielsen TO,
Perou CM, Dumontet C, Reed J, Krajewska M, Treilleux I, Rupin M, et
al: Breast cancer subtypes and response to docetaxel in
node-positive breast cancer: Use of an immunohistochemical
definition in the BCIRG 001 trial. J Clin Oncol. 27:1168–1178.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park S, Koo JS, Min SK, Park HS, Lee JS,
Lee JS, Kim SI and Park BW: Characteristics and outcomes according
to molecular subtypes of breast cancer as classified by a panel of
four biomarkers using immunohistochemistry. Breast. 21:50–57. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Meyers MO, Klauber-Demore N, Ollila DW,
Amos KD, Moore DT, Drobish AA, Burrows EM, Dees EC and Carey LA:
Impact of breast cancer molecular subtypes on locoregional
recurrence in patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy for
locally advanced breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:2851–2857. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T,
Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey
SS, et al: Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas
distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:10869–10874. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie
T, Marron JS, Nobel A, Deng S, Johnsen H, Pesich R, Geisler S, et
al: Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent
gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:8418–8423.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Badve S, Turbin D, Thorat MA, Morimiya A,
Nielsen TO, Perou CM, Dunn S, Huntsman DG and Nakshatri H: FOXA1
expression in breast cancer-correlation with luminal subtype A and
survival. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4415–4421. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang LC, Jin X, Yang HY, He M, Chang H,
Shao ZM and Di GH: Luminal B subtype: A key factor for the worse
prognosis of young breast cancer patients in China. BMC Cancer.
15:2012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Böcker W, Moll R, Poremba C, Holland R,
Van Diest PJ, Dervan P, Bürger H, Wai D, Ina Diallo R, Brandt B, et
al: Common adult stem cells in the human breast give rise to
glandular and myoepithelial cell lineages: A new cell biological
concept. Lab Invest. 82:737–746. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Birnbaum D, Bertucci F, Ginestier C,
Tagett R, Jacquemier J and Charafe-Jauffret E: Basal and luminal
breast cancers: Basic or luminous. Int J Oncol. 25:249–258.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Turner NC, Reisfilho JS, Russell AM,
Springall RJ, Ryder K, Steele D, Savage K, Gillett CE, Schmitt FC,
Ashworth A and Tutt AN: BRCA1 dysfunction in sporadic basal-like
breast cancer. Oncogene. 26:2126–2132. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Millikan RC, Newman B, Tse CK, Moorman PG,
Conway K, Dressler LG, Smith LV, Labbok MH, Geradts J, Bensen JT,
et al: Epidemiology of basal-like breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 109:123–139. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thike AA, Cheok PY, Jaralazaro AR, Tan B,
Tan P and Tan PH: Triple-negative breast cancer:
Clinicopathological characteristics and relationship with
basal-like breast cancer. Mod Pathol. 23:123–133. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rakha E, Ellis I and Reis-Filho J: Are
triple-negative and basal-like breast cancer synonymous? Clin
Cancer Res. 14:618–619. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chacón RD and Costanzo MV: Triple-negative
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 12 (Suppl 2):S32010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Podo F, Buydens LM, Degani H, Hilhorst R,
Klipp E, Gribbestad IS, Van Huffel S, van Laarhoven HW, Luts J,
Monleon D, et al: Triple-negative breast cancer: Present challenges
and new perspectives. Mol Oncol. 4:209–229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Oakman C, Moretti E, Galardi F, Biagioni
C, Santarpia L, Biganzoli L and Di Leo A: Adjuvant systemic
treatment for individual patients with triple negative breast
cancer. Breast. 20 (Suppl 3):S135–S141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
André F and Zielinski CC: Optimal
strategies for the treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast
cancer with currently approved agents. Ann Oncol. 23 (Suppl
6):vi46–vi51. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chevillet JR, Kang Q, Ruf IK, Briggs HA,
Vojtech LN, Hughes SM, Cheng HH, Arroyo JD, Meredith EK,
Gallichotte EN, et al: Quantitative and stoichiometric analysis of
the microRNA content of exosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:148882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wolfers J, Lozier A, Raposo G, Regnault A,
Théry C, Masurier C, Flament C, Pouzieux S, Faure F, Tursz T, et
al: Tumor-derived exosomes are a source of shared tumor rejection
antigens for CTL cross-priming. Nat Med. 7:297–303. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Clayton A, Mitchell JP, Court J, Mason MD
and Tabi Z: Human tumor-derived exosomes selectively impair
lymphocyte responses to interleukin-2. Cancer Res. 67:7458–7466.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Clayton A, Mitchell JP, Court J, Linnane
S, Mason MD and Tabi Z: Human tumor-derived exosomes down-modulate
NKG2D expression. J Immunol. 180:72492008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hannafon BN and Ding WQ: Intercellular
communication by exosome-derived microRNAs in cancer. Int J Mol
Sci. 14:14240–14269. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chaput N, Taïeb J, Schartz NE, André F,
Angevin E and Zitvogel L: Exosome-based immunotherapy. Cancer
Immunol Immun. 53:234–239. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chendrimada TP, Gregory RI, Kumaraswamy E,
Norman J, Cooch N, Nishikura K and Shiekhattar R: TRBP recruits the
Dicer complex to Ago2 for microRNA processing and gene silencing.
Nature. 436:740–744. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hagiwara K, Kosaka N, Yoshioka Y,
Takahashi RU, Takeshita F and Ochiya T: Stilbene derivatives
promote Ago2-dependent tumour-suppressive microRNA activity. Sci
Rep. 2:3142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang J, Jiang C, Shi X, Yu H, Lin H and
Peng Y: Diagnostic value of circulating miR-155, miR-21, and
miR-10b as promising biomarkers in human breast cancer. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 9:10258–10265. 2016.
|
|
35
|
Shan HC and Toyokuni S: Malignant
mesothelioma as an oxidative stress-induced cancer: An update. Free
Radical Bio Med. 86:166–178. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wang W and Luo YP: MicroRNAs in breast
cancer: Oncogene and tumor suppressors with clinical potential. J
Zhejiang Univer B. 16:18–31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li X, Xin S, He Z, Che X, Wang J, Xiao X,
Chen J and Song X: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally
downregulates tumor suppressor PDCD4 and promotes cell
transformation, proliferation, and metastasis in renal cell
carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 33:1631–1642. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Corcoran C, Friel AM, Duffy MJ, Crown J
and O'Driscoll L: Intracellular and extracellular microRNAs in
breast cancer. Clin Chem. 57:18–32. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yong L, Jing Z, Zhang PY, Zhang Y, Sun SY,
Yu SY and Xi QS: MicroRNA-10b targets E-cadherin and modulates
breast cancer metastasis. Med Sci Monit. 18:BR299–BR308.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Guttilla IK and White BA: Coordinate
regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in breast
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 284:23204–23216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen B, Tang H, Liu X, Liu P, Yang L, Xie
X, Ye F, Song C, Xie X and Wei W: miR-22 as a prognostic factor
targets glucose transporter protein type 1 in breast cancer. Cancer
Lett. 356:410–417. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Eades G, Yang M, Yao Y, Zhang Y and Zhou
Q: miR-200a regulates Nrf2 activation by targeting Keap1 mRNA in
breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 286:40725–40733. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu M, Hu C, Xu Q, Chen L, Ma K, Xu N and
Zhu H: Methylseleninic acid activates Keap1/Nrf2 pathway via
up-regulating miR-200a in human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma
cells. Bioscience Rep. 35:e002562015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tao S, He H, Chen Q and Yue W: GPER
mediated estradiol reduces miR-148a to promote HLA-G expression in
breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 451:74–78. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tao S, He H and Chen Q: Estradiol induces
HOTAIR levels via GPER-mediated miR-148a inhibition in breast
cancer. J Transl Med. 13:1312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xu X, Zhang Y, Jasper J, Lykken E,
Alexander PB, Markowitz GJ, McDonnell DP, Li QJ and Wang XF:
miR-148a functions to suppress metastasis and serves as a
prognostic indicator in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget.
7:20381–20394. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Müller V, Gade S, Steinbach B, Loibl S,
von Minckwitz G, Untch M, Schwedler K, Lübbe K, Schem C, Fasching
PA, et al: Changes in serum levels of miR-21, miR-210, and miR-373
in HER2-positive breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant
therapy: A translational research project within the Geparquinto
trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 147:61–68. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hong L, Yang J, Han Y, Lu Q, Cao J and
Syed L: High expression of miR-210 predicts poor survival in
patients with breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Gene. 507:135–138.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yin JY, Deng ZQ, Liu FQ, Qian J, Lin J,
Tang Q, Wen XM, Zhou JD, Zhang YY and Zhu XW: Association between
mir-24 and mir-378 in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues of
breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp Patho. 7:4261–4267. 2014.
|
|
50
|
Ikeda K, Horieinoue K, Ueno T, Suzuki T,
Sato W, Shigekawa T, Osaki A, Saeki T, Berezikov E, Mano H and
Inoue S: miR-378a-3p modulates tamoxifen sensitivity in breast
cancer MCF-7 cells through targeting GOLT1A. Sci Rep. 5:131702015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Savi F, Forno I, Faversani A, Luciani A,
Caldiera S, Gatti S, Foa P, Ricca D, Bulfamante G, Vaira V and
Bosari S: miR-296/Scribble axis is deregulated in human breast
cancer and miR-296 restoration reduces tumour growth in vivo. Clin
Sci (Lond). 127:233–242. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yang H, Yu J, Wang L, Ding D, Zhang L, Chu
C, Chen Q, Xu Z, Zou Q and Liu X: miR-320a is an independent
prognostic biomarker for invasive breast cancer. Oncol Lett.
8:1043–1050. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yu J, Wang JG, Zhang L, Yang HP, Wang L,
Ding D, Chen Q, Yang WL, Ren KH, Zhou DM, et al: MicroRNA-320a
inhibits breast cancer metastasis by targeting metadherin.
Oncotarget. 7:38612–38625. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li L, Yuan L, Luo J, Gao J, Guo J and Xie
X: miR-34a inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer
through down-regulation of Bcl-2 and SIRT1. Clin Exp Med.
13:109–117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chabre O, Libé R, Assie G, Barreau O,
Bertherat J, Bertagna X, Feige JJ and Cherradi N: Serum miR-483-5p
and miR-195 are predictive of recurrence risk in adrenocortical
cancer patients. Endocr Relat Cancer. 20:579–594. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Rask L, Balslev E, Søkilde R, Høgdall E,
Flyger H, Eriksen J and Litman T: Differential expression of
miR-139, miR-486 and miR-21 in breast cancer patients
sub-classified according to lymph node status. Cell Oncol.
37:215–227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Song Q, Xu Y, Yang C, Chen Z, Jia C, Chen
J, Zhang Y, Lai P, Fan X, Zhou X, et al: miR-483-5p promotes
invasion and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting RhoGDI1
and ALCAM. Cancer Res. 74:3031–3042. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhang M, Liu D, Li W, Wu X, Gao CE and Li
X: Identification of featured biomarkers in breast cancer with
microRNA microarray. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 294:1047–1053. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Jia Z, Liu Y, Gao Q, Han Y, Zhang G, Xu S,
Cheng K and Zou W: miR-490-3p inhibits the growth and invasiveness
in triple-negative breast cancer by repressing the expression of
TNKS2. Gene. 593:41–47. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Uen YH, Wang JW, Wang CC, Jhang Y, Chung
JY, Tseng T, Sheu M and Lee S: Mining of potential microRNAs with
clinical correlation-regulation of syndecan-1 expression by
miR-122-5p altered mobility of breast cancer cells and possible
correlation with liver injury. Oncotarget. 9:28165–28175. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Block I, Burton M, Sørensen KP, Andersen
L, Larsen MJ, Bak M, Cold S, Thomassen M, Tan Q and Kruse TA:
Association of miR-548c-5p, miR-7-5p, miR-210-3p, miR-128-3p with
recurrence in systemically untreated breast cancer. Oncotarget.
9:9030–9042. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang B, Yang Z, Wang H, Cao Z, Zhao Y,
Gong C, Ma L, Wang X, Hu X and Chen S: MicroRNA-320a inhibits
proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells by targeting
RAB11A. Am J Cancer Res. 5:2719–2729. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Frères P, Bouznad N, Servais L, Josse C,
Wenric S, Poncin A, Thiry J, Moonen M, Oury C, Lancellotti P, et
al: Variations of circulating cardiac biomarkers during and after
anthracycline-containing chemotherapy in breast cancer patients.
BMC Cancer. 18:1022018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hamdi K, Goerlitz D, Stambouli N, Islam M,
Baroudi O, Neili B, Benayed F, Chivi S, Loffredo C, Jillson IA, et
al: miRNAs in Sera of Tunisian patients discriminate between
inflammatory breast cancer and non-inflammatory breast cancer.
SpringerPlus. 3:6362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Liu Y, Cai Q, Bao PP, Su Y, Cai H, Wu J,
Ye F, Guo X, Zheng W, Zheng Y and Shu XO: Tumor tissue microRNA
expression in association with triple-negative breast cancer
outcomes. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 152:183–191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Fassan M, Baffa R, Palazzo JP, Lloyd J,
Crosariol M, Liu CG, Volinia S, Alder H, Rugge M, Croce CM and
Rosenberg A: MicroRNA expression profiling of male breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res. 11:R582009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Farazi TA, Horlings HM, Ten Hoeve JJ,
Mihailovic A, Halfwerk H, Morozov P, Brown M, Hafner M, Reyal F,
van Kouwenhove M, et al: MicroRNA sequence and expression analysis
in breast tumors by deep sequencing. Cancer Res. 71:4443–4453.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ouyang M, Li Y, Ye S, Ma J, Lu L, Lv W,
Chang G, Li X, Li Q, Wang S and Wang W: MicroRNA profiling implies
new markers of chemoresistance of triple-negative breast cancer.
PLoS One. 9:e962282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Cao ZG, Huang YN, Yao L, Liu YR, Hu X, Hou
YF and Shao ZM: Positive expression of miR-361-5p indicates better
prognosis for breast cancer patients. J Thorac Dis. 8:1772–1779.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Han J, Yu J, Dai Y, Li J, Guo M, Song J
and Zhou X: Overexpression of miR-361-5p in triple-negative breast
cancer (TNBC) inhibits migration and invasion by targeting RQCD1
and inhibiting the EGFR/PI3K/Akt pathway. Bosn J Basic Med Sci.
19:52–59. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Chang YY, Kuo WH, Hung JH, Lee CY, Lee YH,
Chang YC, Lin WC, Shen CY, Huang CS, Hsieh FJ, et al: Deregulated
microRNAs in triple-negative breast cancer revealed by deep
sequencing. Mol Cancer. 14:362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
McFall T, Mcknight B, Rosati R, Kim S,
Huang Y, Viola-Villegas N and Ratnam M: Progesterone receptor A
promotes invasiveness and metastasis of luminal breast cancer by
suppressing regulation of critical microRNAs by estrogen. J Biol
Chem. 293:1163–1177. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Benvenuti S, Sartorebianchi A, Di
Nicolantonio F, Zanon C, Moroni M, Veronese S, Siena S and Bardelli
A: Oncogenic activation of the RAS/RAF signaling pathway impairs
the response of metastatic colorectal cancers to anti-epidermal
growth factor receptor antibody therapies. Cancer Res.
67:2643–2648. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Downward J: Targeting RAS signalling
pathways in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:11–22. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Guertin DA and Sabatini DM: Defining the
role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell. 12:9–22. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zoncu R, Efeyan A and Sabatini DM: mTOR:
From growth signal integration to cancer, diabetes and ageing. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:21–35. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Biankin AV, Waddell N, Kassahn KS, Gingras
MC, Muthuswamy LB, Johns AL, Miller DK, Wilson PJ, Patch AM, Wu J,
et al: Pancreatic cancer genomes reveal aberrations in axon
guidance pathway genes. Nature. 491:399–405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kidd PM: The use of mushroom glucans and
proteoglycans in cancer treatment. Altern Med Rev. 5:4–27.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Iozzo RV and Sanderson RD: Proteoglycans
in cancer biology, tumour microenvironment and angiogenesis. J Cell
Mol Med. 15:1013–1031. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Van Brocklyn JR: Sphingolipid signaling
pathways as potential therapeutic targets in gliomas. Mini Rev Med
Chem. 7:984–990. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Yuan HD, Quan HY, Zhang Y, Kim SH and
Chung SH: 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3-induced apoptosis in HT-29 colon
cancer cells is associated with AMPK signaling pathway. Mol Med
Rep. 3:825–831. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Green AS, Chapuis N, Lacombe C, Mayeux P,
Bouscary D and Tamburini J: LKB1/AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in
hematological malignancies: From metabolism to cancer cell biology.
Cell Cycle. 10:2115–2120. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Dentice M, Luongo C, Ambrosio R, Sibilio
A, Casillo A, Iaccarino A, Troncone G, Fenzi G, Larsen PR and
Salvatore D: β-catenin regulates deiodinase levels and thyroid
hormone signaling in colon cancer cells. Gastroenterol.
143:1037–1047. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
King CR, Kraus MH and Aaronson SA:
Amplification of a novel v-erbB-related gene in a human mammary
carcinoma. Science. 229:974–976. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Normanno N, De Luca A, Maiello MR,
Campiglio M, Napolitano M, Mancino M, Carotenuto A, Viglietto G and
Menard S: The MEK/MAPK pathway is involved in the resistance of
breast cancer cells to the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor
gefitinib. J Cell Physiol. 207:420–427. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Oxnard GR, Arcila ME, Sima CS, Riely GJ,
Chmielecki J, Kris MG, Pao W, Ladanyi M and Miller V: Acquired
resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR mutant lung
cancer: Distinct natural history of patients with tumors harboring
the T790M mutation. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1616–1622. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|