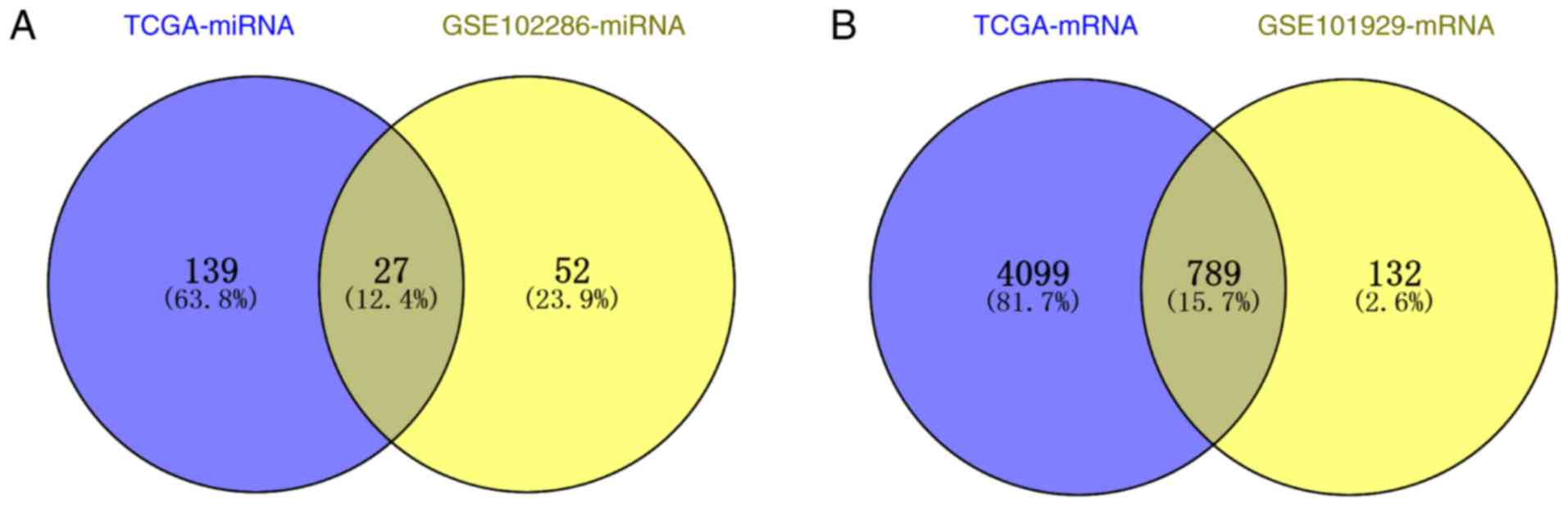
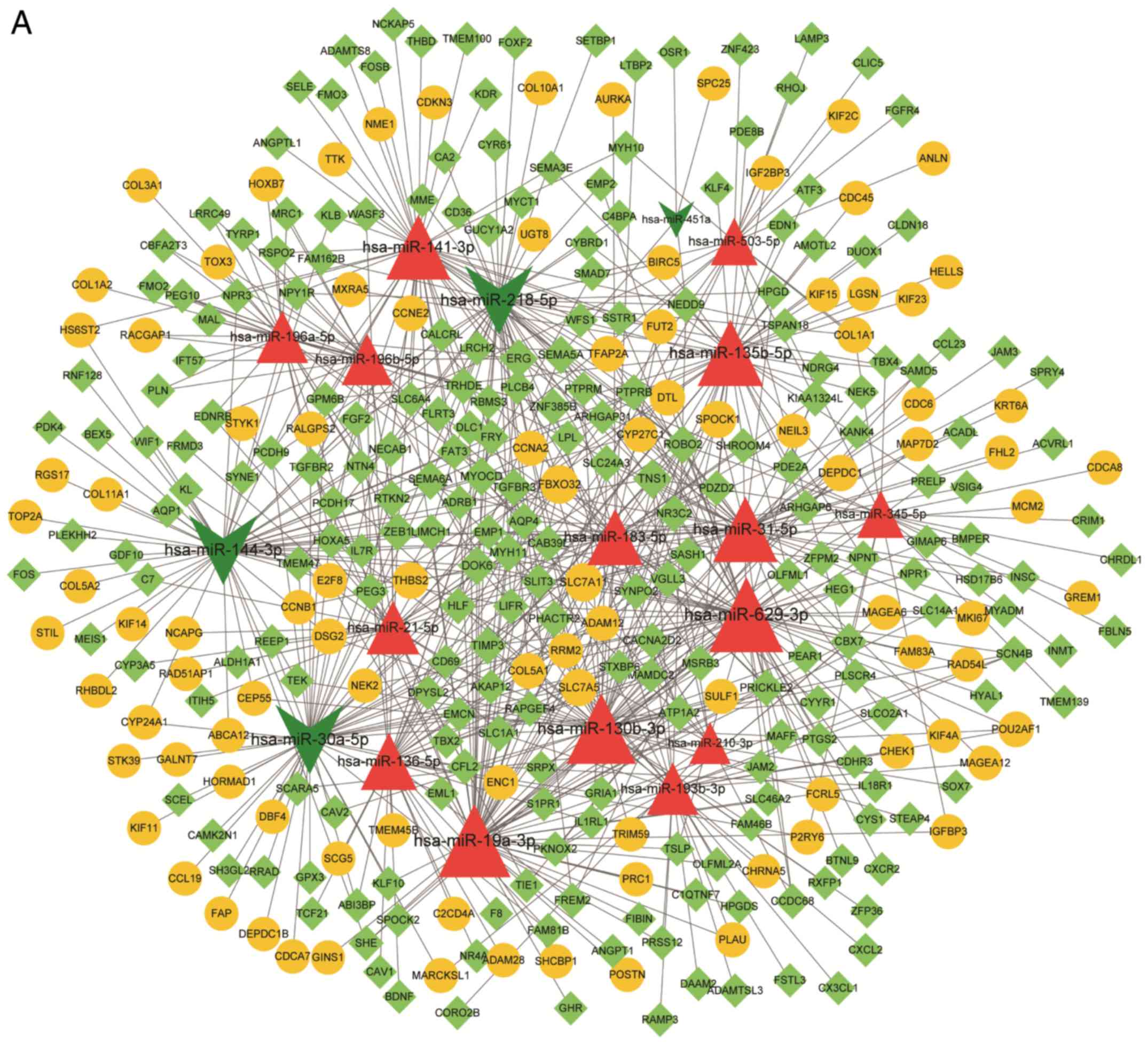
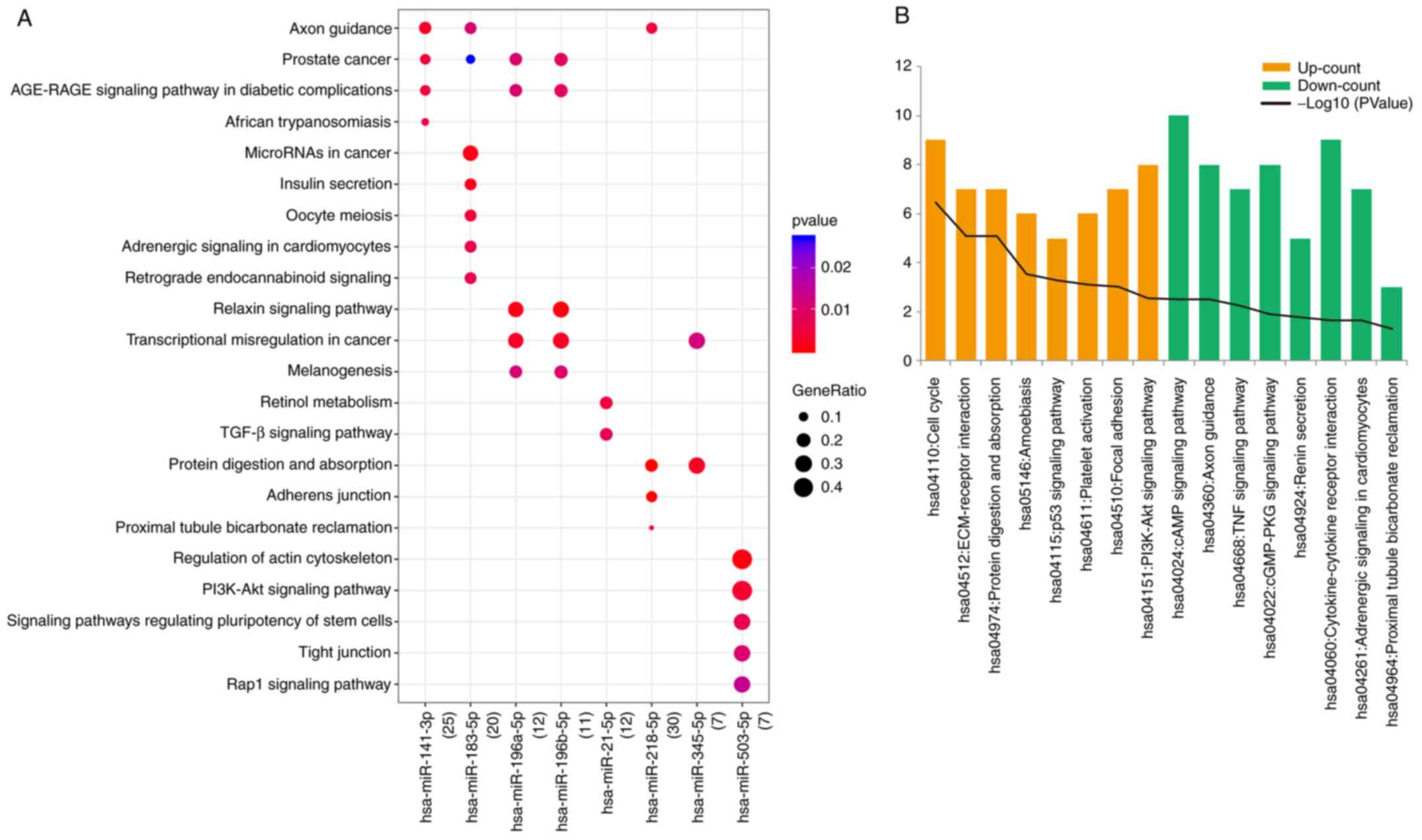
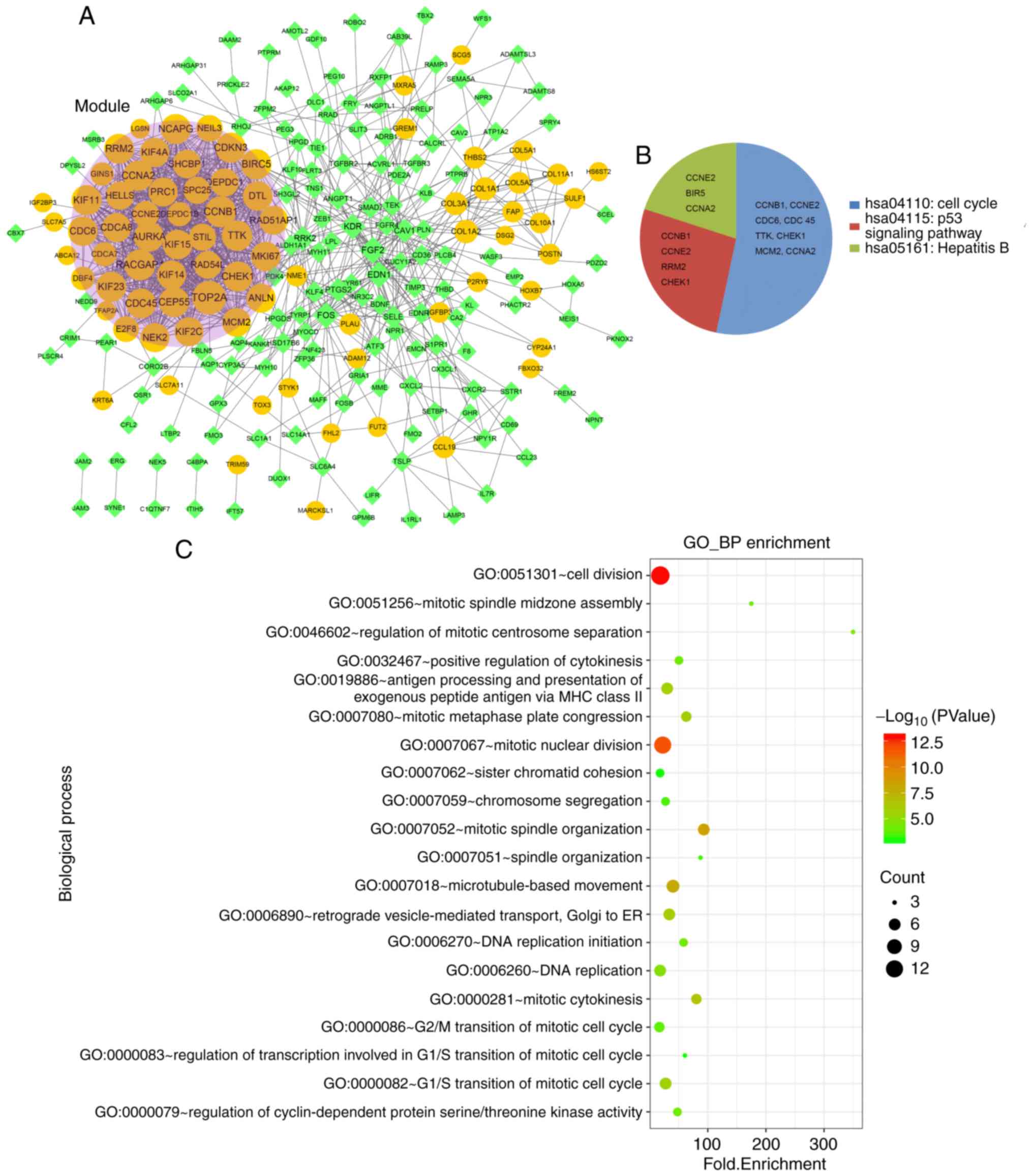
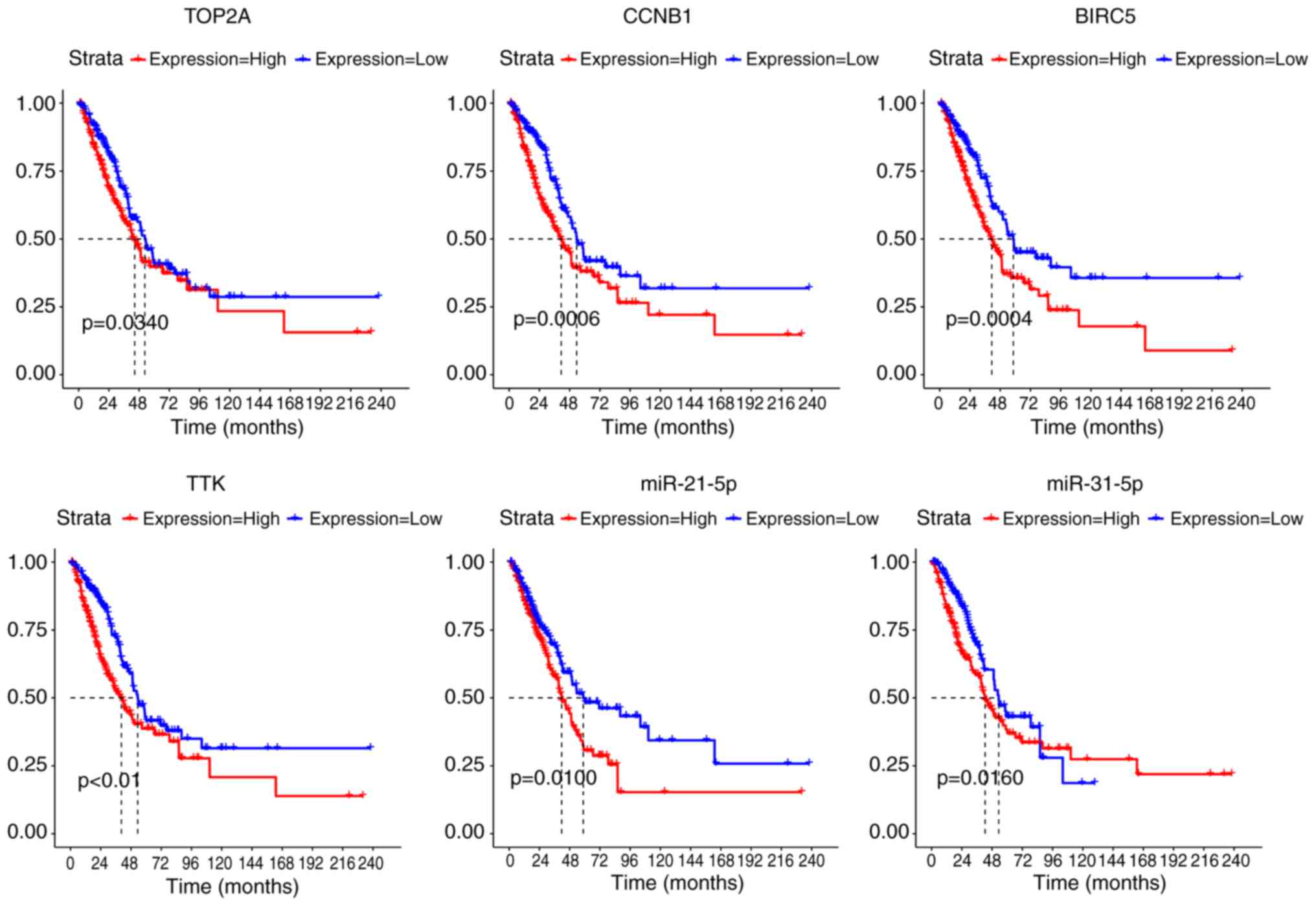
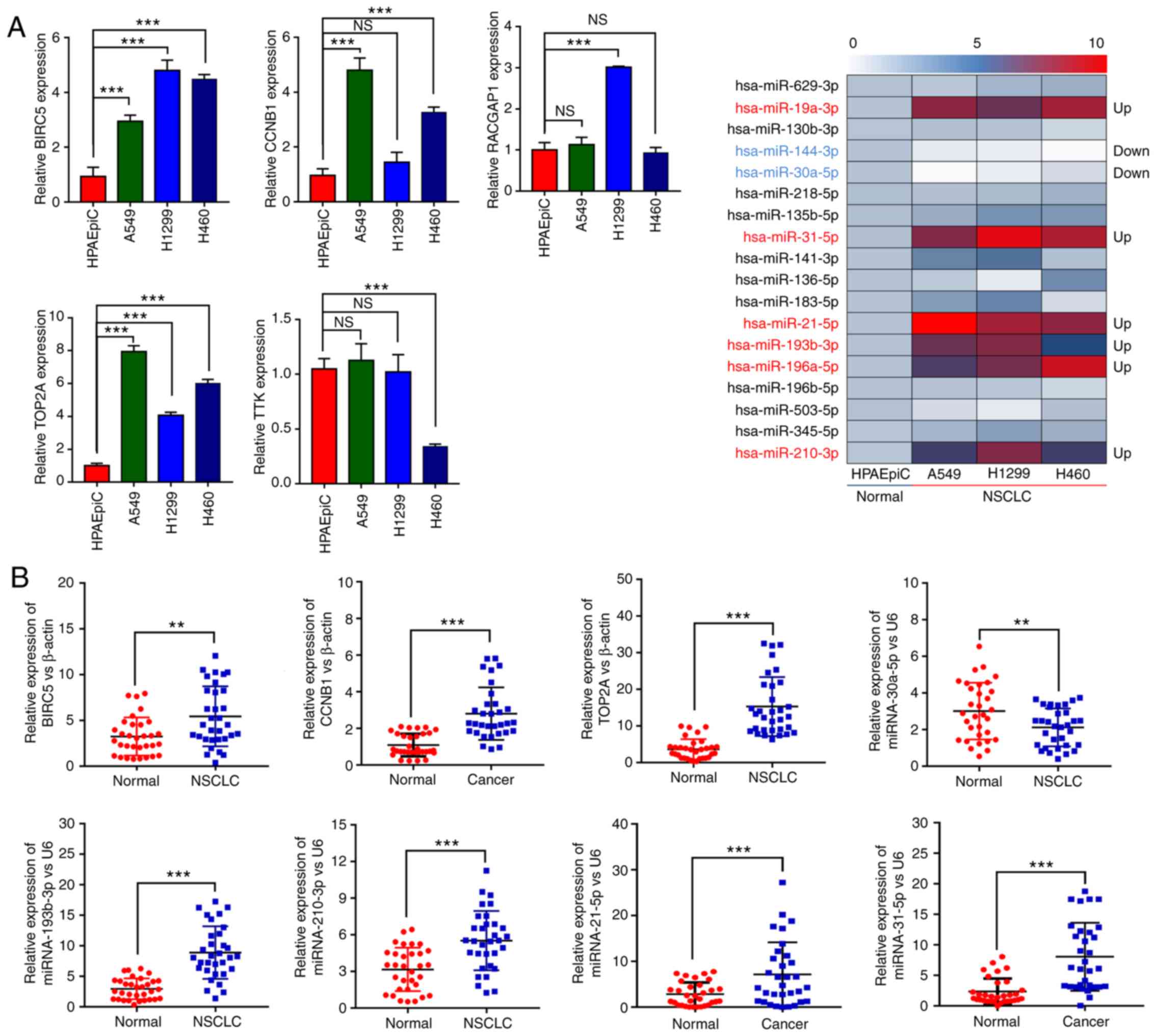
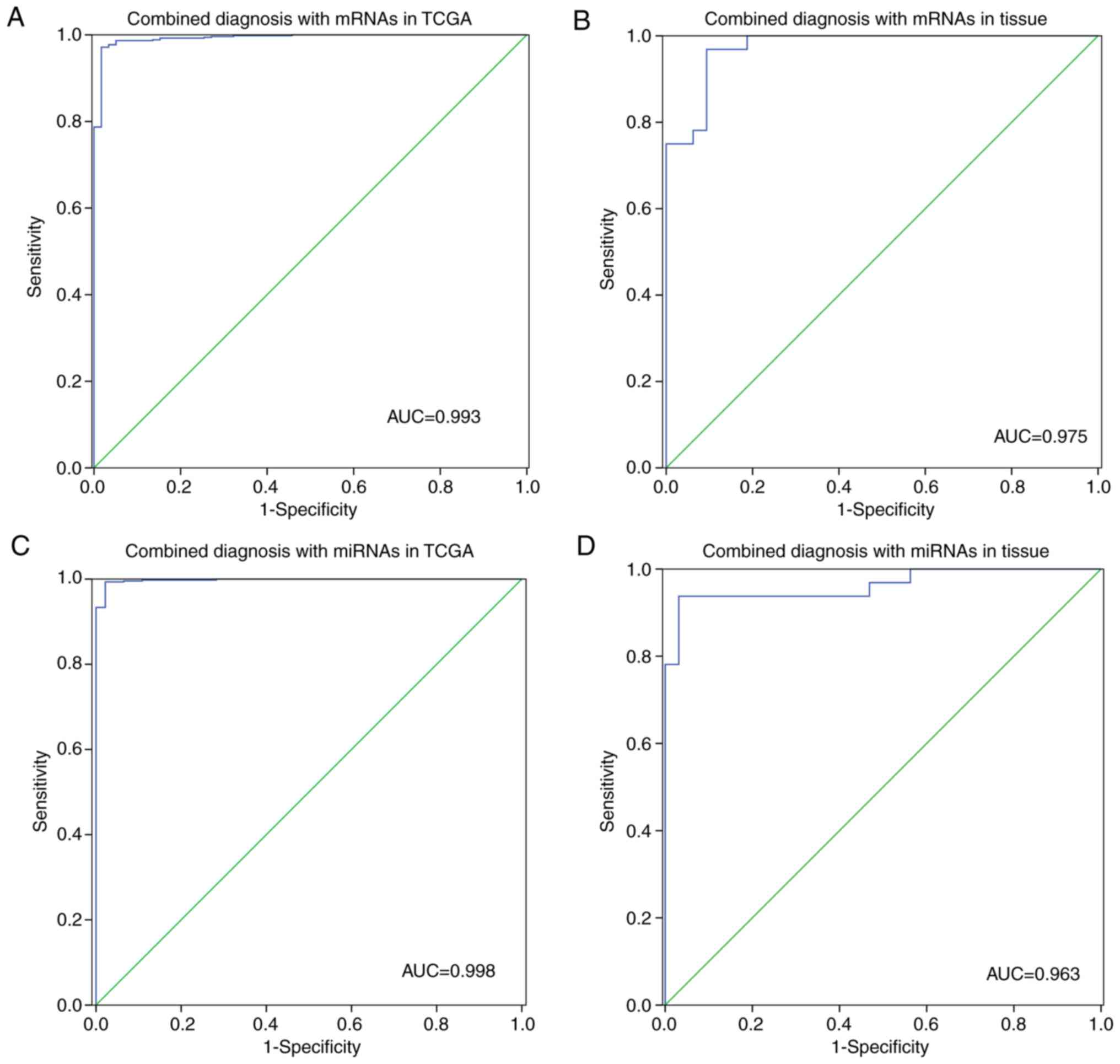
|
1
|
Kasinski AL, Kelnar K, Stahlhut C,
Orellana E, Zhao J, Shimer E, Dysart S, Chen X, Bader AG and Slack
FJ: A combinatorial microRNA therapeutics approach to suppressing
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 34:3547–3555. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fassina A, Cappellesso R and Fassan M:
Classification of non-small cell lung carcinoma in transthoracic
needle specimens using microRNA expression profiling. Chest.
140:1305–1311. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reungwetwattana T, Weroha SJ and Molina
JR: Oncogenic pathways, molecularly targeted therapies, and
highlighted clinical trials in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Clin Lung Cancer. 13:252–266. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Horvath S, Zhang B, Carlson M, Lu KV, Zhu
S, Felciano RM, Laurance MF, Zhao W, Qi S, Chen Z, et al: Analysis
of oncogenic signaling networks in glioblastoma identifies ASPM as
a molecular target. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:17402–17407. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hutter C and Zenklusen JC: The cancer
genome atlas: Creating lasting value beyond its data. Cell.
173:283–285. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang C, Sun C, Liang X, Xie S, Huang J and
Li D: Integrative analysis of microRNA and mRNA expression profiles
in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 23:90–97. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Reddy KB: MicroRNA (miRNA) in cancer.
Cancer Cell Int. 15:382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M,
Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, et
al: Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee HY, Han SS, Rhee H, Park JH, Lee JS,
Oh YM, Choi SS, Shin SH and Kim WJ: Differential expression of
microRNAs and their target genes in non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol
Med Rep. 11:2034–2040. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gallardo E, Navarro A, Viñolas N, Marrades
RM, Diaz T, Gel B, Quera A, Bandres E, Garcia-Foncillas J, Ramirez
J and Monzo M: miR-34a as a prognostic marker of relapse in
surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer. Carcinogenesis.
30:1903–1909. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wei JS, Song YK, Durinck S, Chen QR, Cheuk
AT, Tsang P, Zhang Q, Thiele CJ, Slack A, Shohet J and Khan J: The
MYCN oncogene is a direct target of miR-34a. Oncogene.
27:5204–5213. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mitchell KA, Zingone A, Toulabi L,
Boeckelman J and Ryan BM: Comparative transcriptome profiling
reveals coding and noncoding RNA differences in NSCLC from African
Americans and European Americans. Clin Cancer Res. 23:7412–7425.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dweep H and Gretz N: miRWalk2.0: A
comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat Methods.
12:6972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hsu SD, Chu CH, Tsou AP, Chen SJ, Chen HC,
Hsu PW, Wong YH, Chen YH, Chen GH and Huang HD: miRNAMap 2.0:
Genomic maps of microRNAs in metazoan genomes. Nucleic Acids Res.
36((Database Issue)): D165–D169. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology: The Gene
Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M,
Simonovic M, Roth A, Minguez P, Doerks T, Stark M, Muller J, Bork
P, et al: The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction
networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39((Database Issue)): D561–D568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bandettini WP, Kellman P, Mancini C,
Booker OJ, Vasu S, Leung SW, Wilson JR, Shanbhag SM, Chen MY and
Arai AE: MultiContrast delayed enhancement (MCODE) improves
detection of subendocardial myocardial infarction by late
gadolinium enhancement cardiovascular magnetic resonance: A
clinical validation study. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 14:832012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Therneau T and Lumley T: Survival:
Survival analysis, including penalised likelihood. R package
version 2.36–5. Survival: Survival analysis, including penalised
likelihood R package version 2.36–2.2010. 2011.
|
|
26
|
Zhang B, Kirov S and Snoddy J: WebGestalt:
An integrated system for exploring gene sets in various biological
contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:W741–W748. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Braybrooke JP, O'Byrne KJ, Propper DJ,
Blann A, Saunders M, Dobbs N, Han C, Woodhull J, Mitchell K, Crew
J, et al: A phase II study of razoxane, an antiangiogenic
topoisomerase II inhibitor, in renal cell cancer with assessment of
potential surrogate markers of angiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res.
6:4697–4704. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Terashima M, Ichikawa W, Ochiai A, Kitada
K, Kurahashi I, Sakuramoto S, Katai H, Sano T, Imamura H and Sasako
M; ACTS-GC Group, : TOP2A, GGH, and PECAM1 are associated with
hematogenous, lymph node, and peritoneal recurrence in stage II/III
gastric cancer patients enrolled in the ACTS-GC study. Oncotarget.
8:57574–57582. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kodiakov DS, Klimachëv VV, Avdalian AM,
Bobrov IP, Lazarev AF, Lushnikova EL and Nepomiashchikh LM:
Topoisomerase IIa expression in correlation with clinical and
morphological parameters and proliferation (based on argyrophilic
proteins of nucleolar organizer regions and Ki-67 antigen) in lung
adenocarcinoma. Vopr Onkol. 60:63–68. 2014.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nakayama Y and Yamaguchi N: Role of cyclin
B1 levels in DNA damage and DNA damage-induced senescence. Int Rev
Cell Mol Biol. 305:303–337. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yuan J, Krämer A, Matthess Y, Yan R,
Spänkuch B, Gätje R, Knecht R, Kaufmann M and Strebhardt K: Stable
gene silencing of cyclin B1 in tumor cells increases susceptibility
to taxol and leads to growth arrest in vivo. Oncogene.
25:1753–1762. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Soria JC, Jang SJ, Khuri FR, Hassan K, Liu
D, Hong WK and Mao L: Overexpression of cyclin B1 in early-stage
non-small cell lung cancer and its clinical implication. Cancer
Res. 60:4000–4004. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jung IL, Kang HJ, Kim KC and Kim IG:
PTEN/pAkt/p53 signaling pathway correlates with the radioresponse
of non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Med. 25:517–523.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Altieri DC: The molecular basis and
potential role of survivin in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Trends
Mol Med. 7:542–547. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li F: Survivin study: What is the next
wave? J Cell Physiol. 197:8–29. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shivapurkar N, Reddy J, Chaudhary PM and
Gazdar AF: Apoptosis and lung cancer: A review. J Cell Biochem.
88:885–898. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao H, Zhang X, Han Z, Wang Z and Wang Y:
Plasma anti-BIRC5 IgG may be a useful marker for evaluating the
prognosis of nonsmall cell lung cancer. FEBS Open Bio. 8:829–835.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhu H, Wu H, Liu X, Li B, Chen Y, Ren X,
Liu CG and Yang JM: Regulation of autophagy by a beclin 1-targeted
microRNA, miR-30a, in cancer cells. Autophagy. 5:816–823. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu J, Zeng Y, Xu C, Qin H, Lei Z, Shen D,
Liu Z and Huang JA: Expression profile analysis of microRNAs and
downregulated miR-486-5p and miR-30a-5p in non-small cell lung
cancer. Oncol Rep. 34:1779–1786. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Voronkova M, Luanpitpong S, Riedel H and
Rojanasakul Y: Abstract 1913: SOX9 regulates cancer stem-like cells
in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 77:19132017.
|
|
42
|
Świtlik W, Karbownik MS, Suwalski M, Kozak
J and Szemraj J: miR-30a-5p together with miR-210-3p as a promising
biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer: A preliminary study.
Cancer Biomark. 21:479–488. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yu L, Todd NW, Xing L, Xie Y, Zhang H, Liu
Z, Fang H, Zhang J, Katz RL and Jiang F: Early detection of lung
adenocarcinoma in sputum by a panel of microRNA markers. Int J
Cancer. 127:2870–2878. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yu JR, Tai Y, Jin Y, Hammell MC, Wilkinson
JE, Roe JS, Vakoc CR and Van Aelst L: TGF-β/Smad signaling through
DOCK4 facilitates lung adenocarcinoma metastasis. Genes Dev.
29:250–261. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhan P, Xi GM, Zhang B, Wu Y, Liu HB, Liu
YF, Xu WJ, Zhu Q, Cai F, Zhou ZJ, et al: NCAPG2 promotes tumour
proliferation by regulating G2/M phase and associates with poor
prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. J Cell Mol Med. 21:665–676. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hu H, Li S, Liu J and Ni B: MicroRNA-193b
modulates proliferation, migration, and invasion of non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 44:424–430.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|