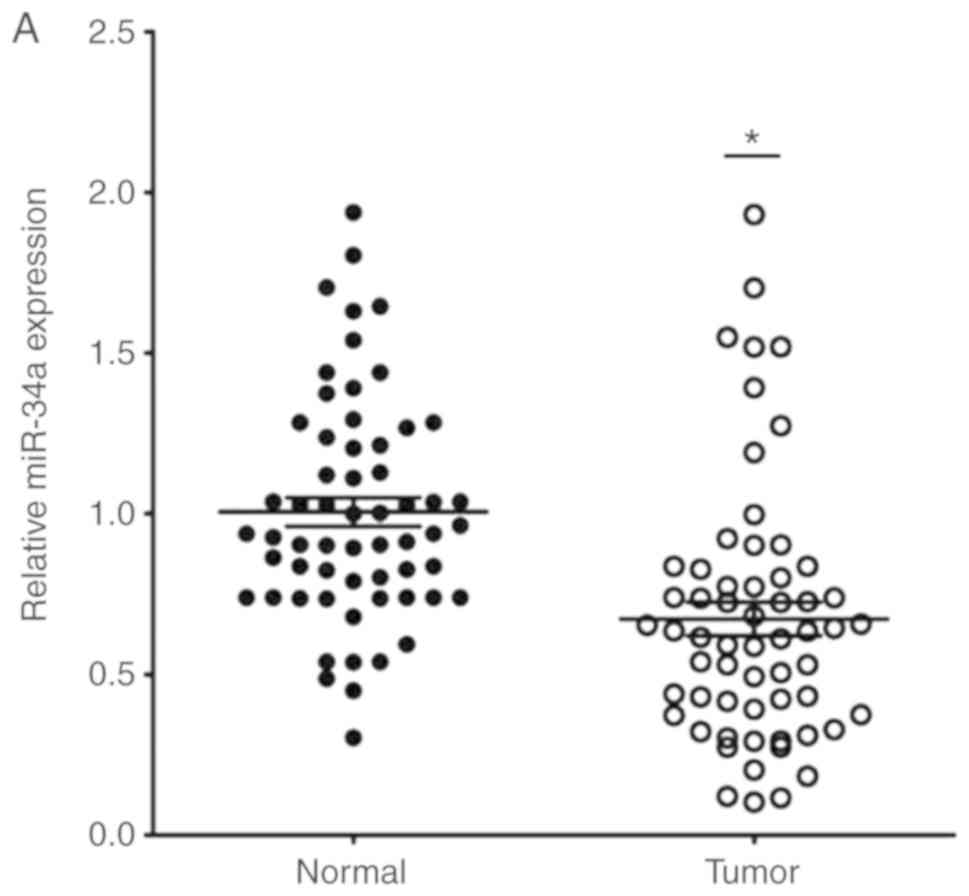
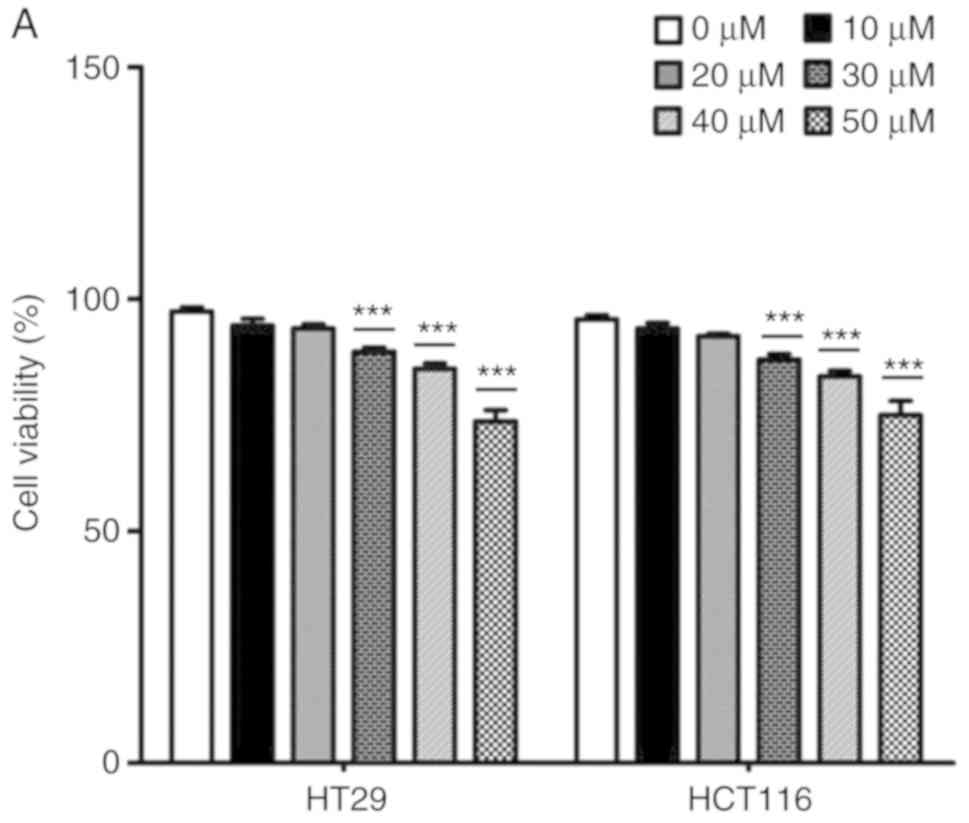
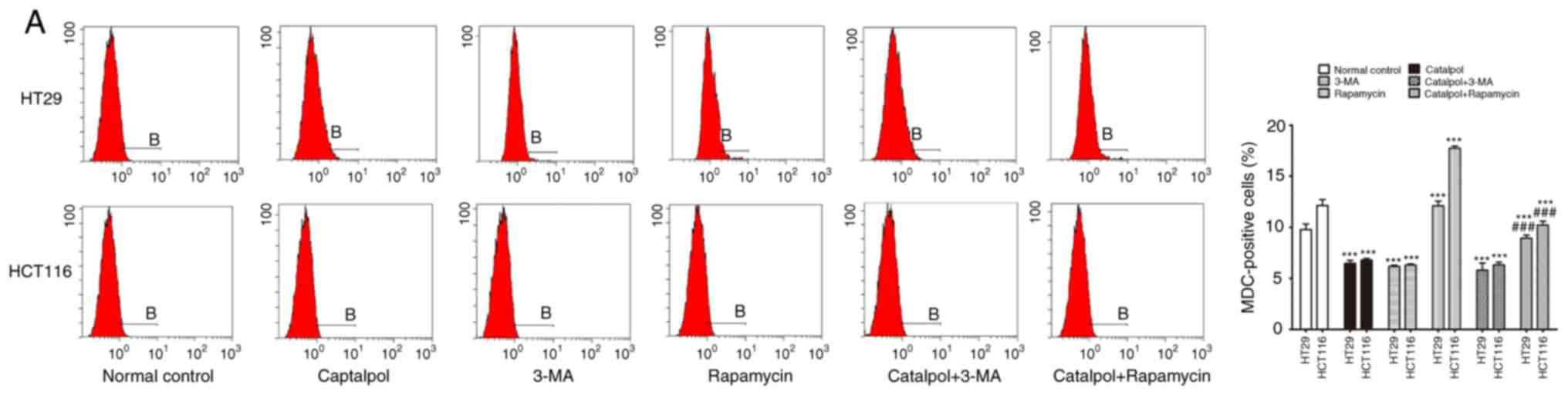
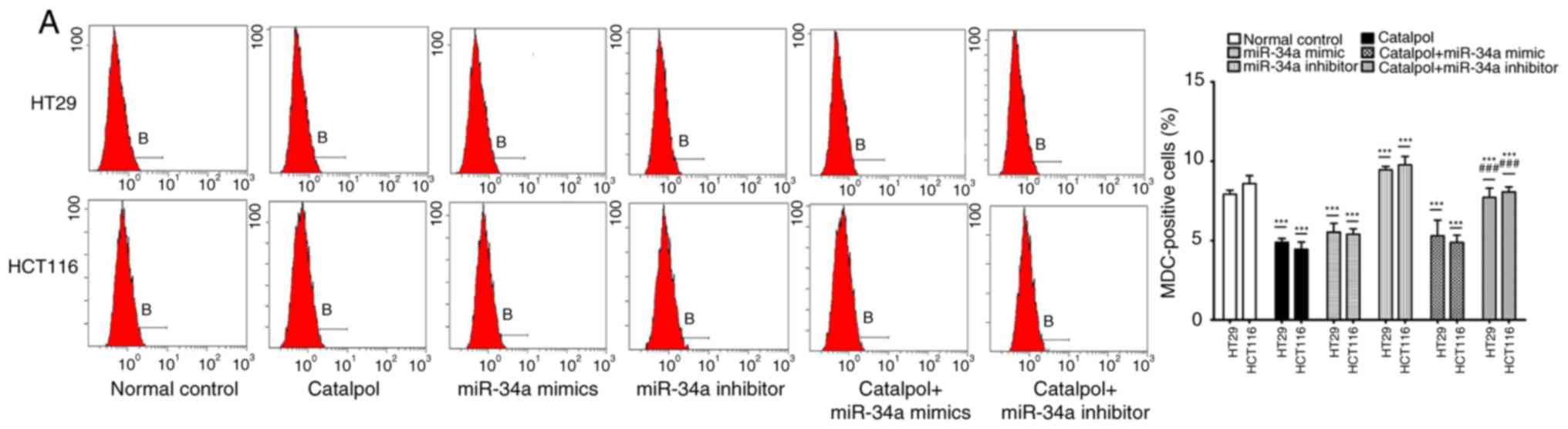
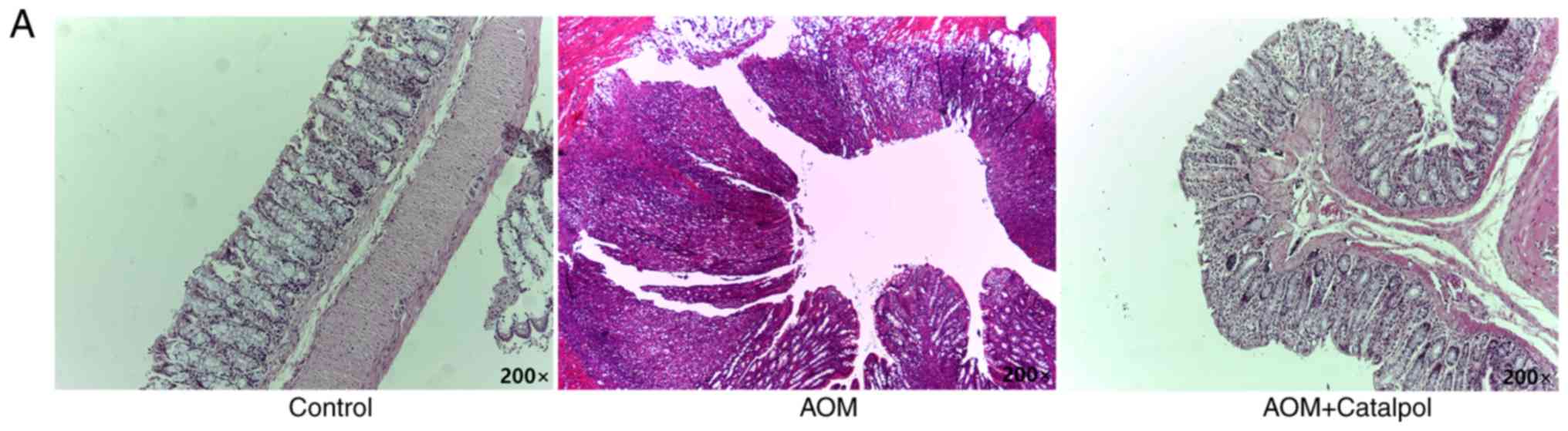
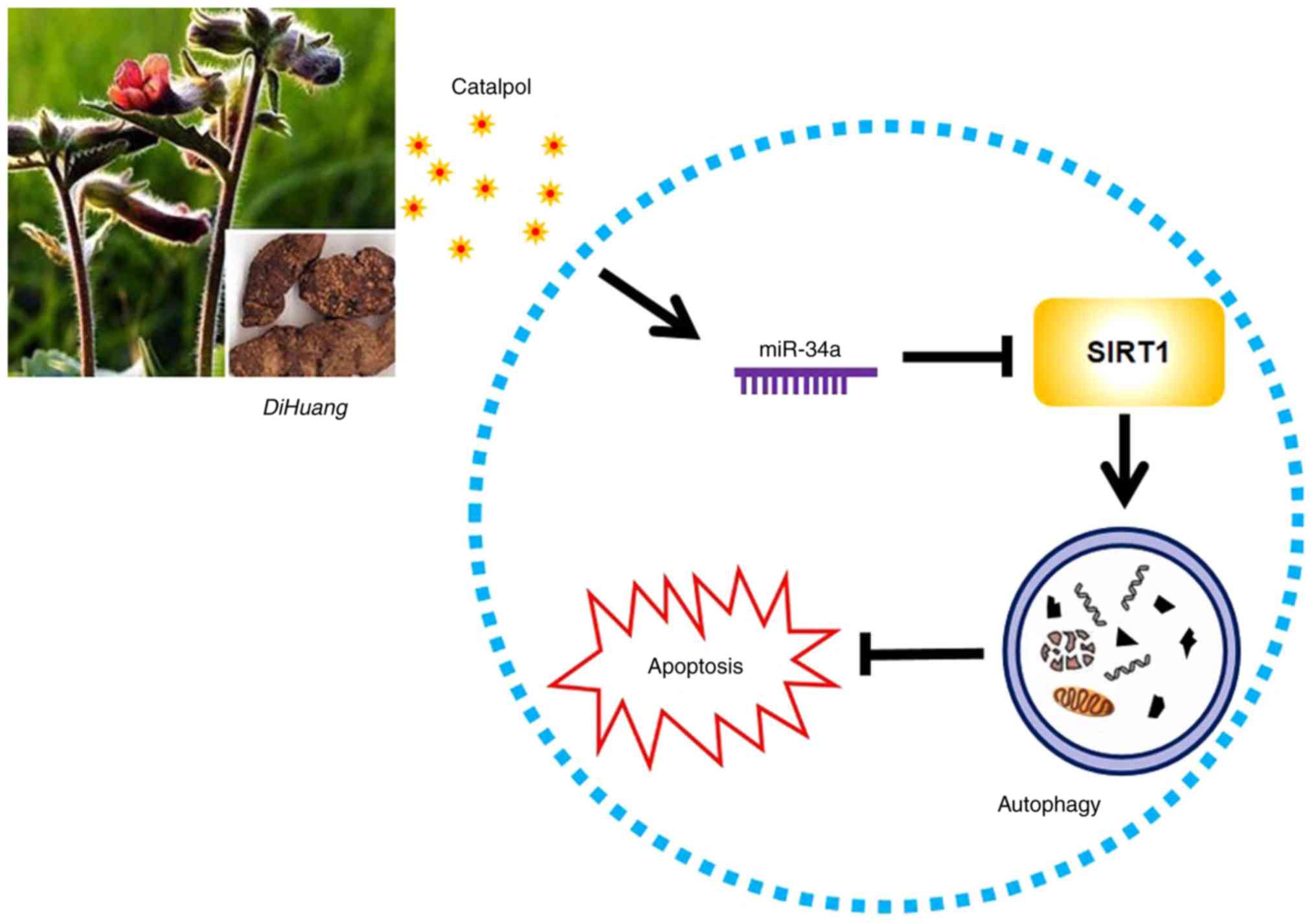
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, Ahnen DJ,
Meester RGS, Barzi A and Jemal A: Colorectal cancer statistics,
2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:177–193. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang Y, Weng W, Peng J, Hong L, Yang L,
Toiyama Y, Gao R, Liu M, Yin M, Pan C, et al: Fusobacterium
nucleatum increases proliferation of colorectal cancer cells and
tumor development in mice by activating Toll-like receptor 4
signaling to nuclear factor-κB, up-regulating expression of
microRNA-21. Gastroenterology. 152:851–866.e24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhu P, Wu Y, Yang A, Fu X, Mao M and Liu
Z: Catalpol suppressed proliferation, growth and invasion of CT26
colon cancer by inhibiting inflammation and tumor angiogenesis.
Biomed Pharmacother. 95:68–76. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xiu LZ, Bo J, Zhi BL, Hao S and An LJ:
Catalpol ameliorates cognition deficits and attenuates oxidative
damage in the brain of senescent mice induced by D-galactose.
Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 88:64–72. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang ZH and Zhansheng H: Catalpol inhibits
migration and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer cells and in
athymic nude mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 103:1708–1719. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang H, Jia R, Wang F, Qiu G, Qiao P, Xu
X and Wu D: Catalpol protects mice against
Lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury
through inhibiting inflammatory and oxidative response. Oncotarget.
9:3887–3894. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW,
Bartel DP and Burge CB: Prediction of mammalian MicroRNA targets.
Cell. 115:787–798. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gao N, Tian JX, Shang YH, Zhao DY and Wu
T: Catalpol suppresses proliferation and facilitates apoptosis of
OVCAR-3 ovarian cancer cells through upregulating microRNA-200 and
downregulating MMP-2 expression. Int J Mol Sci. 15:19394–19405.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu C, Wu F, Liu Y and Meng C: Catalpol
suppresses proliferation and facilitates apoptosis of MCF-7 breast
cancer cells through upregulating microRNA-146a and downregulating
matrix metalloproteinase-16 expression. Mol Med Rep. 12:7609–7614.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu L, Gao H, Wang H, Zhang Y, Xu W, Lin
S, Wang H, Wu Q and Guo J: Catalpol promotes cellular apoptosis in
human HCT116 colorectal cancer cells via microRNA-200 and the
downregulation of PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Oncol Lett.
14:3741–3747. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun C, Wang FJ, Zhang HG, Xu XZ, Jia RC,
Yao L and Qiao PF: miR-34a mediates oxaliplatin resistance of
colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting macroautophagy via
transforming growth factor-β/Smad4 pathway. World J Gastroenterol.
23:1816–1827. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qiao P, Li G, Bi W, Yang L, Yao L and Wu
D: microRNA-34a inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition in human
cholangiocarcinoma by targeting Smad4 through transforming growth
factor-beta/Smad pathway. BMC Cancer. 15:4692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun L, Hu L, Cogdell D, Lu L, Gao C, Tian
W, Zhang Z, Kang Y, Fleming JB and Zhang W: MIR506 induces
autophagy-related cell death in pancreatic cancer cells by
targeting the STAT3 pathway. Autophagy. 13:703–714. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mathew R, Karantza-Wadsworth V and White
E: Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:961–967. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Z, Zhu P, Zhang L, Xiong B, Tao J,
Guan W, Li C, Chen C, Gu J, Duanmu J and Zhang W: Autophagy
inhibition attenuates the induction of anti-inflammatory effect of
catalpol in liver fibrosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 103:1262–1271.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Y, Shao Y, Gao Y, Wan G, Wan D, Zhu
H, Qiu Y and Ye X: Catalpol prevents denervated muscular atrophy
related to the inhibition of autophagy and reduces BAX/BCL2 ratio
via mTOR pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 13:243–253. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz KM and Wittekind
CH: TNM classification of malignant tumors. UICC International
Union Against Cancer. 7th. Wiley-Blackwell; 2009
|
|
18
|
Xu Y, Yang X, Mei S, Sun Y and Li J:
Acquisition of temozolomide resistance by the rat C6 glioma cell
line increases cell migration and side population phenotype. Oncol
Rep. 42:2355–2362. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dong J, Liang W, Wang T, Sui J, Wang J,
Deng Z and Chen D: Saponins regulate intestinal inflammation in
colon cancer and IBD. Pharmacol Res. 144:66–72. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xiong Y, Shi L, Wang L, Zhou Z, Wang C,
Lin Y, Luo D, Qiu J and Chen D: Activation of sirtuin 1 by
catalpol-induced down-regulation of microRNA-132 attenuates
endoplasmic reticulum stress in colitis. Pharmacol Res. 123:73–82.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M and Lowenstein CJ:
miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci. 105:13421–13426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fang C, Qiu S, Sun F, Li W, Wang Z, Yue B,
Wu X and Yan D: Long non-coding RNA HNF1A-AS1 mediated repression
of miR-34a/SIRT1/p53 feedback loop promotes the metastatic
progression of colon cancer by functioning as a competing
endogenous RNA. Cancer Lett. 410:50–62. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lai M, Du G, Shi R, Yao J, Yang G, Wei Y,
Zhang D, Xu Z, Zhang R, Li Y, et al: miR-34a inhibits migration and
invasion by regulating the SIRT1/p53 pathway in human SW480 cells.
Mol Med Rep. 11:3301–3307. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qiao PF, Yao L, Zhang XC, Li GD and Wu DQ:
Heat shock pretreatment improves stem cell repair following
ischemia-reperfusion injury via autophagy. World J Gastroenterol.
21:12822–12834. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou J, Xu G, Ma S, Li F, Yuan M, Xu H and
Huang K: Catalpol ameliorates high-fat diet-induced insulin
resistance and adipose tissue inflammation by suppressing the JNK
and NF-κB pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 467:853–858. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li DQ, Bao YM, Li Y, Wang CF, Liu Y and An
LJ: Catalpol modulates the expressions of Bcl-2 and Bax and
attenuates apoptosis in gerbils after ischemic injury. Brain Res.
1115:179–185. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jin S and White E: Role of autophagy in
cancer: Management of metabolic stress. Autophagy. 3:28–31. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Crespo I, San-Miguel B, Prause C, Marroni
N, Cuevas MJ, González-Gallego J and Tuñón MJ: Glutamine treatment
attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in
TNBS-induced colitis. PLoS One. 7:e504072012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|