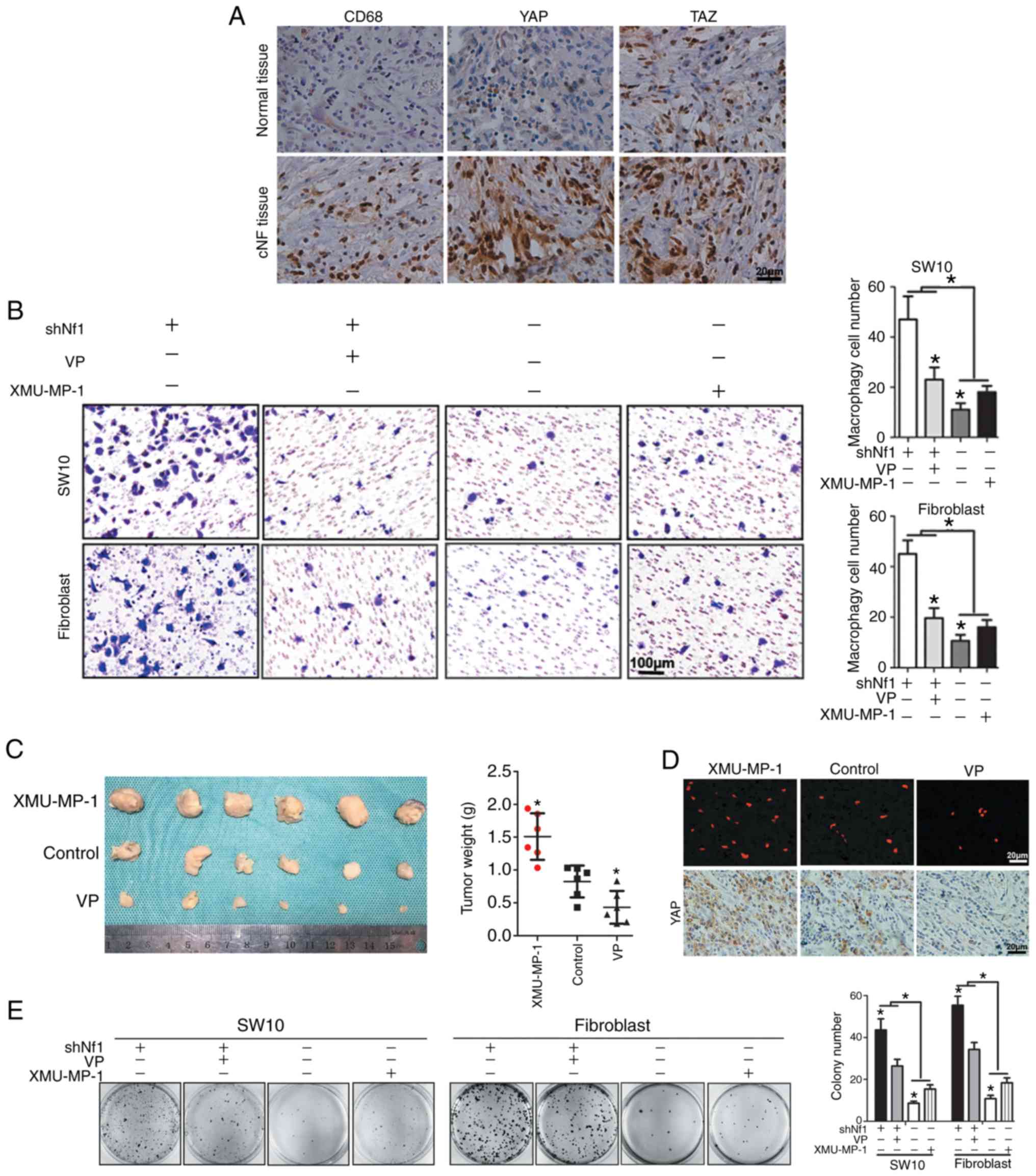
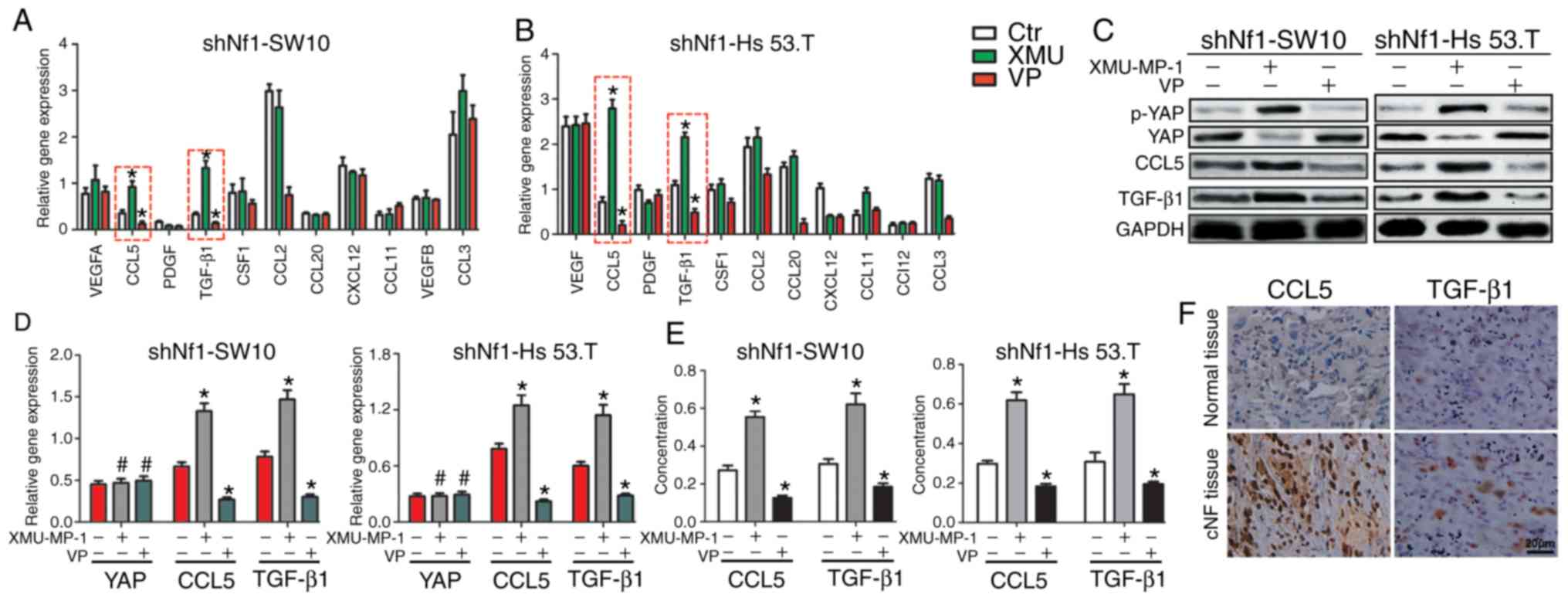
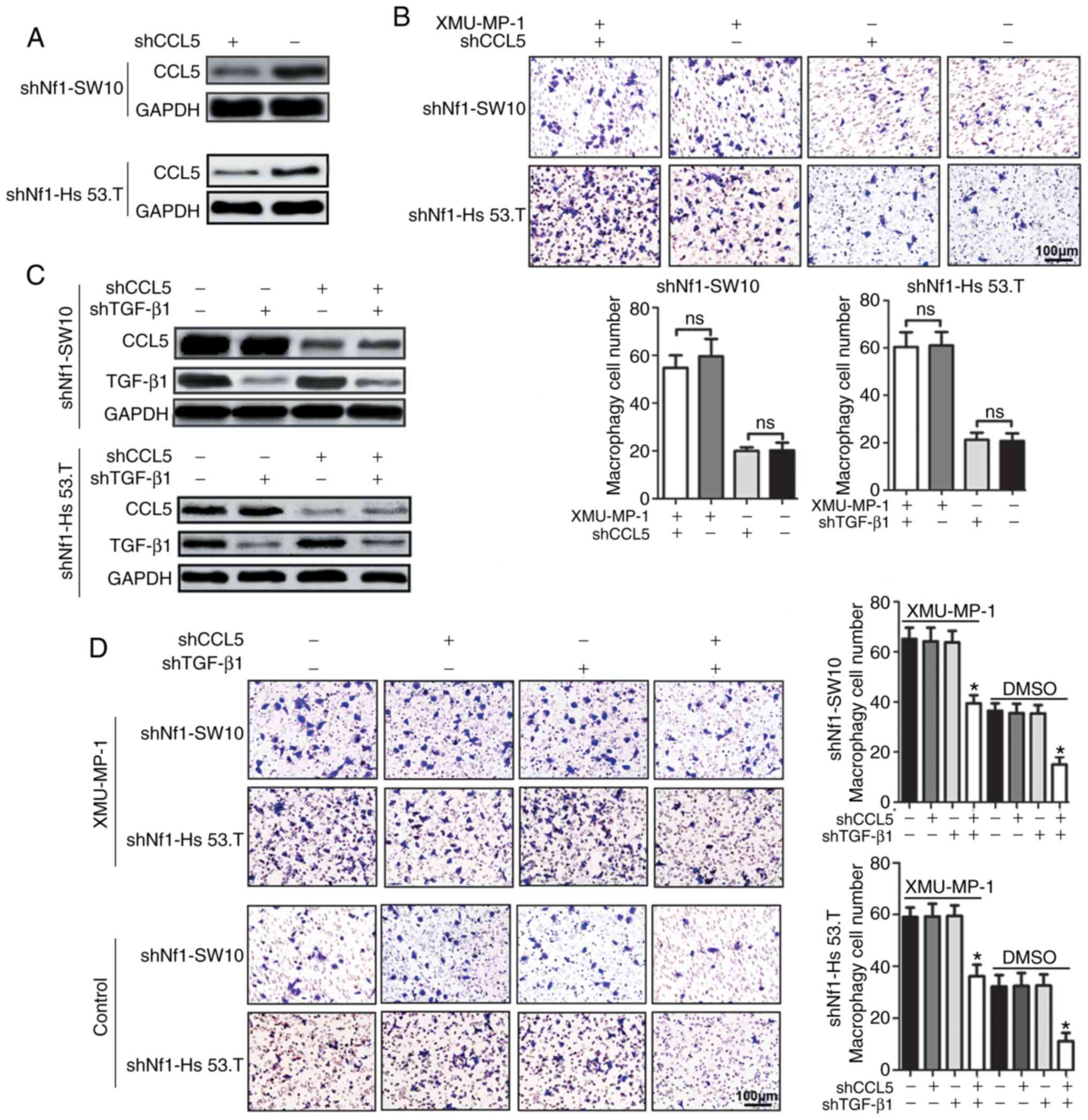
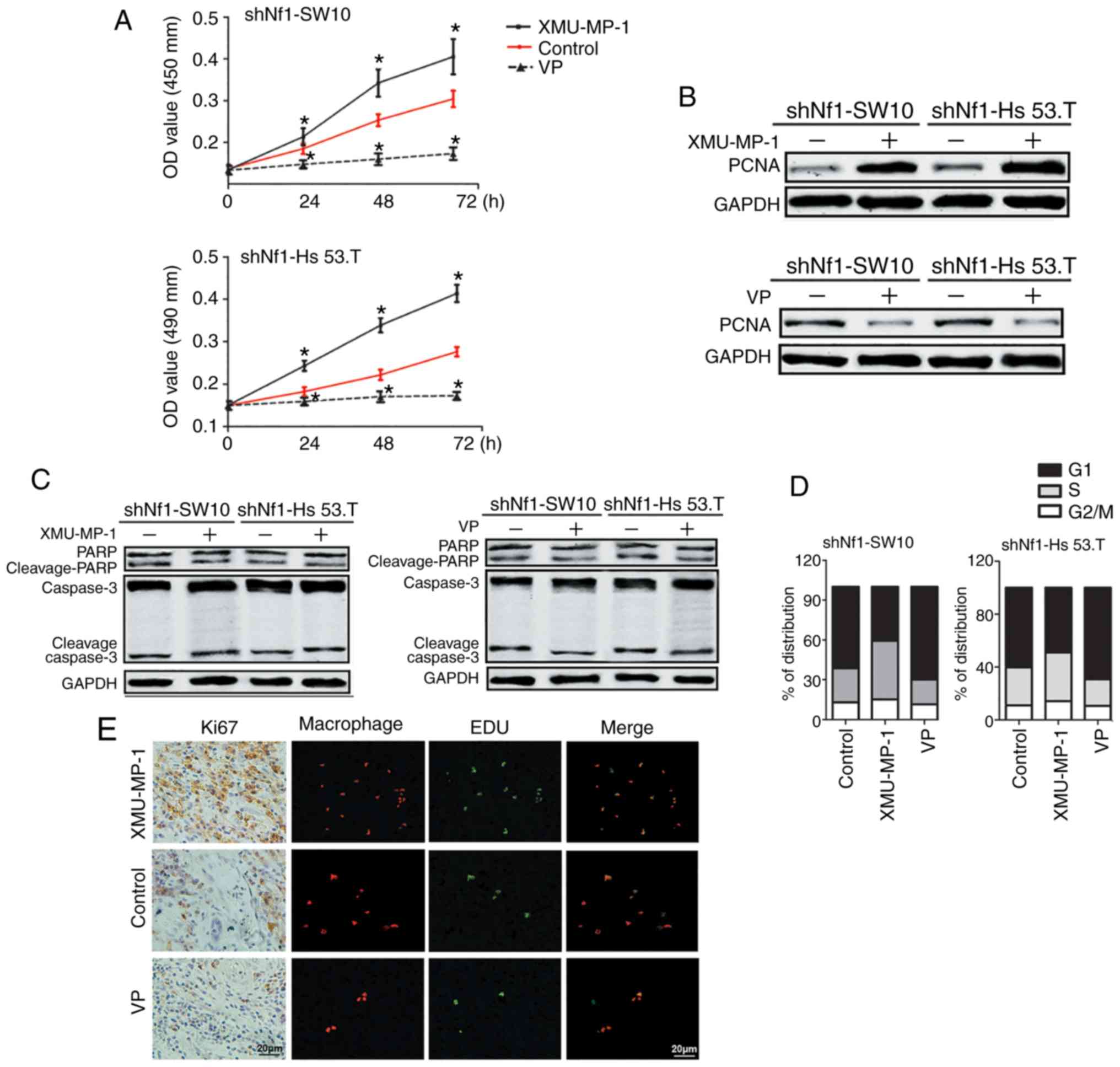
|
1
|
Serra E, Puig S, Otero D, Gaona A, Kruyer
H, Ars E, Estivill X and Lázaro C: Confirmation of a double-hit
model for the NF1 gene in benign neurofibromas. Am J Hum Genet.
61:512–519. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Granström S, Langenbruch A, Augustin M and
Mautner VF: Psychological burden in adult neurofibromatosis type 1
patients: Impact of disease visibility on body image. Dermatology.
224:160–167. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Riccardi VM: Ketotifen suppression of NF1
neurofibroma growth over 30 years. Am J Med Genet A. 167:1570–1577.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gutmann DH, Ferner RE, Listernick RH, Korf
BR, Wolters PL and Johnson KJ: Neurofibromatosis type 1. Nat Rev
Dis Primers. 3:170042017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhu Y, Ghosh P, Charnay P, Burns DK and
Parada LF: Neurofibromas in NF1: Schwann cell origin and role of
tumor environment. Science. 296:920–922. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Demestre M, Herzberg J, Holtkamp N, Hagel
C, Reuss D, Friedrich RE, Kluwe L, Von Deimling A, Mautner VF and
Kurtz A: Imatinib mesylate (Glivec) inhibits Schwann cell viability
and reduces the size of human plexiform neurofibroma in a xenograft
model. J Neurooncol. 98:11–19. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Takata M, Imai T and Hirone T:
Factor-XIIIa-positive cells in normal peripheral nerves and
cutaneous neurofibromas of type-1 neurofibromatosis. Am J
Dermatopathol. 16:37–43. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park SJ, Sawitzki B, Kluwe L, Mautner VF,
Holtkamp N and Kurtz A: Serum biomarkers for neurofibromatosis type
1 and early detection of malignant peripheral nerve-sheath tumors.
BMC Med. 11:1092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rizvi TA, Huang Y, Sidani A, Atit R,
Largaespada DA, Boissy RE and Ratner N: A novel cytokine pathway
suppresses glial cell melanogenesis after injury to adult nerve. J
Neurosci. 22:9831–9840. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Prada CE, Jousma E, Rizvi TA, Wu J, Dunn
RS, Mayes DA, Cancelas JA, Dombi E, Kim MO, West BL, et al:
Neurofibroma-associated macrophages play roles in tumor growth and
response to pharmacological inhibition. Acta Neuropathol.
125:159–168. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Donovan S, Shannon KM and Bollag G: GTPase
activating proteins: Critical regulators of intracellular
signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1602:23–45. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dineen SP, Lynn KD, Holloway SE, Miller
AF, Sullivan JP, Shames DS, Beck AW, Barnett CC, Fleming JB and
Brekken RA: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 mediates
macrophage infiltration into orthotopic pancreatic tumors in mice.
Cancer Res. 68:4340–4346. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Keepers TR, Gross LK and Obrig TG:
Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, macrophage inflammatory protein
1 alpha, and RANTES recruit macrophages to the kidney in a mouse
model of hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Infect Immun. 75:1229–1236.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen Z, Mo J, Brosseau JP, Shipman T, Wang
Y, Liao CP, Cooper JM, Allaway RJ, Gosline SJC, Guinney J, et al:
Spatiotemporal loss of NF1 in Schwann cell lineage leads to
different types of cutaneous neurofibroma susceptible to
modification by the hippo pathway. Cancer Discov. 9:114–129. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rawat SJ, Araiza-Olivera D, Arias-Romero
LE, Villamar-Cruz O, Prudnikova TY, Roder H and Chernoff J: H-ras
inhibits the hippo pathway by promoting Mst1/Mst2
heterodimerization. Curr Biol. 26:1556–1563. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kwon Y, Vinayagam A, Sun X, Dephoure N,
Gygi SP, Hong P and Perrimon N: The Hippo signaling pathway
interactome. Science. 342:737–740. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gérard C and Goldbeter A: The balance
between cell cycle arrest and cell proliferation: Control by the
extracellular matrix and by contact inhibition. Interface Focus.
4:201300752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Murakami S, Shahbazian D, Surana R, Zhang
W, Chen H, Graham GT, White SM, Weiner LM and Yi C: Yes-associated
protein mediates immune reprogramming in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 36:1232–1244. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim W, Khan SK, Liu Y, Xu R, Park O, He Y,
Cha B, Gao B and Yang Y: Hepatic Hippo signaling inhibits
protumoural microenvironment to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gut. 67:1692–1703. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shi GP and Lindholt JS: Mast cells in
abdominal aortic aneurysms. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 11:314–326. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Brosseau JP, Pichard DC, Legius EH,
Wolkenstein P, Lavker RM, Blakeley JO, Riccardi VM, Verma SK,
Brownell I and Le LQ: The biology of cutaneous neurofibromas:
Consensus recommendations for setting research priorities.
Neurology. 91((2 Suppl 1)): S14–S20. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choi K, Komurov K, Fletcher JS, Jousma E,
Cancelas JA, Wu J and Ratner N: An inflammatory gene signature
distinguishes neurofibroma Schwann cells and macrophages from cells
in the normal peripheral nervous system. Sci Rep. 7:433152017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Müller M, Wacker K, Getts D, Ringelstein
EB and Kiefer R: Further evidence for a crucial role of resident
endoneurial macrophages in peripheral nerve disorders: Lessons from
acrylamide-induced neuropathy. Glia. 56:1005–1016. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ribeiro S, Napoli I, White IJ, Parrinello
S, Flanagan AM, Suter U, Parada LF and Lloyd AC: Injury signals
cooperate with Nf1 loss to relieve the tumor-suppressive
environment of adult peripheral nerve. Cell Rep. 5:126–136. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nguyen R, Ibrahim C, Friedrich RE,
Westphal M, Schuhmann M and Mautner VF: Growth behavior of
plexiform neurofibromas after surgery. Genet Med. 15:691–697. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Geller M, Ribeiro MG, Araújo AP, de
Oliveira LJ and Nunes FP: Serum IgE levels in neurofibromatosis 1.
Int J Immunogenet. 33:111–115. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kamide R, Nomura N and Niimura M:
Characterization of mast cells residing in cutaneous neurofibromas.
Dermatologica. 179 (Suppl 1):S1241989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wu J, Williams JP, Rizvi TA, Kordich JJ,
Witte D, Meijer D, Stemmer-Rachamimov AO, Cancelas JA and Ratner N:
Plexiform and dermal neurofibromas and pigmentation are caused by
Nf1 loss in desert hedgehog-expressing cells. Cancer Cell.
13:105–116. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Evans DG: Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2):
A clinical and molecular review. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 4:162009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guo X, Zhao Y, Yan H, Yang Y, Shen S, Dai
X, Ji X, Ji F, Gong XG, Li L, et al: Single tumor-initiating cells
evade immune clearance by recruiting type II macrophages. Genes
Dev. 31:247–259. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brauß TF, Winslow S, Lampe S, Scholz A,
Weigert A, Dehne N, von Stedingk K, Schmid T and Brüne B: The
RNA-binding protein HuR inhibits expression of CCL5 and limits
recruitment of macrophages into tumors. Mol Carcinog. 56:2620–2629.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qin S, Zheng JH, Xia ZH, Qian J, Deng CL
and Yang SL: CTHRC1 promotes wound repair by increasing M2
macrophages via regulating the TGF-β and notch pathways. Biomed
Pharmacother. 113:1085942019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|