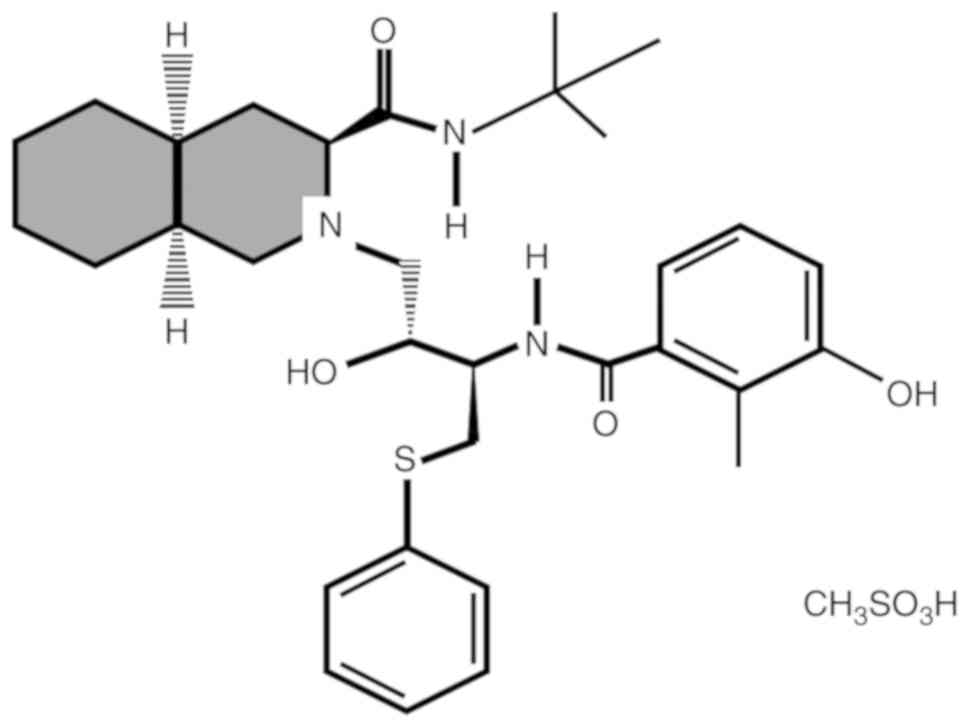
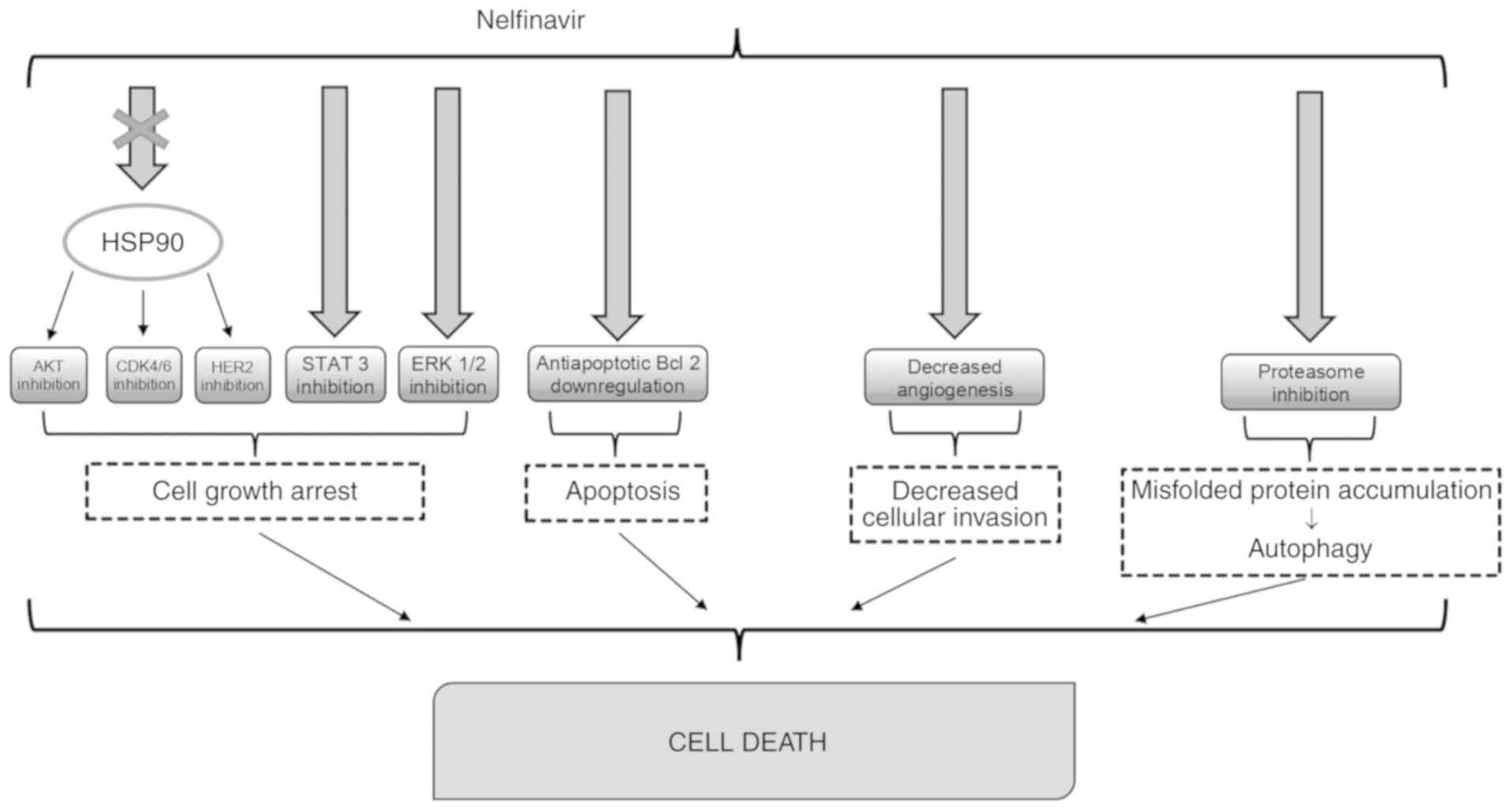
|
1
|
Gantt S, Casper C and Ambinder RF:
Insights into the broad cellular effects of nelfinavir and the HIV
protease inhibitors supporting their role in cancer treatment and
prevention. Curr Opin Oncol. 25:495–502. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Niehues T, Horneff G, Megahed M, Schroten
H and Wahn V: Complete regression of AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma
in a child treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy. AIDS.
13:1148–1149. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sgadari C, Monini P, Barillari G and
Ensoli B: Use of HIV protease inhibitors to block Kaposi's sarcoma
and tumour growth. Lancet Oncol. 4:537–547. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xing F, Liu Y, Wu SY, Wu K, Sharma S, Mo
YY, Feng J, Sanders S, Jin G, Singh R, et al: Loss of XIST in
breast cancer activates MSN-c-Met and reprograms microglia via
Exosomal miRNA to promote brain metastasis. Cancer Res.
78:4316–4330. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ikezoe T, Daar ES, Hisatake J, Taguchi H
and Koeffler HP: HIV-1 protease inhibitors decrease proliferation
and induce differentiation of human myelocytic leukemia cells.
Blood. 96:3553–3559. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pati S, Pelser CB, Dufraine J, Bryant JL,
Reitz MS Jr and Weichold FF: Antitumorigenic effects of HIV
protease inhibitor ritonavir: Inhibition of Kaposi sarcoma. Blood.
99:3771–3779. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Okubo K, Isono M, Asano T and Sato A:
Lopinavir-ritonavir combination induces endoplasmic reticulum
stress and kills urological cancer cells. Anticancer Res.
39:5891–5901. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lu M, Dong H, Bao D, Liu B and Liu H:
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate induces pheochromocytoma cells
apoptosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 844:139–144. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Esposito V, Verdina A, Manente L, Spugnini
EP, Viglietti R, Parrella R, Pagliano P, Parrella G, Galati R, De
Luca A, et al: Amprenavir inhibits the migration in human
hepatocarcinoma cell and the growth of xenografts. J Cell Physiol.
228:640–645. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pore N, Gupta AK, Cerniglia GJ and Maity
A: HIV protease inhibitors decrease VEGF/HIF-1alpha expression and
angiogenesis in glioblastoma cells. Neoplasia. 8:889–895. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun L, Niu L, Zhu X, Hao J, Wang P and
Wang H: Antitumour effects of a protease inhibitor, nelfinavir, in
hepatocellular carcinoma cancer cells. J Chemother. 24:161–166.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dewan MZ, Uchihara JN, Terashima K, Honda
M, Sata T, Ito M, Fujii N, Uozumi K, Tsukasaki K, Tomonaga M, et
al: Efficient intervention of growth and infiltration of primary
adult T-cell leukemia cells by an HIV protease inhibitor,
ritonavir. Blood. 107:716–724. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Srirangam A, Milani M, Mitra R, Guo Z,
Rodriguez M, Kathuria H, Fukuda S, Rizzardi A, Schmechel S, Skalnik
DG, et al: The human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitor
ritonavir inhibits lung cancer cells, in part, by inhibition of
survivin. J Thorac Oncol. 6:661–670. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Timeus F, Crescenzio N, Doria A, Foglia L,
Pagliano S, Ricotti E, Fagioli F, Tovo PA and Cordero di
Montezemolo L: In vitro anti-neuroblastoma activity of
saquinavir and its association with imatinib. Oncol Rep.
27:734–740. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Weichold FF, Bryant JL, Pati S,
Barabitskaya O, Gallo RC and Reitz MS Jr: HIV-1 protease inhibitor
ritonavir modulates susceptibility to apoptosis of uninfected T
cells. J Hum Virol. 2:261–269. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gills JJ, Lopiccolo J, Tsurutani J,
Shoemaker RH, Best CJ, Abu-Asab MS, Borojerdi J, Warfel NA, Gardner
ER, Danish M, et al: Nelfinavir, A lead HIV protease inhibitor, is
a broad-spectrum, anticancer agent that induces endoplasmic
reticulum stress, autophagy, and apoptosis in vitro and in vivo.
Clin Cancer Res. 13:5183–5194. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
National Institute of Diabetes and
Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Protease Inhibitors (HIV). LiverTox,
. Clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury
[Internet]. PMID: 31644200. Bethesda (MD): Sep 1–2012-2017
|
|
18
|
Xie L, Evangelidis T, Xie L and Bourne PE:
Drug discovery using chemical systems biology: Weak inhibition of
multiple kinases may contribute to the anti-cancer effect of
nelfinavir. PLoS Comput Biol. 7:e10020372011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gills JJ, Lopiccolo J and Dennis PA:
Nelfinavir, a new anti-cancer drug with pleiotropic effects and
many paths to autophagy. Autophagy. 4:107–109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kraus M, Bader J, Overkleeft H and
Driessen C: Nelfinavir augments proteasome inhibition by bortezomib
in myeloma cells and overcomes bortezomib and carfilzomib
resistance. Blood Cancer J. 3:e1032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Petrich AM, Leshchenko V, Kuo PY, Xia B,
Thirukonda VK, Ulahannan N, Gordon S, Fazzari MJ, Ye BH, Sparano JA
and Parekh S: Akt inhibitors MK-2206 and nelfinavir overcome mTOR
inhibitor resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:2534–2544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Plastaras JP, Vapiwala N, Ahmed MS,
Gudonis D, Cerniglia GJ, Feldman MD, Frank I and Gupta AK:
Validation and toxicity of PI3K/Akt pathway inhibition by HIV
protease inhibitors in humans. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:628–635. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang W, Mikochik PJ, Ra JH, Lei H,
Flaherty KT, Winkler JD and Spitz FR: HIV protease inhibitor
nelfinavir inhibits growth of human melanoma cells by induction of
cell cycle arrest. Cancer Res. 67:1221–1227. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bernstein WB and Dennis PA: Repositioning
HIV protease inhibitors as cancer therapeutics. Curr Opin HIV AIDS.
3:666–675. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guan M, Fousek K and Chow WA: Nelfinavir
inhibits regulated intramembrane proteolysis of sterol regulatory
element binding protein-1 and activating transcription factor 6 in
castration-resistant prostate cancer. FEBS J. 279:2399–2411. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shim JS, Rao R, Beebe K, Neckers L, Han I,
Nahta R and Liu JO: Selective inhibition of HER2-positive breast
cancer cells by the HIV protease inhibitor nelfinavir. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 104:1576–1590. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Srirangam A, Mitra R, Wang M, Gorski JC,
Badve S, Baldridge L, Hamilton J, Kishimoto H, Hawes J, Li L, et
al: Effects of HIV protease inhibitor ritonavir on Akt-regulated
cell proliferation in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:1883–1896.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pyrko P, Kardosh A, Wang W, Xiong W,
Schönthal AH and Chen TC: HIV-1 protease inhibitors nelfinavir and
atazanavir induce malignant glioma death by triggering endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Cancer Res. 67:10920–10928. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Peñaranda Fajardo NM, Meijer C and Kruyt
FA: The endoplasmic reticulum stress/unfolded protein response in
gliomagenesis, tumor progression and as a therapeutic target in
glioblastoma. Biochem Pharmacol. 118:1–8. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Brüning A, Burger P, Vogel M, Rahmeh M,
Gingelmaiers A, Friese K, Lenhard M and Burges A: Nelfinavir
induces the unfolded protein response in ovarian cancer cells,
resulting in ER vacuolization, cell cycle retardation and
apoptosis. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:226–232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brüning A, Friese K, Burges A and Mylonas
I: Tamoxifen enhances the cytotoxic effects of nelfinavir in breast
cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 12:R452010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bruning A, Vogel M, Mylonas I, Friese K
and Burges A: Bortezomib targets the caspase-like proteasome
activity in cervical cancer cells, triggering apoptosis that can be
enhanced by nelfinavir. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 11:799–809. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gupta AK, Lee JH, Wilke WW, Quon H, Smith
G, Maity A, Buatti JM and Spitz DR: Radiation response in two
HPV-infected head-and-neck cancer cell lines in comparison to a
non-HPV-infected cell line and relationship to signaling through
AKT. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 74:928–933. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gupta AK, Wilke WW, Taylor EN, Bodeker KL,
Hoffman HT, Milhem MM, Buatti JM and Robinson RA: Signaling
pathways in adenoid cystic cancers: Implications for treatment.
Cancer Biol Ther. 8:1947–1951. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Danaher RJ, Wang C, Roland AT, Kaetzel CS,
Greenberg RN and Miller CS: HIV protease inhibitors block oral
epithelial cell DNA synthesis. Arch Oral Biol. 55:95–100. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kimple RJ, Vaseva AV, Cox AD, Baerman KM,
Calvo BF, Tepper JE, Shields JM and Sartor CI: Radiosensitization
of epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2-positive pancreatic cancer
is mediated by inhibition of Akt independent of ras mutational
status. Clin Cancer Res. 16:912–923. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Brüning A, Rahmeh M, Gingelmaier A and
Friese K: The mitochondria-independent cytotoxic effect of
nelfinavir on leukemia cells can be enhanced by sorafenib-mediated
mcl-1 downregulation and mitochondrial membrane destabilization.
Mol Cancer. 9:192010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kraus M, Müller-Ide H, Rückrich T, Bader
J, Overkleeft H and Driessen C: Ritonavir, nelfinavir, saquinavir
and lopinavir induce proteotoxic stress in acute myeloid leukemia
cells and sensitize them for proteasome inhibitor treatment at low
micromolar drug concentrations. Leuk Res. 38:383–392. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Allegra A, Alonci A, Gerace D, Russo S,
Innao V, Calabrò L and Musolino C: New orally active proteasome
inhibitors in multiple myeloma. Leuk Res. 38:1–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Meier-Stephenson V, Riemer J and Narendran
A: The HIV protease inhibitor, nelfinavir, as a novel therapeutic
approach for the treatment of refractory pediatric leukemia. Onco
Targets Ther. 10:2581–2593. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mahoney E, Maddocks K, Flynn J, Jones J,
Cole SL, Zhang X, Byrd JC and Johnson AJ: Identification of
endoplasmic reticulum stress-inducing agents by antagonizing
autophagy: A new potential strategy for identification of
anti-cancer therapeutics in B-cell malignancies. Leuk Lymphoma.
54:2685–2692. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Falduto A, Cimino F, Speciale A, Musolino
C, Gangemi S, Saija A and Allegra A: How gene polymorphisms can
influence clinical response and toxicity following R-CHOP therapy
in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Blood Rev.
31:235–249. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hess G, Smith SM, Berkenblit A and
Coiffier B: Temsirolimus in mantle cell lymphoma and other
non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes. Semin Oncol. 36 (Suppl 3):S37–S45.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Smith SM, van Besien K, Karrison T, Dancey
J, McLaughlin P, Younes A, Smith S, Stiff P, Lester E, Modi S, et
al: Temsirolimus has activity in non-mantle cell non-Hodgkin's
lymphoma subtypes: The University of Chicago phase II consortium. J
Clin Oncol. 28:4740–4746. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Witzig TE, Reeder CB, LaPlant BR, Gupta M,
Johnston PB, Micallef IN, Porrata LF, Ansell SM, Colgan JP,
Jacobsen ED, et al: A phase II trial of the oral mTOR inhibitor
everolimus in relapsed aggressive lymphoma. Leukemia. 25:341–347.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Toffoli G, Corona G, Cattarossi G,
Boiocchi M, Di Gennaro G, Tirelli U and Vaccher E: Effect of highly
active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) on pharmacokinetics and
pharmacodynamics of doxorubicin in patients with HIV-associated
non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 15:1805–1809. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ikezoe T, Saito T, Bandobashi K, Yang Y,
Koeffler HP and Taguchi I: HIV-1 protease inhibitor induces growth
arrest and apoptosis of human multiple myeloma cells via
inactivation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. Mol Cancer Ther.
3:473–479. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kawabata S, Gills JJ, Mercado-Matos JR,
LoPiccolo J, Wilson III W, Hollander MC and Dennis PA: Synergistic
effects of nelfinavir and bortezomib on proteotoxic death of NSCLC
and multiple myeloma cells. Cell Death and Disease. 3:e3532012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Leung-Hagesteijn C, Erdmann N, Cheung G,
Keats JJ, Stewart AK, Reece DE, Chung KC and Tiedemann RE:
Xbp1s-negative tumor B cells and pre-plasmablasts mediate
therapeutic proteasome inhibitor resistance in multiple myeloma.
Cancer Cell. 24:289–304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Neznanov N, Komarov AP, Neznanova L,
Stanhope-Baker P and Gudkov AV: Proteotoxic stress targeted therapy
(PSTT): Induction of protein misfolding enhances the antitumor
effect of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib. Oncotarget.
2:209–221. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mayor T: Navigating the ERAD interaction
network. Nat Cell Biol. 14:46–47. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Obeng EA, Carlson LM, Gutman DM,
Harrington WJ Jr, Lee KP and Boise LH: Proteasome inhibitors induce
a terminal unfolded protein response in multiple myeloma cells.
Blood. 107:4907–4916. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ling SC, Lau EK, Al-Shabeeb A, Nikolic A,
Catalano A, Iland H, Horvath N, Ho PJ, Harrison S, Fleming S, et
al: Response of myeloma to the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib is
correlated with the unfolded protein response regulator XBP-1.
Haematologica. 97:64–72. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Reimold AM, Iwakoshi NN, Manis J,
Vallabhajosyula P, Szomolanyi-Tsuda E, Gravallese EM, Friend D,
Grusby MJ, Alt F and Glimcher LH: Plasma cell differentiation
requires the transcription factor XBP-1. Nature. 412:300–307. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Papandreou I, Denko NC, Olson M, Van
Melckebeke H, Lust S, Tam A, Solow-Cordero DE, Bouley DM, Offner F,
Niwa M and Koong AC: Identification of an Ire1alpha endonuclease
specific inhibitor with cytotoxic activity against human multiple
myeloma. Blood. 117:1311–1314. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chow WA, Jiang C and Guan M: Anti-HIV
drugs for cancer therapeutics: Back to the future? Lancet Oncol.
10:61–71. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Guan M, Fousek K, Jiang C, Guo S, Synold
T, Xi B, Shih CC and Chow WA: Nelfinavir induces liposarcoma
apoptosis through inhibition of regulated intramembrane proteolysis
of SREBP-1 and ATF6. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1796–1806. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yang Y, Ikezoe T, Nishioka C, Bandobashi
K, Takeuchi T, Adachi Y, Kobayashi M, Takeuchi S, Koeffler HP and
Taguchi H: NFV, an HIV-1 protease inhibitor, induces growth arrest,
reduced Akt signalling, apoptosis and docetaxel sensitisation in
NSCLC cell lines. Br J Cancer. 95:1653–1662. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Bono C, Karlin L, Harel S, Mouly E,
Labaume S, Galicier L, Apcher S, Sauvageon H, Fermand JP, Bories JC
and Arnulf B: The human immunodeficiency virus-1 protease inhibitor
nelfinavir impairs proteasome activity and inhibits the
proliferation of multiple myeloma cells in vitro and in vivo.
Haematologica. 97:1101–1109. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Driessen C, Kraus M, Joerger M, Rosing H,
Bader J, Hitz F, Berset C, Xyrafas A, Hawle H, Berthod G, et al:
Treatment with the HIV protease inhibitor nelfinavir triggers the
unfolded protein response and may overcome proteasome inhibitor
resistance of multiple myeloma in combination with bortezomib: A
phase I trial (SAKK 65/08). Haematologica. 101:346–355. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Driessen C, Müller R, Novak U, Cantoni N,
Betticher D, Mach N, Rüfer A, Mey U, Samaras P, Ribi K, et al:
Promising activity of nelfinavir-bortezomib-dexamethasone in
proteasome inhibitor-refractory multiple myeloma. Blood.
132:2097–2100. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kraus M, Malenke E, Gogel J, Müller H,
Rückrich T, Overkleeft H, Ovaa H, Koscielniak E, Hartmann JT and
Driessen C: Ritonavir induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and
sensitizes sarcoma cells toward bortezomib-induced apoptosis. Mol
Cancer Ther. 7:1940–1948. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Besse A, Stolze SC, Rasche L, Weinhold N,
Morgan GJ, Kraus M, Bader J, Overkleeft HS, Besse L and Driessen C:
Carfilzomib resistance due to ABCB1/MDR1 overexpression is overcome
by nelfinavir and lopinavir in multiple myeloma. Leukemia.
32:391–401. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Besse A, Besse L, Kraus M, Mendez-Lopez M,
Bader J, Xin BT, de Bruin G, Maurits E, Overkleeft HS and Driessen
C: Proteasome inhibition in multiple myeloma: Head-to-head
comparison of currently available proteasome inhibitors. Cell Chem
Biol. 26:340–351.e3. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hawley TS, Riz I, Yang W, Wakabayashi Y,
Depalma L, Chang YT, Peng W, Zhu J and Hawley RG: Identification of
an ABCB1 (P-glycoprotein)-positive carfilzomib-resistant myeloma
subpopulation by the pluripotent stem cell fluorescent dye CDy1. Am
J Hematol. 88:265–272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Hitz F, Kraus M, Pabst T, Hess D, Besse L,
Silzle T, Novak U, Seipel K, Rondeau S, Stüdeli S, et al:
Nelfinavir and lenalidomide/dexamethasone in patients with
lenalidomide-refractory multiple myeloma. A phase I/II Trial (SAKK
39/10). Blood Cancer J. 9:702019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hui DY: Effects of HIV protease inhibitor
therapy on lipid metabolism. Prog Lipid Res. 42:81–92. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Riddle TM, Kuhel DG, Woollett LA,
Fichtenbaum CJ and Hui DY: HIV protease inhibitor induces fatty
acid and sterol biosynthesis in liver and adipose tissues due to
the accumulation of activated sterol regulatory element-binding
proteins in the nucleus. J Biol Chem. 276:37514–37519. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Orem J, Fu P, Ness A, Mwanda WO and Remick
SC: Oral combination chemotherapy in the treatment of
AIDS-associated Hodgkin's disease. East Afr Med J. 82 (Suppl.
9):S144–S149. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Brüning A, Burger P, Vogel M, Gingelmaier
A, Friese K and Burges A: Nelfinavir induces mitochondria
protection by ERK1/2-mediated mcl-1 stabilization that can be
overcome by sorafenib. Invest New Drugs. 28:535–542. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Crum-Cianflone NF, Hullsiek KH, Marconi V,
Weintrob A, Ganesan A, Barthel RV, Fraser S, Roediger MP, Agan B
and Wegner S: The impact of nelfinavir exposure on cancer
development among a large cohort of HIV-infected patients. J Acquir
Immune Defic Syndr. 51:305–309. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Giardino Torchia ML, Ciaglia E, Masci AM,
Vitiello L, Fogli M, la Sala A, Mavilio D and Racioppi L: Dendritic
cells/natural killer cross-talk: A novel target for human
immunodeficiency virus type-1 protease inhibitors. PLoS One.
5:e110522010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Bower M, McCall-Peat N, Ryan N, Davies L,
Young AM, Gupta S, Nelson M, Gazzard B and Stebbing J: Protease
inhibitors potentiate chemotherapy-induced neutropenia. Blood.
104:2943–2946. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Gills JJ and Dennis PA: Perifosine: Update
on a novel Akt inhibitor. Curr Oncol Rep. 11:102–110. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wan X, Harkavy B, Shen N, Grohar P and
Helman LJ: Rapamycin induces feedback activation of Akt signaling
through an IGF-1R-dependent mechanism. Oncogene. 26:1932–1940.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Carracedo A, Bacelga J and Pandolfi PP:
Deconstructing feedback-signaling networks to improve anticancer
therapy with mTORC1 inhibitors. Cell Cycle. 7:3805–3859. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Mishra LC, Bhattacharya A, Sharma M and
Bhasin VK: HIV protease inhibitors, indinavir or nelfinavir,
augment antimalarial action of artemisinin in vitro. Am J Trop Med
Hyg. 82:148–150. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kast RE, Boockvar JA, Brüning A, Cappello
F, Chang WW, Cvek B, Dou QP, Duenas-Gonzalez A, Efferth T, Focosi
D, et al: A conceptually new treatment approach for relapsed
glioblastoma: Coordinated undermining of survival paths with nine
repurposed drugs (CUSP9 by the International Initiative for
Accelerated Improvement of Glioblastoma Care. Oncotarget.
4:502–530. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Cho HY, Thomas S, Golden EB, Gaffney KJ,
Hofman FM, Chen TC, Louie SG, Petasis NA and Schönthal AH: Enhanced
killing of chemo-resistant breast cancer cells via controlled
aggravation of ER stress. Cancer Lett. 282:87–97. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Cho HY, Wang W, Jhaveri N, Torres S, Tseng
J, Leong MN, Lee DJ, Goldkorn A, Xu T, Petasis NA, et al: Perillyl
alcohol for the treatment of temozolomide-resistant gliomas. Mol
Cancer Ther. 11:2462–2472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Homewood CA, Warhurst DC, Peters W and
Baggaley VC: Lysosomes, pH and the anti-malarial action of
chloroquine. Nature. 235:50–52. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Shintani T and Klionsky DJ: Autophagy in
health and disease: A double-edged sword. Science. 306:990–995.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Allegra A, Penna G, Alonci A, Russo S,
Greve B, Innao V, Minardi V and Musolino C: Monoclonal antibodies:
Potential new therapeutic treatment against multiple myeloma. Eur J
Haematol. 90:441–468. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Allegra A, Sant'antonio E, Penna G, Alonci
A, D'Angelo A, Russo S, Cannavò A, Gerace D and Musolino C: Novel
therapeutic strategies in multiple myeloma: Role of the heat shock
protein inhibitors. Eur J Haematol. 86:93–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Allegra A, Penna G, Innao V, Greve B,
Maisano V, Russo S and Musolino C: Vaccination of multiple myeloma:
Current strategies and future prospects. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
96:339–354. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Allegra A, Innao V, Gerace D, Vaddinelli D
and Musolino C: Adoptive immunotherapy for hematological
malignancies: Current status and new insights in chimeric antigen
receptor T cells. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 62:49–63. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Ettari R, Zappalà M, Grasso S, Musolino C,
Innao V and Allegra A: Immunoproteasome-selective and non-selective
inhibitors: A promising approach for the treatment of multiple
myeloma. Pharmacol Ther. 182:176–192. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|