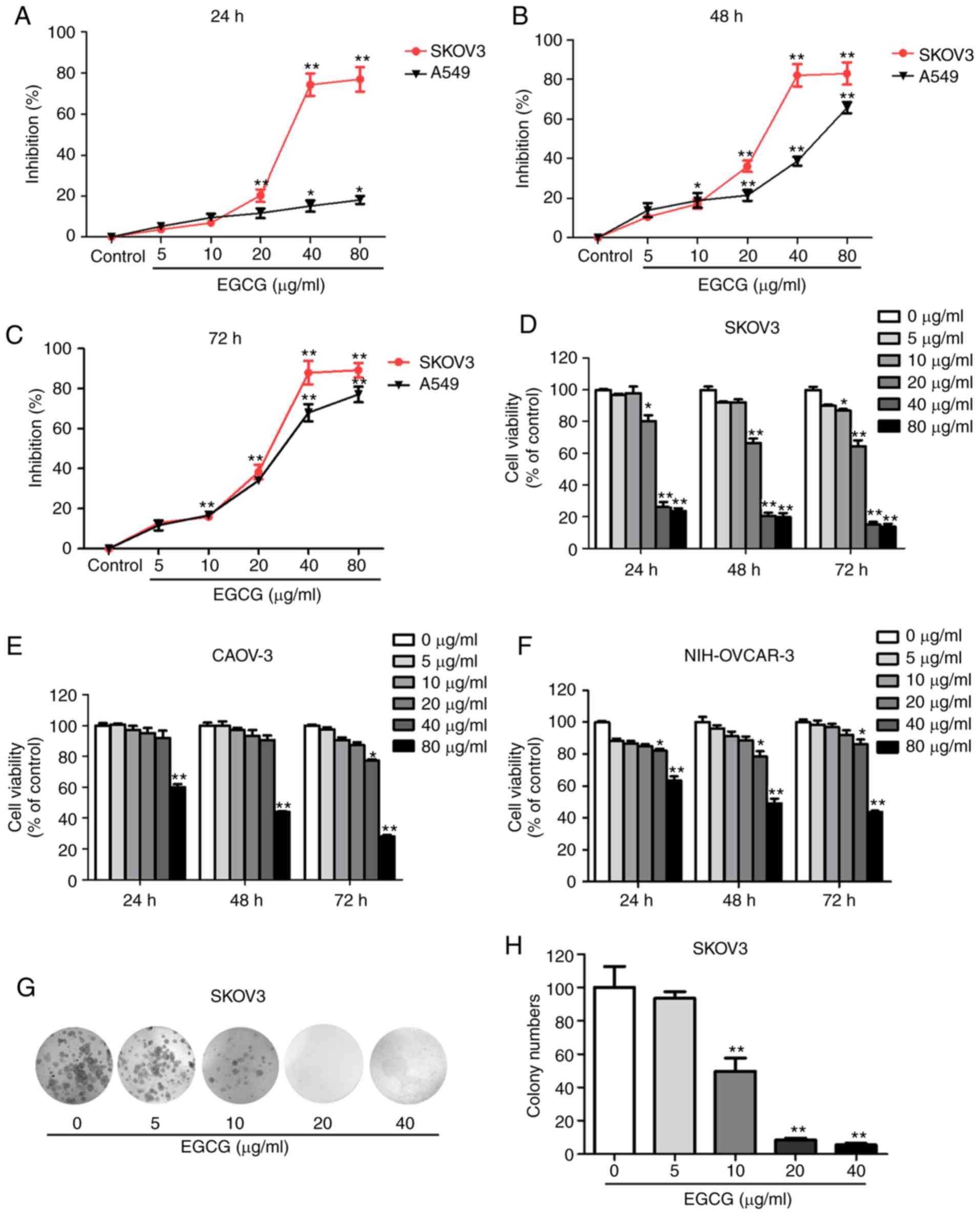
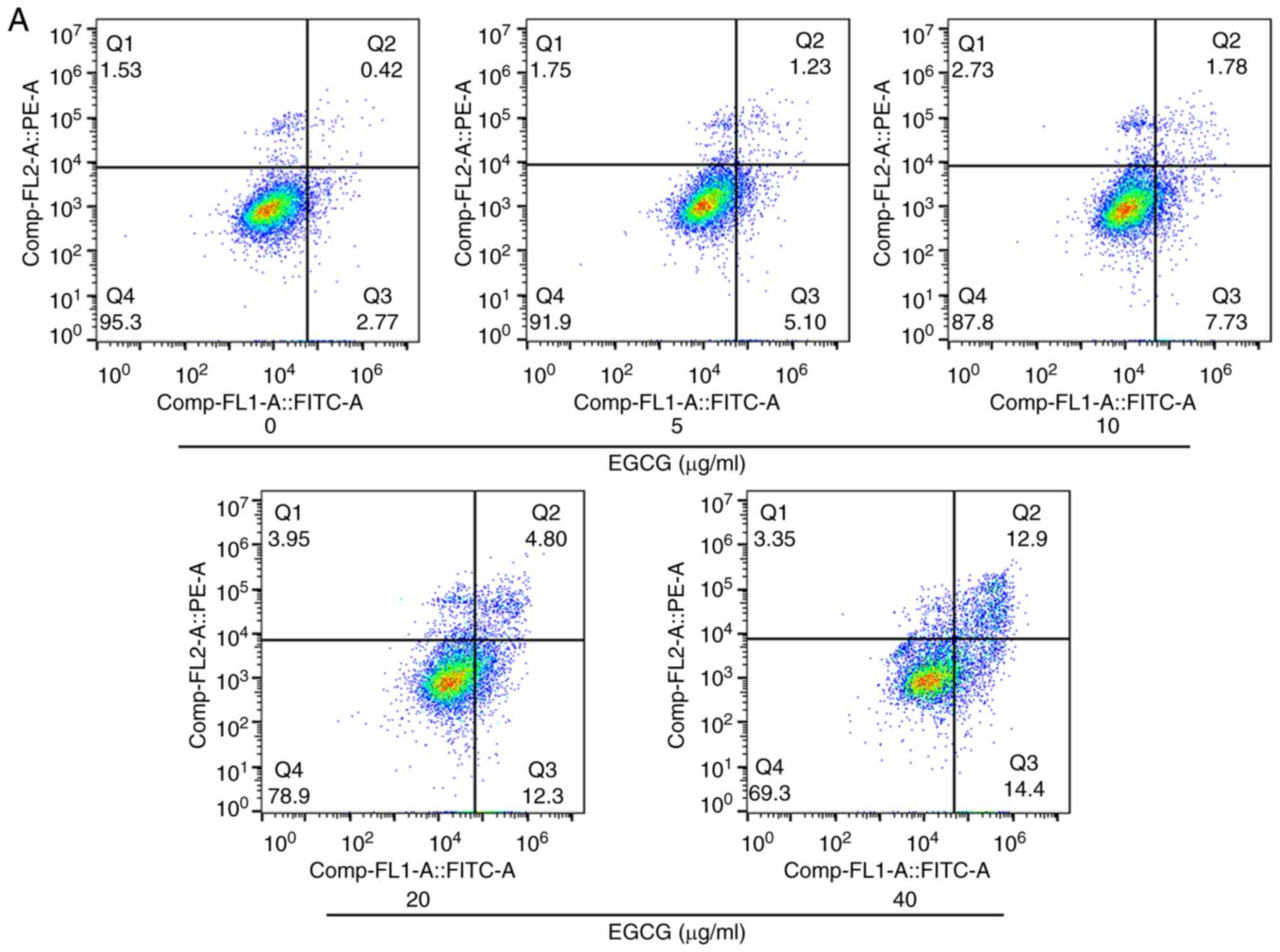
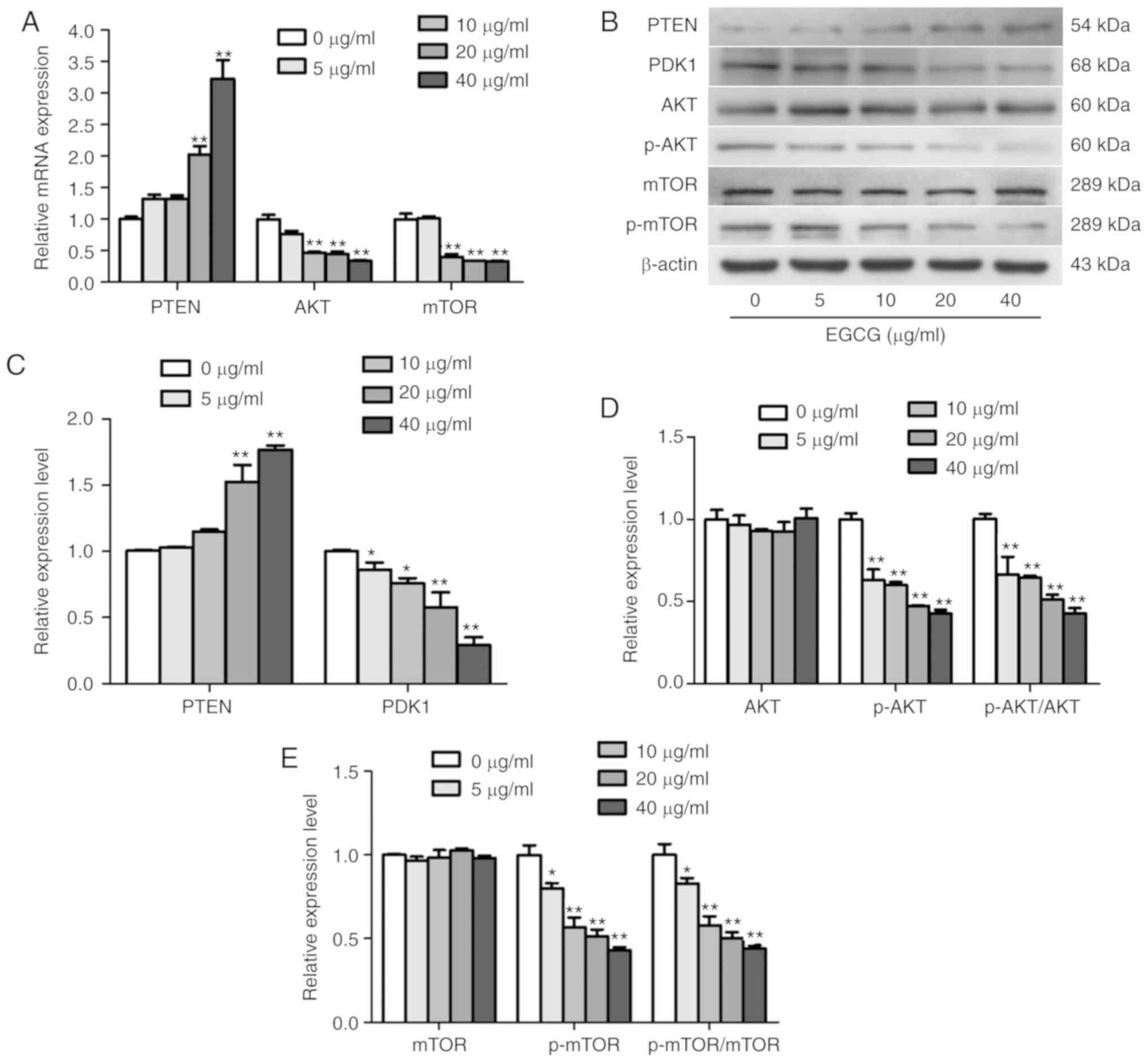
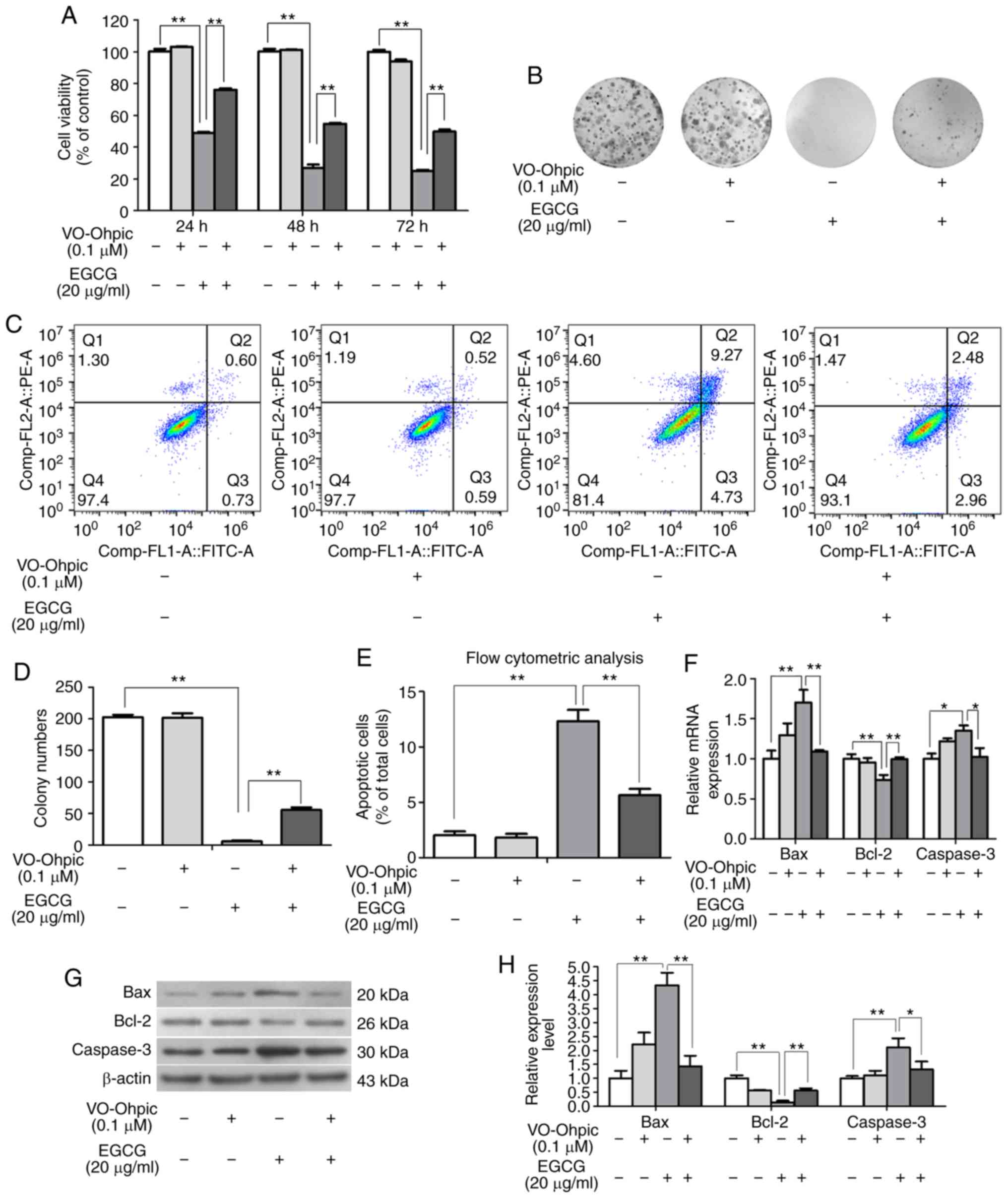
|
1
|
Khan N and Mukhtar H: Tea polyphenols in
promotion of human health. Nutrients. 11(pii): E392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang YQ, Lu JL, Liang YR and Li QS:
Suppressive effects of EGCG on cervical cancer. Molecules. 23(pii):
E23342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang LX, Shi YL, Zhang LJ, Wang KR, Xiang
LP, Cai ZY, Lu JL, Ye JH, Liang YR and Zheng XQ: Inhibitory effects
of (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate on esophageal cancer. Molecules.
24(pii): E9542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sanna V, Singh CK, Jashari R, Adhami VM,
Chamcheu JC, Rady I, Sechi M, Mukhtar H and Siddiqui IA: Targeted
nanoparticles encapsulating (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate for
prostate cancer prevention and therapy. Sci Rep. 7:415732017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hong OY, Noh EM, Jang HY, Lee YR, Lee BK,
Jung SH, Kim JS and Youn HJ: Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits the
growth of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells via inactivation of the
beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 14:441–446. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Flores-Perez A, Marchat LA, Sánchez LL,
Romero-Zamora D, Arechaga-Ocampo E, Ramírez-Torres N, Chávez JD,
Carlos-Reyes Á, Astudillo-de la Vega H, Ruiz-García E, et al:
Differential proteomic analysis reveals that EGCG inhibits HDGF and
activates apoptosis to increase the sensitivity of non-small cells
lung cancer to chemotherapy. Proteomics Clin Appl. 10:172–182.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ying L, Yan F, Williams BR, Xu P, Li X,
Zhao Y, Hu Y, Wang Y, Xu D and Dai J:
(−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate and EZH2 inhibitor GSK343 have
similar inhibitory effects and mechanisms of action on colorectal
cancer cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 45:58–67. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dhatwalia SK, Kumar M and Dhawan DK: Role
of EGCG in containing the progression of lung tumorigenesis-a
multistage targeting approach. Nutr Cancer. 70:334–349. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shi J, Liu F, Zhang W, Liu X, Lin B and
Tang X: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits nicotine-induced
migration and invasion by the suppression of angiogenesis and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 33:2972–2980. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen Y, Wang XQ, Zhang Q, Zhu JY, Li Y,
Xie CF, Li XT, Wu JS, Geng SS, Zhong CY and Han HY:
(−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate inhibits colorectal cancer stem
cells by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Nutrients. 9(pii):
E5722017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu C, Li P, Qu Z, Xiong W, Liu A and
Zhang S: Advances in the antagonism of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate
in the treatment of digestive tract tumors. Molecules. 24(pii):
E17262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rawangkan A, Wongsirisin P, Namiki K, Iida
K, Kobayashi Y, Shimizu Y, Fujiki H and Suganuma M: Green tea
catechin is an alternative immune checkpoint inhibitor that
inhibits PD-L1 expression and lung tumor growth. Molecules.
23(pii): E20712018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma YC, Li C, Gao F, Xu Y, Jiang ZB, Liu JX
and Jin LY: Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits the growth of human
lung cancer by directly targeting the EGFR signaling pathway. Oncol
Rep. 31:1343–1349. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang J, Sun P, Wang Q, Zhang P, Wang Y, Zi
C, Wang X and Sheng J: (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate derivatives
combined with cisplatin exhibit synergistic inhibitory effects on
non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 19:2662019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meng J, Chang C, Chen Y, Bi F, Ji C and
Liu W: EGCG overcomes gefitinib resistance by inhibiting autophagy
and augmenting cell death through targeting ERK phosphorylation in
NSCLC. Onco Targets Ther. 12:6033–6043. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Deng P, Hu C, Xiong Z, Li Y, Jiang J, Yang
H, Tang Y, Cao L and Lu R: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced
vascular normalization in A549-cell xenograft-bearing nude mice:
Therapeutic efficacy in combination with chemotherapy. Cancer Manag
Res. 11:2425–2439. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yan C, Yang J, Shen L and Chen X:
Inhibitory effect of Epigallocatechin gallate on ovarian cancer
cell proliferation associated with aquaporin 5 expression. Arch
Gynecol Obstet. 285:459–467. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang F, Chang Z, Fan Q and Wang L:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the proliferation and migration
of human ovarian carcinoma cells by modulating p38 kinase and
matrix metalloproteinase-2. Mol Med Rep. 9:1085–1089. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Padmakumar S, Parayath NN, Nair SV, Menon
D and Amiji MM: Enhanced anti-tumor efficacy and safety with
metronomic intraperitoneal chemotherapy for metastatic ovarian
cancer using biodegradable nanotextile implants. J Control Release.
305:29–40. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mahalaxmi I, Devi SM, Kaavya J, Arul N,
Balachandar V and Santhy KS: New insight into NANOG: A novel
therapeutic target for ovarian cancer (OC). Eur J Pharmacol.
852:51–57. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pisanic TR II, Cope LM, Lin SF, Yen TT,
Athamanolap P, Asaka R, Nakayama K, Fader AN, Wang TH, Shih IM and
Wang TL: Methylomic analysis of ovarian cancers identifies
tumor-specific alterations readily detectable in early precursor
lesions. Clin Cancer Res. 24:6536–6547. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chuffa LGD, Reiter RJ and Lupi LA:
Melatonin as a promising agent to treat ovarian cancer: Molecular
mechanisms. Carcinogenesis. 38:945–952. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Madariaga A, Lheureux S and Oza A:
Tailoring ovarian cancer treatment: Implications of BRCA1/2
mutations. Cancers. 11(pii): E4162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Roane BM, Arend RC and Birrer MJ: Review:
Targeting the transforming growth Factor-beta pathway in ovarian
cancer. Cancers (Basel). 11(pii): E6682019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tomao F, Marchetti C, Romito A, Di Pinto
A, Di Donato V, Capri O, Palaia I, Monti M, Muzii L and Benedetti
Panici P: Overcoming platinum resistance in ovarian cancer
treatment: From clinical practice to emerging chemical therapies.
Expert Opin Pharmacother. 18:1443–1455. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang X, Feng Y, Wang XY, Zhang YN, Yuan
CN, Zhang SF, Shen YM, Fu YF, Zhou CY, Li X, et al: The inhibition
of UBC13 expression and blockage of the DNMT1-CHFR-Aurora A pathway
contribute to paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer. Cell Death
Dis. 9:932018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yap TA, Carden CP and Kaye SB: Beyond
chemotherapy: Targeted therapies in ovarian cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:167–181. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gasparri M, Bardhi E, Ruscito I, Papadia
A, Farooqi AA, Marchetti C, Bogani G, Ceccacci I, Mueller MD and
Benedetti Panici P: PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in ovarian cancer
treatment: Are we on the right track? Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd.
77:1095–1103. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mabuchi S, Kuroda H, Takahashi R and
Sasano T: The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway as a therapeutic target in
ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 137:173–179. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xinqiang S, Mu Z, Lei C and Mun LY:
Bioinformatics analysis on molecular mechanism of green tea
compound Epigallocatechin-3-gallate against ovarian cancer. Clin
Transl Sci. 10:302–307. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Luo KW, Wei C, Lung WY, Wei XY, Cheng BH,
Cai ZM and Huang WR: EGCG inhibited bladder cancer SW780 cell
proliferation and migration both in vitro and in vivo via
down-regulation of NF-κB and MMP-9. J Nutr Biochem. 41:56–64. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pan H, Chen J, Shen K, Wang X, Wang P, Fu
G, Meng H, Wang Y and Jin B: Mitochondrial modulation by
Epigallocatechin 3-Gallate ameliorates cisplatin induced renal
injury through decreasing oxidative/nitrative stress, inflammation
and NF-kB in mice. PLoS One. 10:e01247752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang L, Yang R, Zhao L, Zhang X, Xu T and
Cui M: Basing on uPAR-binding fragment to design chimeric antigen
receptors triggers antitumor efficacy against uPAR expressing
ovarian cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 117:1091732019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Russell MR, Graham C, D'Amato A,
Gentry-Maharaj A, Ryan A, Kalsi JK, Whetton AD, Menon U, Jacobs I
and Graham RLJ: Diagnosis of epithelial ovarian cancer using a
combined protein biomarker panel. Br J Cancer. 121:483–489. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yarmolinsky J, Relton CL, Lophatananon A,
Muir K, Menon U, Gentry-Maharaj A, Walther A, Zheng J, Fasching P,
Zheng W, et al: Appraising the role of previously reported risk
factors in epithelial ovarian cancer risk: A Mendelian
randomization analysis. PLoS Med. 16:e10028932019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang CS and Hong J: Prevention of chronic
diseases by tea: Possible mechanisms and human relevance. Annu Rev
Nutr. 33:161–181. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang L, He Y, Wu X, Zhao G, Zhang K, Yang
CS, Reiter RJ and Zhang J: Melatonin and
(−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate: Partners in fighting cancer. Cells.
8(pii): E7452019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang L, Xie J, Gan R, Wu Z, Luo H, Chen
X, Lu Y, Wu L and Zheng D: Synergistic inhibition of lung cancer
cells by EGCG and NF-κB inhibitor BAY11-7082. J Cancer.
10:6543–6556. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bhardwaj V and Mandal AKA: Next-Generation
sequencing reveals the role of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate in
regulating putative novel and known microRNAs which target the MAPK
pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer A549 cells. Molecules.
24(pii): E3682019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yu C, Jiao Y, Xue J, Zhang Q, Yang H, Xing
L, Chen G, Wu J, Zhang S, Zhu W and Cao J: Metformin sensitizes
non-small cell lung cancer cells to an Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate
(EGCG) treatment by suppressing the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.
Int J Biol Sci. 13:1560–1569. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li M, Li JJ, Gu QH, An J, Cao LM, Yang HP
and Hu CP: EGCG induces lung cancer A549 cell apoptosis by
regulating Ku70 acetylation. Oncol Rep. 35:2339–2347. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao H, Zhu W, Xie P, Li H, Zhang X, Sun
X, Yu J and Xing L: A phase I study of concurrent chemotherapy and
thoracic radiotherapy with oral epigallocatechin-3-gallate
protection in patients with locally advanced stage III
non-small-cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 110:132–136. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tian M, Tian D, Qiao X, Li J and Zhang L:
Modulation of Myb-induced NF-kB-STAT3 signaling and resulting
cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer by dietary factors. J Cell
Physiol. 234:21126–21134. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen H, Landen CN, Li Y, Alvarez RD and
Tollefsbol TO: Epigallocatechin gallate and sulforaphane
combination treatment induce apoptosis in paclitaxel-resistant
ovarian cancer cells through hTERT and Bcl-2 down-regulation. Exp
Cell Res. 319:697–706. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pérez-Ramírez C, Cañadas-Garre M, Molina
MÁ, Faus-Dáder MJ and Calleja-Hernández MÁ: PTEN and PI3K/AKT in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Pharmacogenomics. 16:1843–1862. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen Q, Weng HY, Tang XP, Lin Y, Yuan Y,
Li Q, Tang Z, Wu HB, Yang S, Li Y, et al: ARL4C stabilized by
AKT/mTOR pathway promotes the invasion of PTEN-deficient primary
human glioblastoma. J Pathol. 247:266–278. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xu JL, Wang ZW, Hu LM, Yin ZQ, Huang MD,
Hu ZB, Shen HB and Shu YQ: Genetic variants in the
PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway predict Platinum-based chemotherapy
response of advanced non-small cell lung cancers in a Chinese
population. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:2157–2162. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lin YT, Wang HC, Hsu YC, Cho CL, Yang MY
and Chien CY: Capsaicin induces autophagy and apoptosis in human
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by downregulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 18(pii): E13432017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chen J, Zhao KN, Li R, Shao R and Chen C:
Activation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and dual inhibitors of PI3K and
mTOR in endometrial cancer. Curr Med Chem. 21:3070–3080. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liu HY, Zhang YY, Zhu BL, Feng FZ, Yan H,
Zhang HY and Zhou B: miR-21 regulates the proliferation and
apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells through PTEN/PI3K/AKT. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:4149–4155. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yap TA, Yan L, Patnaik A, Tunariu N,
Biondo A, Fearen I, Papadopoulos KP, Olmos D, Baird R, Delgado L,
et al: Interrogating two schedules of the AKT inhibitor MK-2206 in
patients with advanced solid tumors incorporating novel
pharmacodynamic and functional imaging biomarkers. Clin Cancer Res.
20:5672–5685. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Pétigny-Lechartier C, Duboc C and Jebahi
A: The mTORC1/2 inhibitor AZD8055 strengthens the efficiency of the
MEK inhibitor trametinib to reduce the Mcl-1/[Bim and Puma] ratio
and to Sensitize Ovarian Carcinoma cells to ABT-737. Mol Cancer
Ther. 16:102–115. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wainberg ZA, Alsina M, Soares HP, Braña I,
Britten CD, Del Conte G, Ezeh P, Houk B, Kern KA, Leong S, et al: A
Multi-Arm phase I study of the PI3K/mTOR inhibitors PF-04691502 and
Gedatolisib (PF-05212384) plus Irinotecan or the MEK inhibitor
PD-0325901 in advanced cancer. Target Oncol. 12:775–785. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Biswas R, Ahn JC and Kim JS: Sulforaphene
synergistically sensitizes cisplatin via enhanced mitochondrial
dysfunction and PI3K/PTEN modulation in ovarian cancer cells.
Anticancer Res. 35:3901–3908. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cai J, Xu L, Tang H, Yang Q, Yi X, Fang Y,
Zhu Y and Wang Z: The role of the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathwayon prognosis
in epithelial ovarian cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncologist.
19:528–535. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ediriweera MK, Tennekoon KH and Samarakoon
SR: Role of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in ovarian cancer:
Biological and therapeutic significance. Semin Cancer Biol.
59:147–160. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Shen J, Yu S, Sun X, Yin M, Fei J and Zhou
J: Identification of key biomarkers associated with development and
prognosis in patients with ovarian carcinoma: Evidence from
bioinformatic analysis. J Ovarian Res. 12:1102019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Steffensen KD, Smoter M, Waldstrøm M,
Grala B, Bodnar L, Stec R, Szczylik C and Jakobsen A: Resistance to
first line platinum paclitaxel chemotherapy in serous epithelial
ovarian cancer: The prediction value of ERCC1 and Tau expression.
Int J Oncol. 44:1736–1744. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|