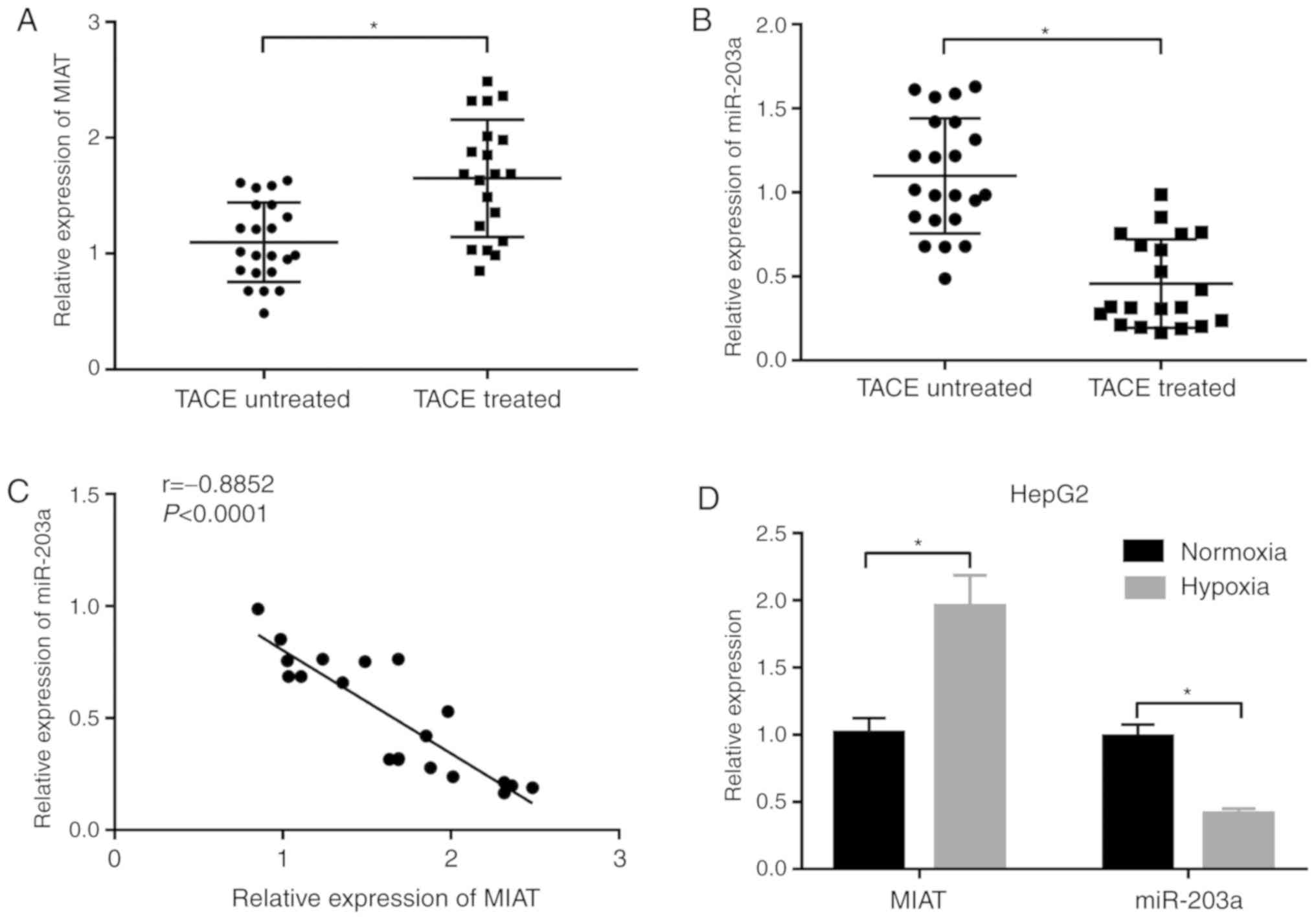
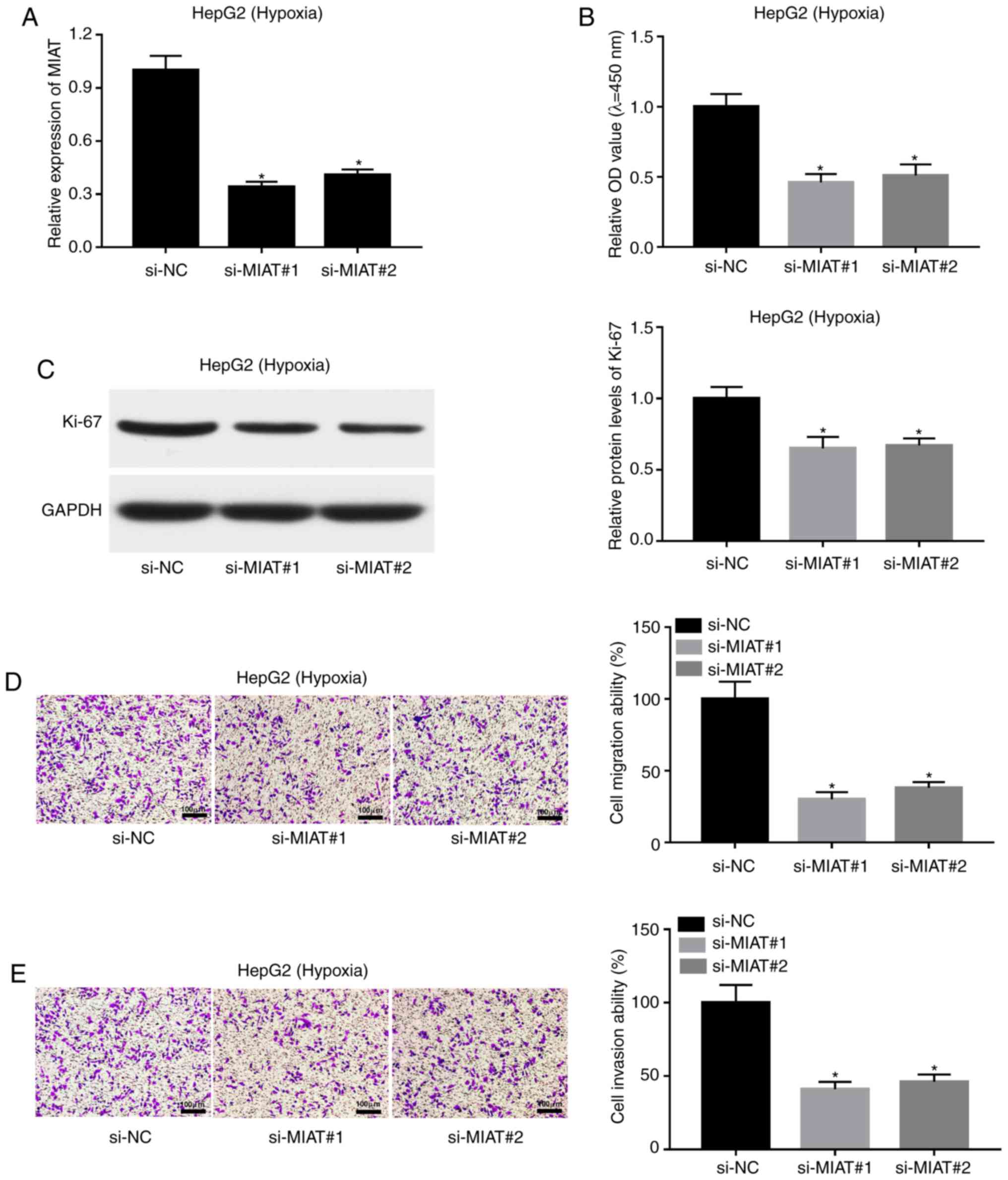
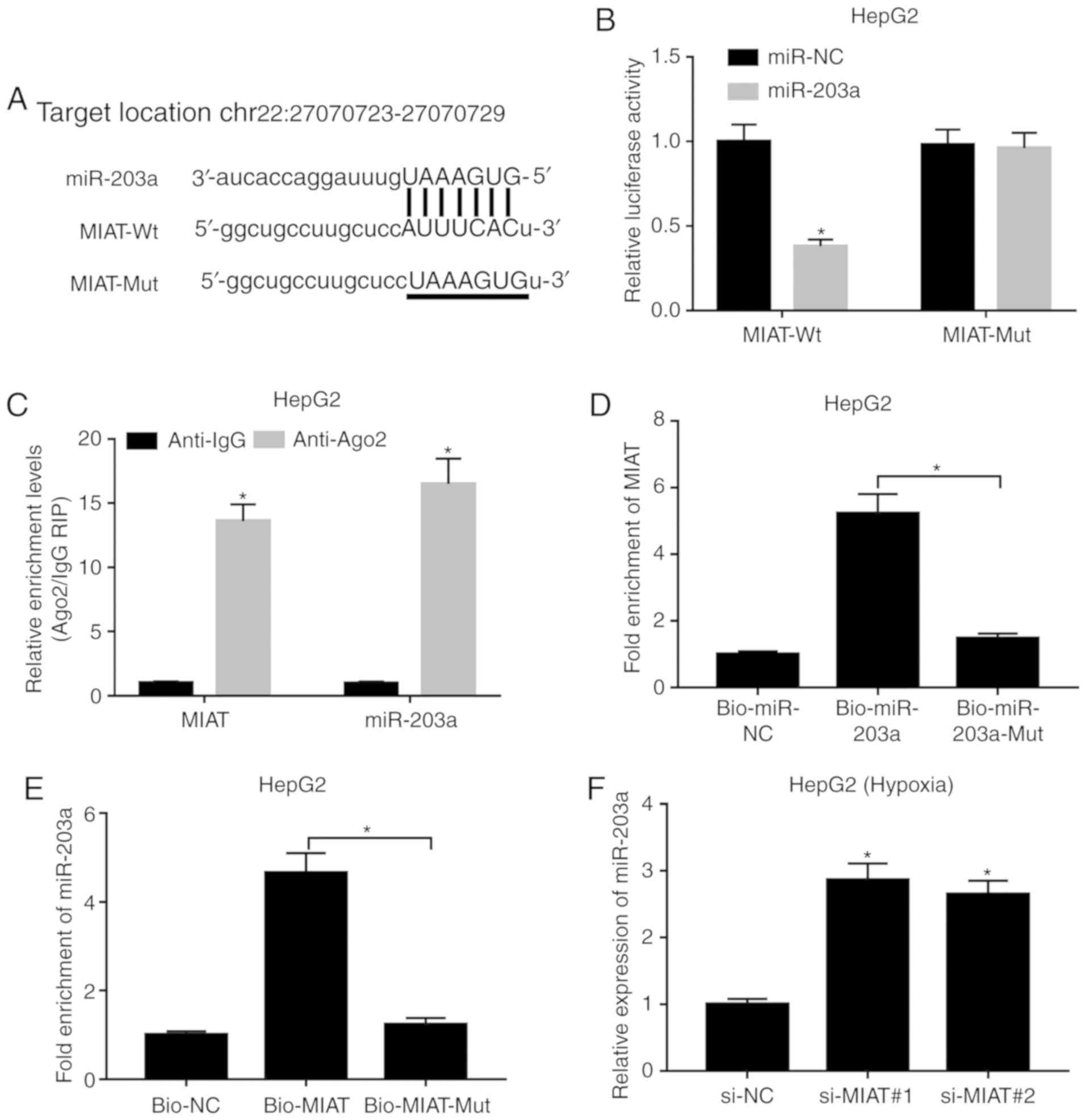
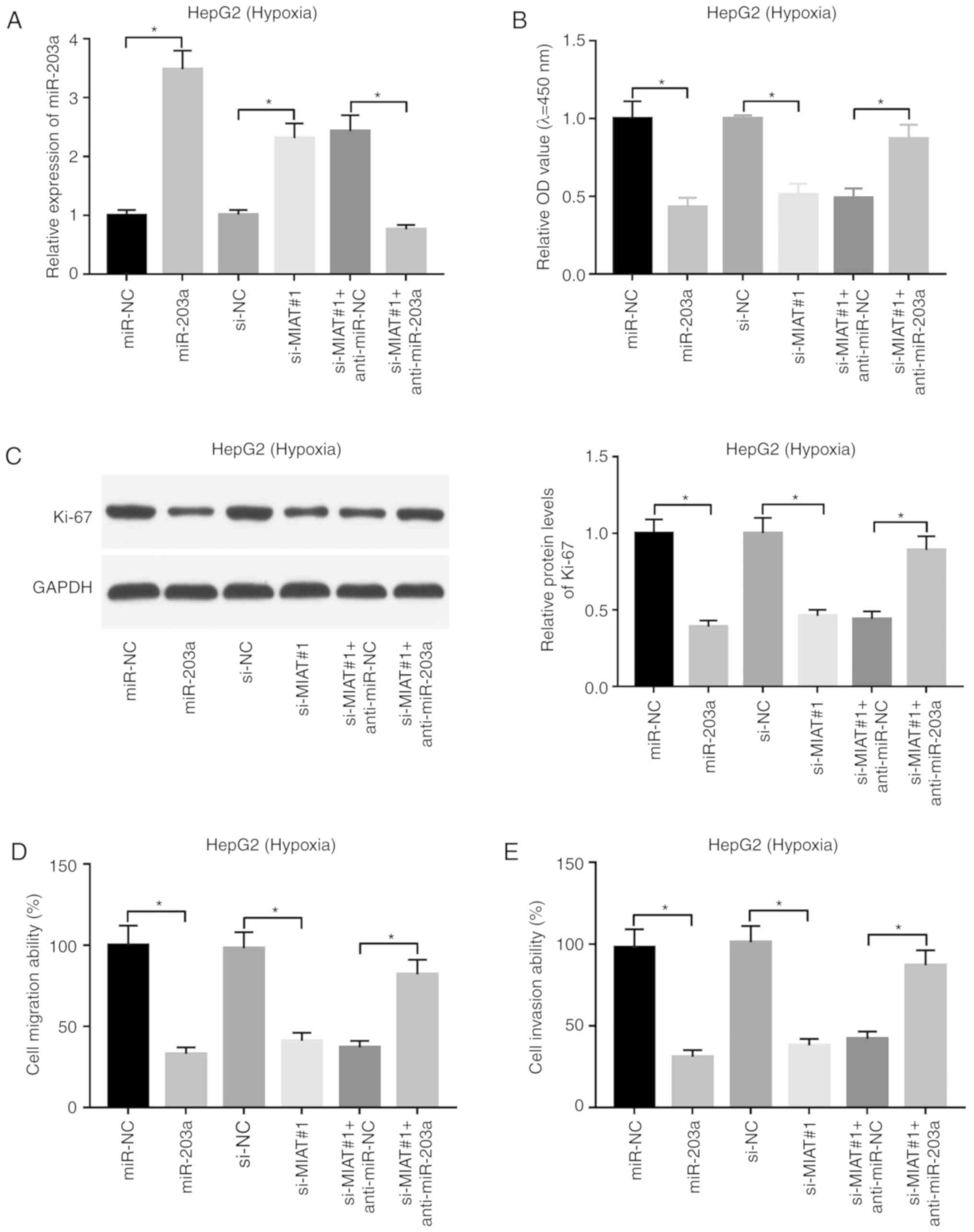
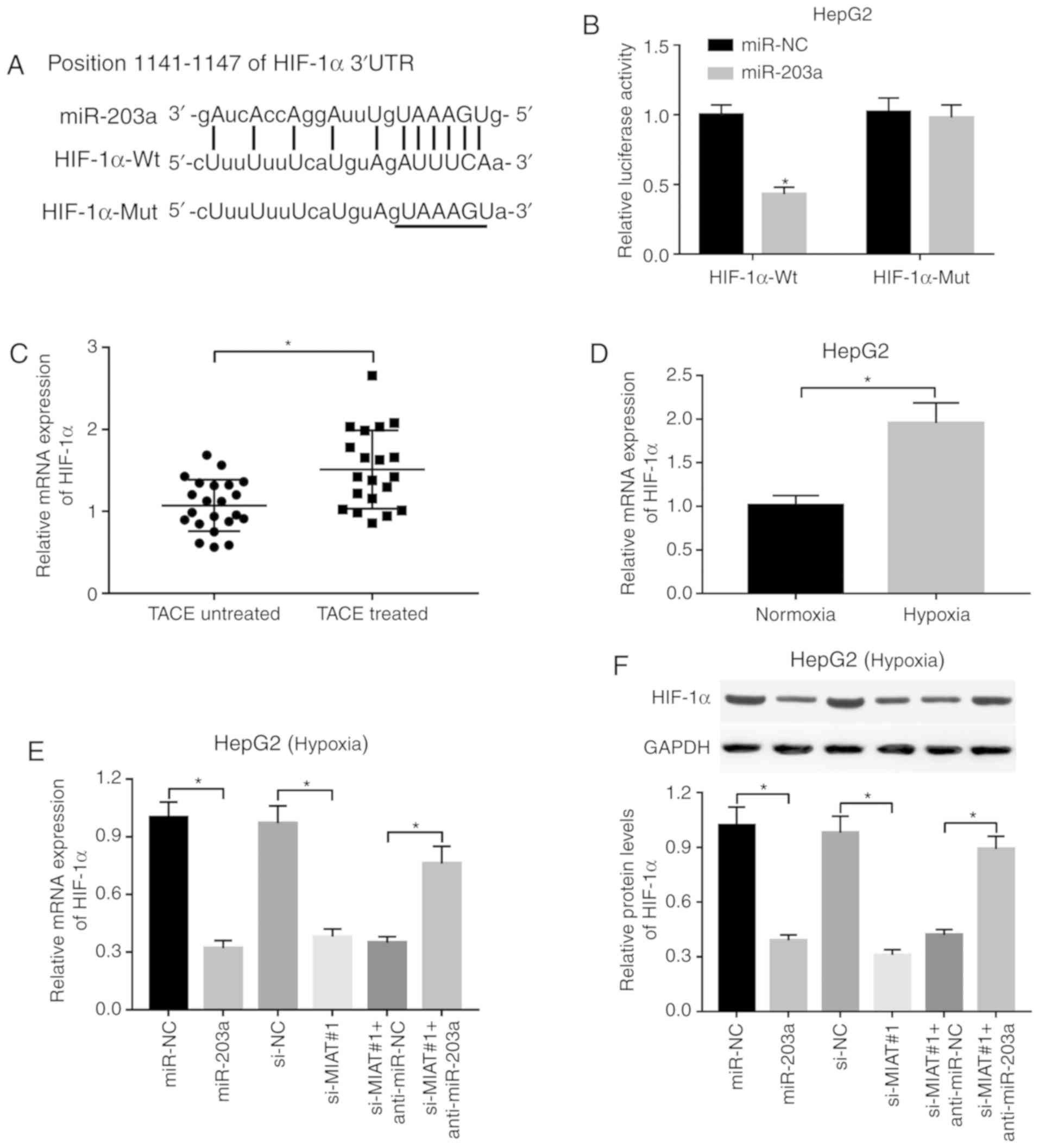
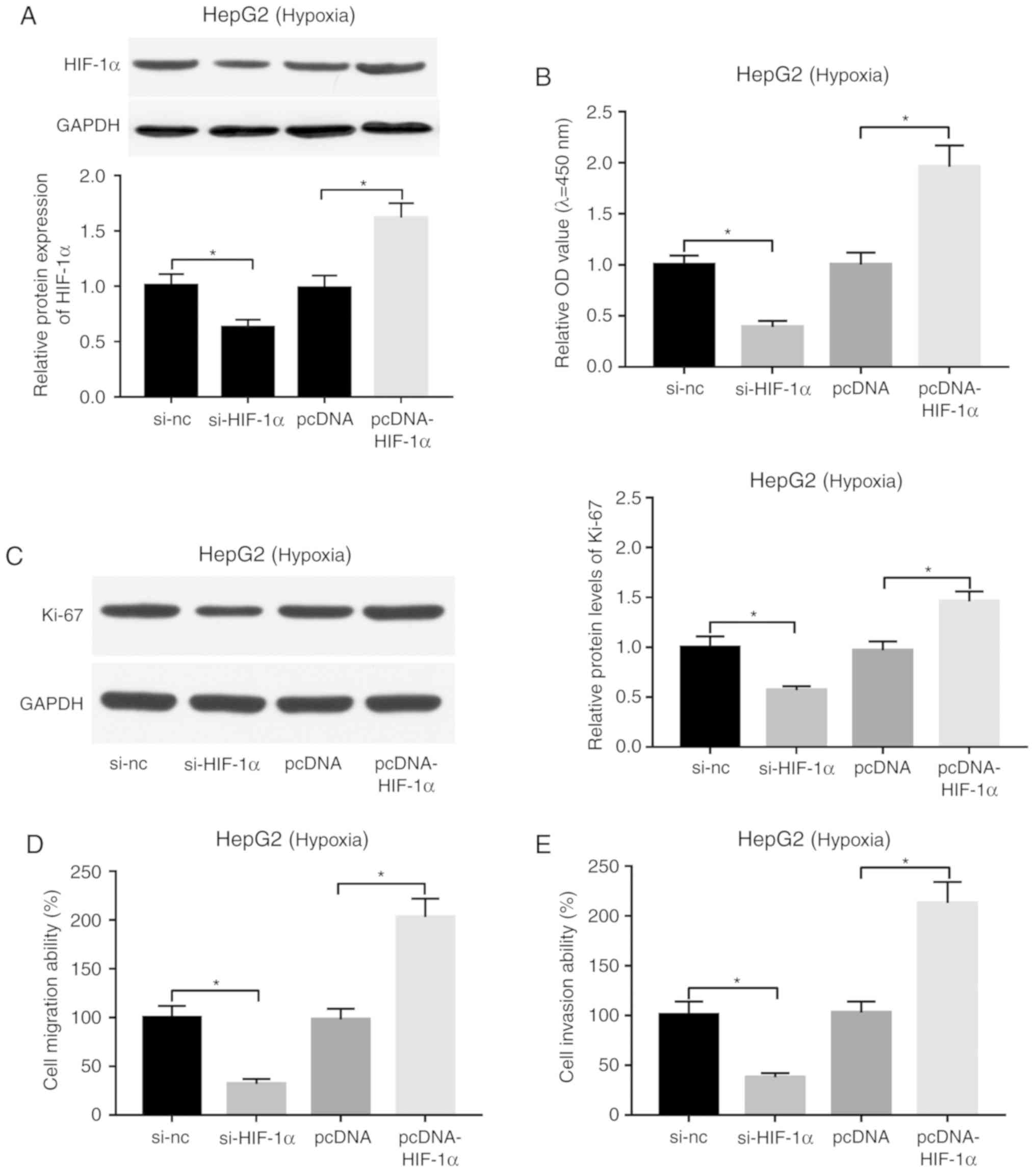
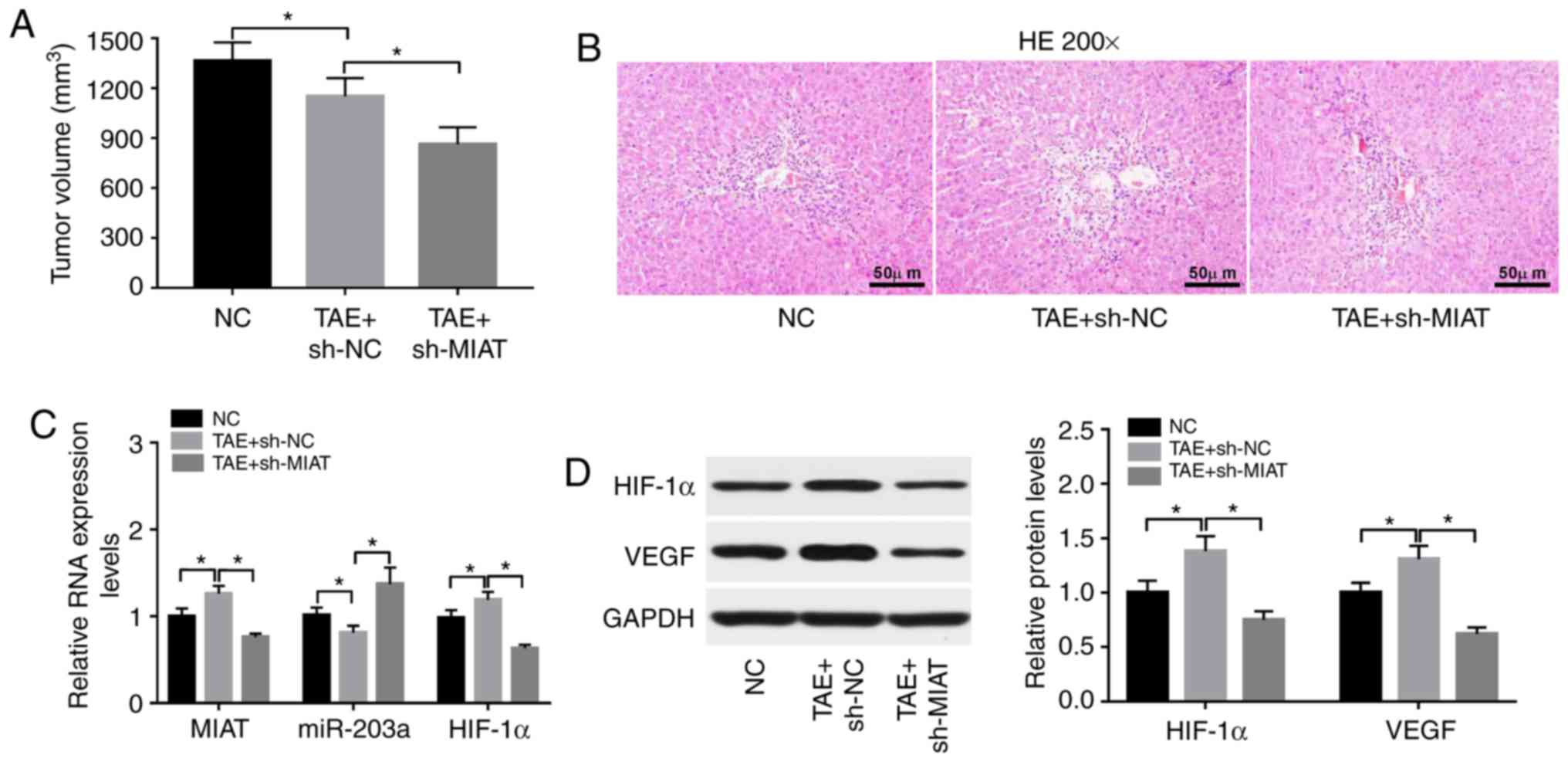
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zheng R, Qu C, Zhang S, Zeng H, Sun K, Gu
X and Chen W: Liver cancer incidence and mortality in China:
Temporal trends and projections to 2030. Chin J Cancer Res.
30:571–579. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fu J and Wang H: Precision diagnosis and
treatment of liver cancer in China. Cancer Lett. 412:283–288. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bruix J and Sherman M: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kudo M, Ueshima K, Kubo S, Sakamoto M,
Tanaka M, Ikai I, Furuse J, Murakami T, Kadoya M, Kokudo N, et al:
Response evaluation criteria in cancer of the liver (RECICL)(2015
revised version). Hepatol Res. 46:3–9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lanza E, Donadon M, Poretti D, Pedicini V,
Tramarin M, Roncalli M, Rhee H, Park YN and Torzilli G:
Transarterial therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer.
6:27–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Muz B, de la Puente P, Azab F and Azab AK:
The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis,
metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia (Auck). 3:83–92.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Eales KL, Hollinshead KE and Tennant DA:
Hypoxia and metabolic adaptation of cancer cells. Oncogenesis.
5:e1902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Greijer AE and Van der Wall E: The role of
hypoxia inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) in hypoxia induced apoptosis. J
Clin Pathol. 57:1009–1014. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liz J and Esteller M: lncRNAs and
microRNAs with a role in cancer development. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1859:169–176. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wong CM, Tsang HC and Ng OL: Non-coding
RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular functions and
pathological implications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
15:137–151. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Choudhry H, Harris AL and McIntyre A: The
tumour hypoxia induced non-coding transcriptome. Mol Aspects Med.
47:35–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chang YN, Zhang K, Hu ZM, Qi HX, Shi ZM,
Han XH, Han YW and Hong W: Hypoxia-Regulated lncRNAs in cancer.
Gene. 575:1–8. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liao J, He Q, Li M, Chen Y, Liu Y and Wang
J: LncRNA MIAT: Myocardial infarction associated and more. Gene.
578:158–161. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun C, Huang L, Li Z, Leng K, Xu Y, Jiang
X and Cui Y: Long non-coding RNA MIAT in development and disease: A
new player in an old game. J Biomed Sci. 25:232018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bountali A, Tonge DP and
Mourtada-Maarabouni M: RNA sequencing reveals a key role for the
long non-coding RNA MIAT in regulating neuroblastoma and
glioblastoma cell fate. Int J Biol Macromol. 130:878–891. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Alipoor FJ, Asadi MH and Torkzadeh-Mahani
M: MIAT lncRNA is overexpressed in breast cancer and its inhibition
triggers senescence and G1 arrest in MCF7 cell line. J Cell
Biochem. 119:6470–6481. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xiang Y, Huang Y, Sun H, Pan Y, Wu M and
Zhang J: Deregulation of miR-520d-3p promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma development via lncRNA MIAT regulation and EPHA2
signaling activation. Biomed Pharmacother. 109:1630–1639. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang Q, Shan K, Qun-Wang X, Zhou RM, Yang
H, Liu C, Li YJ, Yao J, Li XM, Shen Y, et al: Long non-coding
RNA-MIAT promotes neurovascular remodeling in the eye and brain.
Oncotarget. 7:49688–49698. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Petrillo M, Patella F, Pesapane F, Suter
MB, Ierardi AM, Angileri SA, Floridi C, de Filippo M and
Carrafiello G: Hypoxia and tumor angiogenesis in the era of
hepatocellular carcinoma transarterial loco-regional treatments.
Future Oncol. 14:2957–2967. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Z, Zhao Z, Yang Y, Luo M, Zhang M,
Wang X, Liu L, Hou N, Guo Q, Song T, et al: MiR-99b-5p and
miR-203a-3p function as tumor suppressors by targeting IGF-1R in
gastric cancer. Sci Rep. 8:101192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang N, Jiang X, Chen Z, Song X, Wu L,
Zong D, Song D, Yin L, Wang D, Chen C, et al: MiR-203a-3p
suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis through inhibiting
LASP1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
36:1382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fang JF, Zhao HP, Wang ZF and Zheng SS:
Upregulation of RASAL2 promotes proliferation and metastasis, and
is targeted by miR-203 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med Rep.
15:2720–2726. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chang JH, Hwang YH, Lee DJ, Kim DH, Park
JM, Wu HG and Kim IA: MicroRNA-203 modulates the radiation
sensitivity of human malignant glioma cells. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 94:412–420. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Balamurugan K: HIF-1 at the crossroads of
hypoxia, inflammation, and cancer. Int J Cancer. 138:1058–1066.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Masoud GN and Li W: HIF-1α pathway: Role,
regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharmaceutica
Sinica B. 5:378–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen C, Wang J, Liu R and Qian S: RNA
interference of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha improves the
effects of transcatheter arterial embolization in rat liver tumors.
Tumor Biol. 33:1095–1103. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sun X, Jiang H, Jiang X, Tan H, Meng Q,
Sun B, Xu R and Krissansen GW: Antisense hypoxia-inducible
factor-1α augments transcatheter arterial embolization in the
treatment of hepatocellular carcinomas in rats. Hum Gene Ther.
20:314–324. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen CS, Zhao Q, Qian S, Li HL, Guo CY,
Zhang W, Yan ZP, Liu R and Wang JH: Ultrasound-guided RNA
interference targeting HIF-1 alpha improves the effects of
transarterial chemoembolization in rat liver tumors. Onco Targets
Ther. 8:3539–3548. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Phatak P and Donahue JM: Biotinylated
micro-RNA pull down assay for identifying miRNA targets. Bio
Protoc. 7:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhou B, Wang J and Yan Z: Ginsenoside Rg3
attenuates hepatoma VEGF overexpression after hepatic artery
embolization in an orthotopic transplantation hepatocellular
carcinoma rat model. Onco Targets Ther. 7:1945–1954. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kan Z, Sato M, Ivancev K, Uchida B,
Hedgpeth P, Lunderquist A, Rosch J and Yamada R: Distribution and
effect of iodized poppyseed oil in the liver after hepatic artery
embolization: Experimental study in several animal species.
Radiology. 186:861–866. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Daher S, Massarwa M, Benson AA and Khoury
T: Current and future treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: An
updated comprehensive review. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 6:69–78. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kumar Y, Sharma P, Bhatt N and Hooda K:
Transarterial therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: A
comprehensive review with current updates and future directions.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 17:473–478. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Transarterial chemoembolization in
hepatocellular carcinoma treatment, . Barcelona clinic liver cancer
staging system. World J Gastroenterol. 21:10327–10335. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rammohan A, Sathyanesan J, Ramaswami S,
Lakshmanan A, Senthil-Kumar P, Srinivasan UP, Ramasamy R and
Ravichandran P: Embolization of liver tumors: Past, present and
future. World J Radiol. 4:405–412. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Vogl TJ, Naguib NN, Nour-Eldin NE, Rao P,
Emami AH, Zangos S, Nabil M and Abdelkader A: Review on
transarterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma:
Palliative, combined, neoadjuvant, bridging, and symptomatic
indications. Eur J Radiol. 72:505–516. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang Z, Wang S and Liu W: EMT-Related
long non-coding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma: A study with TCGA
database. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 503:1530–1536. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang X, Gao Y, Qin J and Lu S: lncRNA
MIAT promotes proliferation and invasion of HCC cells via sponging
miR-214. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 314:G559–G565.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Furuta M, Kozaki KI, Tanaka S, Arii S,
Imoto I and Inazawa J: MiR-124 and miR-203 are epigenetically
silenced tumor-suppressive microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Carcinogenesis. 31:766–776. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ji D, Jiang C, Zhang L, Liang N, Jiang T,
Yang B and Liang H: LncRNA CRNDE promotes hepatocellular carcinoma
cell proliferation, invasion, and migration through regulating
miR-203/BCAT1 axis. J Cell Physiol. 234:6548–6560. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Luo D, Wang Z and Wu J, Jiang C and Wu J:
The role of hypoxia inducible factor-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.
BioMed Res Int. 2014:4092722014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang L, Huang G, Li X, Zhang Y, Jiang Y,
Shen J, Liu J, Wang Q, Zhu J, Feng X, et al: Hypoxia induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via activation of SNAI1 by
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC
Cancer. 13:1082013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang X, Gao Y, Qin J and Lu S: lncRNA
MIAT promotes proliferation and invasion of HCC cells via sponging
miR-214. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 314:G559–G565.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhao L, Hu K, Cao J, Wang P, Li J, Zeng K,
He X, Tu PF, Tong T and Han L: lncRNA miat functions as a ceRNA to
upregulate sirt1 by sponging miR-22-3p in HCC cellular senescence.
Aging (Albany NY). 11:7098–7122. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen Z, Zuo X, Zhang Y, Han G, Zhang L, Wu
J and Wang X: MiR-3662 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth
through inhibition of HIF-1α-mediated warburg effect. Cell Death
Dis. 9:5492018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xu H, Zhao L, Fang Q, Sun J, Zhang S, Zhan
C, Liu S and Zhang Y: MiR-338-3p inhibits hepatocarcinoma cells and
sensitizes these cells to sorafenib by targeting hypoxia-induced
factor 1α. PLoS One. 9:e1155652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jia XQ, Cheng HQ, Qian X, Bian CX, Shi ZM,
Zhang JP, Jiang BH and Feng ZQ: Lentivirus-Mediated overexpression
of microRNA-199a inhibits cell proliferation of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biochem Biophys. 62:237–244. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|