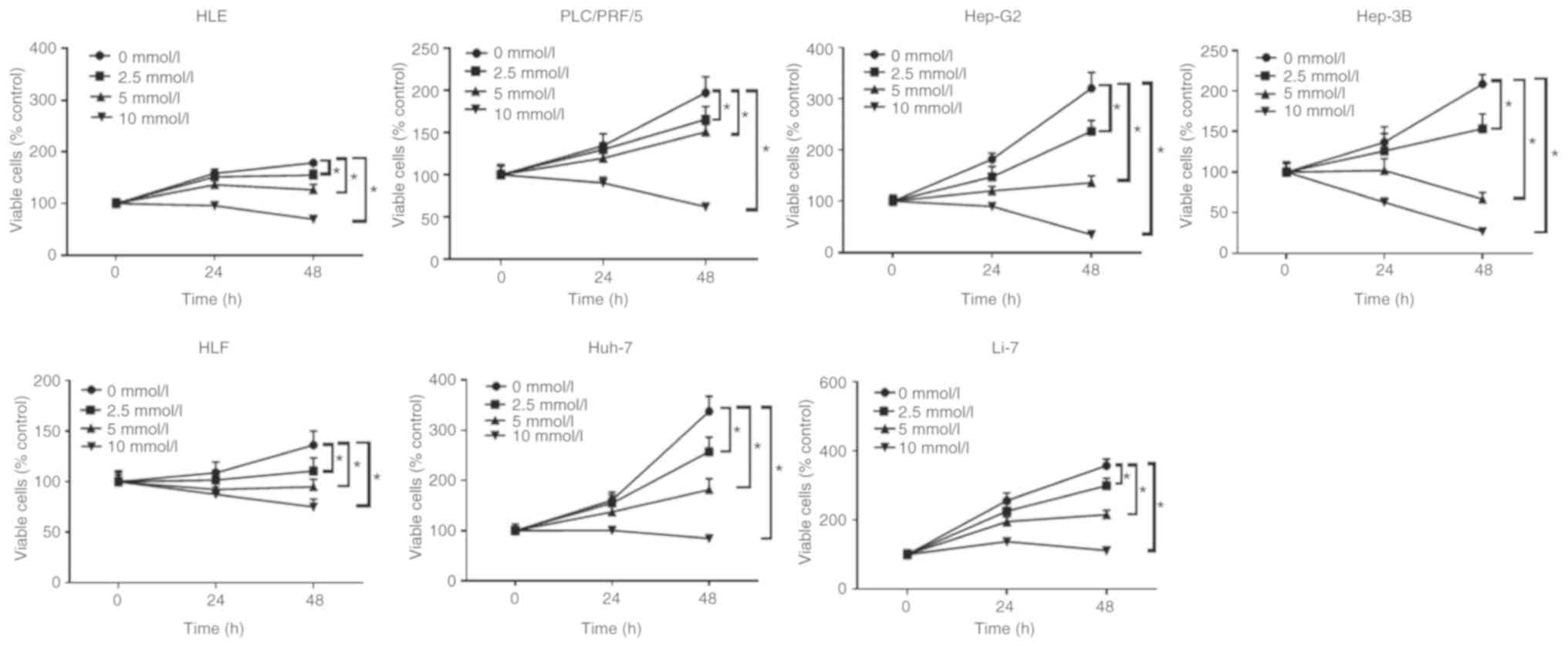
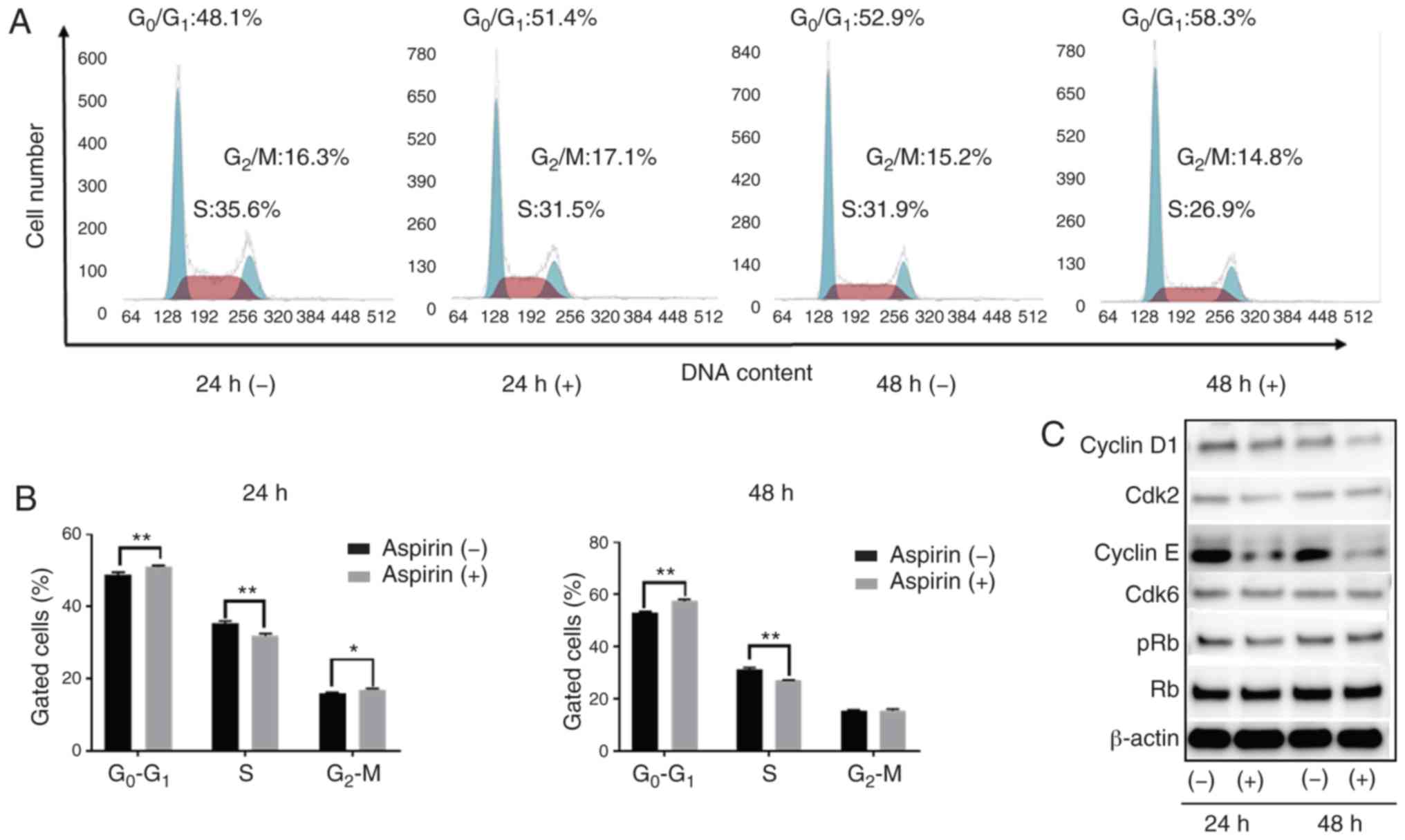
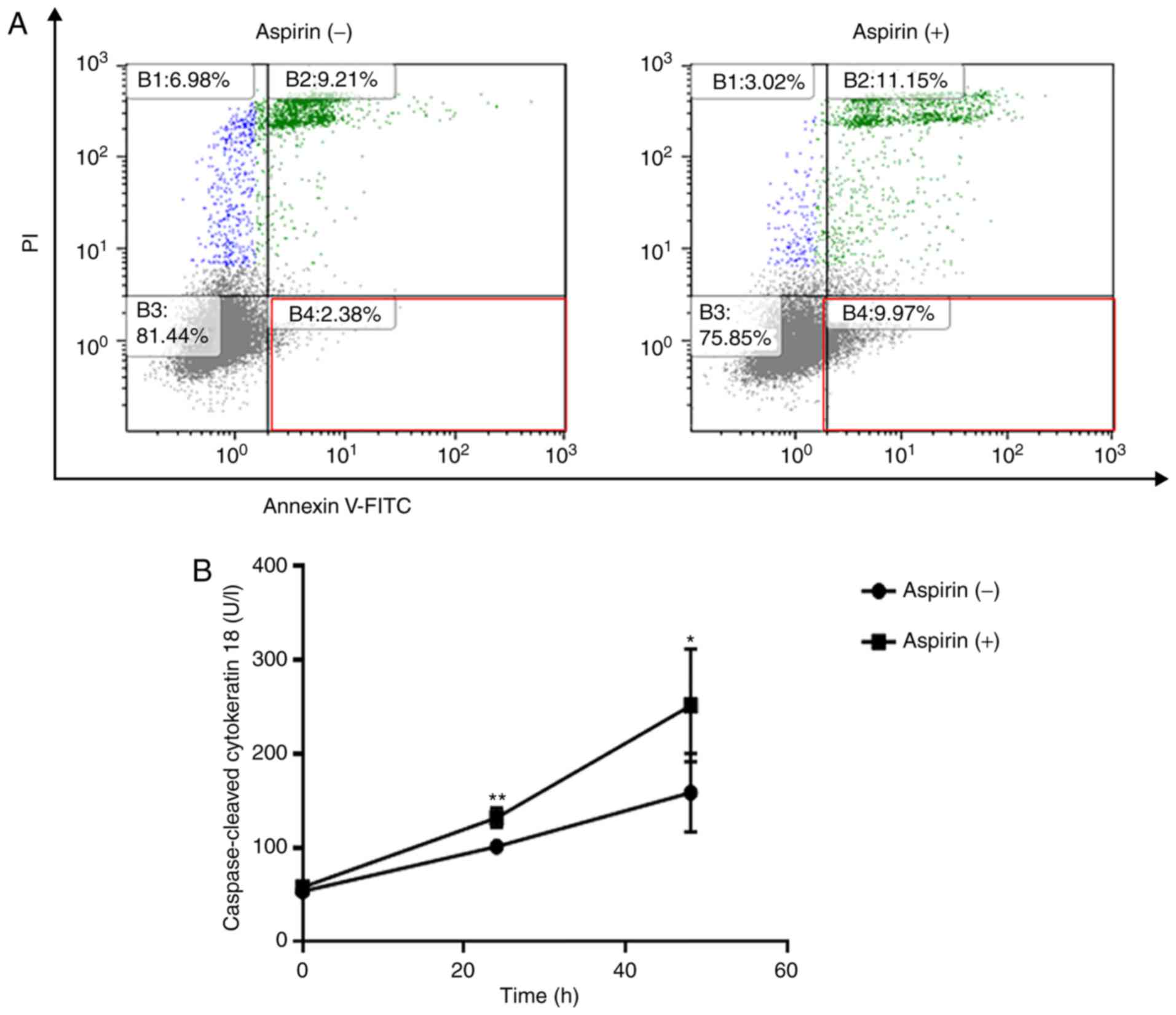
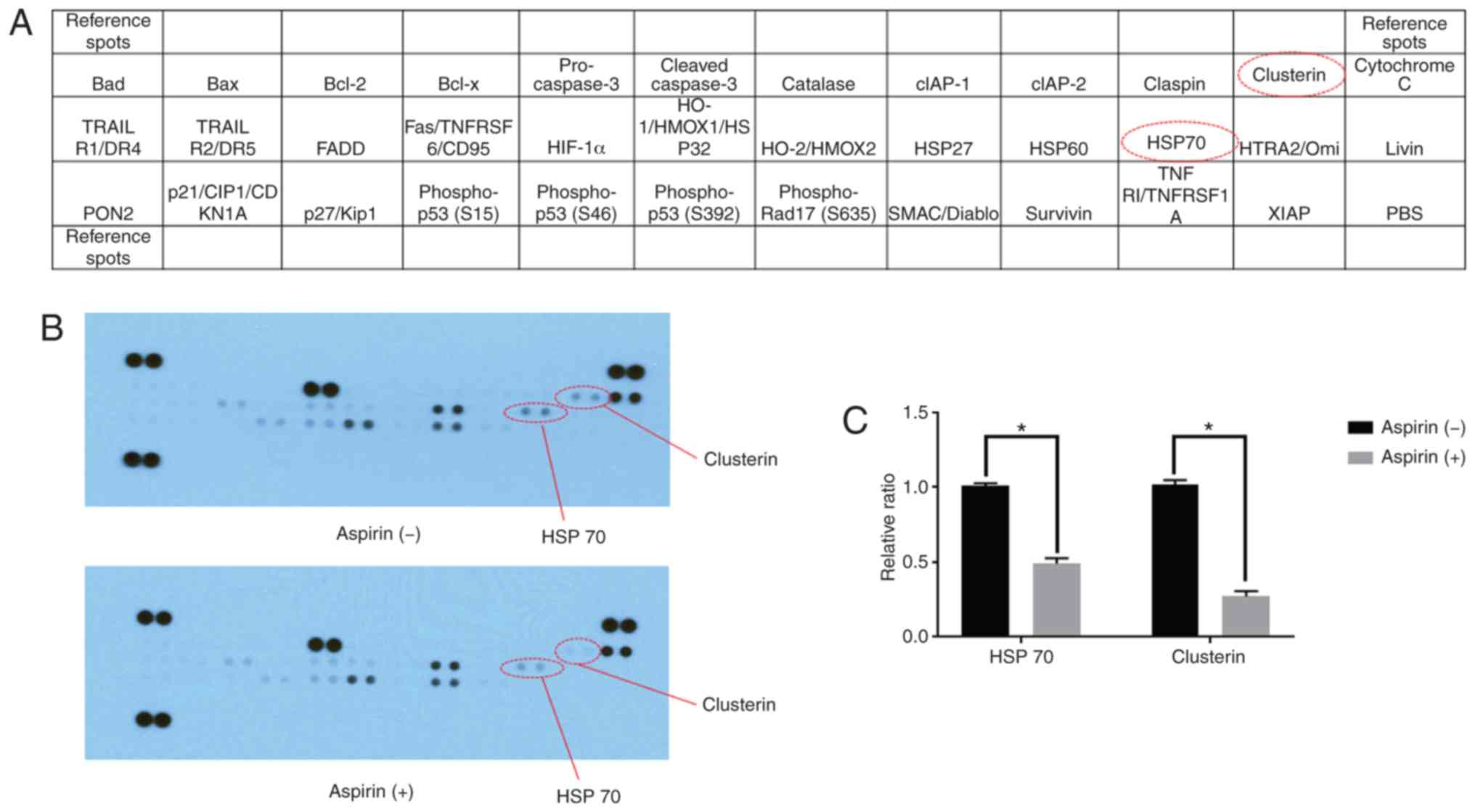
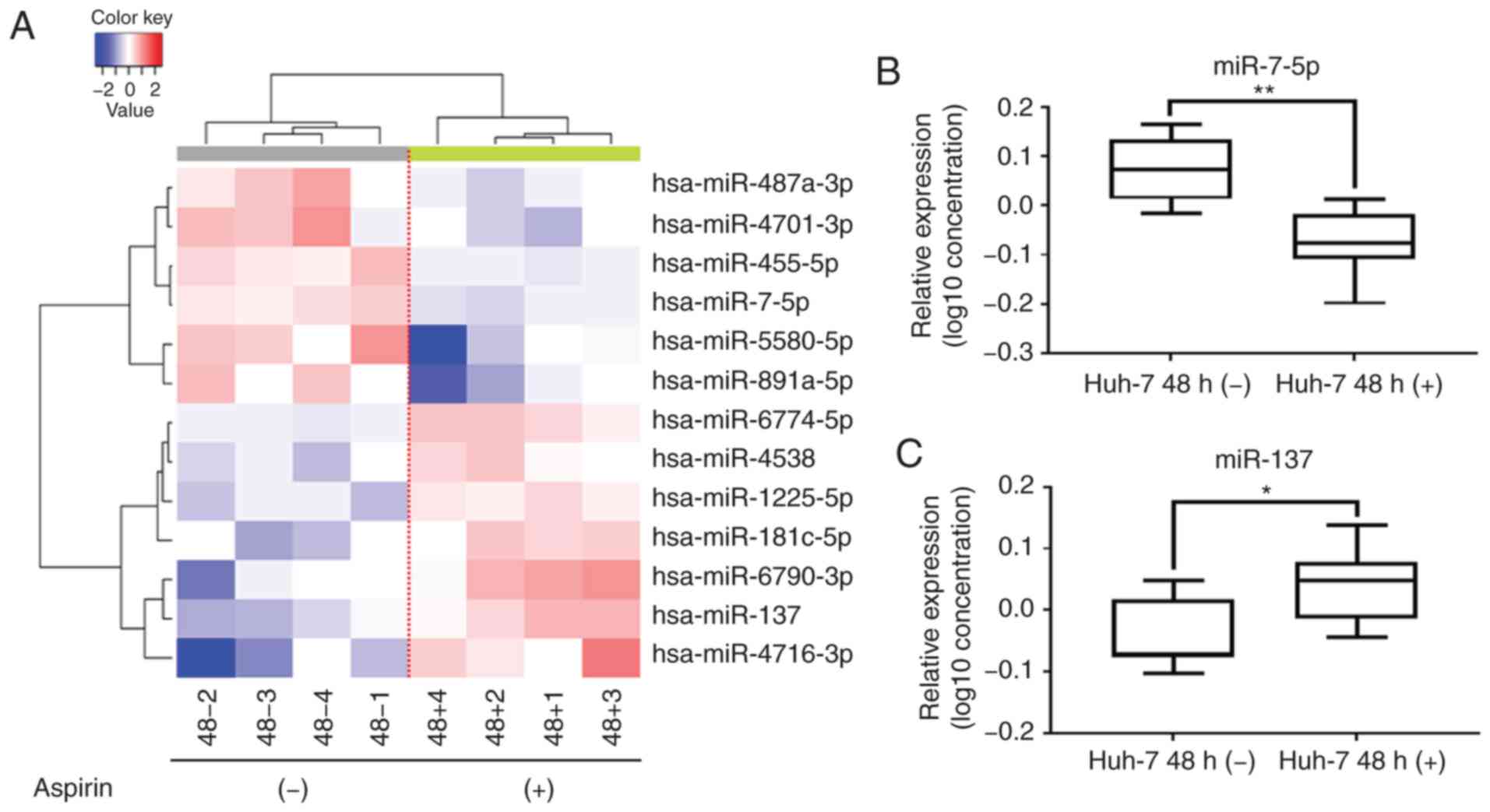
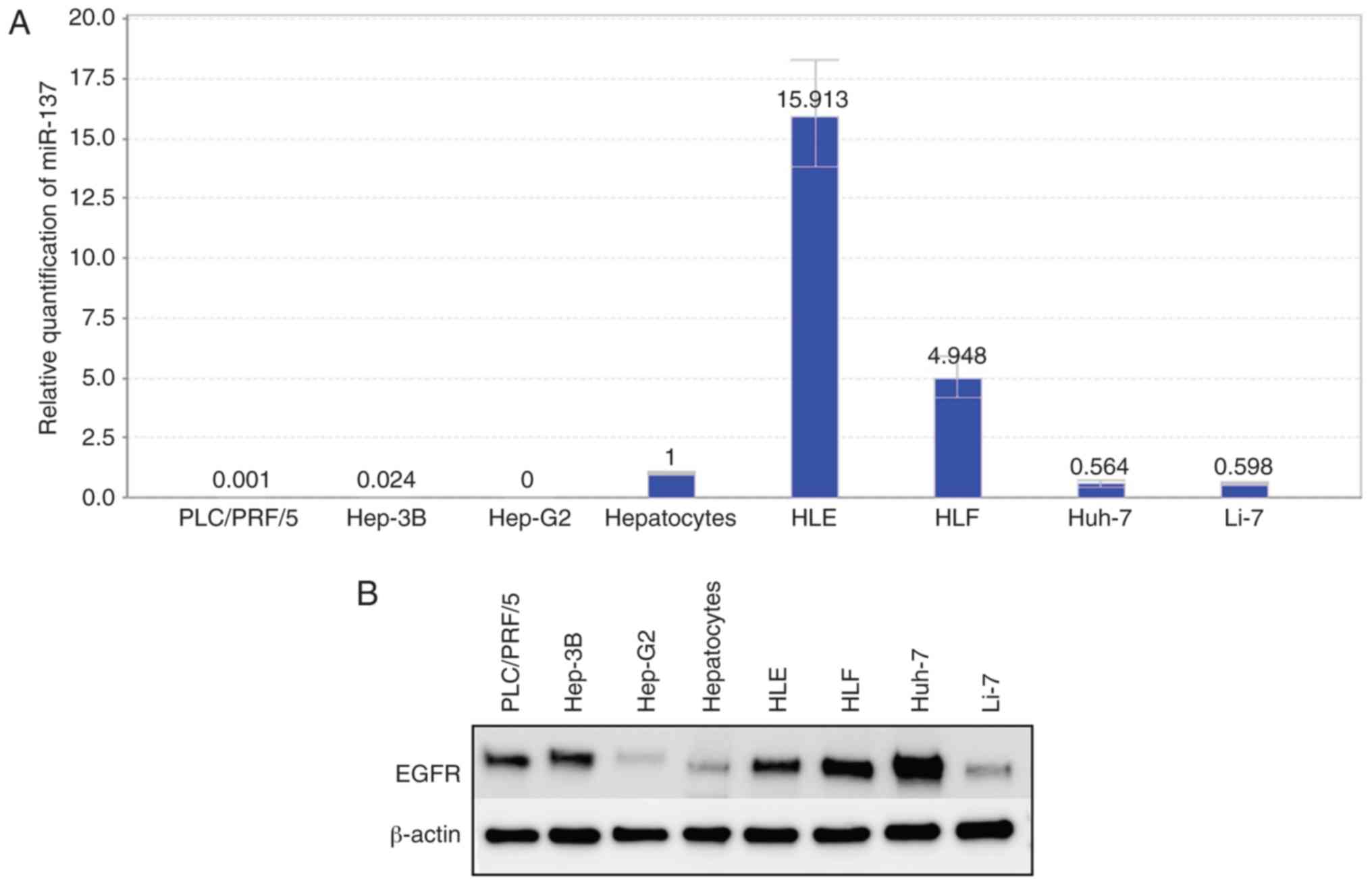
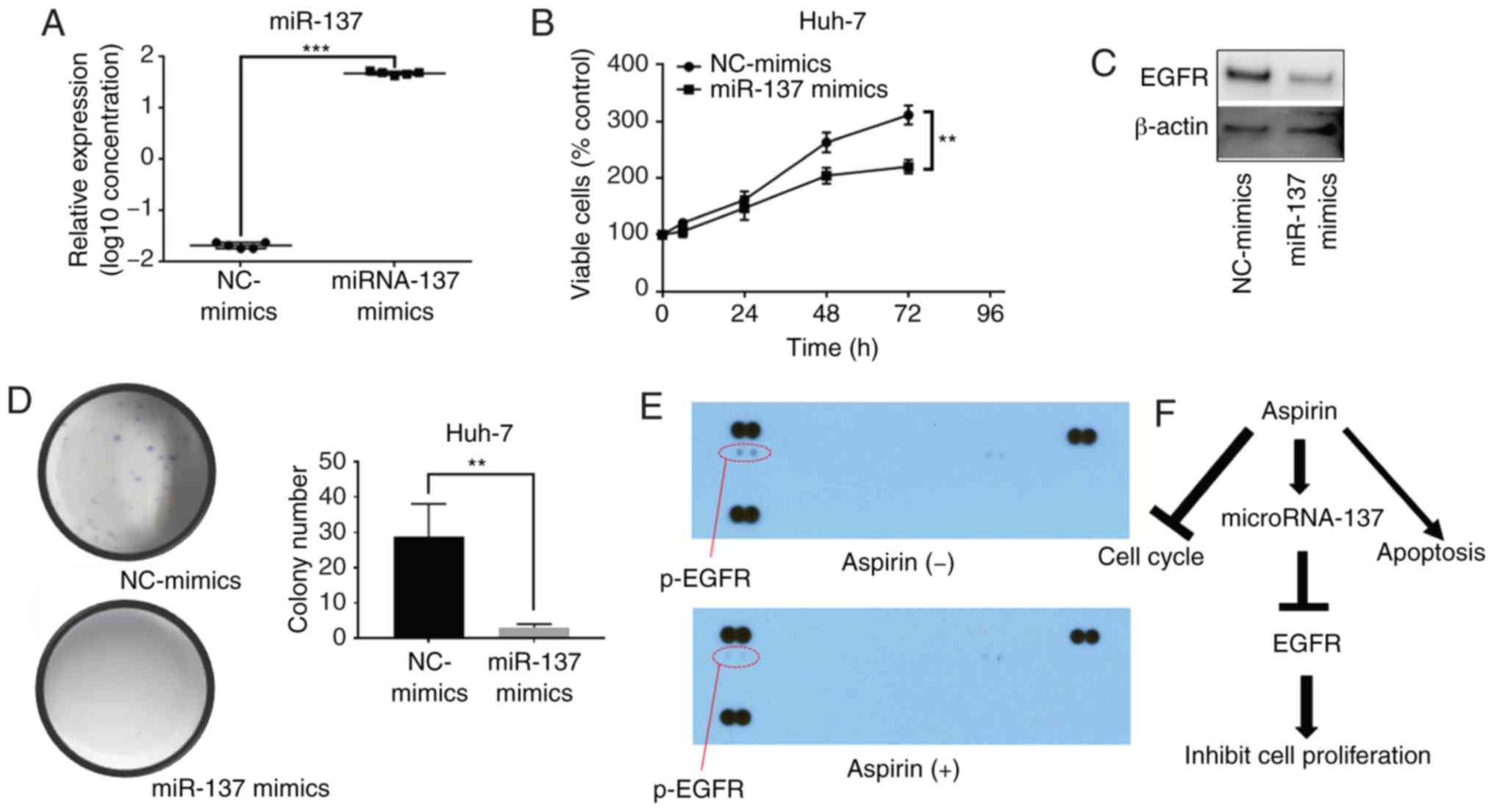
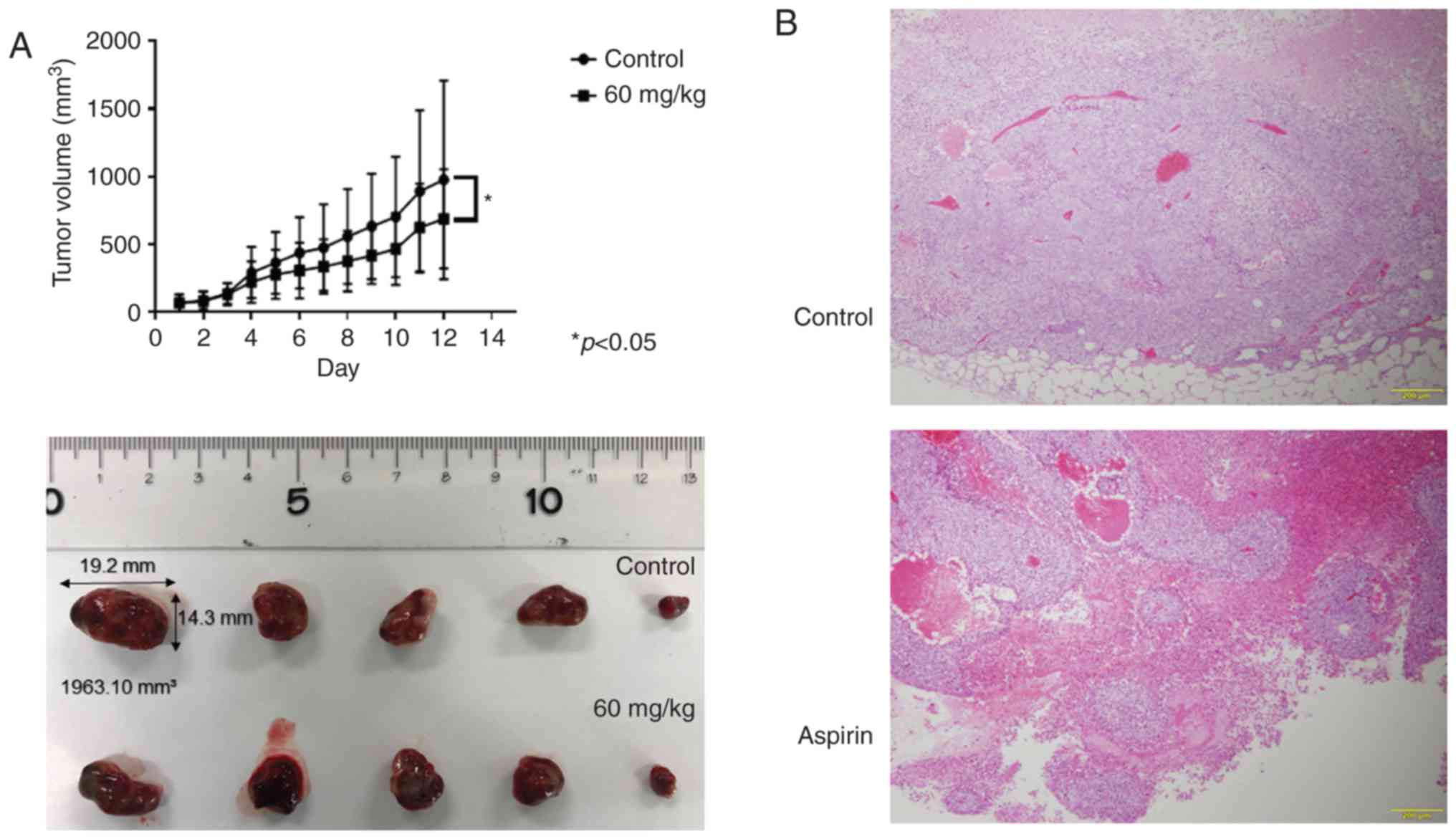
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Petrick JL, Kelly SP, Altekruse SF,
McGlynn KA and Rosenberg PS: Future of hepatocellular carcinoma
incidence in the United States forecast through 2030. J Clin Oncol.
34:1787–1794. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Michel P, Boige V, Andre T, Aparicio T,
Bachet JB, Dahan L, Guimbaud R, Lepage C, Manfredi S, Tougeron D,
et al: Aspirin versus placebo in stage III or high-risk stage II
colon cancer with PIK3CA mutation: A French randomised double-blind
phase III trial (PRODIGE 50-ASPIK). Dig Liver Dis. 50:305–307.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Henry WS, Laszewski T, Tsang T, Beca F,
Beck AH, McAllister SS and Toker A: Aspirin suppresses growth in
PI3K-mutant breast cancer by activating AMPK and inhibiting mTORC1
signaling. Cancer Res. 77:790–801. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yue W, Zheng X, Lin Y, Yang CS, Xu Q,
Carpizo D, Huang H, DiPaola RS and Tan XL: Metformin combined with
aspirin significantly inhibit pancreatic cancer cell growth in
vitro and in vivo by suppressing anti-apoptotic proteins Mcl-1 and
Bcl-2. Oncotarget. 6:21208–21224. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gan H, Lin L, Hu N, Yang Y, Gao Y, Pei Y,
Chen K and Sun B: Aspirin ameliorates lung cancer by targeting the
miR-98/WNT1 axis. Thorac Cancer. 10:744–750. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tao Y, Li Y, Liu X, Deng Q, Yu Y and Yang
Z: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, especially aspirin, are
linked to lower risk and better survival of hepatocellular
carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Cancer Manag Res. 10:2695–2709. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Simon TG, Ma Y, Ludvigsson JF, Chong DQ,
Giovannucci EL, Fuchs CS, Meyerhardt JA, Corey KE, Chung RT, Zhang
X and Chan AT: Association between aspirin use and risk of
hepatocellular carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 4:1683–1690. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang X, Feng H, Li Z, Guo J and Li M:
Aspirin is involved in the cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, cell
migration, and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol
Sci. 19:E20292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu YX, Feng JY, Sun MM, Liu BW, Yang G,
Bu YN, Zhao M, Wang TJ, Zhang WY, Yuan HF and Zhang XD: Aspirin
inhibits the proliferation of hepatoma cells through controlling
GLUT1-mediated glucose metabolism. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 40:122–132.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang Z, Fang W, Liu W, Wang L, Liu B and
Liu S and Liu S: Aspirin induces Beclin-1-dependent autophagy of
human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 823:58–64.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Raza H, John A and Benedict S:
Acetylsalicylic acid-induced oxidative stress, cell cycle arrest,
apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in human hepatoma HepG2
cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 668:15–24. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pavlovic N, Rani B, Gerwins P and
Heindryckx F: Platelets as key factors in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancers (Basel). 11:e10222019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Malehmir M, Pfister D, Gallage S,
Szydlowska M, Inverso D, Kotsiliti E, Leone V, Peiseler M,
Surewaard BGJ, Rath D, et al: Platelet GPIbα is a mediator and
potential interventional target for NASH and subsequent liver
cancer. Nat Med. 25:641–655. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dovizio M, Bruno A, Tacconelli S and
Patrignani P: Mode of action of aspirin as a chemopreventive agent.
Recent Results Cancer Res. 191:39–65. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang S, Yu Y, Ryan PM, Dang M, Clark C,
Kontogiannis V, Rahmani J, Varkaneh HK, Salehisahlabadi A, Day AS
and Zhang Y: Association of aspirin therapy with risk of
hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and dose-response
analysis of cohort studies with 2.5 million participants. Pharmacol
Res. 151:1045852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pathi S, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Nair V,
Lee SO and Safe S: Aspirin inhibits colon cancer cell and tumor
growth and downregulates specificity protein (Sp) transcription
factors. PLoS One. 7:e482082012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Law BK, Waltner-Law ME, Entingh AJ, Chytil
A, Aakre ME, Nørgaard P and Moses HL: Salicylate-induced growth
arrest is associated with inhibition of p70s6k and down-regulation
of c-myc, cyclin D1, cyclin A, and proliferating cell nuclear
antigen. J Biol Chem. 275:38261–38267. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao L and Williams JL: Nitric
oxide-donating aspirin induces G2/M phase cell cycle arrest in
human cancer cells by regulating phase transition proteins. Int J
Oncol. 41:325–330. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dachineni R, Ai G, Kumar DR, Sadhu SS,
Tummala H and Bhat GJ: Cyclin A2 and CDK2 as novel targets of
aspirin and salicylic acid: A potential role in cancer prevention.
Mol Cancer Res. 14:241–252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pozzoli G, Marei HE, Althani A, Boninsegna
A, Casalbore P, Marlier LNJL, Lanzilli G, Zonfrillo M, Petrucci G,
Rocca B, et al: Aspirin inhibits cancer stem cells properties and
growth of glioblastoma multiforme through Rb1 pathway modulation. J
Cell Physiol. 234:15459–15474. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Calderwood SK, Khaleque MA, Sawyer DB and
Ciocca DR: Heat shock proteins in cancer: Chaperones of
tumorigenesis. Trends Biochem Sci. 31:164–172. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mustafi S, Sant DW, Liu ZJ and Wang G:
Ascorbate induces apoptosis in melanoma cells by suppressing
Clusterin expression. Sci Rep. 7:36712017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang F, Kumano M, Beraldi E, Fazli L, Du
C, Moore S, Sorensen P, Zoubeidi A and Gleave ME: Clusterin
facilitates stress-induced lipidation of LC3 and autophagosome
biogenesis to enhance cancer cell survival. Nat Commun. 5:57752014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kang YK, Hong SW, Lee H and Kim WH:
Overexpression of clusterin in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum
Pathol. 35:1340–1346. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang C, Jiang K, Gao D, Kang X, Sun C,
Zhang Q, Li Y, Sun L, Zhang S, Guo K and Liu Y: Clusterin protects
hepatocellular carcinoma cells from endoplasmic reticulum stress
induced apoptosis through GRP78. PLoS One. 8:e559812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xie D, Sham JS, Zeng WF, Che LH, Zhang M,
Wu HX, Lin HL, Wen JM, Lau SH, Hu L and Guan XY: Oncogenic role of
clusterin overexpression in multistage colorectal tumorigenesis and
progression. World J Gastroenterol. 11:3285–3289. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ammar H and Closset JL: Clusterin
activates survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt
pathway. J Biol Chem. 283:12851–12861. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zoubeidi A, Ettinger S, Beraldi E,
Hadaschik B, Zardan A, Klomp LW, Nelson CC, Rennie PS and Gleave
ME: Clusterin facilitates COMMD1 and I-kappaB degradation to
enhance NF-kappaB activity in prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer
Res. 8:119–130. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kuo PC, Chau IY, Li AF, Chau YP, Hsia CY
and Chau GY: Clusterin expression in nontumor tissue in patients
with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma related with
postresectional survival. J Chin Med Assoc. 82:929–934. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kumar S, Stokes J III, Singh UP, Scissum
Gunn K, Acharya A, Manne U and Mishra M: Targeting Hsp70: A
possible therapy for cancer. Cancer Lett. 374:156–166. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hossain MA, Kim DH, Jang JY, Kang YJ, Yoon
JH, Moon JO, Chung HY, Kim GY, Choi YH, Copple BL and Kim ND:
Aspirin induces apoptosis in vitro and inhibits tumor growth of
human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in a nude mouse xenograft
model. Int J Oncol. 40:1298–1304. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Geng L, Chaudhuri A, Talmon G, Wisecarver
JL, Are C, Brattain M and Wang J: MicroRNA-192 suppresses liver
metastasis of colon cancer. Oncogene. 33:5332–5340. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yuan Q, Cao G, Li J, Zhang Y and Yang W:
MicroRNA-136 inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation and invasion
through targeting liver receptor homolog-1/Wnt signaling. Gene.
628:48–55. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yuan K, Xie K, Fox J, Zeng H, Gao H, Huang
C and Wu M: Decreased levels of miR-224 and the passenger strand of
miR-221 increase MBD2, suppressing maspin and promoting colorectal
tumor growth and metastasis in mice. Gastroenterology.
145:853–864.e9. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Morishita A and Masaki T: miRNA in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 45:128–141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu LL, Lu SX, Li M, Li LZ, Fu J, Hu W,
Yang YZ, Luo RZ, Zhang CZ and Yun JP: FoxD3-regulated microRNA-137
suppresses tumour growth and metastasis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting AKT2. Oncotarget. 5:5113–5124. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cui S, Sun Y, Liu Y, Liu C, Wang J, Hao G
and Sun Q: MicroRNA-137 has a suppressive role in liver cancer via
targeting EZH2. Mol Med Rep. 16:9494–9502. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liang L, Li X, Zhang X, Lv Z, He G, Zhao
W, Ren X, Li Y, Bian X, Liao W, et al: MicroRNA-137, an HMGA1
target, suppresses colorectal cancer cell invasion and metastasis
in mice by directly targeting FMNL2. Gastroenterology.
144:624–635.e4. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhu M, Li M, Wang T, Linghu E and Wu B:
MicroRNA-137 represses FBI-1 to inhibit proliferation and in vitro
invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Tumour
Biol. 37:13995–14008. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Buckley AF, Burgart LJ, Sahai V and Kakar
S: Epidermal growth factor receptor expression and gene copy number
in conventional hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol.
129:245–251. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kato K, Gong J, Iwama H, Kitanaka A, Tani
J, Miyoshi H, Nomura K, Mimura S, Kobayashi M, Aritomo Y, et al:
The antidiabetic drug metformin inhibits gastric cancer cell
proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:549–560.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu W, Yin T, Ren J, Li L, Xiao Z, Chen X
and Xie D: Activation of the EGFR/Akt/NF-κB/cyclinD1 survival
signaling pathway in human cholesteatoma epithelium. Eur Arch
Otorhinolaryngol. 271:265–273. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li B, Ding CM, Li YX, Peng JC, Geng N and
Qin WW: Over-regulation of microRNA-133b inhibits cell
proliferation of cisplatin-induced non-small cell lung cancer cells
through PI3K/Akt and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway by targeting
EGFR. Oncol Rep. 39:1227–1234. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Han W and Lo HW: Landscape of EGFR
signaling network in human cancers: Biology and therapeutic
response in relation to receptor subcellular locations. Cancer
Lett. 318:124–134. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dajani OF, Meisdalen K, Guren TK, Aasrum
M, Tveteraas IH, Lilleby P, Thoresen GH, Sandnes D and
Christoffersen T: Prostaglandin E2 upregulates EGF-stimulated
signaling in mitogenic pathways involving Akt and ERK in
hepatocytes. J Cell Physiol. 214:371–380. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li D, Chi G, Chen Z and Jin X:
MicroRNA-1225-5p behaves as a tumor suppressor in human
glioblastoma via targeting of IRS1. OncoTargets Ther. 11:6339–6350.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Sun P, Zhang D, Huang H, Yu Y, Yang Z, Niu
Y and Liu J: MicroRNA-1225-5p acts as a tumor-suppressor in
laryngeal cancer via targeting CDC14B. Biol Chem. 400:237–246.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang S, Chen X, Zhang Z and Wu Z:
MicroRNA-1225-5p inhibits the development and progression of
thyroid cancer via targeting sirtuin 3. Pharmazie. 74:423–427.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Reddy SD, Ohshiro K, Rayala SK and Kumar
R: MicroRNA-7, a homeobox D10 target, inhibits p21-activated kinase
1 and regulates its functions. Cancer Res. 68:8195–8200. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fang Y, Xue JL, Shen Q, Chen J and Tian L:
MicroRNA-7 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting the
phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 55:1852–1862. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kabir TD, Ganda C, Brown RM, Beveridge DJ,
Richardson KL, Chaturvedi V, Candy P, Epis M, Wintle L, Kalinowski
F, et al: A microRNA-7/growth arrest specific 6/TYRO3 axis
regulates the growth and invasiveness of sorafenib-resistant cells
in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 67:216–231. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cheng AM, Byrom MW, Shelton J and Ford LP:
Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an
involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids
Res. 33:1290–1297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mikami J, Kurokawa Y, Takahashi T,
Miyazaki Y, Yamasaki M, Miyata H, Nakajima K, Takiguchi S, Mori M
and Doki Y: Antitumor effect of antiplatelet agents in gastric
cancer cells: An in vivo and in vitro study. Gastric Cancer.
19:817–826. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li S, Dai W, Mo W, Li J, Feng J, Wu L, Liu
T, Yu Q, Xu S, Wang W, et al: By inhibiting PFKFB3, aspirin
overcomes sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 141:2571–2584. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|