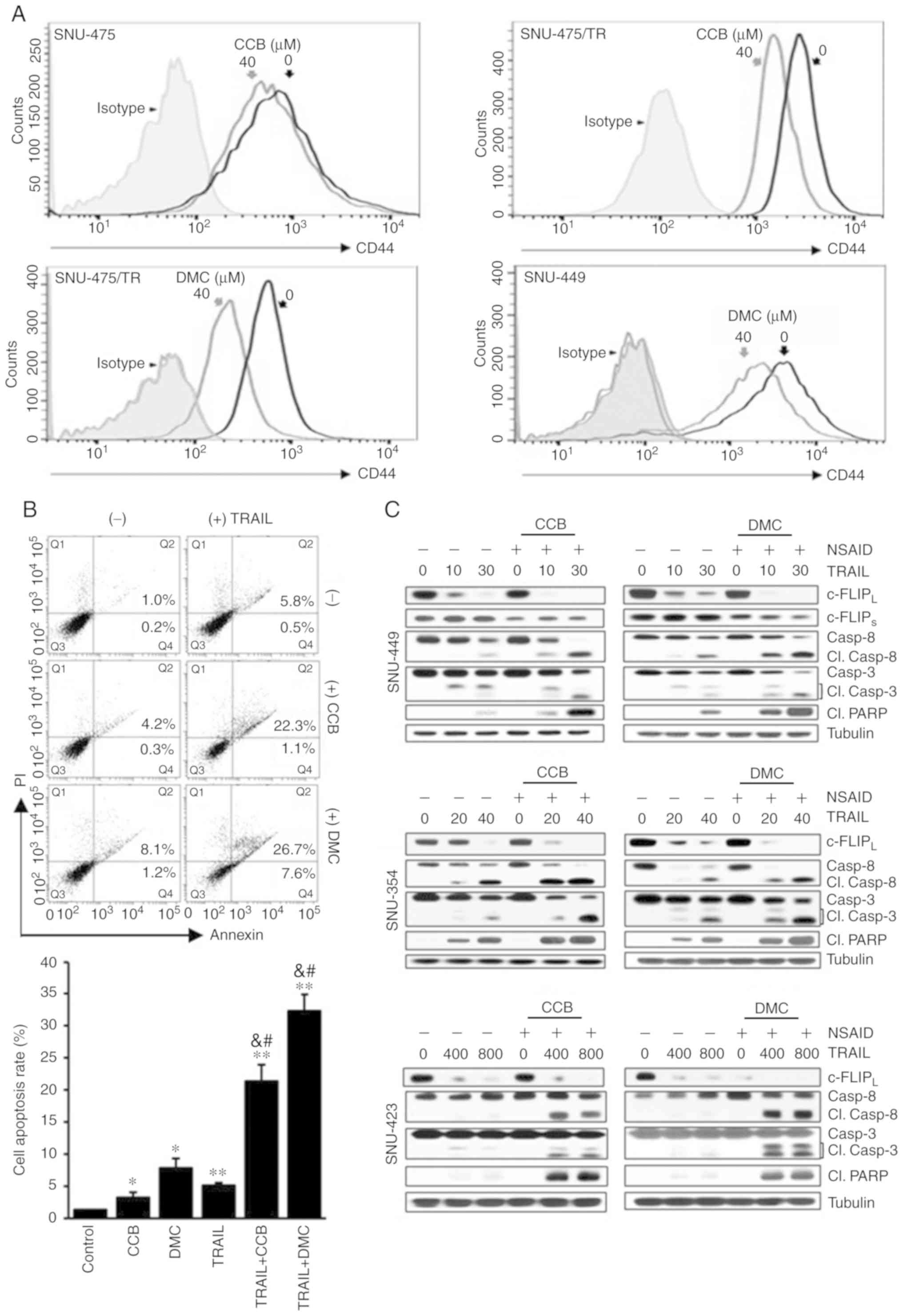
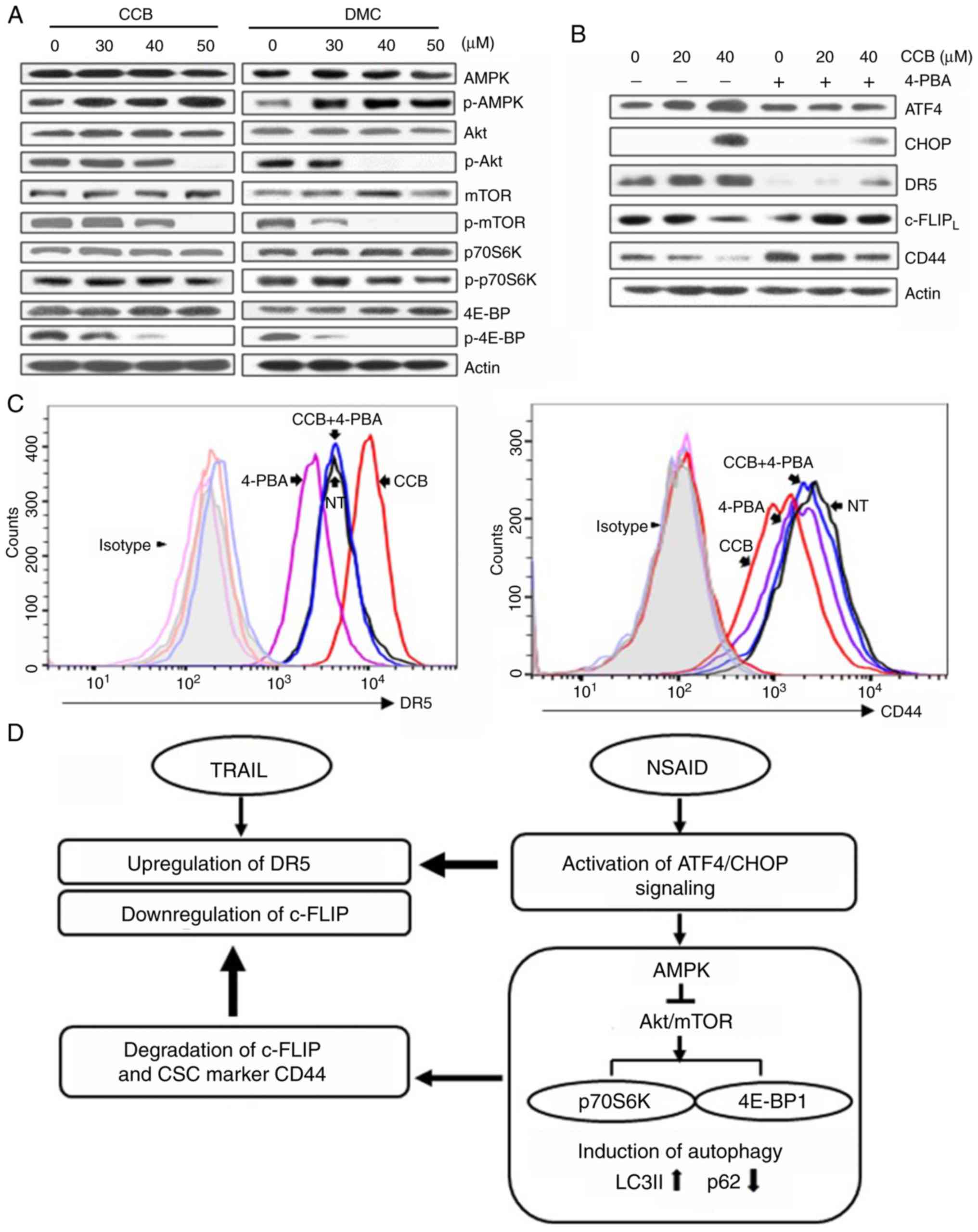
|
1
|
Chen S, Cao Q, Wen W and Wang H: Targeted
therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Challenges and opportunities.
Cancer Lett. 460:1–9. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jiang W, Wu DB, Fu SY, Chen EQ, Tang H and
Zhou TY: Insight into the role of TRAIL in liver diseases. Biomed
Pharmacother. 110:641–645. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Trivedi R and Mishra DP: Trailing TRAIL
resistance: Novel targets for TRAIL sensitization in cancer cells.
Front Oncol. 5:692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang Y, Yang X, Xu T, Kong Q, Zhang Y,
Shen Y, Wei Y, Wang G and Chang KJ: Overcoming resistance to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis in solid tumor cells by simultaneously
targeting death receptors, c-FLIP and IAPs. Int J Oncol.
49:153–163. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Koehler BC, Urbanik T, Vick B, Boger RJ,
Heeger S, Galle PR, Schuchmann M and Schulze-Bergkamen H:
TRAIL-induced apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells is
augmented by targeted therapies. World J Gastroenterol.
15:5924–5935. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim S, Seo SU, Min KJ, Woo SM, Nam JO,
Kubatka P, Kim S, Park JW and Kwon TK: Garcinol enhances
TRAIL-induced apoptotic cell death through up-regulation of DR5 and
down-regulation of c-FLIP expression. Molecules. 23:16142018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jeon MY, Min KJ, Woo SM, Seo SU, Choi YH,
Kim SH, Kim DE, Lee TJ, Kim S, Park JW and Kwon TK: Maritoclax
enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis via CHOP-mediated ipregulation of
DR5 and miR-708-mediated downregulation of cFLIP. Molecules.
23:3030–3043. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Bettigole SE and
Glimcher LH: Tumorigenic and Immunosuppressive effects of
endoplasmic reticulum stress in cancer. Cell. 168:692–706. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Noh HJ, Lee SJ, Sung EG, Song IH, Kim JY,
Woo CH, Kwon TK and Lee TJ: CHOP down-regulates cFLIP(L) expression
by promoting ubiquitin/proteasome-mediated cFLIP(L) degradation. J
Cell Biochem. 113:3692–3700. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sheng J, Qin H, Zhang K, Li B and Zhang X:
Targeting autophagy in chemotherapy-resistant of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 8:354–365. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen L, Meng Y, Sun Q, Zhang Z, Guo X,
Sheng X, Tai G, Cheng H and Zhou Y: Ginsenoside compound K
sensitizes human colon cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via
autophagy-dependent and -independent DR5 upregulation. Cell Death
Dis. 7:e23342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu J, Xu X, Shi S, Wang Q, Saxton B, He W,
Gou X, Jang JH, Nyunoya T, Wang X, et al: Autophagy-mediated
degradation of IAPs and c-FLIP(L) potentiates apoptosis induced by
combination of TRAIL and Chal-24. J Cell Biochem. 117:1136–1144.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Duffy A, Le J, Sausville E and Emadi A:
Autophagy modulation: A target for cancer treatment development.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 75:439–447. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Z, Chen F and Shang L: Advances in
antitumor effects of NSAIDs. Cancer Manag Res. 10:4631–4640. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Endo H, Yano M, Okumura Y and Kido H:
Ibuprofen enhances the anticancer activity of cisplatin in lung
cancer cells by inhibiting the heat shock protein 70. Cell Death
Dis. 5:e10272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu C, Li WB, Liu JB, Lu JW and Feng JF:
Autophagy: Novel applications of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs for primary cancer. Cancer Med. 7:471–484. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ku JL and Park JG: Biology of SNU cell
lines. Cancer Res Treat. 37:1–19. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rozeik MS, Hammam OA, Ali AI, Magdy M,
Khalil H, Anas A, Abo El Hassan AA, Rahim AA and El-Shabasy AI:
Evaluation of CD44 and CD133 as markers of liver cancer stem cells
in Egyptian patients with HCV-induced chronic liver diseases versus
hepatocellular carcinoma. Electron Physician. 9:4708–4717. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee SH, Hyun SK, Kim HB, Kang CD and Kim
SH: Potential role of CD133 expression in the susceptibility of
human liver cancer stem-like cells to TRAIL. Oncol Res. 24:495–509.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pennarun B, Kleibeuker JH, Boersma-van Ek
W, Kruyt FA, Hollema H, de Vries EG and de Jong S: Targeting FLIP
and Mcl-1 using a combination of aspirin and sorafenib sensitizes
colon cancer cells to TRAIL. J Pathol. 229:410–421. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee JY, Jung KH, Morgan MJ, Kang YR, Lee
HS, Koo GB, Hong SS, Kwon SW and Kim YS: Sensitization of
TRAIL-induced cell death by 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3 via CHOP-mediated
DR5 upregulation in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 12:274–285. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hassanzadeh A, Farshdousti Hagh M, Alivand
MR, Akbari AAM, Shams Asenjan K, Saraei R and Solali S:
Down-regulation of intracellular anti-apoptotic proteins,
particularly c-FLIP by therapeutic agents; the novel view to
overcome resistance to TRAIL. J Cell Physiol. 233:6470–6485. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nazim UM, Jeong JK and Park SY:
Ophiopogonin B sensitizes TRAIL-induced apoptosis through
activation of autophagy flux and downregulates cellular FLICE-like
inhibitory protein. Oncotarget. 9:4161–4172. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He MX and He YW: c-FLIP protects T
lymphocytes from apoptosis in the intrinsic pathway. J Immunol.
194:3444–3451. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang P and Mizushima N: LC3- and
p62-based biochemical methods for the analysis of autophagy
progression in mammalian cells. Methods. 75:13–18. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Su M, Mei Y and Sinha S: Role of the
Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis in Cancer. J Oncol.
2013:1027352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nanbu T, Umemura N, Ohkoshi E, Nanbu K,
Sakagami H and Shimada J: Combined SN-38 and gefitinib treatment
promotes CD44 degradation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
cells. Oncol Rep. 39:367–375. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Matter MS, Decaens T, Andersen JB and
Thorgeirsson SS: Targeting the mTOR pathway in hepatocellular
carcinoma: Current state and future trends. J Hepatol. 60:855–865.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Umar A, Steele VE, Menter DG and Hawk ET:
Mechanisms of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in cancer
prevention. Semin Oncol. 43:65–77. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jendrossek V: Targeting apoptosis pathways
by Celecoxib in cancer. Cancer Lett. 332:313–324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Song S, Tan J, Miao Y, Li M and Zhang Q:
Crosstalk of autophagy and apoptosis: Involvement of the dual role
of autophagy under ER stress. J Cell Physiol. 232:2977–2984. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Matsumoto H, Miyazaki S, Matsuyama S,
Takeda M, Kawano M, Nakagawa H, Nishimura K and Matsuo S: Selection
of autophagy or apoptosis in cells exposed to ER-stress depends on
ATF4 expression pattern with or without CHOP expression. Biol Open.
2:1084–1090. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
B'chir W, Chaveroux C, Carraro V, Averous
J, Maurin AC, Jousse C, Muranishi Y, Parry L, Fafournoux P and
Bruhat A: Dual role for CHOP in the crosstalk between autophagy and
apoptosis to determine cell fate in response to amino acid
deprivation. Cell Signal. 26:1385–1391. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen Y, Zhou X, Qiao J and Bao A:
Autophagy is a regulator of TRAIL-induced apoptosis in NSCLC A549
cells. J Cell Commun Signal. 11:219–226. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen L, Meng Y, Guo X, Sheng X, Tai G,
Zhang F, Cheng H and Zhou Y: Gefitinib enhances human colon cancer
cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis of via autophagy- and JNK-mediated
death receptors upregulation. Apoptosis. 21:1291–1301. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Moon HJ, Park SY, Lee SH, Kang CD and Kim
SH: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs sensitize
CD44-overexpressing cancer cells to Hsp90 inhibitor through
autophagy activation. Oncol Res. 27:835–847. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nazio F, Bordi M, Cianfanelli V, Locatelli
F and Cecconi F: Autophagy and cancer stem cells: Molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Cell Death Differ.
26:690–702. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hegazy AM, Yamada D, Kobayashi M, Kohno S,
Ueno M, Ali MA, Ohta K, Tadokoro Y, Ino Y, Todo T, et al:
Therapeutic strategy for targeting aggressive malignant gliomas by
disrupting their energy balance. J Biol Chem. 291:21496–21509.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kumar D, Shankar S and Srivastava RK:
Rottlerin-induced autophagy leads to the apoptosis in breast cancer
stem cells: Molecular mechanisms. Mol Cancer. 12:1712013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ji J and Wang XW: Clinical implications of
cancer stem cell biology in hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Oncol.
39:461–472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Luo Y and Tan Y: Prognostic value of CD44
expression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma:
Meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 16:472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bhattacharya S, Yin J, Winborn CS, Zhang
Q, Yue J and Chaum E: Prominin-1 is a novel regulator of autophagy
in the human retinal pigment epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
58:2366–2387. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Haakenson JK, Khokhlatchev AV, Choi YJ,
Linton SS, Zhang P, Zaki PM, Fu C, Cooper TK, Manni A, Zhu J, et
al: Lysosomal degradation of CD44 mediates ceramide
nanoliposome-induced anoikis and diminished extravasation in
metastatic carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 290:8632–8643. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu W, Schecker J, Würstle S, Schneider F,
Schönfelder M and Schlegel J: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A3 (ALDH1A3)
is regulated by autophagy in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Lett.
417:112–123. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Akrami H, Moradi B, Borzabadi Farahani D
and Mehdizadeh K: Ibuprofen reduces cell proliferation through
inhibiting Wnt/β catenin signaling pathway in gastric cancer stem
cells. Cell Biol Int. 42:949–958. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|