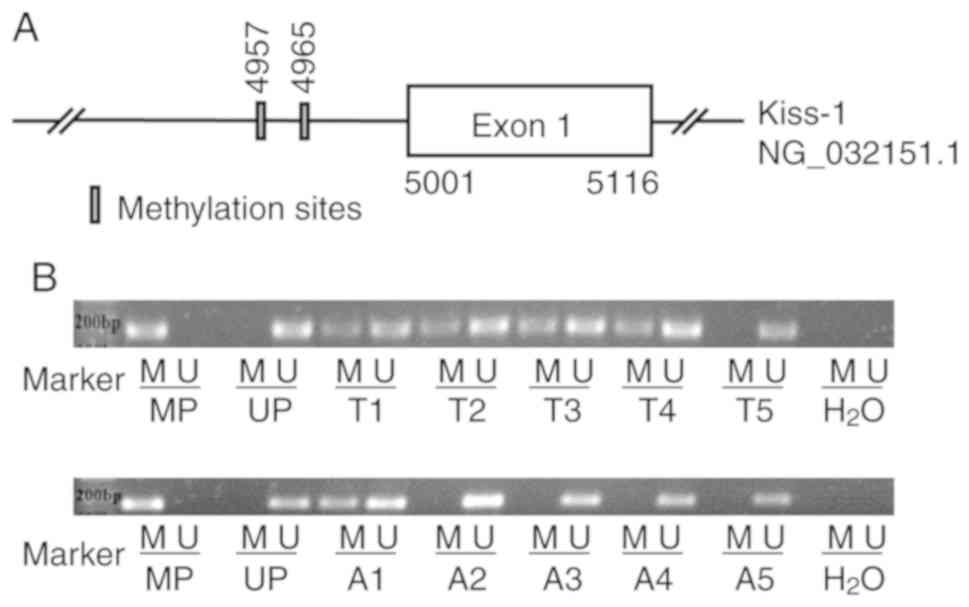
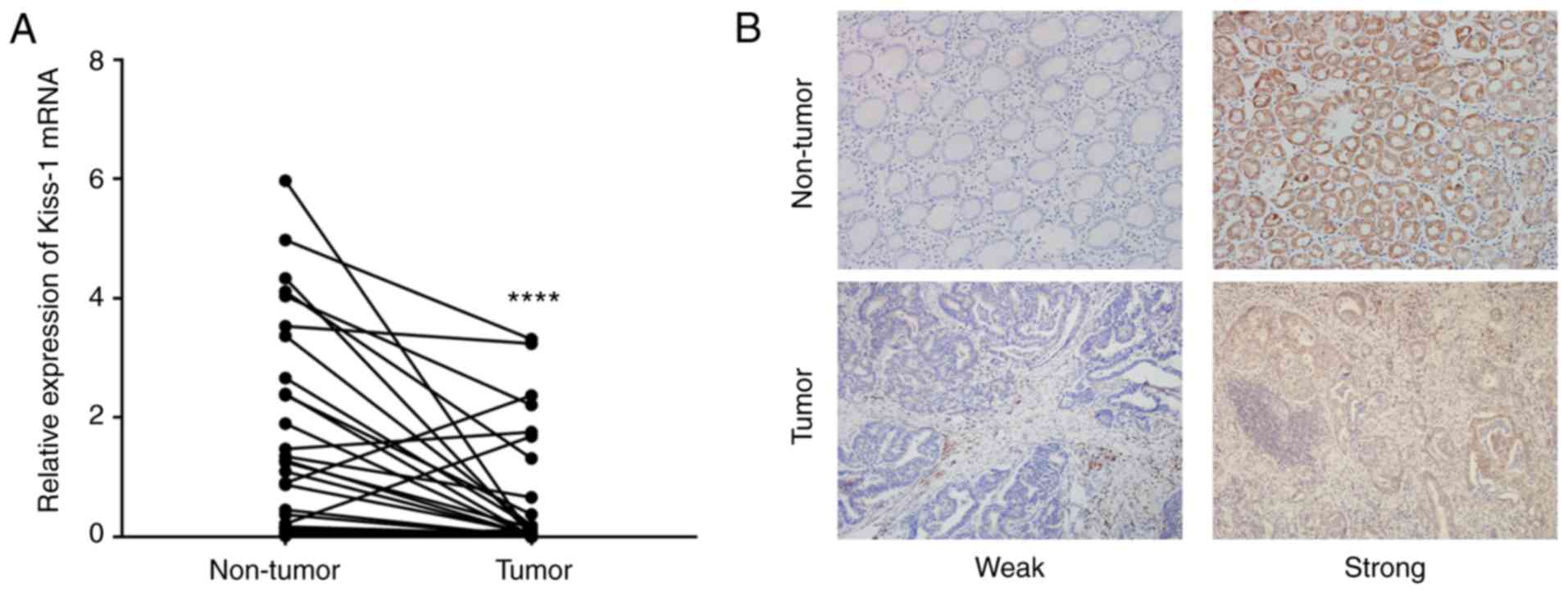
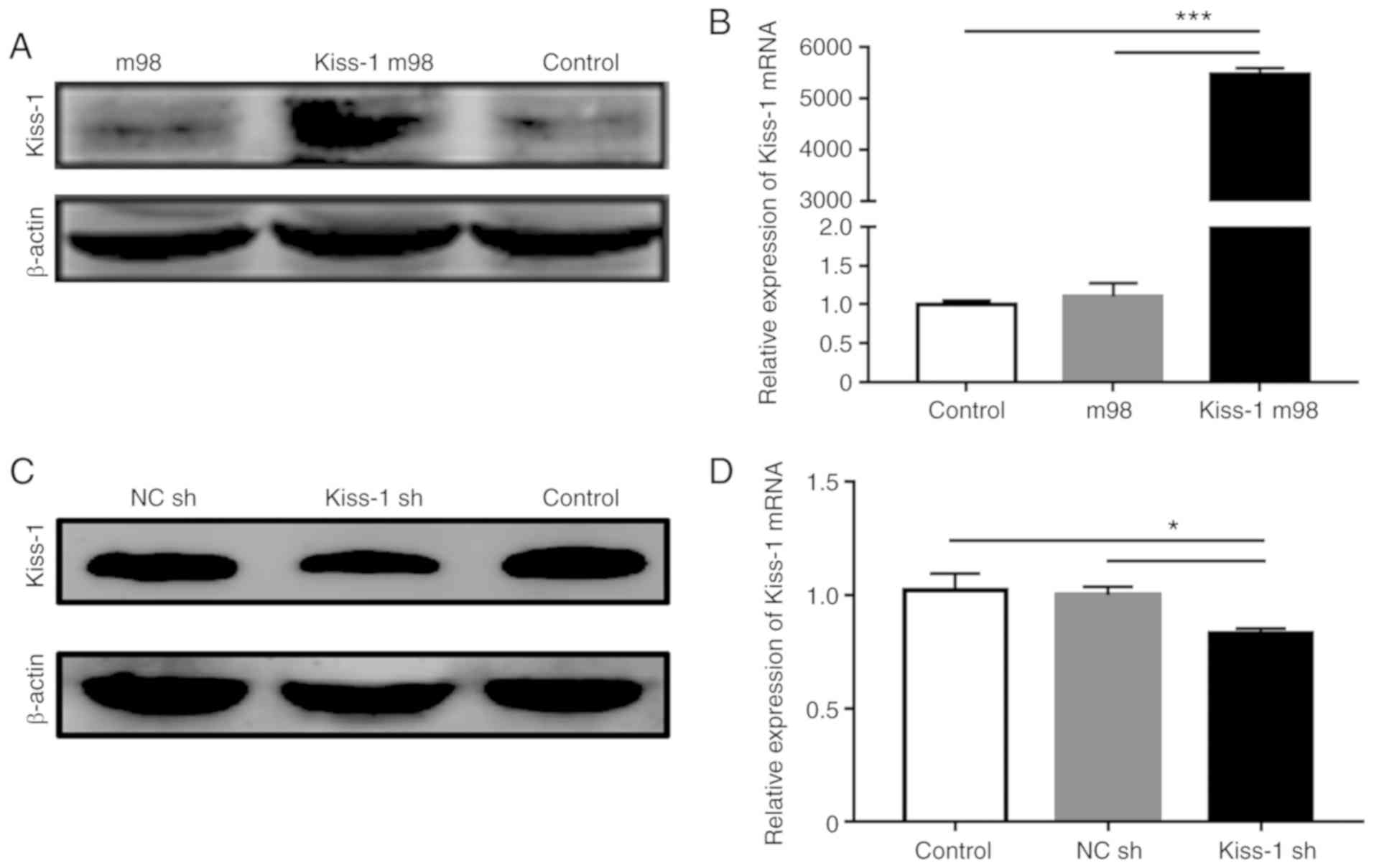
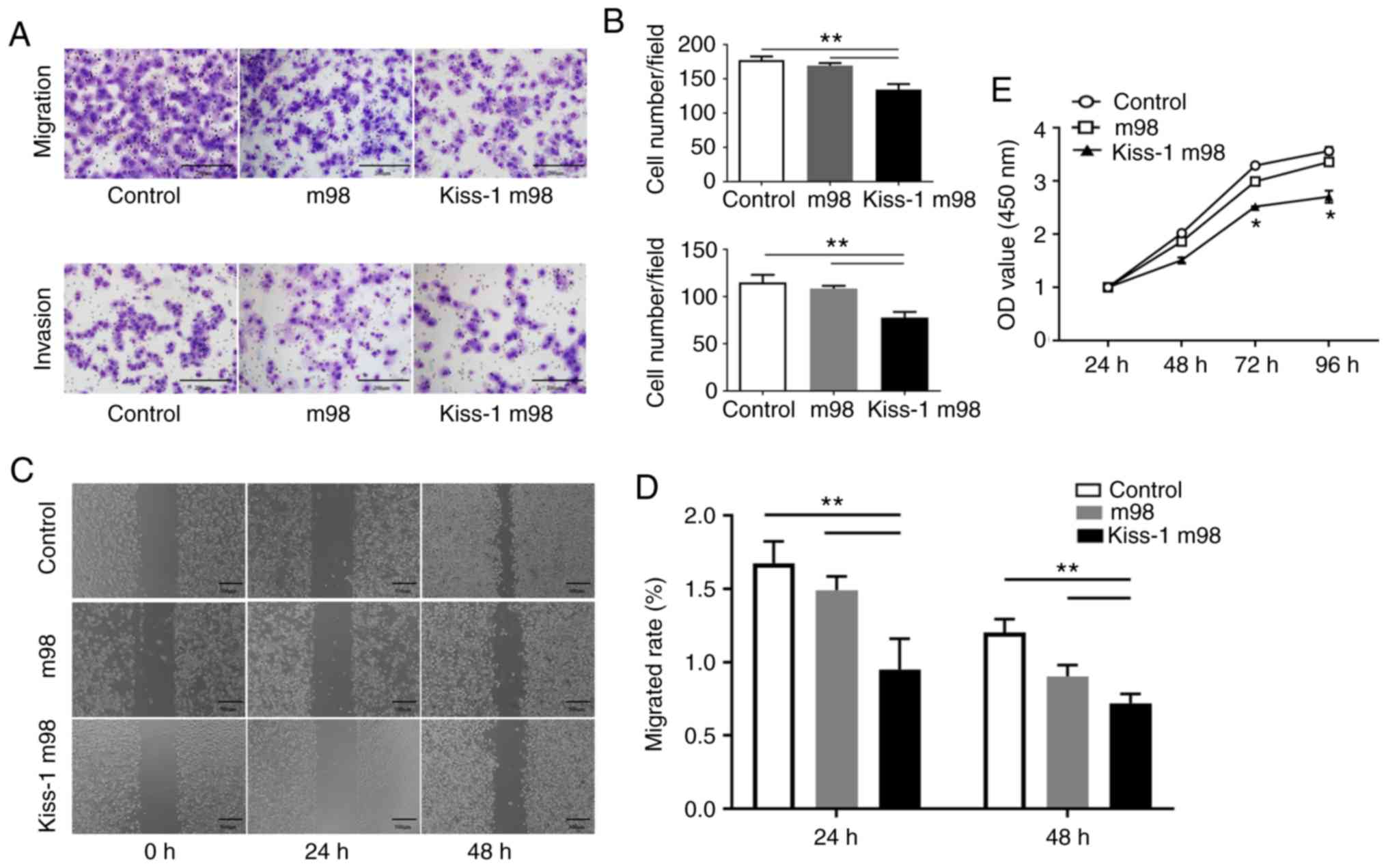
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Sun K, Zheng R, Zeng H, Zhang S,
Xia C, Yang Z, Li H, Zou X and He J: Cancer incidence and mortality
in China, 2014. Chin J Cancer Res. 30:1–12. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Samant RS, Seraj MJ, Saunders MM, Sakamaki
TS, Shevde LA, Harms JF, Leonard TO, Goldberg SF, Budgeon L, Meehan
WJ, et al: Analysis of mechanisms underlying BRMS1 suppression of
metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 18:683–693. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee JH, Miele ME, Hicks DJ, Phillips KK,
Trent JJM, Weissman BE and Welch DR: KiSS-1, a novel human
malignant melanoma metastasis-suppressor gene. J Natl Cancer Inst.
88:1731–1737. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Clements MK, McDonald TP, Wang R, Xie G,
O'Dowd BF, George SR, Austin CP and Liu Q: FMRFamide-related
neuropeptides are agonists of the orphan G-protein-coupled receptor
GPR54. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 284:1189–1193. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stafford LJ, Xia C, Ma W, Cai Y and Liu M:
Identification and characterization of mouse metastasis-suppressor
KiSS1 and its G-protein-coupled receptor. Cancer Res. 62:5399–5404.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang Y, Huang Z, Zhu Z, Zheng X, Liu J,
Han Z, Ma X and Zhang Y: Upregulated UHRF1 promotes bladder cancer
cell invasion by epigenetic silencing of KiSS1. PLoS One.
9:e1042522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moya P, Esteban S, Fernandez-Suarez A,
Maestro M, Morente M and Sánchez-Carbayo M: KiSS-1 methylation and
protein expression patterns contribute to diagnostic and prognostic
assessments in tissue specimens for colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol.
34:471–479. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Teng Y, Mei Y, Hawthorn L and Cowell JK:
WASF3 regulates miR-200 inactivation by ZEB1 through suppression of
KISS1 leading to increased invasiveness in breast cancer cells.
Oncogene. 33:203–211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yamashita S, Tsujino Y, Moriguchi K,
Tatematsu M and Ushijima T: Chemical genomic screening for
methylation-silenced genes in gastric cancer cell lines using
5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine treatment and oligonucleotide microarray.
Cancer Sci. 97:64–71. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wolf K, Wu YI, Liu Y, Geiger J, Tam E,
Overall C, Stack MS and Friedl P: Multi-step pericellular
proteolysis controls the transition from individual to collective
cancer cell invasion. Nat Cell Biol. 9:893–904. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hou JM, Krebs M, Ward T, Sloane R, Priest
L, Hughes A, Clack G, Ranson M, Blackhall F and Dive C: Circulating
tumor cells as a window on metastasis biology in lung cancer. Am J
Pathol. 178:989–996. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kienast Y, von Baumgarten L, Fuhrmann M,
Klinkert WEF, Goldbrunner R, Herms J and Winkler F: Real-time
imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis formation. Nat
Med. 16:116–122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee JH and Welch DR: Suppression of
metastasis in human breast carcinoma MDA-MB-435 cells after
transfection with the metastasis suppressor gene, KiSS-1. Cancer
Res. 57:2384–2387. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee JH and Welch DR: Identification of
highly expressed genes in metastasis-suppressed chromosome 6/human
malignant melanoma hybrid cells using subtractive hybridization and
differential display. Int J Cancer. 71:1035–1044. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kotani M, Detheux M, Vandenbogaerde A,
Communi D, Vanderwinden JM, Poul EL, Brézillon S, Tyldesley R,
Suarez-Huerta N, Vandeput F, et al: The metastasis suppressor gene
KiSS-1 encodes kisspeptins, the natural ligands of the orphan G
protein-coupled receptor GPR54. J Biol Chem. 276:34631–34636. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ohtaki T, Shintani Y, Honda S, Matsumoto
H, Hori A, Kanehashi K, Terao Y, Kumano S, Takatsu Y, Masuda Y, et
al: Metastasis suppressor gene KiSS-1 encodes peptide ligand of a
G-protein-coupled receptor. Nature. 411:613–617. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fang JY and Lu YY: Effects of histone
acetylation and DNA methylation on p21( WAF1) regulation. World J
Gastroenterol. 8:400–405. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kumar R and Xi Y: MicroRNA, epigenetic
machinery and lung cancer. Thora Cancer. 2:35–44. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen SQ, Chen ZH, Lin SY, Dai QB, Fu LX
and Chen RQ: KISS1 methylation and expression as predictors of
disease progression in colorectal cancer patients. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:10071–10081. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cebrian V, Fierro M, Orenes-Piñero E, Grau
L, Moya P, Ecke T, Alvarez M, Gil M, Algaba F, Bellmunt J, et al:
KISS1 methylation and expression as tumor stratification biomarkers
and clinical outcome prognosticators for bladder cancer patients.
Am J Pathol. 179:540–546. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kostakis ID, Agrogiannis G, Vaiopoulos AG,
Mylona E, Patsouris E, Kouraklis G and Koutsilieris M: KISS1 and
KISS1R expression in gastric cancer. J BUON. 23:79–84.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kostakis ID, Agrogiannis G, Vaiopoulos AG,
Mylona E, Patsouris E, Kouraklis G and Koutsilieris M: A
clinicopathological analysis of KISS1 and KISS1R expression in
colorectal cancer. APMIS. 123:629–637. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ji K, Ye L, Ruge F, Hargest R, Mason MD
and Jiang WG: Implication of metastasis suppressor gene, Kiss-1 and
its receptor Kiss-1R in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 14:7232014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huo X, Zhang L and Li T: Analysis of the
association of the expression of KiSS-1 in colorectal cancer
tissues with the pathology and prognosis. Oncol Lett. 15:3056–3060.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guan Z, Zhang J, Song S and Dai D:
Promoter methylation and expression of TIMP3 gene in gastric
cancer. Diagn Pathol. 8:1102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee KH and Kim JR: Kiss-1 suppresses MMP-9
expression by activating p38 MAP kinase in human stomach cancer.
Oncol Res. 18:107–116. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen S, Chen W, Zhang X, Lin S and Chen Z:
Overexpression of KiSS-1 reduces colorectal cancer cell invasion by
downregulating MMP-9 via blocking PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signal pathway.
Int J Oncol. 48:1391–1398. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang CH, Qiao C, Wang RC and Zhou WP:
KiSS-1-mediated suppression of the invasive ability of human
pancreatic carcinoma cells is not dependent on the level of KiSS-1
receptor GPR54. Mol Med Rep. 13:123–129. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jiang Y, Berk M, Singh LS, Tan H, Yin L,
Powell CT and Xu Y: KiSS1 suppresses metastasis in human ovarian
cancer via inhibition of protein kinase C alpha. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 22:369–376. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang H, Jones J, Turner T, He QP, Hardy S,
Grizzle WE, Welch DR and Yates C: Clinical and biological
significance of KISS1 expression in prostate cancer. Am J Pathol.
180:1170–1178. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kang HS, Baba T, Mandai M, Matsumura N,
Hamanishi J, Kharma B, Kondoh E, Yoshioka Y, Oishi S, Fujii N, et
al: GPR54 is a target for suppression of metastasis in endometrial
cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:580–590. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang GM, Liu JF, Zhang L, Sun Q, Zhou Y,
Xu HB, Zhang YJ, Cai F, Cheng ZN, Xiang P and Jiang H: Inhibition
of KiSS-1 on metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma implant tumor
in nude mice. Am J Transl Res. 11:904–910. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|