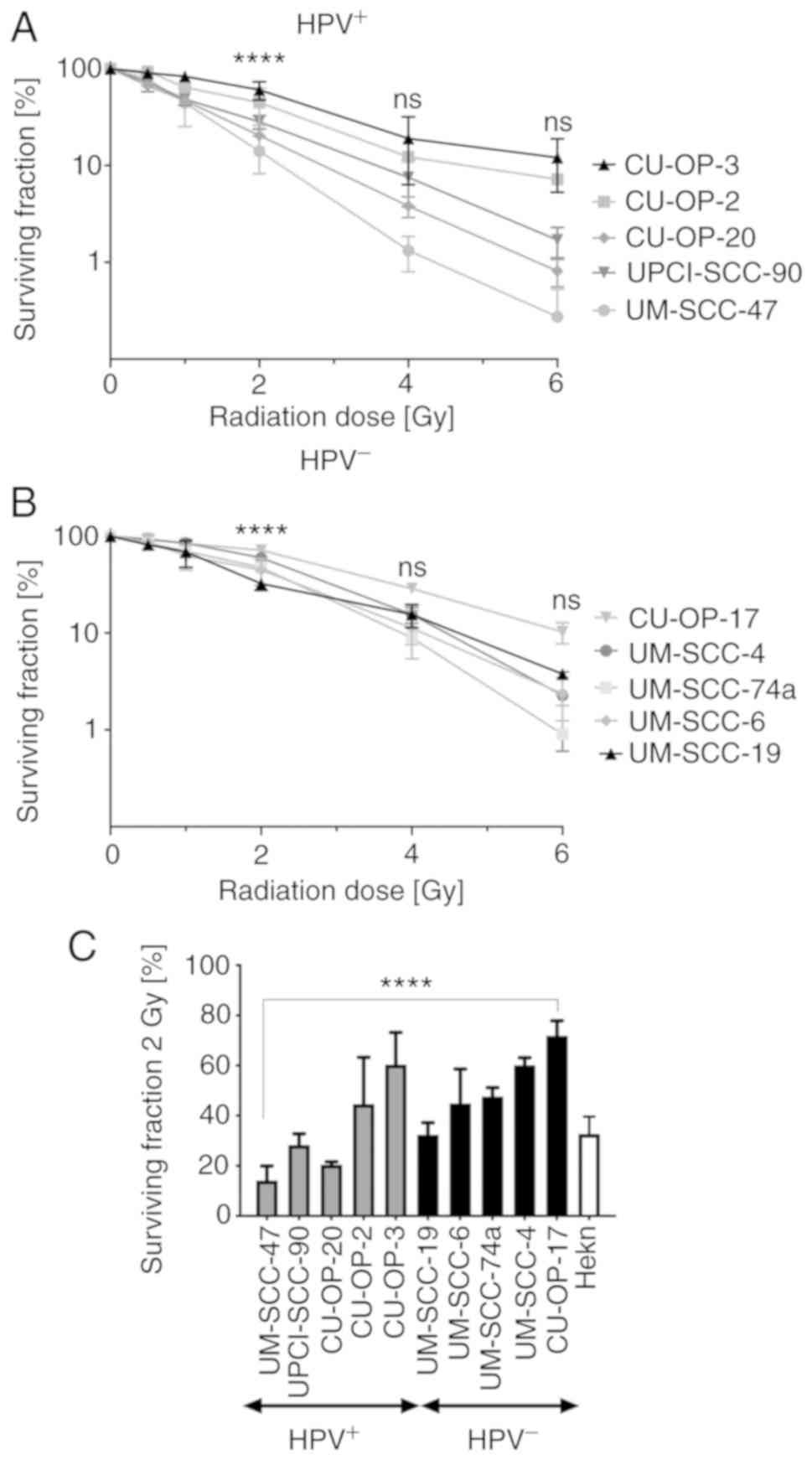
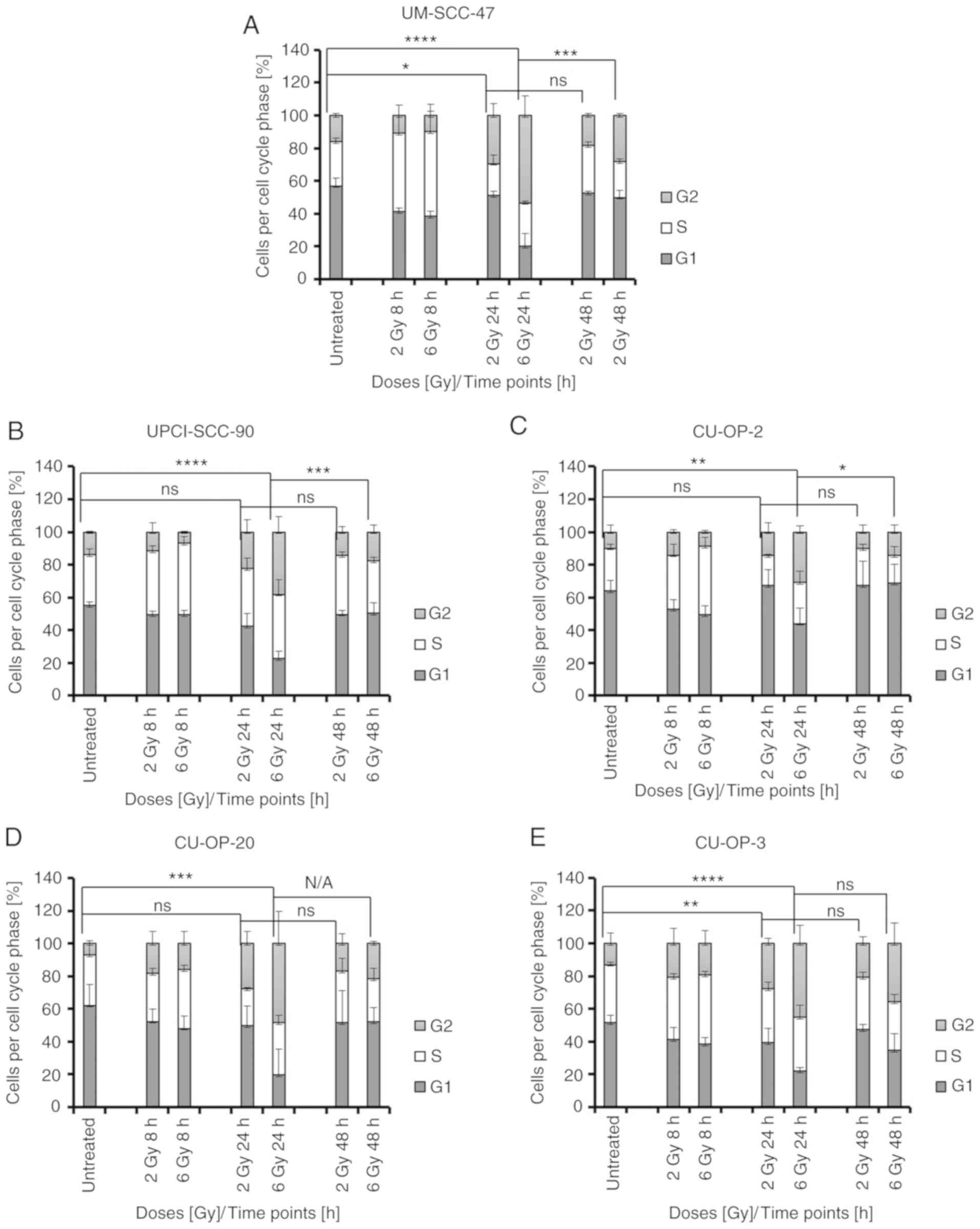
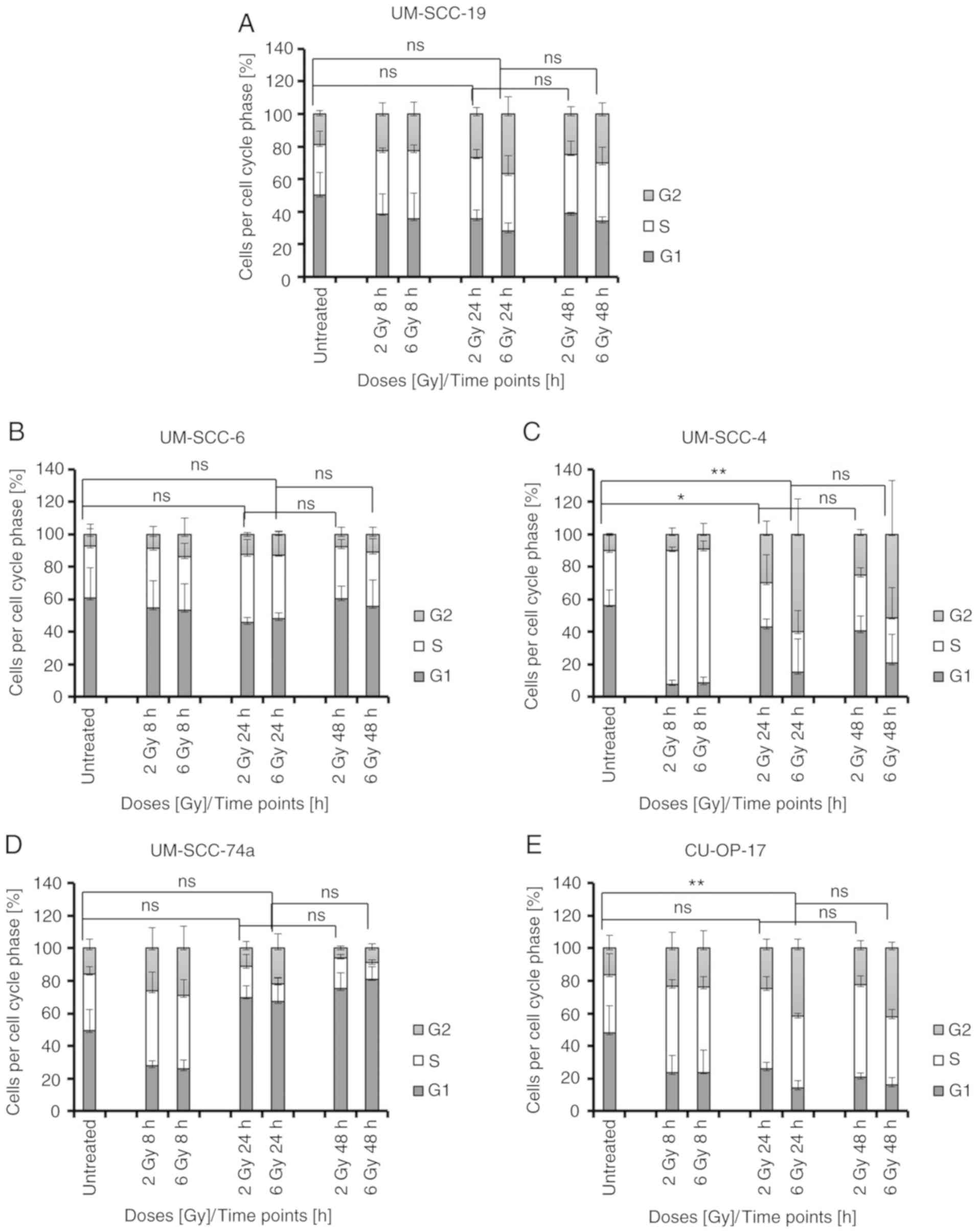
|
1
|
Evans M, Newcombe R, Fiander A, Powell J,
Rolles M, Thavaraj S, Robinson M and Powell N: Human
papillomavirus-associated oropharyngeal cancer: An observational
study of diagnosis, prevalence and prognosis in a UK population.
BMC Cancer. 13:2202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Haeggblom L, Attoff T, Yu J, Holzhauser S,
Vlastos A, Mirzae L, Ährlund-Richter A, Munck-Wikland E, Marklund
L, Hammarstedt-Nordenvall L, et al: Changes in incidence and
prevalence of human papillomavirus in tonsillar and base of tongue
cancer during 2000–2016 in the Stockholm region and Sweden. Head
Neck. 41:1583–1590. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Näsman A, Nordfors C, Holzhauser S,
Vlastos A, Tertipis N, Hammar U, Hammarstedt-Nordenvall L, Marklund
L, Munck-Wikland E, Ramqvist T, et al: Incidence of human
papillomavirus positive tonsillar and base of tongue carcinoma: A
stabilisation of an epidemic of viral induced carcinoma? Eur J
Cancer. 51:55–61. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chaturvedi AK, Engels EA, Pfeiffer RM,
Hernandez BY, Xiao W, Kim E, Jiang B, Goodman MT, Sibug-Saber M,
Cozen W, et al: Human papillomavirus and rising oropharyngeal
cancer incidence in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 29:4294–4301.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Näsman A, Du J and Dalianis T: A global
epidemic increase of an HPV-induced tonsil and tongue base
cancer-potential benefit from a pan-gender use of HPV vaccine. J
Intern Med. 287:134–152. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mellin H, Friesland S, Lewensohn R,
Dalianis T and Munck-Wikland E: Human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA in
tonsillar cancer: Clinical correlates, risk of relapse, and
survival. Int J Cancer. 89:300–304. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schache AG, Powell NG, Cuschieri KS,
Robinson M, Leary S, Mehanna H, Rapozo D, Long A, Cubie H, Junor E,
et al: HPV-related oropharynx cancer in the United Kingdom: An
evolution in the understanding of disease etiology. Cancer Res.
76:6598–6606. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schache AG, Simcock R, Gilbert DC and Shaw
RJ: Changing face of HPV related cancer in the UK. BMJ.
343:d66752011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bersani C, Mints M, Tertipis N, Haeggblom
L, Sivars L, Ährlund-Richter A, Vlastos A, Smedberg C, Grün N,
Munck-Wikland E, et al: A model using concomitant markers for
predicting outcome in human papillomavirus positive oropharyngeal
cancer. Oral Oncol. 68:53–59. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Owadally W, Hurt C, Timmins H, Parsons E,
Townsend S, Patterson J, Hutcheson K, Powell N, Beasley M,
Palaniappan N, et al: PATHOS: A phase II/III trial of
risk-stratified, reduced intensity adjuvant treatment in patients
undergoing transoral surgery for human papillomavirus (HPV)
positive oropharyngeal cancer. BMC Cancer. 15:6022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Arenz A, Ziemann F, Mayer C, Wittig A,
Dreffke K, Preising S, Wagner S, Klussmann JP, Engenhart-Cabillic R
and Wittekindt C: Increased radiosensitivity of HPV-positive head
and neck cancer cell lines due to cell cycle dysregulation and
induction of apoptosis. Strahlenther Onkol. 190:839–846. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kimple RJ, Smith MA, Blitzer GC, Torres
AD, Martin JA, Yang RZ, Peet CR, Lorenz LD, Nickel KP, Klingelhutz
AJ, et al: Enhanced radiation sensitivity in HPV-positive head and
neck cancer. Cancer Res. 73:4791–4800. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rieckmann T, Tribius S, Grob TJ, Meyer F,
Busch CJ, Petersen C, Dikomey E and Kriegs M: HNSCC cell lines
positive for HPV and p16 possess higher cellular radiosensitivity
due to an impaired DSB repair capacity. Radiother Oncol.
107:242–246. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vlashi E, Chen AM, Boyrie S, Yu G, Nguyen
A, Brower PA, Hess CB and Pajonk F: Radiation-induced
dedifferentiation of head and neck cancer cells into cancer stem
cells depends on human papillomavirus status. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 94:1198–1206. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang L, Wang X, Li Y, Han S, Zhu J, Wang
X, Molkentine DP, Blanchard P, Yang Y, Zhang R, et al: Human
papillomavirus status and the relative biological effectiveness of
proton radiotherapy in head and neck cancer cells. Head Neck.
39:708–715. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reid P, Wilson P, Li Y, Marcu LG,
Staudacher AH, Brown MP and Bezak E: Experimental investigation of
radiobiology in head and neck cancer cell lines as a function of
HPV status, by MTT assay. Sci Rep. 8:77442018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Reid P, Wilson P, Li Y, Marcu LG,
Staudacher AH, Brown MP and Bezak E: In vitro investigation of head
and neck cancer stem cell proportions and their changes following
X-ray irradiation as a function of HPV status. PLoS One.
12:e01861862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pirotte EF, Holzhauser S, Owens D, Quine
S, Al-Hussaini A, Christian AD, Giles PJ, Man ST, Evans M and
Powell NG: Sensitivity to inhibition of DNA repair by olaparib in
novel oropharyngeal cancer cell lines infected with human
papillomavirus. PLoS One. 13:e02079342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nordfors C, Vlastos A, Du J,
Ahrlund-Richter A, Tertipis N, Grün N, Romanitan M, Haeggblom L,
Roosaar A, Dahllöf G, et al: Human papillomavirus prevalence is
high in oral samples of patients with tonsillar and base of tongue
cancer. Oral Oncol. 50:491–497. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
West CM, Davidson SE, Roberts SA and
Hunter RD: Intrinsic radiosensitivity and prediction of patient
response to radiotherapy for carcinoma of the cervix. Br J Cancer.
68:819–823. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Watson JV, Chambers SH and Smith PJ: A
pragmatic approach to the analysis of DNA histograms with a
definable G1 peak. Cytometry. 8:1–8. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liao Y, Smyth GK and Shi W: FeatureCounts:
An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads
to genomic features. Bioinformatics. 30:923–930. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Robinson JT, Thorvaldsdottir H, Winckler
W, Guttman M, Lander ES, Getz G and Mesirov JP: Integrative
genomics viewer. Nat Biotechnol. 29:24–26. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false fiscovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
26
|
Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol I, Connors
J, Gascoyne R, Horsman D, Jones SJ and Marra MA: Circos: An
information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res.
19:1639–1645. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nulton TJ, Kim NK, DiNardo LJ, Morgan IM
and Windle B: Patients with integrated HPV16 in head and neck
cancer show poor survival. Oral Oncol. 80:52–55. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McBride AA and Warburton A: The role of
integration in oncogenic progression of HPV-associated cancers.
PLoS Pathog. 13:e10062112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Haeggblom L, Nordfors C, Tertipis N,
Bersani C, Ramqvist T, Näsman A and Dalianis T: Effects of
irradiation on human leukocyte antigen class I expression in human
papillomavirus positive and negative base of tongue and mobile
tongue squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Int J Oncol.
50:1423–1430. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Spanos WC, Nowicki P, Lee DW, Hoover A,
Hostager B, Gupta A, Anderson ME and Lee JH: Immune response during
therapy with cisplatin or radiation for human
papillomavirus-related head and neck cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head
Neck Surg. 135:1137–1146. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vermeer DW, Spanos WC, Vermeer PD, Bruns
AM, Lee KM and Lee JH: Radiation-induced loss of cell surface CD47
enhances immune-mediated clearance of human papillomavirus-positive
cancer. Int J Cancer. 133:120–129. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|