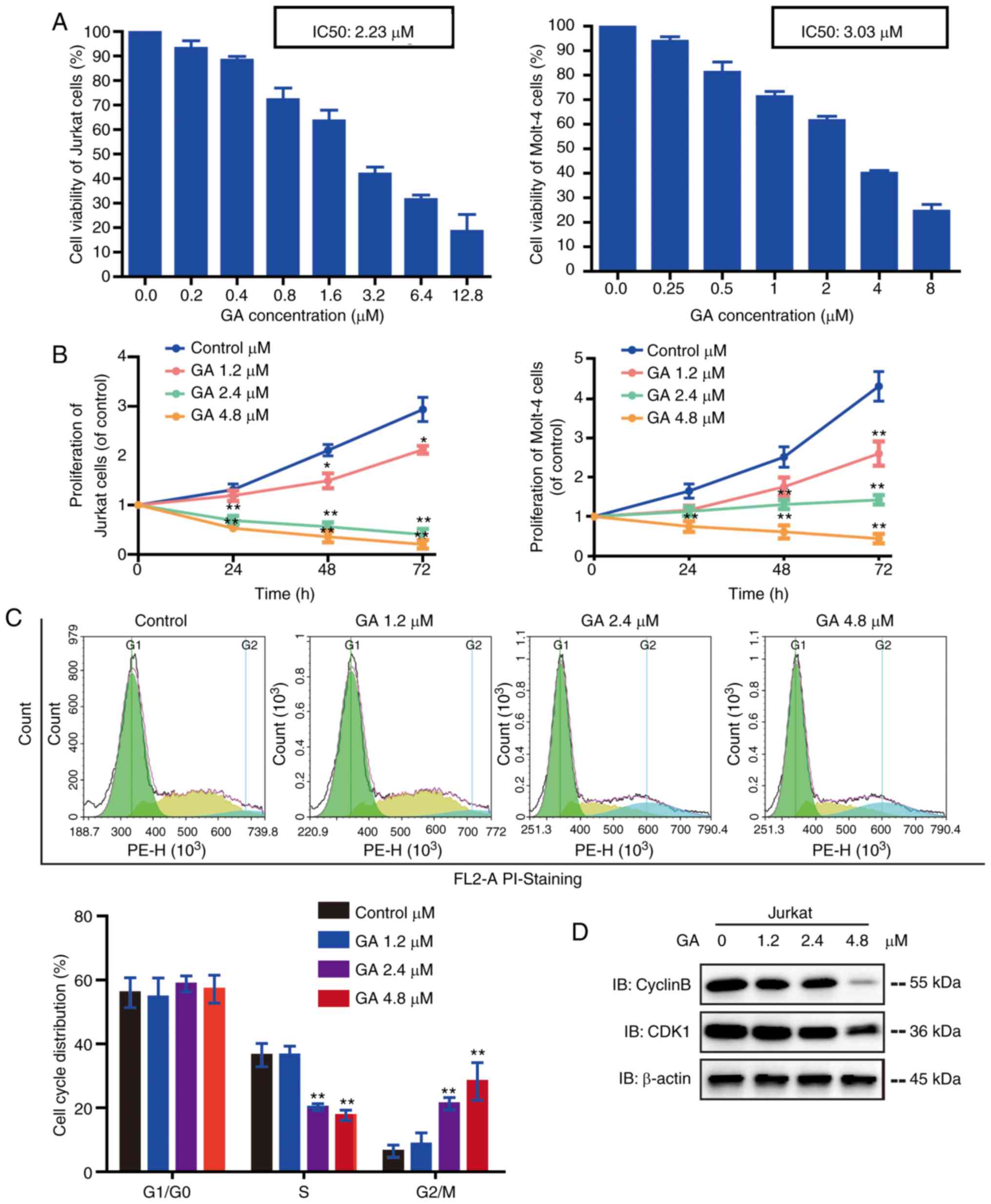
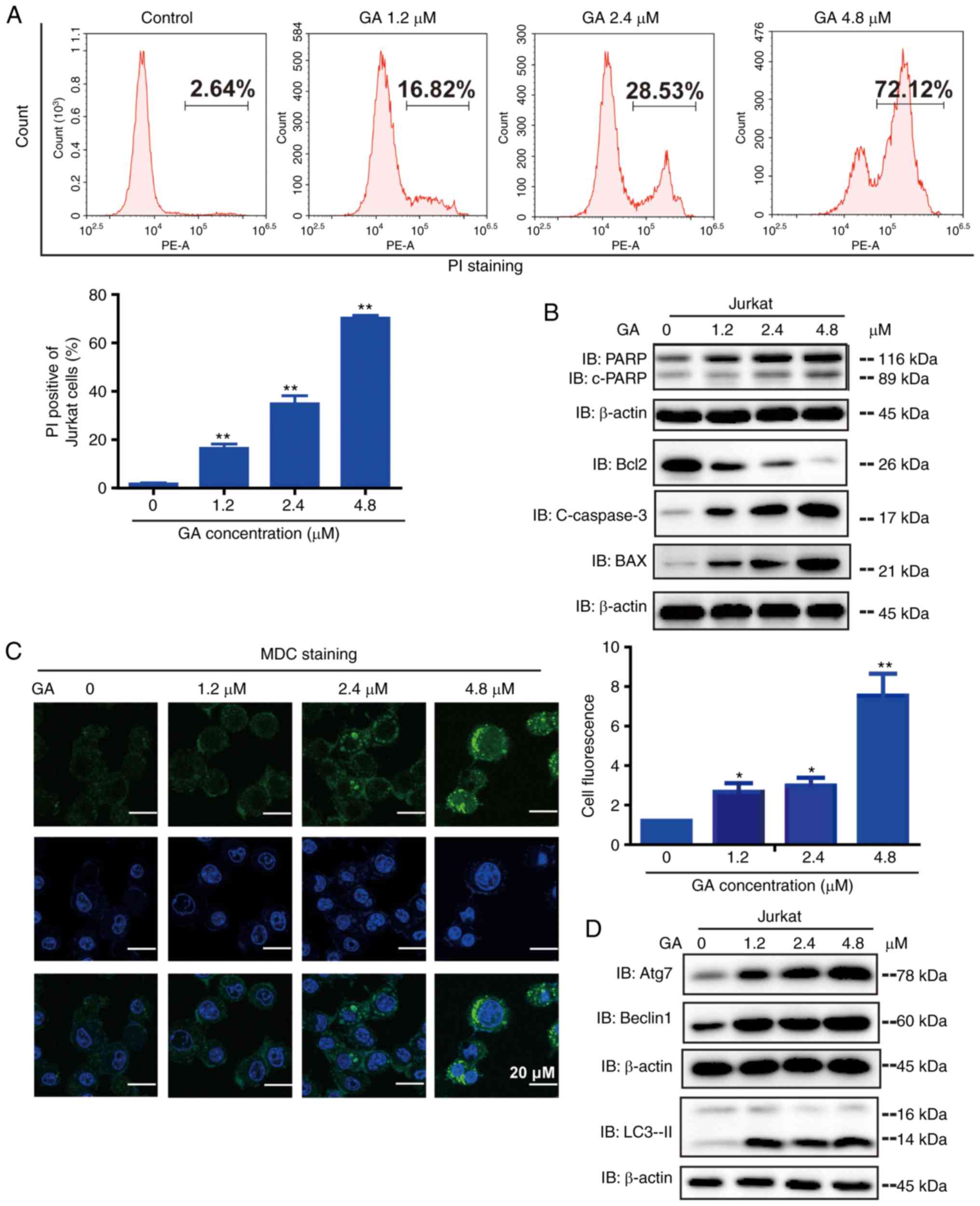
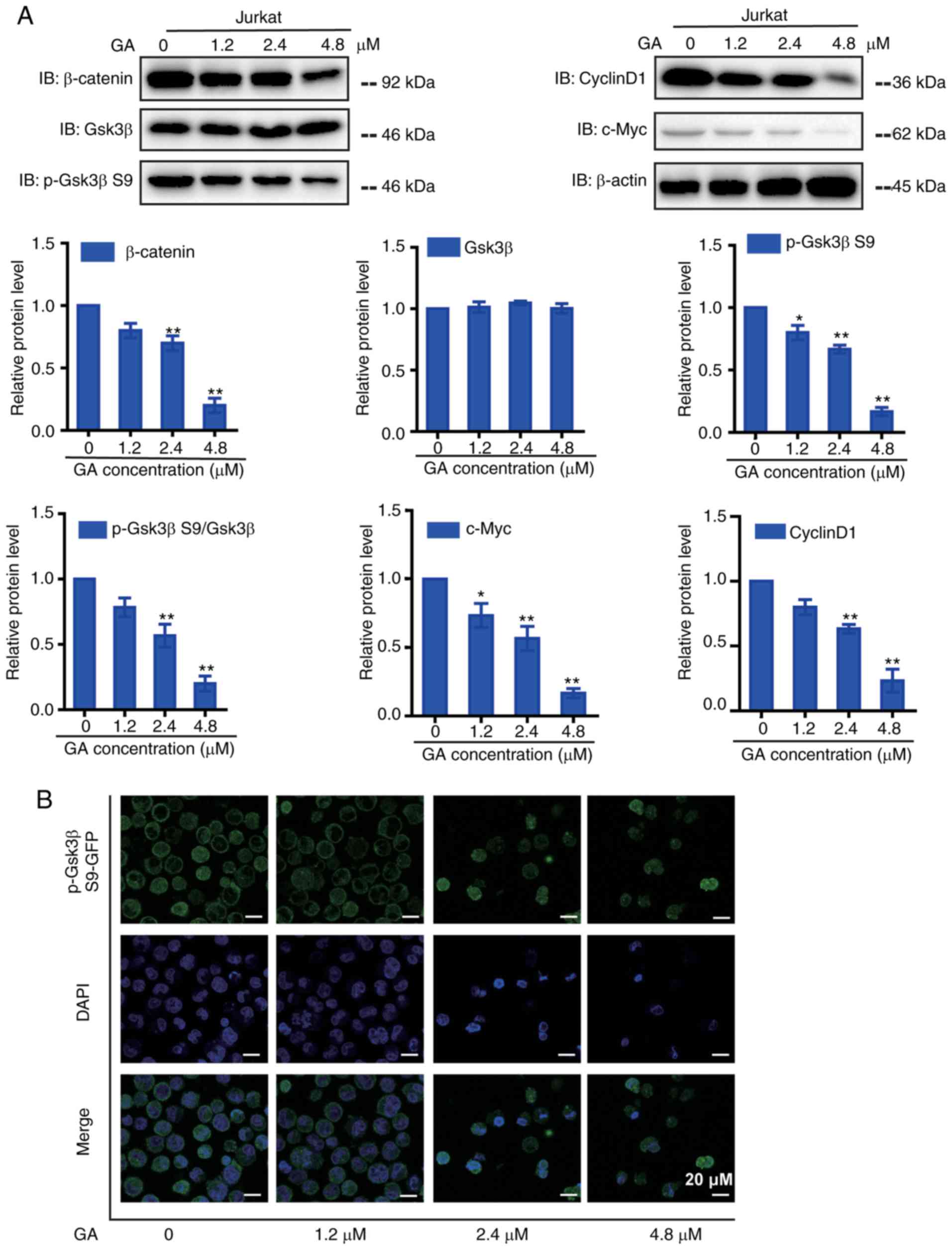
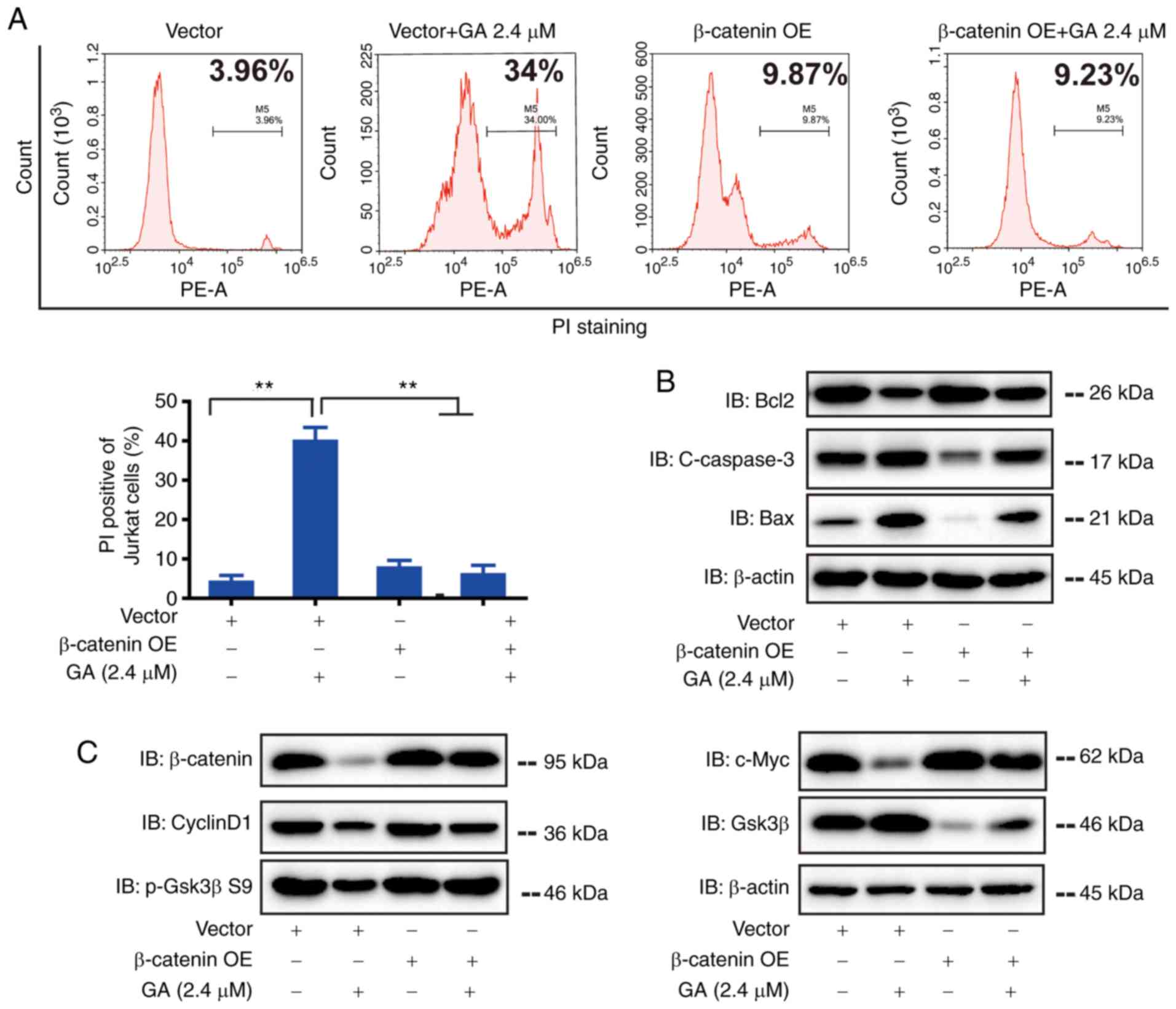
|
1
|
Belmonte M, Hoofd C, Weng AP and Giambra
V: Targeting leukemia stem cells: Which pathways drive self-renewal
activity in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia? Curr Oncol.
23:34–41. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Van Vlierberghe P and Ferrando A: The
molecular basis of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin
Invest. 122:3398–3406. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Coustan-Smith E, Song G, Clark C, Key L,
Liu P, Mehrpooya M, Stow P, Su X, Shurtleff S, Pui CH, et al: New
markers for minimal residual disease detection in acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 117:6267–6276. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pui CH, Carroll WL, Meshinchi S and Arceci
RJ: Biology, risk stratification, and therapy of pediatric acute
leukemias: An update. J Clin Oncol. 29:5512011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pui CH, Robison LL and Look AT: Acute
lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet. 371:1030–1043. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cailleteau C, Micallef L, Lepage C, Cardot
PJ, Beneytout JL, Liagre B and Battu S: Investigating the
relationship between cell cycle stage and diosgenin-induced
megakaryocytic differentiation of HEL cells using sedimentation
field-flow fractionation. Anal Bioanal Chem. 398:1273–1283. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Leger DY, Liagre B and Beneytout JL: Role
of MAPKs and NF-kappaB in diosgenin-induced megakaryocytic
differentiation and subsequent apoptosis in HEL cells. Int J Oncol.
28:201–207. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cragg GM and Newman DJ: Nature: A vital
source of leads for anticancer drug development. Phytochem Rev.
8:313–331. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yu J, Guo QL, You QD, Lin SS, Li Z, Gu HY,
Zhang HW, Tan Z and Wang X: Repression of telomerase reverse
transcriptase mRNA and hTERT promoter by gambogic acid in human
gastric carcinoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 58:434–443.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kasibhatla S, Jessen KA, Maliartchouk S,
Wang JY, English NM, Drewe J, Qiu L, Archer SP, Ponce AE, Sirisoma
N, et al: A role for transferrin receptor in triggering apoptosis
when targeted with gambogic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:12095–12100. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao L, Guo QL, You QD, Wu ZQ and Gu HY:
Gambogic acid induces apoptosis and regulates expressions of Bax
and Bcl-2 protein in human gastric carcinoma MGC-803 cells. Biol
Pharm Bull. 27:998–1003. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Duan D, Zhang B, Yao J, Liu Y, Sun J, Ge
C, Peng S and Fang J: Gambogic acid induces apoptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells by targeting cytosolic
thioredoxin reductase. Free Radic Biol Med. 69:15–25. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu X, Liu Y, Wang L, He J, Zhang H, Chen
X, Li Y, Yang J and Tao J: Gambogic acid induces apoptosis by
regulating the expression of Bax and Bcl-2 and enhancing caspase-3
activity in human malignant melanoma A375 cells. Int J Dermatol.
48:186–192. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li C, Qi Q, Lu N, Dai Q, Li F, Wang X, You
Q and Guo Q: Gambogic acid promotes apoptosis and resistance to
metastatic potential in MDA-MB-231 human breast carcinoma cells.
Biochem Cell Biol. 90:718–730. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi X, Chen X, Li X, Lan X, Zhao C, Liu S,
Huang H, Liu N, Liao S, Song W, et al: Gambogic acid induces
apoptosis in imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells via
inducing proteasome inhibition and caspase-dependent Bcr-Abl
downregulation. Clin Cancer Res. 20:151–163. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chantarasriwong O, Batova A, Chavasiri W
and Theodorakis EA: Chemistry and biology of the caged Garcinia
xanthones. Chemistry. 16:9944–9962. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kashyap D, Mondal R, Tuli HS, Kumar G and
Sharma AK: Molecular targets of gambogic acid in cancer: Recent
trends and advancements. Tumour Biol. 37:12915–12925. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Luo H, Vong CT, Chen H, Gao Y, Lyu P, Qiu
L, Zhao M, Liu Q, Cheng Z, Zou J, et al: Naturally occurring
anti-cancer compounds: Shining from Chinese herbal medicine. Chin
Med. 14:482019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Teimouri M, Junaid M, Saleem S, Khan A and
Ali A: In-vitro analysis of selective nutraceuticals binding to
human transcription factors through computer aided molecular
docking predictions. Bioinformation. 12:354–358. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rubinfeld B, Albert I, Porfiri E, Fiol C,
Munemitsu S and Polakis P: Binding of GSK3beta to the
APC-beta-catenin complex and regulation of complex assembly.
Science. 272:1023–1026. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li VS, Ng SS, Boersema PJ, Low TY,
Karthaus WR, Gerlach JP, Mohammed S, Heck AJ, Maurice MM, Mahmoudi
T and Clevers H: Wnt signaling through inhibition of β-catenin
degradation in an intact axin1 complex. Cell. 149:1245–1256. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H,
Zawel L, da Costa LT, Morin PJ, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW:
Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science.
281:1509–1512. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tetsu O and McCormick F: Beta-Catenin
regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature.
398:422–426. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cadigan KM and Nusse R: Wnt signaling: A
common theme in animal development. Genes Dev. 11:3286–3305. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nejak-Bowen KN and Monga SP: Beta-catenin
signaling, liver regeneration and hepatocellular cancer: Sorting
the good from the bad. Semin Cancer Biol. 21:44–58. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Abrahamsson AE, Geron I, Gotlib J, Dao KH,
Barroga CF, Newton IG, Giles FJ, Durocher J, Creusot RS, Karimi M,
et al: Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta missplicing contributes to
leukemia stem cell generation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:3925–3929. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Banerji V, Frumm SM, Ross KN, Li LS,
Schinzel AC, Hahn CK, Kakoza RM, Chow KT, Ross L, Alexe G, et al:
The intersection of genetic and chemical genomic screens identifies
GSK-3α as a target in human acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Invest.
122:935–947. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Z, Smith KS, Murphy M, Piloto O,
Somervaille TC and Cleary ML: Glycogen synthase kinase 3 in MLL
leukaemia maintenance and targeted therapy. Nature. 455:1205–1209.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Staal FJ, Famili F, Garcia Perez L and
Pike-Overzet K: Aberrant Wnt signaling in leukemia. Cancers
(Basel). 8:782016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Weerkamp F, van Dongen JJ and Staal FJ:
Notch and Wnt signaling in T-lymphocyte development and acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 20:1197–1205. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Weng AP, Millholland JM, Yashiro-Ohtani Y,
Arcangeli ML, Lau A, Wai C, Del Bianco C, Rodriguez CG, Sai H,
Tobias J, et al: A: c-Myc is an important direct target of Notch1
in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Genes Dev.
20:2096–2109. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Koch U and Radtke F: Mechanisms of T cell
development and transformation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:539–562.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
den Hoed MA, Pluijm SM, te Winkel ML, de
Groot-Kruseman HA, Fiocco M, Hoogerbrugge P, Leeuw JA, Bruin MC,
van der Sluis IM, Bresters D, et al: Aggravated bone density
decline following symptomatic osteonecrosis in children with acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 100:1564–1570. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sutton R, Shaw PJ, Venn NC, Law T,
Dissanayake A, Kilo T, Haber M, Norris MD, Fraser C, Alvaro F, et
al: Persistent MRD before and after allogeneic BMT predicts relapse
in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol.
168:395–404. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bleckmann K and Schrappe M: Advances in
therapy for Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia of
childhood and adolescence. Br J Haematol. 172:855–869. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Du J, Wang T, Li Y, Zhou Y, Wang X, Yu X,
Ren X, An Y, Wu Y, Sun W, et al: DHA inhibits proliferation and
induces ferroptosis of leukemia cells through autophagy dependent
degradation of ferritin. Free Radic Biol Med. 131:356–369. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu Y, Wang W, Xu J, Li L, Dong Q, Shi Q,
Zuo G, Zhou L, Weng Y, Tang M, et al: Dihydroartemisinin inhibits
tumor growth of human osteosarcoma cells by suppressing
Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncol Rep. 30:1723–1730. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Giambra V, Jenkins CE, Lam SH, Hoofd C,
Belmonte M, Wang X, Gusscott S, Gracias D and Weng AP: Leukemia
stem cells in T-ALL require active Hif1α and Wnt signaling. Blood.
125:3917–3927. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gottardi CJ and Gumbiner BM: Distinct
molecular forms of beta-catenin are targeted to adhesive or
transcriptional complexes. J Cell Biol. 167:339–349. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gao S, Li X, Ding X, Jiang L and Yang Q:
Huaier extract restrains the proliferative potential of
endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells through increased ATM by
suppressing miR-203. Sci Rep. 7:73132017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gavet O and Pines J: Progressive
activation of CyclinB1-Cdk1 coordinates entry to mitosis. Dev Cell.
18:533–543. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang Y, Krivtsov AV, Sinha AU, North TE,
Goessling W, Feng Z, Zon LI and Armstrong SA: The Wnt/beta-catenin
pathway is required for the development of leukemia stem cells in
AML. Science. 327:1650–1653. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Heidel FH, Bullinger L, Feng Z, Wang Z,
Neff TA, Stein L, Kalaitzidis D, Lane SW and Armstrong SA: Genetic
and pharmacologic inhibition of β-catenin targets
imatinib-resistant leukemia stem cells in CML. Cell Stem Cell.
10:412–424. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hamilton A, Helgason GV, Schemionek M,
Zhang B, Myssina S, Allan EK, Nicolini FE, Müller-Tidow C, Bhatia
R, Brunton VG, et al: Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells are not
dependent on Bcr-Abl kinase activity for their survival. Blood.
119:1501–1510. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Perrotti D, Jamieson C, Goldman J and
Skorski T: Chronic myeloid leukemia: Mechanisms of blastic
transformation. J Clin Invest. 120:2254–2264. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sparks AB, Morin PJ, Vogelstein B and
Kinzler KW: Mutational analysis of the APC/beta-catenin/Tcf pathway
in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 58:1130–1134. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Beurel E, Grieco SF and Jope RS: Glycogen
synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): Regulation, actions, and diseases.
Pharmacol Ther. 148:114–131. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Frame S, Cohen P and Biondi RM: A common
phosphate binding site explains the unique substrate specificity of
GSK3 and Its Inactivation by Phosphorylation. Mol Cell.
7:1321–1327. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huber BE and Thorgeirsson SS: Analysis of
c-myc expression in a human hepatoma cell line. Cancer Res.
47:3414–3420. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hönscheid P, Datta K and Muders MH:
Autophagy: Detection, regulation and its role in cancer and therapy
response. Int J Radiat Biol. 90:628–635. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Schneider JL and Cuervo AM: Autophagy and
human disease: Emerging themes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 26:16–23.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ghavami S, Gupta S, Ambrose E, Hnatowich
M, Freed DH and Dixon IM: Autophagy and heart disease: Implications
for cardiac ischemia-reperfusion damage. Curr Mol Med. 14:616–629.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hashimoto D, Bläuer M, Hirota M, Ikonen
NH, Sand J and Laukkarinen J: Autophagy is needed for the growth of
pancreatic adenocarcinoma and has a cytoprotective effect against
anticancer drugs. Eur J Cancer. 50:1382–1390. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ryter SW and Choi AMK: Autophagy in lung
disease pathogenesis and therapeutics. Redox Biol. 4:215–225. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kimura S, Fujita N, Noda T and Yoshimori
T: Monitoring autophagy in mammalian cultured cells through the
dynamics of LC3. Methods Enzymol. 452:1–12. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liu G, Liu J, Pian L, Gui S and Lu B:
α-lipoic acid protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver
cirrhosis through the suppression of the TGF-β/Smad3 pathway and
autophagy Mol Med Rep. 19:841–850. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gao C, Cao W, Bao L, Zuo W, Xie G, Cai T,
Fu W, Zhang J, Wu W, Zhang X and Chen YG: Autophagy negatively
regulates Wnt signalling by promoting Dishevelled degradation. Nat
Cell Biol. 12:781–790. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhang Y, Wang F, Han L, Wu Y, Li S, Yang
X, Wang Y, Ren F, Zhai Y, Wang D, et al: GABARAPL1 Negatively
regulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling by mediating Dvl2 degradation
through the autophagy pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 27:503–512.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|