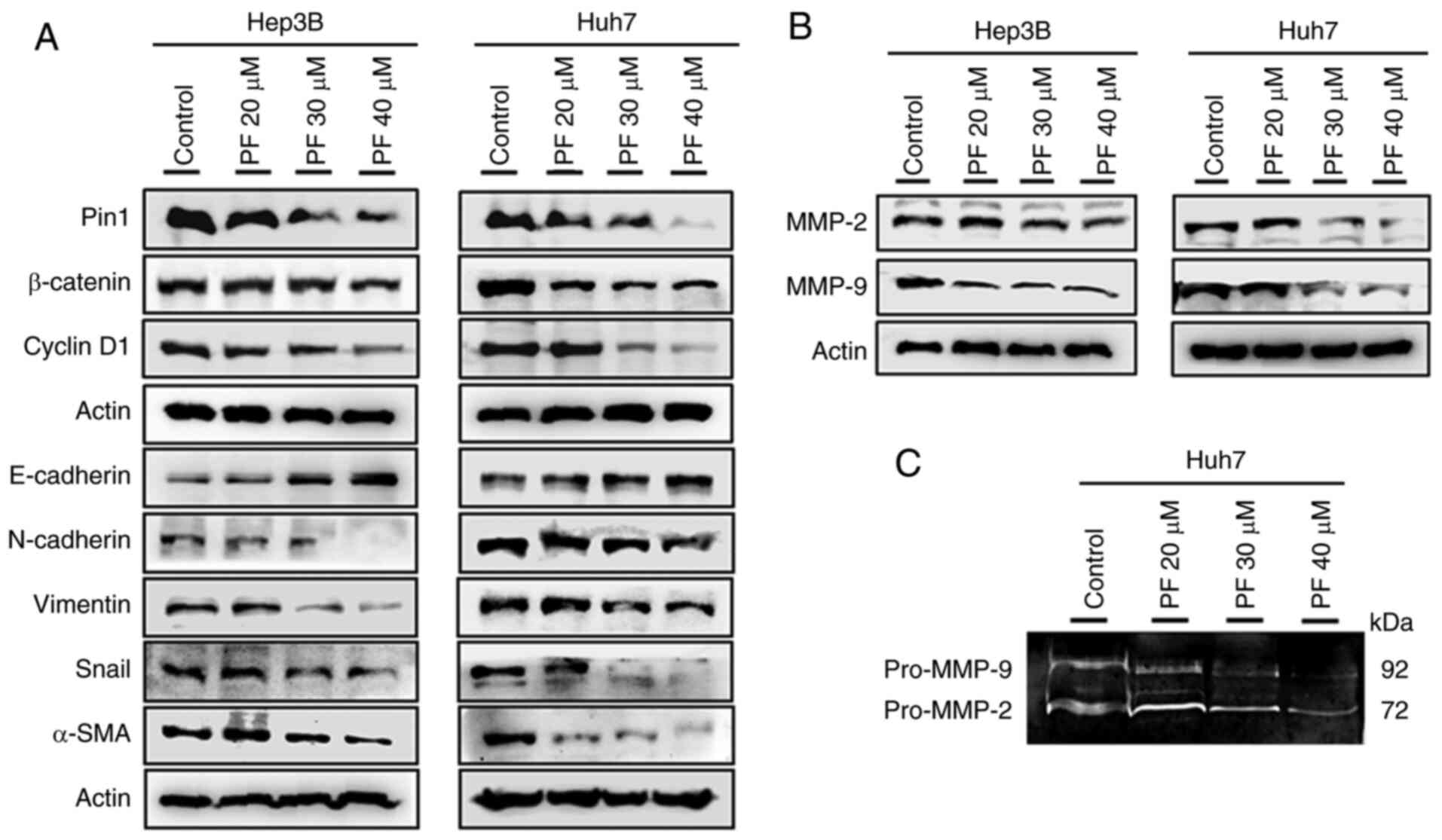
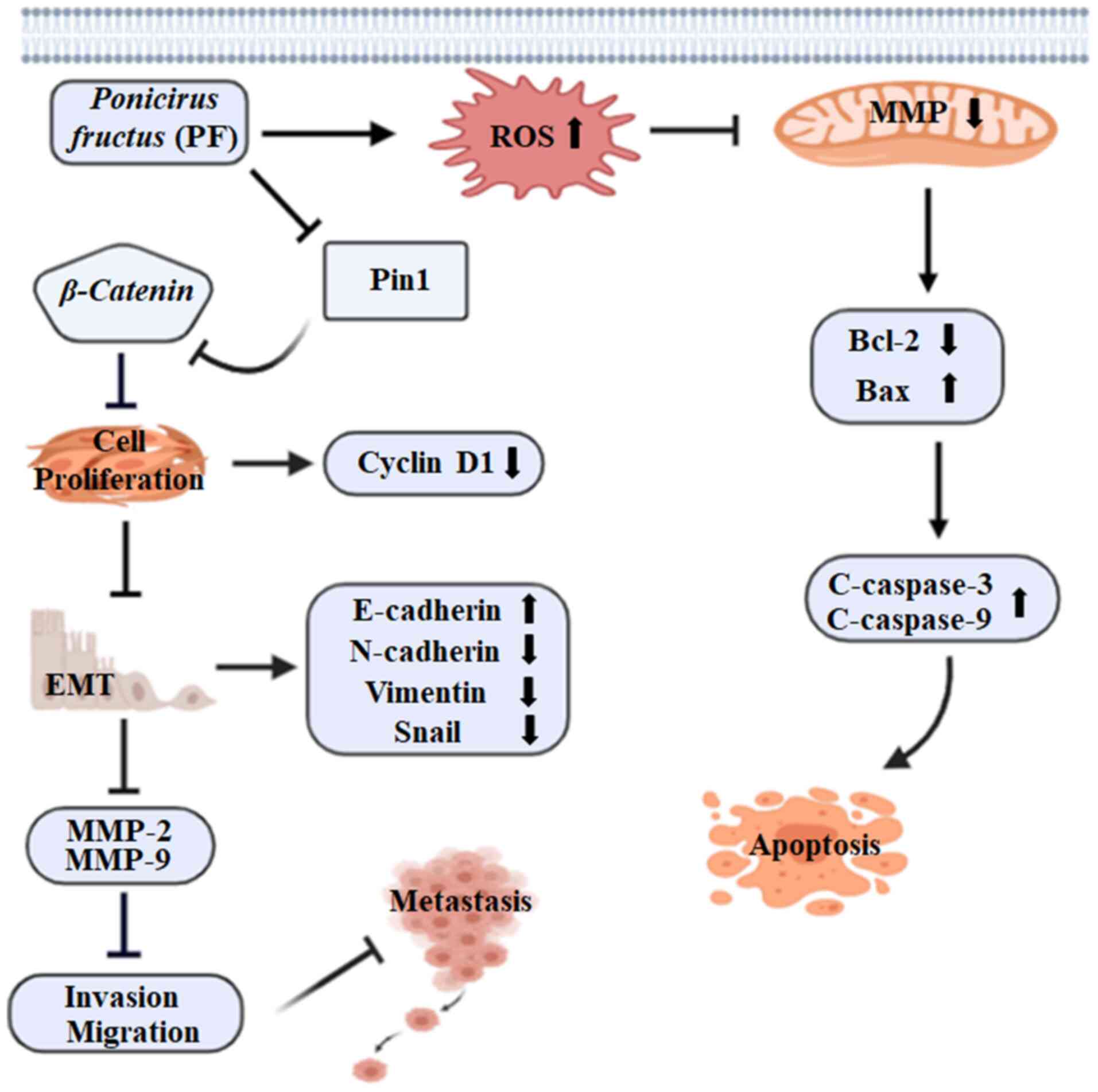
|
1
|
Naghavi M, Wang H, Lozano R, Davis A,
Liang X, Zhou M, Vollset SE, Ozgoren AA, Abdalla S, Abd-Allah F, et
al: Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and
cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: A
systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013.
Lancet. 385:117–171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mederacke I: Liver fibrosis-mouse models
and relevance in human liver diseases. Z Gastroenterol. 51:55–62.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
El-Serag HB: Hepatocellular carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 365:1118–1127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Morise Z, Kawabe N, Tomishige H, Nagata H,
Kawase J, Arakawa S, Yoshida R and Isetani M: Recent advances in
liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Surg. 1:212014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu Y, Shen H, Yu H, Zhong F, Zhang Y,
Zhang C, Zhao J, Li H, Chen J, Liu Y and Yang P: Systematic
proteomic analysis of human hepotacellular carcinoma cells reveals
molecular pathways and networks involved in metastasis. Mol
Biosyst. 7:1908–1916. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
European Association For The Study Of The
Liver; European Organisation For Research And Treatment Of Cancer,
. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 56:908–943. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rosen HR, Ghany MG, Chung RT and Lok ASF:
NAM 2017 report: A national plan to eliminate hepatitis B and C in
the United States by 2030 and the AASLD's response. Hepatology.
66:1020–1022. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nault JC, Galle PR and Marquardt JU: The
role of molecular enrichment on future therapies in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Hepatol. 69:237–247. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bruix J, Qin S, Merle P, Granito A, Huang
YH, Bodoky G, Pracht M, Yokosuka O, Rosmorduc O, Breder V, et al:
Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who
progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 389:56–66.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu KP, Hanes SD and Hunter T: A human
peptidyl-prolyl isomerase essential for regulation of mitosis.
Nature. 380:544–547. 1996. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zheng H, You H, Zhou XZ, Murray SA, Uchida
T, Wulf G, Gu L, Tang X, Lu KP and Xiao ZX: The prolyl isomerase
Pin1 is a regulator of p53 in genotoxic response. Nature.
419:849–853. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bernis C, Vigneron S, Burgess A, Labbé JC,
Fesquet D, Castro A and Lorca T: Pin1 stabilizes Emi1 during G2
phase by preventing its association with SCF(betatrcp). EMBO Rep.
8:91–98. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liou YC, Ryo A, Huang HK, Lu PJ, Bronson
R, Fujimori F, Uchida T, Hunter T and Lu KP: Loss of Pin1 function
in the mouse causes phenotypes resembling cyclin D1-null
phenotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:1335–1340. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ryo A, Nakamura M, Wulf G, Liou YC and Lu
KP: Pin1 regulates turnover and subcellular localization of
beta-catenin by inhibiting its interaction with APC. Nat Cell Biol.
3:793–801. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ryo A, Nakamura M, Wulf G, Liou YC and Lu
KP: Pin1 regulates turnover and subcellular localization of
beta-catenin by inhibiting its interaction with APC. Nat Cell Biol.
3:793–801. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen K, Zhang S, Ji Y, Li J, An P, Ren H,
Liang R, Yang J and Li Z: Baicalein inhibits the invasion and
metastatic capabilities of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via
down-regulation of the ERK pathway. PLoS One. 8:e729272013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gupta GP and Massagué J: Cancer
metastasis: Building a framework. Cell. 127:679–695. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meyer T and Hart IR: Mechanisms of tumour
metastasis. Eur J Cancer. 34:214–221. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Radisky ES and Radisky DC: Matrix
metalloproteinase-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 15:201–212. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song J, Zhang X, Ge Q, Yuan C, Chu L,
Liang HF, Liao Z, Liu Q, Zhang Z and Zhang B: CRISPR/Cas9-mediated
knockout of HBsAg inhibits proliferation and tumorigenicity of
HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem.
119:8419–8431. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Itoh Y and Nagase H: Matrix
metalloproteinases in cancer. Essays Biochem. 38:21–36. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Green DR and Kroemer G: The
pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science. 305:626–629.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yuan H, Mutomba M, Prinz I and Gottlieb
RA: Differential processing of cytosolic and mitochondrial
caspases. Mitochondrion. 1:61–69. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zaidieh T, Smith JR, Ball KE and An Q: ROS
as a novel indicator to predict anticancer drug efficacy. BMC
Cancer. 19:12242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Newman DJ and Cragg GM: Natural products
as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J Nat Prod. 79:629–661.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vallejo MJ, Salazar L and Grijalva M:
Oxidative stress modulation and ROS-mediated toxicity in cancer: A
review on in vitro models for plant-derived compounds. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2017:45860682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Greenwell M and Rahman PK: Medicinal
Plants: Their use in anticancer treatment. Int J Pharm Sci Res.
6:4103–4112. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zheng X, Zhao MG, Jiang CH, Sheng XP, Yang
HM, Liu Y, Yao XM, Zhang J and Yin ZQ: Triterpenic acids-enriched
fraction from Cyclocarya paliurus attenuates insulin resistance and
hepatic steatosis via PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway. Phytomedicine.
66:1531302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sumorek-Wiadro J, Zając A, Maciejczyk A
and Jakubowicz-Gil J: Furanocoumarins in anticancer therapy-for and
against. Fitoterapia. 142:1044922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu DJ, Jun JH, Kim TJ, Suh DK, Youn DH and
Kim TW: The relaxing effect of Poncirus fructus and its
flavonoid content on porcine coronary artery. Lab Anim Res.
31:33–39. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kornblum HI, Raymon HK, Morrison RS,
Cavanaugh KP, Bradshaw RA and Leslie FM: Epidermal growth factor
and basic fibroblast growth factor: Effects on an overlapping
population of neocortical neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 535:255–263.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jang Y, Kim EK and Shim WS:
Phytotherapeutic effects of the fruits of Poncirus
trifoliata (L.) Raf. on cancer, inflammation, and digestive
dysfunction. Phytother Res. 32:616–624. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hong J, Min HY, Xu GH, Lee JG, Lee SH, Kim
YS, Kang SS and Lee SK: Growth inhibition and G1 cell cycle arrest
mediated by 25-methoxyhispidol A, a novel triterpenoid, isolated
from the fruit of Poncirus trifoliata in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Planta Med. 74:151–155. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yi JM, Kim MS, Koo HN, Song BK, Yoo YH and
Kim HM: Poncirus trifoliata fruit induces apoptosis in human
promyelocytic leukemia cells. Clin Chim Acta. 340:179–185. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Choi AR, Lee IK, Woo EE, Kwon JW, Yun BS
and Park HR: New glabretal triterpenes from the immature fruits of
Poncirus trifoliata and their selective cytotoxicity. Chem
Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 63:1065–1069. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Niyazi M, Niyazi I and Belka C: Counting
colonies of clonogenic assays by using densitometric software.
Radiat Oncol. 2:42007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Munakarmi S, Chand L, Shin HB, Jang KY and
Jeong YJ: Indole-3-carbinol derivative DIM mitigates carbon
tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice by inhibiting
inflammatory response, apoptosis and regulating oxidative stress.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:20482020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ahmed AG, Hussein UK, Ahmed AE, Kim KM,
Mahmoud HM, Hammouda O, Jang KY and Bishayee A: Mustard seed
(Brassica nigra) extract exhibits antiproliferative effect against
human lung cancer cells through differential regulation of
apoptosis, cell cycle, migration, and invasion. Molecules.
25:20692020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Skulachev VP: Why are mitochondria
involved in apoptosis? Permeability transition pores and apoptosis
as selective mechanisms to eliminate superoxide-producing
mitochondria and cell. FEBS Lett. 397:7–10. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zamzami N, Susin SA, Marchetti P, Hirsch
T, Gómez-Monterrey I, Castedo M and Kroemer G: Mitochondrial
control of nuclear apoptosis. J Exp Med. 183:1533–1544. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xiong Y, Ye T, Wang M, Xia Y, Wang N, Song
X, Wang F, Liu L, Zhu Y, Yang F, et al: A novel cinnamide YLT26
induces breast cancer cells apoptosis via ROS-mitochondrial
apoptotic pathway in vitro and inhibits lung metastasis in vivo.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:1863–1876. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Finkel T: Signal transduction by reactive
oxygen species. J Cell Biol. 194:7–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang T, Li J, Dong Y, Zhai D, Lai L, Dai
F, Deng H, Chen Y, Liu M and Yi Z: Cucurbitacin E inhibits breast
tumor metastasis by suppressing cell migration and invasion. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 135:445–458. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bhuvarahamurthy V, Kristiansen GO,
Johannsen M, Loening SA, Schnorr D, Jung K and Staack A: In
situ gene expression and localization of metalloproteinases
MMP1, MMP2, MMP3, MMP9, and their inhibitors TIMP1 and TIMP2 in
human renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 15:1379–1384.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim SY, Yi HK, Yun BS, Lee DY, Hwang PH,
Park HR and Kim MS: The extract of the immature fruit of
Poncirus trifoliata induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer
cells via mitochondrial autophagy. Food Sci Hum Wellness. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Braillon A: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
Lancet. 380:469–471. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye QH, Jia HL, He P,
Zanetti KA, Kammula US, Chen Y, Qin LX, Tang ZY and Wang XW:
Prediction of venous metastases, recurrence, and prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma based on a unique immune response
signature of the liver microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 10:99–111.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Min SH, Zhou XZ and Lu KP: The role of
Pin1 in the development and treatment of cancer. Arch Pharm Res.
39:1609–1620. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wulf GM, Ryo A, Wulf GG, Lee SW, Niu T,
Petkova V and Lu KP: Pin1 is overexpressed in breast cancer and
cooperates with Ras signaling in increasing the transcriptional
activity of c-Jun towards cyclin D1. EMBO J. 20:3459–3472. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xu GG and Etzkorn FA: Pin1 as an
anticancer drug target. Drug News Perspect. 22:399–407. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nakayama K, Hatakeyama S, Maruyama S,
Kikuchi A, Onoé K, Good RA and Nakayama KI: Impaired degradation of
inhibitory subunit of NF-kappa B (I kappa B) and beta-catenin as a
result of targeted disruption of the beta-TrCP1 gene. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 100:8752–8757. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cho YS, Park SY, Kim DJ, Lee SH, Woo KM,
Lee KA, Lee YJ, Cho YY and Shim JH: TPA-induced cell transformation
provokes a complex formation between Pin1 and 90 kDa ribosomal
protein S6 kinase 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 367:85–92. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nejak-Bowen KN, Thompson MD, Singh S,
Bowen WC Jr, Dar MJ, Khillan J, Dai C and Monga SP: Accelerated
liver regeneration and hepatocarcinogenesis in mice overexpressing
serine-45 mutant beta-catenin. Hepatology. 51:1603–1613. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cheng CW, Chow AK, Pang R, Fok EW, Kwong
YL and Tse E: PIN1 inhibits apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
through modulation of the antiapoptotic function of survivin. Am J
Pathol. 182:765–775. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Brembeck FH, Rosário M and Birchmeier W:
Balancing cell adhesion and Wnt signaling, the key role of
beta-catenin. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 16:51–59. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Inagawa S, Itabashi M, Adachi S, Kawamoto
T, Hori M, Shimazaki J, Yoshimi F and Fukao K: Expression and
prognostic roles of beta-catenin in hepatocellular carcinoma:
Correlation with tumor progression and postoperative survival. Clin
Cancer Res. 8:450–456. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
David CJ and Manley JL: Alternative
pre-mRNA splicing regulation in cancer: Pathways and programs
unhinged. Genes Dev. 24:2343–2364. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ko H, Kim S, Jin CH, Lee E, Ham S, Yook JI
and Kim K: Protein kinase casein kinase 2-mediated upregulation of
N-cadherin confers anoikis resistance on esophageal carcinoma
cells. Mol Cancer Res. 10:1032–1038. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Shenoy AK, Jin Y, Luo H, Tang M, Pampo C,
Shao R, Siemann DW, Wu L, Heldermon CD, Law BK, et al:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition confers pericyte properties on
cancer cells. J Clin Invest. 126:4174–4186. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Tsai JH and Yang J: Epithelial-mesenchymal
plasticity in carcinoma metastasis. Genes Dev. 27:2192–2206. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Cheng Y, Chen T, Yang X, Xue J and Chen J:
Atractylon induces apoptosis and suppresses metastasis in hepatic
cancer cells and inhibits growth in vivo. Cancer Manag Res.
11:5883–5894. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kamat AA, Fletcher M, Gruman LM, Mueller
P, Lopez A, Landen CN Jr, Han L, Gershenson DM and Sood AK: The
clinical relevance of stromal matrix metalloproteinase expression
in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:1707–1714. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Deryugina EI and Quigley JP: Tumor
angiogenesis: MMP-mediated induction of intravasation- and
metastasis- sustaining neovasculature. Matrix Biol. 44-46:94–112.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Iyer RP, Patterson NL, Fields GB and
Lindsey ML: The history of matrix metalloproteinases: Milestones,
myths, and misperceptions. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
303:H919–H930. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kessenbrock K, Wang CY and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases in stem cell regulation and cancer. Matrix Biol.
44-46:184–190. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhu M, Li W, Dong X, Chen Y, Lu Y, Lin B,
Guo J and Li M: Benzyl-isothiocyanate induces apoptosis and
inhibits migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
in vitro. J Cancer. 8:240–248. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kang MH and Reynolds CP: Bcl-2 inhibitors:
Targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:1126–1132. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wang F, He L, Dai WQ, Xu YP, Wu D, Lin CL,
Wu SM, Cheng P, Zhang Y, Shen M, et al: Salinomycin inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 7:e506382012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zhang Z, Lapolla SM, Annis MG, Truscott M,
Roberts GJ, Miao Y, Shao Y, Tan C, Peng J, Johnson AE, et al: Bcl-2
homodimerization involves two distinct binding surfaces, a
topographic arrangement that provides an effective mechanism for
Bcl-2 to capture activated Bax. J Biol Chem. 279:43920–43928. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Dewson G and Kluck RM: Mechanisms by which
Bak and Bax permeabilise mitochondria during apoptosis. J Cell Sci.
122:2801–2808. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Indran IR, Tufo G, Pervaiz S and Brenner
C: Recent advances in apoptosis, mitochondria and drug resistance
in cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1807:735–745. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Ly JD, Grubb DR and Lawen A: The
mitochondrial membrane potential (deltapsi(m)) in apoptosis; an
update. Apoptosis. 8:115–128. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ye T, Zhu S, Zhu Y, Feng Q, He B, Xiong Y,
Zhao L, Zhang Y, Yu L and Yang L: Cryptotanshinone induces melanoma
cancer cells apoptosis via ROS-mitochondrial apoptotic pathway and
impairs cell migration and invasion. Biomed Pharmacother.
82:319–326. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|