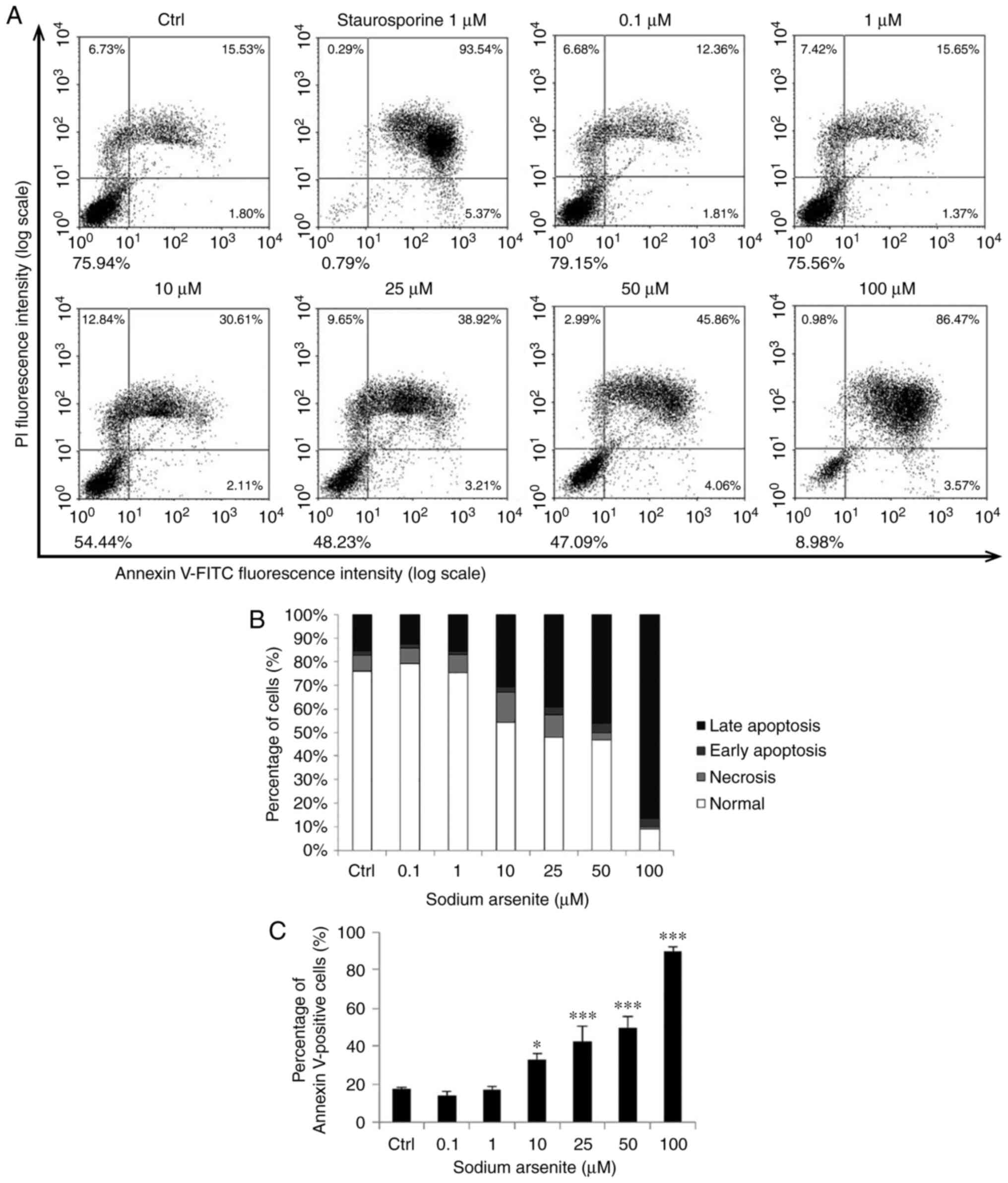
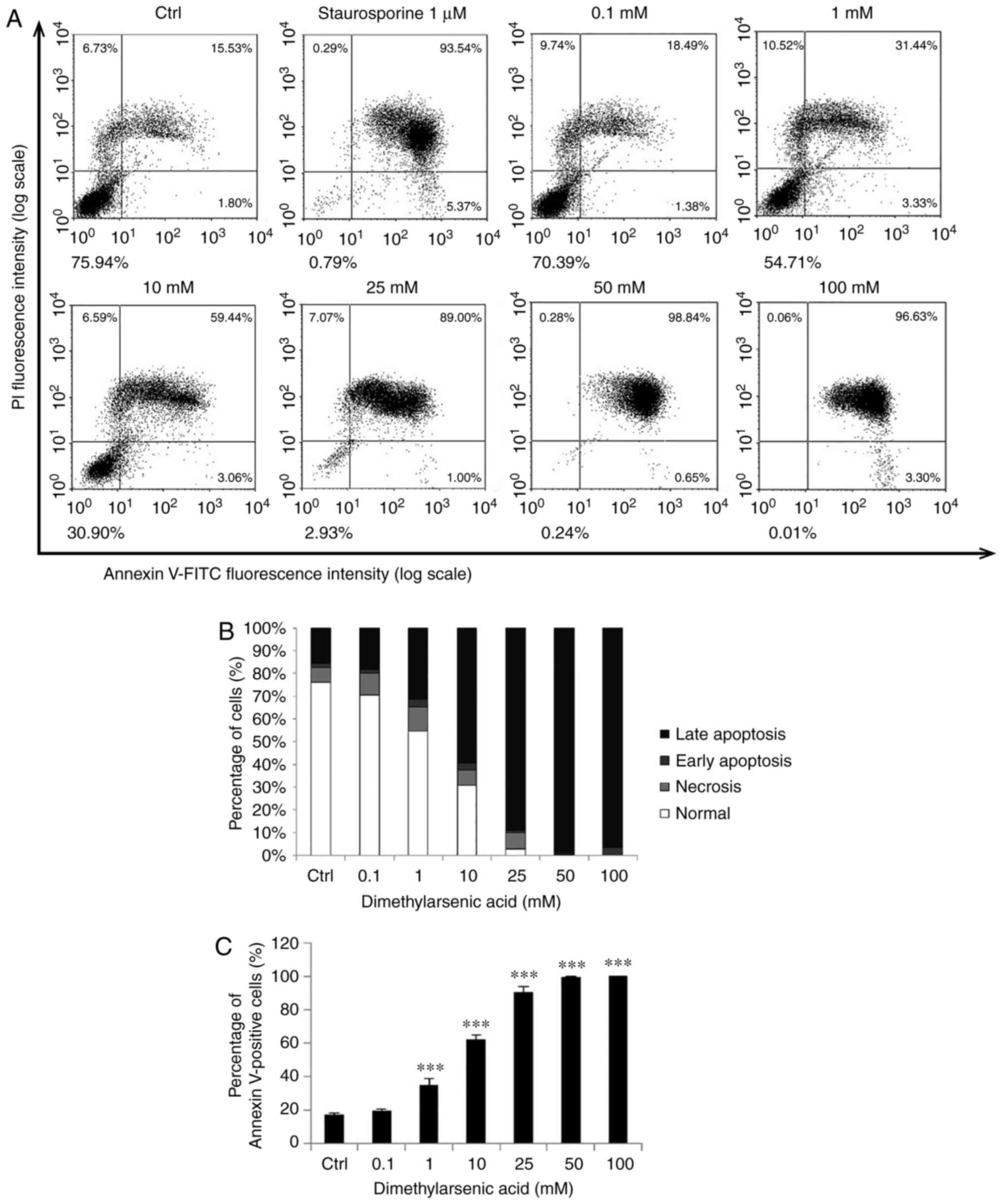
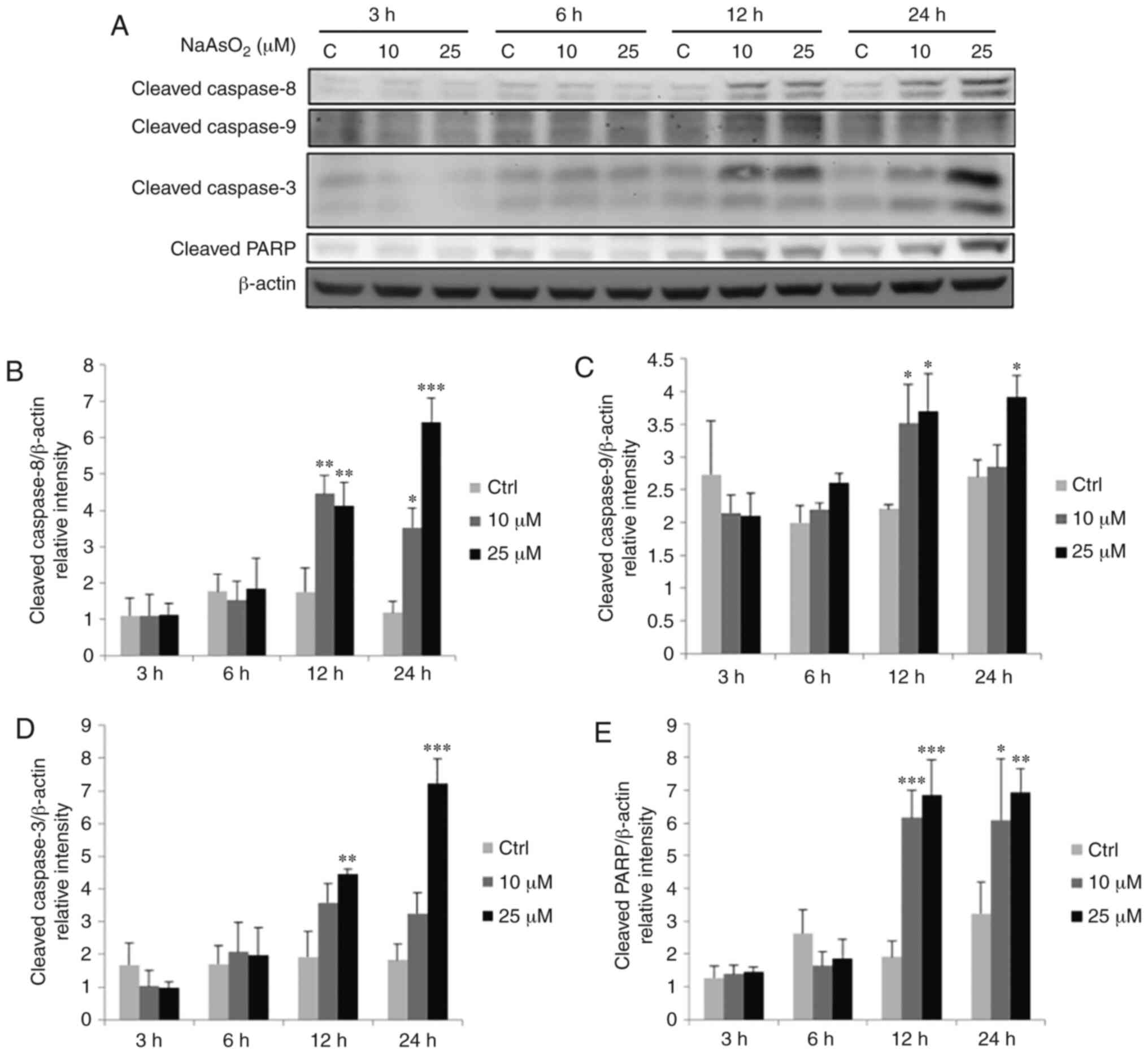
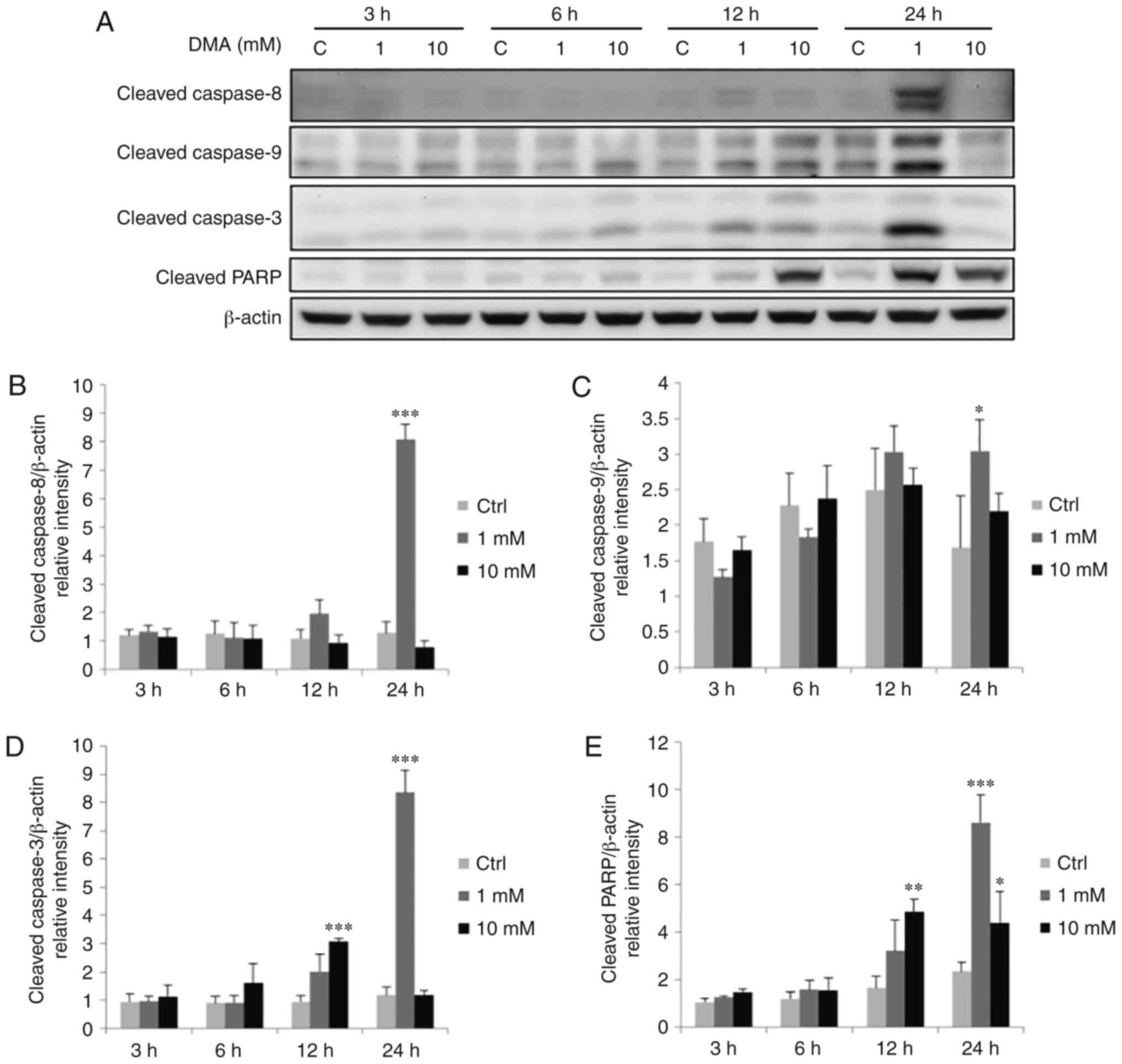
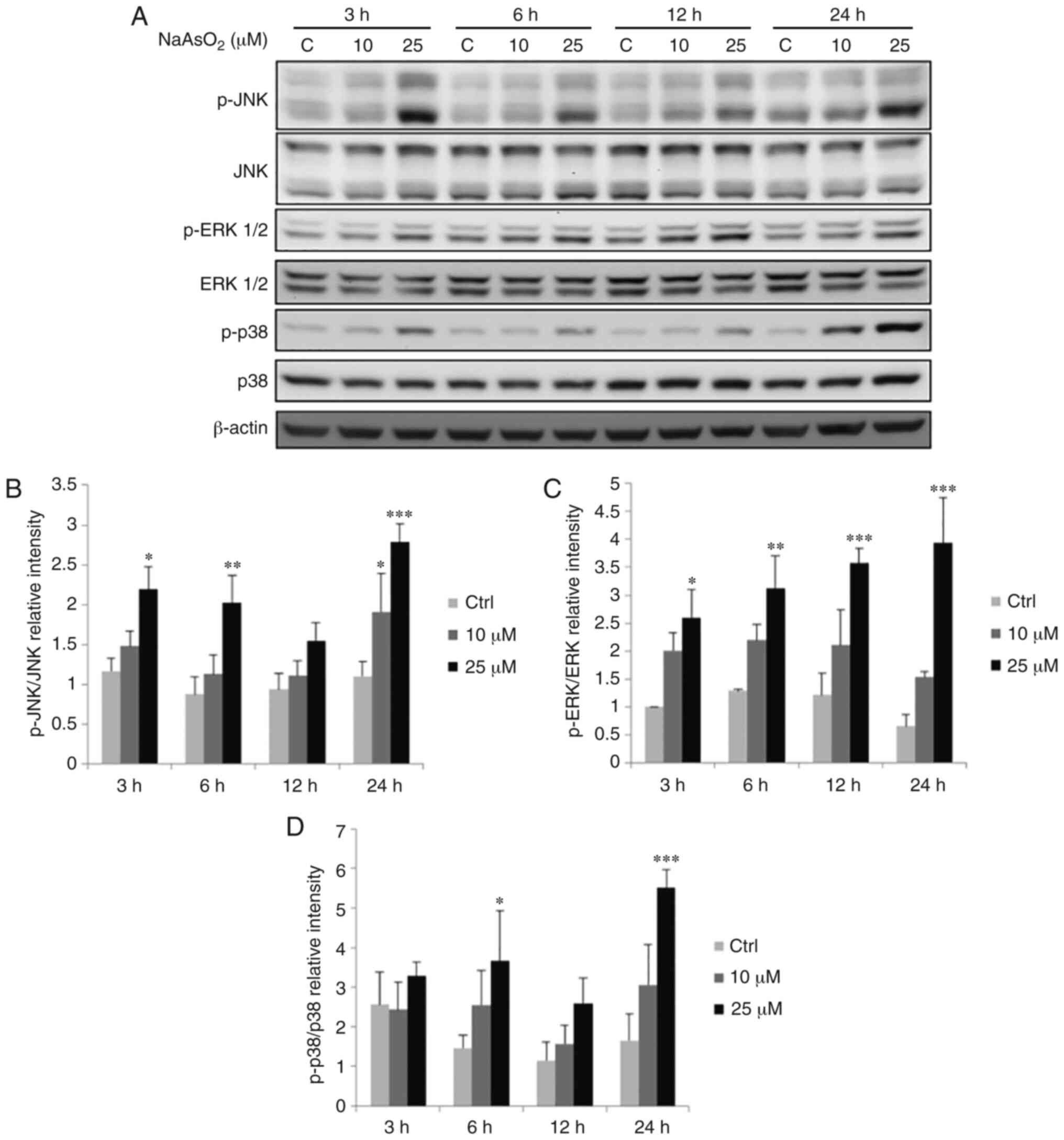
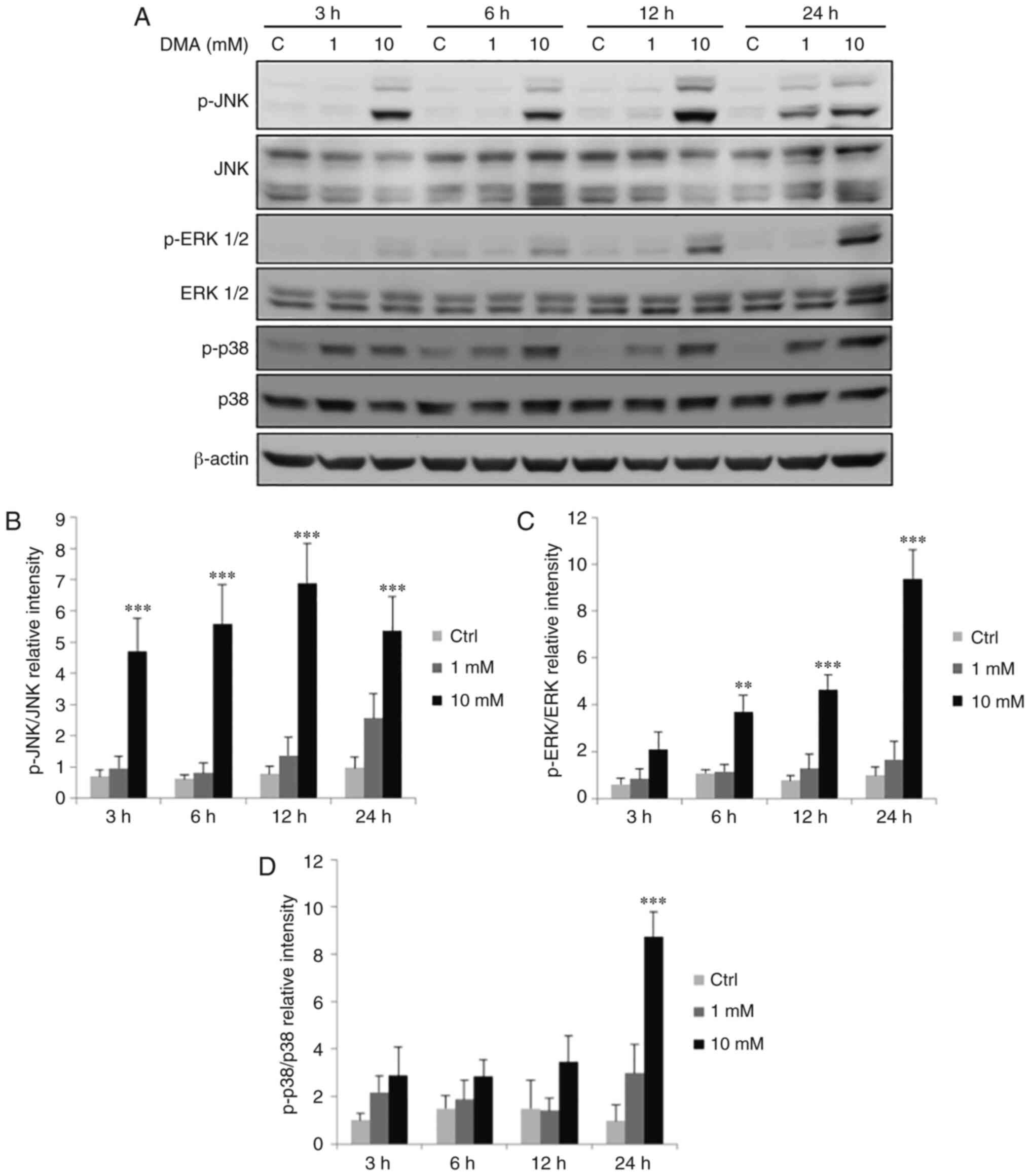
|
1
|
David MC, Randal SW and Stephen YL: Head
and neck cancer. Cancer. 113 (Suppl 7):S1911–S1932. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Laraway DC, Lakshmiah R, Lowe D, Roe B and
Rogers SN: Quality of life in older people with oral cancer. Br J
Oral Maxillofac Surg. 50:715–720. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sudbø J: Human papillomavirus infection as
a risk factor for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N
Engl J Med. 345:376–377. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ko YC, Huang YL, Lee CH, Chen MJ, Lin LM
and Tsai CC: Betel quid chewing, cigarette smoking and alcohol
consumption related to oral cancer in Taiwan. J Oral Pathol Med.
24:450–453. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bernier J and Cooper JS: Chemoradition
after surgery for high-risk head and neck cancer patients: How
strong is the evidence? Oncologist. 10:215–224. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen CJ, You SL, Lin LH, Hsu WL and Yang
YW: Cancer epidemiology and control in Taiwan: A brief review. Jpn
J Clin Oncol. 32 (Suppl):S66–S81. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mandal BK and Suzuki KT: Arsenic round the
world: A review. Talanta. 58:201–235. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Calatayud M, Devesa V and Vélez D:
Differential toxicity and gene expression in Caco-2 cells exposed
to arsenic species. Toxicol Lett. 218:70–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shen ZX, Chen GQ, Ni JH, Li XS, Xiong SM,
Qiu QY, Zhu J, Tang W, Sun GL, Yang KQ, et al: Use of arsenic
trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute
promyelocytic leukemia (APL): II. Clinical efficacy and
pharmacokinetics in relapsed patients. Blood. 89:3354–3360. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yedjou C, Tchounwou P, Jenkins J and
McMurray R: Basic mechanisms of arsenic trioxide (ATO)-induced
apoptosis in human leukemia (HL-60) cells. J Hematol Oncol.
3:282010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Q, Hilsenbeck S and Gazitt Y: Arsenic
trioxide-induced apoptosis in myeloma cells: p53-dependent G1 or
G2/M cell cycle arrest, activation of caspase-8 or caspase-9, and
synergy with APO2/TRAIL. Blood. 101:4078–4087. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mandegary A, Torshabi M, Seyedabadi M,
Amirheidari B, Sharif E and Ghahremani MH: Indomethacin-enhanced
anticancer effect of arsenic trioxide in A549 cell line:
Involvement of apoptosis and phospho-ERK and p38 MAPK pathways.
Biomed Res Int. 2013:2375432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang HY, Zhang B, Zhou JN, Wang DX, Xu YC,
Zeng Q, Jia YL, Xi JF, Nan X, He LJ, et al: Arsenic trioxide
inhibits liver cancer stem cells and metastasis by targeting
SRF/MCM7 complex. Cell Death Dis. 10:4532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim EY, Lee SS, Shin JH, Kim SH, Shin DH
and Baek SY: Anticancer effect of arsenic trioxide on
cholangiocarcinoma: In vitro experiments and in vivo xenograft
mouse model. Clin Exp Med. 14:215–224. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mu YF, Chen YH, Chang MM, Chen YC and
Huang BM: Arsenic compounds induce apoptosis through caspase
pathway activation in MA-10 Leydig tumor cells. Oncol Lett.
18:944–954. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Byun JM, Lee DS, Landen CN, Kim DH, Kim
YN, Lee KB, Sung MS, Park SG and Jeong DH: Arsenic trioxide and
tetraarsenic oxide induce cytotoxicity and have a synergistic
effect with cisplatin in paclitaxel-resistant ovarian cancer cells.
Acta Oncol. 58:1594–1602. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim MJ, Jung JH, Lee WS, Yun JW, Lu JN, Yi
SM, Kim HJ, Chang SH, Kim GS, Hong SC and Ha WS: Arsenic hexoxide
enhances TNF-α-induced anticancer effects by inhibiting NF-κB
activity at a safe dose in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Oncol
Rep. 31:2305–2311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nagappan A, Lee WS, Yun JW, Lu JN, Chang
SH, Jeong JH, Kim GS, Jung JM and Hong SC: Tetraarsenic hexoxide
induces G2/M arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via PI3K/Akt
suppression and p38 MAPK activation in SW620 human colon cancer
cells. PLoS One. 12:e01745912017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mann KK, Wallner B, Lossos IS and Miller
WH Jr: Darinaparsin: A novel organic arsenical with promising
anticancer activity. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 18:1727–1734.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cheng X, Quintás-Cardama A, Golemovic M,
Zingaro R, Gao MZ, Freireich EJ, Andreeff M, Kantarjian HM and
Verstovsek S: The organic arsenic derivative GMZ27 induces
PML-RARα-independent apoptosis in myeloid leukemia cells.
Anticancer Res. 32:2871–2880. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kasibhatla S and Tseng B: Why target
apoptosis in cancer treatment? Mol Cancer Ther. 2:573–580.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
D'Arcy MS: Cell death: A review of the
major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Cell Biol Int.
43:582–592. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM: Death receptors:
Signaling and modulation. Science. 281:1305–1308. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Akao Y, Nakagawa Y and Akiyama K: Arsenic
trioxide induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma cell lines through the
activation of caspase 3 in vitro. FEBS Lett. 455:59–62. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen GQ, Zhu J, Shi XG, Ni JN, Zhong HJ,
Si GY, Jin XL, Tang W, Li XS, Xong SM, et al: In vitro studies on
cellular and molecular mechanisms of arsenic trioxide
(As2O3) in the treatment of acute
promyelocytic leukemia: As2O3 induces NB4
cell apoptosis with downregulation of Bcl-2 expression and
modulation of PML-RAR/PML proteins. Blood. 88:1052–1061. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
You Z, Liu SP, Du J, Wu YH and Zhang SZ:
Advancements in MAPK signaling pathways and MAPK-targeted therapies
for ameloblastoma: A review. J Oral Pathol Med. 48:201–205. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wada T and Penninger JM: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases in apoptosis regulation. Oncogene. 23:2838–2849.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hayakawa J, Ohmichi M, Kurachi H, Ikegami
H, Kimura A, Matsuoka T, Jikihara H, Mercola D and Murata Y:
Inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase or
c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase cascade, differentially activated
by cisplatin, sensitizes human ovarian cancer cell line. J Biol
Chem. 274:31648–31654. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kang YH and Lee SJ: The role of p38 MAPK
and JNK in Arsenic trioxide-induced mitochondrial cell death in
human cervical cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 217:23–33. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang CY and Meng CL: Regulation of PG
synthase by EGF and PDGF in human oral, breast, stomach, and
fibrosarcoma cancer cell lines. J Dent Res. 73:1407–1415. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wong DY, Chang KW, Chen CF and Chang RC:
Characterization of two new cell lines derived from oral cavity
human squamous cell carcinomas-OC1 and OC2. J Oral Maxillofac Surg.
48:385–390. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu WC, Hsiao JR, Lian YY, Lin CY and Huang
BM: The apoptotic effect of cordycepin on human OEC-M1 oral cancer
cell line. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 60:103–111. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kang FC, Wang SC, So EC, Chang MM, Wong
KL, Cheng KS, Chen YC and Huang BM: Propofol may increase caspase
and MAPK pathways, and suppress the Akt pathway to induce apoptosis
in MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor cells. Oncol Rep. 41:3565–3574.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kang FC, Chen YC, Wang SC, So EC and Huang
BM: Propofol induces apoptosis by activating caspases and the MAPK
pathways, and inhibiting the Akt pathway in TM3 mouse Leydig
stem/progenitor cells. Int J Mol Med. 46:439–448. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J
Biol Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chang MM, Lai MS, Hong SY, Pan BS, Huang
H, Yang SH, Wu CC, Sun HS, Chuang JI, Wang CY and Huang BM:
FGF9/FGFR2 increase cell proliferation by activating ERK1/2,
Rb/E2F1, and cell cycle pathways in mouse Leydig tumor cells.
Cancer Sci. 109:3503–3518. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chang MM, Pan BS, Wang CY and Huang BM:
Cordycepin-induced unfolded protein response-dependent cell death,
and AKT/MAPK-mediated drug resistance in mouse testicular tumor
cells. Cancer Med. 8:3949–3964. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
van Engeland M, Ramaekers FC, Schutte B
and Reutelingsperger CP: A novel assay to measure loss of plasma
membrane asymmetry during apoptosis of adherent cells in culture.
Cytometry. 24:131–139. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li W and Chou IN: Effects of sodium
arsenite on the cytoskeleton and cellular glutathione levels in
cultured cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 114:132–139. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ochi T, Nakajimar F and Fukumori N:
Different effects of inorganic and dimethylated arsenic compounds
on cell morphology, cytoskeletal organization, and DNA synthesis in
cultured Chinese hamster V79 cells. Arch Toxicol. 72:566–573. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zuk A, Targosz-Korecka M and Szymonski M:
Effect of selected drugs used in asthma treatment on morphology and
elastic properties of red blood cells. Int J Nanomedicine.
6:249–57. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vahter M: Methylation of inorganic arsenic
in different mammalian species and population groups. Sci Prog.
82:69–88. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lin KW, Behl S, Furst A, Chien P and Toia
RF: Formation of dimethylarsinic acid from methylation of sodium
arsenite in lumbricus terrestris. Toxicol In Vitro. 12:197–199.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hartwell LH and Weinert TA: Checkpoints:
Controls that ensure the order of cell cycle events. Science.
246:629–634. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yih LH, Wu YC, Hsu NC and Kuo HH: Arsenic
trioxide induces abnormal mitotic spindles through a PIP4KIIγ/Rho
pathway. Toxicol Sci. 128:115–125. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ling YH, Jiang JD, Holland JF and
Perez-Soler R: Arsenic trioxide produces polymerization of
microtubules and mitotic arrest before apoptosis in human tumor
cell lines. Mol Pharmacol. 62:529–538. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Concin N, Stimpfl M, Zeillinger C, Wolff
U, Hefler L, Sedlak J, Leodolter S and Zeillinger R: Role of p53 in
G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in response to
gamma-irradiation in ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Int J Oncol.
22:51–57. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shu CH, Yang WK, Shih YL, Kuo ML and Huang
TS: Cell cycle G2/M arrest and activation of cyclin-dependent
kinases associated with low-dose paclitaxel-induced sub-G1
apoptosis. Apoptosis. 2:463–470. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tyagi AK, Singh RP, Agarwal C, Chan DC and
Agarwal R: Silibinin strongly synergizes human prostate carcinoma
DU145 cells to doxorubicin-induced growth Inhibition, G2-M arrest,
and apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res. 8:3512–3519. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Brown JM and Attardi LD: The role of
apoptosis in cancer development and treatment response. Nat Rev
Cancer. 5:231–237. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Fan TJ, Han LH, Cong RS and Liang J:
Caspase family proteases and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 37:719–727. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cheng B, Yang X, Han Z, An L and Liu S:
Arsenic trioxide induced the apoptosis of laryngeal cancer via
down-regulation of survivin mRNA. Auris Nasus Larynx. 35:95–101.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jiang XH, Wong BC, Yuen ST, Jiang SH, Cho
CH, Lai KC, Lin MC, Kung HF and Lam SK: Arsenic trioxide induces
apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells through up-regulation of
p53 and activation ofcaspase-3. Int J Cancer. 91:173–179. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wu X, Shi J, Wu Y, Tao Y, Hou J, Meng X,
Hu X, Han Y, Jiang W, Tang S, et al: Arsenic trioxide-mediated
growth inhibition of myeloma cells is associated with an extrinsic
or intrinsic signaling pathway through activation of TRAIL or TRAIL
receptor 2. Cancer Biol Ther. 10:1201–1214. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Binet F, Chiasson S and Girard D: Evidence
that endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and caspase-4 activation
occur in human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 391:18–23.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lunghi P, Giuliani N, Mazzera L, Lombardi
G, Ricca M, Corradi A, Cantoni AM, Salvatore L, Riccioni R,
Costanzo A, et al: Targeting MEK/MAPK signal transduction module
potentiates ATO-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells through
multiple signaling pathways. Blood. 112:2450–2462. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kircelli F, Akay C and Gazitt Y: Arsenic
trioxide induces p53-dependent apoptotic signals in myeloma cells
with SiRNA-silenced p53: MAP kinase pathway is preferentially
activated in cells expressing inactivated p53. Int J Oncol.
30:993–1001. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lam HK, Li K, Chik KW, Yang M, Liu VC, Li
CK, Fok TF, Ng PC, Shing MM, Chuen CK and Yuen PM: Arsenic trioxide
mediates intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis and cell
cycle arrest in acute megakaryocytic leukemia. Int J Oncol.
27:537–545. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ivanov VN and Hei TK: Regulation of
apoptosis in human melanoma and neuroblastoma cells by statins,
sodium arsenite and TRAIL: A role of combined treatment versus
monotherapy. Apoptosis. 16:1268–1284. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Shen L and Zhang G, Lou Z, Xu G and Zhang
G: Cryptotanshinone enhances the effect of Arsenic trioxide in
treating liver cancer cell by inducing apoptosis through
downregulating phosphorylated- STAT3 in vitro and in vivo. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 17:1062017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang X and Zhang M: Synergistic effects of
valproic acid and arsenic trioxide on RPMI8226 cells in
vitro and the possible underlying mechanisms. Mol Med Rep.
12:1449–1456. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Amrán D, Sánchez Y, Fernández C, Ramos AM,
de Blas E, Bréard J, Calle C and Aller P: Arsenic trioxide
sensitizes promonocytic leukemia cells to TNFalpha-induced
apoptosis via p38-MAPK-regulated activation of both
receptor-mediated and mitochondrial pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1773:1653–1663. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Alvarado-Kristensson M, Melander F,
Leandersson K, Rönnstrand L, Wernstedt C and Andersson T: p38-MAPK
signals survival by phosphorylation of caspase-8 and caspase-3 in
human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 199:449–458. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Grethe S, Ares MP, Andersson T and
Pörn-Ares MI: p38 MAPK mediates TNF-induced apoptosis in
endothelial cells via phosphorylation and downregulation of
Bcl-x(L). Exp Cell Res. 298:632–642. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Choi WS, Eom DS, Han BS, Kim WK, Han BH,
Choi EJ, Oh TH, Markelonis GJ, Cho JW and Oh YJ: Phosphorylation of
p38 MAPK induced by oxidative stress is linked to activation of
both caspase-8- and −9-mediated apoptotic pathways in dopaminergic
neurons. J Biol Chem. 279:20451–2060. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Falchi L, Verstovsek S, Ravandi-Kashani F
and Kantarjian HM: The evolution of arsenic in the treatment of
acute promyelocytic leukemia and other myeloid neoplasms: Moving
toward an effective oral, outpatient therapy. Cancer.
122:1160–1168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Torka P, Al Ustwani O, Wetzler M, Wang ES
and Griffiths EA: Swallowing a bitter pill-oral arsenic trioxide
for acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood Rev. 30:201–211. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|