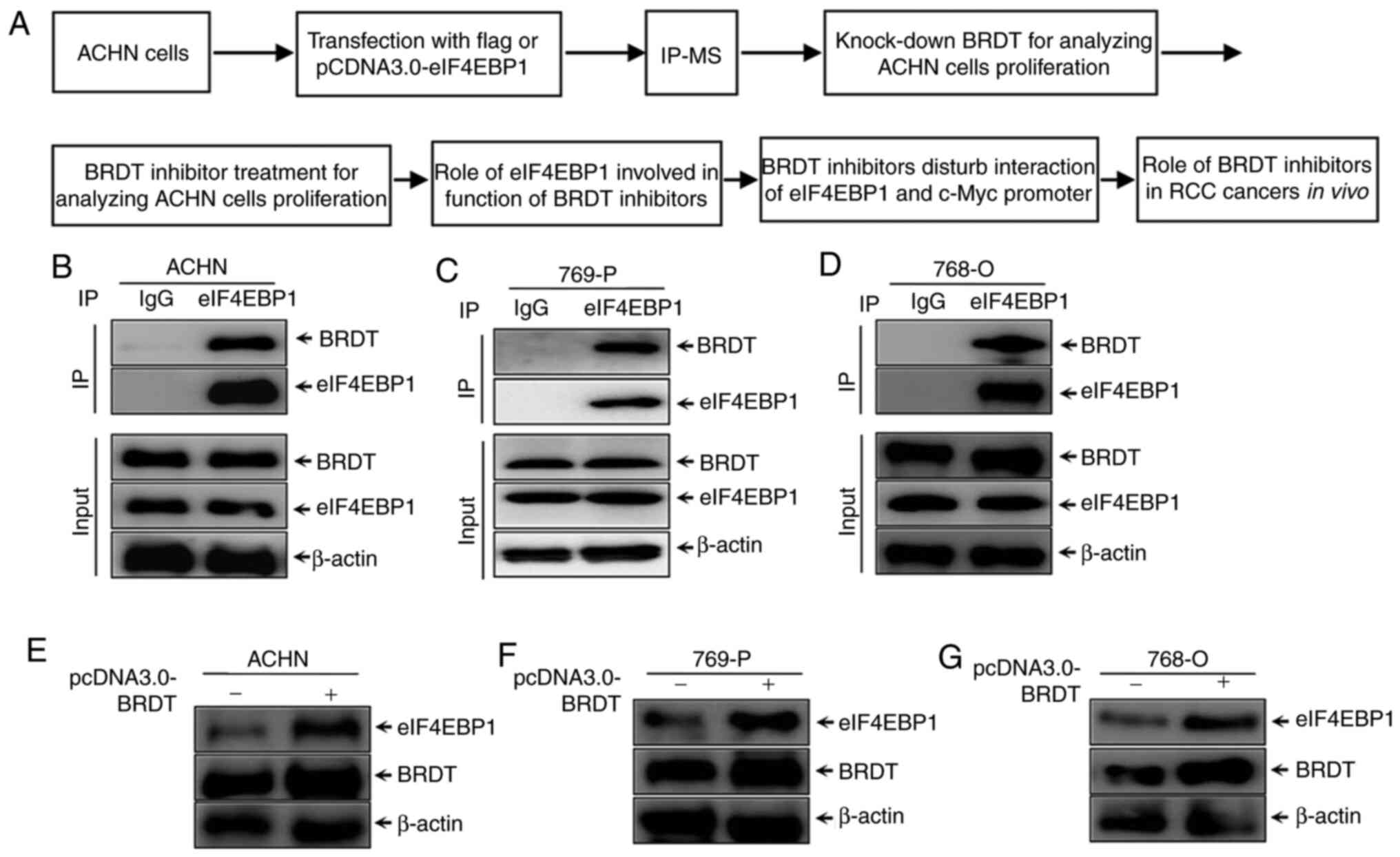
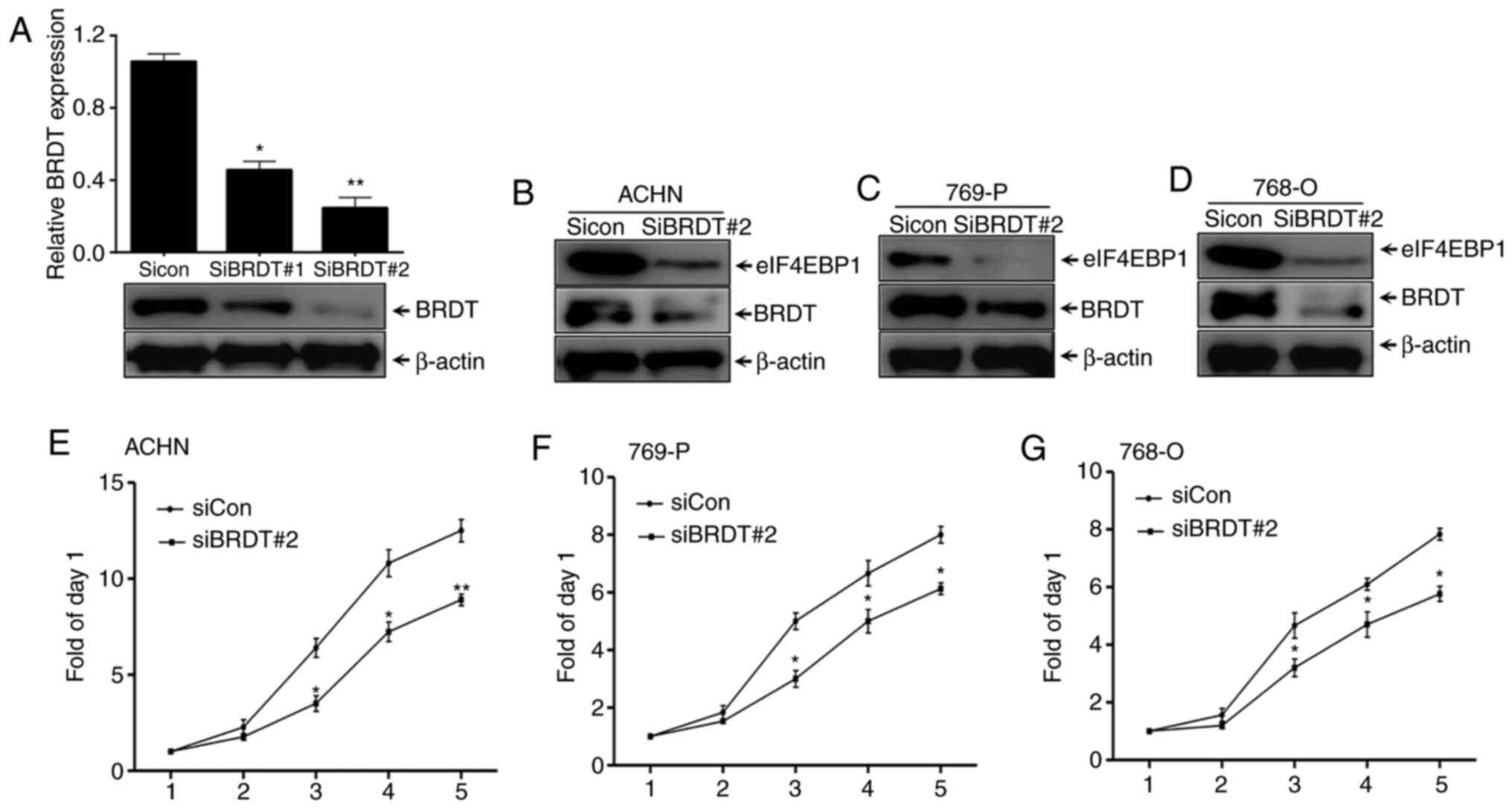
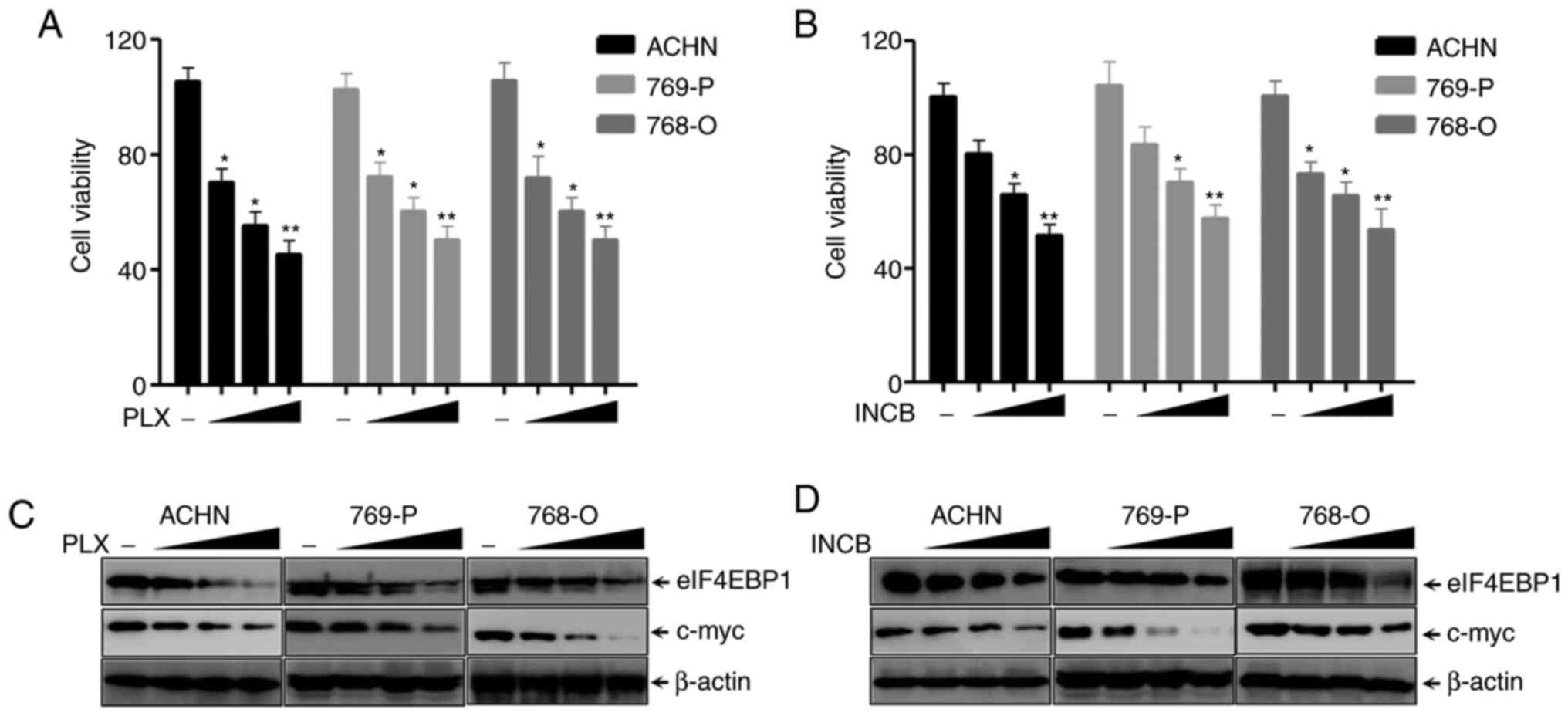
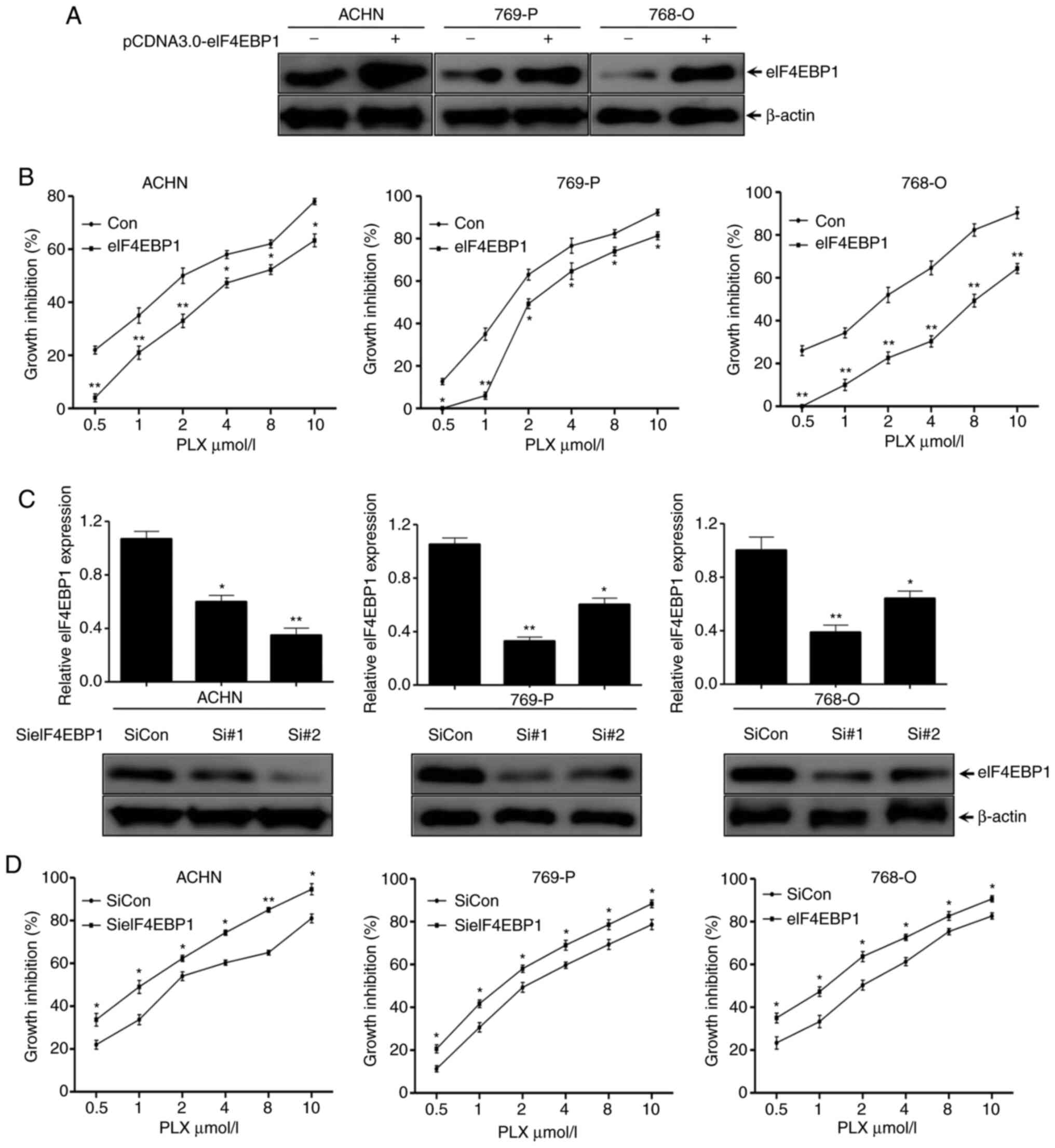
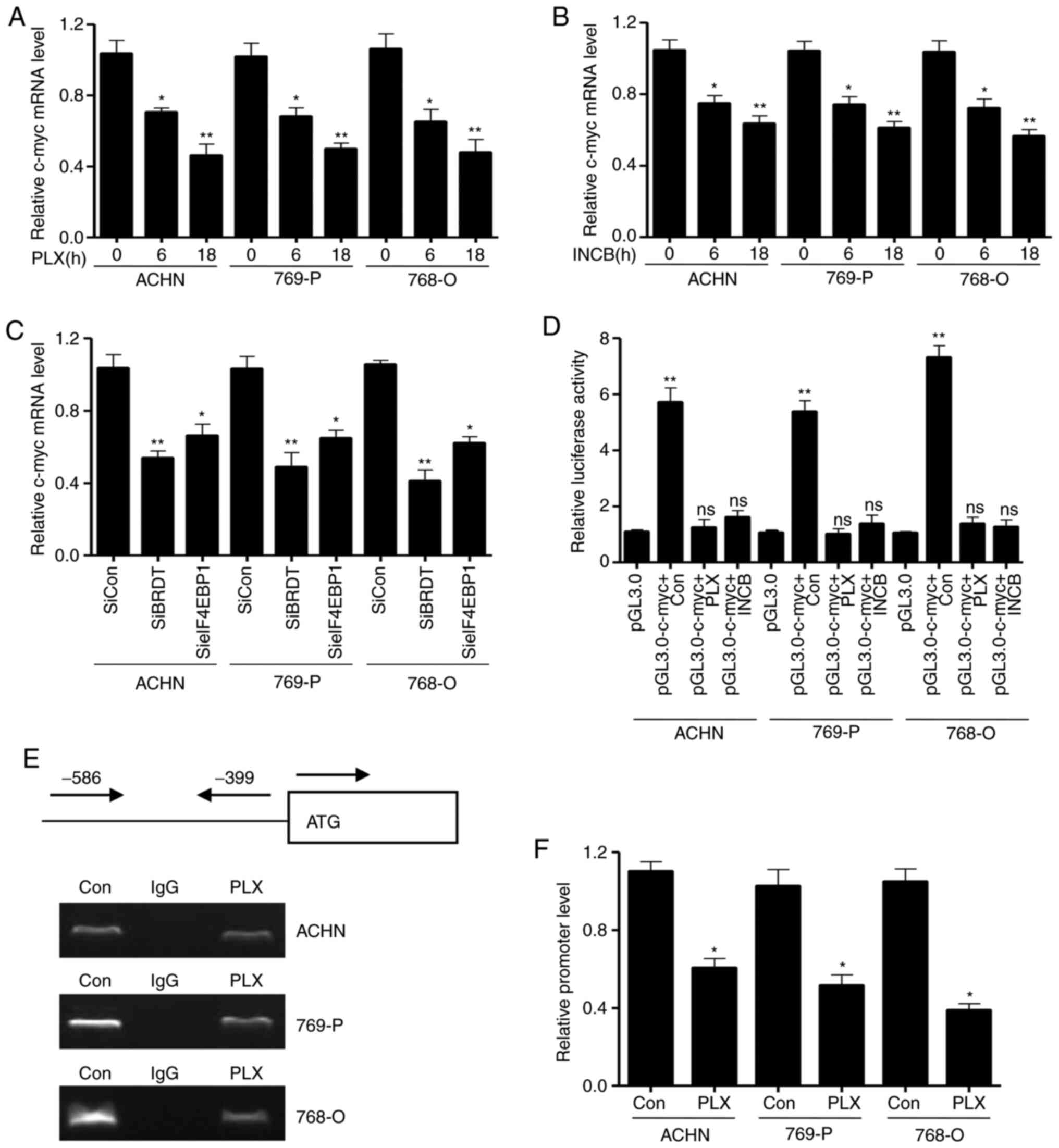
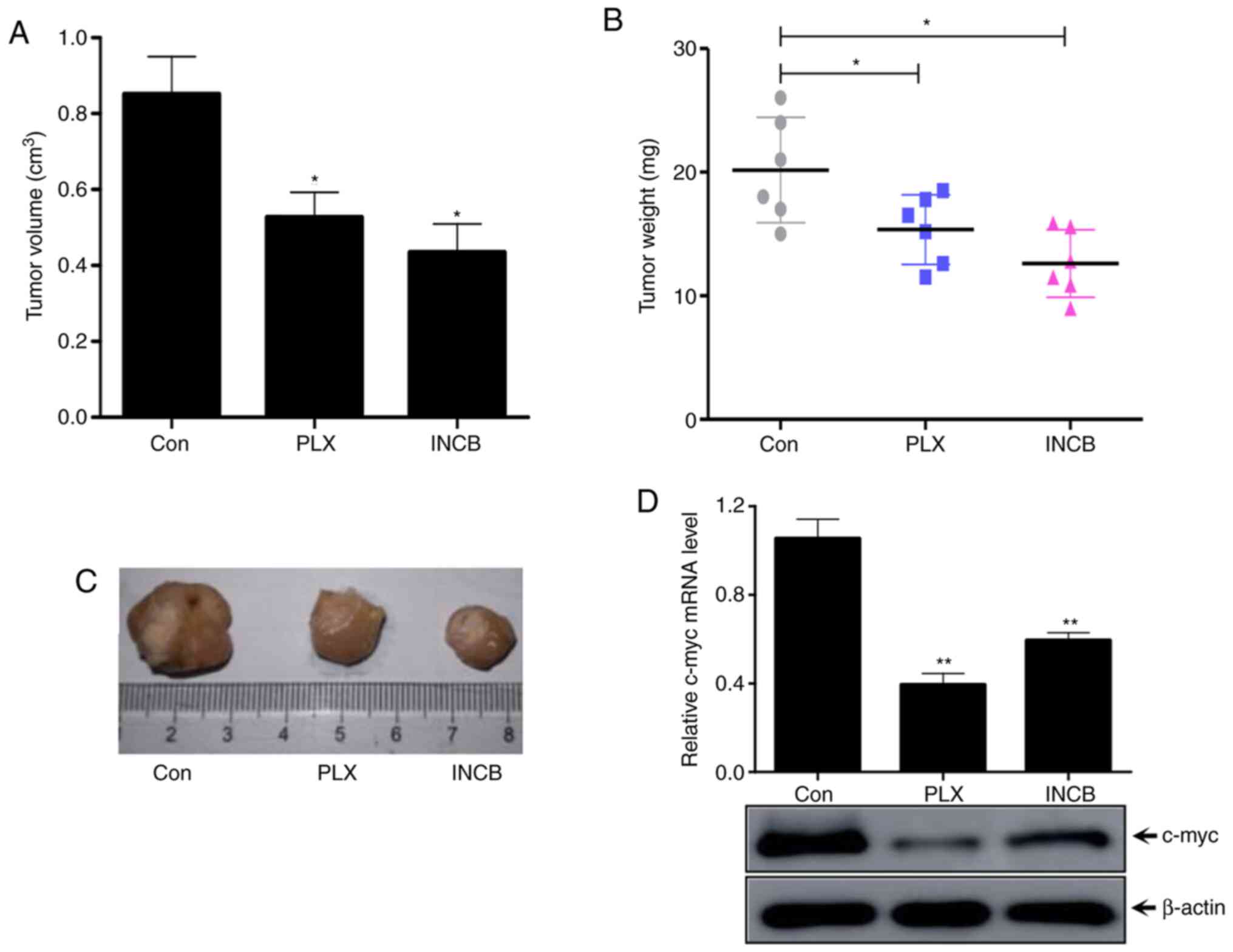
|
1
|
Cella D, Grünwald V, Escudier B, Hammers
HJ, George S, Nathan P, Grimm MO, Rini BI, Doan J, Ivanescu C, et
al: Patient-Reported outcomes of patients with advanced renal cell
carcinoma treated with nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib
(CheckMate 214): A randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.
20:297–310. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Powles T: Re: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab
versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. Eur Urol.
74:679–680. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chevrier S, Levine JH, Zanotelli VR,
Silina K, Schulz D, Bacac M, Ries CH, Ailles L, Jewett MA, Moch H,
et al: An immune atlas of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cell.
169:736–749. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Song E, Song W, Ren M, Xing L, Ni W, Li Y,
Gong M, Zhao M, Ma X, Zhang X and An R: Identification of potential
crucial genes associated with carcinogenesis of clear cell renal
cell carcinoma. J Cell Biochem. 119:5163–5174. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Q, Ding H, He Y, Li X, Cheng Y, Xu Q,
Yang Y, Liao G, Meng X, Huang C and Li J: NLRC5 mediates cell
proliferation, migration, and invasion by regulating the
wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 444:9–19. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang X, Yan L, Jiao W, Ren J, Xing N,
Zhang Y, Zang Y, Wang J and Xu Z: The clinical and biological
significance of MICA in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients.
Tumour Biol. 37:2153–2159. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu H, Wang Z, Xu Q, Zhang Y, Zhai Y, Bai
J, Liu M, Hui Z and Xu N: Inhibition of STAT1 sensitizes renal cell
carcinoma cells to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Cancer Biol Ther.
13:401–407. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wozniak MB, Le Calvez-Kelm F,
Abedi-Ardekani B, Byrnes G, Durand G, Carreira C, Michelon J,
Janout V, Holcatova I, Foretova L, et al: Integrative genome-wide
gene expression profiling of clear cell renal cell carcinoma in
czech republic and in the United States. PLoS One. 8:e578862013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu J, Wang H, Ricketts CJ, Yang Y, Merino
MJ, Zhang H, Shi G, Gan H, Linehan WM, Zhu Y and Ye D: Germline
mutations of renal cancer predisposition genes and clinical
relevance in Chinese patients with sporadic, early-onset disease.
Cancer. 125:1060–1069. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ghatalia P, Gordetsky J, Kuo F, Dulaimi E,
Cai KQ, Devarajan K, Bae S, Naik G, Chan TA, Uzzo R, et al:
Prognostic impact of immune gene expression signature and tumor
infiltrating immune cells in localized clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer. 7:1392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pal S, Gong J, Mhatre SK, Lin SW, Surinach
A, Ogale S, Vohra R, Wallen H and George D: Real-World treatment
patterns and adverse events in metastatic renal cell carcinoma from
a large US claims database. BMC Cancer. 19:5482019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Karner C, Kew K, Wakefield V, Masento N
and Edwards SJ: Targeted therapies for previously treated advanced
or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Systematic review and network
meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 9:e246912019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Suarez-Alvarez B, Morgado-Pascual JL,
Rayego-Mateos S, Rodriguez RM, Rodrigues-Diez R, Cannata-Ortiz P,
Sanz AB, Egido J, Tharaux PL, Ortiz A, et al: Inhibition of
bromodomain and extraterminal domain family proteins ameliorates
experimental renal damage. J Am Soc Nephrol. 28:504–519. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
McDaniel KF, Wang L, Soltwedel T, Fidanze
SD, Hasvold LA, Liu D, Mantei RA, Pratt JK, Sheppard GS, Bui MH, et
al: Discovery of
N-(4-(2,4-Difluorophenoxy)-3-(6-methyl-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)ethanesulfonamide
(ABBV-075/Mivebresib), a potent and orally available bromodomain
and extraterminal domain (BET) family bromodomain inhibitor. J Med
Chem. 60:8369–8384. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Manterola M, Brown TM, Oh MY, Garyn C,
Gonzalez BJ and Wolgemuth DJ: BRDT is an essential epigenetic
regulator for proper chromatin organization, silencing of sex
chromosomes and crossover formation in male meiosis. PLoS Genet.
14:e10072092018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
De Rijck J, de Kogel C, Demeulemeester J,
Vets S, El Ashkar S, Malani N, Bushman FD, Landuyt B, Husson SJ,
Busschots K, et al: The BET family of proteins targets moloney
murine leukemia virus integration near transcription start sites.
Cell Rep. 5:886–894. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dibenedetto AJ, Guinto JB, Ebert TD, Bee
KJ, Schmidt MM and Jackman TR: Zebrafish brd2a and brd2b are
paralogous members of the bromodomain-ET (BET) family of
transcriptional coregulators that show structural and expression
divergence. BMC Dev Biol. 8:392008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang L and Wolgemuth DJ: BET protein BRDT
complexes with HDAC1, PRMT5, and TRIM28 and functions in
transcriptional repression during spermatogenesis. J Cell Biochem.
117:1429–1438. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pivot-Pajot C, Caron C, Govin J, Vion A,
Rousseaux S and Khochbin S: Acetylation-Dependent chromatin
reorganization by BRDT, a testis-specific bromodomain-containing
protein. Mol Cell Biol. 23:5354–5365. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bourova-Flin E, Chuffart F, Rousseaux S
and Khochbin S: The role of bromodomain testis-specific factor,
BRDT, in cancer: A biomarker and a possible therapeutic target.
Cell J. 19:1–8. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Barda S, Yogev L, Paz G, Yavetz H, Lehavi
O, Hauser R, Doniger T, Breitbart H and Kleiman SE: BRDT gene
sequence in human testicular pathologies and the implication of its
single nucleotide polymorphism (rs3088232) on fertility. Andrology.
2:641–647. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Suyama T, Shiraishi T, Zeng Y, Yu W,
Parekh N, Vessella RL, Luo J, Getzenberg RH and Kulkarni P:
Expression of cancer/testis antigens in prostate cancer is
associated with disease progression. Prostate. 70:1778–1787. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lagerholm S, Lagerholm S, Dutta S and Nair
P: Non-Invasive detection of c-myc p64, c-myc p67 and c-erbb-2 in
colorectal cancer. Scand J Gastroenterol. 40:1343–1350. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ozer HG, El-Gamal D, Powell B, Hing ZA,
Blachly JS, Harrington B, Mitchell S, Grieselhuber NR, Williams K,
Lai TH, et al: BRD4 profiling identifies critical chronic
lymphocytic leukemia oncogenic circuits and reveals sensitivity to
PLX51107, a novel structurally distinct BET inhibitor. Cancer
Discov. 8:458–477. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Erkes DA, Field CO, Capparelli C, Tiago M,
Purwin TJ, Chervoneva I, Berger AC, Hartsough EJ, Villanueva J and
Aplin AE: The next-generation BET inhibitor, PLX51107, delays
melanoma growth in a CD8-mediated manner. Pigment Cell Melanoma
Res. 32:687–696. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stubbs MC, Burn TC, Sparks R, Maduskuie T,
Diamond S, Rupar M, Wen X, Volgina A, Zolotarjova N, Waeltz P, et
al: The novel bromodomain and extraterminal domain inhibitor
INCB054329 induces vulnerabilities in myeloma cells that inform
rational combination strategies. Clin Cancer Res. 25:300–311. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wilson AJ, Stubbs M, Liu P, Ruggeri B and
Khabele D: The BET inhibitor INCB054329 reduces homologous
recombination efficiency and augments PARP inhibitor activity in
ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 149:575–584. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yao Z, Yang S, Zhao H, Yang H and Jiang X:
BET inhibitor I-BET151 sensitizes GBM cells to temozolomide via
PUMA induction. Cancer Gene Ther. 27:226–234. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guo NH, Zheng JF, Zi FM and Cheng J:
I-BET151 suppresses osteoclast formation and inflammatory cytokines
secretion by targetting BRD4 in multiple myeloma. Biosci Rep.
39:BSR201812452019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang C, Cigliano A, Jiang L, Li X, Fan B,
Pilo MG, Liu Y, Gui B, Sini M, Smith JW, et al: 4EBP1/eIF4E and
p70S6K/RPS6 axes play critical and distinct roles in
hepatocarcinogenesis driven by AKT and N-Ras proto-oncogenes in
mice. Hepatology. 61:200–213. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chao MW, Wang LT, Lai CY, Yang XM, Cheng
YW, Lee KH, Pan SL and Teng CM: eIF4E binding protein 1 expression
is associated with clinical survival outcomes in colorectal cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:24092–24104. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
William M, Leroux LP, Chaparro V, Lorent
J, Graber TE, M'Boutchou MN, Charpentier T, Fabié A, Dozois CM,
Stäger S, et al: eIF4E-Binding proteins 1 and 2 limit macrophage
anti-inflammatory responses through translational repression of
IL-10 and cyclooxygenase-2. J Immunol. 200:4102–4116. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bao Y, Wu X, Chen J, Hu X, Zeng F, Cheng
J, Jin H, Lin X and Chen LF: Brd4 modulates the innate immune
response through mnk2-eIF4E pathway-dependent translational control
of IkBα. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:E3993–E4001. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Batool A, Majeed ST, Aashaq S, Majeed R,
Shah G, Nazir N and Andrabi KI: Eukaryotic initiation factor 4E
(eIF4E) sequestration mediates 4E-BP1 response to rapamycin. Int J
Biol Macromol. 125:651–659. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Modrak-Wojcik A, Gorka M, Niedzwiecka K,
Zdanowski K, Zuberek J, Niedzwiecka A and Stolarski R: Eukaryotic
translation initiation is controlled by cooperativity effects
within ternary complexes of 4E-BP1, eIF4E, and the mRNA 5′ cap.
FEBS Lett. 587:3928–3934. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gao W, Lam JW, Li JZ, Chen SQ, Tsang RK,
Chan JY and Wong TS: MicroRNA-138-5p controls sensitivity of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma to radiation by targeting EIF4EBP1. Oncol
Rep. 37:913–920. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cha YL, Li PD, Yuan LJ, Zhang MY, Zhang
YJ, Rao HL, Zhang HZ, Zheng XF and Wang HY: EIF4EBP1 overexpression
is associated with poor survival and disease progression in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e1174932015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wang Z, Feng X, Molinolo AA, Martin D,
Vitale-Cross L, Nohata N, Ando M, Wahba A, Amornphimoltham P, Wu X,
et al: 4E-BP1 is a tumor suppressor protein reactivated by mTOR
inhibition in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res. 79:1438–1450. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Furic L, Rong L, Larsson O, Koumakpayi IH,
Yoshida K, Brueschke A, Petroulakis E, Robichaud N, Pollak M,
Gaboury LA, et al: EIF4E phosphorylation promotes tumorigenesis and
is associated with prostate cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 107:14134–14139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
D'Abronzo LS and Ghosh PM: EIF4E
phosphorylation in prostate cancer. Neoplasia. 20:563–573. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee M, Kim EJ and Jeon MJ: MicroRNAs 125a
and 125b inhibit ovarian cancer cells through post-transcriptional
inactivation of EIF4EBP1. Oncotarget. 7:8726–8742. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Delmore JE, Issa GC, Lemieux ME, Rahl PB,
Shi J, Jacobs HM, Kastritis E, Gilpatrick T, Paranal RM, Qi J, et
al: BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target
c-myc. Cell. 146:904–917. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bandopadhayay P, Bergthold G, Nguyen B,
Schubert S, Gholamin S, Tang Y, Bolin S, Schumacher SE, Zeid R,
Masoud S, et al: BET bromodomain inhibition of MYC-amplified
medulloblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 20:912–925. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Coudé MM, Braun T, Berrou J, Dupont M,
Bertrand S, Masse A, Raffoux E, Itzykson R, Delord M, Riveiro ME,
et al: BET inhibitor OTX015 targets BRD2 and BRD4 and decreases
c-MYC in acute leukemia cells. Oncotarget. 6:17698–17712. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Baker EK, Taylor S, Gupte A, Sharp PP,
Walia M, Walsh NC, Zannettino AC, Chalk AM, Burns CJ and Walkley
CR: BET inhibitors induce apoptosis through a MYC independent
mechanism and synergise with CDK inhibitors to kill osteosarcoma
cells. Sci Rep. 5:101202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shao Q, Kannan A, Lin Z, Stack BJ, Suen JY
and Gao L: BET protein inhibitor JQ1 attenuates myc-amplified MCC
tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res. 74:7090–7102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shi J, Wang Y, Zeng L, Wu Y, Deng J, Zhang
Q, Lin Y, Li J, Kang T, Tao M, et al: Disrupting the interaction of
BRD4 with diacetylated twist suppresses tumorigenesis in basal-like
breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 25:210–225. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Takashima Y, Kikuchi E, Kikuchi J, Suzuki
M, Kikuchi H, Maeda M, Shoji T, Furuta M, Kinoshita I, Dosaka-Akita
H, et al: Bromodomain and extraterminal domain inhibition
synergizes with WEE1-inhibitor AZD1775 effect by impairing
non-homologous end joining and enhancing DNA damage in non-small
cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 15:1114–1124. 2019.
|
|
50
|
Wang SS, Chen G, Li SH, Pang JS, Cai KT,
Yan HB, Huang ZG and He RQ: Identification and validation of an
individualized autophagy-clinical prognostic index in bladder
cancer patients. Onco Targets Ther. 12:3695–3712. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wei W, Cao W, Zhan Z, Yan L, Xie Y and
Xiao Q: MiR-1284 suppresses gastric cancer progression by targeting
EIF4A1. Onco Targets Ther. 12:3965–3976. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xing ZY, Wang Y, Cheng L, Chen J, He XZ
and Xing W: Bromodomain-Containing protein 4 (BRD4) inhibition
sensitizes palomid 529-induced anti-renal cell carcinoma cell
activity in vitro and in vivo. Cell Physiol Biochem. 50:640–653.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liao S, Maertens O, Cichowski K and
Elledge SJ: Genetic modifiers of the BRD4-NUT dependency of NUT
midline carcinoma uncovers a synergism between BETis and CDK4/6is.
Genes Dev. 32:1188–1200. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tan Y, Wang L, Du Y, Liu X, Chen Z, Weng
X, Guo J, Chen H, Wang M and Wang X: Inhibition of BRD4 suppresses
tumor growth in prostate cancer via the enhancement of FOXO1
expression. Int J Oncol. 53:2503–2517. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gao Z, Yuan T, Zhou X, Ni P, Sun G, Li P,
Cheng Z and Wang X: Targeting BRD4 proteins suppresses the growth
of NSCLC through downregulation of eIF4E expression. Cancer Biol
Ther. 19:407–415. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hsu HS, Lin MH, Jang YH, Kuo TT, Liu CC
and Cheng TH: The 4E-BP1/eIF4E ratio is a determinant for rapamycin
response in esophageal cancer cells. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
149:378–385. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wang H, Liu Y, Ding J, Huang Y, Liu J, Liu
N, Ao Y, Hong Y, Wang L, Zhang L, et al: Targeting mTOR suppressed
colon cancer growth through 4EBP1/eIF4E/PUMA pathway. Cancer Gene
Ther. 27:448–460. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Schwartz YB, Kahn TG, Stenberg P, Ohno K,
Bourgon R and Pirrotta V: Alternative epigenetic chromatin states
of polycomb target genes. PLoS Genet. 6:e10008052010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Thieffry D and Sanchez L: Alternative
epigenetic states understood in terms of specific regulatory
structures. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 981:135–153. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|