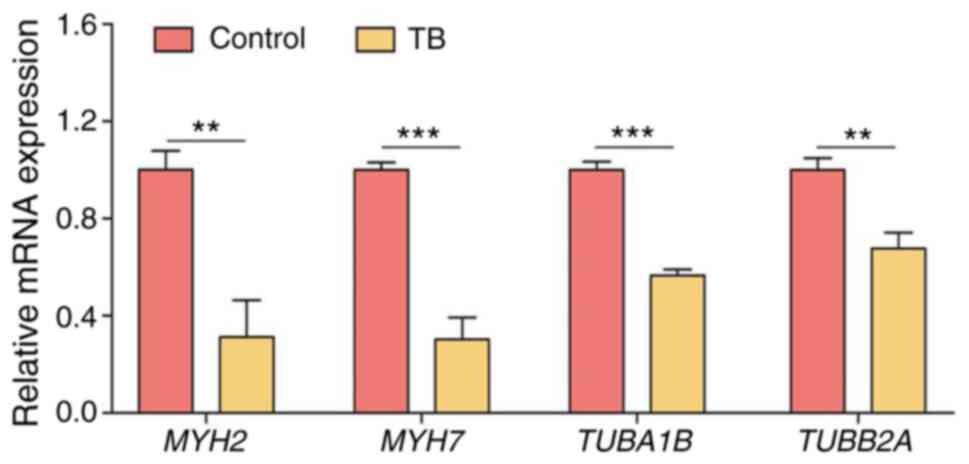
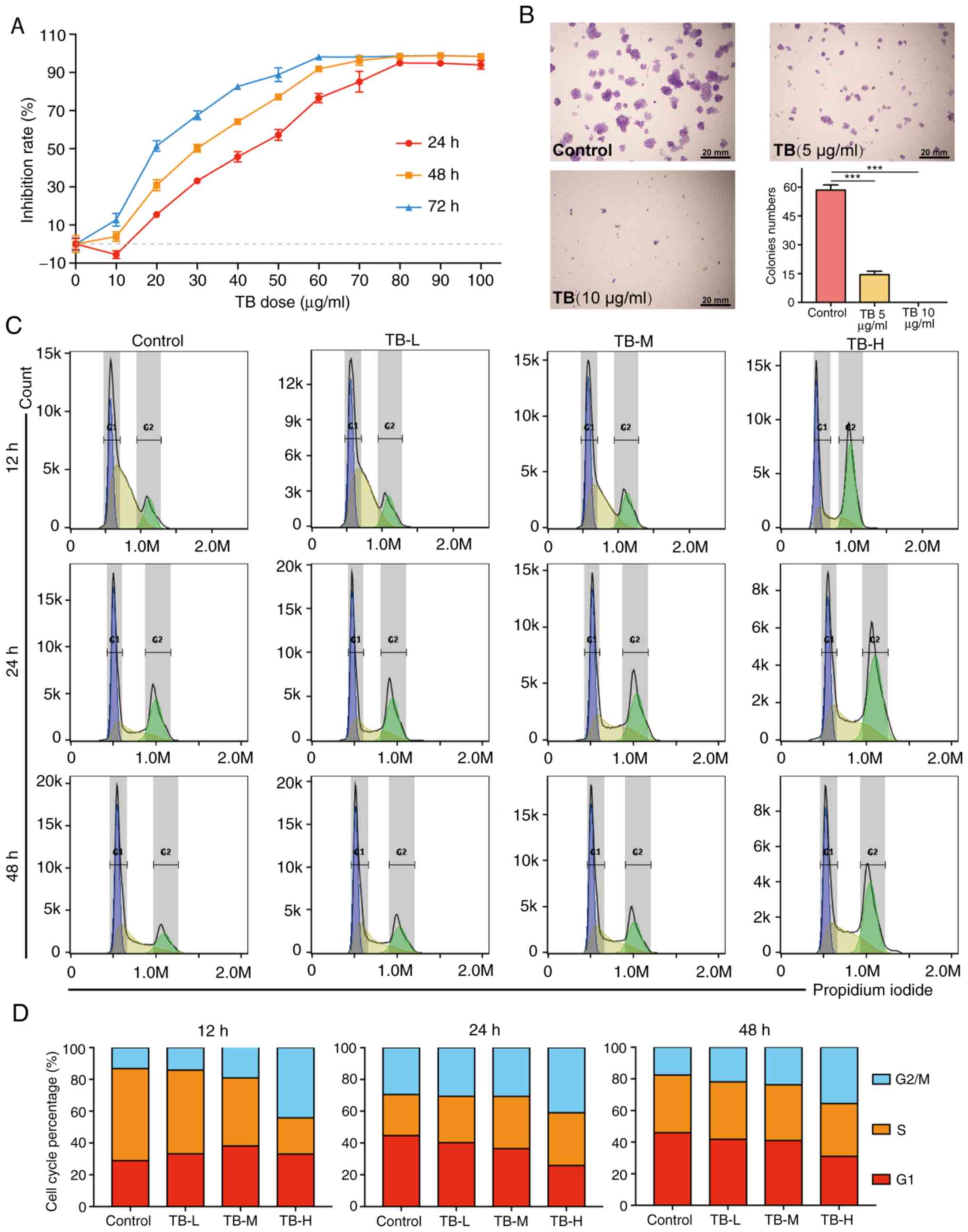
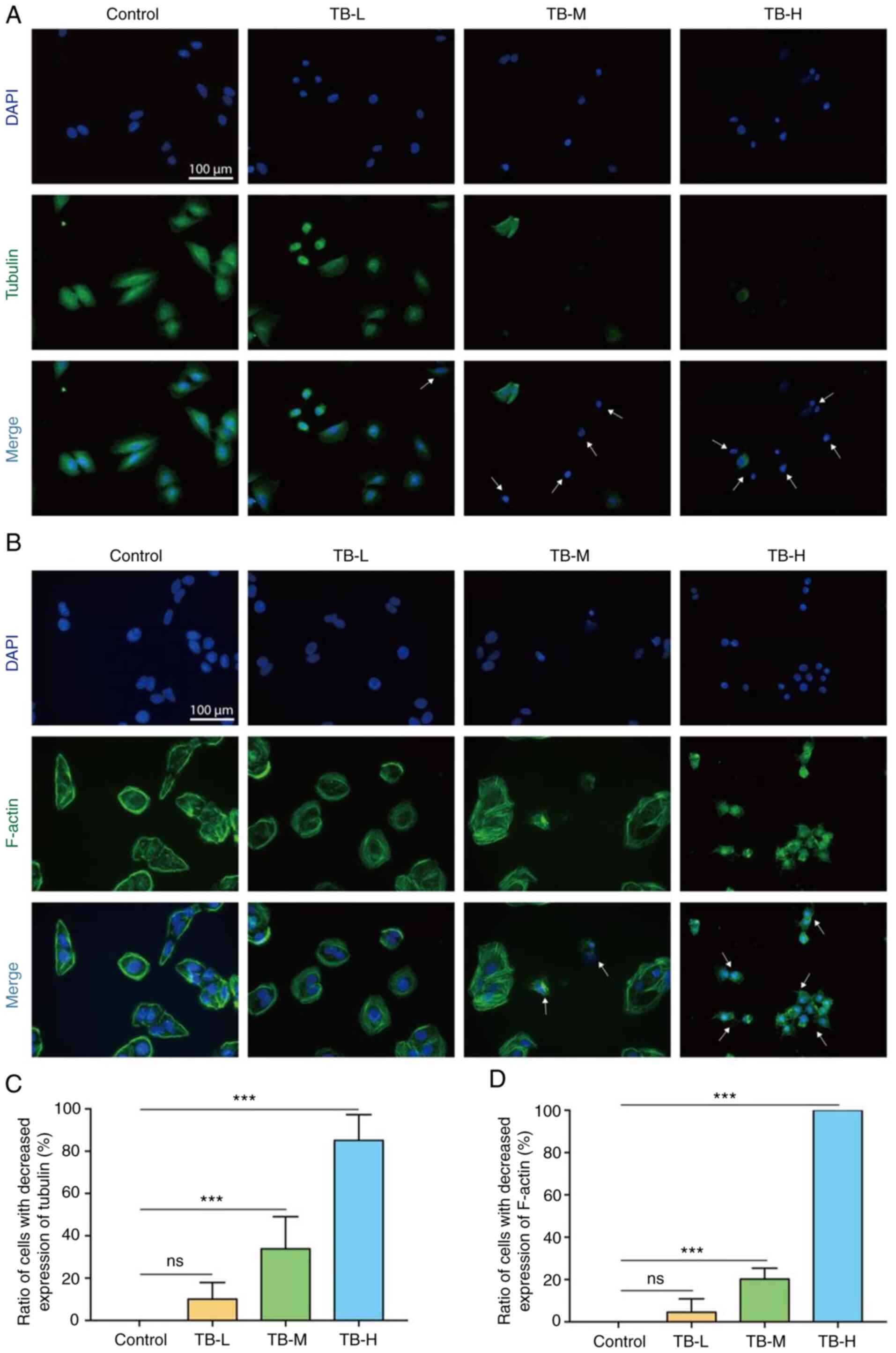
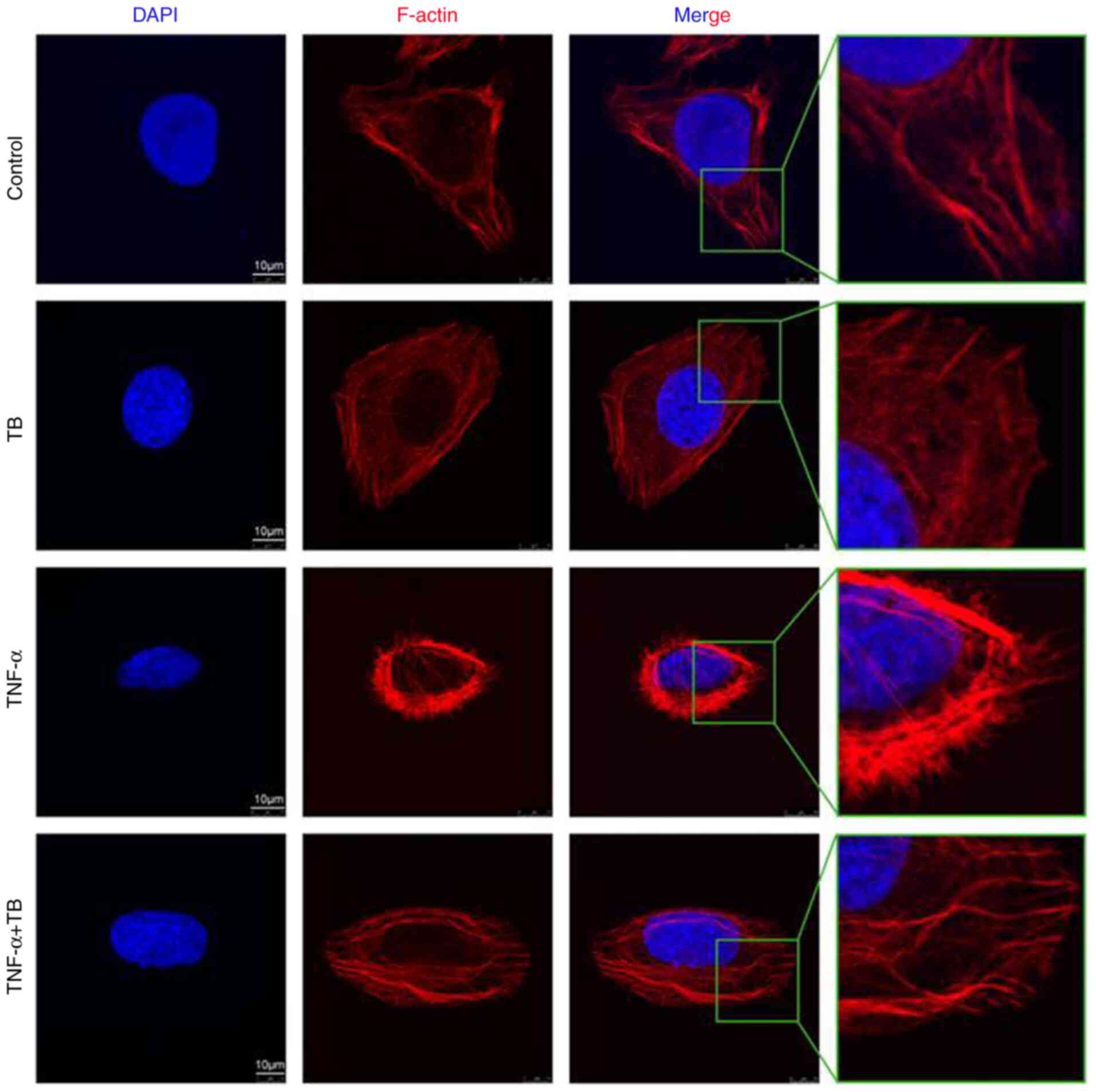
|
1
|
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ and Savage SA:
Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: Data
from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program.
Cancer. 115:1531–1543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ and Savage SA:
International osteosarcoma incidence patterns in children and
adolescents, middle ages and elderly persons. Int J Cancer.
125:229–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Valery PC, Laversanne M and Bray F: Bone
cancer incidence by morphological subtype: A global assessment.
Cancer Causes Control. 26:1127–1139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bielack SS, Kempf-Bielack B, Delling G,
Exner GU, Flege S, Helmke K, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M, Werner M,
Winkelmann W, et al: Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma
of the extremities or trunk: An analysis of 1,702 patients treated
on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J
Clin Oncol. 20:776–790. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Whelan JS, Bielack SS, Marina N, Smeland
S, Jovic G, Hook JM, Krailo M, Anninga J, Butterfass-Bahloul T,
Böhling T, et al: EURAMOS-1, an international randomised study for
osteosarcoma: Results from pre-randomisation treatment. Ann Oncol.
26:407–414. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guo J, Reddick WE, Glass JO, Ji Q, Billups
CA, Wu J, Hoffer FA, Kaste SC, Jenkins JJ, Ortega Flores XC, et al:
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging as a
prognostic factor in predicting event-free and overall survival in
pediatric patients with osteosarcoma. Cancer. 118:3776–3785. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Le Vu B, de Vathaire F, Shamsaldin A,
Hawkins MM, Grimaud E, Hardiman C, Diallo I, Vassal G, Bessa E,
Campbell S, et al: Radiation dose, chemotherapy and risk of
osteosarcoma after solid tumours during childhood. Int J Cancer.
77:370–377. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Calvert GT, Randall RL, Jones KB,
Cannon-Albright L, Lessnick S and Schiffman JD: At-risk populations
for osteosarcoma: The syndromes and beyond. Sarcoma.
2012:1523822012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Klein MJ and Siegal GP: Osteosarcoma:
Anatomic and histologic variants. Am J Clin Pathol. 125:555–581.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meyers PA, Schwartz CL, Krailo M,
Kleinerman ES, Betcher D, Bernstein ML, Conrad E, Ferguson W,
Gebhardt M, Goorin AM, et al: Osteosarcoma: A randomized,
prospective trial of the addition of ifosfamide and/or muramyl
tripeptide to cisplatin, doxorubicin, and high-dose methotrexate. J
Clin Oncol. 23:2004–2011. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kempf-Bielack B, Bielack SS, Jurgens H,
Branscheid D, Berdel WE, Exner GU, Göbel U, Helmke K, Jundt G,
Kabisch H, et al: Osteosarcoma relapse after combined modality
therapy: An analysis of unselected patients in the cooperative
osteosarcoma study group (COSS). J Clin Oncol. 23:559–568. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jensen GS, Beaman JL, He Y, Guo Z and Sun
H: Reduction of body fat and improved lipid profile associated with
daily consumption of a Puer tea extract in a hyperlipidemic
population: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Clin Interv
Aging. 11:367–376. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang M, Wang C and Chen H: Green, oolong
and black tea extracts modulate lipid metabolism in hyperlipidemia
rats fed high-sucrose diet. J Nutr Biochem. 12:14–20. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu LY, Juan CC, Hwang LS, Hsu YP, Ho PH
and Ho LT: Green tea supplementation ameliorates insulin resistance
and increases glucose transporter IV content in a fructose-fed rat
model. Eur J Nutr. 43:116–124. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Imai K, Suga K and Nakachi K:
Cancer-preventive effects of drinking green tea among a Japanese
population. Prev Med. 26:769–775. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakachi K, Suemasu K, Suga K, Takeo T,
Imai K and Higashi Y: Influence of drinking green tea on breast
cancer malignancy among Japanese patients. Jpn J Cancer Res.
89:254–261. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jin W, Zhou L, Yan B, Yan L, Liu F, Tong
P, Yu W, Dong X, Xie L, Zhang J, et al: Theabrownin triggers DNA
damage to suppress human osteosarcoma U2OS cells by activating p53
signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 22:4423–4436. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou L, Wu F, Jin W, Yan B, Chen X, He Y,
Yang W, Du W, Zhang Q, Guo Y, et al: Theabrownin inhibits cell
cycle progression and tumor growth of lung carcinoma through
c-myc-Related mechanism. Front Pharmacol. 8:752017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hay ED: An overview of
epithelio-mesenchymal transformation. Acta Anat (Basel). 154:8–20.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chapman HA: Epithelial-mesenchymal
interactions in pulmonary fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 73:413–435.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang G, Yuan J and Li K: EMT transcription
factors: Implication in osteosarcoma. Med Oncol. 30:6972013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
De Craene B and Berx G: Regulatory
networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:97–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Damsky CH, Richa J, Solter D, Knudsen K
and Buck CA: Identification and purification of a cell surface
glycoprotein mediating intercellular adhesion in embryonic and
adult tissue. Cell. 34:455–466. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kobielak A and Fuchs E: Alpha-catenin: At
the junction of intercellular adhesion and actin dynamics. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 5:614–625. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oka H, Shiozaki H, Kobayashi K, Inoue M,
Tahara H, Kobayashi T, Takatsuka Y, Matsuyoshi N, Hirano S,
Takeichi M, et al: Expression of E-cadherin cell adhesion molecules
in human breast cancer tissues and its relationship to metastasis.
Cancer Res. 53:1696–1701. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gumbiner BM: Cell adhesion: The molecular
basis of tissue architecture and morphogenesis. Cell. 84:345–357.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hirohashi S: Inactivation of the
E-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion system in human cancers. Am J
Pathol. 153:333–339. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Min C, Eddy SF, Sherr DH and Sonenshein
GE: NF-kappaB and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of cancer. J
Cell Biochem. 104:733–744. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hendrix MJ, Seftor EA, Chu YW, Trevor KT
and Seftor RE: Role of intermediate filaments in migration,
invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 15:507–525. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cano A, Perez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I,
Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, Portillo F and Nieto MA: The
transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yang H, Zhang Y, Zhou Z, Jiang X and Shen
A: Snail-1 regulates VDR signaling and inhibits
1,25(OH)-D3 action in osteosarcoma. Eur J Pharmacol.
670:341–346. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sharili AS, Allen S, Smith K, Hargreaves
J, Price J and McGonnell I: Expression of Snail2 in long bone
osteosarcomas correlates with tumour malignancy. Tumour Biol.
32:515–526. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gheldof A, Hulpiau P, van Roy F, De Craene
B and Berx G: Evolutionary functional analysis and molecular
regulation of the ZEB transcription factors. Cell Mol Life Sci.
69:2527–2541. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang Y, Yang Y, Gao R, Yang X, Yan X,
Wang C, Jiang S and Yu L: RLIM interacts with Smurf2 and promotes
TGF-β induced U2OS cell migration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
414:181–185. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Arima Y, Inoue Y, Shibata T, Hayashi H,
Nagano O, Saya H and Taya Y: Rb depletion results in deregulation
of E-cadherin and induction of cellular phenotypic changes that are
characteristic of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer
Res. 68:5104–5112. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Barnes PJ and Karin M: Nuclear
factor-kappaB: A pivotal transcription factor in chronic
inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med. 336:1066–1071. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Karin M and Greten FR: NF-kappaB: Linking
inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression.
Nat Rev Immunol. 5:749–759. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huang S, Pettaway CA, Uehara H, Bucana CD
and Fidler IJ: Blockade of NF-kappaB activity in human prostate
cancer cells is associated with suppression of angiogenesis,
invasion, and metastasis. Oncogene. 20:4188–4197. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Helbig G, Christopherson KW II,
Bhat-Nakshatri P, Kumar S, Kishimoto H, Miller KD, Broxmeyer HE and
Nakshatri H: NF-kappaB promotes breast cancer cell migration and
metastasis by inducing the expression of the chemokine receptor
CXCR4. J Biol Chem. 278:21631–21638. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Radisky DC and Bissell MJ: NF-kappaB links
oestrogen receptor signalling and EMT. Nat Cell Biol. 9:361–363.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chua HL, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Clare SE,
Morimiya A, Badve S and Nakshatri H: NF-kappaB represses E-cadherin
expression and enhances epithelial to mesenchymal transition of
mammary epithelial cells: Potential involvement of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2.
Oncogene. 26:711–724. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Medici D and Nawshad A: Type I collagen
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through ILK-dependent
activation of NF-kappaB and LEF-1. Matrix Biol. 29:161–165. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang X, Belguise K, Kersual N, Kirsch KH,
Mineva ND, Galtier F, Chalbos D and Sonenshein GE: Oestrogen
signalling inhibits invasive phenotype by repressing RelB and its
target BCL2. Nat Cell Biol. 9:470–478. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sarkar FH, Li Y, Wang Z and Kong D:
NF-kappaB signaling pathway and its therapeutic implications in
human diseases. Int Rev Immunol. 27:293–319. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huang CY, Lee CY, Chen MY, Yang WH, Chen
YH, Chang CH, Hsu HC, Fong YC and Tang CH: Stromal cell-derived
factor-1/CXCR4 enhanced motility of human osteosarcoma cells
involves MEK1/2, ERK and NF-kappaB-dependent pathways. J Cell
Physiol. 221:204–212. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Felx M, Guyot MC, Isler M, Turcotte RE,
Doyon J, Khatib AM, Leclerc S, Moreau A and Moldovan F:
Endothelin-1 (ET-1) promotes MMP-2 and MMP-9 induction involving
the transcription factor NF-kappaB in human osteosarcoma. Clin Sci
(Lond). 110:645–654. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Iyer SV, Ranjan A, Elias HK, Parrales A,
Sasaki H, Roy BC, Umar S, Tawfik OW and Iwakuma T: Genome-wide RNAi
screening identifies TMIGD3 isoform1 as a suppressor of NF-κB and
osteosarcoma progression. Nat Commun. 7:135612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhou J, Liu Q, Qian R, Liu S, Hu W and Liu
Z: Paeonol antagonizes oncogenesis of osteosarcoma by inhibiting
the function of TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Acta Histochem.
122:1514552020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yang M, Liu B, Jin L, Tao H and Yang Z:
Estrogen receptor β exhibited anti-tumor effects on osteosarcoma
cells by regulating integrin, IAP, NF-kB/BCL-2 and PI3K/Akt signal
pathway. J Bone Oncol. 9:15–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|