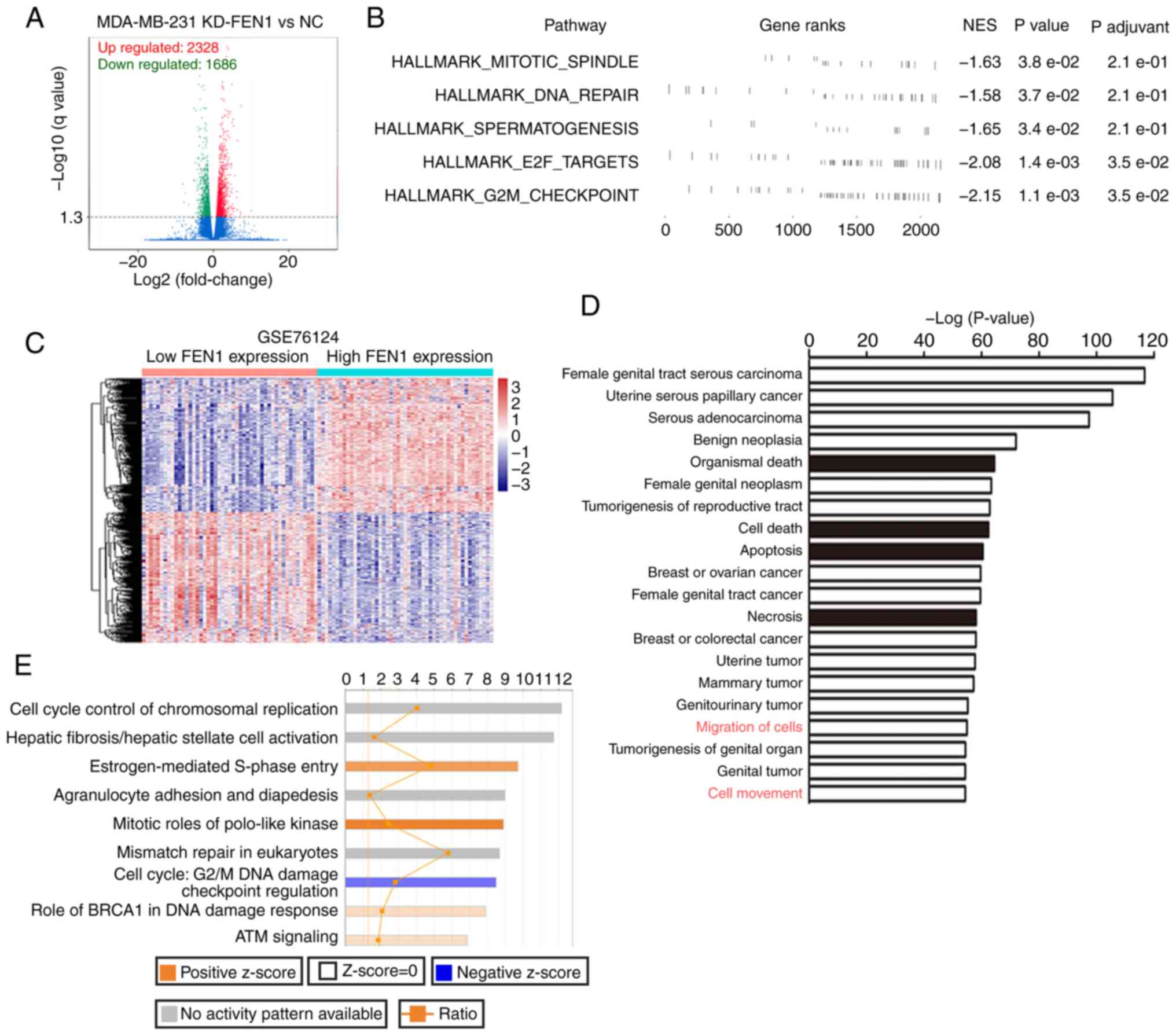
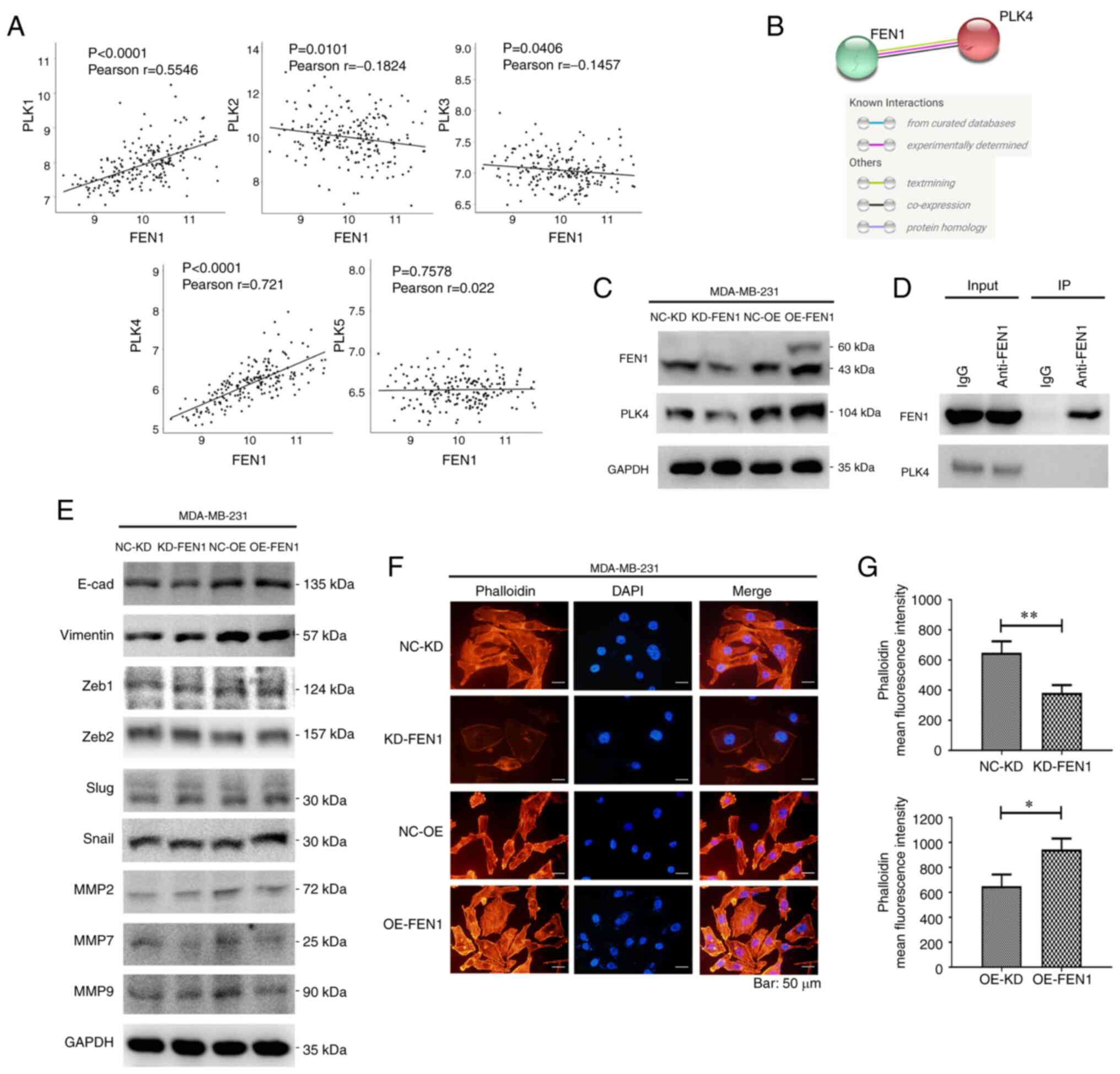
|
1
|
Bianchini G, Balko JM, Mayer IA, Sanders
ME and Gianni L: Triple-negative breast cancer: Challenges and
opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
13:674–690. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM,
Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P and Narod SA:
Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of
recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4429–4434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tischkowitz M, Brunet JS, Bégin LR,
Huntsman DG, Cheang MC, Akslen LA, Nielsen TO and Foulkes WD: Use
of immunohistochemical markers can refine prognosis in triple
negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 7:1342007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bakhoum SF, Ngo B, Laughney AM, Cavallo
JA, Murphy CJ, Ly P, Shah P, Sriram RK, Watkins TBK, Taunk NK, et
al: Chromosomal instability drives metastasis through a cytosolic
DNA response. Nature. 553:467–472. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jing A, Vizeacoumar FS, Parameswaran S,
Haave B, Cunningham CE, Wu Y, Arnold R, Bonham K, Freywald A, Han J
and Vizeacoumar FJ: Expression-based analyses indicate a central
role for hypoxia in driving tumor plasticity through
microenvironment remodeling and chromosomal instability. NPJ Syst
Biol Appl. 4:382018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Robinson DR, Wu YM, Lonigro RJ, Vats P,
Cobain E, Everett J, Cao X, Rabban E, Kumar-Sinha C, Raymond V, et
al: Integrative clinical genomics of metastatic cancer. Nature.
548:297–303. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pilie PG, Tang C, Mills GB and Yap TA:
State-of-the-art strategies for targeting the DNA damage response
in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 16:81–104. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Balakrishnan L and Bambara RA: Flap
endonuclease 1. Annu Rev Biochem. 82:119–138. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Abdel-Fatah TM, Russell R, Albarakati N,
Maloney DJ, Dorjsuren D, Rueda OM, Moseley P, Mohan V, Sun H,
Abbotts R, et al: Genomic and protein expression analysis reveals
flap endonuclease 1 (FEN1) as a key biomarker in breast and ovarian
cancer. Mol Oncol. 8:1326–1338. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ali R, Rakha EA, Madhusudan S and Bryant
HE: DNA damage repair in breast cancer and its therapeutic
implications. Pathology. 49:156–165. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He L, Luo L, Zhu H, Yang H, Zhang Y, Wu H,
Sun H, Jiang F, Kathera CS, Liu L, et al: FEN1 promotes tumor
progression and confers cisplatin resistance in non-small-cell lung
cancer. Mol Oncol. 11:640–654. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He L, Yang H, Zhou S, Zhu H, Mao H, Ma Z,
Wu T, Kumar AK, Kathera C, Janardhan A, et al: Synergistic
antitumor effect of combined paclitaxel with FEN1 inhibitor in
cervical cancer cells. DNA Repair (Amst). 63:1–9. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He L, Zhang Y, Sun H, Jiang F, Yang H, Wu
H, Zhou T, Hu S, Kathera CS, Wang X, et al: Targeting DNA flap
endonuclease 1 to impede breast cancer progression. EBioMedicine.
14:32–43. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hwang JC, Sung WW, Tu HP, Hsieh KC, Yeh
CM, Chen CJ, Tai HC, Hsu CT, Shieh GS, Chang JG, et al: The
overexpression of FEN1 and RAD54B May Act as independent prognostic
factors of lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01394352015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Isohookana J, Haapasaari KM, Soini Y,
Leppanen J and Karihtala P: Proteins of the retinoblastoma pathway,
FEN1 and MGMT are novel potential prognostic biomarkers in
pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 214:840–847. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim JM, Sohn HY, Yoon SY, Oh JH, Yang JO,
Kim JH, Song KS, Rho SM, Yoo HS, Kim YS, et al: Identification of
gastric cancer-related genes using a cDNA microarray containing
novel expressed sequence tags expressed in gastric cancer cells.
Clin Cancer Res. 11:473–482. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Narayan S and Sharma R: Molecular
mechanism of adenomatous polyposis coli-induced blockade of base
excision repair pathway in colorectal carcinogenesis. Life Sci.
139:145–152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nikolova T, Christmann M and Kaina B: FEN1
is overexpressed in testis, lung and brain tumors. Anticancer Res.
29:2453–2459. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sato M, Girard L, Sekine I, Sunaga N,
Ramirez RD, Kamibayashi C and Minna JD: Increased expression and no
mutation of the Flap endonuclease (FEN1) gene in human lung cancer.
Oncogene. 22:7243–7246. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singh P, Yang M, Dai H, Yu D, Huang Q, Tan
W, Kernstine KH, Lin D and Shen B: Overexpression and
hypomethylation of flap endonuclease 1 gene in breast and other
cancers. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1710–1717. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang J, Zhou L, Li Z, Zhang T, Liu W, Liu
Z, Yuan YC, Su F, Xu L, Wang Y, et al: YY1 suppresses FEN1
over-expression and drug resistance in breast cancer. BMC Cancer.
15:502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xie C, Wang K and Chen D: Flap
endonuclease 1 silencing is associated with increasing the
cisplatin sensitivity of SGC7901 gastric cancer cells. Mol Med Rep.
13:386–392. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang K, Keymeulen S, Nelson R, Tong TR,
Yuan YC, Yun X, Liu Z, Lopez J, Raz DJ and Kim JY: Overexpression
of flap endonuclease 1 correlates with enhanced proliferation and
poor prognosis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Am J Pathol.
188:242–251. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zeng X, Qu X, Zhao C, Xu L, Hou K, Liu Y,
Zhang N, Feng J, Shi S, Zhang L, et al: FEN1 mediates miR-200a
methylation and promotes breast cancer cell growth via MET and EGFR
signaling. FASEB J. 33:10717–10730. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Forbes SA, Beare D, Boutselakis H, Bamford
S, Bindal N, Tate J, Cole CG, Ward S, Dawson E, Ponting L, et al:
COSMIC: Somatic cancer genetics at high-resolution. Nucleic Acids
Res. 45:D777–D783. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rhodes DR, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Mahavisno
V, Varambally R, Yu J, Briggs BB, Barrette TR, Anstet MJ,
Kincead-Beal C, Kulkarni P, et al: Oncomine 3.0: Genes, pathways,
and networks in a collection of 18,000 cancer gene expression
profiles. Neoplasia. 9:166–180. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu W, Zhang L, Shi J, Liu Y, Zhou L, Hou
K, Qu X and Teng Y: Clinical significance of pAkt and pErk1/2
expression in early-stage breast cancer patients treated with
anthracycline-based adjuvant chemotherapy. Oncol Lett. 9:1707–1714.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kramer A, Green J, Pollard J Jr and
Tugendreich S: Causal analysis approaches in Ingenuity pathway
analysis. Bioinformatics. 30:523–530. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li H, Xu L, Li C, Zhao L, Ma Y, Zheng H,
Li Z, Zhang Y, Wang R, Liu Y and Qu X: Ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b
represses IGF-I-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition via ZEB2
and microRNA-200c regulation in gastric cancer cells. Mol Cancer.
13:1362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tian X, Zhou D, Chen L, Tian Y, Zhong B,
Cao Y, Dong Q, Zhou M, Yan J, Wang Y, et al: Polo-like kinase 4
mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in neuroblastoma via
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 9:542018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liao Z, Zhang H, Fan P, Huang Q, Dong K,
Qi Y, Song J, Chen L, Liang H, Chen X, et al: High PLK4 expression
promotes tumor progression and induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in
colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 54:479–490. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kazazian K, Go C, Wu H, Brashavitskaya O,
Xu R, Dennis JW, Gingras AC and Swallow CJ: Plk4 promotes cancer
invasion and metastasis through Arp2/3 complex regulation of the
actin cytoskeleton. Cancer Res. 77:434–447. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rosario CO, Kazazian K, Zih FS,
Brashavitskaya O, Haffani Y, Xu RS, George A, Dennis JW and Swallow
CJ: A novel role for Plk4 in regulating cell spreading and
motility. Oncogene. 34:3441–3451. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Foulkes WD, Smith IE and Reis-Filho JS:
Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1938–1948. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang K, Xie C and Chen D: Flap
endonuclease 1 is a promising candidate biomarker in gastric cancer
and is involved in cell proliferation and apoptosis. Int J Mol Med.
33:1268–1274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sang Y, Bo L, Gu H, Yang W and Chen Y:
Flap endonuclease-1 rs174538 G>A polymorphisms are associated
with the risk of esophageal cancer in a Chinese population. Thorac
Cancer. 8:192–196. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zeng X, Che X, Liu YP, Qu XJ, Xu L, Zhao
CY, Zheng CL, Hou KZ and Teng Y: FEN1 knockdown improves
trastuzumab sensitivity in human epidermal growth factor 2-positive
breast cancer cells. Exp Ther Med. 14:3265–3272. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lam JS, Seligson DB, Yu H, Li A, Eeva M,
Pantuck AJ, Zeng G, Horvath S and Belldegrun AS: Flap endonuclease
1 is overexpressed in prostate cancer and is associated with a high
gleason score. BJU Int. 98:445–451. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Qi L, Zhou B, Chen J, Hu W, Bai R, Ye C,
Weng X and Zheng S: Significant prognostic values of differentially
expressed-aberrantly methylated hub genes in breast cancer. J
Cancer. 10:6618–6634. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zitouni S, Nabais C, Jana SC, Guerrero A
and Bettencourt-Dias M: Polo-like kinases: Structural variations
lead to multiple functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:433–452.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li Z, Dai K, Wang C, Song Y, Gu F, Liu F
and Fu L: Expression of polo-like kinase 4(PLK4) in breast cancer
and its response to taxane-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J
Cancer. 7:1125–1132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ling H, Hanashiro K, Luong TH, Benavides L
and Fukasawa K: Functional relationship among PLK2, PLK4 and ROCK2
to induce centrosome amplification. Cell Cycle. 14:544–553. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME,
Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y and Pietenpol JA: Identification of human
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for
selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest. 121:2750–2767.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|