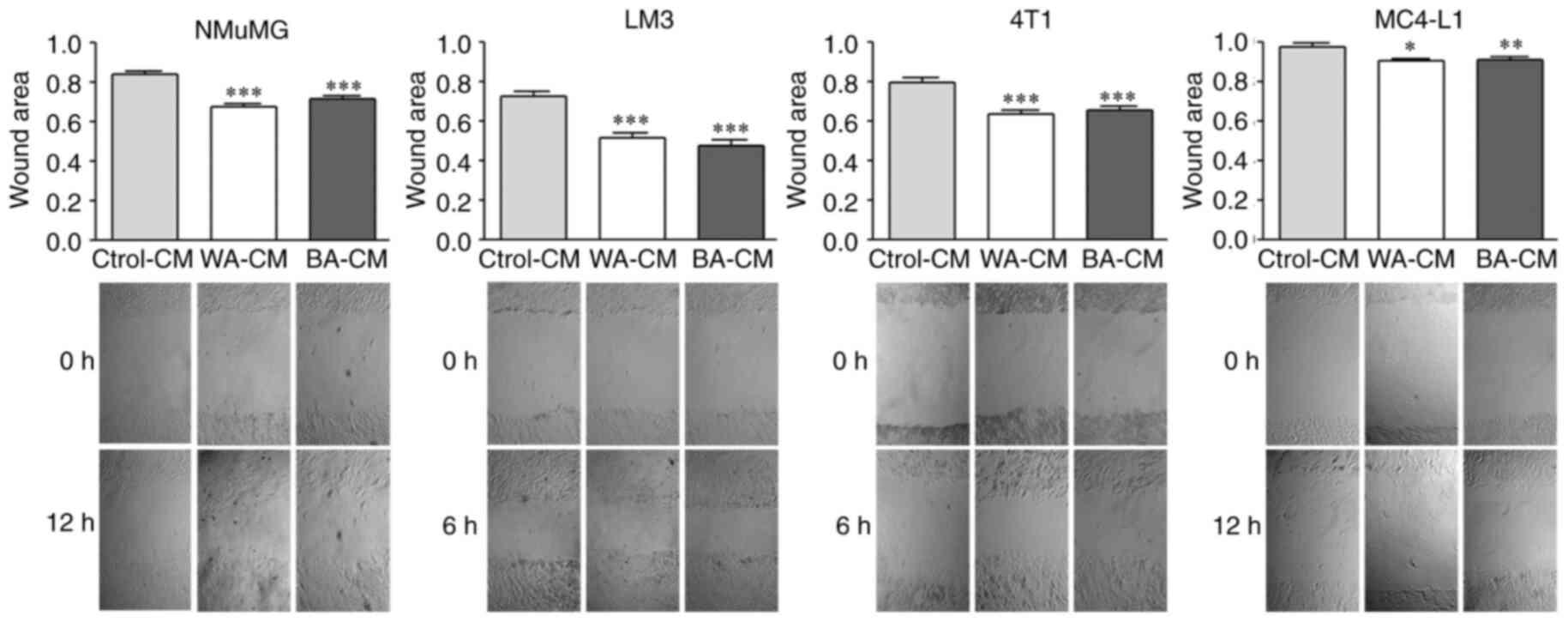
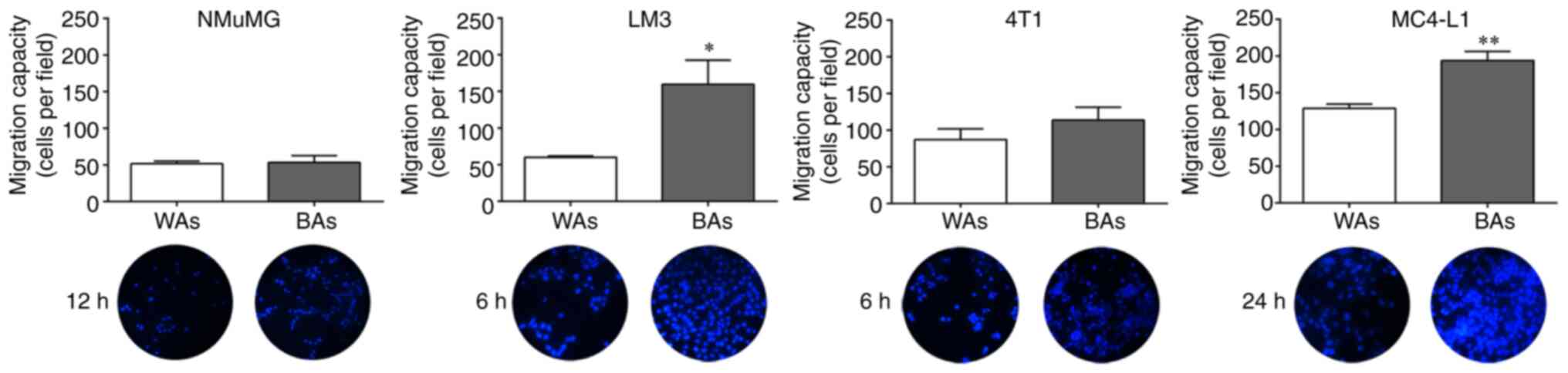
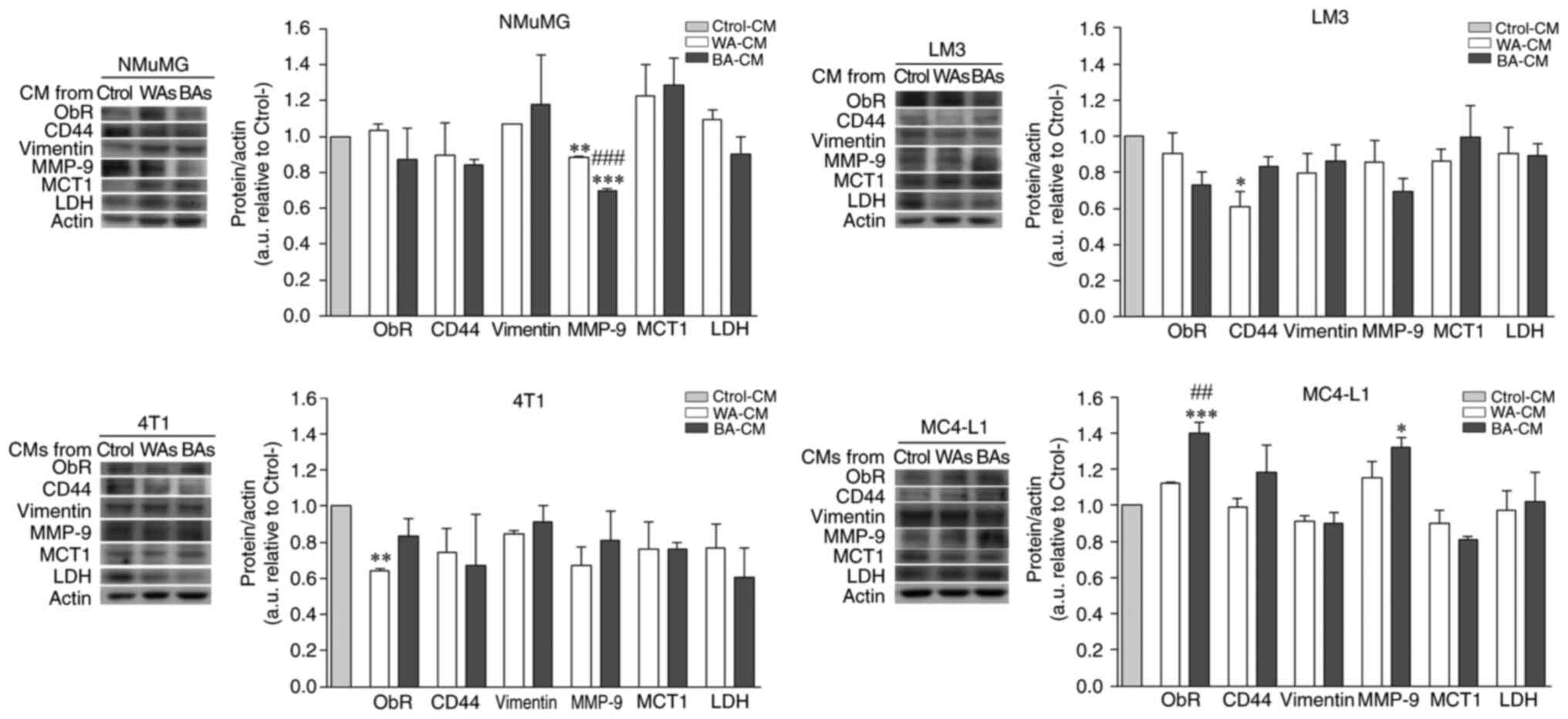
|
1
|
Peinado H, Zhang H, Matei IR, Costa-Silva
B, Hoshino A, Rodrigues G, Psaila B, Kaplan RN, Bromberg JF, Kang
Y, et al: Pre-metastatic niches: Organ-specific homes for
metastases. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:302–317. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Dirat B, Bochet L, Dabek M, Daviaud D,
Dauvillier S, Majed B, Wang YY, Meulle A, Salles B, Le Gonidec S,
et al: Cancer-associated adipocytes exhibit an activated phenotype
and contribute to breast cancer invasion. Cancer Res. 71:2455–2465.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Fletcher SJ, Sacca PA, Pistone-Creydt M,
Coló FA, Serra MF, Santino FE, Sasso CV, Lopez-Fontana CM, Carón
RW, Calvo JC and Pistone-Creydt V: Human breast adipose tissue:
Characterization of factors that change during tumor progression in
human breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:1–13. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Pistone Creydt V, Fletcher SJ, Giudice J,
Bruzzone A, Chasseing NA, Gonzalez EG, Sacca PA and Calvo JC: Human
adipose tissue from normal and tumoral breast regulates the
behavior of mammary epithelial cells. Clin Transl Oncol.
15:124–131. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wu Q, Li B, Li Z, Li J and Sun S and Sun
S: Cancer-associated adipocytes: Key players in breast cancer
progression. J Hematol Oncol. 12:952019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Pope BD, Warren CR, Parker KK and Cowan
CA: Microenvironmental control of adipocyte fate and function.
Trends Cell Biol. 26:745–755. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Park A: Distinction of white, beige and
brown adipocytes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem
Cells. 6:33–42. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang YY, Attané C, Milhas D, Dirat B,
Dauvillier S, Guerard A, Gilhodes J, Lazar I, Alet N, Laurent V, et
al: Mammary adipocytes stimulate breast cancer invasion through
metabolic remodeling of tumor cells. JCI Insight. 2:e874892017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bussard KM, Mutkus L, Stumpf K,
Gomez-Manzano C and Marini FC: Tumor-associated stromal cells as
key contributors to the tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res.
18:842016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cannon B and Nedergaard J: Brown adipose
tissue: Function and physiological significance. Physiol Rev.
84:277–359. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sepa-Kishi DM and Ceddia RB: White and
beige adipocytes: Are they metabolically distinct? Horm Mol Biol
Clin Investig. 332018.doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2018-0003.
|
|
12
|
Harms M and Seale P: Brown and beige fat:
Development, function and therapeutic potential. Nat Med.
19:1252–1263. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Vitali A, Murano I, Zingaretti MC,
Frontini A, Ricquier D and Cinti S: The adipose organ of
obesity-prone C57BL/6J mice is composed of mixed white and brown
adipocytes. J Lipid Res. 53:619–629. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Master SR, Hartman JL, D'Cruz CM, Moody
SE, Keiper EA, Ha SI, Cox JD, Belka GK and Chodosh LA: Functional
microarray analysis of mammary organogenesis reveals a
developmental role in adaptive thermogenesis. Mol Endocrinol.
16:1185–1203. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gouon-Evans V and Pollard JW: Unexpected
deposition of brown fat in mammary gland during postnatal
development. Mol Endocrinol. 16:2618–2627. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cao Q, Hersl J, La H, Smith M, Jenkins J,
Goloubeva O, Dilsizian V, Tkaczuk K, Chen W and Jones L: A pilot
study of FDG PET/CT detects a link between brown adipose tissue and
breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 14:1262014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jones LP, Buelto D, Tago E and
Owusu-Boaitey KE: Abnormal mammary adipose tissue environment of
Brca1 mutant mice show a persistent deposition of highly
vascularized multilocular adipocytes. J Cancer Sci Ther. 8 (Suppl
2):S42011.
|
|
18
|
Singh R, Parveen M, Basgen JM, Fazel S,
Meshesha MF, Thames EC, Moore B, Martinez L, Howard CB, Vergnes L,
et al: Increased expression of beige/brown adipose markers from
host and breast cancer cells influence xenograft formation in mice.
Mol Cancer Res. 14:78–92. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wu Q, Li J, Li Z, Sun S, Zhu S, Wang L, Wu
J, Yuan J, Zhang Y, Sun S and Wang C: Exosomes from the
tumour-adipocyte interplay stimulate beige/brown differentiation
and reprogram metabolism in stromal adipocytes to promote tumour
progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:2232019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Orava J, Nuutila P, Lidell ME, Oikonen V,
Noponen T, Viljanen T, Scheinin M, Taittonen M, Niemi T, Enerbäck S
and Virtanen KA: Different metabolic responses of human brown
adipose tissue to activation by cold and insulin. Cell Metab.
14:272–279. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang F, Gao S, Chen F, Fu Z, Yin H, Lu X,
Yu J and Lu C: Mammary fat of breast cancer: Gene expression
profiling and functional characterization. PLoS One. 9:e1097422014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Urtreger A, Ladeda V, Puricelli L, Rivelli
A, Vidal M, Delustig E and Joffe E: Modulation of fibronectin
expression and proteolytic activity associated with the invasive
and metastatic phenotype in two new murine mammary tumor cell
lines. Int J Oncol. 11:489–496. 1997.
|
|
23
|
Lanari C, Lüthy I, Lamb CA, Fabris V,
Pagano E, Helguero LA, Sanjuan N, Merani S and Molinolo AA: Five
novel hormone-responsive cell lines derived from murine mammary
ductal carcinomas: In vivo and in vitro effects of estrogens and
progestins 1. Cancer Res. 61:293–302. 2001.
|
|
24
|
Creydt VP, Sacca PA, Tesone AJ, Vidal L
and Calvo JC: Adipocyte differentiation influences the
proliferation and migration of normal and tumoral breast epithelial
cells. Mol Med Rep. 3:433–439. 2010.
|
|
25
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kraus NA, Ehebauer F, Zapp B, Rudolphi B,
Kraus BJ and Kraus D: Quantitative assessment of adipocyte
differentiation in cell culture. Adipocyte. 5:351–358. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wu J, Boström P, Sparks LM, Ye L, Choi JH,
Giang AH, Khandekar M, Virtanen KA, Nuutila P, Schaart G, et al:
Beige Adipocytes are a distinct type of thermogenic fat cell in
mouse and human. Cell. 150:366–376. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Cohen AW, Razani B, Schubert W, Williams
TM, Wang XB, Iyengar P, Brasaemle DL, Scherer PE and Lisanti MP:
Role of caveolin-1 in the modulation of lipolysis and lipid droplet
formation. Diabetes. 53:1261–1270. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Nieman KM, Kenny HA, Penicka CV, Ladanyi
A, Buell-Gutbrod R, Zillhardt MR, Romero IL, Carey MS, Mills GB,
Hotamisligil GS, et al: Adipocytes promote ovarian cancer
metastasis and provide energy for rapid tumor growth. Nat Med.
17:1498–1503. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bochet L, Lehuédé C, Dauvillier S, Wang
YY, Dirat B, Laurent V, Dray C, Guiet R, Maridonneau-Parini I, Le
Gonidec S, et al: Adipocyte-derived fibroblasts promote tumor
progression and contribute to the desmoplastic reaction in breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 73:5657–5668. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lee J, Hong BS, Ryu HS, Lee HB, Lee M,
Park IA, Kim J, Han W, Noh DY and Moon HG: Transition into
inflammatory cancer associated adipocytes in breast cancer
microenvironment requires microRNA regulatory mechanism. PLoS One.
12:e01741262017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Muller C: Tumour-surrounding adipocytes
are active players in breast cancer progression. Ann Endocrinol
(Paris). 74:108–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Cai J, Li B, Wang J, Liu K, Zhang Y, Liao
Y and Lu F: Tamoxifen-prefabricated beige adipose tissue improves
fat graft survival in mice. Plast Reconstr Surg. 141:930–940. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Petrovic N, Walden TB, Shabalina IG,
Timmons JA, Cannon B and Nedergaard J: Chronic peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) activation of
epididymally derived white adipocyte cultures reveals a population
of thermogenically competent, UCP1-containing adipocytes
molecularly distinct from classic brown adipocytes. J Biol Chem.
285:7153–7164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cedikova M, Kripnerová M, Dvorakova J,
Pitule P, Grundmanova M, Babuska V, Mullerova D and Kuncova J:
Mitochondria in white, brown, and beige adipocytes. Stem Cells Int.
2016:60673492016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Pisani DF, Barquissau V, Chambard JC,
Beuzelin D, Ghandour RA, Giroud M, Mairal A, Pagnotta S, Cinti S,
Langin D and Amri EZ: Mitochondrial fission is associated with UCP1
activity in human brite/beige adipocytes. Mol Metab. 7:35–44. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wikstrom JD, Mahdaviani K, Liesa M, Sereda
SB, Si Y, Las G, Twig G, Petrovic N, Zingaretti C, Graham A, et al:
Hormone-induced mitochondrial fission is utilized by brown
adipocytes as an amplification pathway for energy expenditure. EMBO
J. 33:418–436. 2014.
|
|
38
|
Wilson-Fritch L, Burkart A, Bell G,
Mendelson K, Leszyk J, Nicoloro S, Czech M and Corvera S:
Mitochondrial biogenesis and remodeling during adipogenesis and in
response to the insulin sensitizer rosiglitazone. Mol Cell Biol.
23:1085–1094. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Castro É, Silva TEO and Festuccia T:
Critical review of beige adipocyte thermogenic activation and
contribution to whole-body energy expenditure. Horm Mol Biol Clin
Investig. 31:2017.doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2017-0042.
|
|
40
|
Ward PS and Thompson CB: Metabolic
reprogramming: A cancer hallmark even warburg did not anticipate.
Cancer Cell. 21:297–308. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Beloribi-Djefaflia S, Vasseur S and
Guillaumond F: Lipid metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells.
Oncogenesis. 5:e1892016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wang Y, Tonouchi M, Miskovic D, Hatta H
and Bonen A: T3 increases lactate transport and the expression of
MCT4, but not MCT1, in rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 285:E622–E628. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Petersen C, Nielsen MD, Andersen ES, Basse
AL, Isidor MS, Markussen LK, Viuff BM, Lambert IH, Hansen JB and
Pedersen SF: MCT1 and MCT4 expression and lactate flux activity
increase during white and brown adipogenesis and impact adipocyte
metabolism. Sci Rep. 7:131012017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Whitaker-Menezes D, Martinez-Outschoorn
UE, Lin Z, Ertel A, Flomenberg N, Witkiewicz AK, Birbe RC, Howell
A, Pavlides S, Gandara R, et al: Evidence for a stromal-epithelial
‘Lactate Shuttle’ in human tumors: MCT4 is a marker of oxidative
stress in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Cycle. 10:1772–1783.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Li Z, Wu Q and Sun S, Wu J, Li J, Zhang Y,
Wang C, Yuan J and Sun S: Monocarboxylate transporters in breast
cancer and adipose tissue are novel biomarkers and potential
therapeutic targets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 501:962–967. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Liberti MV and Locasale JW: The warburg
effect: How does it benefit cancer cells? Trends Biochem Sci.
41:211–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Pavlides S, Whitaker-Menezes D,
Castello-Cros R, Flomenberg N, Witkiewicz AK, Frank PG, Casimiro
MC, Wang C, Fortina P, Addya S, et al: The reverse warburg effect:
Aerobic glycolysis in cancer associated fibroblasts and the tumor
stroma. Cell Cycle. 8:3984–4001. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Schäffler A, Schölmerich J and Buechler C:
Mechanisms of disease: Adipokines and breast cancer-endocrine and
paracrine mechanisms that connect adiposity and breast cancer. Nat
Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 3:345–354. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Choi J, Cha YJ and Koo JS: Adipocyte
biology in breast cancer: From silent bystander to active
facilitator. Prog Lipid Res. 69:11–20. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Gnerlich JL, Yao KA, Fitchev PS,
Goldschmidt RA, Bond MC, Cornwell M and Crawford SE: Peritumoral
expression of adipokines and fatty acids in breast cancer. Ann Surg
Oncol. 20 (Suppl 3):S731–S738. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Ertunc ME, Sikkeland J, Fenaroli F,
Griffiths G, Daniels MP, Cao H, Saatcioglu F and Hotamisligil GS:
Secretion of fatty acid binding protein aP2 from adipocytes through
a nonclassical pathway in response to adipocyte lipase activity. J
Lipid Res. 56:423–434. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Hotamisligil GS and Bernlohr DA: Metabolic
functions of FABPs-mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 11:592–605. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Guaita-Esteruelas S, Bosquet A, Saavedra
P, Gumà J, Girona J, Lam EW, Amillano K, Borràs J and Masana L:
Exogenous FABP4 increases breast cancer cell proliferation and
activates the expression of fatty acid transport proteins. Mol
Carcinog. 56:208–217. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Guaita-Esteruelas S, Saavedra-García P,
Bosquet A, Borràs J, Girona J, Amiliano K, Rodríguez-Balada M,
Heras M, Masana L and Gumà J: Adipose-derived fatty acid-binding
proteins plasma concentrations are increased in breast cancer
patients. Oncologist. 22:1309–1315. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Witkiewicz AK, Kline J, Queenan M, Brody
JR, Tsirigos A, Bilal E, Pavlides S, Ertel A, Sotgia F and Lisanti
MP: Molecular profiling of a lethal tumor microenvironment, as
defined by stromal caveolin-1 status in breast cancers. Cell Cycle.
10:1794–1809. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Wang P, Renes J, Bouwman F, Bunschoten A,
Mariman E and Keijer J: Absence of an adipogenic effect of
rosiglitazone on mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes: Increase of lipid
catabolism and reduction of adipokine expression. Diabetologia.
50:654–665. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Sanchez-Alvarez R, Martinez-Outschoorn UE,
Lamb R, Hulit J, Howell A, Gandara R, Sartini M, Rubin E, Lisanti
MP and Sotgia F: Mitochondrial dysfunction in breast cancer cells
prevents tumor growth: Understanding chemoprevention with
metformin. Cell Cycle. 12:172–182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Martinez-Outschoorn U, Sotgia F and
Lisanti MP: Tumor microenvironment and metabolic synergy in breast
cancers: Critical importance of mitochondrial fuels and function.
Semin Oncol. 41:195–216. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Huang CK, Chang PH, Kuo WH, Chen CL, Jeng
YM, Chang KJ, Shew JY, Hu CM and Lee WH: Adipocytes promote
malignant growth of breast tumours with monocarboxylate transporter
2 expression via β-hydroxybutyrate. Nat Commun. 8:147062017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Köhrmann A, Kammerer U, Kapp M, Dietl J
and Anacker J: Expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in
primary human breast cancer and breast cancer cell lines: New
findings and review of the literature. BMC Cancer. 9:1882009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Iida J, Clancy R, Dorchak J, Somiari RI,
Somiari S, Cutler ML, Mural RJ and Shriver CD: DNA aptamers against
exon v10 of CD44 inhibit breast cancer cell migration. PLoS One.
9:e887122014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Nam KS, Oh S, Lee KM, Yoo SA and Shin I:
CD44 regulates cell proliferation, migration, and invasion via
modulation of c-Src transcription in human breast cancer cells.
Cell Signal. 27:1882–1894. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Villarroya F, Cereijo R, Villarroya J and
Giralt M: Brown adipose tissue as a secretory organ. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 13:26–35. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Chen SQ, Niu Q, Ju LP, Alimujiang M, Yan
H, Bai NN, Xu J, Fang QC, Han JF, Yang Y and Jia WP: Predicted
secreted protein analysis reveals synaptogenic function of Clstn3
during WAT browning and BAT activation in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
40:999–1009. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|