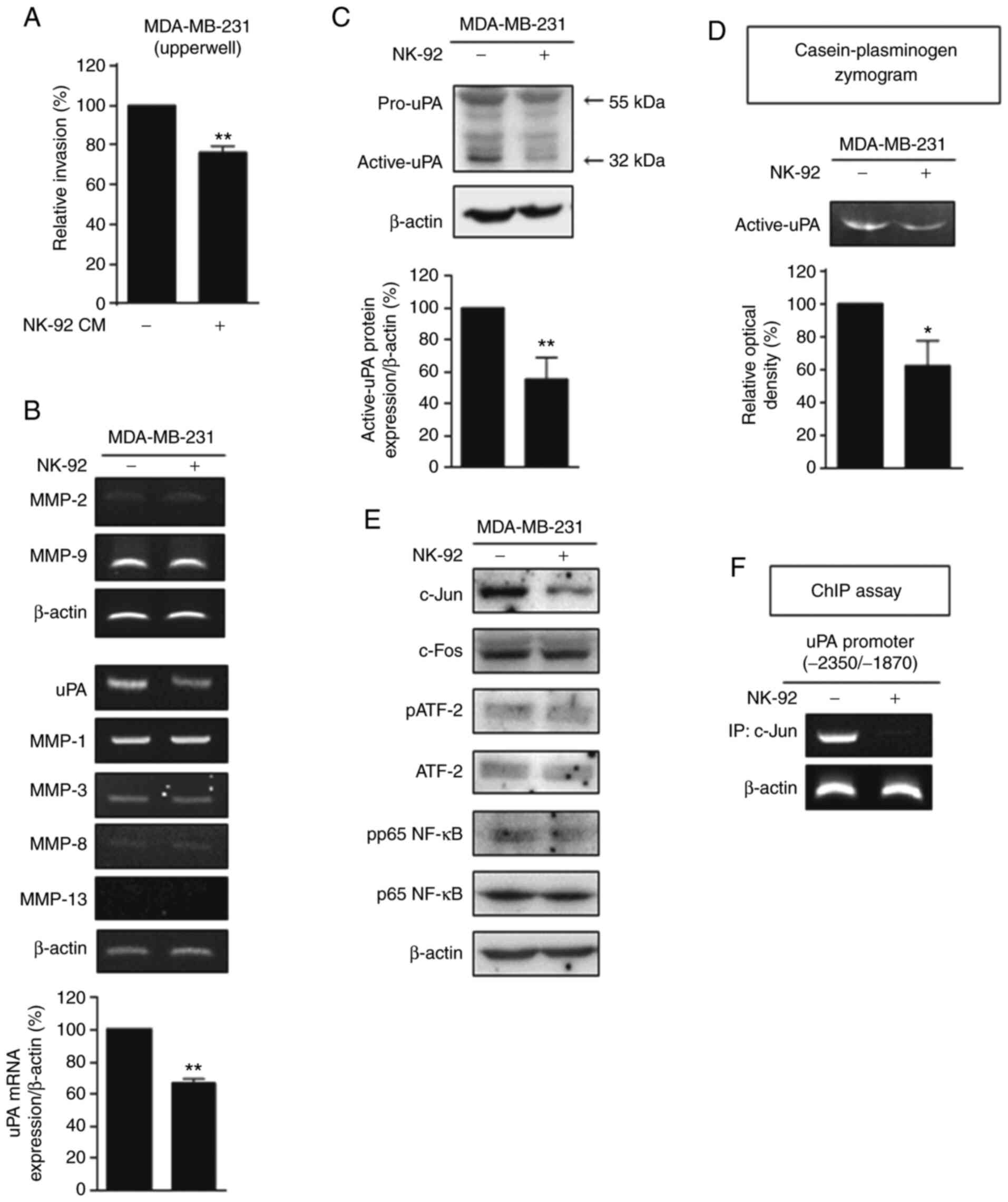
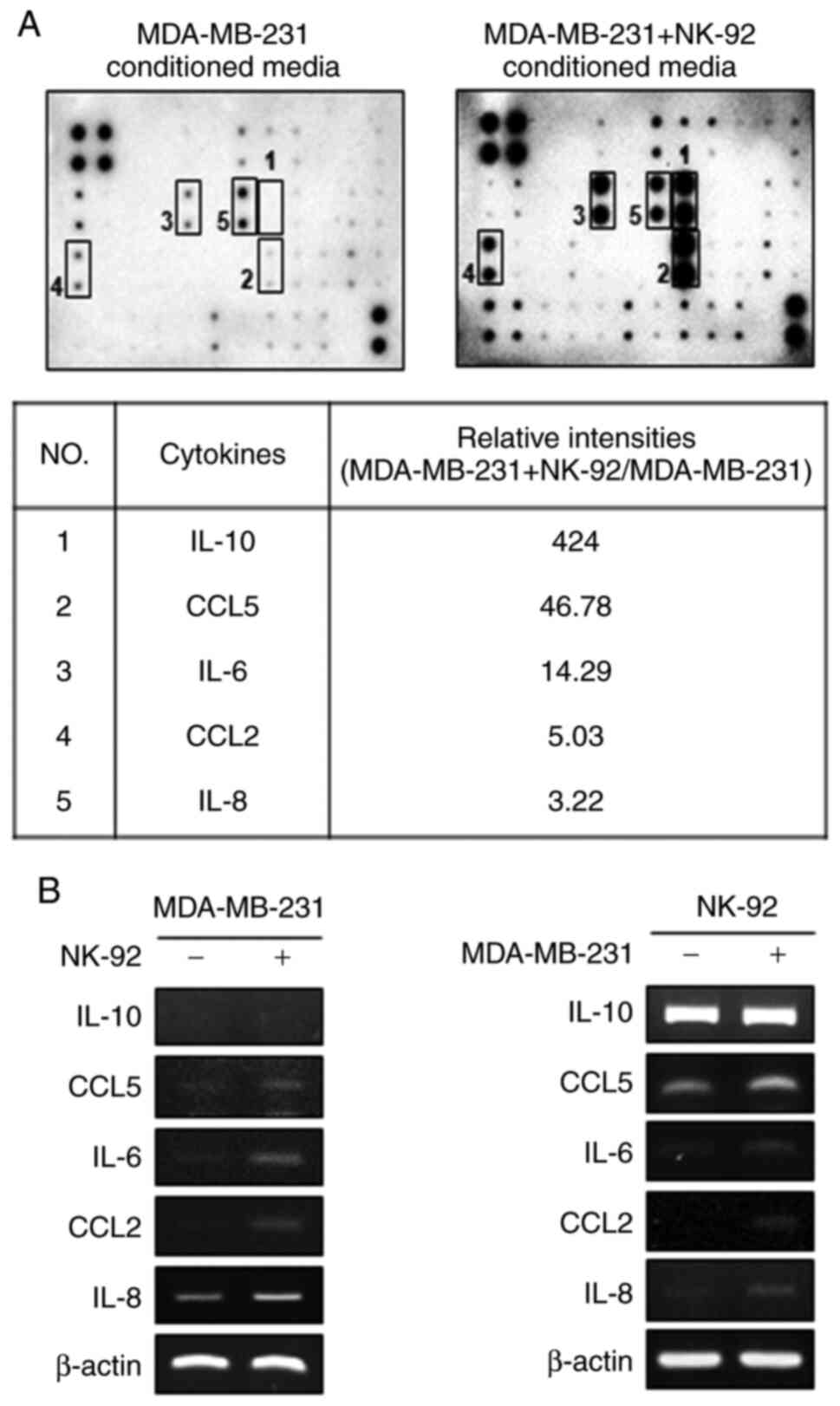
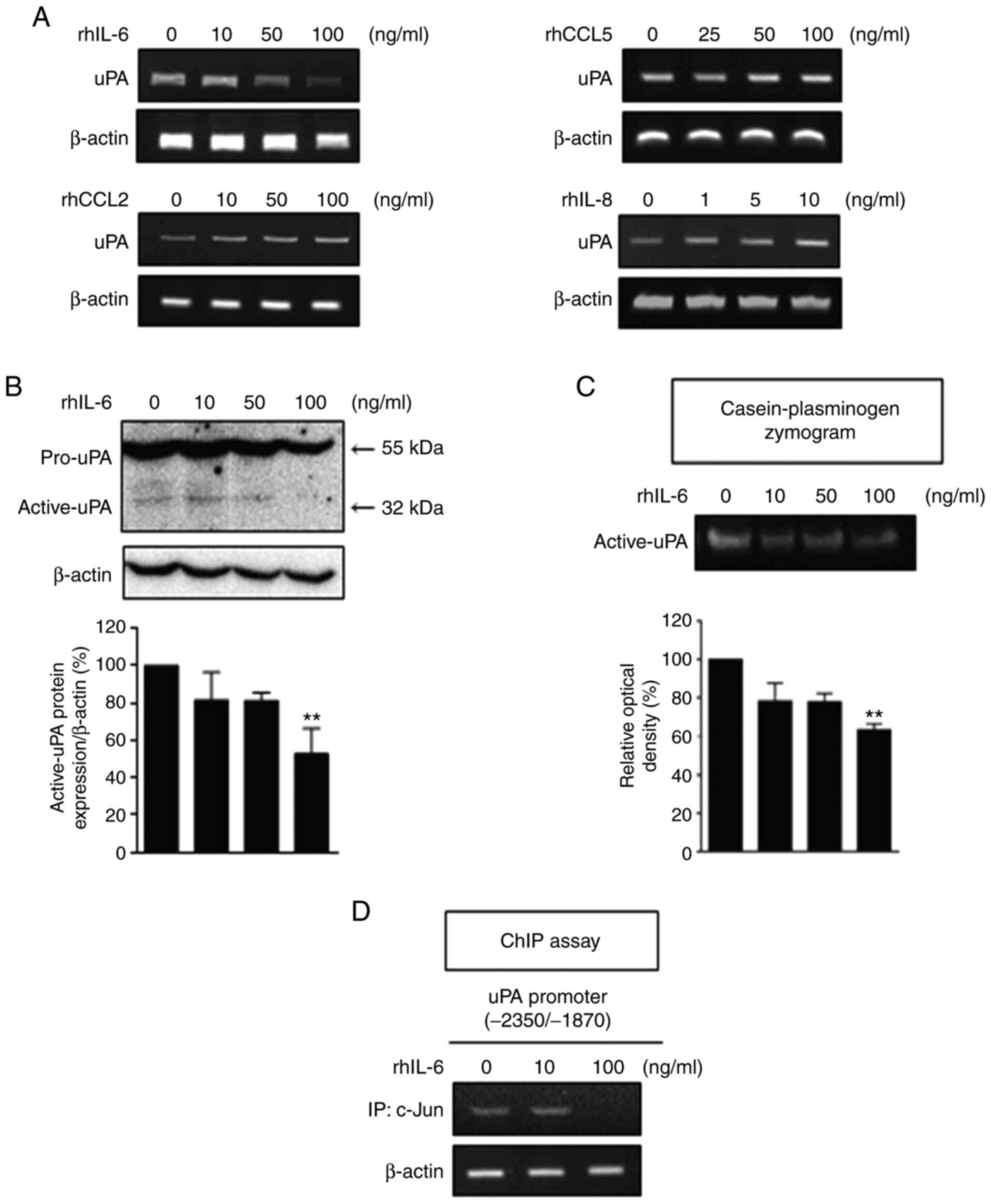
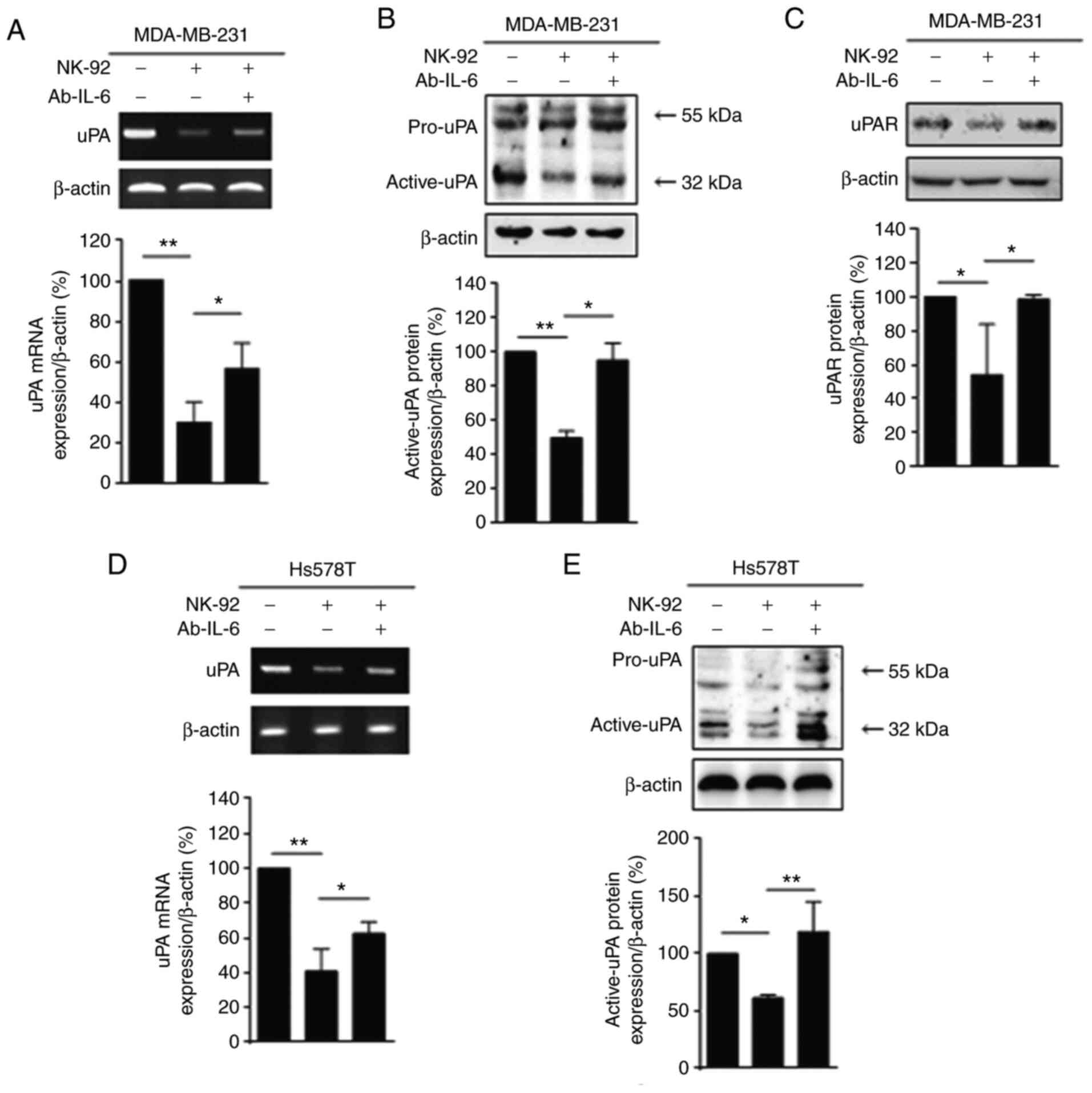
|
1
|
Bouchardy C, Fioretta G, Verkooijen HM,
Vlastos G, Schaefer P, Delaloye JF, Neyroud-Caspar I, Balmer Majno
S, Wespi Y, Forni M, et al: Recent increase of breast cancer
incidence among women under the age of forty. Br J Cancer.
96:1743–1746. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Curado MP: Breast cancer in the world:
Incidence and mortality. Salud Publica Mex. 53:372–384. 2011.
|
|
3
|
Redig AJ and McAllister SS: Breast cancer
as a systemic disease: A view of metastasis. J Intern Med.
274:113–126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Nakhjavani M, Hardingham JE, Palethorpe
HM, Price TJ and Townsend AR: Druggable molecular targets for the
treatment of triple negative breast cancer. J Breast Cancer.
22:341–361. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bayraktar S and Glück S: Molecularly
targeted therapies for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 138:21–35. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kenny PA, Nelson CM and Bissell MJ: The
Ecology of Tumors: By perturbing the microenvironment, wounds and
infection may be key to tumor development. Scientist.
20:302006.
|
|
7
|
Wang M, Zhao J, Zhang L, Wei F, Lian Y, Wu
Y, Gong Z, Zhang S, Zhou J, Cao K, et al: Role of tumor
microenvironment in tumorigenesis. J Cancer. 8:761–773. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wu J and Lanier LL: Natural killer cells
and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 90:127–156. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cheng M, Chen Y, Xiao W, Sun R and Tian Z:
NK cell-based immunotherapy for malignant diseases. Cell Mol
Immunol. 10:230–252. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mandal A and Viswanathan C: Natural killer
cells: In health and disease. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther.
8:47–55. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
López-Soto A, Gonzalez S, Smyth MJ and
Galluzzi L: Control of metastasis by NK cells. Cancer Cell.
32:135–154. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Guillerey C, Huntington ND and Smyth MJ:
Targeting natural killer cells in cancer immunotherapy. Nat
Immunol. 17:1025–1036. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jiao Y, Huntington ND, Belz GT and Seillet
C: Type 1 innate lymphoid cell biology: Lessons learnt from natural
killer cells. Front Immunol. 7:4262016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sun Y, Yao Z, Zhao Z, Xiao H, Xia M, Zhu
X, Jiang X and Sun C: Natural killer cells inhibit metastasis of
ovarian carcinoma cells and show therapeutic effects in a murine
model of ovarian cancer. Exp Ther Med. 16:1071–1078. 2018.
|
|
15
|
Aznavoorian S, Murphy AN,
Stetler-Stevenson WG and Liotta LA: Molecular aspects of tumor cell
invasion and metastasis. Cancer. 71:1368–1383. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Stamenkovic I: Matrix metalloproteinases
in tumor invasion and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 10:415–433.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Song H, Ki SH, Kim SG and Moon A:
Activating transcription factor 2 mediates matrix
metalloproteinase-2 transcriptional activation induced by p38 in
breast epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 66:10487–10496. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lee S, Lee E, Ko E, Ham M, Lee HM, Kim ES,
Koh M, Lim HK, Jung J, Park SY and Moon A: Tumor-associated
macrophages secrete CCL2 and induce the invasive phenotype of human
breast epithelial cells through upregulation of ERO1-α and MMP-9.
Cancer Lett. 437:25–34. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Pepper MS: Role of the matrix
metalloproteinase and plasminogen activator-plasmin systems in
angiogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 21:1104–1117. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kumari S and Malla R: New insight on the
role of plasminogen receptor in cancer progression. Cancer Growth
Metastasis. 8:35–42. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lijnen HR: Matrix metalloproteinases and
cellular fibrinolytic activity. Biochemistry (Mosc). 67:92–98.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wilkins-Port CE, Higgins SP, Higgins CE,
Kobori-Hotchkiss I and Higgins PJ: Complex regulation of the
pericellular proteolytic microenvironment during tumor progression
and wound repair: Functional interactions between the serine
protease and matrix metalloproteinase cascades. Biochem Res Int.
2012:4543682012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Holst-Hansen C, Johannessen B,
Høyer-Hansen G, Rømer J, Ellis V and Brünner N: Urokinase-type
plasminogen activation in three human breast cancer cell lines
correlates with their in vitro invasiveness. Clin Exp Metastasis.
14:297–307. 1996.
|
|
25
|
Crippa MP: Urokinase-type plasminogen
activator. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 39:690–694. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mauro CD, Pesapane A, Formisano L, Rosa R,
D'Amato V, Ciciola P, Servetto A, Marciano R, Orsini RC, Monteleone
F, et al: Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR)
expression enhances invasion and metastasis in RAS mutated tumors.
Sci Rep. 7:93882017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Mahmood N, Mihalcioiu C and Rabbani SA:
Multifaceted role of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA)
and its receptor (uPAR): Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic
applications. Front Oncol. 8:242018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Moon A, Kim MS, Kim TG, Kim SH, Kim HE,
Chen YQ and Kim HR: H-ras, but not N-ras, induces an invasive
phenotype in human breast epithelial cells: A role for MMP-2 in the
H-ras-induced invasive phenotype. Int J Cancer. 85:176–181. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Stepanova V, Jayaraman PS, Zaitsev SV,
Lebedeva T, Bdeir K, Kershaw R, Holman KR, Parfyonova YV, Semina
EV, Beloglazova IB, et al: Urokinase-type plasminogen activator
(uPA) promotes angiogenesis by attenuating proline-rich homeodomain
protein (PRH) transcription factor activity and de-repressing
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor expression. J
Biol Chem. 291:15029–15045. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lampelj M, Arko D, Cas-Sikosek N, Kavalar
R, Ravnik M, Jezersek-Novakovic B, Dobnik S, Dovnik NF and Takac I:
Urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) and plasminogen activator
inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1) in breast cancer-correlation with
traditional prognostic factors. Radiol Oncol. 49:357–364. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Annecke K, Schmitt M, Euler U, Zerm M,
Paepke D, Paepke S, von Minckwitz G, Thomssen C and Harbeck N: uPA
and PAI-1 in breast cancer: Review of their clinical utility and
current validation in the prospective NNBC-3 trial. Adv Clin Chem.
45:31–45. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Duffy MJ, McGowan PM, Harbeck N, Thomssen
C and Schmitt M: uPA and PAI-1 as biomarkers in breast cancer:
Validated for clinical use in level-of-evidence-1 studies. Breast
Cancer Res. 16:4282014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Fauriat C, Long EO, Ljunggren HG and
Bryceson YT: Regulation of human NK-cell cytokine and chemokine
production by target cell recognition. Blood. 115:2167–2176. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sun W, Liu DB, Li W, Zhang LL, Long GX,
Wang JF, Mei Q and Hu GQ: Interleukin-6 promotes the migration and
invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines and upregulates the
expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Int J Oncol. 44:1551–1560. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Razidlo GL, Burton KM and McNiven MA:
Interleukin-6 promotes pancreatic cancer cell migration by rapidly
activating the small GTPase CDC42. J Biol Chem. 293:11143–11153.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Gopinathan G, Milagre C, Pearce OM,
Reynolds LE, Hodivala-Dilke K, Leinster DA, Zhong H, Hollingsworth
RE, Thompson R, Whiteford JR and Balkwill F: Interleukin-6
stimulates defective angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 75:3098–3107. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wegiel B, Bjartell A, Culig Z and Persson
JL: Interleukin-6 activates PI3K/Akt pathway and regulates cyclin
A1 to promote prostate cancer cell survival. Int J Cancer.
122:1521–1529. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hsu CY, Bristow R, Cha MS, Wang BG, Ho CL,
Kurman RJ, Wang TL and Shih IeM: Characterization of active
mitogen-activated protein kinase in ovarian serous carcinomas. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:6432–6436. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Leu CM, Wong FH, Chang C, Huang SF and Hu
CP: Interleukin-6 acts as an antiapoptotic factor in human
esophageal carcinoma cells through the activation of both STAT3 and
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Oncogene. 22:7809–7818.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ulisse S, Baldini E, Sorrenti S and
D'Armiento M: The urokinase plasminogen activator system: A target
for anti-cancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 9:32–71. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Sidenius N and Blasi F: The urokinase
plasminogen activator system in cancer: Recent advances and
implication for prognosis and therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
22:205–222. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|