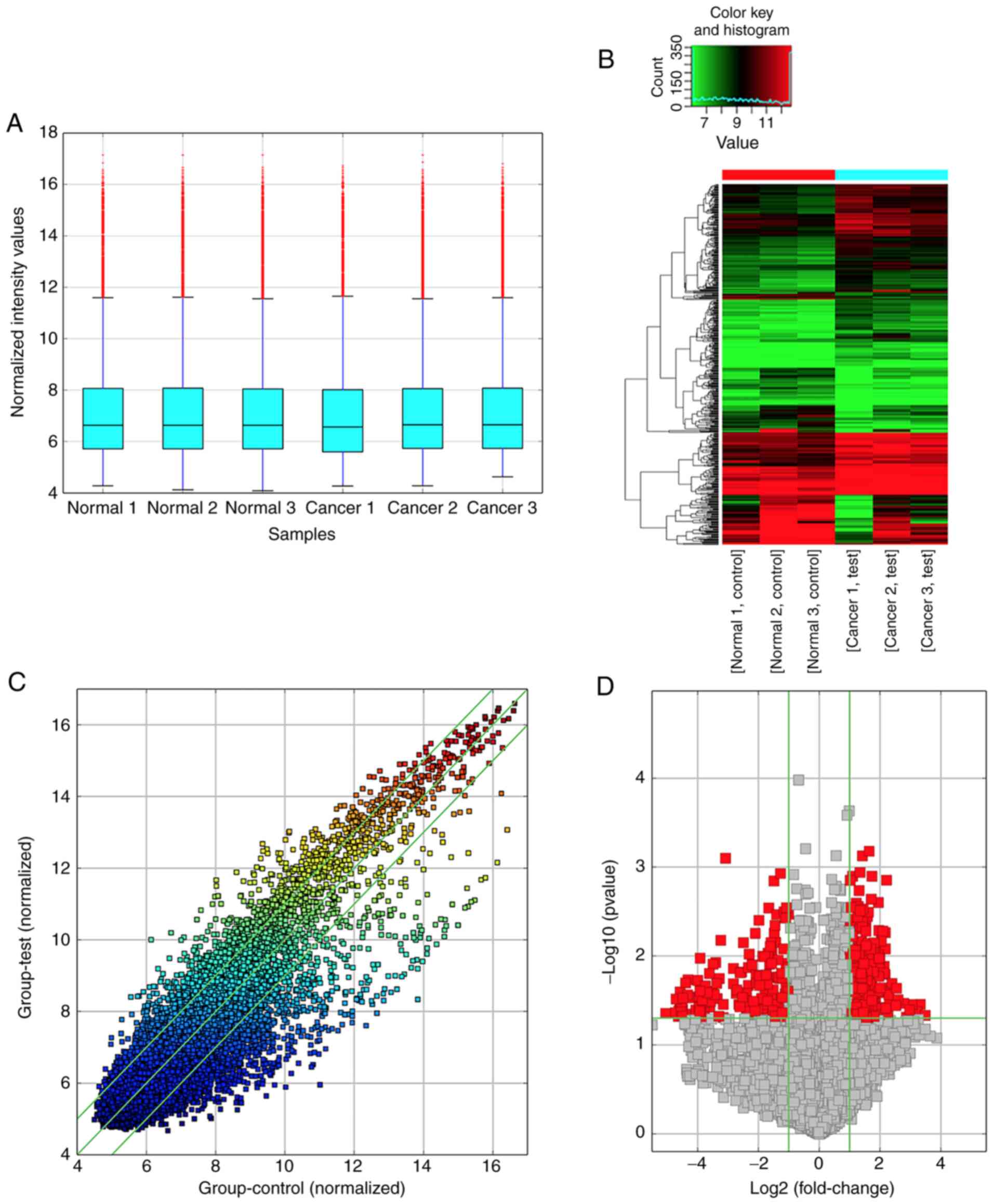
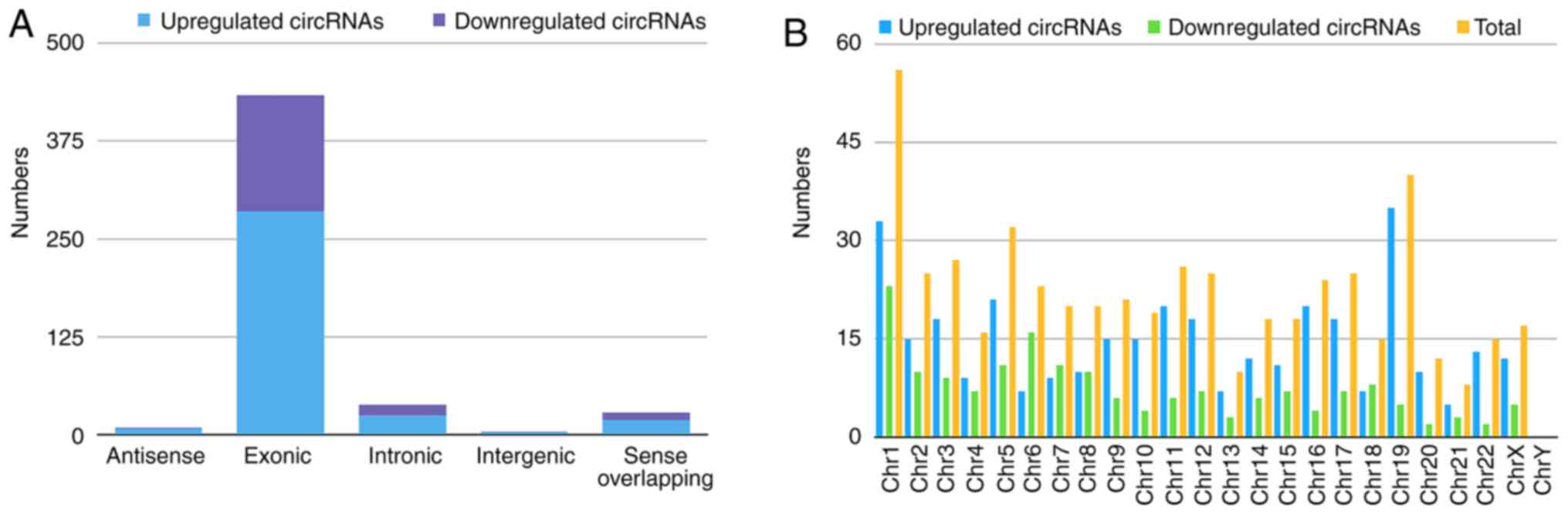
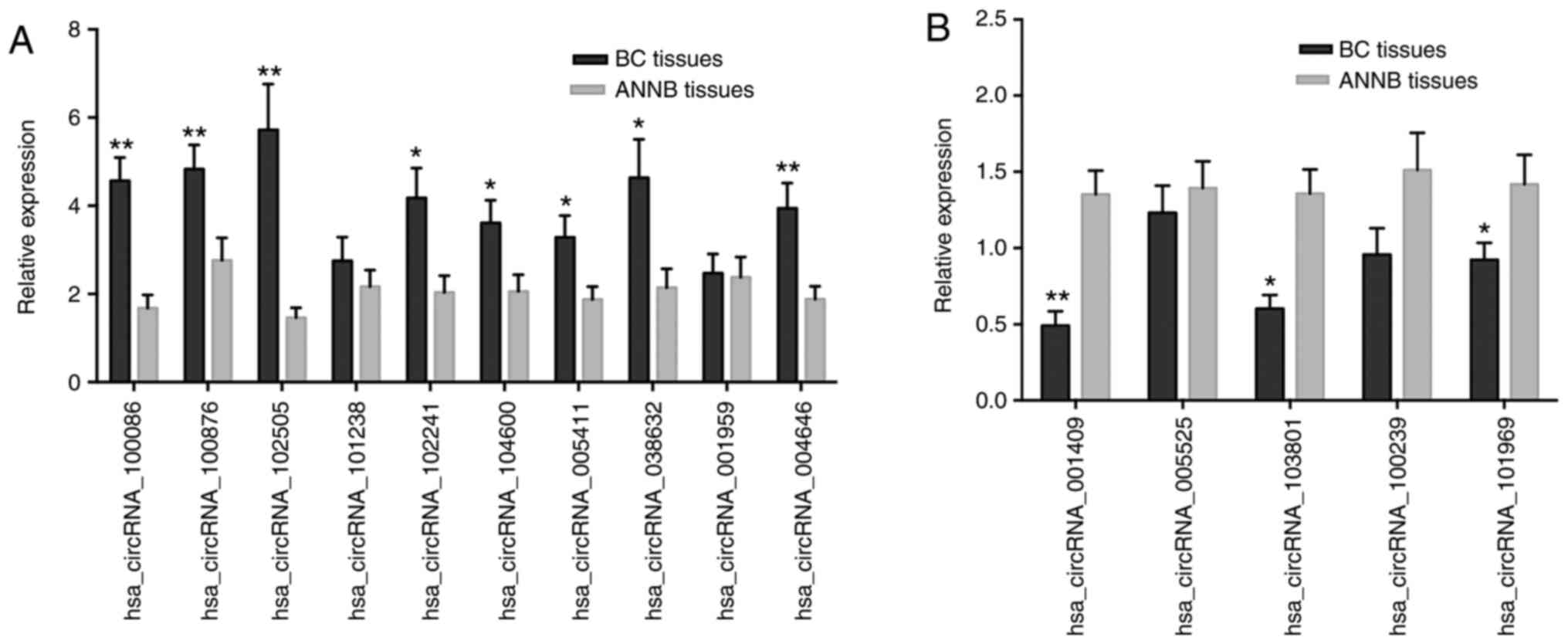
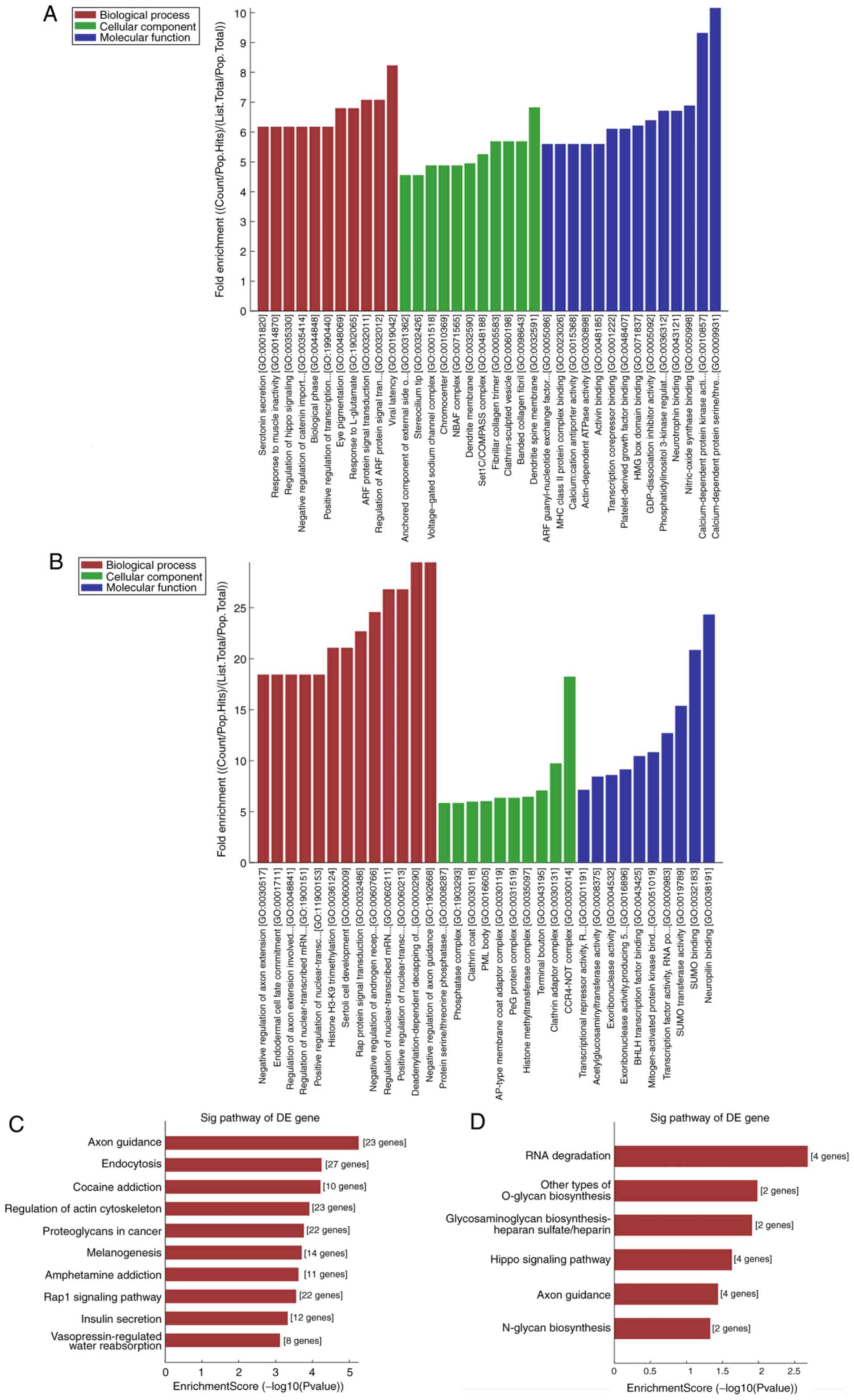
|
1
|
Kaufman DS, Shipley WU and Feldman AS:
Bladder cancer. Lancet. 374:239–249. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kim WT, Kim YH, Jeong P, Seo SP, Kang HW,
Kim YJ, Yun SJ, Lee SC, Moon SK, Choi Y, et al: Urinary cell-free
nucleic acid IQGAP3: A new non-invasive diagnostic marker for
bladder cancer. Oncotarget. 9:14354–14365. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fatica A and Bozzoni I: Long non-coding
RNAs: New players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev
Genet. 15:7–21. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li PF, Chen SC, Xia T, Jiang XM, Shao YF,
Xiao BX and Guo JM: Non-coding RNAs and gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:5411–5419. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Qu S, Yang X, Li X, Wang J, Gao Y, Shang
R, Sun W, Dou K and Li H: Circular RNA: A new star of noncoding
RNAs. Cancer Lett. 365:141–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Greene J, Baird AM, Brady L, Lim M, Gray
SG, McDermott R and Finn SP: Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, Function
and Role in Human Diseases. Front Mol Biosci. 4:382017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chen LL and Yang L: Regulation of circRNA
biogenesis. RNA Biol. 12:381–388. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang XO, Wang HB, Zhang Y, Lu X, Chen LL
and Yang L: Complementary sequence-mediated exon circularization.
Cell. 159:134–147. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Cocquerelle C, Mascrez B, Hétuin D and
Bailleul B: Mis-splicing yields circular RNA molecules. FASEB J.
7:155–160. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Salzman J, Chen RE, Olsen MN, Wang PL and
Brown PO: Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression.
PLoS Genet. 9:e10037772013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Vidal AF, Sandoval GT, Magalhaes L, Santos
SE and Ribeiro-dos-Santos A: Circular RNAs as a new field in gene
regulation and their implications in translational research.
Epigenomics. 8:551–562. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Xu S, Zhou L, Ponnusamy M, Zhang L, Dong
Y, Zhang Y, Wang Q, Liu J and Wang K: A comprehensive review of
circRNA: From purification and identification to disease marker
potential. PeerJ. 6:e55032018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang X, Zhou H, Jing W, Luo P, Qiu S, Liu
X, Zhu M, Liang C, Yu M and Tu J: The circular RNA hsa_circ_0001445
regulates the proliferation and migration of hepatocellular
carcinoma and may serve as a diagnostic biomarker. Dis Markers.
2018:30734672018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jiang MM, Mai ZT, Wan SZ, Chi YM, Zhang X,
Sun BH and Di QG: Microarray profiles reveal that circular RNA
hsa_circ_0007385 functions as an oncogene in non-small cell lung
cancer tumorigenesis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 144:667–674. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhong Z, Lv M and Chen J: Screening
differential circular RNA expression profiles reveals the
regulatory role of circTCF25-miR-103a-3p/miR-107-CDK6 pathway in
bladder carcinoma. Sci Rep. 6:309192016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cai D, Liu Z and Kong G: Molecular and
bioinformatics analyses identify 7 circular RNAs involved in
regulation of oncogenic transformation and cell proliferation in
human bladder cancer. Med Sci Monit. 24:1654–1661. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Enright AJ, John B, Gaul U, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome Biol.
5:R12003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Pasquinelli AE: MicroRNAs and their
targets: Recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal
relationship. Nat Rev Genet. 13:271–282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat
Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gerlich M and Neumann S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nuclc Acids Res. 28:27–30. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Shi Z, Kadeer A, Wang M, Wen B, Li M,
Huang J, Gao Y, Liu E, Liu D, Jia D and Liang C: The deregulation
of miR-133b is associated with poor prognosis in bladder cancer.
Pathol Res Pract. 215:354–357. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yu QF, Liu P, Li ZY, Zhang CF, Chen SQ, Li
ZH, Zhang GY and Li JC: MiR-103/107 induces tumorigenicity in
bladder cancer cell by suppressing PTEN. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:8616–8623. 2018.
|
|
26
|
Wang F, Zu Y, Zhu S, Yang Y, Huang W, Xie
H and Li G: Long noncoding RNA MAGI2-AS3 regulates CCDC19
expression by sponging miR-15b-5p and suppresses bladder cancer
progression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 507:231–235. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li Y, Wan B, Liu L, Zhou L and Zeng Q:
Circular RNA circMTO1 suppresses bladder cancer metastasis by
sponging miR-221 and inhibiting epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 508:991–996. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sun M, Zhao W, Chen Z, Li M, Li S, Wu B
and Bu R: Circ_0058063 regulates CDK6 to promote bladder cancer
progression by sponging miR-145-5p. J Cell Physiol. 234:4812–4824.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhao X, Wang Y, Yu Q, Yu P, Zheng Q, Yang
X and Gao D: Circular RNAs in gastrointestinal cancer: Current
knowledge, biomarkers and targeted therapy (Review). Int J Mol Med.
46:1611–1632. 2020.
|
|
30
|
Zhang JR and Sun HJ: Roles of circular
RNAs in diabetic complications: From molecular mechanisms to
therapeutic potential. Gene. 763:1450662020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hua L, Huang L, Zhang X, Feng H and Shen
B: Knockdown of circular RNA CEP128 suppresses proliferation and
improves cytotoxic efficacy of temozolomide in glioma cells by
regulating miR-145-5p. Neuroreport. 30:1231–1238. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gan J, Yuan J, Liu Y, Lu Z, Xue Y, Shi L
and Zeng H: Circular RNA_101237 mediates anoxia/reoxygenation
injury by targeting let-7a-5p/IGF2BP3 in cardiomyocytes. Int J Mol
Med. 45:451–460. 2020.
|
|
33
|
Chen S, Li T, Zhao Q, Xiao B and Guo J:
Using circular RNA hsa_circ_0000190 as a new biomarker in the
diagnosis of gastric cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 466:167–171. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xiao-Long M, Kun-Peng Z and Chun-Lin Z:
Circular RNA circ_HIPK3 is down-regulated and suppresses cell
proliferation, migration and invasion in osteosarcoma. J Cancer.
9:1856–1862. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Yao JT, Zhao SH, Liu QP, Lv MQ, Zhou DX,
Liao ZJ and Nan KJ: Over-expression of CircRNA_100876 in non-small
cell lung cancer and its prognostic value. Pathol Res Pract.
213:453–456. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yuan W, Peng S, Wang J, Wei C, Ye Z, Wang
Y, Wang M, Xu H, Jiang S, Sun D, et al: Identification and
characterization of circRNAs as competing endogenous RNAs for
miRNA-mRNA in colorectal cancer. PeerJ. 7:e76022019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Su Y, Du Z, Zhong G, Ya Y, Bi J, Shi J,
Chen L, Dong W and Lin T: circ5912 suppresses cancer progression
via inducing MET in bladder cancer. Aging (Albany NY).
11:10826–10838. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Chaar I, Amara S, Elamine OE, Khiari M,
Ounissi D, Khalfallah T, Ben Hmida A, Mzabi S and Bouraoui S:
Biological significance of promoter hypermethylation of p14/ARF
gene: Relationships to p53 mutational status in Tunisian population
with colorectal carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 35:1439–1449. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hsu HS and Wang YC, Tseng RC, Chang JW,
Chen JT, Shih CM, Chen CY and Wang YC: 5′ cytosine-phospho-guanine
island methylation is responsible for p14ARF inactivation and
inversely correlates with p53 overexpression in resected non-small
cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:4734–4741. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Iida S, Akiyama Y, Nakajima T, Ichikawa W,
Nihei Z, Sugihara K and Yuasa Y: Alterations and hypermethylation
of the p14(ARF) gene in gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 87:654–658.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ito T, Nishida N, Fukuda Y, Nishimura T,
Komeda T and Nakao K: Alteration of the p14(ARF) gene and p53
status in human hepatocellular carcinomas. J Gastroenterol.
39:355–361. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Domínguez G, Carballido J, Silva J, Silva
JM, García JM, Menéndez J, Provencio M, España P and Bonilla F:
p14ARF promoter hypermethylation in plasma DNA as an indicator of
disease recurrence in bladder cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res.
8:980–985. 2002.
|
|
43
|
Berggren P, Kumar R, Sakano S, Hemminki L,
Wada T, Steineck G, Adolfsson J, Larsson P, Norming U, Wijkström H
and Hemminki K: Detecting homozygous deletions in the
CDKN2A(p16(INK4a))/ARF(p14(ARF)) gene in urinary bladder cancer
using real-time quantitative PCR. Clin Cancer Res. 9:235–242.
2003.
|
|
44
|
Liang Z, Xie W, Wu R, Geng H, Zhao L, Xie
C, Li X, Zhu M, Zhu W, Zhu J, et al: Inhibition of tobacco
smoke-induced bladder MAPK activation and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in mice by curcumin. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:4503–4513.
2015.
|
|
45
|
Miller JE and Reese JC: Ccr4-Not complex:
The control freak of eukaryotic cells. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol.
47:315–333. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Noel N, Couteau J, Maillet G, Gobet F,
D'Aloisio F, Minier C and Pfister C: TP53 and FGFR3 gene mutation
assessment in urine: Pilot study for bladder cancer diagnosis.
Anticancer Res. 35:4915–4921. 2015.
|
|
47
|
Knowles MA: Role of FGFR3 in urothelial
cell carcinoma: Biomarker and potential therapeutic target. World J
Urol. 25:581–593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Dong L, Lin F, Wu W, Liu Y and Huang W:
Verteporfin inhibits YAP-induced bladder cancer cell growth and
invasion via Hippo signaling pathway. Int J Med Sci. 15:645–652.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zhong Z, Huang M, Lv M, He Y, Duan C,
Zhang L and Chen J: Circular RNA MYLK as a competing endogenous RNA
promotes bladder cancer progression through modulating VEGFA/VEGFR2
signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 403:305–317. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Li F, Zhang L, Li W, Deng J, Zheng J, An
M, Lu J and Zhou Y: Circular RNA ITCH has inhibitory effect on ESCC
by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget. 6:6001–6013.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Chen P, Zhao L, Pan X, Jin L, Lin C, Xu W,
Xu J, Guan X, Wu X, Wang Y, et al: Tumor suppressor microRNA-136-5p
regulates the cellular function of renal cell carcinoma. Oncol
Lett. 15:5995–6002. 2018.
|
|
52
|
Shen S, Yue H, Li Y, Qin J, Li K, Liu Y
and Wang J: Upregulation of miR-136 in human non-small cell lung
cancer cells promotes Erk1/2 activation by targeting PPP2R2A.
Tumour Biol. 35:631–640. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Yan M, Li X, Tong D, Han C, Zhao R, He Y
and Jin X: miR-136 suppresses tumor invasion and metastasis by
targeting RASAL2 in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncol Rep.
36:65–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Scelfo A, Piunti A and Pasini D: The
controversial role of the Polycomb group proteins in transcription
and cancer: How much do we not understand Polycomb proteins? FEBS
J. 282:1703–1722. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Haindl M, Harasim T, Eick D and Muller S:
The nucleolar SUMO-specific protease SENP3 reverses SUMO
modification of nucleophosmin and is required for rRNA processing.
EMBO Rep. 9:273–279. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Eifler K and Vertegaal AC: Mapping the
SUMOylated landscape. FEBS J. 282:3669–3680. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Ma RG, Zhang Y, Sun TT and Cheng B:
Epigenetic regulation by polycomb group complexes: Focus on roles
of CBX proteins. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 15:412–428. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Li J, Xu Y, Long XD, Wang W, Jiao HK, Mei
Z, Yin QQ, Ma LN, Zhou AW, Wang LS, et al: Cbx4 governs HIF-1α to
potentiate angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma by its SUMO E3
ligase activity. Cancer Cell. 25:118–131. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Fukagawa A, Ishii H, Miyazawa K and Saitoh
M: δEF1 associates with DNMT1 and maintains DNA methylation of the
E-cadherin promoter in breast cancer cells. Cancer Med. 4:125–135.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|