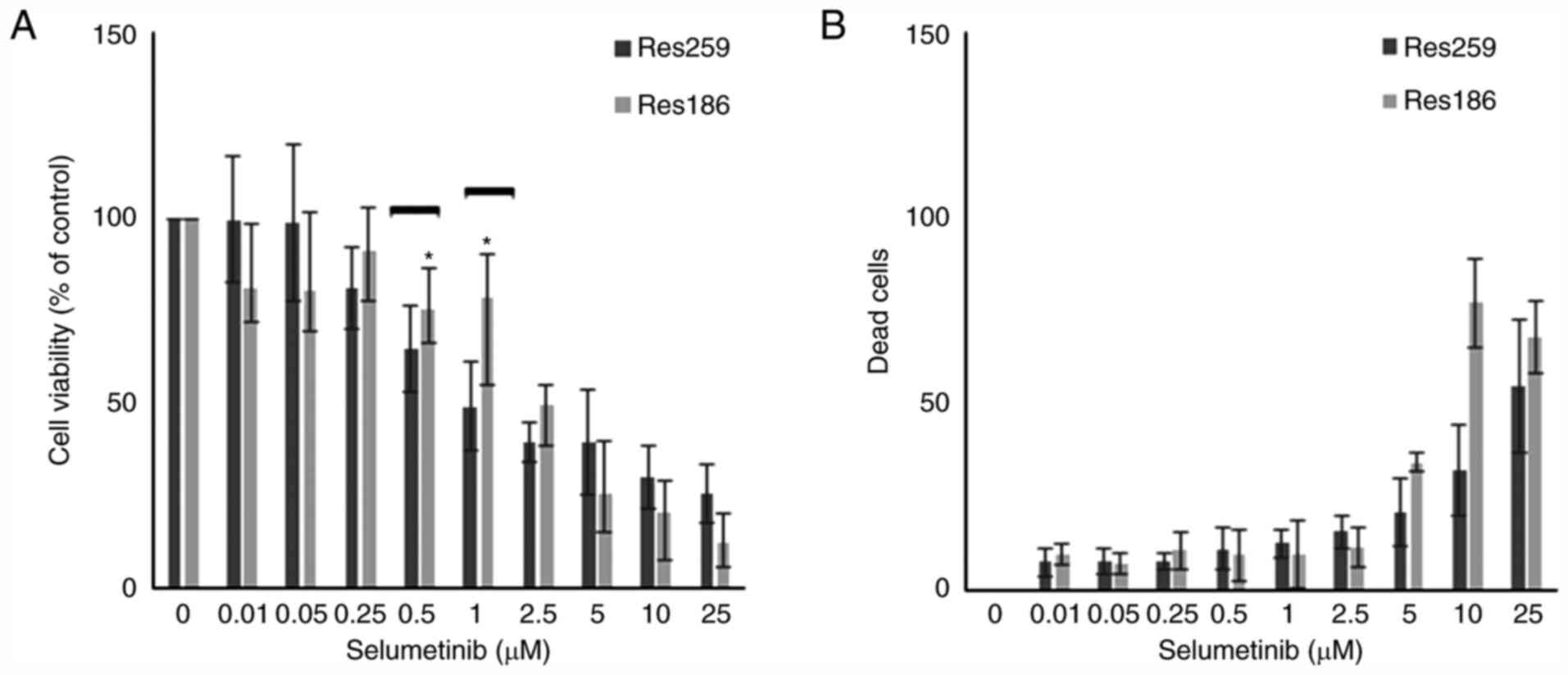
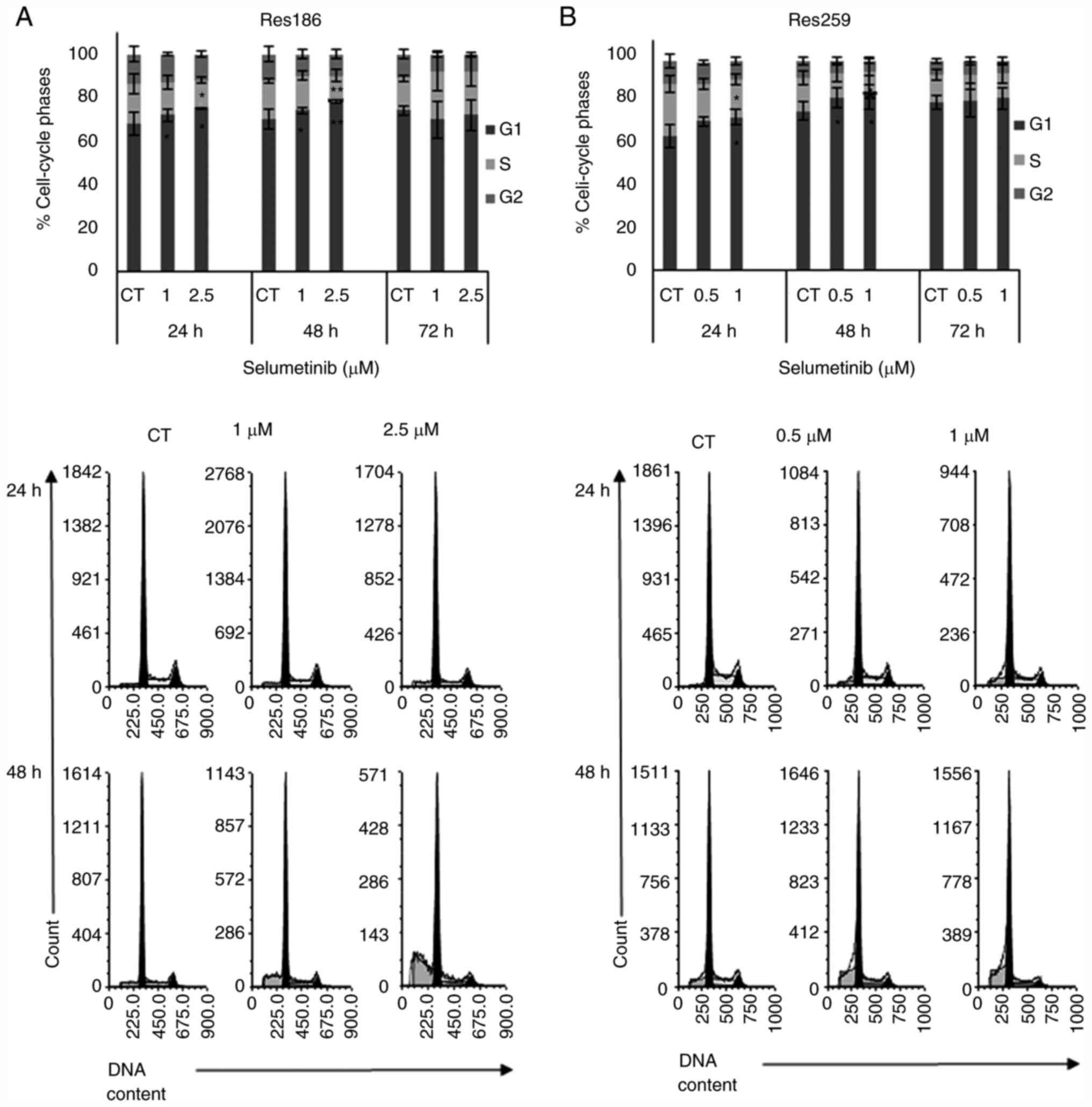
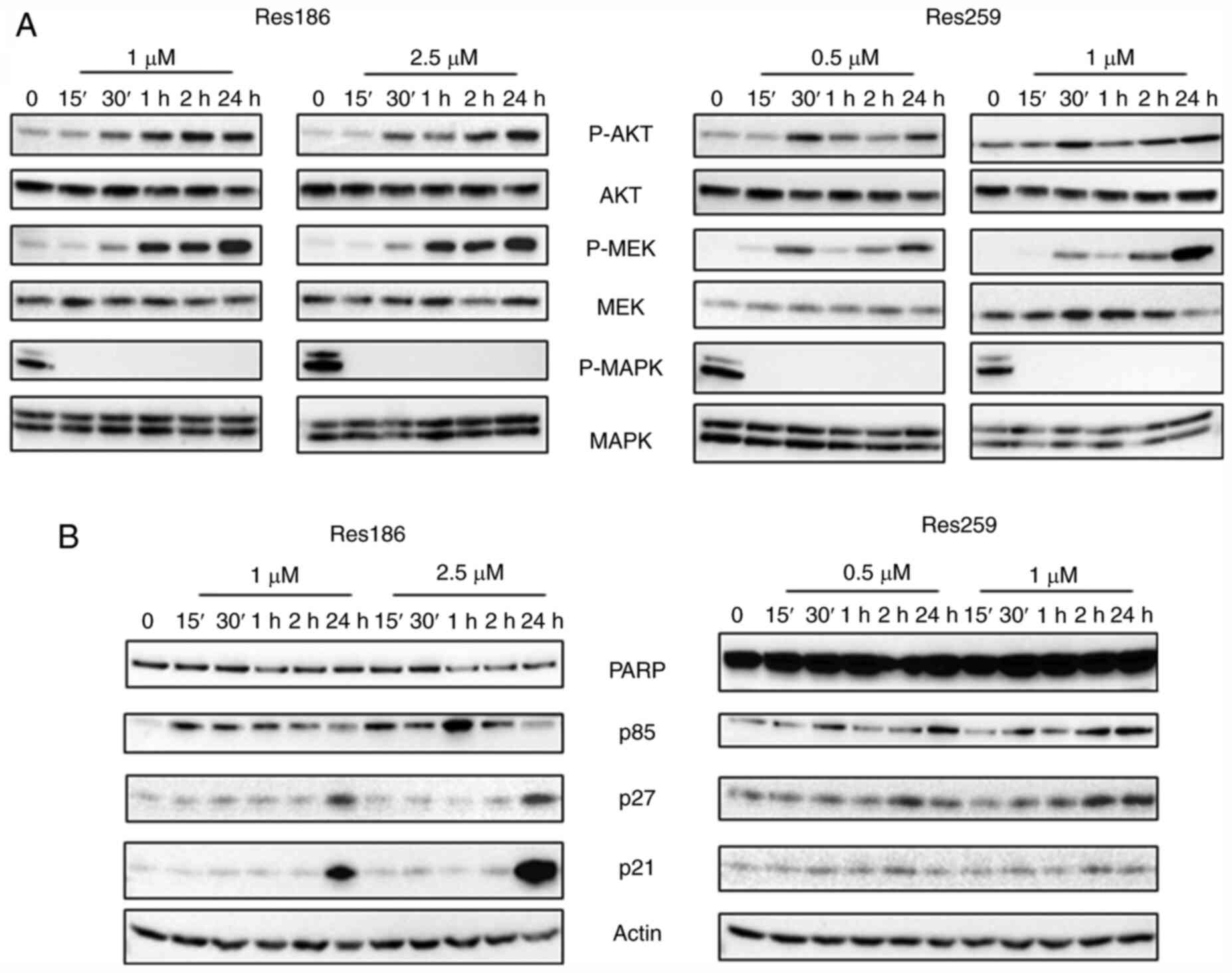
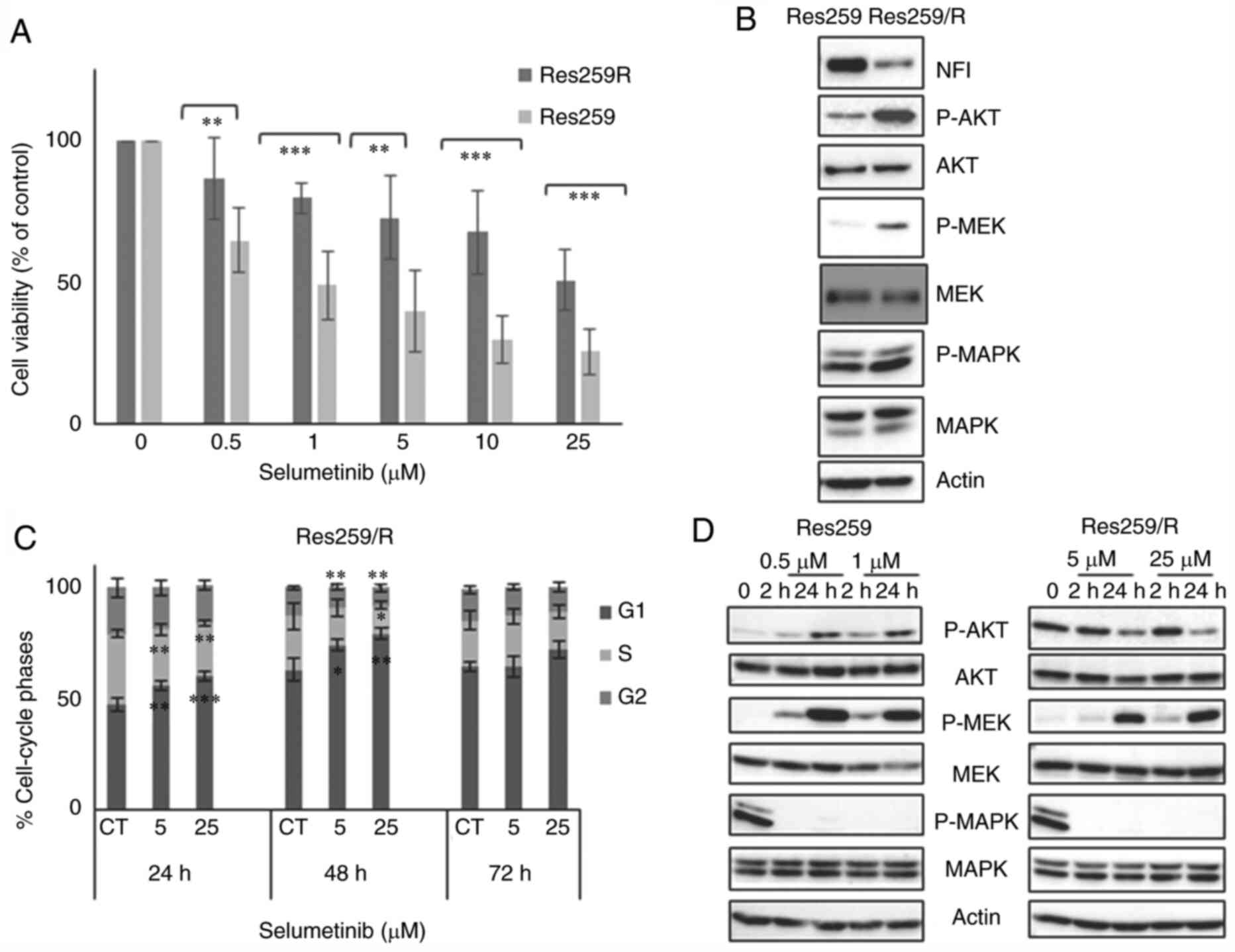
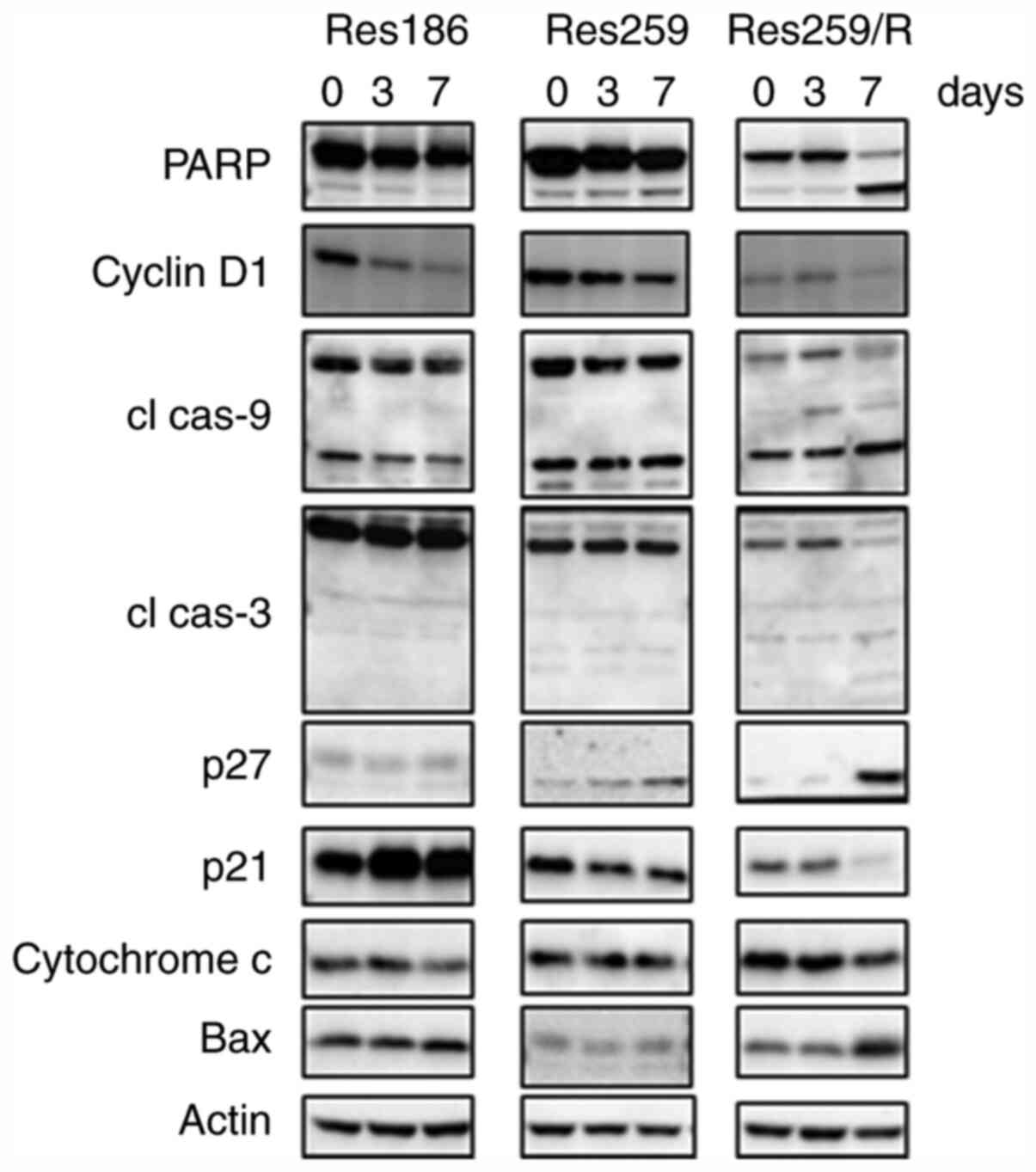
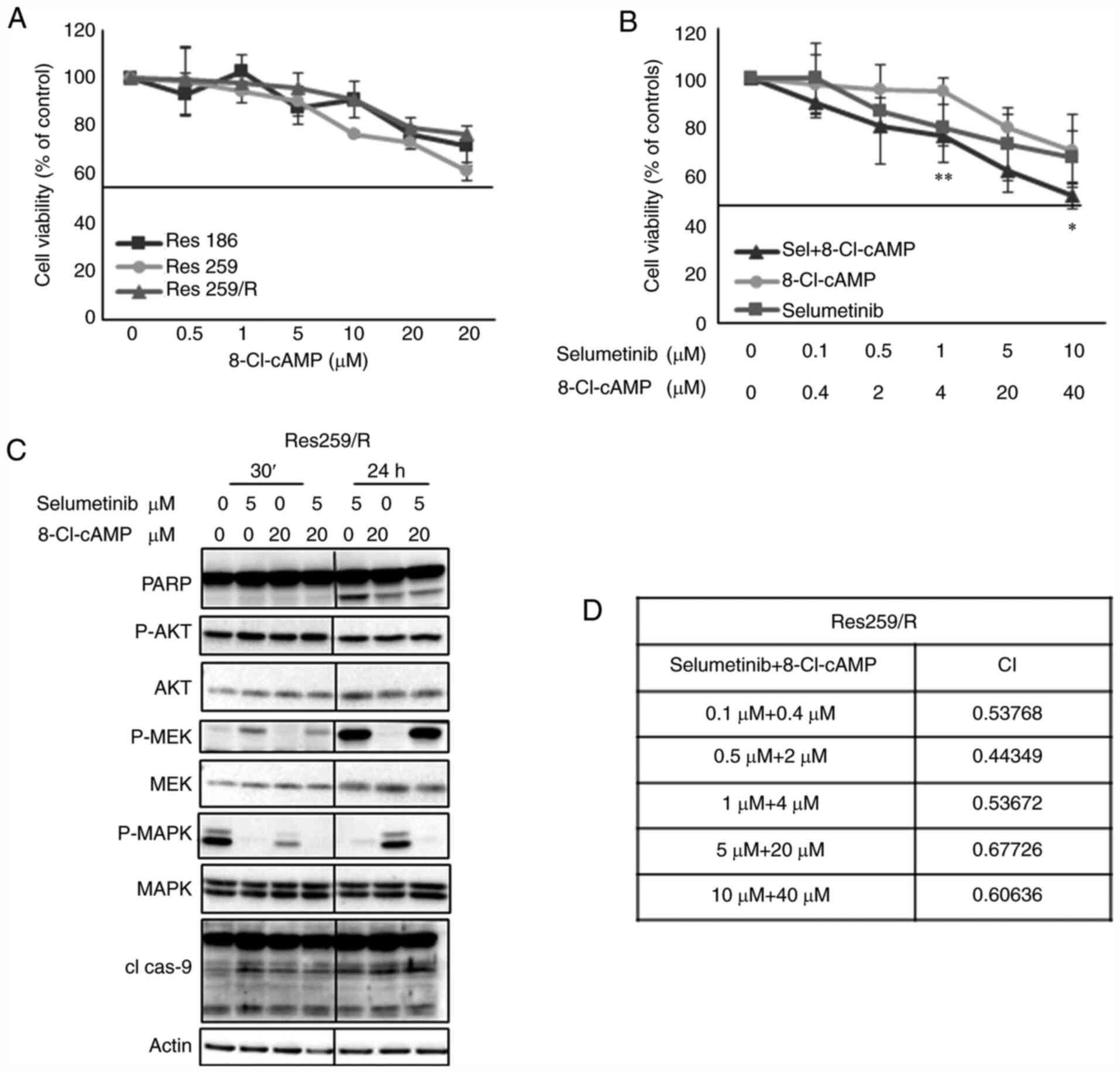
|
1
|
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Fulop J, Liu M,
Blanda R, Kromer C, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C and Barnholtz-Sloan JS:
CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system
tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2008-2012. Neuro Oncol. 17
(Suppl 4):iv1–iv62. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Johnson KJ, Cullen J, Barnholtz-Sloan JS,
Ostrom QT, Langer CE, Turner MC, McKean-Cowdin R, Fisher JL, Lupo
PJ, Partap S, et al: Childhood brain tumor epidemiology: A brain
tumor epidemiology consortium review. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 23:2716–2736. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von
Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD,
Kleihues P and Ellison DW: The 2016 world health organization
classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary.
Acta Neuropathol. 131:803–82. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sievert AJ and Fisher MJ: Pediatric
low-grade gliomas. J Child Neurol. 24:1397–1408. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bergthold G, Bandopadhayay P, Bi WL,
Ramkissoon L, Stiles C, Segal RA, Beroukhim R, Ligon KL, Grill J
and Kieran MW: Pediatric low-grade gliomas: How modern biology
reshapes the clinical field. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1845:294–307.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chalil A and Ramaswamy V: Low grade
gliomas in children. J Child Neurol. 31:517–522. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dasgupta T, Olow AK, Yang X, Hashizume R,
Nicolaides TP, Tom M, Aoki Y, Berger MS, Weiss WA, Stalpers LJ, et
al: Survival advantage combining a BRAF inhibitor and radiation in
BRAF V600E-mutant glioma. Neurooncol. 126:385–393. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ater Jl, Zhou T, Holmes E, Mazewski CM,
Booth TN, Freyer DR, Lazarus KH, Packer RJ, Prados M, Sposto R, et
al: Randomized study of two chemotherapy regimens for treatment of
low-grade glioma in young children: A report from the children's
oncology group. J Clin Oncol. 30:2641–2647. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bandopadhayay P, Bergthold G, London WB,
Goumnerova LC, Morales La Madrid A, Marcus KJ, Guo D, Ullrich NJ,
Robison NJ, Chi SN, et al: Long-term outcome of 4,040 children
diagnosed with pediatric low-grade gliomas: An analysis of the
surveillance epidemiology and end results (SEER) database. Pediatr
Blood Cancer. 61:1173–1179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Weuken JW and Wesseling P: MAPK pathway
activation through BRAF gene fusion in pilocytic astrocytomas; a
novel oncogenic fusion gene with diagnostic, prognostic, and
therapeutic potential. J Pathol. 222:324–328. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guo YJ, Pan WW, Liu SB, Shen ZF, Xu Y and
Hu LL: ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med.
19:1997–2007. 2019.
|
|
12
|
Pfister S, Janzarik WG, Remke M, Ernst A,
Werft W, Becker N, Toedt G, Wittmann A, Kratz C, Olbrich H, et al:
BRAF gene duplication constitutes a mechanism of MAPK pathway
activation in low-grade astrocytomas. J Clin Invest. 118:1739–1749.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tateishi K, Nakamura T and Yamamoto T:
Molecular genetics and therapeutic targets of pediatric low-grade
gliomas. Brain Tumor Pathol. 36:74–83. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Roskoski R Jr: MEK1/2 dual-specificity
protein kinases: Structure and regulation. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 417:5–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roskoski R Jr: ERK1/2 MAP kinases:
Structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol Res. 66:105–143.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Roskoski R Jr: Allosteric MEK1/2
inhibitors including cobimetanib and trametinib in the treatment of
cutaneous melanomas. Pharmacol Res. 117:20–31. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yeh TC, Marsh V, Bernat BA, Ballard J,
Colwell H, Evans RJ, Parry J, Smith D, Brandhuber BJ, Gross S, et
al: Biological characterization of ARRY-142886 (AZD6244), a potent,
highly selective mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2
inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res. 13:1576–1583. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Davies BR, Logie A, McKay JS, Martin P,
Steele S, Jenkins R, Cockerill M, Cartlidge S and Smith PD: AZD6244
(ARRY- 142886), a potent inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein
kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 kinases: Mechanism
of action in vivo, pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamics relationship,
and potential for combination in preclinical models. Mol Cancer
Ther. 6:2209–2219. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deming DA, Cavalcante LL, Lubner SJ,
Mulkerin DL, Conte L, Eickhoff JC, Kolesar JM, Fioravanti S, Greten
TF, Compton K, et al: A phase I study of selumetinib
(AZD6244/ARRY-142866), a MEK1/2 inhibitor, in combination with
cetuximab in refractory solid tumors and KRAS mutant colorectal
cancer. Invest New Drugs. 34:168–175. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Greystoke A, Steele N, Arkenau HT,
Blackhall F, Haris N, Lindsay CR, Califano R, Voskoboynik M,
Summers Y, So K, et al: SELECT-3: A phase I study of selumetinib in
combination with platinum-doublet chemotherapy for advanced NSCLC
in the first-line setting. Br J Cancer. 117:938–946. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Melosky B, Bradbury P, Tu D, Florescu M,
Reiman A, Nicholas G, Basappa N, Rothenstein J, Goffin JR, Laurie
SA, et al: Selumetinib in patients receiving standard pemetrexed
and platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced or metastatic KRAS
wildtype or unknown non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer: A
randomized, multicenter, phase II study. Canadian cancer trials
group (CCTG) IND.219. Lung Cancer. 133:48–55. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Torii S, Yamamoto T, Tsuchiya Y and
Nishida E: ERK MAP kinase in G cell cycle progression and cancer.
Cancer Sci. 97:697–702. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bax DA, Little SE, Gaspar N, Perryman L,
Marshall L, Viana-Pereira M, Jones TA, Williams RD, Grigoriadis A,
Vassal G, et al: Molecular and phenotypic characterisation of
paediatric glioma cell lines as models for preclinical drug
development. PLoS One. 4:e52092009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chou TC: Drug combination studies and
their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer
Res. 15:440–446. 2011.
|
|
25
|
Adjei AA, Cohen RB, Franklin WB, Morris C,
Wilson D, Molina JR, Hanson LJ, Gore L, Chow L, Leong S, et al:
Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral,
small-molecule mitogen-activated protein kinase 1/2 inhibitor
AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancers. J Clin
Oncol. 26:2139–2146. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen YH and Gutmann DH: The molecular and
cell biology of pediatric low-grade gliomas. Oncogene.
33:2019–2026. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Khatua S, Gutmann DH and Packer RJ:
Neurofibromatosis type 1 and optic pathway glioma: Molecular
interplay and therapeutic insights. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 65:2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang L, Jackson E, Woerner BM, Perry A,
Piwnica-Worms D and Rubin JB: Blocking CXCR4-mediated cyclic AMP
suppression inhibits brain tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res.
67:651–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Warriton NM, Gianino SM, Jackson E,
Goldhoff P, Garbow JR, Piwnica-Worms D, Gutmann DH and Rubin JB:
Cyclic AMP suppression is sufficient to induce gliomagenesis in a
mouse model of neurofibromatosis-1. Cancer Res. 70:5717–5727. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xing F, Luan Y, Cai J, Wu S, Mai J, Gu J,
Zhang H, Li K, Lin Y, Xiao X, et al: The anti-Warburg effect
elicited by the cAMP-PGC1α pathway drives differentiation of
glioblastoma cells into astrocytes. Cell Rep. 23:2832–2833. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Goldhoff P, Warrington NM, Limbrick DD Jr,
Hope A, Woerner BM, Jackson E, Perry A, Piwnica-Worms D and Rubin
JR: Targeted inhibition of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase-4 promotes
brain tumor regression. Clin Cancer Res. 14:7717–7725. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lucchi S, Calebiro D, de Filippis T,
Grassi ES, Borghi MO and Persani L: 8-Chloro-cyclic AMP and protein
kinase A I-selective cyclic AMP analogs inhibit cancer cell growth
through different mechanisms. PLoS One. 6:e207852011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cheng YM, Zhu Q, Yao YY, Tang Y, Wang MM
and Zou LF: 8-Chloroadenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate induces cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells through
multiple mechanisms. Oncol Lett. 4:1384–1388. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Grassi ES, Dicitore A, Negri I, Borghi MO,
Vitale G and Persani L: 8-Cl-cAMP and PKA I-selective cAMP analogs
effectively inhibit undifferentiated thyroid cancer cell growth.
Endocrine. 56:388–398. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Garcia MA, Solomon DA and Haas-Kogan DA:
Exploiting molecular biology for diagnosis and targeted management
of pediatric low-grade gliomas. Future Oncol. 12:1493–506. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Banerjee RI, Jakacki A, Onar-Thomas S, Wu
T, Nicolaides T, Young Poussaint J, Fangusaro J, Phillips A, Perry
A, Turner D, et al: A phase I trial of the MEK inhibitor
selumetinib (AZD6244) in pediatric patients with recurrent or
refractory low-grade glioma: A pediatric brain tumor consortium
(PBTC) study. Neuro Oncol. 19:1135–1144. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Smith AM, Zhang CRZ, Cristino AS, Grady
JP, Fink JL and Moore AS: PTEN deletion drives acute myeloid
leukemia resistance to MEK inhibitors. Oncotarget. 10:5755–5767.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hur EH, Goo BK, Moon J, Choi Y, Hwang JJ,
Kim CS, Bae KS, Choi J, Cho SY, Yang SH, et al: Induction of
immunoglobulin transcription factor 2 and resistance to MEK
inhibitor in melanoma cells. Oncotarget. 20:41387–41400. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lim SY, Menzies AM and Rizos H: Mechanisms
and strategies to overcome resistance to molecularly targeted
therapy for melanoma. Cancer. 123:21–29. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Nörz D, Grottke A, Bach J, Herzberger C,
Hofmann BT, Nashan B, Jücker M and Ewald F: Discontinuing MEK
inhibitors in tumor cells with an acquired resistance increases
migration and invasion. Cell Signal. 27:2191–2200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Simeone E, Grimaldi AM, Festino L, Vanella
V, Palla M and Ascierto PA: Combination treatment of patients with
BRAF-mutant melanoma: A new standard of care. BioDrugs. 31:51–61.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Welsh SJ, Rizos H, Scolyer RA and Long GV:
Resistance to combination BRAF and MEK inhibition in metastatic
melanoma: Where to next? Eur J Cancer. 62:76–85. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Solit DB, Garraway LA, Pratilas CA, Sawai
A, Getz G, Basso A, Ye Q, Lobo JM, She Y, Osman I, et al: BRAF
mutation predicts sensitivity to MEK inhibition. Nature.
439:358–362. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dizdar L, Werner TA, Drusenheimer JC,
Möhlendick B, Raba K, Boeck I, Anlauf M, Schott M, Göring W,
Esposito I, et al: BRAFV600E mutation: A promising
target in colorectal neuroendocrine carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
144:1379–1390. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gilmartin AG, Bleam MR, Groy A, Moss KG,
Minthorn EA, Kulkarni SG, Rominger CM, Erskine S, Fisher KE, Yang
J, et al: GSK1120212 (JTP-74057) is an inhibitor of MEK activity
and activation with favorable pharmacokinetic properties for
sustained in vivo pathway inhibition. Clin Cancer Res. 17:989–1000.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Catalanotti F, Solit DB, Pulitzer MP,
Berger MF, Scott SN, Iyriboz T, Lacouture ME, Panageas KS, Wolchok
JD, Carvajal RD, et al: Phase II trial of MEK inhibitor selumetinib
(AZD6244, ARRY-142886) in patients with BRAFV600E/K-mutated
melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 19:2257–2264. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Burger MC, Ronellenfitsch W, Lorenz NI,
Wagner M, Voss M, Capper D, Tzaridis T, Herrlinger U, Steinbach JP,
Stoffels G, et al: Dabrafenib in patients with recurrent, BRAF
V600E mutated malignant glioma and leptomeningeal disease. Oncol
Rep. 38:3291–3296. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ranzani M, Alifrangis C, Perna D,
Dutton-Regester K, Pritchard A, Wong K, Rashid M, Robles-Espinoza
CD, Hayward NK, McDemott U, et al: BRAF/NRAS wild-type melanoma,
NF1 status and sensitivity to trametinib. Pigment Cell Melanoma
Res. 28:117–119. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ming Z, Lim SY, Kefford RF and Rizos H:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase dependency in BRAF/RAS wild-type
melanoma: A rationale for combination inhibitors. Pigment Cell
Melanoma Res. 33:345–357. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Fangusaro J, Onar-Thomas A, Pussaint TY,
Wu S, Ligon AH, Lindman N, Banerjee A, Pacher RJ, Kilburn LB,
Goldman S, Polack IF, et al: Selumetinb in paedriatic patients with
BRAF-aberrant or neurofibromatosis type 1-associated recurrant,
refractory, or progressive low-grade glioma: A multicenter, phases
2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 20:1011–1022. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Grasso S, Tristante E, Saceda M, Carbonell
P, Mayor-López L, Carballo-Santana M, Carrasco-García E,
Rocamora-Reverte L, García-Morales P, Carballo F, et al: Resistance
to Selumetinib (AZD6244) in colorectal cancer cell lines is
mediated by p70S6K and RPS6 activation. Neoplasia. 16:845–860.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tentler JJ, Nallapareddy S, Tan AC,
Spreafico A, Pitts TM, Morelli MP, Selby HM, Kachaeva MI, Flanigan
SA, Kulikowski GN, et al: Identification of predictive markers of
response to the MEK1/2 inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244) in
K-ras-mutated colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:3351–3362.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kerstjens M, Driessen EM, Willekes M,
Pinhanços SS, Schneider P, Pieters R and Stam RW: MEK inhibition is
a promising therapeutic strategy for MLL-rearranged infant acute
lymphoblastic leukemia patients carrying RAS mutations. Oncotarget.
8:14835–14846. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Meng J, Peng H, Dai B, Guo W, Wang L, Ji
L, Minna JD, Chresta CM, Smith PD, Fang B and Roth JA: High level
of AKT activity is associated with resistance to MEK inhibitor
AZD6244 (ARRY-142886). Cancer Biol Ther. 8:2073–2080. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sweetlove M, Wrightson E, Kolekar S,
Rewcastle GW, Baguley BC, Shepherd PR and Jamieson SM: Inhibitors
of pan-PI3K signaling synergize with BRAF or MEK inhibitors to
prevent BRAF-mutant melanoma cell growth. Front Oncol. 5:1352015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tsubaki M, Takeda T, Noguchi M, Jinushi M,
Seki S, Morii Y, Shimomura K, Imano M, Satou T and Nishida S:
Overactivation of Akt contributes to MEK inhibitor primary and
acquired resistance in colorectal cancer cells. Cancers (Basel).
25:11–12. 2019.
|
|
57
|
Balmanno K, Chell SD, Gillings AS, Hayat S
and Cook SJ: Intrinsic resistance to the MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244
(ARRY-142886) is associated with weak ERK1/2 signalling and /or
strong PI3K signalilling in colorectal cancer cell lines. Int J
Cancer. 125:2332–2341. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chen Z, Cheng K, Walton Z, Wang Y, Ebi H,
Shimamura T, Liu Y, Tupper T, Ouyang J, Li J, et al: A murine lung
cancer co-clinical trial identifies genetic modifiers of
therapeutic response. Nature. 483:613–617. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chang T, Krisman K, Theobald EH, Xu J,
Akutagawa J, Lauchle JO, Kogan S, Braun BS and Shannon K: Sustained
MEK inhibition abrogates myeloproliferative disease in Nf1 mutant
mice. J Clin Invest. 123:335–339. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
See WL, Tan IL, Mukherjee J, Nicolaides T
and Pieper RO: Sensitivity of glioblastomas to clinically available
MEK inhibitors is defined by neurofibromin 1 deficiency. Cancer
Res. 72:3350–3359. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Nissan MH, Pratilas CA, Jones AM, Ramirez
R, Won H, Liu C, Tiwari S, Kong L, Hanrahan AJ, Yao Z, et al: Loss
of NF1 in cutaneous melanoma is associated with RAS activation and
MEK dependence. Cancer Res. 74:2340–2350. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Whittaker SR, Theurillat JP, Van Allen E,
Wagle N, Hsiao J, Cowley GS, Schadendorf D, Root DE and Garraway
LA: A genome-scale RNA interference screen implicates NF1 loss in
resistance to RAF inhibition. Cancer Discov. 3:350–362. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li Y, Dong Q and Cui Q: Synergistic
inhibition of MEK and reciprocal feedback networks for targeted
intervention in malignancy. Cancer Biol Med. 16:415–434.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Chen CH, Hsia TC, Yeh MH, Chen TW, Chen
YJ, Wei YL, Tu CY and Huang WC: MEK inhibitors induce Akt
activation and drug resistance by suppressing negative feedback
ERK-mediated HER2 phosphorylation at Thr701. Mol Oncol.
11:1273–1287. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Iizuka-Ohashi M, Watanabe M, Sukeno M,
Morita M, Hoang NTH, Kuchimaru T, Kizaka-Kondoh S, Sowa Y,
Sakaguchi K, Taguchi T, et al: Blockage of the mevalonate pathway
overcomes the apoptotic resistance to MEK inhibitors with
suppressing the activation of Akt in cancer cells. Oncotarget.
9:19597–19612. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Coussy F, El Botty R, Lavigne M, Gu C,
Fuhrmann L, Briaux A, de Koning L, Dahmani A, Montaudon E, Morisset
L, et al: Combination of PI3K and MEK inhibitors yields durable
remission in PDX models of PIK3CA-mutated metaplastic breast
cancers. J Hematol Oncol. 13:132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Liu X, Hu J, Song X, Utpatel K, Zhang Y,
Wang P, Lu X, Zhang J, Xu M, Su T, et al: Combined treatment with
MEK and mTOR inhibitors is effective in in vitro and in vivo models
of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 3:9302019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Ewald F, Nörz D, Grottke A, Bach J,
Herzberger C, Hofmann BT, Nashan B and Jücker M: Vertical targeting
of AKT and mTOR as well as dual targeting of AKT and MEK signaling
is synergistic in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer. 16:1195–1205.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Meng J, Dai B, Fang B, Bekele BN, Bornmann
WG, Sun D, Peng Z, Herbst RS, Papadimitrakopoulou V, Minna JD, et
al: Combination treatment with MEK and AKT inhibitors is more
effective than each drug alone in human non-small cell lung cancer
in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 29:e141242010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Arnold A, Yuan M, Price A, Harris L,
Eberhart CG and Raabe EH: Synergistic activity of mTORC1/2 kinase
and MEK inhibitors suppresses pediatric low-grade glioma
tumorigenicity and vascularity. Neuro Oncol. 22:563–574. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Choi KY, Cho YJ, Kim JS, Ahn YH and Hong
SH: SHC1 sensitizes cancer cells to the 8-Cl-cAMP treatment.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 463:673–678. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Grbovic O, Jovic V, Ruzdijic S, Pejanovic
V, Rakic L and Kanazir S: 8-Cl-cAMP affects glioma cell-cycle
kinetics and selectively induces apoptosis. Cancer Invest.
20:972–982. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Langeveld CH, Jongenelen CA, Heimans JJ
and Stoof JC: Growth inhibition of human glioma cells induced by
8-chloroadenosine, an active metabolite of 8-chloro cyclic
adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate. Cancer Res. 52:3994–3999.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Xing F, Luan Y, Cai J, Wu S, Mai J, Gu J,
Zhang H, Li K, Lin Y, Xiao X, et al: The anti-Warburg effect
elicited by the cAMP-PGC1α pathway drives differentiation of
glioblastoma cells into astrocytes. Cell Rep. 18:468–481. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|