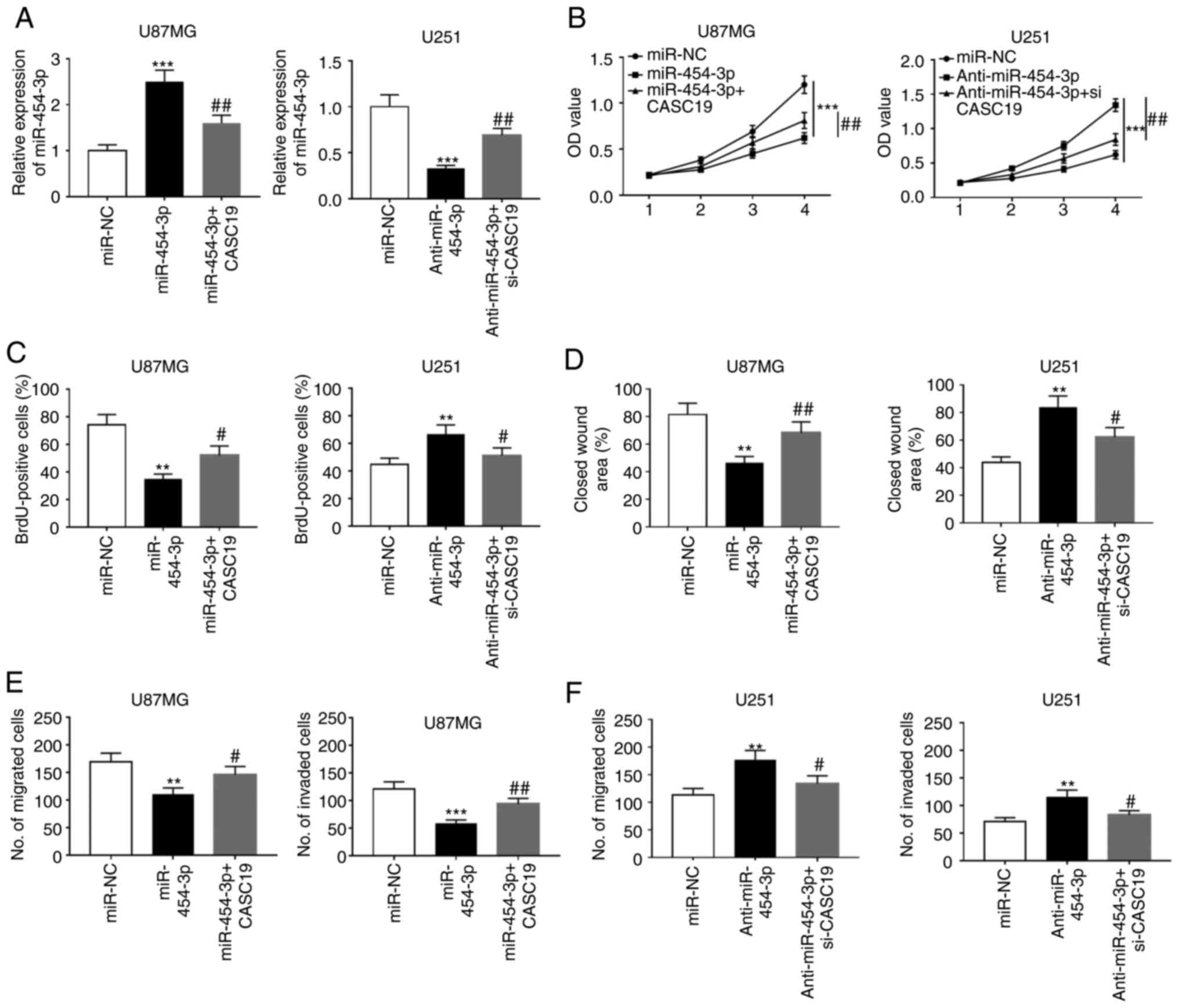
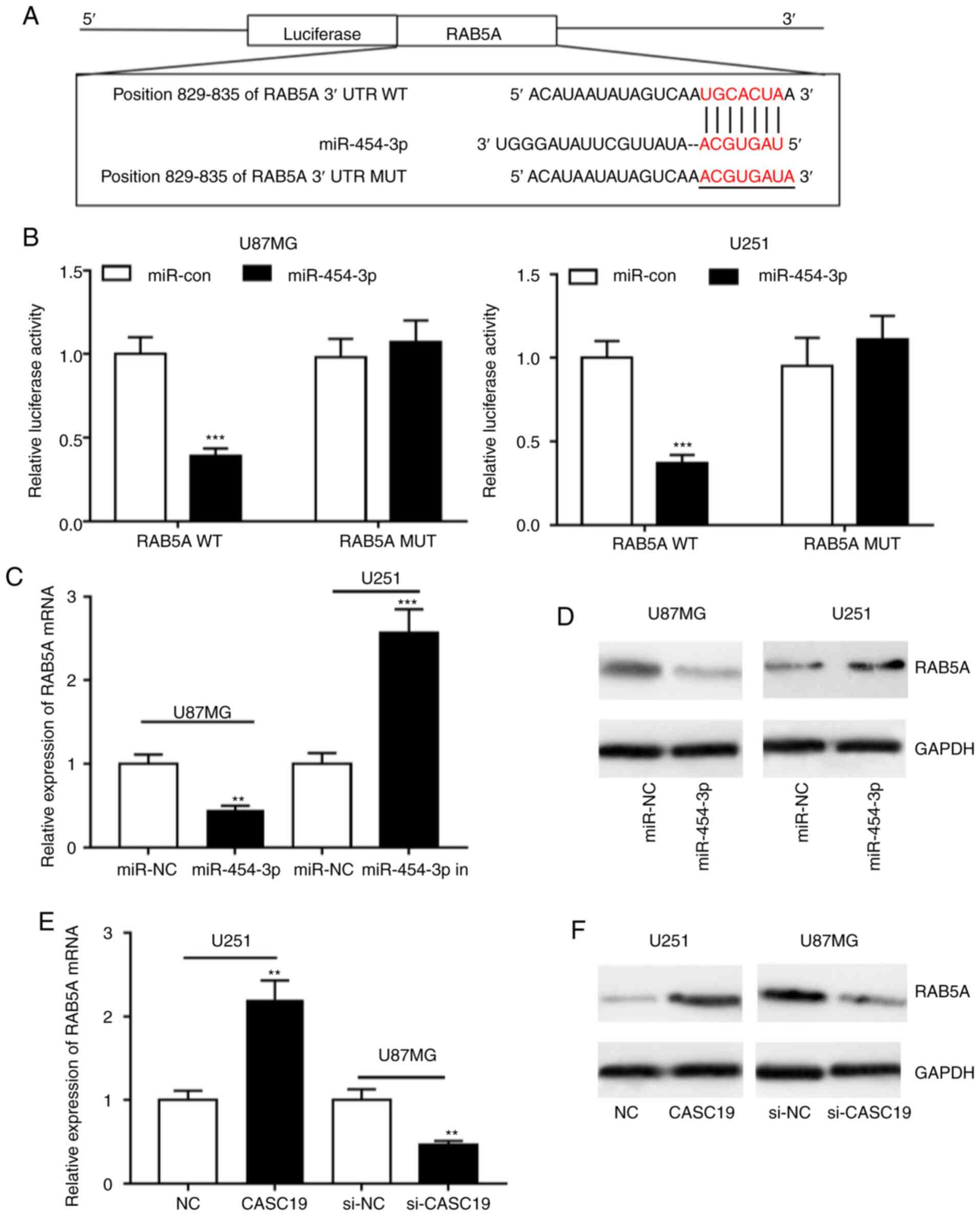
|
1
|
Rynkeviciene R, Simiene J, Strainiene E,
Stankevicius V, Usinskiene J, Miseikyte Kaubriene E, Meskinyte I,
Cicenas J and Suziedelis K: Non-coding RNAs in glioma. Cancers
(Basel). 11:172018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Meng L, Ma P, Cai R, Guan Q, Wang M and
Jin B: Long noncoding RNA ZEB1-AS1 promotes the tumorigenesis of
glioma cancer cells by modulating the miR-200c/141-ZEB1 axis. Am J
Transl Res. 10:3395–3412. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tom MC, Park DYJ, Yang K, Leyrer CM, Wei
W, Jia X, Varra V, Yu JS, Chao ST, Balagamwala EH, et al: Malignant
transformation of molecularly classified adult low-grade glioma.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 105:1106–1112. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ghafouri-Fard S and Taheri M: UCA1 long
non-coding RNA: An update on its roles in malignant behavior of
cancers. Biomed Pharmacother. 120:1094592019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang X, Hong R, Chen W, Xu M and Wang L:
The role of long noncoding RNA in major human disease. Bioorg Chem.
92:1032142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zeng XY, Jiang XY, Yong JH, Xie H, Yuan J,
Zeng D, Dou YY and Xiao SS: lncRNA ABHD11-AS1, regulated by the
EGFR pathway, contributes to the ovarian cancer tumorigenesis by
epigenetically suppressing TIMP2. Cancer Med. 8:7074–7085. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fu X, Wang D, Shu T, Cui D and Fu Q:
LncRNA NR2F2-AS1 positively regulates CDK4 to promote cancer cell
proliferation in prostate carcinoma. Aging Male. Sep 28–2019.(Epub
ahead of print). doi: 10.1080/13685538.2019.1670157. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Song Z, Zhang X, Lin Y, Wei Y, Liang S and
Dong C: LINC01133 inhibits breast cancer invasion and metastasis by
negatively regulating SOX4 expression through EZH2. J Cell Mol Med.
23:7554–7565. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang WJ, Guo CA, Li R, Xu ZP, Yu JP, Ye Y,
Zhao J, Wang J, Wang WA, Zhang A, et al: Long non-coding RNA CASC19
is associated with the progression and prognosis of advanced
gastric cancer. Aging (Albany NY). 11:5829–5847. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou Q, Liu J, Quan J, Liu W, Tan H and Li
W: MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of glioma: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Sci. 109:2651–2659.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ye J, Xu M, Tian X, Cai S and Zeng S:
Research advances in the detection of miRNA. J Pharm Anal.
9:217–226. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Diana A, Gaido G and Murtas D: MicroRNA
signature in human normal and tumoral neural stem cells. Int J Mol
Sci. 20:41232019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lu Z, Li X, Xu Y, Chen M, Chen W, Chen T,
Tang Q and He Z: microRNA-17 functions as an oncogene by
downregulating Smad3 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell
Death Dis. 10:7232019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ji X, Guo H, Yin S and Du H: miR-139-5p
functions as a tumor suppressor in cervical cancer by targeting
TCF4 and inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Onco Targets Ther.
12:7739–7748. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shao N, Xue L, Wang R, Luo K, Zhi F and
Lan Q: miR-454-3p is an exosomal biomarker and functions as a tumor
suppressor in glioma. Mol Cancer Ther. 18:459–469. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu K, Li S, Liu J, Hong Y, Chen ZJ and Du
Y: Role of RAB5A in FSHR-mediated signal transduction in human
granulosa cells. Reproduction. 155:505–514. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li Y, Sun X, Ji D, Kong X, Liu D, Zhao Z,
Yan J and Chen S: Expression of Rab5a correlates with tumor
progression in pancreatic carcinoma. Virchows Arch. 470:527–536.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shen MX and Ding JB: Expression levels and
roles of EMC-6, Beclin1, and Rab5a in the cervical cancer. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:3038–3046. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Teske C, Schweitzer C, Palamidessi A, Aust
DE, Scita G, Weitz J and Welsch T: Modulation of RAB5A early
endosome trafficking in response to KRas mediated macropinocytic
fluxes in pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
493:528–533. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fu Z, Luo W, Wang J, Peng T, Sun G, Shi J,
Li Z and Zhang B: Malat1 activates autophagy and promotes cell
proliferation by sponging miR-101 and upregulating STMN1, RAB5A and
ATG4D expression in glioma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
492:480–486. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu B, Cao W and Ma H: Knockdown of lncRNA
LSINCT5 suppresses growth and metastasis of human glioma cells via
up-regulating miR-451. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol.
47:2507–2515. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu X, Zhu Q, Guo Y, Xiao Z, Hu L and Xu
Q: LncRNA LINC00689 promotes the growth, metastasis and glycolysis
of glioma cells by targeting miR-338-3p/PKM2 axis. Biomed
Pharmacother. 117:1090692019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cui B, Li B, Liu Q and Cui Y: lncRNA CCAT1
promotes glioma tumorigenesis by sponging miR-181b. J Cell Biochem.
118:4548–4557. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gao YF, Liu JY, Mao XY, He ZW, Zhu T, Wang
ZB, Li X, Yin JY, Zhang W, Zhou HH and Liu ZQ: LncRNA FOXD1-AS1
acts as a potential oncogenic biomarker in glioma. CNS Neurosci
Ther. 26:66–75. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gao XF, He HQ, Zhu XB, Xie SL and Cao Y:
LncRNA SNHG20 promotes tumorigenesis and cancer stemness in
glioblastoma via activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.
Neoplasma. 66:532–542. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Khan AQ, Ahmed EI, Elareer NR, Junejo K,
Steinhoff M and Uddin S: Role of miRNA-regulated cancer stem cells
in the pathogenesis of human malignancies. Cells. 8:8402019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Szelenberger R, Kacprzak M, Saluk-Bijak J,
Zielinska M and Bijak M: Plasma MicroRNA as a novel diagnostic.
Clin Chim Acta. 499:98–107. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang S, Zhang G, Zheng W, Xue Q, Wei D,
Zheng Y and Yuan J: MiR-454-3p and miR-374b-5p suppress migration
and invasion of bladder cancer cells through targetting ZEB2.
Biosci Rep. 38:BSR201814362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zuo J, Yu H, Xie P, Liu W, Wang K and Ni
H: miR-454-3p exerts tumor-suppressive functions by down-regulation
of NFATc2 in glioblastoma. Gene. 710:233–239. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xie Z, Li X, Chen H, Zeng A, Shi Y and
Tang Y: The lncRNA-DLEU2/miR-186-5p/PDK3 axis promotes the progress
of glioma cells. Am J Transl Res. 11:4922–4934. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Feng X and Yang S: Long non-coding RNA
LINC00243 promotes proliferation and glycolysis in non-small cell
lung cancer cells by positively regulating PDK4 through sponging
miR-507. Mol Cell Biochem. 463:127–136. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu SS, Chen XM, Zheng HX, Shi SL and Li
Y: Knockdown of Rab5a expression decreases cancer cell motility and
invasion through integrin-mediated signaling pathway. J Biomed Sci.
18:582011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang D, Lu C and Ai H: Rab5a is
overexpressed in oral cancer and promotes invasion through ERK/MMP
signaling. Mol Med Rep. 16:4569–4576. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Geng D, Zhao W, Feng Y and Liu J:
Overexpression of Rab5a promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell
proliferation and invasion via FAK signaling pathway. Tumour Biol.
37:3341–3347. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sheng J, Wang L, Han Y, Chen W, Liu H,
Zhang M, Deng L and Liu YN: Dual roles of protein as a template and
a sulfur provider: A general approach to metal sulfides for
efficient photothermal therapy of cancer. Small. 14:17025292018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Verma JK, Rastogi R and Mukhopadhyay A:
Leishmania donovani resides in modified early endosomes by
upregulating Rab5a expression via the downregulation of miR-494.
PLoS Pathog. 13:e10064592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|