|
1
|
Torre LA, Islami F, Siegel RL, Ward EM and
Jemal A: Global cancer in women: Burden and trends. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 26:444–457. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wu G, Zhou W, Pan X, Sun Y, Xu H, Shi P,
Li J, Gao L and Tian X: miR-100 reverses cisplatin resistance in
breast cancer by suppressing HAX-1. Cell Physiol Biochem.
47:2077–2087. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cook KL, Clarke PA, Parmar J, Hu R,
Schwartz-Roberts JL, Abu-Asab M, Wärri A, Baumann WT and Clarke R:
Knockdown of estrogen receptor-α induces autophagy and inhibits
antiestrogen-mediated unfolded protein response activation,
promoting ROS-induced breast cancer cell death. FASEB J.
28:3891–3905. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hu R, Warri A, Jin L, Zwart A, Riggins RB,
Fang HB and Clarke R: NF-κB signaling is required for XBP1
(unspliced and spliced)-mediated effects on antiestrogen
responsiveness and cell fate decisions in breast cancer. Mol Cell
Biol. 35:379–390. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yeung BH, Kwan BW, He QY, Lee AS, Liu J
and Wong AS: Glucose-regulated protein 78 as a novel effector of
BRCA1 for inhibiting stress-induced apoptosis. Oncogene.
27:6782–6789. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang X, Cook KL, Warri A, Cruz IM, Rosim
M, Riskin J, Helferich W, Doerge D, Clarke R and Hilakivi-Clarke L:
Lifetime genistein intake increases the response of mammary tumors
to tamoxifen in rats. Clin Cancer Res. 23:814–824. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Christowitz C, Davis T, Isaacs A, van
Niekerk G, Hattingh S and Engelbrecht AM: Mechanisms of
doxorubicin-induced drug resistance and drug resistant tumour
growth in a murine breast tumour model. BMC Cancer. 19:7572019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ma W, Teng Y, Hua H, Hou J, Luo T and
Jiang Y: Upregulation of heat shock protein 27 confers resistance
to actinomycin D-induced apoptosis in cancer cells. FEBS J.
280:4612–4624. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
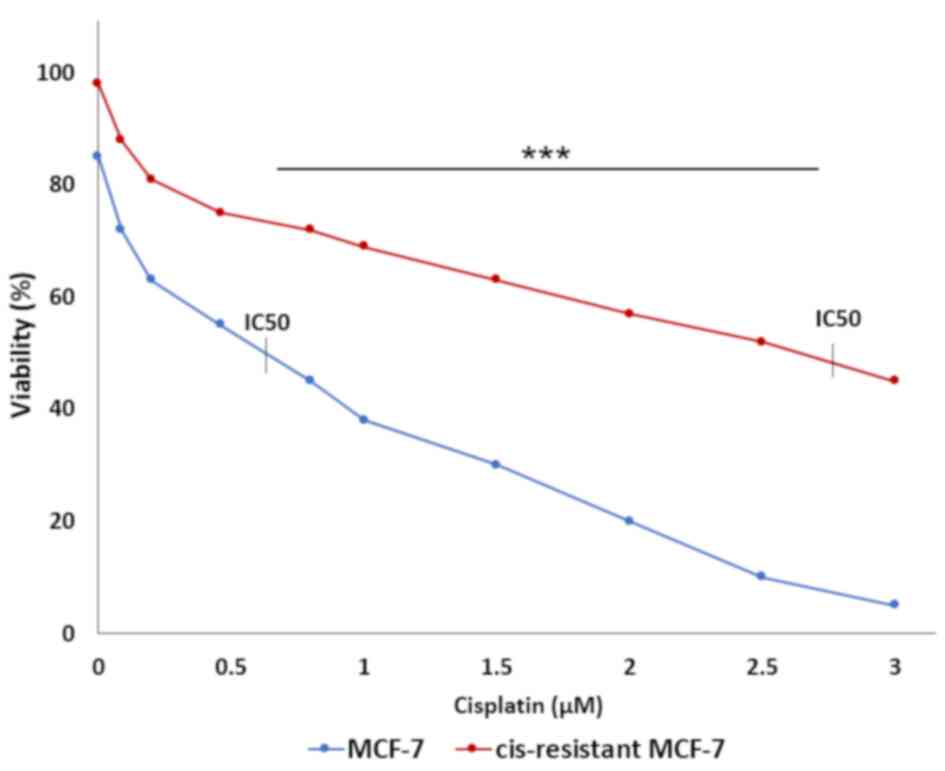
Wang Q, Cui K, Espin-Garcia O, Cheng D,
Qiu X, Chen Z, Moore M, Bristow RG, Xu W, Der S, et al: Resistance
to bleomycin in cancer cell lines is characterized by prolonged
doubling time, reduced DNA damage and evasion of G2/M arrest and
apoptosis. PLoS One. 8:e823632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
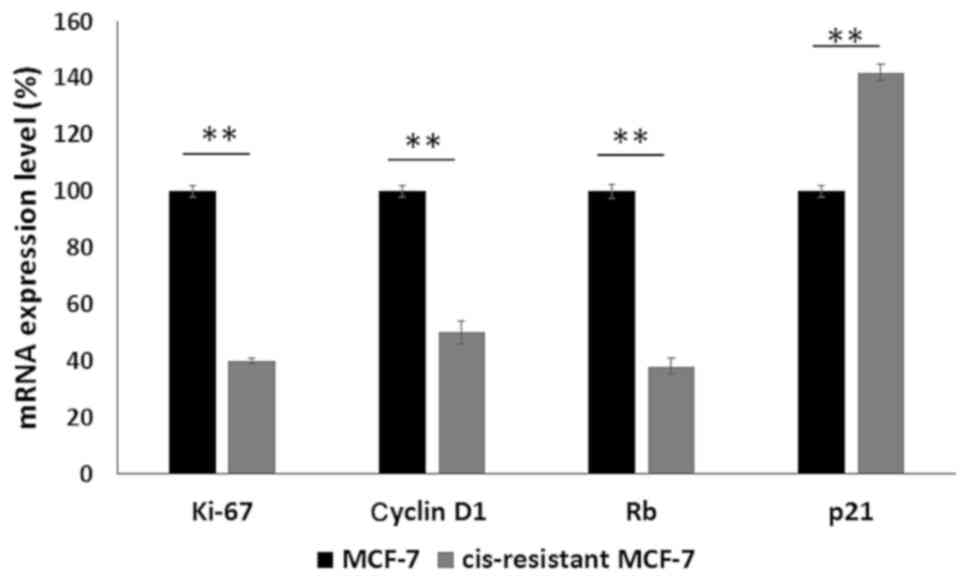
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kaufman RJ: Stress signaling from the
lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum: Coordination of gene
transcriptional and translational controls. Genes Dev.
13:1211–1233. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
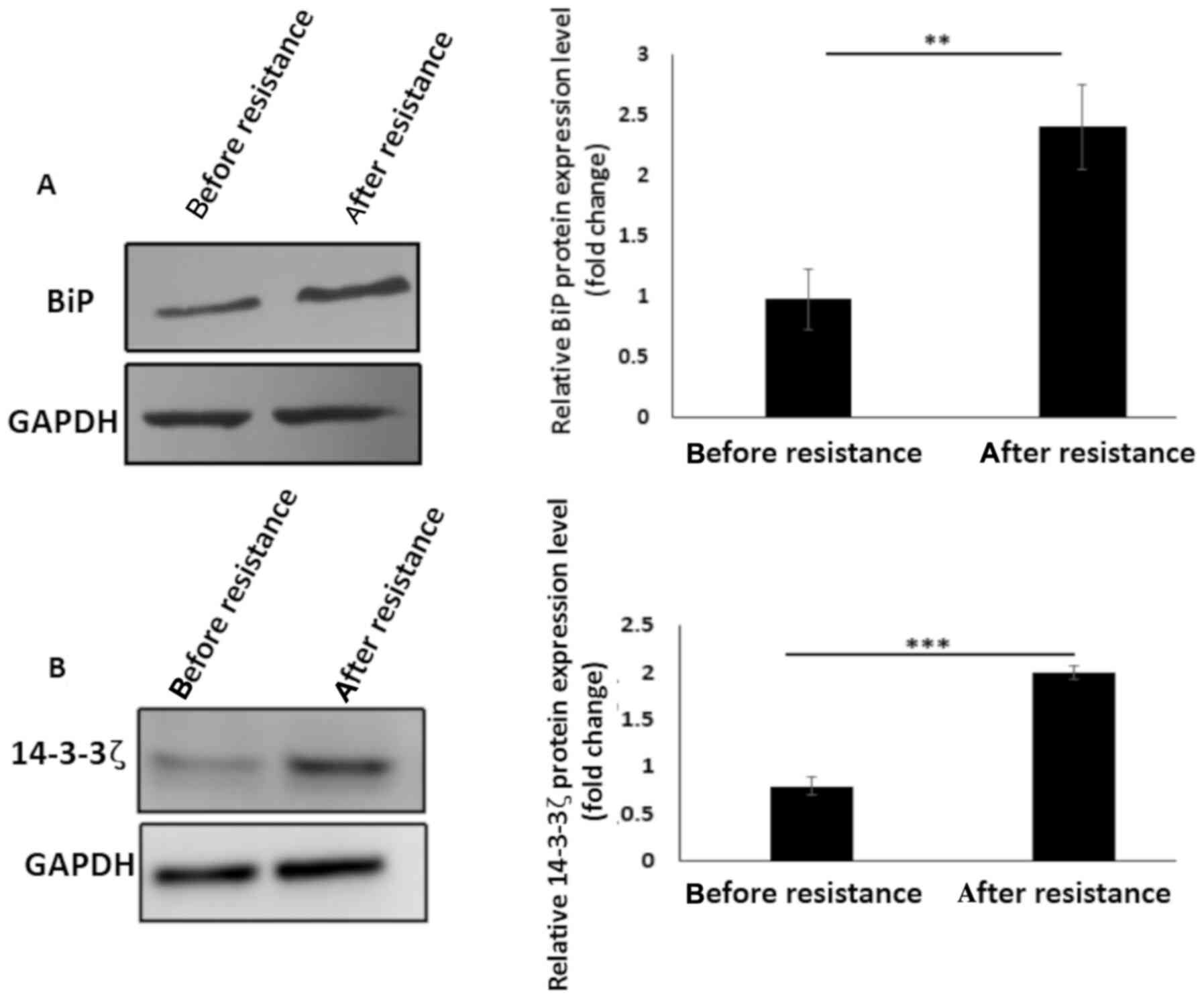
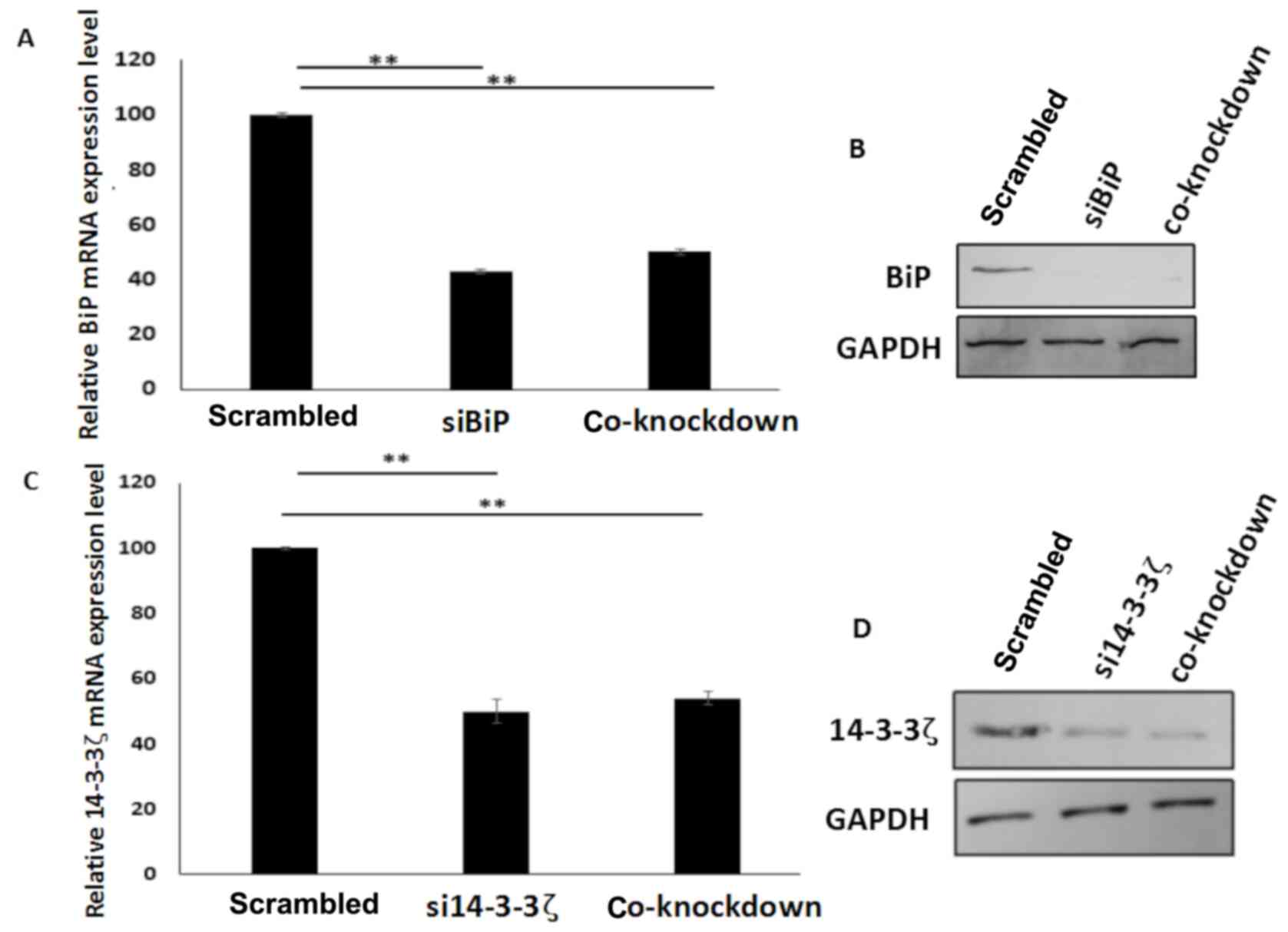
|
|
12
|
Luo B and Lee AS: The critical roles of
endoplasmic reticulum chaperones and unfolded protein response in
tumorigenesis and anticancer therapies. Oncogene. 32:805–818. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kosakowska-Cholody T, Lin J, Srideshikan
SM, Scheffer L, Tarasova NI and Acharya JK: HKH40A downregulates
GRP78-BiP expression in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 5:e12402014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Avril T, Vauléon E and Chevet E:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling and chemotherapy resistance
in solid cancers. Oncogenesis. 6:e3732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee E, Nichols P, Spicer D, Groshen S, Yu
MC and Lee AS: GRP78 as a novel predictor of responsiveness to
chemotherapy in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 66:7849–7853. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Andruska N, Zheng X, Yang X, Helferich WG
and Shapiro DJ: Anticipatory estrogen activation of the unfolded
protein response is linked to cell proliferation and poor survival
in estrogen receptor α-positive breast cancer. Oncogene.
34:3760–3769. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Davies MPA, Barraclough DL, Stewart C,
Joyce KA, Eccles RM, Barraclough R, Rudland PS and Sibson DR:
Expression and splicing of the unfolded protein response gene XBP-1
are significantly associated with clinical outcome of
endocrine-treated breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 123:85–88. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee E, Nichols P, Groshen S, Spicer D and
Lee AS: GRP78 as potential predictor for breast cancer response to
adjuvant taxane therapy. Int J Cancer. 128:726–731. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gottesman MM: Mechanisms of cancer drug
resistance. Annu Rev Med. 53:615–627. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB
and Johnston PG: Cancer drug resistance: An evolving paradigm. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:714–726. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Longley DB and Johnston PG: Molecular
mechanisms of drug resistance. J Pathol. 205:275–292. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fernandez PM, Tabbara SO, Jacobs LK,
Manning FC, Tsangaris TN, Schwartz AM, Kennedy KA and Patierno SR:
Overexpression of the glucose-regulated stress gene GRP78 in
malignant but not benign human breast lesions. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 59:15–26. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pyrko P, Schönthal AH, Hofman FM, Chen TC
and Lee AS: The unfolded protein response regulator GRP78/BiP as a
novel target for increasing chemosensitivity in malignant gliomas.
Cancer Res. 67:9809–9816. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee HK, Xiang C, Cazacu S, Finniss S,
Kazimirsky G, Lemke N, Lehman NL, Rempel SA, Mikkelsen T and Brodie
C: GRP78 is overexpressed in glioblastomas and regulates glioma
cell growth and apoptosis. Neuro Oncol. 10:236–243. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Epple LM, Dodd RD, Merz AL, Dechkovskaia
AM, Herring M, Winston BA, Lencioni AM, Russell RL, Madsen H, Nega
M, et al: Induction of the unfolded protein response drives
enhanced metabolism and chemoresistance in glioma cells. PLoS One.
8:e732672013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tsuruo T, Naito M, Tomida A, Fujita N,
Mashima T, Sakamoto H and Haga N: Molecular targeting therapy of
cancer: Drug resistance, apoptosis and survival signal. Cancer Sci.
94:15–21. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Salazar M, Hernández-Tiedra S, Torres S,
Lorente M, Guzmán M and Velasco G: Detecting autophagy in response
to ER stress signals in cancer. Methods Enzymol. 489:297–317. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sokolowska I, Woods AG, Gawinowicz MA, Roy
U and Darie CC: Identification of potential tumor differentiation
factor (TDF) receptor from steroid-responsive and steroid-resistant
breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 287:1719–1733. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baptista MZ, Sarian LO, Vassallo J, Pinto
GA, Soares FA and de Souza GA: Prognostic significance of GRP78
expression patterns in breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant
chemotherapy. Int J Biol Markers. 26:188–196. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
La X, Zhang L, Li H, Li Z, Song G, Yang P
and Yang Y: Ajuba receptor mediates the internalization of
tumor-secreted GRP78 into macrophages through different endocytosis
pathways. Oncotarget. 9:15464–15479. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Y, Wang JH, Zhang XL, Wang XL and
Yang L: Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone glucose-regulated protein
78 in gastric cancer: An emerging biomarker. Oncol Lett.
15:6087–6093. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shimizu A, Kaira K, Yasuda M, Asao T and
Ishikawa O: Clinical and pathological significance of ER stress
marker (BiP/GRP78 and PERK) expression in malignant melanoma.
Pathol Oncol Res. 23:111–116. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Peñaranda Fajardo NM, Meijer C and Kruyt
FA: The endoplasmic reticulum stress/unfolded protein response in
gliomagenesis, tumor progression and as a therapeutic target in
glioblastoma. Biochem Pharmacol. 118:1–8. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Uramoto H, Sugio K, Oyama T, Nakata S, Ono
K, Yoshimastu T, Morita M and Yasumoto K: Expression of endoplasmic
reticulum molecular chaperone Grp78 in human lung cancer and its
clinical significance. Lung Cancer. 49:55–62. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Scriven P, Coulson S, Haines R,
Balasubramanian S, Cross S and Wyld L: Activation and clinical
significance of the unfolded protein response in breast cancer. Br
J Cancer. 101:1692–1698. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xing X, Li Y, Liu H, Wang L and Sun L:
Glucose regulated protein 78 (GRP78) is overexpressed in colorectal
carcinoma and regulates colorectal carcinoma cell growth and
apoptosis. Acta Histochem. 113:777–782. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Daneshmand S, Quek ML, Lin E, Lee C, Cote
RJ, Hawes D, Cai J, Groshen S, Lieskovsky G, Skinner DG, et al:
Glucose-regulated protein GRP78 is up-regulated in prostate cancer
and correlates with recurrence and survival. Hum Pathol.
38:1547–1552. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zheng HC, Takahashi H, Li XH, Hara T,
Masuda S, Guan YF and Takano Y: Overexpression of GRP78 and GRP94
are markers for aggressive behavior and poor prognosis in gastric
carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 39:1042–1049. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Langer R, Feith M, Siewert JR, Wester HJ
and Hoefler H: Expression and clinical significance of glucose
regulated proteins GRP78 (BiP) and GRP94 (GP96) in human
adenocarcinomas of the esophagus. BMC Cancer. 8:702008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nagelkerke A, Bussink J, Sweep FC and Span
PN: The unfolded protein response as a target for cancer therapy.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1846:277–284. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Baumeister P, Dong D, Fu Y and Lee AS:
Transcriptional induction of GRP78/BiP by histone deacetylase
inhibitors and resistance to histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced
apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:1086–1094. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Roué G, Pérez-Galán P, Mozos A,
López-Guerra M, Xargay-Torrent S, Rosich L, Saborit-Villarroya I,
Normant E, Campo E and Colomer D: The Hsp90 inhibitor IPI-504
overcomes bortezomib resistance in mantle cell lymphoma in vitro
and in vivo by down-regulation of the prosurvival ER chaperone
BiP-Grp78. Blood. 117:1270–1279. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Al-Rawashdeh FY, Scriven P, Cameron IC,
Vergani PV and Wyld L: Unfolded protein response activation
contributes to chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22:1099–1105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang L, Wang S, Wangtao, Wang Y, Wang J,
Jiang L, Li S, Hu X and Wang Q: Upregulation of GRP78 and GRP94 and
its function in chemotherapy resistance to VP-16 in human lung
cancer cell line SK-MES-1. Cancer Invest. 27:453–458. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kern J, Untergasser G, Zenzmaier C, Sarg
B, Gastl G, Gunsilius E and Steurer M: GRP-78 secreted by tumor
cells blocks the antiangiogenic activity of bortezomib. Blood.
114:3960–3967. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang J, Yin Y, Hua H, Li M, Luo T, Xu L,
Wang R, Liu D, Zhang Y and Jiang Y: Blockade of GRP78 sensitizes
breast cancer cells to microtubules-interfering agents that induce
the unfolded protein response. J Cell Mol Med. 13((9B)): 3888–3897.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Morrison DK: The 14-3-3 proteins:
Integrators of diverse signaling cues that impact cell fate and
cancer development. Trends Cell Biol. 19:16–23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lee JA, Park JE, Lee DH, Park SG, Myung
PK, Park BC and Cho S: G1 to S phase transition protein 1 induces
apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 activation by dissociating
14-3-3 from ASK1. Oncogene. 27:1297–1305. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dong S, Kang S, Gu TL, Kardar S, Fu H,
Lonial S, Khoury HJ, Khuri F and Chen J: 14-3-3 integrates
prosurvival signals mediated by the AKT and MAPK pathways in
ZNF198-FGFR1-transformed hematopoietic cells. Blood. 110:360–369.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Obsilová V, Silhan J, Boura E, Teisinger J
and Obsil T: 14-3-3 proteins: A family of versatile molecular
regulators. Physiol Res. 57 (Suppl 3):S11–S21. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Masters SC, Subramanian RR, Truong A, Yang
H, Fujii K, Zhang H and Fu H: Survival-promoting functions of
14-3-3 proteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 30:360–365. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ralhan R, Desouza LV, Matta A, Tripathi
SC, Ghanny S, Datta Gupta S, Bahadur S and Siu KW: Discovery and
verification of head-and-neck cancer biomarkers by differential
protein expression analysis using iTRAQ labeling, multidimensional
liquid chromatography, and tandem mass spectrometry. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 7:1162–1173. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ralhan R, Desouza LV, Matta A, Tripathi
SC, Ghanny S, Dattagupta S, Thakar A, Chauhan SS and Siu K:
WiTRAQ-multidimensional liquid chromatography and tandem mass
spectrometry-based identification of potential biomarkers of oral
epithelial dysplasia and novel networks between inflammation and
premalignancy. J Proteome Res. 8:300–309. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Arora S, Matta A, Shukla NK, Deo SV and
Ralhan R: Identification of differentially expressed genes in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 42:97–108. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sharma R, Samantaray S, Shukla NK and
Ralhan R: Transcriptional gene expression profile of human
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Genomics. 81:481–488. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Fan T, Li R, Todd NW, Qiu Q, Fang HB, Wang
H, Shen J, Zhao RY, Caraway NP, Katz RL, et al: Up-regulation of
14-3-3zeta in lung cancer and its implication as prognostic and
therapeutic target. Cancer Res. 67:7901–7906. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Neal CL, Yao J, Yang W, Zhou X, Nguyen NT,
Lu J, Danes CG, Guo H, Lan KH, Ensor J, et al: 14-3-3zeta
overexpression defines high risk for breast cancer recurrence and
promotes cancer cell survival. Cancer Res. 69:3425–3432. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yang X, Cao W, Zhang L, Zhang W, Zhang X
and Lin H: Targeting 14-3-3zeta in cancer therapy. Cancer Gene
Ther. 19:153–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yang X, Cao W, Zhou J, Zhang W, Zhang X,
Lin W, Fei Z, Lin H and Wang B: 14-3-3ζ positive expression is
associated with a poor prognosis in patients with glioblastoma.
Neurosurgery. 68:932–938, discussion 938. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Chatterjee D, Goldman M, Braastad CD,
Darnowski J, Wyche JH, Pantazis P and Goodglick L: Reduction of
9-nitrocamptothecin-triggered apoptosis in DU-145 human prostate
cancer cells by ectopic expression of 14-3-3zeta. Int J Oncol.
25:503–509. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Shen J, Person MD, Zhu J, Abbruzzese JL
and Li D: Protein expression profiles in pancreatic adenocarcinoma
compared with normal pancreatic tissue and tissue affected by
pancreatitis as detected by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and
mass spectrometry. Cancer Res. 64:9018–9026. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Jang JS, Cho HY, Lee YJ, Ha WS and Kim HW:
The differential proteome profile of stomach cancer: Identification
of the biomarker candidates. Oncol Res. 14:491–499. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Coelho DS and Domingos PM: Physiological
roles of regulated Ire1 dependent decay. Front Genet. 5:762014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A, Zhang Y,
Chung P, Harding HP and Ron D: Coupling of stress in the ER to
activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase
IRE1. Science. 287:664–666. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Nishitoh H, Matsuzawa A, Tobiume K,
Saegusa K, Takeda K, Inoue K, Hori S, Kakizuka A and Ichijo H: ASK1
is essential for endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal cell
death triggered by expanded polyglutamine repeats. Genes Dev.
16:1345–1355. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhang L, Chen J and Fu H: Suppression of
apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1-induced cell death by 14-3-3
proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:8511–8515. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Goldman EH, Chen L and Fu H: Activation of
apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 by reactive oxygen species
through dephosphorylation at serine 967 and 14-3-3 dissociation. J
Biol Chem. 279:10442–10449. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Brennan GP, Jimenez-Mateos EM, McKiernan
RC, Engel T, Tzivion G and Henshall DC: Transgenic overexpression
of 14-3-3 zeta protects hippocampus against endoplasmic reticulum
stress and status epilepticus in vivo. PLoS One. 8:e544912013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Brobey RK, Dheghani M, Foster PP, Kuro-O M
and Rosenblatt KP: Klotho regulates 14-3-3ζ monomerization and
binding to the ASK1 signaling complex in response to oxidative
stress. PLoS One. 10:e01419682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yde CW and Issinger OG: Enhancing
cisplatin sensitivity in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by
down-regulation of Bcl-2 and cyclin D1. Int J Oncol. 29:1397–1404.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lauritzen G, Jensen MB, Boedtkjer E,
Dybboe R, Aalkjaer C, Nylandsted J and Pedersen SF:
Cisplatin-induced cell death in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: Roles of
ΔNErbB2 and pH regulatory ion transporters NHE1 and NBCn1. Exp Cell
Res. 316:2538–2553. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Jiang Y, Ji F, Liu Y, He M, Zhang Z, Yang
J, Wang N, Zhong C, Jin Q, Ye X, et al: Cisplatin-induced autophagy
protects breast cancer cells from apoptosis by regulating
yes-associated protein. Oncol Rep. 38:3668–3676. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Al-Taweel N, Varghese E, Florea AM and
Büsselberg D: Cisplatin (CDDP) triggers cell death of MCF-7 cells
following disruption of intracellular calcium
([Ca(2+)]i) homeostasis. J Toxicol Sci.
39:765–774. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Lee AS: GRP78 induction in cancer:
Therapeutic and prognostic implications. Cancer Res. 67:3496–3499.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wang M, Wey S, Zhang Y, Ye R and Lee AS:
Role of the unfolded protein response regulator GRP78/BiP in
development, cancer, and neurological disorders. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 11:2307–2316. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Li J, Ni M, Lee B, Barron E, Hinton DR and
Lee AS: The unfolded protein response regulator GRP78/BiP is
required for endoplasmic reticulum integrity and stress-induced
autophagy in mammalian cells. Cell Death Differ. 15:1460–1471.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−ΔΔ C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW and Dempfle L:
Relative expression software tool (REST©) for group-wise
comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results
in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:e362002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A,
Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork
P, et al: STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with
increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide
experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 47(D1): D607–D613. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Bruno S and Darzynkiewicz Z: Cell cycle
dependent expression and stability of the nuclear protein detected
by Ki-67 antibody in HL-60 cells. Cell Prolif. 25:31–40. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
He Y, Liu Z, Qiao C, Xu M, Yu J and Li G:
Expression and significance of Wnt signaling components and their
target genes in breast carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 9:137–143. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Sherr CJ: Cancer cell cycles. Science.
274:1672–1677. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Xiong Y, Hannon GJ, Zhang H, Casso D,
Kobayashi R and Beach D: p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin
kinases. Nature. 366:701–704. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Lukyanova NY, Rusetskya NV, Tregubova NA
and Chekhun VF: Molecular profile and cell cycle in MCF-7 cells
resistant to cisplatin and doxorubicin. Exp Oncol. 31:87–91.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Salvesen GS and Abrams JM: Caspase
activation - stepping on the gas or releasing the brakes? Lessons
from humans and flies. Oncogene. 23:2774–2784. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Castri P, Lee YJ, Ponzio T, Maric D, Spatz
M, Bembry J and Hallenbeck J: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and its
cleavage products differentially modulate cellular protection
through NF-kappaB-dependent signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1843:640–651. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Lin JF, Lin YC, Tsai TF, Chen HE, Chou KY
and Hwang TIS: Cisplatin induces protective autophagy through
activation of BECN1 in human bladder cancer cells. Drug Des Devel
Ther. 2017.1517-1533.2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Pozuelo-Rubio M: Regulation of autophagic
activity by 14-3-3ζ proteins associated with class III
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase. Cell Death Differ. 18:479–492. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Lee AS: The glucose-regulated proteins:
stress induction and clinical applications. Trends Biochem Sci.
26:504–10. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Hendershot LM: The ER function BiP is a
master regulator of ER function. Mt Sinai J Med. 71:289–297.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Ye X, Zhou Xu and Zhang H: Exploring the
role of autophagy-related gene 5 (ATG5) yields important insights
into autophagy in autoimmune/autoinflammatory. Front Immunol.
9:2332018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhu Y, Zhao L, Liu L, Gao P, Tian W, Wang
X, Jin H, Xu H and Chen Q: Beclin 1 cleavage by caspase-3
inactivates autophagy and promotes apoptosis. Protein Cell.
1:468–477. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Lee AS, Brandhorst S, Rangel DF, Navarrete
G, Cohen P, Longo VD, Chen J, Groshen S, Morgan TE and Dubeau L:
Effects of prolonged GRP78 haploinsufficiency on organ homeostasis,
behavior, cancer and chemo-toxic resistance in aged mice. Sci Rep.
7:409192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Suh DH, Kim MK, Kim HS, Chung HH and Song
YS: Unfolded protein response to autophagy as a promising druggable
target for anticancer therapy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1271:20–32. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Tallóczy Z, Jiang W, Virgin HW IV, Leib
DA, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ, Eskelinen EL and Levine B: Regulation
of starvation- and virus-induced autophagy by the eIF2α kinase
signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:190–195. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Kouroku Y, Fujita E, Tanida I, Ueno T,
Isoai A, Kumagai H, Ogawa S, Kaufman RJ, Kominami E and Momoi T: ER
stress (PERK/eIF2alpha phosphorylation) mediates the
polyglutamine-induced LC3 conversion, an essential step for
autophagy formation. Cell Death Differ. 14:230–239. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Ogata M, Hino S, Saito A, Morikawa K,
Kondo S, Kanemoto S, Murakami T, Taniguchi M, Tanii I, Yoshinaga K,
et al: Autophagy is activated for cell survival after endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Mol Cell Biol. 26:9220–9231. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Funderburk SF, Wang QJ and Yue Z: The
Beclin 1-VPS34 complex--at the crossroads of autophagy and beyond.
Trends Cell Biol. 20:355–362. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Zhang L, Wang H, Ding K and Xu J: FTY720
induces autophagy related apoptosis and necroptosis in human
glioblastoma cells. Toxicol Lett. 236:432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Wirawan E, Vande Walle L, Kersse K,
Cornelis S, Claerhout S, Vanoverberghe I, Roelandt R, De Rycke R,
Verspurten J, Declercq W, et al: Caspase-mediated cleavage of
Beclin-1 inactivates Beclin-1-induced autophagy and enhances
apoptosis by promoting the release of proapoptotic factors from
mitochondria. Cell Death Dis. 1:e182010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Neumeister P, Pixley FJ, Xiong Y, Xie H,
Wu K, Ashton A, Cammer M, Chan A, Symons M, Stanley ER, et al:
Cyclin D1 governs adhesion and motility of macrophages. Mol Biol
Cell. 14:2005–2015. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Holnthoner W, Pillinger M, Groger M, Wolff
K, Ashton AW, Albanese C, Neumeister P, Pestell RG and Petzelbauer
P: Fibroblast growth factor-2 induces Lef/Tcf-dependent
transcription in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem.
277:45847–45853. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Barrios CH, Sampaio C, Vinholes J and
Caponero R: What is the role of chemotherapy in estrogen
receptor-positive, advanced breast cancer? Ann Oncol. 20:1157–1162.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Alqahtani A, Ayesh HSK and Halawani H:
PIK3CA gene mutations in solid malignancies: Association with
clinicopathological parameters and prognosis. Cancers (Basel).
12:932019. View Article : Google Scholar
|