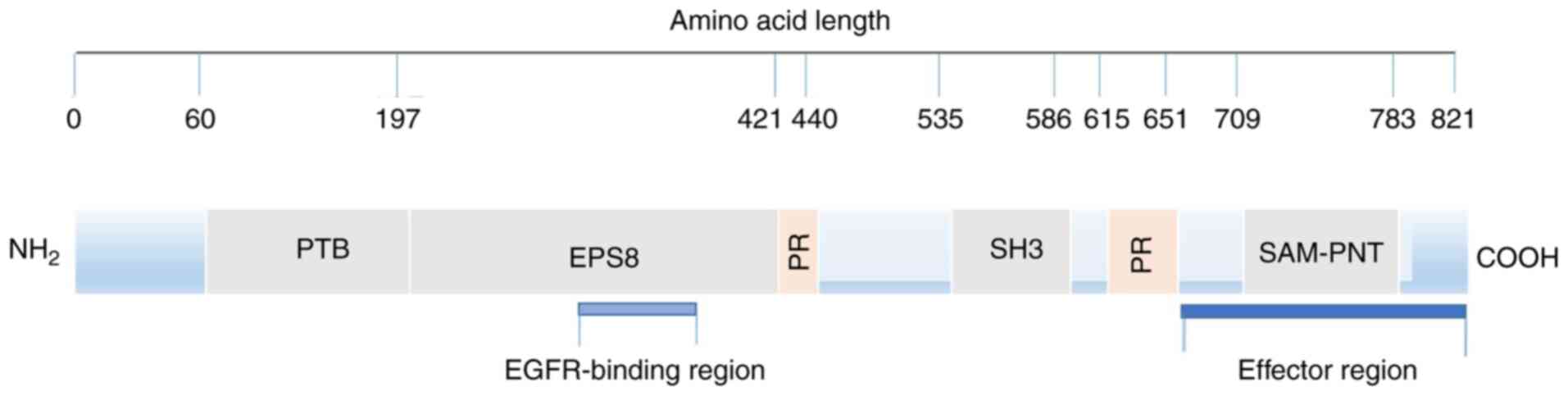
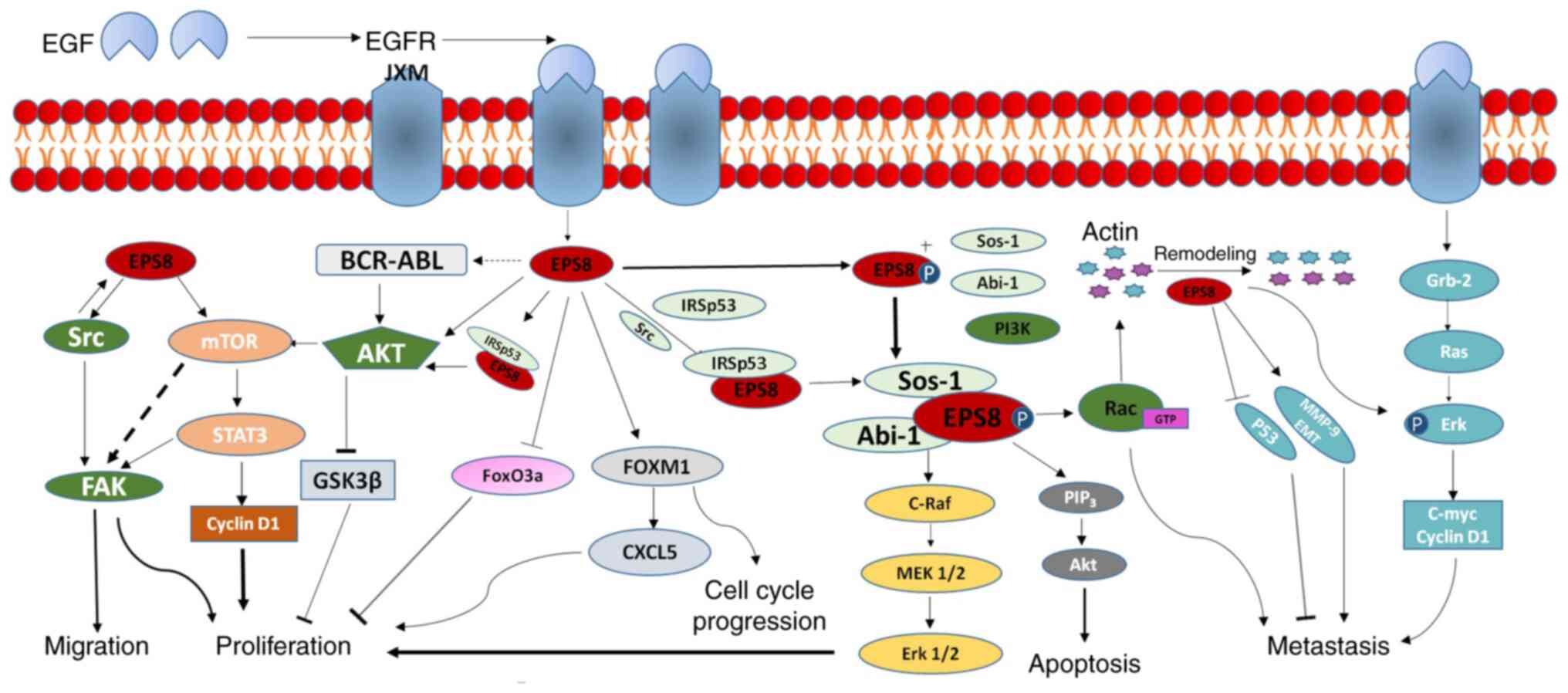
|
1
|
Correction: Mitochondrial sirtuins in
cancer: Emerging roles and therapeutic potential. Cancer Res.
76:36552016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fazioli F, Minichiello L, Matoska V,
Castagnino P, Miki T, Wong WT and Di Fiore PP: Eps8, a substrate
for the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase, enhances
EGF-dependent mitogenic signals. EMBO J. 12:3799–3808. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wong WT, Carlomagno F, Druck T, Barletta
C, Croce CM, Huebner K, Kraus MH and Di Fiore PP: Evolutionary
conservation of the EPS8 gene and its mapping to human chromosome
12q23-q24. Oncogene. 9:3057–3061. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tocchetti A, Confalonieri S, Scita G, Di
Fiore PP and Betsholtz C: In silico analysis of the EPS8 gene
family: Genomic organization, expression profile, and protein
structure. Genomics. 81:234–244. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Di Fiore PP and Scita G: Eps8 in the midst
of GTPases. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 34:1178–1183. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Offenhäuser N, Borgonovo A, Disanza A,
Romano P, Ponzanelli I, Iannolo G, Di Fiore PP and Scita G: The
eps8 family of proteins links growth factor stimulation to actin
reorganization generating functional redundancy in the Ras/Rac
pathway. Mol Biol Cell. 15:91–98. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maa MC, Hsieh CY and Leu TH:
Overexpression of p97Eps8 leads to cellular transformation:
Implication of pleckstrin homology domain in p97Eps8-mediated ERK
activation. Oncogene. 20:106–112. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Avantaggiato V, Torino A, Wong WT, Di
Fiore PP and Simeone A: Expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase
substrate genes eps8 and eps15 during mouse development. Oncogene.
11:1191–1198. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ion A, Crosby AH, Kremer H, Kenmochi N,
Van Reen M, Fenske C, Van Der Burgt I, Brunner HG, Montgomery K,
Kucherlapati RS, et al: Detailed mapping, mutation analysis, and
intragenic polymorphism identification in candidate Noonan syndrome
genes MYL2, DCN, EPS8, and RPL6. J Med Genet. 37:884–886. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang Y, Prasad M, Lemon WJ, Hampel H,
Wright FA, Kornacker K, LiVolsi V, Frankel W, Kloos RT, Eng C, et
al: Gene expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma reveals highly
consistent profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:15044–15049. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang W, Wyckoff JB, Frohlich VC, Oleynikov
Y, Hüttelmaier S, Zavadil J, Cermak L, Bottinger EP, Singer RH,
White JG, et al: Single cell behavior in metastatic primary mammary
tumors correlated with gene expression patterns revealed by
molecular profiling. Cancer Res. 62:6278–6288. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maa MC, Lee JC, Chen YJ, Chen YJ, Lee YC,
Wang ST, Huang CC, Chow NH and Leu TH: Eps8 facilitates cellular
growth and motility of colon cancer cells by increasing the
expression and activity of focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem.
282:19399–19409. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Welsch T, Endlich K, Giese T, Büchler MW
and Schmidt J: Eps8 is increased in pancreatic cancer and required
for dynamic actin-based cell protrusions and intercellular
cytoskeletal organization. Cancer Lett. 255:205–218. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen YJ, Shen MR, Chen YJ, Maa MC and Leu
TH: Eps8 decreases chemosensitivity and affects survival of
cervical cancer patients. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:1376–1385. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yap LF, Jenei V, Robinson CM, Moutasim K,
Benn TM, Threadgold SP, Lopes V, Wei W, Thomas GJ and Paterson IC:
Upregulation of Eps8 in oral squamous cell carcinoma promotes cell
migration and invasion through integrin-dependent Rac1 activation.
Oncogene. 28:2524–2534. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu M, Shorts-Cary L, Knox AJ,
Kleinsmidt-DeMasters B, Lillehei K and Wierman ME: Epidermal growth
factor receptor pathway substrate 8 is overexpressed in human
pituitary tumors: Role in proliferation and survival.
Endocrinology. 150:2064–2671. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bashir M, Kirmani D, Bhat HF, Baba RA,
Hamza R, Naqash S, Wani NA, Andrabi KI, Zargar MA and Khanday FA:
P66shc and its downstream Eps8 and Rac1 proteins are upregulated in
esophageal cancers. Cell Commun Signal. 8:132010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen H, Wu X, Pan ZK and Huang S:
Integrity of SOS1/EPS8/ABI1 tri-complex determines ovarian cancer
metastasis. Cancer Res. 70:9979–9990. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chu PY, Liou JH, Lin YM, Chen CJ, Chen MK,
Lin SH, Yeh CM, Wang HK, Maa MC, Leu TH, et al: Expression of Eps8
correlates with poor survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Asia
Pac J Clin Oncol. 8:e77–e81. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen C, Liang Z, Huang W, Li X, Zhou F, Hu
X, Han M, Ding X and Xiang S: Eps8 regulates cellular proliferation
and migration of breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 46:205–214. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wen Q, Jiao X, Kuang F, Hou B, Zhu Y, Guo
W, Sun G, Ba Y, Yu D, Wang D, et al: FoxO3a inhibiting expression
of EPS8 to prevent progression of NSCLC: A new negative loop of
EGFR signaling. EBioMedicine. 40:198–209. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang G, Lu YB and Guan QL: EPS8 is
a potential oncogene in glioblastoma. Onco Targets Ther.
12:10523–10534. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fukuhisa H, Seki N, Idichi T, Kurahara H,
Yamada Y, Toda H, Kita Y, Kawasaki Y, Tanoue K, Mataki Y, et al:
Gene regulation by antitumor miR-130b-5p in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma: The clinical significance of oncogenic EPS8. J Hum
Genet. 64:521–534. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He YZ, Liang Z, Wu MR, Wen Q, Deng L, Song
CY, Wu BY, Tu SF, Huang R and Li YH: Overexpression of EPS8 is
associated with poor prognosis in patients with acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Leuk Res. 39:575–581. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang R, Liu H, Chen Y, He Y, Kang Q, Tu
S, He Y, Zhou X, Wang L, Yang J, et al: EPS8 regulates
proliferation, apoptosis and chemosensitivity in BCR-ABL positive
cells via the BCR-ABL/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Oncol Rep. 39:119–128.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen Y, Xie X, Wu A, Wang L, Hu Y, Zhang H
and Li Y: A synthetic cell-penetrating peptide derived from nuclear
localization signal of EPS8 exerts anticancer activity against
acute myeloid leukemia. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:122018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang H, Zhou L, Zhou W, Xie X, Wu M, Chen
Y, Hu Y, Du J, He Y and Li Y: EPS8-mediated regulation of multiple
myeloma cell growth and survival. Am J Cancer Res. 9:1622–1634.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Behlouli A, Bonnet C, Abdi S, Bouaita A,
Lelli A, Hardelin JP, Schietroma C, Rous Y, Louha M, Cheknane A, et
al: EPS8, encoding an actin-binding protein of cochlear hair cell
stereocilia, is a new causal gene for autosomal recessive profound
deafness. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 9:552014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Morton CJ, Pugh DJ, Brown EL, Kahmann JD,
Renzoni DA and Campbell ID: Solution structure and peptide binding
of the SH3 domain from human Fyn. Structure. 4:705–714. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Matoskova B, Wong WT, Salcini AE, Pelicci
PG and Di Fiore PP: Constitutive phosphorylation of eps8 in tumor
cell lines: Relevance to malignant transformation. Mol Cell Biol.
15:3805–3812. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shi X, Betzi S, Lugari A, Opi S, Restouin
A, Parrot I, Martinez J, Zimmermann P, Lecine P, Huang M, et al:
Structural recognition mechanisms between human Src homology domain
3 (SH3) and ALG-2-interacting protein X (Alix). FEBS Lett.
586:1759–1764. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Scita G, Nordstrom J, Carbone R, Tenca P,
Giardina G, Gutkind S, Bjarnegård M, Betsholtz C and Di Fiore PP:
EPS8 and E3B1 transduce signals from Ras to Rac. Nature.
401:290–293. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lanzetti L, Rybin V, Malabarba MG,
Christoforidis S, Scita G, Zerial M and Di Fiore PP: The Eps8
protein coordinates EGF receptor signalling through Rac and
trafficking through Rab5. Nature. 408:374–377. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kishan KV, Newcomer ME, Rhodes TH and
Guilliot SD: Effect of pH and salt bridges on structural assembly:
Molecular structures of the monomer and intertwined dimer of the
Eps8 SH3 domain. Protein Sci. 10:1046–1055. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Inobe M, Ki K, Miyagoe Y, Yi N and Takeda
S: Identification of EPS8 as a Dvl1-associated molecule. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 266:216–221. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Funato Y, Terabayashi T, Suenaga N, Seiki
M, Takenawa T and Miki H: IRSp53/Eps8 complex is important for
positive regulation of Rac and cancer cell motility/invasiveness.
Cancer Res. 64:5237–5244. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Disanza A, Mantoani S, Hertzog M, Gerboth
S, Frittoli E, Steffen A, Berhoerster K, Kreienkamp HJ, Milanesi F,
Di Fiore PP, et al: Regulation of cell shape by Cdc42 is mediated
by the synergic actin-bundling activity of the Eps8-IRSp53 complex.
Nat Cell Biol. 8:1337–1347. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Prieto-Echagüe V, Chan PM, Craddock BP,
Manser E and Miller WT: PTB domain-directed substrate targeting in
a tyrosine kinase from the unicellular choanoflagellate Monosiga
brevicollis. PLoS One. 6:e192962011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Forman-Kay JD and Pawson T: Diversity in
protein recognition by PTB domains. Curr Opin Struct Biol.
9:690–695. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Slupsky CM, Gentile LN, Donaldson LW,
Mackereth CD, Seidel JJ, Graves BJ and McIntosh LP: Structure of
the Ets-1 pointed domain and mitogen-activated protein kinase
phosphorylation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:12129–12134. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Castagnino P, Biesova Z, Wong WT, Fazioli
F, Gill GN and Di Fiore PP: Direct binding of eps8 to the
juxtamembrane domain of EGFR is phosphotyrosine- and
SH2-independent. Oncogene. 10:723–729. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Disanza A, Carlier MF, Stradal TE, Didry
D, Frittoli E, Confalonieri S, Croce A, Wehland J, Di Fiore PP and
Scita G: Eps8 controls actin-based motility by capping the barbed
ends of actin filaments. Nat Cell Biol. 6:1180–1188. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Scita G, Tenca P, Areces LB, Tocchetti A,
Frittoli E, Giardina G, Ponzanelli I, Sini P, Innocenti M and Di
Fiore PP: An effector region in Eps8 is responsible for the
activation of the Rac-specific GEF activity of Sos-1 and for the
proper localization of the Rac-based actin-polymerizing machine. J
Cell Biol. 154:1031–1044. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kirkland G, Paizis K, Wu LL, Katerelos M
and Power DA: Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor mRNA is
upregulated in the peri-infarct region of the remnant kidney model:
In vitro evidence suggests a regulatory role in myofibroblast
transformation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 9:1464–1473. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Miao H, Wei BR, Peehl DM, Li Q, Alexandrou
T, Schelling JR, Rhim JS, Sedor JR, Burnett E and Wang B:
Activation of EphA receptor tyrosine kinase inhibits the Ras/MAPK
pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 3:527–530. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Carpenter G and Cohen S: Epidermal growth
factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 48:193–216. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Buday L and Downward J: Epidermal growth
factor regulates p21ras through the formation of a complex of
receptor, Grb2 adapter protein, and Sos nucleotide exchange factor.
Cell. 73:611–620. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ozanne B, Richards CS, Hendler F, Burns D
and Gusterson B: Over-expression of the EGF receptor is a hallmark
of squamous cell carcinomas. J Pathol. 149:9–14. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rubin Grandis J, Zeng Q and Drenning SD:
Epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated stat3 signaling blocks
apoptosis in head and neck cancer. Laryngoscope. 110:868–874. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Song JI and Grandis JR: STAT signaling in
head and neck cancer. Oncogene. 19:2489–2895. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Grandis JR, Drenning SD, Chakraborty A,
Zhou MY, Zeng Q, Pitt AS and Tweardy DJ: Requirement of Stat3 but
not Stat1 activation for epidermal growth factor receptor- mediated
cell growth In vitro. J Clin Invest. 102:1385–1392. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Minden A, Lin A, McMahon M, Lange-Carter
C, Dérijard B, Davis RJ, Johnson GL and Karin M: Differential
activation of ERK and JNK mitogen-activated protein kinases by
Raf-1 and MEKK. Science. 266:1719–1723. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lin A, Minden A, Martinetto H, Claret FX,
Lange-Carter C, Mercurio F, Johnson GL and Karin M: Identification
of a dual specificity kinase that activates the Jun kinases and
p38-Mpk2. Science. 268:286–290. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Minden A, Lin A, Claret FX, Abo A and
Karin M: Selective activation of the JNK signaling cascade and
c-Jun transcriptional activity by the small GTPases Rac and
Cdc42Hs. Cell. 81:1147–1157. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Schaller MD, Borgman CA and Parsons JT:
Autonomous expression of a noncatalytic domain of the focal
adhesion-associated protein tyrosine kinase pp125FAK. Mol Cell
Biol. 13:785–791. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hanks SK, Calalb MB, Harper MC and Patel
SK: Focal adhesion protein-tyrosine kinase phosphorylated in
response to cell attachment to fibronectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
89:8487–8491. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Parsons JT: Focal adhesion kinase: The
first ten years. J Cell Sci. 116:1409–1416. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hanks SK, Ryzhova L, Shin NY and Brábek J:
Focal adhesion kinase signaling activities and their implications
in the control of cell survival and motility. Front Biosci.
8:d982–d996. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yu CL, Meyer DJ, Campbell GS, Larner AC,
Carter-Su C, Schwartz J and Jove R: Enhanced DNA-binding activity
of a Stat3-related protein in cells transformed by the Src
oncoprotein. Science. 269:81–83. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bromberg JF, Horvath CM, Besser D, Lathem
WW and Darnell JE Jr: Stat3 activation is required for cellular
transformation by v-src. Mol Cell Biol. 18:2553–2558. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Turkson J, Bowman T, Garcia R, Caldenhoven
E, De Groot RP and Jove R: Stat3 activation by Src induces specific
gene regulation and is required for cell transformation. Mol Cell
Biol. 18:2545–2552. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Leu TH, Yeh HH, Huang CC, Chuang YC, Su SL
and Maa MC: Participation of p97Eps8 in Src-mediated
transformation. J Biol Chem. 279:9875–9881. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Maa MC, Lai JR, Lin RW and Leu TH:
Enhancement of tyrosyl phosphorylation and protein expression of
eps8 by v-Src. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1450:341–351. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sachdev S, Bu Y and Gelman IH:
Paxillin-Y118 phosphorylation contributes to the control of
Src-induced anchorage-independent growth by FAK and adhesion. BMC
Cancer. 9:122009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ma RY, Tong TH, Cheung AM, Tsang AC, Leung
WY and Yao KM: Raf/MEK/MAPK signaling stimulates the nuclear
translocation and transactivating activity of FOXM1c. J Cell Sci.
118:795–806. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Koo CY, Muir KW and Lam EW: FOXM1: From
cancer initiation to progression and treatment. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1819:28–37. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Laoukili J, Kooistra MR, Brás A, Kauw J,
Kerkhoven RM, Morrison A, Clevers H and Medema RH: FoxM1 is
required for execution of the mitotic programme and chromosome
stability. Nat Cell Biol. 7:126–136. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Costa RH: FoxM1 dances with mitosis. Nat
Cell Biol. 7:108–110. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kwok CT, Leung MH, Qin J, Qin Y, Wang J,
Lee YL and Yao KM: The Forkhead box transcription factor FOXM1 is
required for the maintenance of cell proliferation and protection
against oxidative stress in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell
Res. 16:651–661. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wang H, The MT, Ji Y, Patel V,
Firouzabadian S, Patel AA, Gutkind JS and Yeudall WA: EPS8
upregulates FOXM1 expression, enhancing cell growth and motility.
Carcinogenesis. 31:1132–1141. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ngan AWL, Grace Tsui M, So DHF, Leung WY,
Chan DW and Yao KM: Novel nuclear partnering role of EPS8 with
FOXM1 in regulating cell proliferation. Front Oncol. 9:1542019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Innocenti M, Frittoli E, Ponzanelli I,
Falck JR, Brachmann SM, Di Fiore PP and Scita G: Phosphoinositide
3-kinase activates Rac by entering in a complex with Eps8, Abi1,
and Sos-1. J Cell Biol. 160:17–23. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Chiu CF, Chang YW, Kuo KT, Shen YS, Liu
CY, Yu YH, Cheng CC, Lee KY, Chen FC, Hsu MK, et al: NF-κB-driven
suppression of FOXO3a contributes to EGFR mutation-independent
gefitinib resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:E2526–E2535.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Accili D and Arden KC: FoxOs at the
crossroads of cellular metabolism, differentiation, and
transformation. Cell. 117:421–426. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hall A: Rho GTPases and the actin
cytoskeleton. Science. 279:509–514. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Nobes CD and Hall A: Rho, rac, and cdc42
GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes
associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia.
Cell. 81:53–62. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hall A and Nobes CD: Rho GTPases:
Molecular switches that control the organization and dynamics of
the actin cytoskeleton. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.
355:965–970. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Bian D, Su S, Mahanivong C, Cheng RK, Han
Q, Pan ZK, Sun P and Huang S: Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates
ovarian cancer cell migration via a ras-MEK kinase 1 pathway.
Cancer Res. 64:4209–4217. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lambert JM, Lambert QT, Reuther GW,
Malliri A, Siderovski DP, Sondek J, Collard JG and Der CJ: Tiam1
mediates Ras activation of Rac by a PI(3)K-independent mechanism.
Nat Cell Biol. 4:621–625. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Shin EY, Shin KS, Lee CS, Woo KN, Quan SH,
Soung NK, Kim YG, Cha CI, Kim SR, Park D, et al: Phosphorylation of
p85 beta PIX, a Rac/Cdc42-specific guanine nucleotide exchange
factor, via the Ras/ERK/PAK2 pathway is required for basic
fibroblast growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth. J Biol Chem.
277:44417–44430. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Nimnual AS, Yatsula BA and Bar-Sagi D:
Coupling of Ras and Rac guanosine triphosphatases through the Ras
exchanger Sos. Science. 279:560–563. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Tod J, Hanley CJ, Morgan MR, Rucka M,
Mellows T, Lopez MA, Kiely P, Moutasim KA, Frampton SJ, Sabnis D,
et al: Pro-migratory and TGF-β-activating functions of αvβ6
integrin in pancreatic cancer are differentially regulated via an
Eps8-dependent GTPase switch. J Pathol. 243:37–50. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Nasri E, Wiesen LB, Knapik JA and
Fredenburg KM: Eps8 expression is significantly lower in p16+ head
and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs) compared with p16-
HNSCCs. Hum Pathol. 72:45–51. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Cattaneo MG, Cappellini E and Vicentini
LM: Silencing of Eps8 blocks migration and invasion in human
glioblastoma cell lines. Exp Cell Res. 318:1901–1912. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Lengyel E: Ovarian cancer development and
metastasis. Am J Pathol. 177:1053–1064. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Jesionowska A, Cecerska-Heryc E, Matoszka
N and Dolegowska B: Lysophosphatidic acid signaling in ovarian
cancer. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 35:578–584. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Pua TL, Wang FQ and Fishman DA: Roles of
LPA in ovarian cancer development and progression. Future Oncol.
5:1659–1673. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Fang X, Schummer M, Mao M, Yu S, Tabassam
FH, Swaby R, Hasegawa Y, Tanyi JL, LaPushin R, Eder A, et al:
Lysophosphatidic acid is a bioactive mediator in ovarian cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1582:257–264. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Yu S, Murph MM, Lu Y, Liu S, Hall HS, Liu
J, Stephens C, Fang X and Mills GB: Lysophosphatidic acid receptors
determine tumorigenicity and aggressiveness of ovarian cancer
cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 100:1630–1642. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Wang P, Wu X, Chen W, Liu J and Wang X:
The lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptors their expression and
significance in epithelial ovarian neoplasms. Gynecol Oncol.
104:714–720. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Pierre S, Bats AS and Coumoul X:
Understanding SOS (Son of Sevenless). Biochem Pharmacol.
82:1049–1056. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Schmidt A and Hall A: Guanine nucleotide
exchange factors for Rho GTPases: turning on the switch. Genes Dev.
16:1587–1609. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Innocenti M, Tenca P, Frittoli E, Faretta
M, Tocchetti A, Di Fiore PP and Scita G: Mechanisms through which
Sos-1 coordinates the activation of Ras and Rac. J Cell Biol.
156:125–136. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Kotula L: Abi1, a critical molecule
coordinating actin cytoskeleton reorganization with PI-3 kinase and
growth signaling. FEBS Lett. 586:2790–2794. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Fan PD and Goff SP: Abl interactor 1 binds
to sos and inhibits epidermal growth factor- and v-Abl-induced
activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases. Mol Cell
Biol. 20:7591–7601. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Stone TA and Deber CM: Therapeutic design
of peptide modulators of protein-protein interactions in membranes.
Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 1859:577–585. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Cunningham AD, Qvit N and Mochly-Rosen D:
Peptides and peptidomimetics as regulators of protein-protein
interactions. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 44:59–66. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Helmer D and Schmitz K: Peptides and
peptide analogs to inhibit protein-protein interactions. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 917:147–183. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Fosgerau K and Hoffmann T: Peptide
therapeutics: Current status and future directions. Drug Discov
Today. 20:122–128. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Ellert-Miklaszewska A, Poleszak K and
Kaminska B: Short peptides interfering with signaling pathways as
new therapeutic tools for cancer treatment. Future Med Chem.
9:199–221. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Bae DG, Kim TD, Li G, Yoon WH and Chae CB:
Anti-flt1 peptide, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor
1-specific hexapeptide, inhibits tumor growth and metastasis. Clin
Cancer Res. 11:2651–2561. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Yu X, Liang C, Zhang Y, Zhang W and Chen
H: Inhibitory short peptides targeting EPS8/ABI1/SOS1 tri-complex
suppress invasion and metastasis of ovarian cancer cells. BMC
Cancer. 19:8782019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Raftopoulou M and Hall A: Cell migration:
Rho GTPases lead the way. Dev Biol. 265:23–32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Miki H, Yamaguchi H, Suetsugu S and
Takenawa T: IRSp53 is an essential intermediate between Rac and
WAVE in the regulation of membrane ruffling. Nature. 408:732–735.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Liu PS, Jong TH, Maa MC and Leu TH: The
interplay between Eps8 and IRSp53 contributes to Src-mediated
transformation. Oncogene. 29:3977–3989. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Wang H, Patel V, Miyazaki H, Gutkind JS
and Yeudall WA: Role for EPS8 in squamous carcinogenesis.
Carcinogenesis. 30:165–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
McCawley LJ, Li S, Wattenberg EV and
Hudson LG: Sustained activation of the mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathway. A mechanism underlying receptor tyrosine kinase
specificity for matrix metalloproteinase-9 induction and cell
migration. J Biol Chem. 274:4347–4353. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Liu WW, Meng J, Cui J and Luan YS:
Characterization and Function of MicroRNA*s in Plants. Front Plant
Sci. 8:22002017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Wu WK, Lee CW, Cho CH, Fan D, Wu K, Yu J
and Sung JJ: MicroRNA dysregulation in gastric cancer: A new player
enters the game. Oncogene. 29:5761–5771. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Yu M, Xue H, Wang Y, Shen Q, Jiang Q,
Zhang X, Li K, Jia M, Jia J, Xu J and Tian Y: miR-345 inhibits
tumor metastasis and EMT by targeting IRF1-mediated mTOR/STAT3/AKT
pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 50:975–983. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Ying X, Zhang W, Fang M, Zhang W, Wang C
and Han L: miR-345-5p regulates proliferation, cell cycle, and
apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells by targeting AKT2. J Cell
Biochem. 2018:(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
114
|
Feng A, Yuan X and Li X: MicroRNA-345
inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of
gastric cancer by targeting FOXQ1. Oncol Rep. 38:2752–2760. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zhang J, Wang C, Yan S, Yang Y, Zhang X
and Guo W: miR-345 inhibits migration and stem-like cell phenotype
in gastric cancer via inactivation of Rac1 by targeting EPS8. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 52:259–267. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Li Q, Zhang N, Jia Z, Le X, Dai B, Wei D,
Huang S, Tan D and Xie K: Critical role and regulation of
transcription factor FoxM1 in human gastric cancer angiogenesis and
progression. Cancer Res. 69:3501–3509. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Kedmi M, Ben-Chetrit N, Körner C, Mancini
M, Ben-Moshe NB, Lauriola M, Lavi S, Biagioni F, Carvalho S,
Cohen-Dvashi H, et al: EGF induces microRNAs that target
suppressors of cell migration: miR-15b targets MTSS1 in breast
cancer. Sci Signal. 8:ra292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Santo EE, Stroeken P, Sluis PV, Koster J,
Versteeg R and Westerhout EM: FOXO3a is a major target of
inactivation by PI3K/AKT signaling in aggressive neuroblastoma.
Cancer Res. 73:2189–2198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Gorsic LK, Stark AL, Wheeler HE, Wong SS,
Im HK and Dolan ME: EPS8 inhibition increases cisplatin sensitivity
in lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e822202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Smolensky D, Rathore K, Bourn J and
Cekanova M: Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT Pathway Sensitizes Oral
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells to Anthracycline-Based Chemotherapy
In Vitro. J Cell Biochem. 118:2615–2624. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Li F, Zhao X, Sun R, Ou J, Huang J, Yang
N, Xu T, Li J, He X, Li C, et al: EGFR-rich extracellular vesicles
derived from highly metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
accelerate tumour metastasis through PI3K/AKT pathway-suppressed
ROS. J Extracell Vesicles. 10:e120032020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Rotow J and Bivona TG: Understanding and
targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat Rev Cancer.
17:637–658. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Li H, Zeng J and Shen K: PI3K/AKT/mTOR
signaling pathway as a therapeutic target for ovarian cancer. Arch
Gynecol Obstet. 290:1067–1078. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Slomovitz BM and Coleman RL: The
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway as a therapeutic target in endometrial
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 18:5856–5864. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Mabuchi S, Kuroda H, Takahashi R and
Sasano T: The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway as a therapeutic target in
ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 137:173–179. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Narayanankutty A: PI3K/Akt/ mTOR Pathway
as a therapeutic target for colorectal cancer: A review of
preclinical and clinical evidence. Curr Drug Targets. 20:1217–1226.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Jiang X, Wang J, Deng X, Xiong F, Zhang S,
Gong Z, Li X, Cao K, Deng H, He Y, et al: The role of
microenvironment in tumor angiogenesis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
39:2042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Kirkwood JM, Butterfield LH, Tarhini AA,
Zarour H, Kalinski P and Ferrone S: Immunotherapy of cancer in
2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:309–335. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Novellino L, Castelli C and Parmiani G: A
listing of human tumor antigens recognized by T cells: March 2004
update. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 54:187–207. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Xie X, Zhou W, Hu Y, Chen Y, Zhang H and
Li Y: A dual-function epidermal growth factor receptor pathway
substrate 8 (Eps8)-derived peptide exhibits a potent cytotoxic T
lymphocyte-activating effect and a specific inhibitory activity.
Cell Death Dis. 9:3792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
He YJ, Zhou J, Zhao TF, Hu LS, Gan JY,
Deng L and Li Y: Eps8 vaccine exerts prophylactic antitumor effects
in a murine model: A novel vaccine for breast carcinoma. Mol Med
Rep. 8:662–668. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Wang L, Cai SH, Xiong WY, He YJ, Deng L
and Li YH: Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay
for detecting the eps8 gene in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Lab.
59:1261–1269. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Sun P, Zhou X, He Y, Liu H, Wang Y, Chen
Y, Li M, He Y, Li G and Li Y: Effect of trichostatin A on Burkitt's
lymphoma cells: Inhibition of EPS8 activity through Phospho-Erk1/2
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 497:990–996. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|