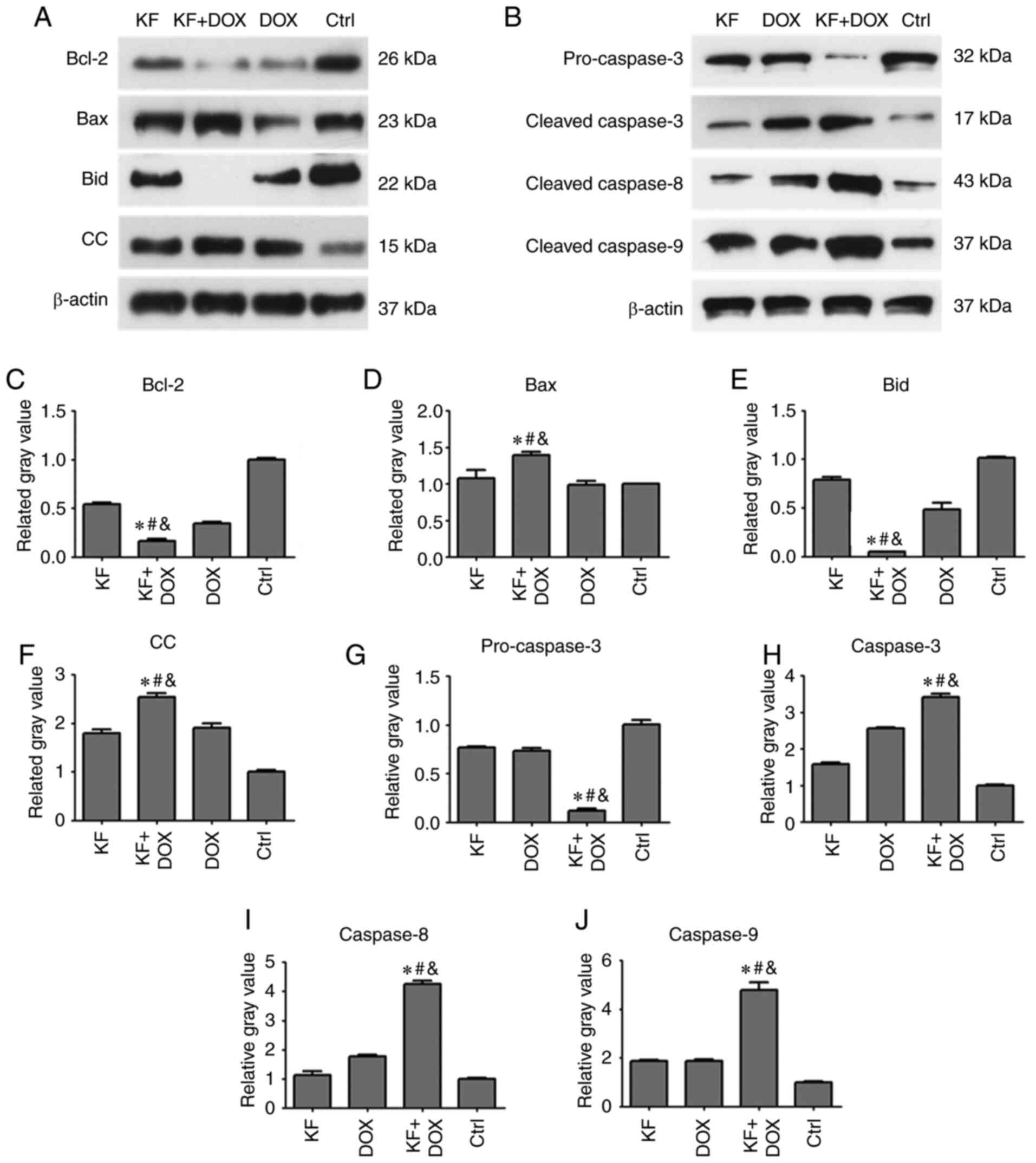
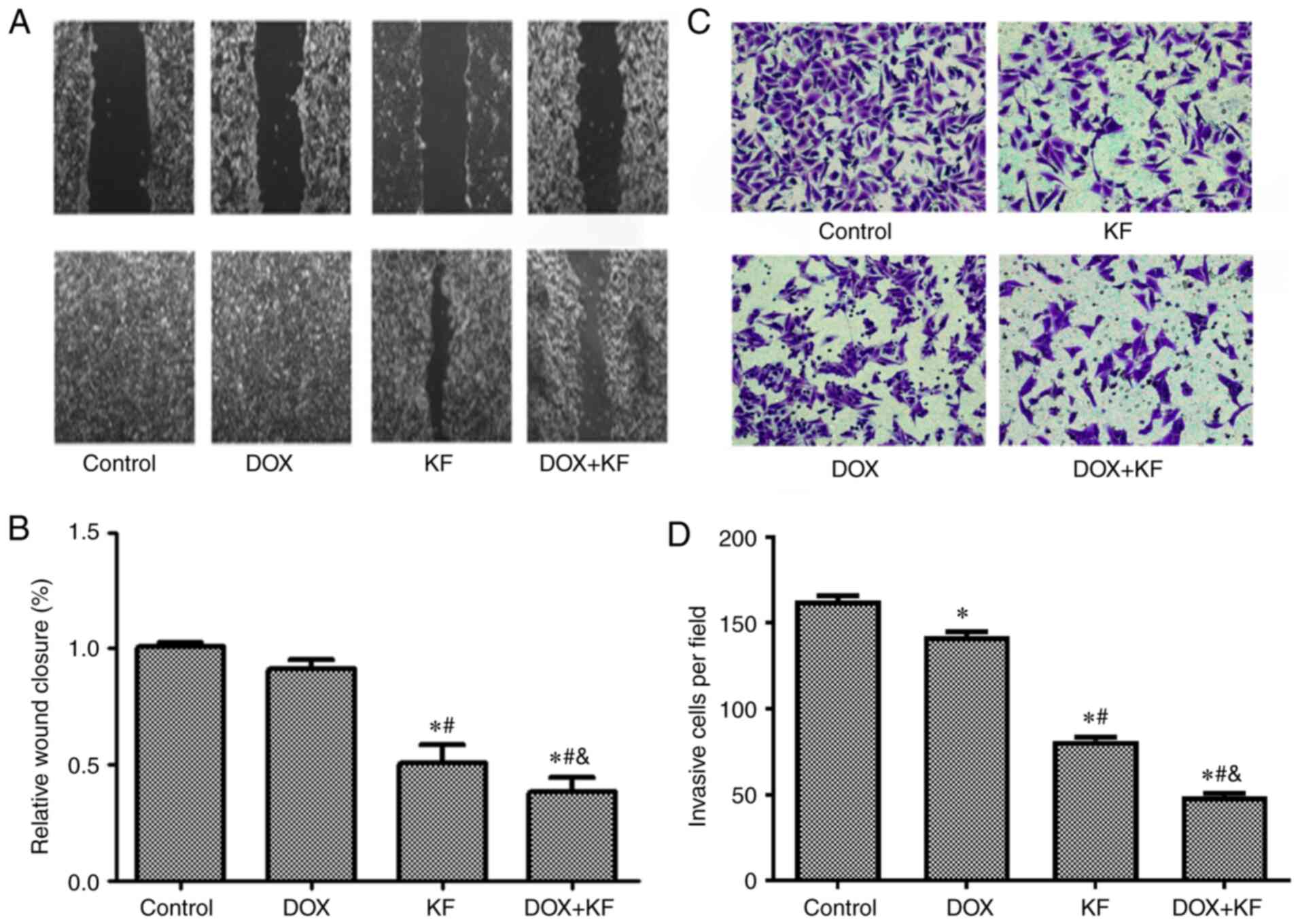
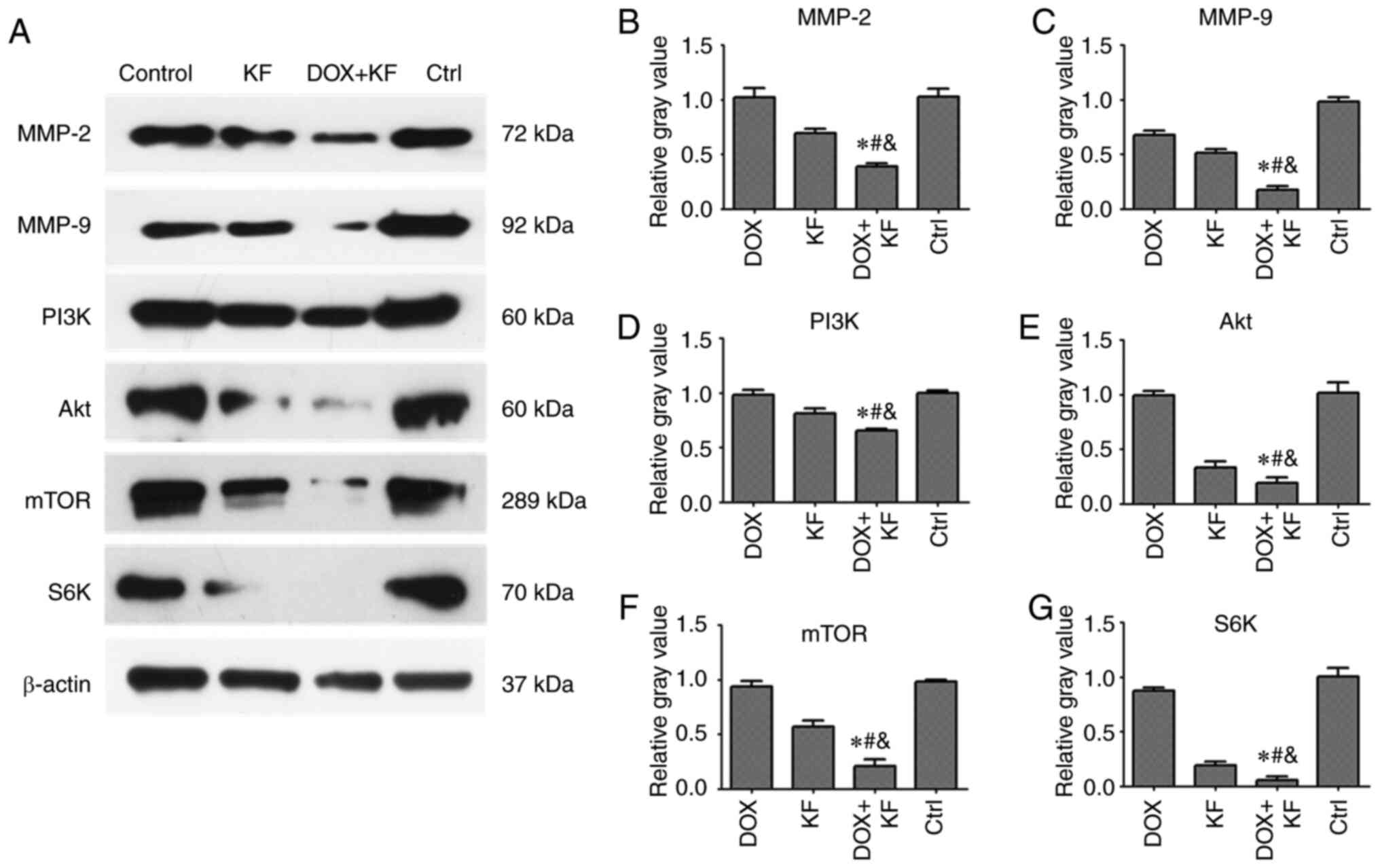
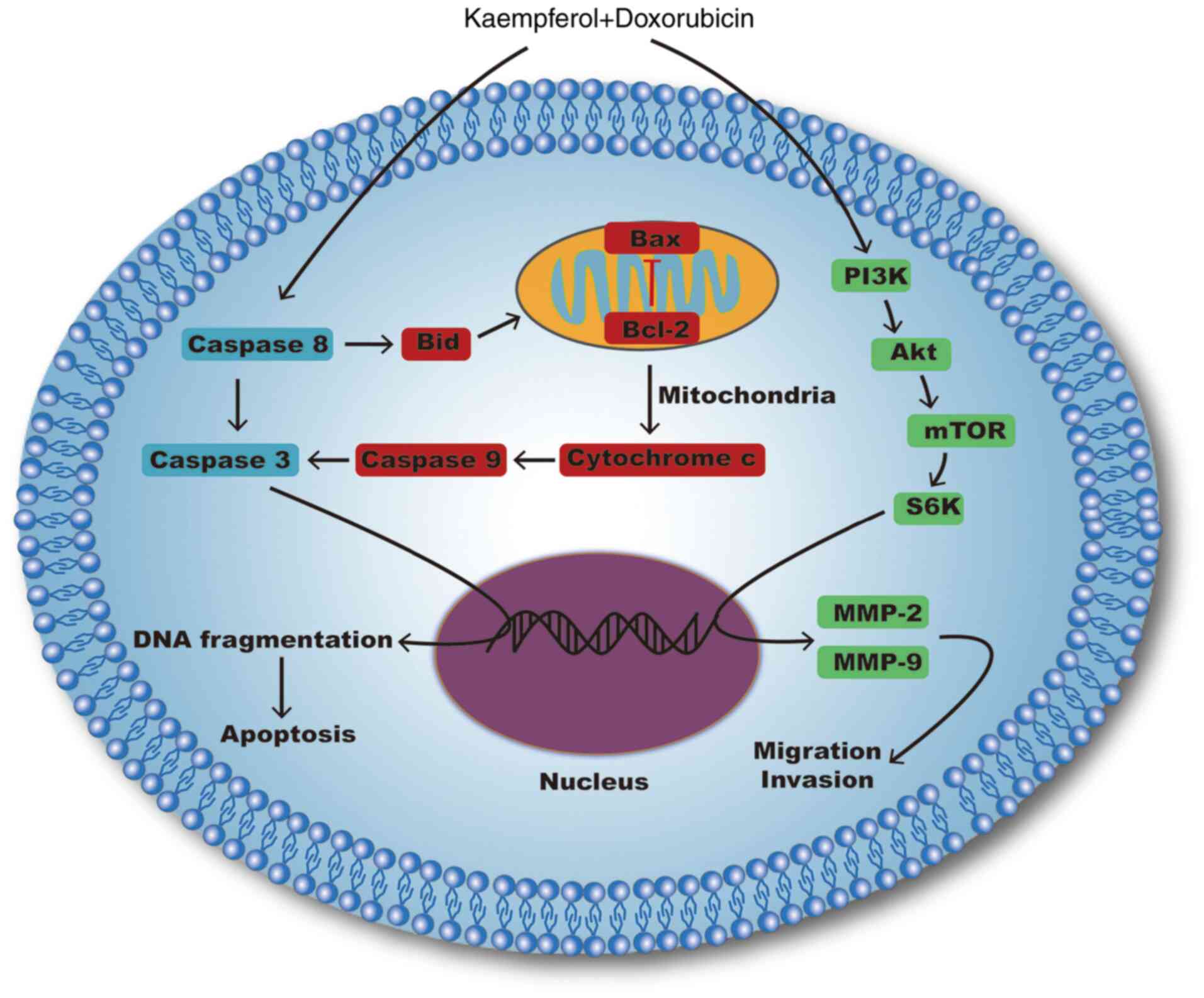
|
1
|
Forner A, Reig M and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 391:1301–1314. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Anwanwan D, Singh SK, Singh S, Saikam V
and Singh R: Challenges in liver cancer and possible treatment
approaches. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1873:1883142020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jiao B and Gao JJ: Intensive research on
the prospective use of complementary and alternative medicine to
treat systemic lupus erythematosus. Drug Discov Ther. 7:167–171.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang H, Peng X and Zhong C: Idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis: The current status of its epidemiology,
diagnosis, and treatment in China. Intractable Rare Dis Res.
2:88–93. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gao J, Inagaki Y, Li X, Kokudo N and Tang
W: Research progress on natural products from traditional Chinese
medicine in treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Drug Discov Ther.
7:46–57. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Melendez-Martinez AJ, Nascimento AF, Wang
Y, Liu C, Mao Y and Wang XD: Effect of tomato extract
supplementation against high-fat diet-induced hepatic lesions.
Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2:198–208. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tao Z, Gao J, Zhang G, Xue M, Yang W, Tong
C and Yuan Y: Shufeng Jiedu Capsule protect against acute lung
injury by suppressing the MAPK/NF-κB pathway. BioSci Trends.
8:45–51. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qi FH, Wang ZX, Cai PP, Zhao L, Gao JJ,
Okudo N, Li AY, Han JQ and Tang W: Traditional Chinese medicine and
related active compounds: A review of their role on hepatitis B
virus infection. Drug Discov Ther. 7:212–24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xia J, Inagaki Y, Gao J, Qi F, Song P, Han
G, Sawakami T, Gao B, Luo C, Kokudo N, et al: Combination of
Cinobufacini and Doxorubicin increases apoptosis of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells through the Fas- and mitochondria-mediated
pathways. Am J Chin Med. 45:1537–1556. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xia J, Rong L, Sawakami T, Inagaki Y, Song
P, Hasegawa K, Sakamoto Y and Tang W: Shufeng Jiedu Capsule and its
active ingredients induce apoptosis, inhibit migration and
invasion, and enhances doxorubicin therapeutic efficacy in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 99:921–930. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wong R, Sagar CM and Sagar SM: Integration
of Chinese medicine into supportive cancer care: A modern role for
an ancient tradition. Cancer Treat Rev. 27:235–246. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Holland TM, Agarwal P, Wang Y, Leurgans
SE, Bennett DA, Booth SL and Morris MC: Dietary flavonols and risk
of Alzheimer dementia. Neurology. 29:e1749–e1756. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Veeresham C, Rama Rao A and Asres K:
Aldose reductase inhibitors of plant origin. Phytotherapy Research.
28:317–333. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Khalil MI and Sulaiman SA: The potential
role of honey and its polyphenols in preventing heart diseases: A
review. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 7:315–321. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen AY and Chen YC: A review of the
dietary flavonoid, kaempferol on human health and cancer
chemoprevention. Food Chem. 138:2099–2107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Niestroy J, Barbara A, Herbst K, Rode S,
van Liempt M and Roos PH: Single and concerted effects of
benzo[a]pyrene and flavonoids on the AhR and Nrf2-pathway in the
human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2. Toxicol In Vitro.
25:671–683. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Calderón-Montaño JM, Burgos-Morón E,
Pérez-Guerrero C and López-Lázaro M: A review on the dietary
flavonoid kaempferol. Mini Rev Med Chem. 11:298–344. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim SH and Choi KC: Anti-cancer effect and
underlying mechanism(s) of kaempferol, a phytoestrogen, on the
regulation of apoptosis in diverse cancer cell models. Toxicol Res.
29:229–234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Speth PA, van Hoesel QG and Haanen C:
Clinical pharmacokinetics of doxorubicin. Clin Pharmacokinet.
15:15–31. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chatterjee K, Zhang J, Honbo N and
Karliner JS: Doxorubicin cardiomyopathy. Cardiology. 115:155–162.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kaczmarek A, Brinkman BM, Heyndrickx L,
Vandenabeele P and Krysko DV: Severity of doxorubicin-induced small
intestinal mucositis is regulated by the TLR-2 and TLR-9 pathways.
J Pathol. 226:598–608. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bun S, Yunokawa M, Tamaki Y, Shimomura A,
Shimoi T, Kodaira M, Shimizu C, Yonemori K, Fujiwara Y, Makino Y,
et al: Symptom management: The utility of regional cooling for
hand-foot syndrome induced by pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in
ovarian cancer. Support Care Cancer. 26:2161–2166. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin J, Fang L, Li H, Li Z, Lyu L, Wang H
and Xiao J: Astragaloside IV alleviates doxorubicin induced
cardiomyopathy by inhibiting NADPH oxidase derived oxidative
stress. Eur J Pharmacol. 859:1724902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li J, Wu Y, Wang D, Zou L, Fu C, Zhang J
and Leung GP: Oridonin synergistically enhances the anti-tumor
efficacy of doxorubicin against aggressive breast cancer via
pro-apoptotic and anti-angiogenic effects. Pharmacol Res.
146:1043132019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu Z, Chen L, Xiao Z, Zhu Y, Jiang H, Jin
Y, Gu C, Wu Y, Wang L, Zhang W, et al: Potentiation of the
anticancer effect of doxorubicinin drug-resistant gastric cancer
cells by tanshinone IIA. Phytomedicine. 51:58–67. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Caldwell S and Park SH: The epidemiology
of hepatocellular cancer: From the perspectives of public health
problem to tumor biology. Journal of Gastroenterology. 44 (Suppl
19):S96–S101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
El-Serag HB, Marrero JA, Rudolph L and
Reddy KR: Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 134:1752–1763. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gnoni A, Santini D, Scartozzi M, Russo A,
Licchetta A, Palmieri V, Lupo L, Faloppi L, Palasciano G, Memeo V,
et al: Hepatocellular carcinoma treatment over sorafenib:
Epigenetics, microRNAs and microenvironment. Is there a light at
the end of the tunnel? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 19:1623–1635.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Han G, Xia J, Gao J, Inagaki Y, Tang W and
Kokudo N: Anti-tumor effects and cellular mechanisms of
resveratrol. Drug Discov Ther. 9:1–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Anand David AV, Arulmoli R and Parasuraman
S: Overviews of biological importance of quercetin: A bioactive
flavonoid. Pharmacogn Rev. 10:84–89. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ren J, Lu Y, Qian Y, Chen B, Wu T and Ji
G: Recent progress regarding kaempferol for the treatment of
various diseases. Exp Ther Med. 18:2759–2776. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Seydi E, Salimi A, Rasekh HR, Mohsenifar Z
and Pourahmad J: Selective cytotoxicity of luteolin and kaempferol
on cancerous hepatocytes obtained from Rat model of hepatocellular
carcinoma: Involvement of ROS-mediated mitochondrial targeting.
Nutr Cancer. 70:594–604. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Han B, Yu YQ, Yang QL, Shen CY and Wang
XJ: Kaempferol induces autophagic cell death of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells via activating AMPK signaling. Oncotarget.
8:86227–86239. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Guo H, Ren F, Zhang L, Zhang X, Yang R,
Xie B, Li Z, Hu Z, Duan Z and Zhang J: Kaempferol induces apoptosis
in HepG2 cells via activation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 13:2791–2800. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang WW, Chiu YJ, Fan MJ, Lu HF, Yeh HF,
Li KH, Chen PY, Chung JG and Yang JS: Kaempferol induced apoptosis
via endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondria-dependent pathway
in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells. Mol Nutr Food Res.
54:1585–1595. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhu G, Liu X, Li H, Yan Y, Hong X and Lin
Z: Kaempferol inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of
liver cancer HepG2 cells by down-regulation of microRNA-21. Int J
Immunopathol Pharmacol. 32:20587384188143412018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|