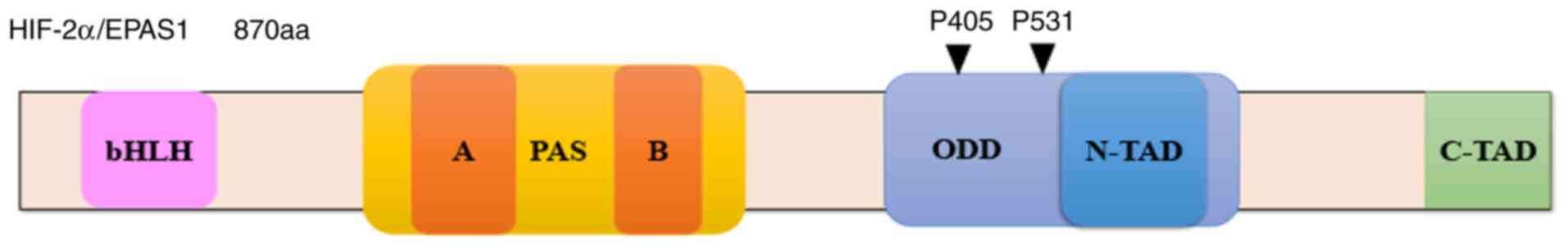
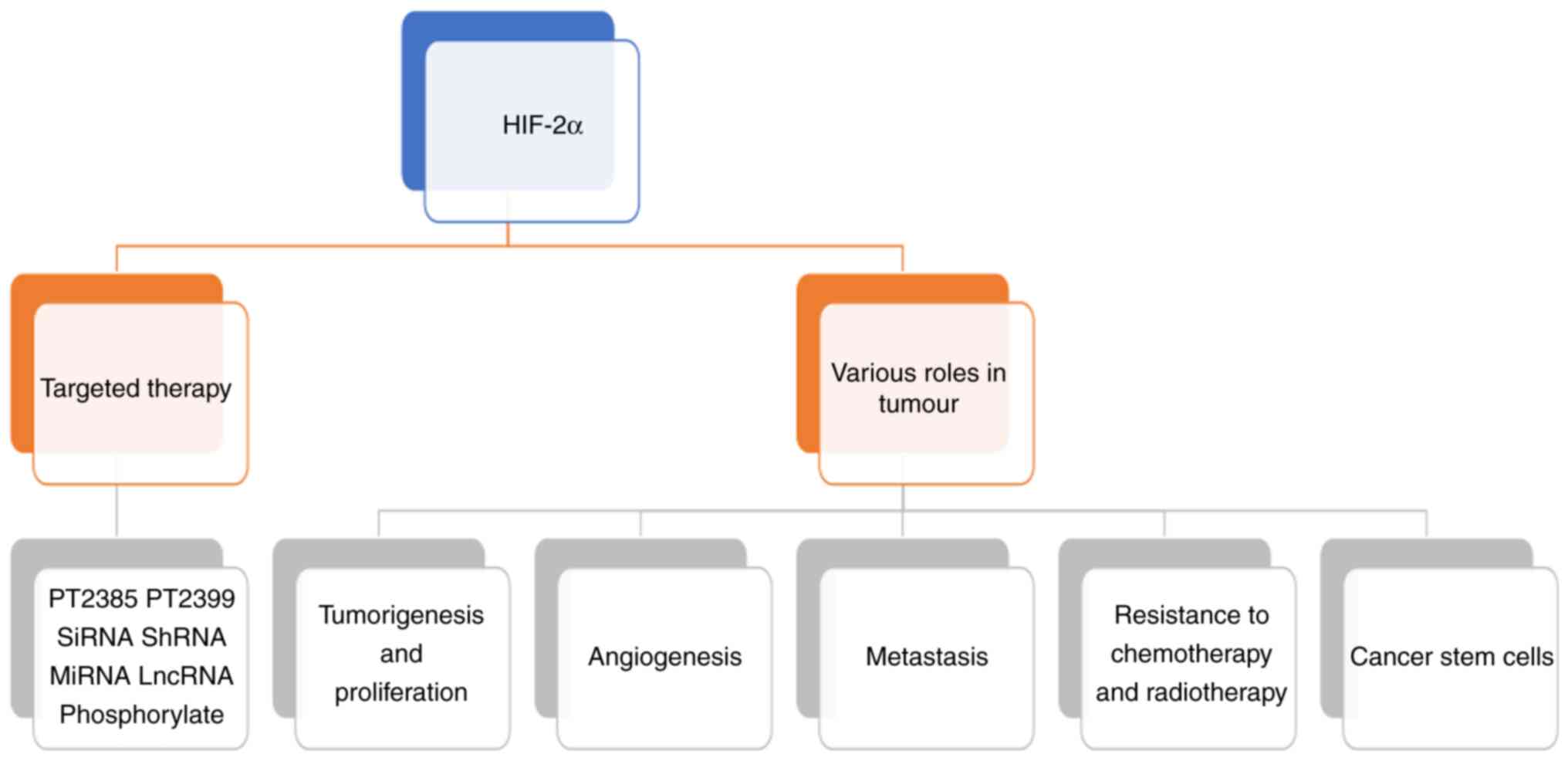
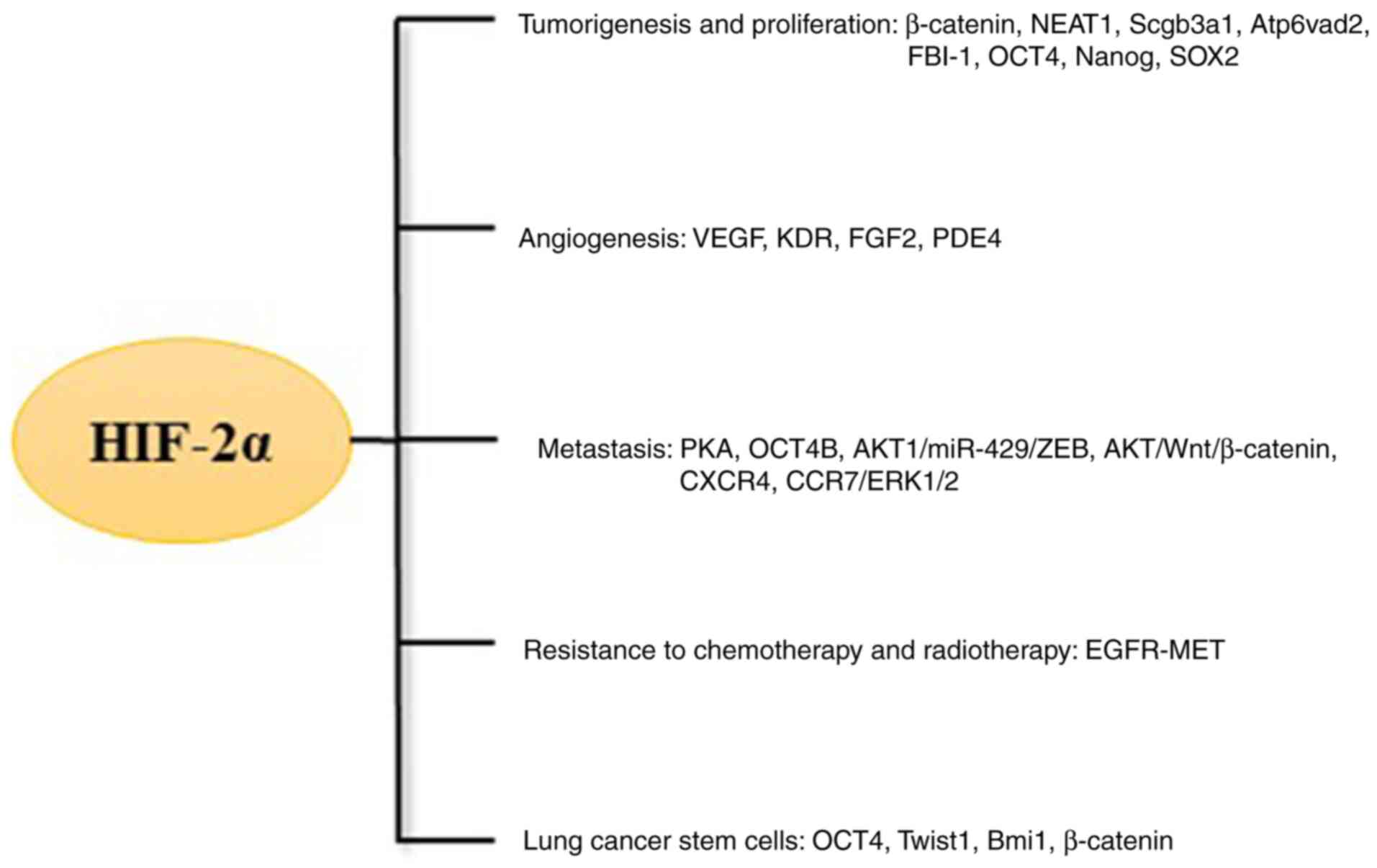
|
1
|
Tian H, McKnight SL and Russell DW:
Endothelial PAS domain protein 1 (EPAS1), a transcription factor
selectively expressed in endothelial cells. Genes Dev. 11:72–82.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ema M, Taya S, Yokotani N, Sogawa K,
Matsuda Y and Fujii-Kuriyama Y: A novel bHLH-PAS factor with close
sequence similarity to hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha regulates
the VEGF expression and is potentially involved in lung and
vascular development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:4273–4278. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wiesener MS, Turley H, Allen WE, Willam C,
Eckardt KU, Talks KL, Wood SM, Gatter KC, Harris AL, Pugh CW, et
al: Induction of endothelial PAS domain protein-1 by hypoxia:
Characterization and comparison with hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha. Blood. 92:2260–2268. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Favier J, Kempf H, Corvol P and Gasc JM:
Cloning and expression pattern of EPAS1 in the chicken embryo.
Colocalization with tyrosine hydroxylase. FEBS Lett. 462:19–24.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Talks KL, Turley H, Gatter KC, Maxwell PH,
Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ and Harris AL: The expression and
distribution of the hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and
HIF-2alpha in normal human tissues, cancers, and tumor-associated
macrophages. Am J Pathol. 157:411–421. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Blancher C, Moore JW, Talks KL, Houlbrook
S and Harris AL: Relationship of hypoxia-inducible factor
(HIF)-1alpha and HIF-2alpha expression to vascular endothelial
growth factor induction and hypoxia survival in human breast cancer
cell lines. Cancer Res. 60:7106–7113. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rajakumar A, Whitelock KA, Weissfeld LA,
Daftary AR, Markovic N and Conrad KP: Selective overexpression of
the hypoxia-inducible transcription factor, HIF-2alpha, in
placentas from women with preeclampsia. Biol Reprod. 64:499–506.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brusselmans K, Bono F, Maxwell P, Dor Y,
Dewerchin M, Collen D, Herbert JM and Carmeliet P:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha (HIF-2alpha) is involved in the
apoptotic response to hypoglycemia but not to hypoxia. J Biol Chem.
276:39192–39196. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen J, Chen J, Huang J, Li Z, Gong Y, Zou
B, Liu X, Ding L, Li P, Zhu Z, et al: HIF-2α upregulation mediated
by hypoxia promotes NAFLD-HCC progression by activating lipid
synthesis via the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway. Aging (Albany NY).
11:10839–10860. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Saito T, Fukai A, Mabuchi A, Ikeda T, Yano
F, Ohba S, Nishida N, Akune T, Yoshimura N, Nakagawa T, et al:
Transcriptional regulation of endochondral ossification by
HIF-2alpha during skeletal growth and osteoarthritis development.
Nat Med. 16:678–686. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen W, Hill H, Christie A, Kim MS,
Holloman E, Pavia-Jimenez A, Homayoun F, Ma Y, Patel N, Yell P, et
al: Targeting renal cell carcinoma with a HIF-2 antagonist. Nature.
539:112–117. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Choueiri TK and Kaelin WG Jr: Targeting
the HIF2-VEGF axis in renal cell carcinoma. Nat Med. 26:1519–1530.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun DR, Wang ZJ, Zheng QC and Zhang HX:
Exploring the inhibition mechanism on HIF-2 by inhibitor PT2399 and
0X3 using molecular dynamics simulations. J Mol Recognit.
31:e27302018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sasagawa T, Nagamatsu T, Morita K, Mimura
N, Iriyama T, Fujii T and Shibuya M: HIF-2α, but not HIF-1α,
mediates hypoxia-induced up-regulation of Flt-1 gene expression in
placental trophoblasts. Sci Rep. 8:173752018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Spirina LV, Yurmazov ZA, Gorbunov AK,
Usynin EA, Lushnikova NA and Kovaleva IV: Molecular protein and
expression profile in the primary tumors of clear cell renal
carcinoma and metastases. Cells. 9:16802020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cui XG, Han ZT, He SH, Wu XD, Chen TR,
Shao CH, Chen DL, Su N, Chen YM, Wang T, et al: HIF1/2α mediates
hypoxia-induced LDHA expression in human pancreatic cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 8:24840–24852. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
He C, Sun XP, Qiao H, Jiang X, Wang D, Jin
X, Dong X, Wang J, Jiang H and Sun X: Downregulating
hypoxia-inducible factor-2α improves the efficacy of doxorubicin in
the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 103:528–534.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cleven AH, Wouters BG, Schutte B, Spiertz
AJ, van Engeland M and de Bruïne AP: Poorer outcome in stromal
HIF-2 alpha- and CA9-positive colorectal adenocarcinomas is
associated with wild-type TP53 but not with BNIP3 promoter
hypermethylation or apoptosis. Br J Cancer. 99:727–733. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kong X, Zhao Y, Li X, Tao Z, Hou M and Ma
H: Overexpression of HIF-2α-dependent NEAT1 promotes the
progression of non-small cell lung cancer through
miR-101-3p/SOX9/Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem.
52:368–381. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Påhlman S and Mohlin S: Hypoxia and
hypoxia-inducible factors in neuroblastoma. Cell Tissue Res.
372:269–275. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao D, Wang S, Chu X and Han D: LncRNA
HIF2PUT inhibited osteosarcoma stem cells proliferation, migration
and invasion by regulating HIF2 expression. Artif Cells Nanomed
Biotechnol. 47:1342–1348. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Y, Chen Y, Bao L, Zhang B, Wang JE,
Kumar A, Xing C, Wang Y and Luo W: CHD4 promotes breast cancer
progression as a coactivator of hypoxia-inducible factors. Cancer
Res. 80:3880–3891. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Onita T, Ji PG, Xuan JW, Sakai H, Kanetake
H, Maxwell PH, Fong GH, Gabril MY, Moussa M and Chin JL:
Hypoxia-induced, perinecrotic expression of endothelial
Per-ARNT-Sim domain protein-1/hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha
correlates with tumor progression, vascularization, and focal
macrophage infiltration in bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
8:471–480. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lim E, Kuo CC, Tu HF and Yang CC: The
prognosis outcome of oral squamous cell carcinoma using HIF-2alpha.
J Chin Med Assoc. 80:651–656. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Munksgaard Persson M, Johansson ME, Monsef
N, Planck M, Beckman S, Seckl MJ, Rönnstrand L, Påhlman S and
Pettersson HM: HIF-2α expression is suppressed in SCLC cells, which
survive in moderate and severe hypoxia when HIF-1α is repressed. Am
J Pathol. 180:494–504. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shneor D, Folberg R, Pe'er J, Honigman A
and Frenkel S: Stable knockdown of CREB, HIF-1 and HIF-2 by
replication-competent retroviruses abrogates the responses to
hypoxia in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 24:64–74.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Westerlund I, Shi Y, Toskas K, Fell SM, Li
S, Surova O, Södersten E, Kogner P, Nyman U, Schlisio S and
Holmberg J: Combined epigenetic and differentiation-based treatment
inhibits neuroblastoma tumor growth and links HIF2α to tumor
suppression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:E6137–E6146. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Imamura T, Kikuchi H, Herraiz MT, Park DY,
Mizukami Y, Mino-Kenduson M, Lynch MP, Rueda BR, Benita Y, Xavier
RJ and Chung DC: HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha have divergent roles in
colon cancer. Int J Cancer. 124:763–771. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Coliat P, Ramolu L, Jégu J, Gaiddon C,
Jung AC and Pencreach E: Constitutive or induced HIF-2 addiction is
involved in resistance to Anti-EGFR treatment and radiation therapy
in HNSCC. Cancers (Basel). 11:16072019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Koh MY, Nguyen V, Lemos R Jr, Darnay BG,
Kiriakova G, Abdelmelek M, Ho TH, Karam J, Monzon FA, Jonasch E and
Powis G: Hypoxia-induced SUMOylation of E3 ligase HAF determines
specific activation of HIF2 in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 75:316–329. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen R, Xu M, Nagati J and Garcia JA:
Coordinate regulation of stress signaling and epigenetic events by
Acss2 and HIF-2 in cancer cells. PLoS One. 12:e1902412017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Choudhry H, Albukhari A, Morotti M, Haider
S, Moralli D, Smythies J, Schödel J, Green CM, Camps C, Buffa F, et
al: Tumor hypoxia induces nuclear paraspeckle formation through
HIF-2α dependent transcriptional activation of NEAT1 leading to
cancer cell survival. Oncogene. 34:4482–4490. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen R, Xu M, Nagati JS, Hogg RT, Das A,
Gerard RD and Garcia JA: The acetate/ACSS2 switch regulates HIF-2
stress signaling in the tumor cell microenvironment. PLoS One.
10:e1165152015.
|
|
34
|
Wu XH, Qian C and Yuan K: Correlations of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α/hypoxia-inducible factor-2α expression
with angiogenesis factors expression and prognosis in non-small
cell lung cancer. Chin Med J (Engl). 124:11–18. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Niu Y, Bao L, Chen Y, Wang C, Luo M, Zhang
B, Zhou M, Wang JE, Fang YV, Kumar A, et al: HIF2-Induced long
noncoding RNA RAB11B-AS1 Promotes hypoxia-mediated angiogenesis and
breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 80:964–975. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sato A, Virgona N, Ando A, Ota M and Yano
T: A redox-silent analogue of tocotrienol inhibits cobalt(II)
chloride-induced VEGF expression via Yes signaling in mesothelioma
cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 37:865–870. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kamai T, Tokura Y, Uematsu T, Sakamoto K,
Suzuki I, Takei K, Narimatsu T, Kambara T, Yuki H, Betsunoh H, et
al: Elevated serum levels of cardiovascular biomarkers are
associated with progression of renal cancer. Open Heart.
5:e0006662018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu YL, Yu JM, Song XR, Wang XW, Xing LG
and Gao BB: Regulation of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and
metastasis by hypoxia-inducible factor in non small cell lung
cancer cell lines. Cancer Biol Ther. 5:1320–1326. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Fiska A and
Koukourakis MI: Hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha (HIF-2 alpha)
induces angiogenesis in breast carcinomas. Appl Immunohistochem Mol
Morphol. 14:78–82. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bangoura G, Yang LY, Huang GW and Wang W:
Expression of HIF-2alpha/EPAS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 10:525–530. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Alam MW, Persson CU, Reinbothe S, Kazi JU,
Rönnstrand L, Wigerup C, Ditzel HJ, Lykkesfeldt AE, Påhlman S and
Jögi A: HIF2α contributes to antiestrogen resistance via positive
bilateral crosstalk with EGFR in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget.
7:11238–11250. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhao D, Zhai B, He C, Tan G, Jiang X, Pan
S, Dong X, Wei Z, Ma L, Qiao H, et al: Upregulation of HIF-2α
induced by sorafenib contributes to the resistance by activating
the TGF-α/EGFR pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell
Signal. 26:1030–1039. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Moreno Roig E, Groot AJ, Yaromina A,
Hendrickx TC, Barbeau LMO, Giuranno L, Dams G, Ient J, Olivo
Pimentel V, van Gisbergen MW, et al: HIF-1α and HIF-2α differently
regulate the radiation sensitivity of NSCLC cells. Cells. 8:452019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Koukourakis MI, Bentzen SM, Giatromanolaki
A, Wilson GD, Daley FM, Saunders MI, Dische S, Sivridis E and
Harris AL: Endogenous markers of two separate hypoxia response
pathways (hypoxia inducible factor 2 alpha and carbonic anhydrase
9) are associated with radiotherapy failure in head and neck cancer
patients recruited in the CHART randomized trial. J Clin Oncol.
24:727–735. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Das B, Pal B, Bhuyan R, Li H, Sarma A,
Gayan S, Talukdar J, Sandhya S, Bhuyan S, Gogoi G, et al: MYC
Regulates the HIF2α stemness pathway via Nanog and Sox2 to maintain
self-renewal in cancer stem cells. versus Non-stem cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 79:4015–4025. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hou J, Zhang H, Liu J, Zhao Z, Wang J, Lu
Z, Hu B, Zhou J, Zhao Z, Feng M, et al: YTHDF2 reduction fuels
inflammation and vascular abnormalization in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 18:1632019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhao CX, Luo CL and Wu XH: Hypoxia
promotes 786-O cells invasiveness and resistance to sorafenib via
HIF-2α/COX-2. Med Oncol. 32:4192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Vukovic M, Guitart AV, Sepulveda C,
Villacreces A, O'Duibhir E, Panagopoulou TI, Ivens A,
Menendez-Gonzalez J, Iglesias JM, Allen L, et al: Hif-1α and Hif-2α
synergize to suppress AML development but are dispensable for
disease maintenance. J Exp Med. 212:2223–2234. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jiang L, Shi S, Shi Q, Zhang H, Xia Y and
Zhong T: MicroRNA-519d-3p inhibits proliferation and promotes
apoptosis by targeting HIF-2α in cervical cancer under hypoxic
conditions. Oncol Res. 26:1055–1062. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pangou E, Befani C, Mylonis I, Samiotaki
M, Panayotou G, Simos G and Liakos P: HIF-2α phosphorylation by
CK1δ promotes erythropoietin secretion in liver cancer cells under
hypoxia. J Cell Sci. 129:4213–4226. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liu N, Luo J, Kuang D, Xu S, Duan Y, Xia
Y, Wei Z, Xie X, Yin B, Chen F, et al: Lactate inhibits ATP6V0d2
expression in tumor-associated macrophages to promote
HIF-2α-mediated tumor progression. J Clin Invest. 129:631–646.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang Z, Wei Y, Zhang R, Su L, Gogarten SM,
Liu G, Brennan P, Field JK, McKay JD, Lissowska J, et al:
Multi-Omics analysis reveals a HIF network and hub gene EPAS1
associated with lung adenocarcinoma. Ebiomedicine. 32:93–101. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Luan Y, Gao C, Miao Y, Li Y, Wang Z and
Qiu X: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of
HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha expression in small cell lung cancer.
Pathol Res Pract. 209:184–189. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yu S, Ren H, Li Y, Liang X, Ning Q, Chen
X, Chen M and Hu T: HOXA4-dependent transcriptional activation of
AXL promotes cisplatin-resistance in lung adenocarcinoma cells.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 18:2062–2067. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Iwamoto S, Tanimoto K, Nishio Y, Putra AC,
Fuchita H, Ohe M, Sutani A, Kuraki T, Hiyama K, Murakami I, et al:
Association of EPAS1 gene rs4953354 polymorphism with
susceptibility to lung adenocarcinoma in female Japanese
non-smokers. J Thorac Oncol. 9:1709–1713. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sárosi V, Balikó Z, Smuk G, László T,
Szabó M, Ruzsics I and Mezősi E: The frequency of EGFR mutation in
lung adenocarcinoma and the efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitor
therapy in a hungarian cohort of patients. Pathol Oncol Res.
22:755–761. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gao ZJ, Wang Y, Yuan WD, Yuan JQ and Yuan
K: HIF-2α not HIF-1α overexpression confers poor prognosis in
non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283177096372017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Xu Y, Zhao Y, Xu W, Luo F, Wang B, Li Y,
Pang Y and Liu Q: Involvement of HIF-2α-mediated inflammation in
arsenite-induced transformation of human bronchial epithelial
cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 272:542–550. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Pang Y, Xu Y, Li H, Li Y, Zhao Y, Jiang R,
Shen L, Zhou J, Wang X and Liu Q: The inhibition of HIF-2α on the
ATM/Chk-2 pathway is involved in the promotion effect of arsenite
on benzo(a)pyrene-induced cell transformation. Toxicol Lett.
218:105–117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhou Q, Chen T, Ibe JC, Raj JU and Zhou G:
Loss of either hypoxia inducible factor 1 or 2 promotes lung cancer
cell colonization. Cell Cycle. 10:2233–2234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kamlah F, Eul BG, Li S, Lang N, Marsh LM,
Seeger W, Grimminger F, Rose F and Hänze J: Intravenous injection
of siRNA directed against hypoxia-inducible factors prolongs
survival in a Lewis lung carcinoma cancer model. Cancer Gene Ther.
16:195–205. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yuan S, Xiang Y, Wang G, Zhou M, Meng G,
Liu Q, Hu Z, Li C, Xie W, Wu N, et al: Hypoxia-sensitive LINC01436
is regulated by E2F6 and acts as an oncogene by targeting
miR-30a-3p in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Oncol. 13:840–856.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Martinengo C, Poggio T, Menotti M, Scalzo
MS, Mastini C, Ambrogio C, Pellegrino E, Riera L, Piva R, Ribatti
D, et al: ALK-dependent control of hypoxia-inducible factors
mediates tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 74:6094–6106.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hong CF, Chen WY and Wu CW: Upregulation
of Wnt signaling under hypoxia promotes lung cancer progression.
Oncol Rep. 38:1706–1714. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Mazumdar J, Hickey MM, Pant DK, Durham AC,
Sweet-Cordero A, Vachani A, Jacks T, Chodosh LA, Kissil JL, Simon
MC and Keith B: HIF-2alpha deletion promotes Kras-driven lung tumor
development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:14182–14187. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang X, Cao P, Li Z, Wu D, Wang X and
Liang G: EPAS-1 mediates SP-1-dependent FBI-1 expression and
regulates tumor cell survival and proliferation. Int J Mol Sci.
15:15689–15699. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Higashi K, Yamagishi T, Ueda Y, Ishigaki
Y, Shimasaki M, Nakamura Y, Oguchi M, Takegami T, Sagawa M and
Tonami H: Correlation of HIF-1α/HIF-2α expression with FDG uptake
in lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Nucl Med. 30:708–715. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yu L and Hales CA: Long-term exposure to
hypoxia inhibits tumor progression of lung cancer in rats and mice.
BMC Cancer. 11:3312011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Kim WY, Perera S, Zhou B, Carretero J, Yeh
JJ, Heathcote SA, Jackson AL, Nikolinakos P, Ospina B, Naumov G, et
al: HIF2alpha cooperates with RAS to promote lung tumorigenesis in
mice. J Clin Invest. 119:2160–2170. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Shao JS, Sun J, Wang S, Chung K, Du JT,
Wang J, Qiu XS, Wang EH and Wu GP: HPV16 E6/E7 upregulates HIF-2α
and VEGF by inhibiting LKB1 in lung cancer cells. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177171372017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Karoor V, Le M, Merrick D, Fagan KA,
Dempsey EC and Miller YE: Alveolar hypoxia promotes murine lung
tumor growth through a VEGFR-2/EGFR-dependent mechanism. Cancer
Prev Res (Phila). 5:1061–1071. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Giatromanolaki A, Koukourakis MI, Sivridis
E, Turley H, Talks K, Pezzella F, Gatter KC and Harris AL: Relation
of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and 2 alpha in operable
non-small cell lung cancer to angiogenic/molecular profile of
tumours and survival. Br J Cancer. 85:881–890. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Pullamsetti SS, Banat GA, Schmall A,
Szibor M, Pomagruk D, Hänze J, Kolosionek E, Wilhelm J, Braun T,
Grimminger F, et al: Phosphodiesterase-4 promotes proliferation and
angiogenesis of lung cancer by crosstalk with HIF. Oncogene.
32:1121–1134. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhen Q, Zhang Y, Gao L, Wang R, Chu W,
Zhao X, Li Z, Li H, Zhang B, Lv B and Liu J: EPAS1 promotes
peritoneal carcinomatosis of non-small-cell lung cancer by
enhancing mesothelial-mesenchymal transition. Strahlenther Onkol.
197:141–149. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chan SM, Lin BF, Wong CS, Chuang WT, Chou
YT and Wu ZF: Levobuipivacaine-Induced Dissemination of A549 lung
cancer cells. Sci Rep. 7:86462017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Shaikh D, Zhou Q, Chen T, Ibe JC, Raj JU
and Zhou G: cAMP-dependent protein kinase is essential for
hypoxia-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration, and
invasion in lung cancer cells. Cell Signal. 24:2396–2406. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Lin SC, Chung CH, Chung CH, Kuo MH, Hsieh
CH, Chiu YF, Shieh YS, Chou YT and Wu CW: OCT4B mediates
hypoxia-induced cancer dissemination. Oncogene. 38:1093–1105. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Jia R, Liang Y, Chen R, Liu G, Wang H,
Tang M, Zhou X, Wang H, Yang Y, Wei H, et al: Osteopontin
facilitates tumor metastasis by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal
plasticity. Cell Death Dis. 7:e25642016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhou R, Zhou X, Yin Z, Guo J, Hu T, Jiang
S, Liu L, Dong X, Zhang S and Wu G: Tumor invasion and metastasis
regulated by microRNA-184 and microRNA-574-5p in small-cell lung
cancer. Oncotarget. 6:44609–44622. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Li Y, Qiu X, Zhang S, Zhang Q and Wang E:
Hypoxia induced CCR7 expression via HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha
correlates with migration and invasion in lung cancer cells. Cancer
Biol Ther. 8:322–330. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Gao ZJ, Yuan WD, Yuan JQ, Yuan K and Wang
Y: Downregulation of HIF-2α reverse the chemotherapy resistance of
lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells to Cisplatin. Med Sci Monit.
24:1104–1111. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Stoleriu MG, Steger V, Mustafi M,
Michaelis M, Cinatl J, Schneider W, Nolte A, Kurz J, Wendel HP,
Schlensak C and Walker T: A new strategy in the treatment of
chemoresistant lung adenocarcinoma via specific siRNA transfection
of SRF, E2F1, Survivin, HIF and STAT3. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.
46:877–886. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Moreno Roig E, Groot AJ, Yaromina A,
Hendrickx TC, Barbeau LMO, Giuranno L, Dams G, Ient J, Olivo
Pimentel V, van Gisbergen MW, et al: HIF-1α and HIF-2α differently
regulate the radiation sensitivity of NSCLC Cells. Cells. 8:452019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Sun JC, He F, Yi W, Wan MH, Li R, Wei X,
Wu R and Niu DL: High expression of HIF-2α and its
anti-radiotherapy effect in lung cancer stem cells. Genet Mol Res.
14:18110–18120. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zhen Q, Liu JF, Liu JB, Wang RF, Chu WW,
Zhang YX, Tan GL, Zhao XJ and Lv BL: Endothelial PAS
domain-containing protein 1 confers TKI-resistance by mediating
EGFR and MET pathways in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer
Biol Ther. 16:549–557. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Hajizadeh F, Okoye I, Esmaily M, Ghasemi
Chaleshtari M, Masjedi A, Azizi G, Irandoust M, Ghalamfarsa G and
Jadidi-Niaragh F: Hypoxia inducible factors in the tumor
microenvironment as therapeutic targets of cancer stem cells. Life
Sci. 237:1169522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Ye XQ, Li Q, Wang GH, Sun FF, Huang GJ,
Bian XW, Yu SC and Qian GS: Mitochondrial and energy
metabolism-related properties as novel indicators of lung cancer
stem cells. Int J Cancer. 129:820–831. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Gao Y, Feng J, Wu L, Zhan S and Sun J:
Expression and pathological mechanism of MMP-9 and HIF-2α in
CD133(+) lung cancer stem cells. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.
95:2607–2611. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wei-Hua W, Ning Z, Qian C and Dao-Wen J:
ZIC2 promotes cancer stem cell traits via up-regulating OCT4
expression in lung adenocarcinoma cells. J Cancer. 11:6070–6080.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Zhang X, Hu F, Li C, Zheng X, Zhang B,
Wang H, Tao G, Xu J, Zhang Y and Han B: OCT4&SOX2-specific
cytotoxic T lymphocytes plus programmed cell death protein 1
inhibitor presented with synergistic effect on killing lung cancer
stem-like cells in vitro and treating drug-resistant lung cancer
mice in vivo. J Cell Physiol. 234:6758–6768. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Xu J, Wang H, Zheng X,
Lou Y and Han B: Antigen presentation of the Oct4 and Sox2 peptides
by CD154-activated B lymphocytes enhances the killing effect of
cytotoxic T lymphocytes on tumor stem-like cells derived from
cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells. J Cancer. 9:367–374. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Phiboonchaiyanan PP and Chanvorachote P:
Suppression of a cancer stem-like phenotype mediated by
alpha-lipoic acid in human lung cancer cells through
down-regulation of β-catenin and Oct-4. Cell Oncol (Dordr).
40:497–510. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Kobayashi I, Takahashi F, Nurwidya F, Nara
T, Hashimoto M, Murakami A, Yagishita S, Tajima K, Hidayat M,
Shimada N, et al: Oct4 plays a crucial role in the maintenance of
gefitinib-resistant lung cancer stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 473:125–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Xu Y, Li Y, Pang Y, Ling M, Shen L, Yang
X, Zhang J, Zhou J, Wang X and Liu Q: EMT and stem cell-like
properties associated with HIF-2α are involved in arsenite-induced
transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells. PLoS One.
7:e377652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wang R, Sun Q, Wang P, Liu M, Xiong S, Luo
J, Huang H, Du Q, Geller DA and Cheng B: Notch and Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway play important roles in activating liver cancer
stem cells. Oncotarget. 7:5754–5768. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Zhu JY, Yang X, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Wang SJ,
Li Y, Wang XQ, Meng Y, Zhu MM, Ma X, et al: Curcumin suppresses
lung cancer stem cells via inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin and Sonic
Hedgehog Pathways. Phytother Res. 31:680–688. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Li C, Lu HJ, Na FF, Deng L, Xue JX, Wang
JW, Wang YQ, Li QL and Lu Y: Prognostic role of hypoxic inducible
factor expression in non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:3607–3612. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Putra AC, Eguchi H, Lee KL, Yamane Y,
Gustine E, Isobe T, Nishiyama M, Hiyama K, Poellinger L and
Tanimoto K: The A Allele at rs13419896 of EPAS1 is associated with
enhanced expression and poor prognosis for non-small cell lung
cancer. PLoS One. 10:e01344962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
de Haas S, Delmar P, Bansal AT, Moisse M,
Miles DW, Leighl N, Escudier B, Van Cutsem E, Carmeliet P, Scherer
SJ, et al: Genetic variability of VEGF pathway genes in six
randomized phase III trials assessing the addition of bevacizumab
to standard therapy. Angiogenesis. 17:909–920. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Ma H, Liu B, Wang S and Liu J:
MicroRNA-383 is a tumor suppressor in human lung cancer by
targeting endothelial PAS domain-containing protein 1. Cell Biochem
Funct. 34:613–619. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Sato M, Tanaka T, Maeno T, Sando Y, Suga
T, Maeno Y, Sato H, Nagai R and Kurabayashi M: Inducible expression
of endothelial PAS domain protein-1 by hypoxia in human lung
adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Role of Src family kinases-dependent
pathway. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 26:127–134. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|