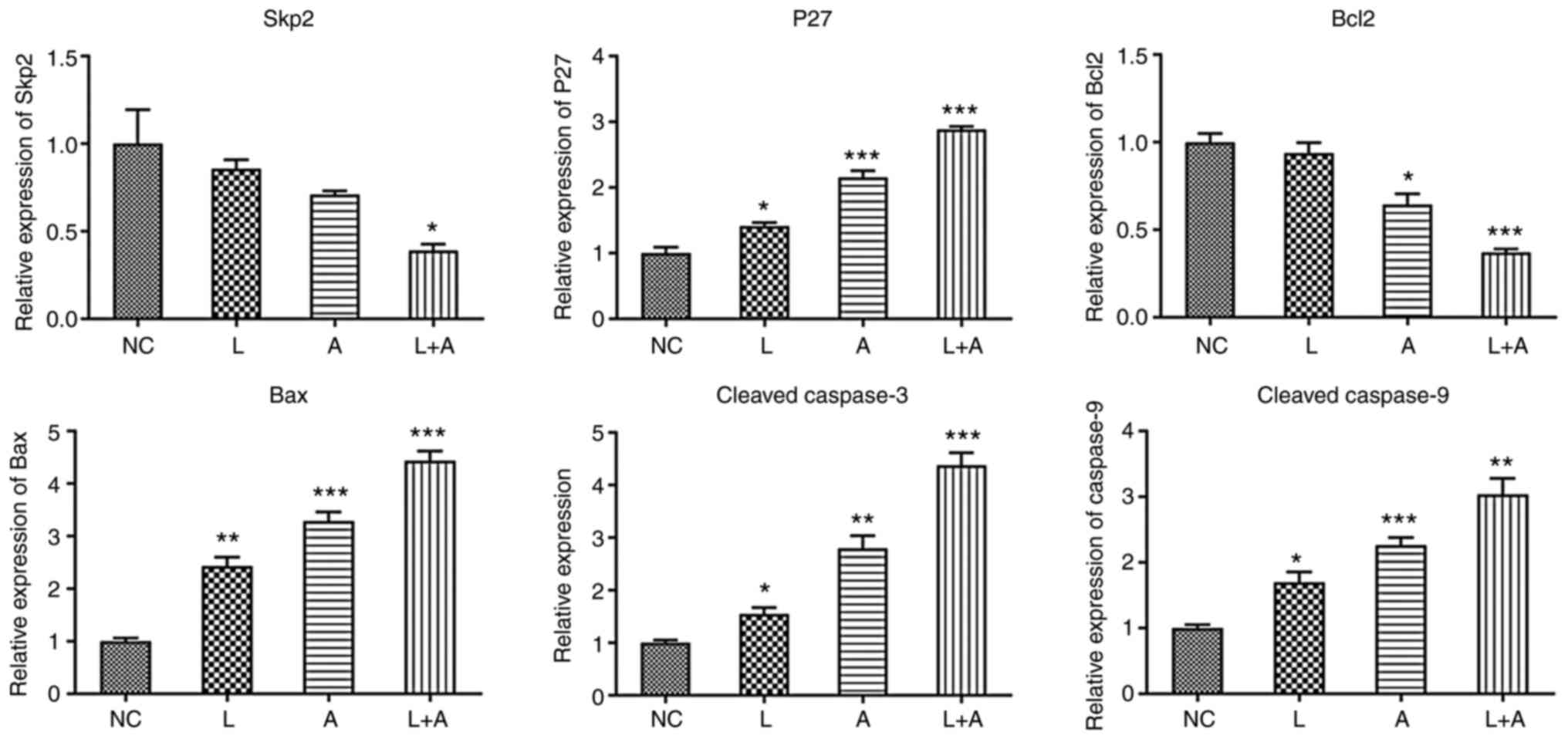
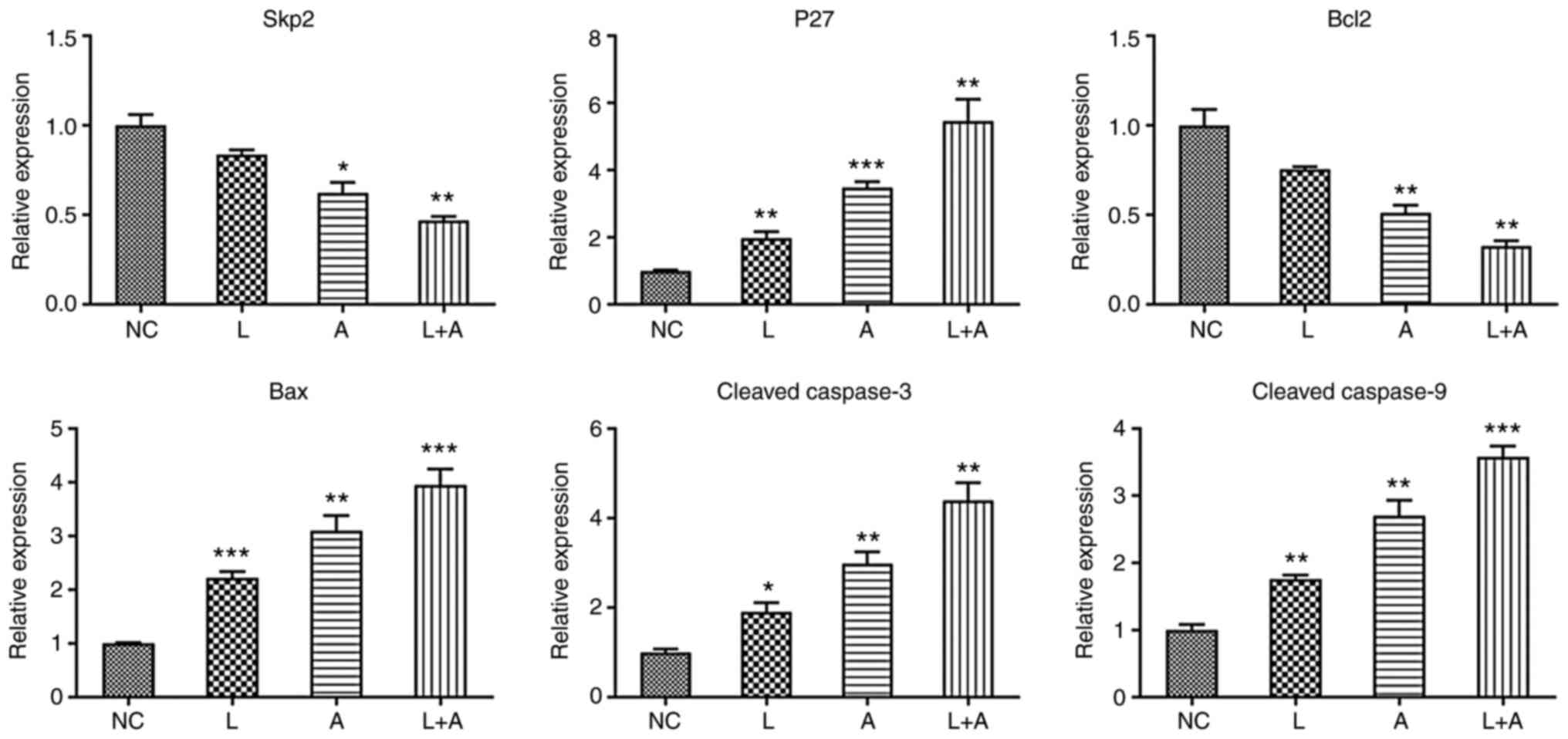
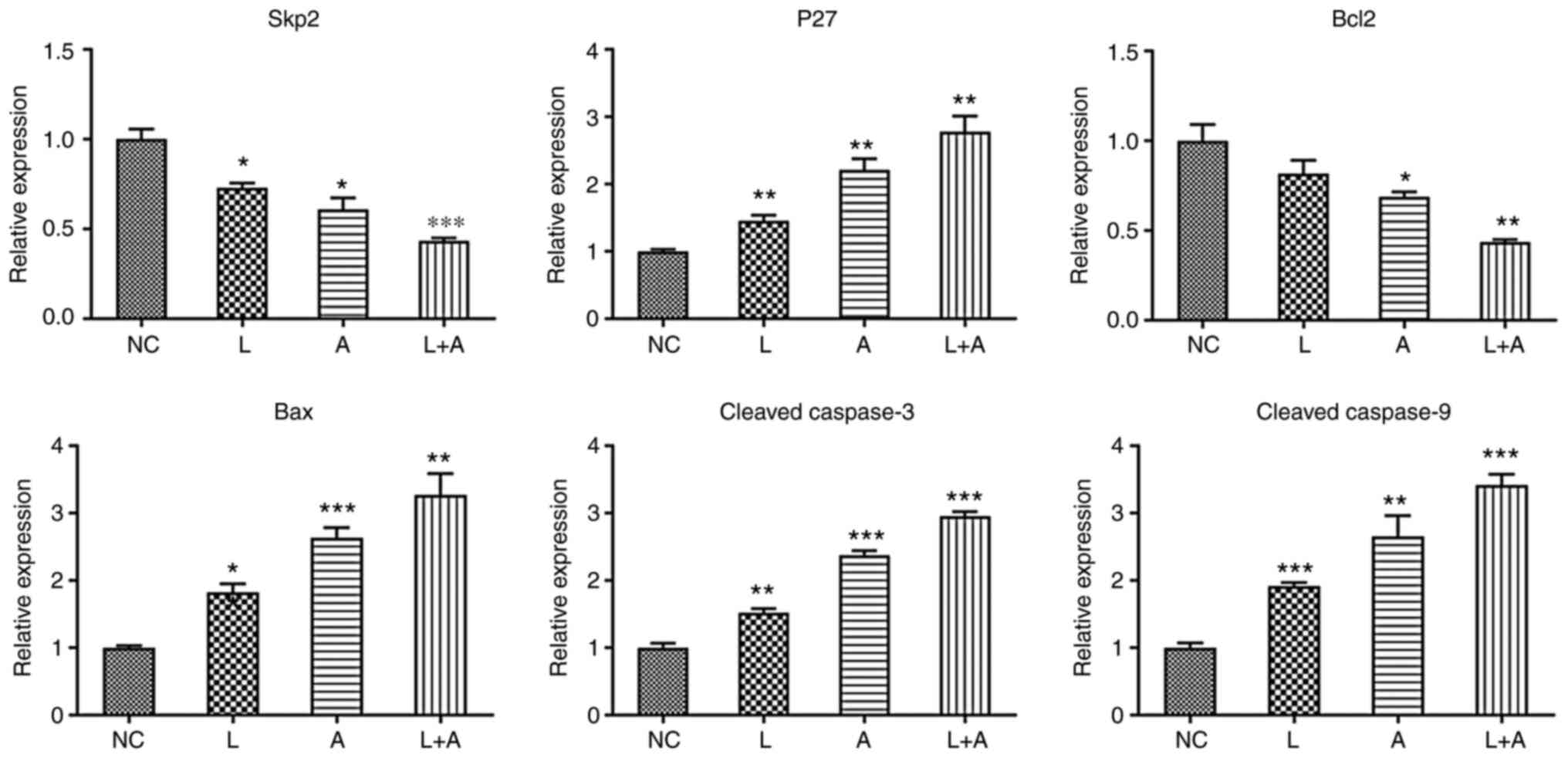
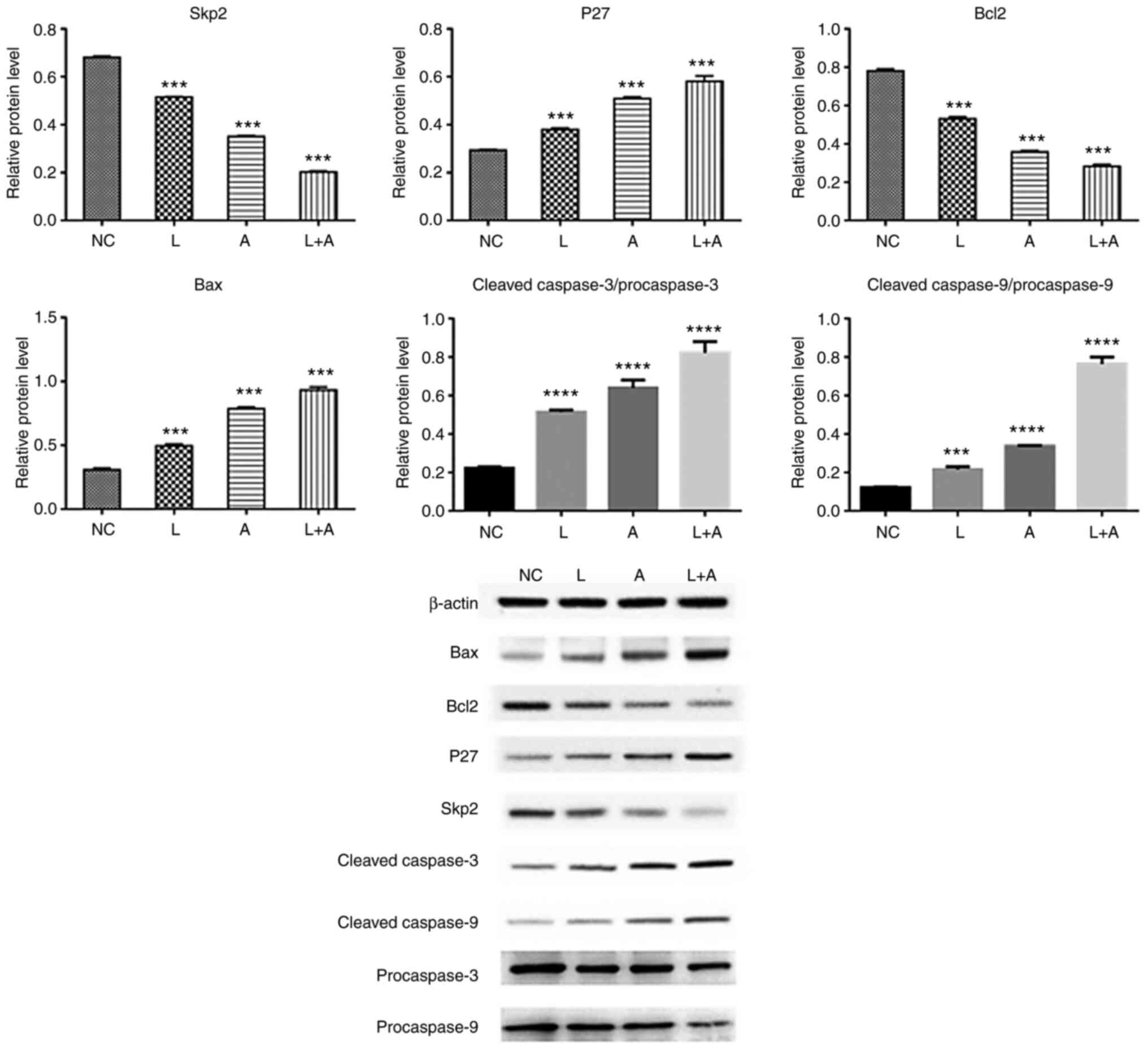
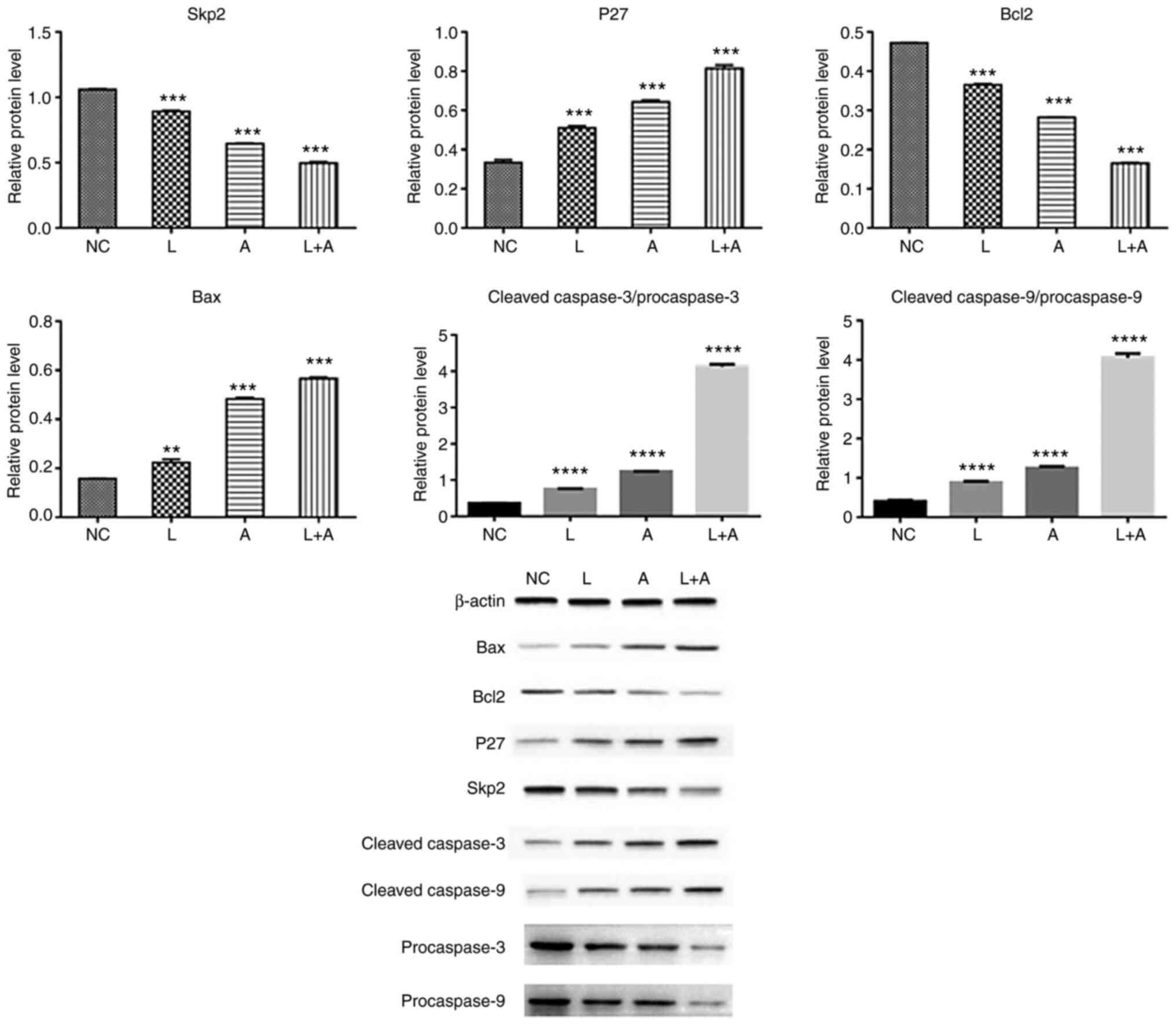
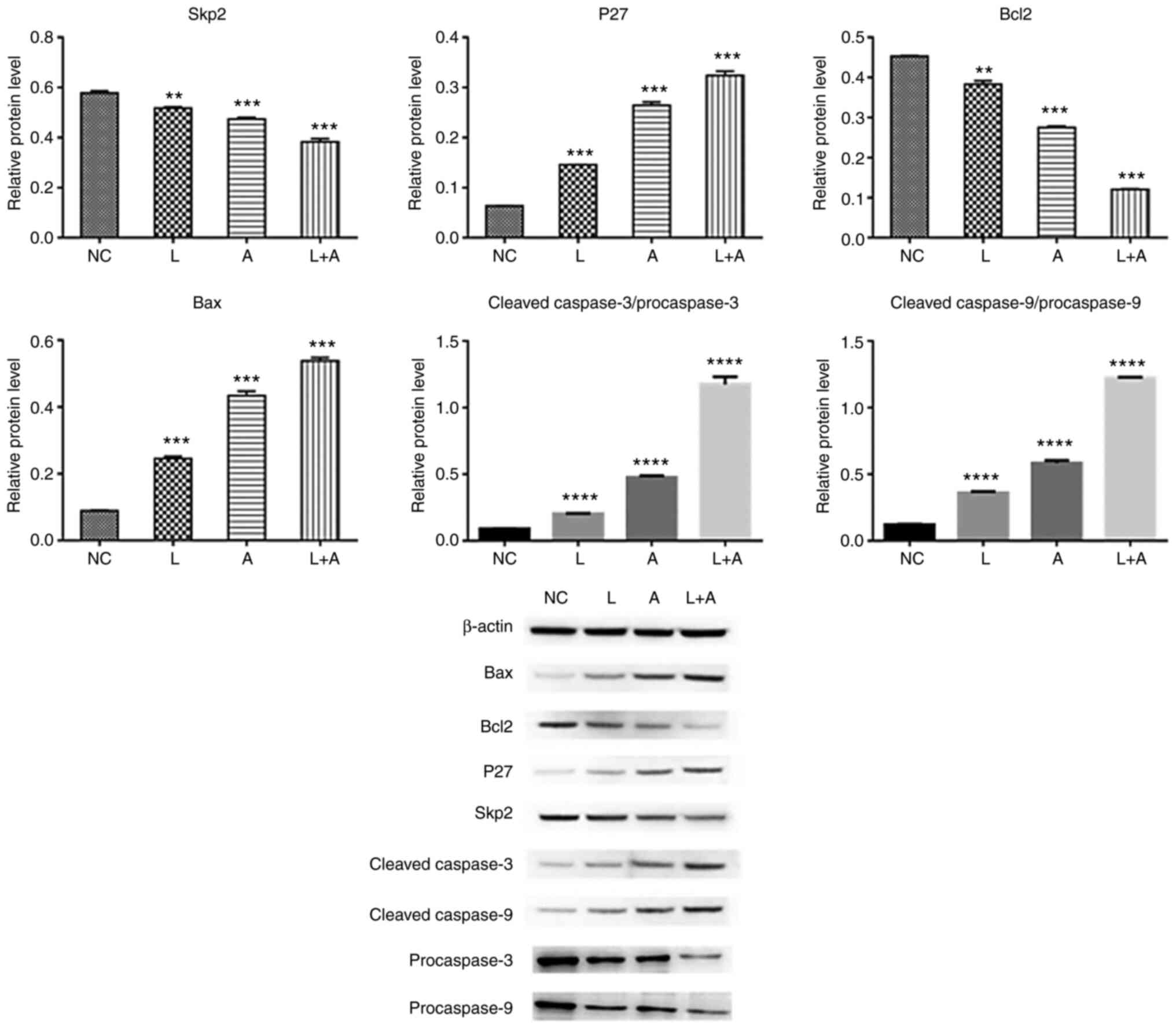
|
1
|
Sakamoto KM, Grant S, Saleiro D, Crispino
JD, Hijiya N, Giles F, Platanias L and Eklund EA: Targeting novel
signaling pathways for resistant acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Genet
Metab. 114:397–402. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Horner MJ, Ries LAG, Krapcho M, Neyman N,
Aminou R, Howlader N, Altekruse SF, Feuer EJ, Huang L, Mariotto A,
Miller BA, et al: SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2006.
National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD: 2009
|
|
3
|
Pan R, Hogdal LJ, Benito JM, Bucci D, Han
L, Borthakur G, Cortes J, DeAngelo DJ, Debose L, Mu H, et al:
Selective BCL-2 inhibition by ABT-199 causes on-target cell death
in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Discov. 4:362–375. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stuani L, Sabatier M and Sarry JE:
Exploiting metabolic vulnerabilities for personalized therapy in
acute myeloid leukemia. BMC Biol. 17:572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Staudt D, Murray HC and McLachlan T:
Targeting oncogenic signaling in mutant FLT3 acute myeloid
leukemia: The path to least resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 19:31982018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kantarjian HM: Therapy for elderly
patients with acute myeloid leukemia: A problem in search of
solutions. Cancer. 109:1007–1010. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kantarjian H, O'Brien S, Cortes J, Giles
F, Faderl S, Jabbour E, Garcia-Manero G, Wierda W, Pierce S, Shan J
and Estey E: Results of intensive chemotherapy in 998 patients age
65 years or older with acute myeloid leukemia or high-risk
myelodysplastic syndrome: Predictive prognostic models for outcome.
Cancer. 106:1090–1098. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nazha A and Ravandi F: Acute myeloid
leukemia in the elderly: Do we know who should be treated and how?
Leuk Lymphoma. 55:979–987. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Döhner H, Estey EH, Amadori S, Appelbaum
FR, Büchner T, Burnett AK, Dombret H, Fenaux P, Grimwade D, Larson
RA, et al: Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in
adults: Recommendations from an international expert panel, on
behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 115:453–474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lerch E, Espeli V, Zucca E, Leoncini L,
Scali G, Mora O, Bordoni A, Cavalli F and Ghielmini M: Prognosis of
acute myeloid leukemia in the general population: Data from
southern Switzerland. Tumori. 95:303–310. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu S, Xiong Y, Xu J, Liang X, Fu Y, Liu D,
Yu X and Wu D: Identification of dysfunctional gut microbiota
through rectal swab in patients with different severity of acute
pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 65:3223–3237. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Engelman JA: Targeting PI3K signalling in
cancer: Opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:550–562. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Park S, Chapuis N, Tamburini J, Bardet V,
Cornillet-Lefebvre P, Willems L, Green A, Mayeux P, Lacombe C and
Bouscary D: Role of the PI3K/AKT and mTOR signaling pathways in
acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 95:819–828. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vanhaesebroeck B, Stephens L and Hawkins
P: PI3K signalling: The path to discovery and understanding. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:195–203. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fransecky L, Mochmann LH and Baldus CD:
Outlook on PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibition in acute leukemia. Mol Cell
Ther. 3:22015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lindblad O, Cordero E, Puissant A,
Macaulay L, Ramos A, Kabir NN, Sun J, Vallon-Christersson J,
Haraldsson K, Hemann MT, et al: Aberrant activation of the
PI3K/mTOR pathway promotes resistance to sorafenib in AML.
Oncogene. 35:5119–5131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kulsoom B, Shamsi TS, Afsar NA, Memon Z,
Ahmed N and Hasnain SN: Bax, Bcl-2, and Bax/Bcl-2 as prognostic
markers in acute myeloid leukemia: Are we ready for Bcl-2-directed
therapy? Cancer Manag Res. 10:403–416. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bhola PD and Letai A: Mitochondria-judges
and executioners of cell death sentences. Mol Cell. 61:695–704.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
DeStefano CB and Hourigan CS:
Personalizing initial therapy in acute myeloid leukemia:
Incorporating novel agents into clinical practice. Ther Adv
Hematol. 9:109–121. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lagadinou ED, Sach A, Callahan K, Rossi
RM, Neering SJ, Minhajuddin M, Ashton JM, Pei S, Grose V, O'Dwyer
KM, et al: BCL-2 inhibition targets oxidative phosphorylation and
selectively eradicates quiescent human leukemia stem cells. Cell
Stem Cell. 12:329–341. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Campos L, Rouault JP, Sabido O, Oriol P,
Roubi N, Vasselon C, Archimbaud E, Magaud JP and Guyotat D: High
expression of bcl-2 protein in acute myeloid leukemia cells is
associated with poor response to chemotherapy. Blood. 81:3091–3096.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Konopleva M, Konoplev S, Hu W, Zaritskey
AY, Afanasiev BV and Andreeff M: Stromal cells prevent apoptosis of
AML cells by up-regulation of anti-apoptotic proteins. Leukemia.
16:1713–1724. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Matsunaga T, Takemoto N, Sato T, Takimoto
R, Tanaka I, Fujimi A, Akiyama T, Kuroda H, Kawano Y, Kobune M, et
al: Interaction between leukemic-cell VLA-4 and stromal fibronectin
is a decisive factor for minimal residual disease of acute
myelogenous leukemia. Nat Med. 9:1158–1165. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hazlehurst LA, Argilagos RF and Dalton WS:
Beta1 integrin mediated adhesion increases Bim protein degradation
and contributes to drug resistance in leukaemia cells. Br J
Haematol. 136:269–275. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tabe Y, Jin L, Tsutsumi-Ishii Y, Xu Y,
McQueen T, Priebe W, Mills GB, Ohsaka A, Nagaoka I, Andreeff M and
Konopleva M: Activation of integrin-linked kinase is a critical
prosurvival pathway induced in leukemic cells by bone
marrow-derived stromal cells. Cancer Res. 67:684–694. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kojima K, McQueen T, Chen Y, Jacamo R,
Konopleva M, Shinojima N, Shpall E, Huang X and Andreeff M: p53
activation of mesenchymal stromal cells partially abrogates
microenvironment-mediated resistance to FLT3 inhibition in AML
through HIF-1α-mediated down-regulation of CXCL12. Blood.
118:4431–4439. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Roche S, Koegl M and Courtneidge SA: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase alpha is required for DNA synthesis
induced by some, but not all, growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 91:9185–9189. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shivakrupa R, Bernstein A, Watring N and
Linnekin D: Phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase is required for growth
of mast cells expressing the kit catalytic domain mutant. Cancer
Res. 63:4412–4419. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
West KA, Castillo SS and Dennis PA:
Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway and chemotherapeutic resistance.
Drug Resist Updat. 5:234–248. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Martelli AM, Tabellini G, Bortul R,
Tazzari PL, Cappellini A, Billi AM and Cocco L: Involvement of the
phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway in the resistance
to therapeutic treatments of human leukemias. Histol Histopathol.
20:239–252. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Luo J, Manning BD and Cantley LC:
Targeting the PI3K-Akt pathway in human cancer: Rationale and
promise. Cancer Cell. 4:257–262. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou F, Mei H, Wu Q and Jin R: Expression
of histone H2AX phosphorylation and its potential to modulate
adriamycin resistance in K562/A02 cell line. J Huazhong Univ Sci
Technolog Med Sci. 31:154–158. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Daver N, Cortes J, Kantarjian H and
Ravandi F: Acute myeloid leukemia: Advancing clinical trials and
promising therapeutics. Expert Rev Hematol. 9:433–445. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pollyea DA, Stevens BM, Jones CL, Winters
A, Pei S, Minhajuddin M, D'Alessandro A, Culp-Hill R, Riemondy KA,
Gillen AE, et al: Venetoclax with azacitidine disrupts energy
metabolism and targets leukemia stem cells in patients with acute
myeloid leukemia. Net Med. 24:1859–1866. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li H, Li J, Cheng J, Chen X, Zhou L and Li
Z: AML-derived mesenchymal stem cells upregulate CTGF expression
through the BMP pathway and induce K562-ADM fusiform transformation
and chemoresistance. Oncol Rep. 42:1035–1046. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Manda-Handzlik A, Bystrzycka W, Wachowska
M, Sieczkowska S, Stelmaszczyk-Emmel A, Demkow U and Ciepiela O:
The influence of agents differentiating HL-60 cells toward
granulocyte-like cells on their ability to release neutrophil
extracellular traps. Immunol Cell Biol. 96:413–425. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
She M, Niu X, Chen X, Li J, Zhou M, He Y,
Le Y and Guo K: Resistance of leukemic stem-like cells in AML cell
line KG1a to natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Cancer
Lett. 318:173–179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang Y, Kuramitsu Y, Baron B, Kitagawa T,
Tokuda K, Akada J, Maehara SI, Maehara Y and Nakamura K: PI3K
inhibitor LY294002, as opposed to wortmannin, enhances AKT
phosphorylation in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells.
Int J Oncol. 50:606–612. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chiou JT, Lee YC, Huang CH, Shi YJ, Wang
LJ and Chang LS: Autophagic HuR mRNA degradation induces survivin
and MCL1 downregulation in YM155-treated human leukemia cells.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 387:1148572020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu H, Huang M, Ren D, He J, Zhao F, Yi C
and Huang Y: The synergistic effects of low dose fluorouracil and
TRAIL on TRAIL-resistant human gastric adenocarcinoma AGS cells.
Biomed Res Int. 2013:2938742013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xu Q, Simpson SE, Scialla TJ, Bagg A and
Carroll M: Survival of acute myeloid leukemia cells requires PI3
kinase activation. Blood. 102:972–980. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kojima K, Shimanuki M, Shikami M, Samudio
IJ, Ruvolo V, Corn P, Hanaoka N, Konopleva M, Andreeff M and
Nakakuma H: The dual PI3 kinase/mTOR inhibitor PI-103 prevents p53
induction by Mdm2 inhibition but enhances p53-mediated
mitochondrial apoptosis in p53 wild-type AML. Leukemia.
22:1728–1736. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Park S, Chapuis N, Bardet V, Tamburini J,
Gallay N, Willems L, Knight ZA, Shokat KM, Azar N, Viguié F, et al:
PI-103, a dual inhibitor of Class IA phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase
and mTOR, has antileukemic activity in AML. Leukemia. 22:1698–1706.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen W, Drakos E, Grammatikakis I,
Schlette EJ, Li J, Leventaki V, Staikou-Drakopoulou E, Patsouris E,
Panayiotidis P, Medeiros LJ and Rassidakis GZ: mTOR signaling is
activated by FLT3 kinase and promotes survival of FLT3-mutated
acute myeloid leukemia cells. Mol Cancer. 9:2922010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Souers AJ, Leverson JD, Boghaert ER,
Ackler SL, Catron ND, Chen J, Dayton BD, Ding H, Enschede SH,
Fairbrother WJ, et al: ABT-199, a potent and selective BCL-2
inhibitor, achieves antitumor activity while sparing platelets. Nat
Med. 19:202–208. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Phase I study of ABT-199 (GDC-0199) in
patients with relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma, . Responses
observed in diffuse large B-cell (DLBCL) and follicular lymphoma
(FL) at higher cohort doses. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 12((8 Suppl
16)): S18–S19. 2014.
|
|
48
|
Roberts AW, Davids MS, Pagel JM, Kahl BS,
Puvvada SD, Gerecitano JF, Kipps TJ, Anderson MA, Brown JR,
Gressick L, et al: Targeting BCL2 with venetoclax in relapsed
chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 374:311–322. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nii T, Prabhu VV, Ruvolo V, Madhukar N,
Zhao R, Mu H, Heese L, Nishida Y, Kojima K, Garnett MJ, et al:
Imipridone ONC212 activates orphan G protein-coupled receptor
GPR132 and integrated stress response in acute myeloid leukemia.
Leukemia. 33:2805–2816. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chen JY, Wang MC and Hung WC:
Bcr-Abl-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of Emi1 to stabilize Skp2
protein via inhibition of ubiquitination in chronic myeloid
leukemia cells. J Cell Physiol. 226:407–413. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sabri S, Keyhani M and Akbari MT: Whole
exome sequencing of chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Iran J
Public Health. 45:346–352. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yue ZX, Gao RQ, Gao C, Liu SG, Zhao XX,
Xing TY, Niu J, Li ZG, Zheng HY and Ding W: The prognostic
potential of coilin in association with p27 expression in pediatric
acute lymphoblastic leukemia for disease relapse. Cancer Cell Int.
18:1062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Haferlach C, Bacher U, Kohlmann A,
Schindela S, Alpermann T, Kern W, Schnittger S and Haferlach T:
CDKN1B, encoding the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (p27), is
located in the minimally deleted region of 12p abnormalities in
myeloid malignancies and its low expression is a favorable
prognostic marker in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica.
96:829–836. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Fasihi-Ramandi M, Moridnia A, Najafi A and
Sharifi M: Inducing apoptosis and decreasing cell proliferation in
human acute promyelocytic leukemia through regulation expression of
CASP3 by Let-7a-5p blockage. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus.
34:70–77. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Marsden VS, O'Connor L, O'Reilly LA, Silke
J, Metcalf D, Ekert PG, Huang DCS, Cecconi F, Kuida K, Tomaselli
KJ, et al: Apoptosis initiated by Bcl-2-regulated caspase
activation independently of the cytochrome c/Apaf-1/caspase-9
apoptosome. Nature. 419:634–637. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Endo A, Tomizawa D, Aoki Y, Morio T,
Mizutani S and Takagi M: EWSR1/ELF5 induces acute myeloid leukemia
by inhibiting p53/p21 pathway. Cancer Sci. 107:1745–1754. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cahan P and Graubert TA: Integrated
genomics of susceptibility to alkylator-induced leukemia in mice.
BMC Genomics. 11:6382010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|