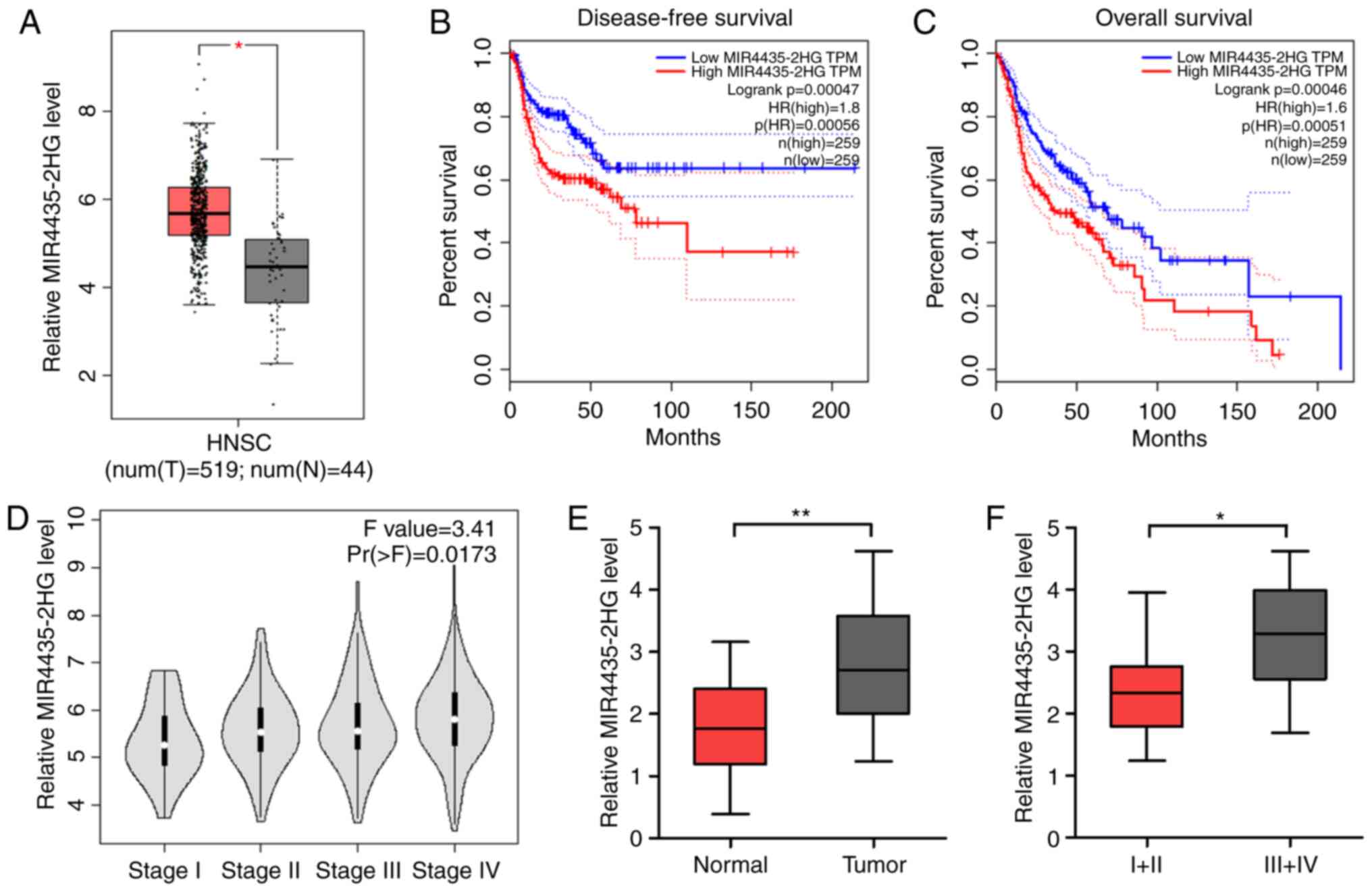
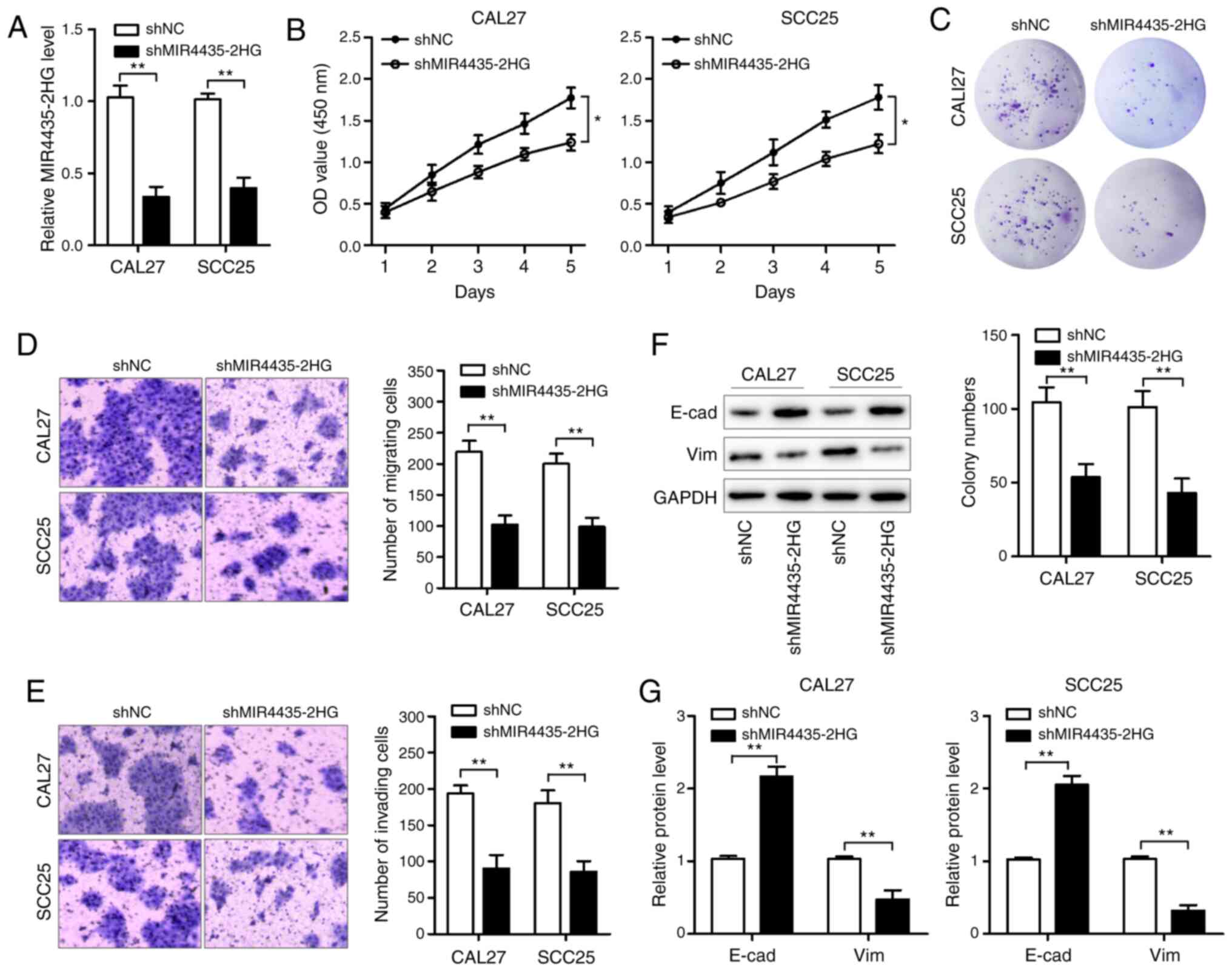
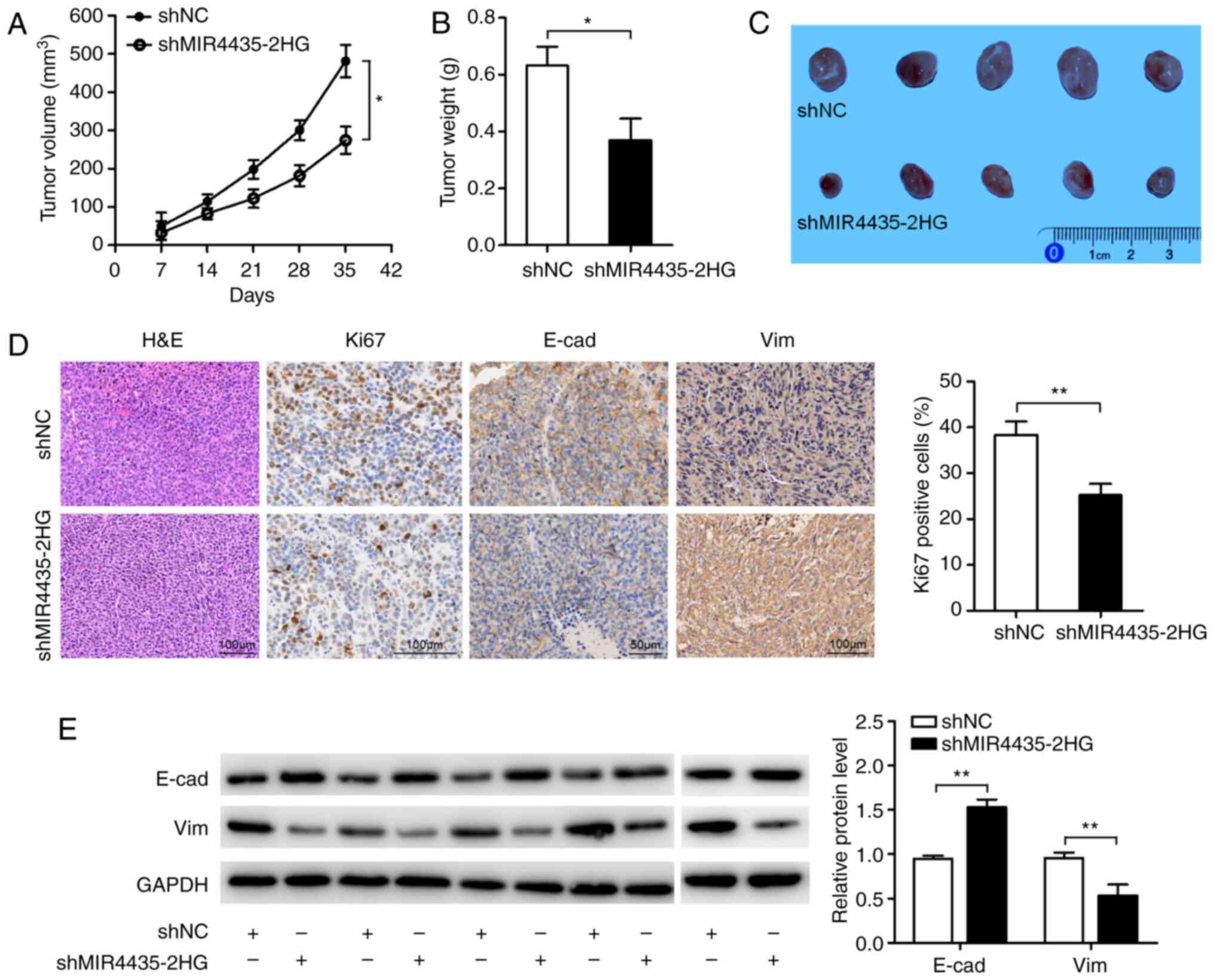
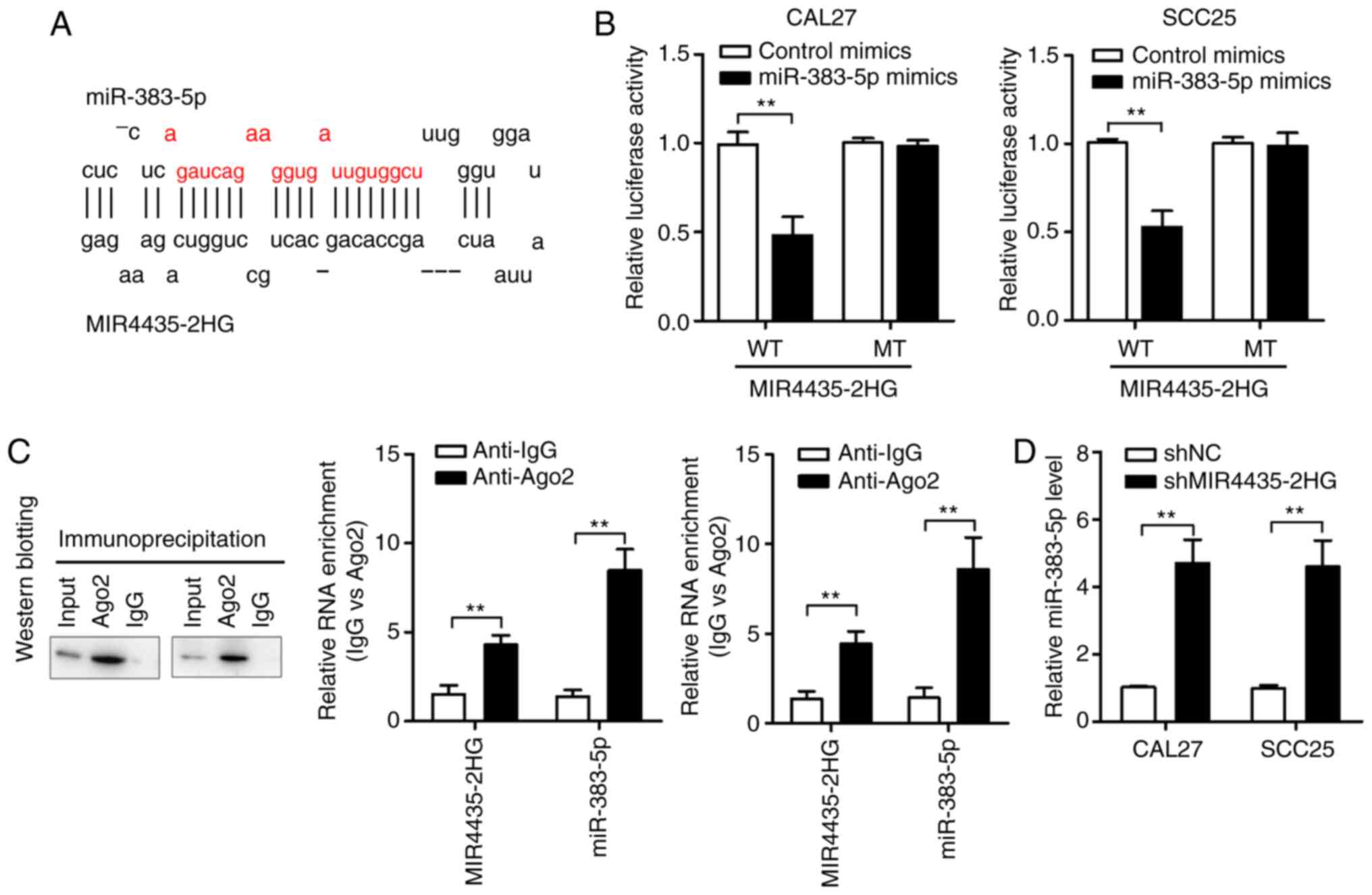
|
1
|
Rothenberg SM and Ellisen LW: The
molecular pathogenesis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J
Clin Invest. 122:1951–1957. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tuttle TR, Mierzwa ML, Wells SI, Fox SR
and Ben-Jonathan N: The cyclic GMP/protein kinase G pathway as a
therapeutic target in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer
Lett. 370:279–285. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ and Brakenhoff
RH: The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:9–22. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lan T, Ma W, Hong Z, Wu L, Chen X and Yuan
Y: Long non-coding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 12 (SNHG12)
promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis by targeting miR-199a/b-5p in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:112017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu S, Zhang J, Yin L, Wang X, Zheng Y,
Zhang Y, Gu J, Yang L, Yang J, Zheng P, et al: The lncRNA RUNX1-IT1
regulates C-FOS transcription by interacting with RUNX1 in the
process of pancreatic cancer proliferation, migration and invasion.
Cell Death Dis. 11:4122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhong J, Tu X, Kong Y, Guo L, Li B, Zhong
W, Cheng Y, Jiang Y and Jiang Q: LncRNA H19 promotes odontoblastic
differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells by regulating
miR-140-5p and BMP-2/FGF9. Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:2022020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Q, Wu J, Huang H, Jiang Y, Huang Y,
Fang H, Zheng G, Zhou X, Wu Y, Lei C and Hu D: lncRNA LIFR-AS1
suppresses invasion and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer
via the miR-942-5p/ZNF471 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 20:1802020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ban Y, Tan P, Cai J, Li J, Hu M, Zhou Y,
Mei Y, Tan Y, Li X, Zeng Z, et al: LNCAROD is stabilized by m6A
methylation and promotes cancer progression via forming a ternary
complex with HSPA1A and YBX1 in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Mol Oncol. 14:1282–1296. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xie X, Xiong G, Wang Q, Ge Y and Cui X:
Long non-coding RNA LINC00460 promotes head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma cell progression by sponging miR-612 to up-regulate AKT2.
Am J Transl Res. 11:6326–6340. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang H, Wu M, Lu Y, He K, Cai X, Yu X, Lu
J and Teng L: LncRNA MIR4435-2HG targets desmoplakin and promotes
growth and metastasis of gastric cancer by activating Wnt/β-catenin
signaling. Aging (Albany NY). 11:6657–6673. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu L, Wang A, Gao M, Duan X and Li Z:
LncRNA MIR4435-2HG triggers ovarian cancer progression by
regulating miR-128-3p/CKD14 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 20:1452020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu H, Zhang B, Yang Y, Li Z, Zhao P, Wu W,
Zhang H and Mao J: LncRNA MIR4435-2HG potentiates the proliferation
and invasion of glioblastoma cells via modulating
miR-1224-5p/TGFBR2 axis. J Cell Mol Med. 24:6362–6372. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dong X, Yang Z, Yang H, Li D and Qiu X:
Long non-coding RNA MIR4435-2HG promotes colorectal cancer
proliferation and metastasis through miR-206/YAP1 Axis. Front
Oncol. 10:1602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang S, Li C, Liu J, Geng F, Shi X, Li Q,
Lu Z and Pan Y: Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transiton through regulation of the lncRNA
MIR4435-2HG/miR-296-5p/Akt2/SNAI1 signaling pathway. FEBS J.
287:4032–4047. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang M, He X, Huang X, Wang J, He Y and
Wei L: LncRNA MIR4435-2HG-mediated upregulation of TGF-β1 promotes
migration and proliferation of nonsmall cell lung cancer cells.
Environ Toxicol. 35:582–590. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen Y and Wang X: miRDB: An online
database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic
Acids Res. 48:D127–D131. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:e050052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Foki E, Stanisz I, Kadletz L, Kotowski U,
Seemann R, Schmid R and Heiduschka G: HS-173, a selective PI3K
inhibitor, induces cell death in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma cell lines. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 133:26–31. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Khalil A and Jameson MJ: Downregulation of
IGF1R expression inhibits growth and enhances cisplatin sensitivity
of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells in vitro. Horm
Cancer. 10:11–23. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li SJ, Yang XN and Qian HY: Antitumor
effects of WNT2B silencing in GLUT1 overexpressing cisplatin
resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res.
5:300–308. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhuang Z, Yu P, Xie N, Wu Y, Liu H, Zhang
M, Tao Y, Wang W, Yin H, Zou B, et al: MicroRNA-204-5p is a tumor
suppressor and potential therapeutic target in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Theranostics. 10:1433–1453. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang Y, Cao W, Wu K, Qin X, Wang X, Li Y,
Yu B, Zhang Z, Wang X, Yan M, et al: LncRNA LINC00460 promotes EMT
in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by facilitating
peroxiredoxin-1 into the nucleus. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
38:3652019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu Y, Wang Y, Diao P, Zhang W, Li J, Ge H,
Song Y, Li Z, Wang D, Liu L, et al: Therapeutic targeting of BRD4
in head neck squamous cell carcinoma. Theranostics. 9:1777–1793.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kong Q, Liang C, Jin Y, Pan Y, Tong D,
Kong Q and Zhou J: The lncRNA MIR4435-2HG is upregulated in
hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cancer cell proliferation by
upregulating miRNA-487a. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 24:262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Galle E, Thienpont B, Cappuyns S, Venken
T, Busschaert P, Van Haele M, Van Cutsem E, Roskams T, van Pelt J,
Verslype C, et al: DNA methylation-driven EMT is a common mechanism
of resistance to various therapeutic agents in cancer. Clin
Epigenetics. 12:272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hong H, Sui C, Qian T, Xu X, Zhu X, Fei Q,
Yang J and Xu M: Long noncoding RNA LINC00460 conduces to tumor
growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through
miR-342-3p-dependent AGR2 up-regulation. Aging (Albany NY).
12:10544–10555. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yan K, Hou L, Liu T, Jiao W, Ma Q, Fang Z,
Zhang S, Song D, Liu J, Gao X and Fan Y: lncRNA OGFRP1 functions as
a ceRNA to promote the progression of prostate cancer by regulating
SARM1 level via miR-124-3p. Aging (Albany NY). 12:8880–8892. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu HT, Ma RR, Lv BB, Zhang H, Shi DB, Guo
XY, Zhang GH and Gao P: LncRNA-HNF1A-AS1 functions as a competing
endogenous RNA to activate PI3K/AKT signalling pathway by sponging
miR-30b-3p in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 122:1825–1836. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tian Y, Xia S, Ma M and Zuo Y: LINC00096
promotes the proliferation and invasion by sponging miR-383-5p and
regulating RBM3 expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Onco
Targets Ther. 12:10569–10578. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jiang J, Xie C, Liu Y, Shi Q and Chen Y:
Up-regulation of miR-383-5p suppresses proliferation and enhances
chemosensitivity in ovarian cancer cells by targeting TRIM27.
Biomed Pharmacother. 109:595–601. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wei C and Gao JJ: Downregulated miR-383-5p
contributes to the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer
cells and is associated with poor prognosis. PeerJ. 7:e78822019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gao G, Shi X, Long Y, Yao Z, Shen J and
Shen L: The prognostic and clinicopathological significance of RBM3
in the survival of patients with tumor: A Prisma-compliant
meta-analysis. Medicine. 99:e200022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dong W, Dai ZH, Liu FC, Guo XG, Ge CM,
Ding J, Liu H and Yang F: The RNA-binding protein RBM3 promotes
cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating
circular RNA SCD-circRNA 2 production. EBioMedicine. 45:155–167.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen P, Yue X, Xiong H, Lu X and Ji Z:
RBM3 upregulates ARPC2 by binding the 3′UTR and contributes to
breast cancer progression. Int J Oncol. 54:1387–1397.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fuentes-Fayos AC, Vazquez-Borrego MC,
Jimenez-Vacas JM, Bejarano L, Pedraza-Arévalo S, L-López F,
Blanco-Acevedo C, Sánchez-Sánchez R, Reyes O, Ventura S, et al:
Splicing machinery dysregulation drives glioblastoma
development/aggressiveness: Oncogenic role of SRSF3. Brain.
143:3273–3293. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Melling N, Bachmann K, Hofmann B, El
Gammal AT, Reeh M, Mann O, Moebius C, Blessmann M, Izbicki JR and
Grupp K: Prevalence and clinical significance of RBM3
immunostaining in non-small cell lung cancers. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 145:873–879. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Boman K, Segersten U, Ahlgren G, Eberhard
J, Uhlén M, Jirström K and Malmström PU: Decreased expression of
RNA-binding motif protein 3 correlates with tumour progression and
poor prognosis in urothelial bladder cancer. BMC Urol. 13:172013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|