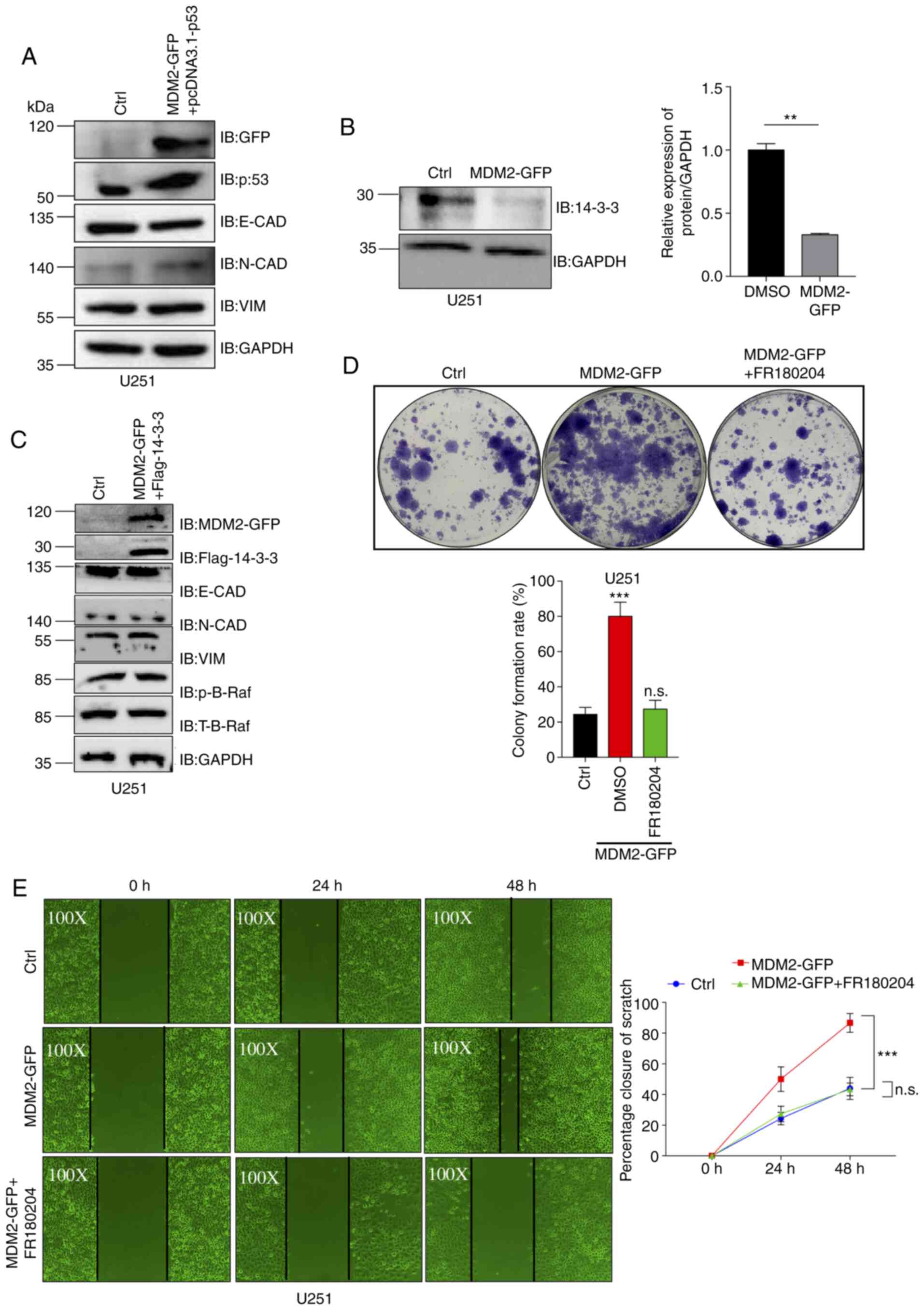
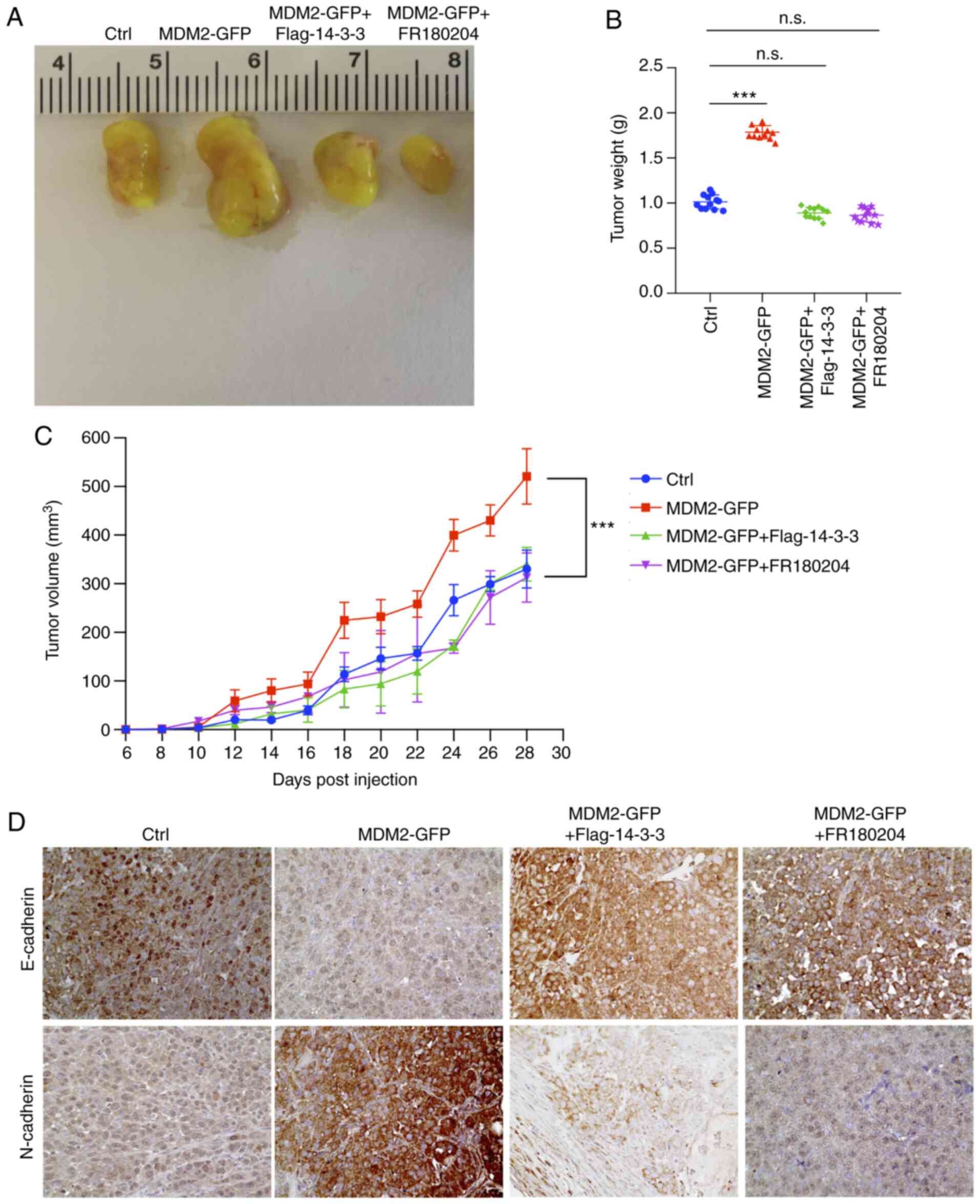
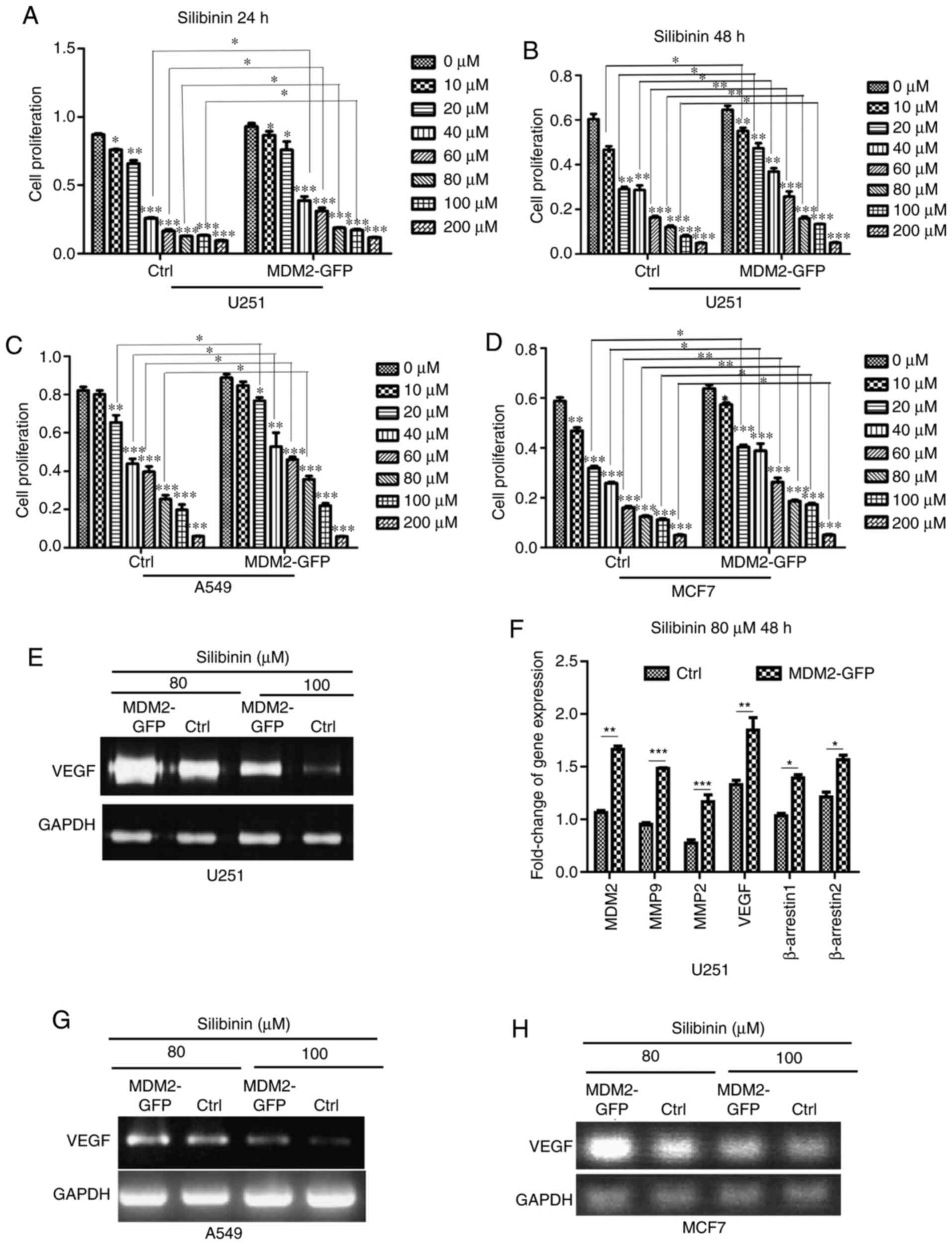
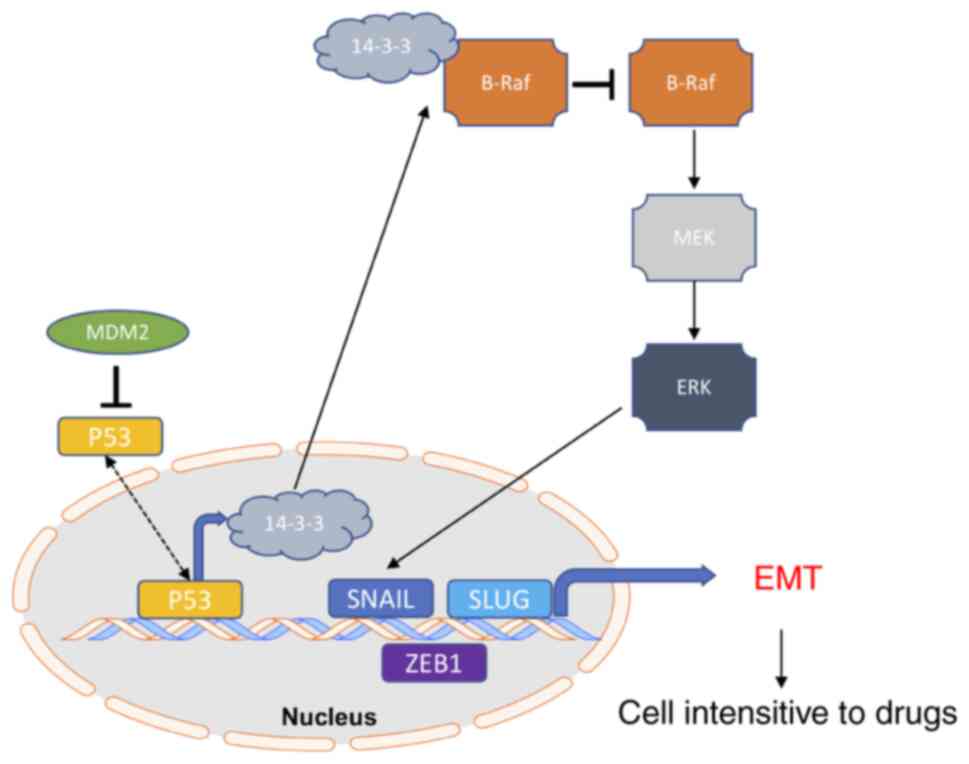
|
1
|
Fakharzadeh SS, Trusko SP and George DL:
Tumorigenic potential associated with enhanced expression of a gene
that is amplified in a mouse tumor cell line. EMBO J. 10:1565–1569.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xia YZ, Yang L, Xue GM, Zhang C, Guo C,
Yang YW, Li SS, Zhang LY, Guo QL and Kong LY: Combining GRP78
suppression and MK2206-induced Akt inhibition decreases
doxorubicin-induced P-glycoprotein expression and mitigates
chemoresistance in human osteosarcoma. Oncotarget. 7:56371–56382.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A and Oren M: Mdm2
promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature. 387:296–299. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Momand J, Zambetti GP, Olson DC, George D
and Levine AJ: The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the
p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell.
69:1237–1245. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jung CR, Lim JH, Choi Y, Kim DG, Kang KJ,
Noh SM and Im DS: Enigma negatively regulates p53 through MDM2 and
promotes tumor cell survival in mice. J Clin Invest. 120:4493–4506.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in cancer onset and progression. Bull Acad Natl Med.
193:1969–1979. 2009.(In French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Iwakuma T and Agarwal N: MDM2 binding
protein, a novel metastasis suppressor. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
31:633–640. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang SP, Wang WL, Chang YL, Wu CT, Chao
YC, Kao SH, Yuan A, Lin CW, Yang SC, Chan WK, et al: p53 controls
cancer cell invasion by inducing the MDM2-mediated degradation of
Slug. Nat Cell Biol. 11:694–704. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Osborne JK, Zaganjor E and Cobb MH: Signal
control through Raf: In sickness and in health. Cell Res. 22:14–22.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stephen AG, Esposito D, Bagni RK and
McCormick F: Dragging ras back in the ring. Cancer Cell.
25:272–281. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Min L, He B and Hui L: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases in hepatocellular carcinoma development. Semin
Cancer Biol. 21:10–20. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tzivion G, Gupta VS, Kaplun L and Balan V:
14-3-3 proteins as potential oncogenes. Semin Cancer Biol.
16:203–213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang J and Zhou Y: 14-3-3 Proteins in
glutamatergic synapses. Neural Plast. 2018:84076092018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vergroesen PP, Kingma I, Emanuel KS,
Hoogendoorn RJ, Welting TJ, van Royen BJ, van Dieën JH and Smit TH:
Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: A
vicious circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 23:1057–1070. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stevers LM, Sijbesma E, Botta M,
MacKintosh C, Obsil T, Landrieu I, Cau Y, Wilson AJ, Karawajczyk A,
Eickhoff J, et al: Modulators of 14-3-3 protein-protein
interactions. J Med Chem. 61:3755–3778. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park E, Rawson S, Li K, Kim BW, Ficarro
SB, Pino GG, Sharif H, Marto JA, Jeon H and Eck MJ: Architecture of
autoinhibited and active BRAF-MEK1-14-3-3 complexes. Nature.
575:545–550. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aitken A: 14-3-3 proteins: A historic
overview. Semin Cancer Biol. 16:162–172. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li X, Wang QJ, Pan N, Lee S, Zhao Y, Chait
BT and Yue Z: Phosphorylation-dependent 14-3-3 binding to LRRK2 is
impaired by common mutations of familial Parkinson's disease. PLoS
One. 6:e171532011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nichols RJ, Dzamko N, Morrice NA, Campbell
DG, Deak M, Ordureau A, Macartney T, Tong Y, Shen J, Prescott AR
and Alessi DR: 14-3-3 binding to LRRK2 is disrupted by multiple
Parkinson's disease-associated mutations and regulates cytoplasmic
localization. Biochem J. 430:393–404. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kilani RT, Maksymowych WP, Aitken A, Boire
G, St-Pierre Y, Li Y and Ghahary A: Detection of high levels of 2
specific isoforms of 14-3-3 proteins in synovial fluid from
patients with joint inflammation. J Rheumatol. 34:1650–1657.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Neal CL and Yu D: 14-3-3ζ as a prognostic
marker and therapeutic target for cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
14:1343–1354. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lamba S, Ravichandran V and Major EO:
Glial cell type-specific subcellular localization of 14-3-3 zeta:
An implication for JCV tropism. Glia. 57:971–977. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kelly MN, Johnston DA, Peel BA, Morgan TW,
Palmer GE and Sturtevant JE: Bmh1p (14-3-3) mediates pathways
associated with virulence in Candida albicans. Microbiology
(Reading). 155:1536–1546. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Halbach T, Scheer N and Werr W:
Transcriptional activation by the PHD finger is inhibited through
an adjacent leucine zipper that binds 14-3-3 proteins. Nucleic
Acids Res. 28:3542–3550. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ritt DA, Monson DM, Specht SI and Morrison
DK: Impact of feedback phosphorylation and Raf heterodimerization
on normal and mutant B-Raf signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 30:806–819.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tzivion G and Avruch J: 14-3-3 proteins:
Active cofactors in cellular regulation by serine/threonine
phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 277:3061–3064. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tzivion G, Luo Z and Avruch J: A dimeric
14-3-3 protein is an essential cofactor for Raf kinase activity.
Nature. 394:88–92. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liau NPD, Wendorff TJ, Quinn JG, Steffek
M, Phung W, Liu P, Tang J, Irudayanathan FJ, Izadi S, Shaw AS, et
al: Negative regulation of RAF kinase activity by ATP is overcome
by 14-3-3-induced dimerization. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 27:134–141.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kondo Y, Ognjenović J, Banerjee S,
Karandur D, Merk A, Kulhanek K, Wong K, Roose JP, Subramaniam S and
Kuriyan J: Cryo-EM structure of a dimeric B-Raf:14-3-3 complex
reveals asymmetry in the active sites of B-Raf kinases. Science.
366:109–115. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ahmed N, Abubaker K, Findlay J and Quinn
M: Epithelial mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell-like
phenotypes facilitate chemoresistance in recurrent ovarian cancer.
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 10:268–278. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang TH, Wang HS and Soong YK:
Paclitaxel-induced cell death: Where the cell cycle and apoptosis
come together. Cancer. 88:2619–2628. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang Q, Huang J, Wu Q, Cai Y, Zhu L, Lu X,
Chen S, Chen C and Wang Z: Acquisition of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition is associated with Skp2 expression in
paclitaxel-resistant breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer.
110:1958–1967. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang P, Liu H, Xia F, Zhang QW, Zhang YY,
Zhao Q, Chao ZH, Jiang ZW and Jiang CC: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition is necessary for acquired resistance to cisplatin and
increases the metastatic potential of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
cells. Int J Mol Med. 33:151–159. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gu MF, Liu LZ, He LJ, Yuan WX, Zhang R,
Luo GY, Xu GL, Zhang HM, Yan CX and Li JJ: Sequential
chemoradiotherapy with gemcitabine and cisplatin for locoregionally
advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 132:215–223. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li QQ, Xu JD, Wang WJ, Cao XX, Chen Q,
Tang F, Chen ZQ, Liu XP and Xu ZD: Twist1-mediated
adriamycin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition relates to
multidrug resistance and invasive potential in breast cancer cells.
Clin Cancer Res. 15:2657–2665. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
McConkey DJ, Choi W, Marquis L, Martin F,
Williams MB, Shah J, Svatek R, Das A, Adam L, Kamat A, et al: Role
of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in drug sensitivity
and metastasis in bladder cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
28:335–344. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li L, Feng J, Chen Y, Li S, Ou M, Sun W
and Tang L: Estradiol shows anti-skin cancer activities through
decreasing MDM2 expression. Oncotarget. 8:8459–8474. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li S, Ma L, Ou M, Feng J, Liao Y, Wang G
and Tang L: A novel inducible lentiviral system for multi-gene
expression with human HSP70 promoter and tetracycline-induced
promoter. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 101:3689–3702. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li S, Song Y, Quach C, Guo H, Jang GB,
Maazi H, Zhao S, Sands NA, Liu Q, In GK, et al: Transcriptional
regulation of autophagy-lysosomal function in BRAF-driven melanoma
progression and chemoresistance. Nat Commun. 10:16932019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Weselling P and Capper D: WHO 2016
classification of gilomas. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 44:139–150.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lu X, Yan C, Huang Y, Shi D, Fu Z, Qiu J
and Yin Y: Mouse double minute 2 (MDM2) upregulates Snail
expression and induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget.
7:37177–37191. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Galvan JA, Zlobec I, Wartenberg M, Lugli
A, Gloor B, Perren A and Karamitopoulou E: Expression of E-cadherin
repressors SNAIL, ZEB1 and ZEB2 by tumour and stromal cells
influences tumour-budding phenotype and suggests heterogeneity of
stromal cells in pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 112:1944–1950.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Schulte J, Weidig M, Balzer P, Richter P,
Franz M, Junker K, Gajda M, Friedrich K, Wunderlich H, Östman A, et
al: Expression of the E-cadherin repressors Snail, Slug and Zeb1 in
urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder: Relation to stromal
fibroblast activation and invasive behaviour of carcinoma cells.
Histochem Cell Biol. 138:847–860. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Weichhart T: mTOR as regulator of
lifespan, aging, and cellular senescence: A Mini-review.
Gerontology. 64:127–134. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bertacchini J, Heidari N, Mediani L,
Capitani S, Shahjahani M, Ahmadzadeh A and Saki N: Targeting
PI3K/AKT/mTOR network for treatment of leukemia. Cell Mol Life Sci.
72:2337–2347. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hermida MA, Dinesh Kumar J and Leslie NR:
GSK3 and its interactions with the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling
network. Adv Biol Regul. 65:5–15. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bollag G, Hirth P, Tsai J, Zhang J,
Ibrahim PN, Cho H, Spevak W, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Habets G, et al:
Clinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor needs broad target blockade in
BRAF-mutant melanoma. Nature. 467:596–599. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Garber K: Cancer research. Melanoma drug
vindicates targeted approach. Science. 326:16192009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
DeSilva DR, Jones EA, Favata MF, Jaffee
BD, Magolda RL, Trzaskos JM and Scherle PA: Inhibition of
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase blocks T cell proliferation
but does not induce or prevent anergy. J Immunol. 160:4175–4181.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Favata MF, Horiuchi KY, Manos EJ, Daulerio
AJ, Stradley DA, Feeser WS, Van Dyk DE, Pitts WJ, Earl RA, Hobbs F,
et al: Identification of a novel inhibitor of mitogen-activated
protein kinase kinase. J Biol Chem. 273:18623–18632. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ohori M, Takeuchi M, Maruki R, Nakajima H
and Miyake H: FR180204, a novel and selective inhibitor of
extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ameliorates collagen-induced
arthritis in mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
374:311–316. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Alexaki VI, Javelaud D, Van Kempen LC,
Mohammad KS, Dennler S, Luciani F, Hoek KS, Juàrez P, Goydos JS,
Fournier PJ, et al: GLI2-mediated melanoma invasion and metastasis.
J Natl Cancer Inst. 102:1148–1159. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Smith JA, Maloney DJ, Hecht SM and
Lannigan DA: Structural basis for the activity of the RSK-specific
inhibitor, SL0101. Bioorg Med Chem. 15:5018–5034. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Smith JA, Maloney DJ, Clark DE, Xu Y,
Hecht SM and Lannigan DA: Influence of rhamnose substituents on the
potency of SL0101, an inhibitor of the Ser/Thr kinase, RSK. Bioorg
Med Chem. 14:6034–6042. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hu W, Feng Z and Levine AJ: The regulation
of multiple p53 stress responses is mediated through MDM2. Genes
Cancer. 3:199–208. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chen DY, Dai DF, Hua Y and Qi WQ: p53
suppresses 14-3-3γ by stimulating proteasome-mediated 14-3-3γ
protein degradation. Int J Oncol. 46:818–824. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Radhakrishnan VM, Putnam CW, Qi W and
Martinez JD: P53 suppresses expression of the 14-3-3γ oncogene. BMC
Cancer. 11:3782011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhang Y, Dube C, Gibert M Jr, Cruickshanks
N, Wang B, Coughlan M, Yang Y, Setiady I, Deveau C, Saoud K, et al:
The p53 pathway in glioblastoma. Cancers. 10:2972018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Singh RP and Agarwal R: Cosmeceuticals and
silibinin. Clin Dermatol. 27:479–484. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cheung CW, Gibbons N, Johnson DW and Nicol
DL: Silibinin-a promising new treatment for cancer. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 10:186–195. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hauck PM, Wolf ER, Olivos DJ III, Batuello
CN, McElyea KC, McAtarsney CP, Cournoyer RM, Sandusky GE and Mayo
LD: Early-stage metastasis requires Mdm2 and Not p53 gain of
function. Mol Cancer Res. 15:1598–1607. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chen Y, Wang DD, Wu YP, Su D, Zhou TY, Gai
RH, Fu YY, Zheng L, He QJ, Zhu H and Yang B: MDM2 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of ovarian cancer
SKOV3 cells. Br J Cancer. 117:1192–1201. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Her NG, Oh JW, Oh YJ, Han S, Cho HJ, Lee
Y, Ryu GH and Nam DH: Potent effect of the MDM2 inhibitor AMG232 on
suppression of glioblastoma stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 9:7922018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Jung CH, Kim J, Park JK, Hwang SG, Moon
SK, Kim WJ and Um HD: Mdm2 increases cellular invasiveness by
binding to and stabilizing the Slug mRNA. Cancer Lett. 335:270–277.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Lionarons DA, Hancock DC, Rana S, East P,
Moore C, Murillo MM, Carvalho J, Spencer-Dene B, Herbert E, Stamp
G, et al: RAC1P29S induces a mesenchymal phenotypic
switch via serum response factor to promote melanoma development
and therapy resistance. Cancer Cell. 36:68–83.e9. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li S, Song Y, Quach C, Nemecio D and Liang
C: Revisiting the role of autophagy in melanoma. Autophagy.
15:1843–1844. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin
MJ, Abeliovich H, Acevedo Arozena A, Adachi H, Adams CM, Adams PD,
Adeli K, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays
for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 12:1–222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Xu Y, Ren J, He X, Chen H, Wei T and Feng
W: YWHA/14-3-3 proteins recognize phosphorylated TFEB by a
noncanonical mode for controlling TFEB cytoplasmic localization.
Autophagy. 15:1017–1030. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhitomirsky B, Yunaev A, Kreiserman R,
Kaplan A, Stark M and Assaraf YG: Lysosomotropic drugs activate
TFEB via lysosomal membrane fluidization and consequent inhibition
of mTORC1 activity. Cell Death Dis. 9:11912018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Nezich CL, Wang C, Fogel AI and Youle RJ:
MiT/TFE transcription factors are activated during mitophagy
downstream of Parkin and Atg5. J Cell Biol. 210:435–450. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Hafner A, Bulyk ML, Jambhekar A and Lahav
G: The multiple mechanisms that regulate p53 activity and cell
fate. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:199–210. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Robin M, Issa AR, Santos CC, Napoletano F,
Petitgas C, Chatelain G, Ruby M, Walter L, Birman S, Domingos PM,
et al: Drosophila p53 integrates the antagonism between autophagy
and apoptosis in response to stress. Autophagy. 15:771–784. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Shibue T and Weinberg RA: EMT, CSCs, and
drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:611–629. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Xu X, Zhang L, He X, Zhang P, Sun C, Xu X,
Lu Y and Li F: TGF-β plays a vital role in triple-negative breast
cancer (TNBC) drug-resistance through regulating stemness, EMT and
apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 502:160–165. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hata AN, Rowley S, Archibald HL,
Gomez-Caraballo M, Siddiqui FM, Ji F, Jung J, Light M, Lee JS,
Debussche L, et al: Synergistic activity and heterogeneous acquired
resistance of combined MDM2 and MEK inhibition in KRAS mutant
cancers. Oncogene. 36:6581–6591. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|