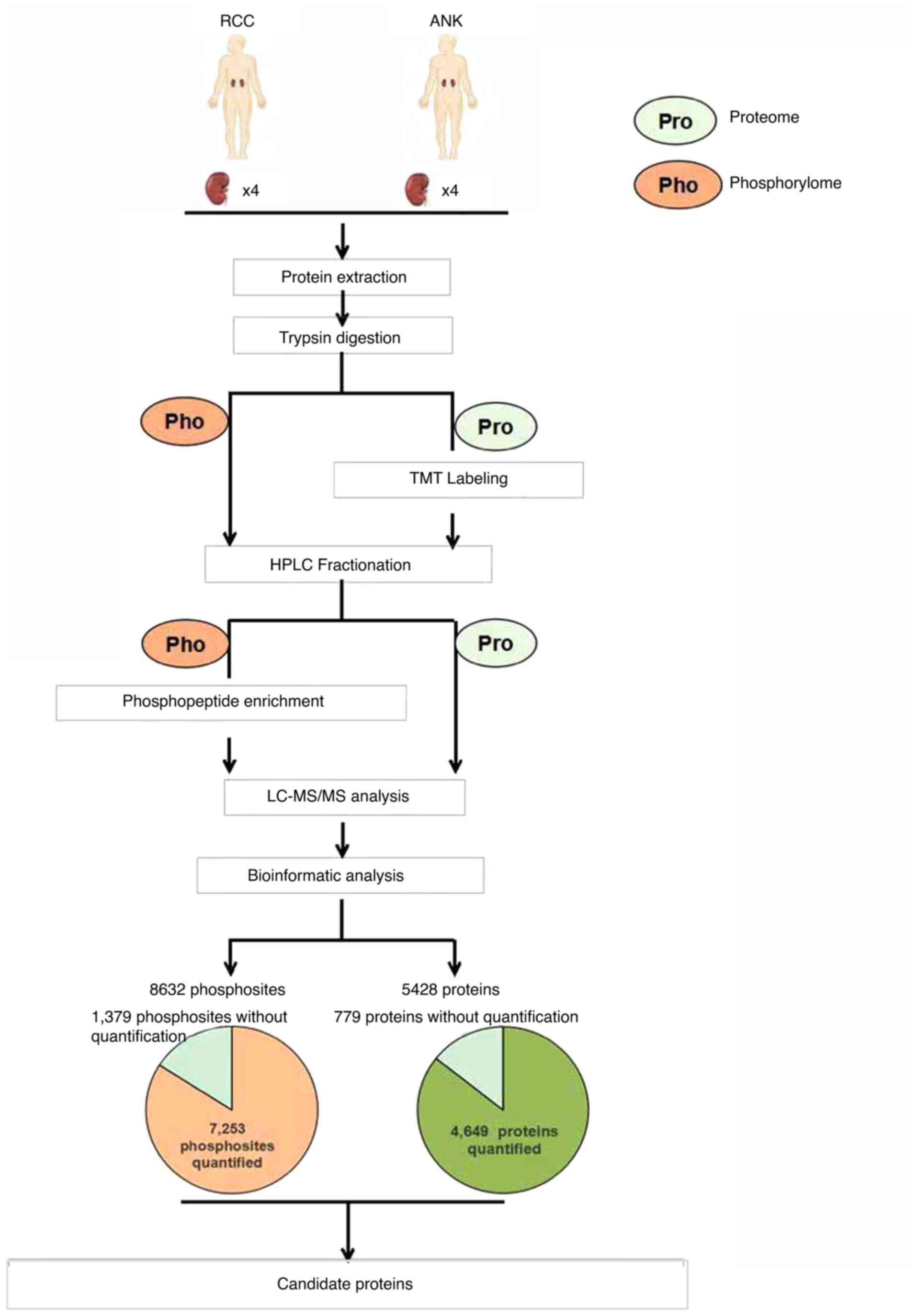
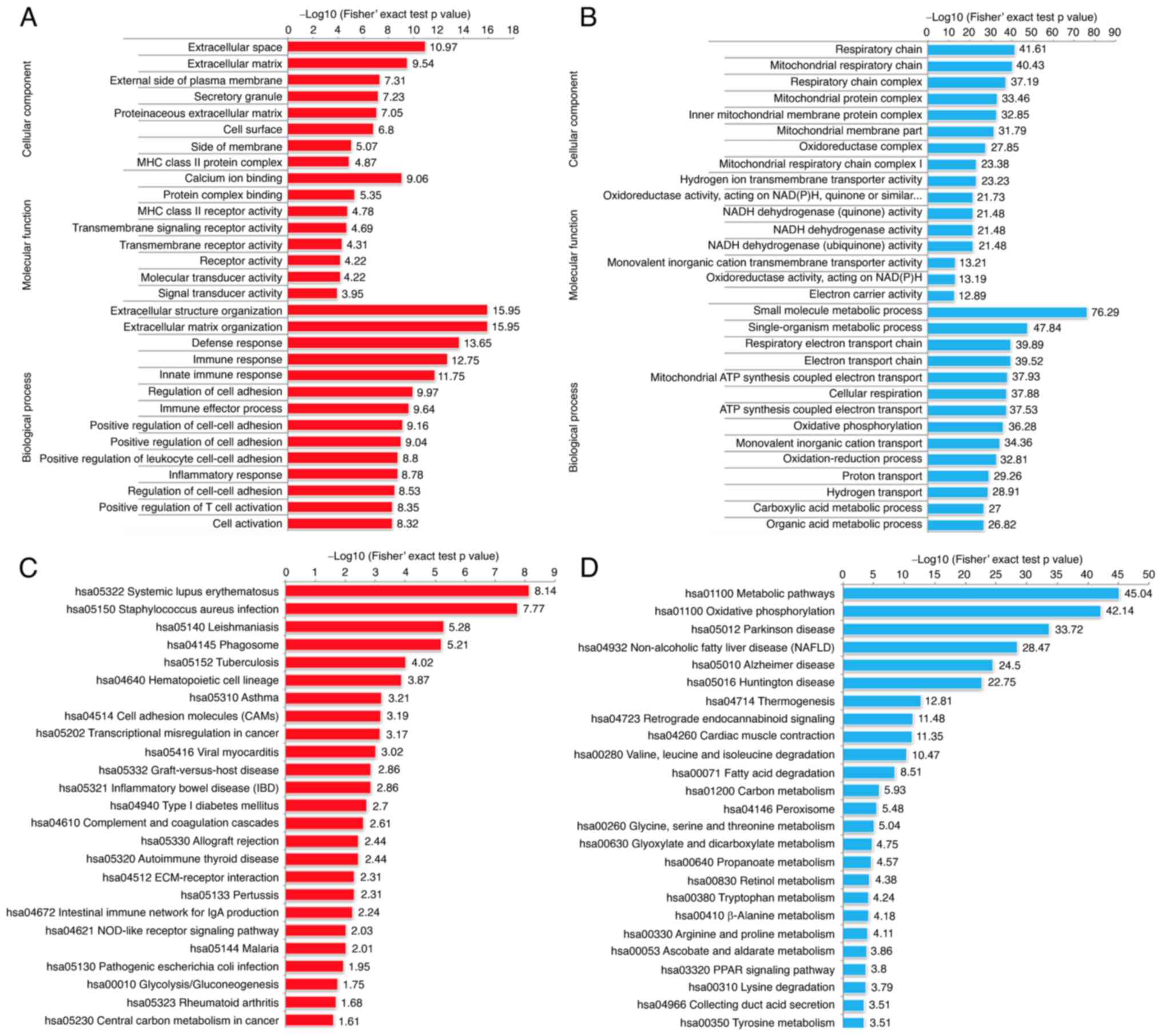
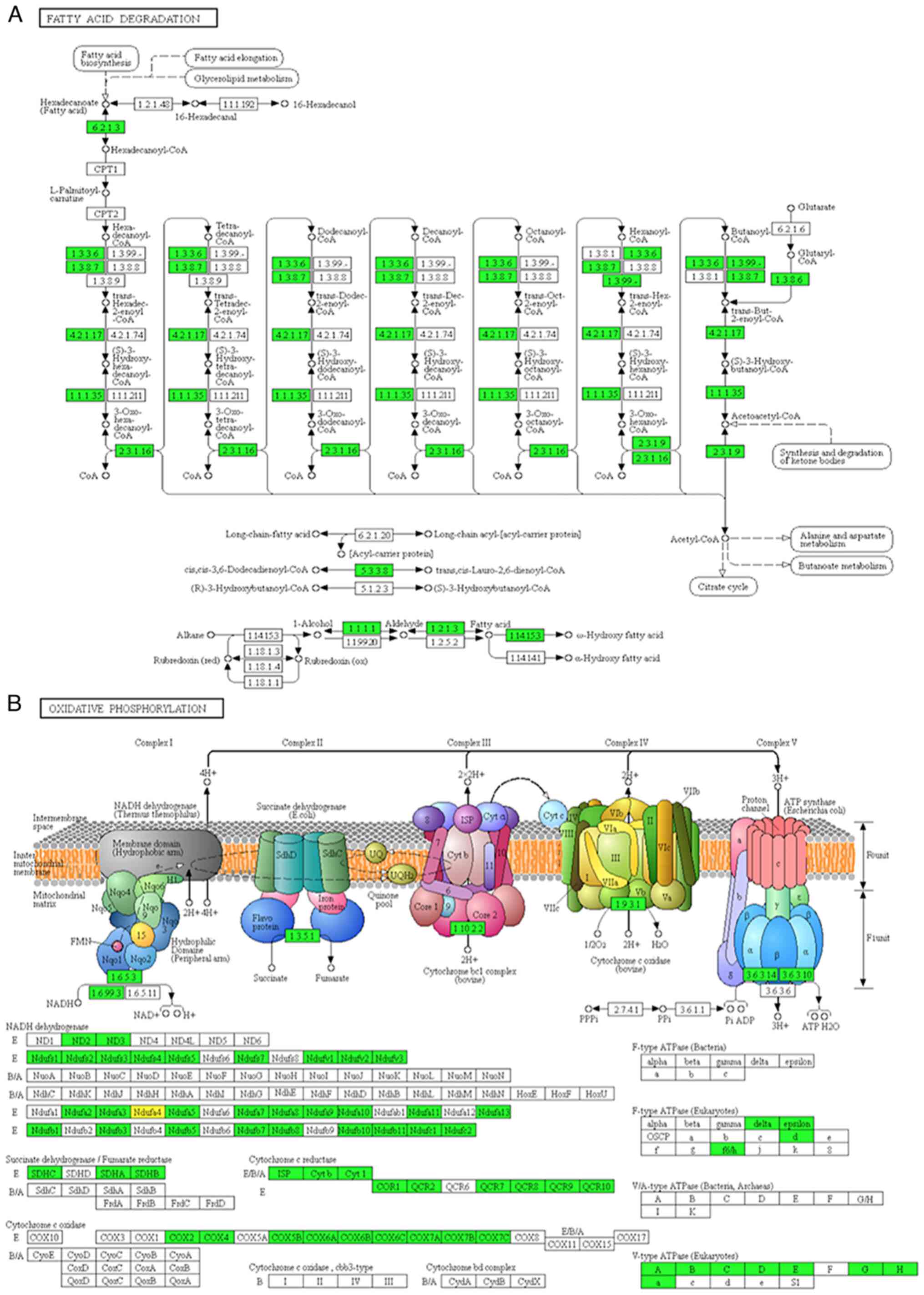
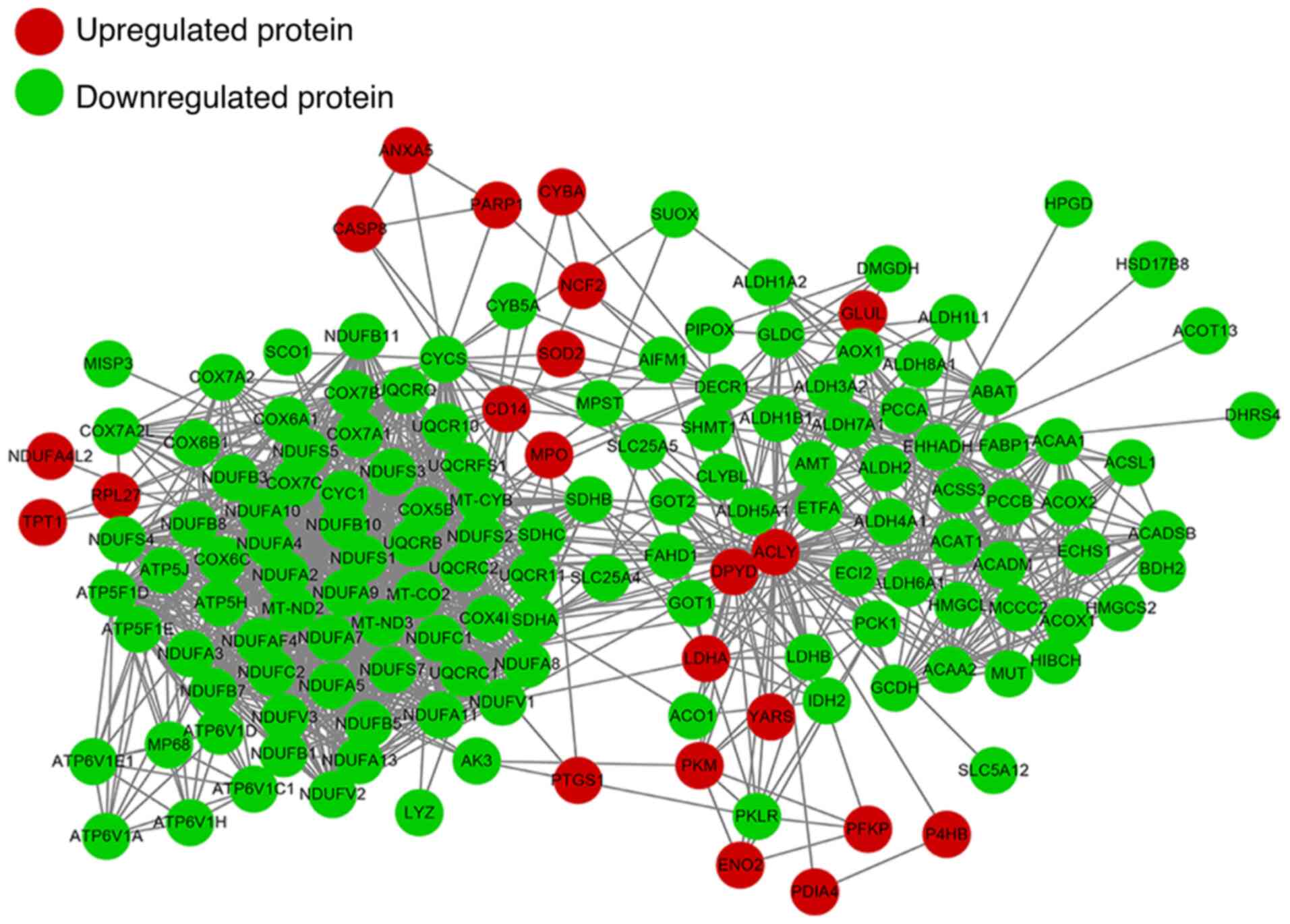
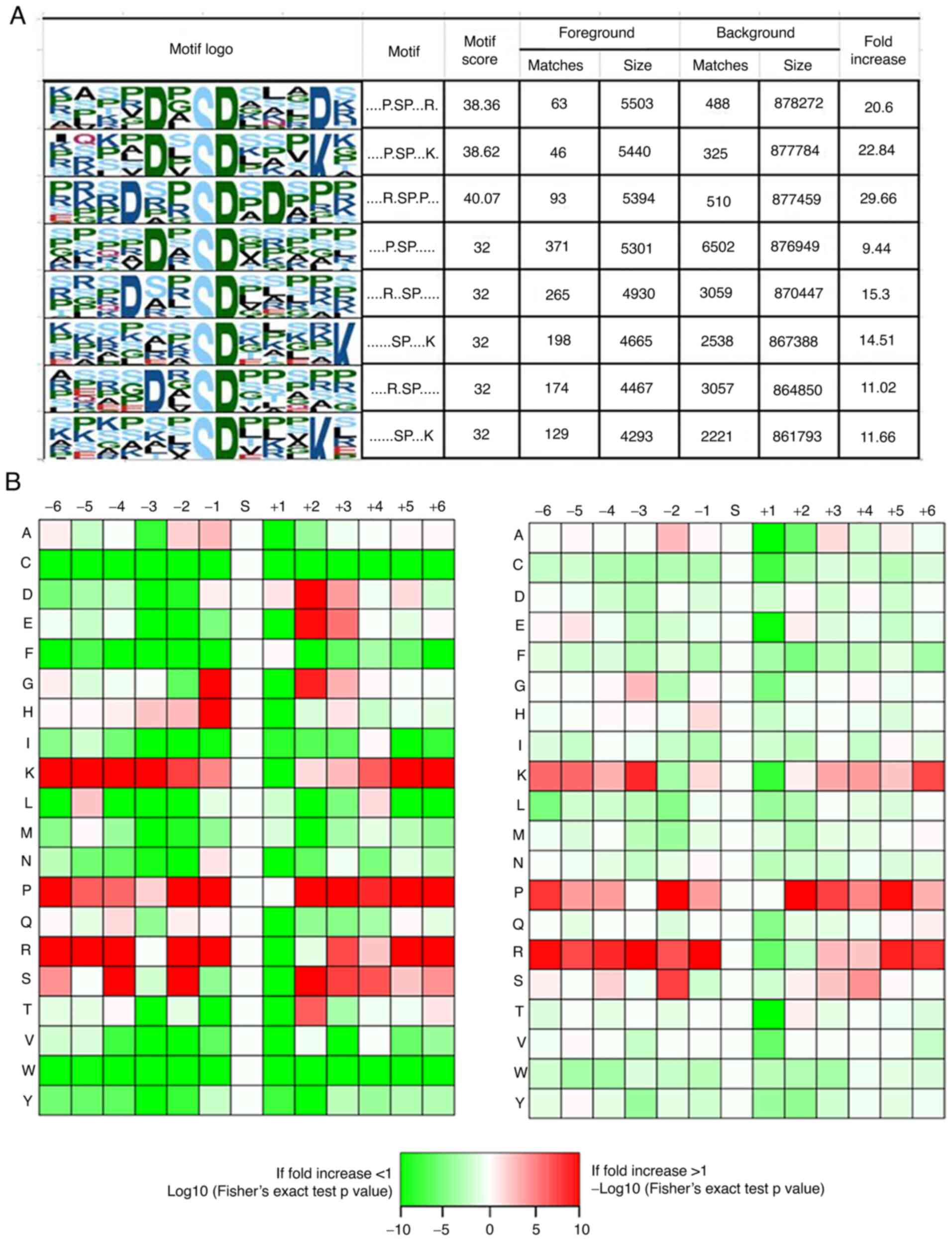
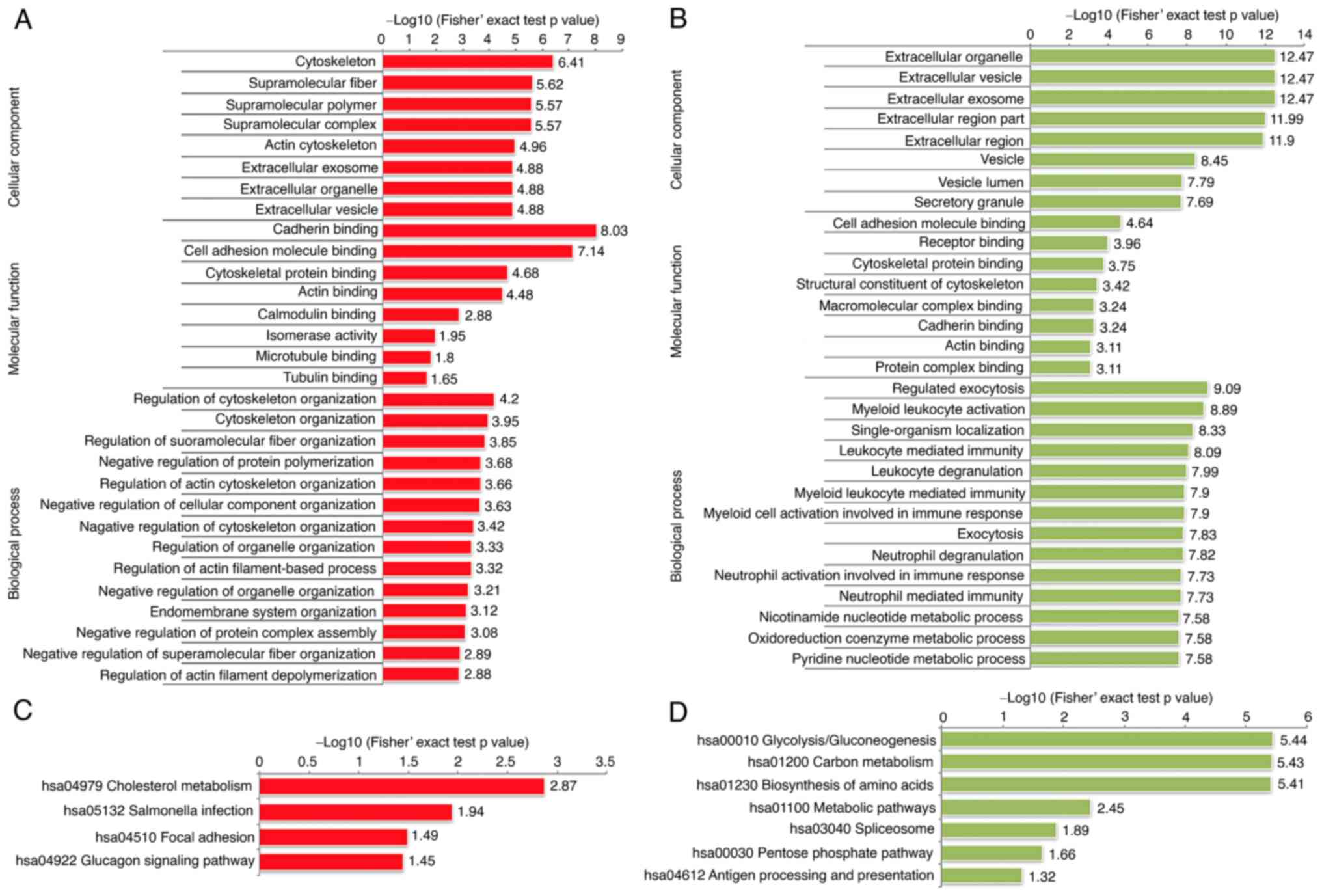
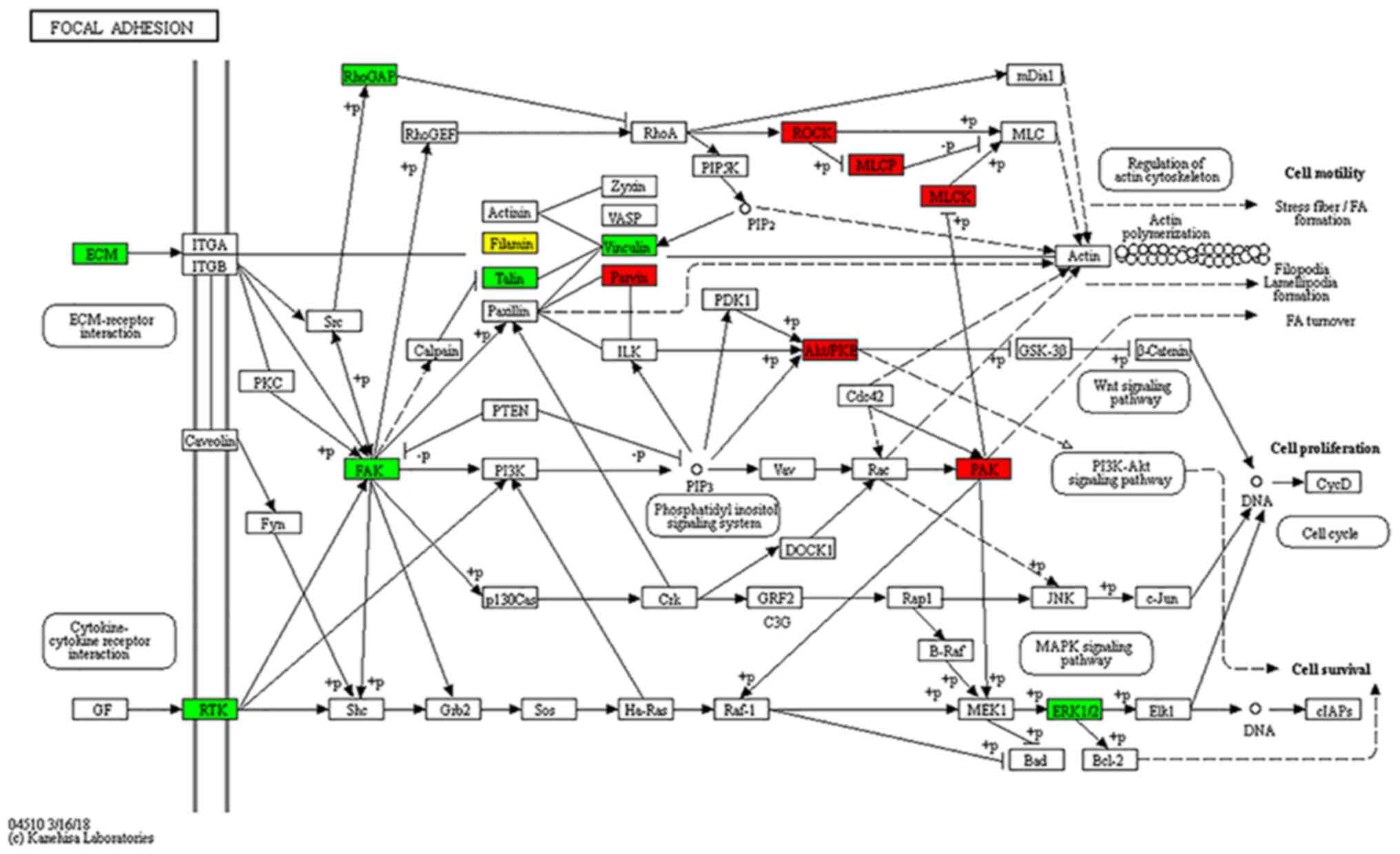
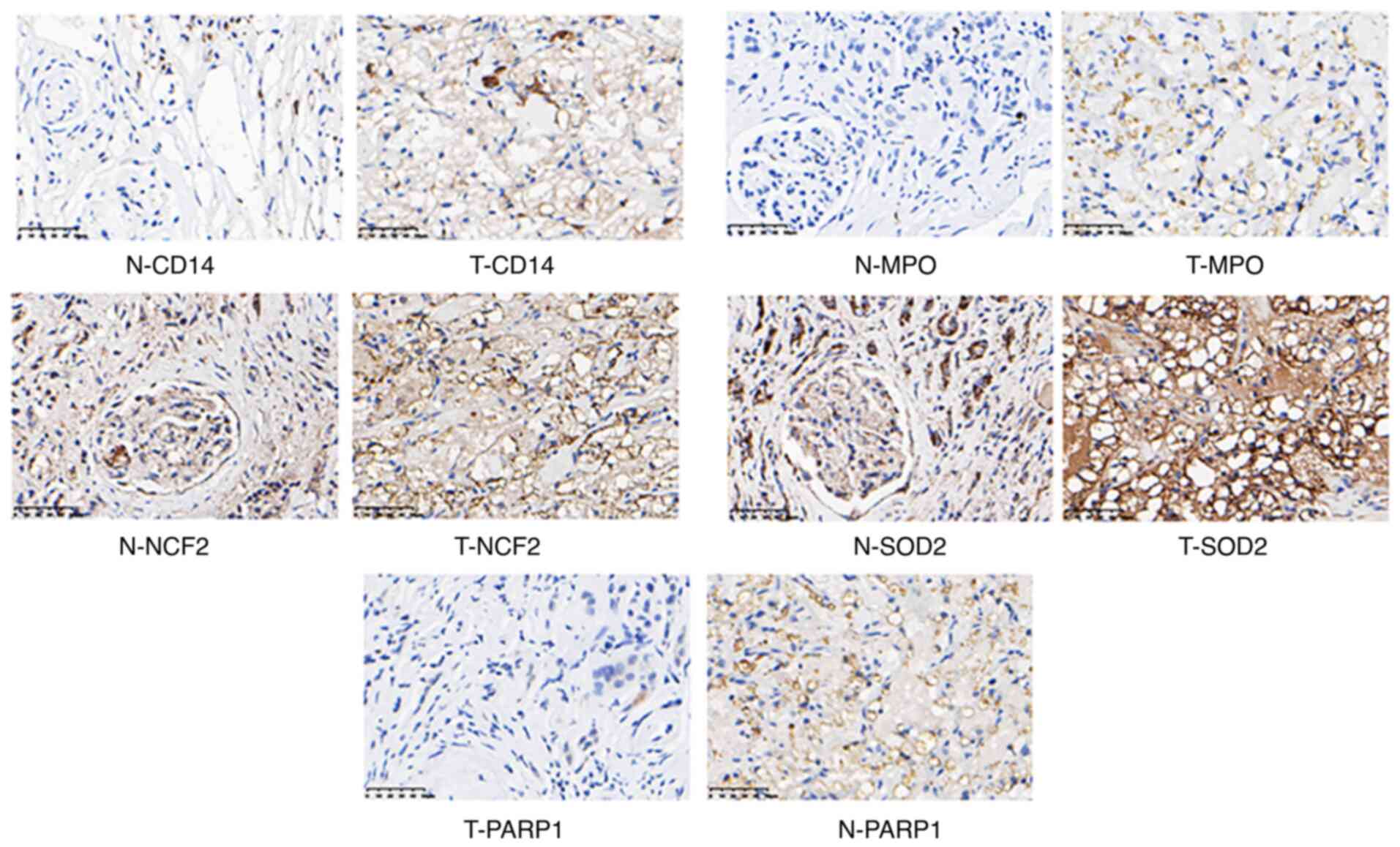
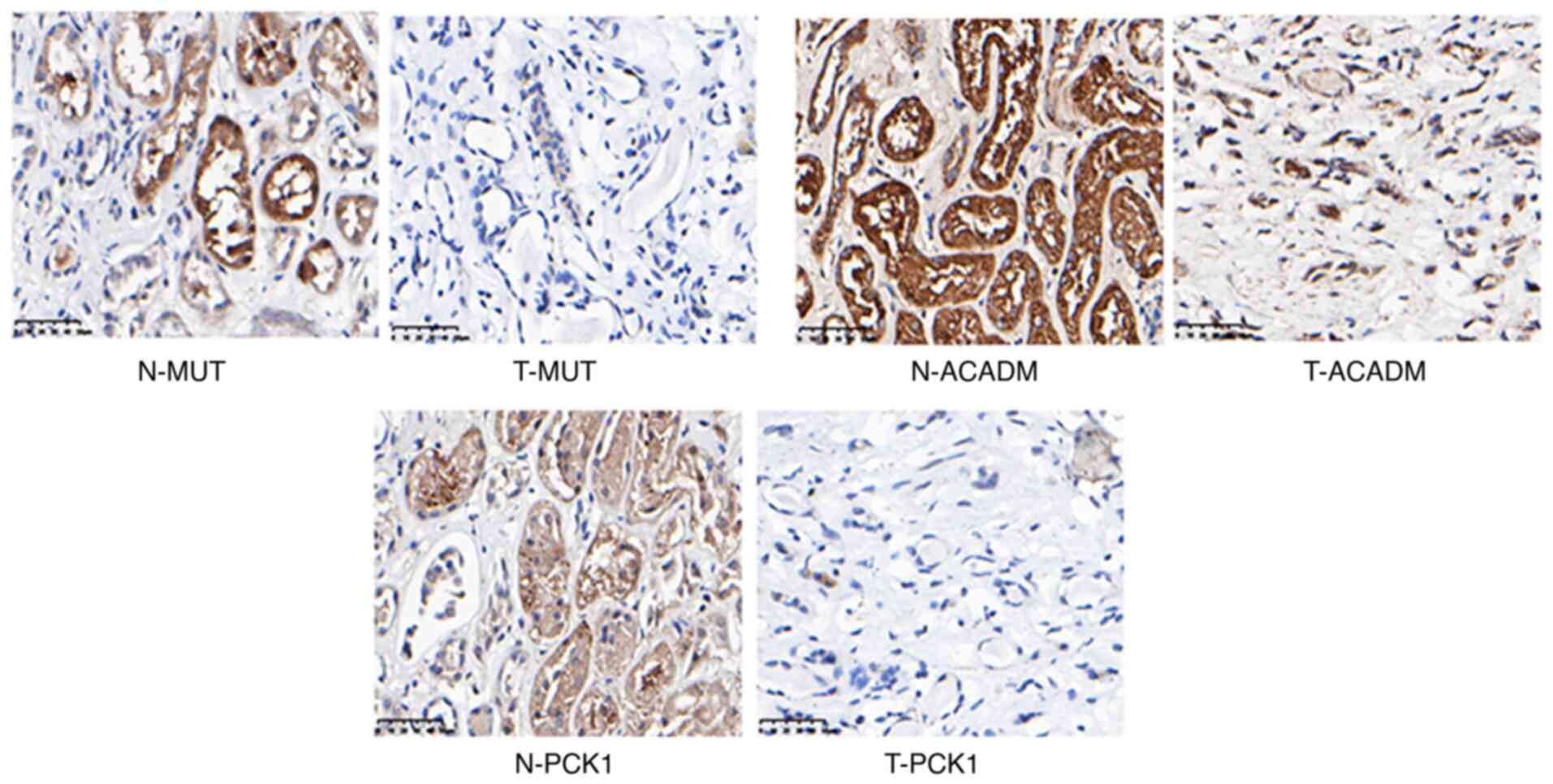
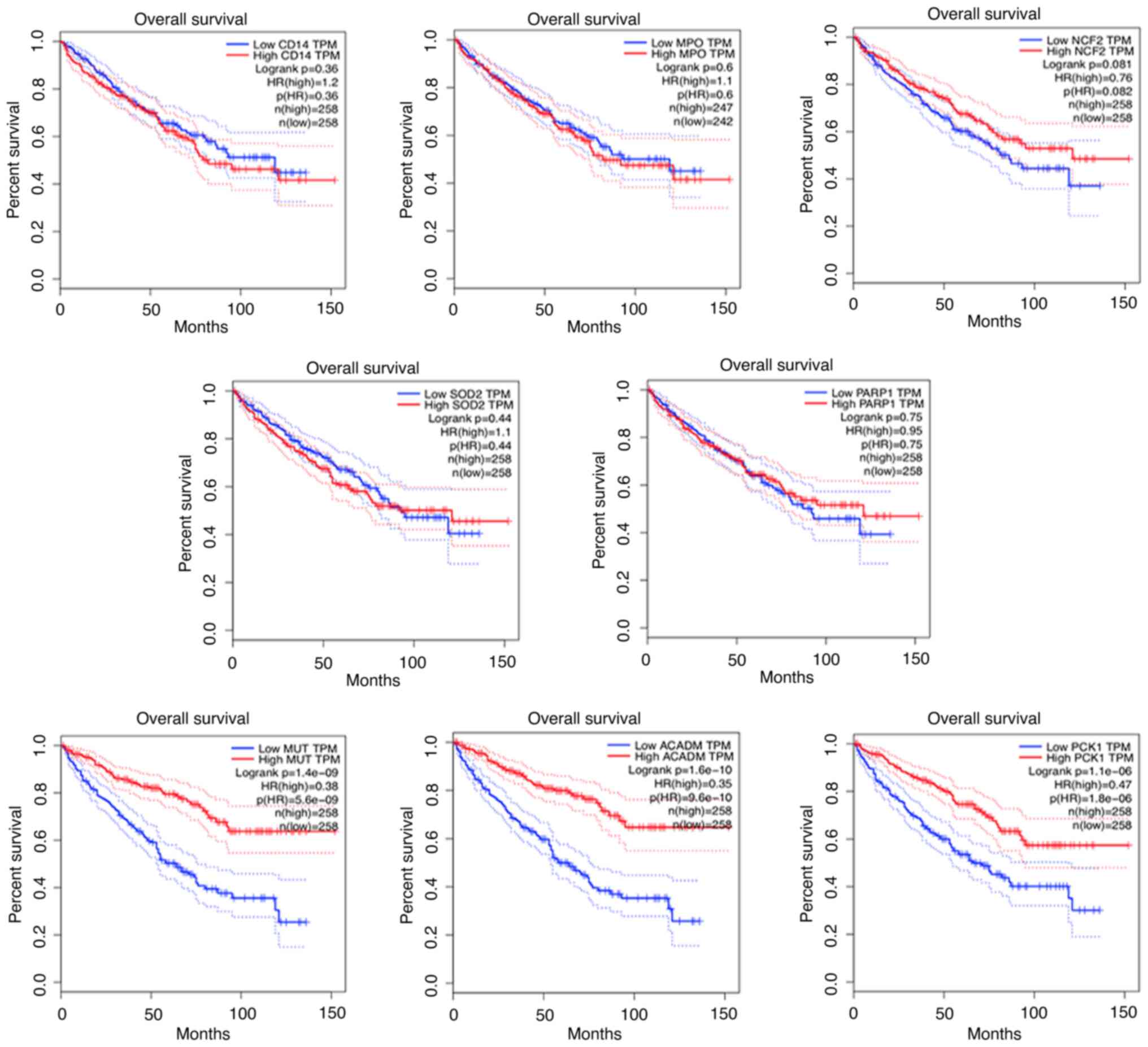
|
1
|
Smith RA, Andrews K, Brooks D, DeSantis
CE, Fedewa SA, Lortet-Tieulent J, Manassaram-Baptiste D, Brawley OW
and Wender RC: Cancer screening in the United States, 2016: A
review of current American cancer society guidelines and current
issues in cancer screening. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:96–114. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Owens B: Kidney cancer. Nature.
537:S972016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chow WH, Dong LM and Devesa SS:
Epidemiology and risk factors for kidney cancer. Nat Rev Urol.
7:245–257. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jonasch E, Gao J and Rathmell WK: Renal
cell carcinoma. BMJ. 349:g47972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zarrabi K, Fang C and Wu S: New treatment
options for metastatic renal cell carcinoma with prior
anti-angiogenesis therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 10:382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sánchez-Gastaldo A, Kempf E, González Del
Alba A and Duran I: Systemic treatment of renal cell cancer: A
comprehensive review. Cancer Treat Rev. 60:77–89. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Keskin O, Tuncbag N and Gursoy A:
Predicting protein-protein interactions from the molecular to the
proteome level. Chem Rev. 116:4884–4909. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aebersold R and Mann M: Mass-spectrometric
exploration of proteome structure and function. Nature.
537:347–355. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Riley NM and Coon JJ: Phosphoproteomics in
the age of rapid and deep proteome profiling. Anal Chem. 88:74–94.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Silva AMN, Vitorino R, Domingues MRM,
Spickett CM and Domingues P: Post-translational modifications and
mass spectrometry detection. Free Radic Biol Med. 65:925–941. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Na S and Paek E: Software eyes for protein
post-translational modifications. Mass Spectrom Rev. 34:133–147.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Humphrey SJ, James DE and Mann M: Protein
phosphorylation: A major switch mechanism for metabolic regulation.
Trends Endocrinol Metab. 26:676–687. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Butterfield DA, Gu L, Di Domenico F and
Robinson RA: Mass spectrometry and redox proteomics: Applications
in disease. Mass Spectrom Rev. 33:277–301. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Konstantinopoulos PA, Karamouzis MV and
Papavassiliou AG: Post-translational modifications and regulation
of the RAS superfamily of GTPases as anticancer targets. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 6:541–555. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Okamura N, Masuda T, Gotoh A, Shirakawa T,
Terao S, Kaneko N, Suganuma K, Watanabe M, Matsubara T, Seto R, et
al: Quantitative proteomic analysis to discover potential
diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets in human renal cell
carcinoma. Proteomics. 8:3194–3203. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Masui O, White NM, DeSouza LV, Krakovska
O, Matta A, Metias S, Khalil B, Romaschin AD, Honey RJ, Stewart R,
et al: Quantitative proteomic analysis in metastatic renal cell
carcinoma reveals a unique set of proteins with potential
prognostic significance. Mol Cell Proteomics. 12:132–144. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Atrih A, Mudaliar MA, Zakikhani P, Lamont
DJ, Huang JT, Bray SE, Barton G, Fleming S and Nabi G: Quantitative
proteomics in resected renal cancer tissue for biomarker discovery
and profiling. Br J Cancer. 110:1622–1633. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gottlieb E and Mostoslavsky R: Cancer and
metabolism: Why should we care? Semin Cell Dev Biol. 43:1–2. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
DeBerardinis RJ and Chandel NS:
Fundamentals of cancer metabolism. Sci Adv. 2:e16002002016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cantor JR and Sabatini DM: Cancer cell
metabolism: One hallmark, many faces. Cancer Discov. 2:881–898.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wallace DC: Mitochondria and cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 12:685–698. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Andrejeva G and Rathmell JC: Similarities
and distinctions of cancer and immune metabolism in inflammation
and tumors. Cell Metab. 26:49–70. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ganapathy-Kanniappan S and Geschwind JF:
Tumor glycolysis as a target for cancer therapy: Progress and
prospects. Mol Cancer. 12:1522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Swaney DL, Beltrao P, Starita L, Guo A,
Rush J, Fields S, Krogan NJ and Villén J: Global analysis of
phosphorylation and ubiquitylation cross-talk in protein
degradation. Nat Methods. 10:676–682. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Robles MS, Humphrey SJ and Mann M:
Phosphorylation is a central mechanism for circadian control of
metabolism and physiology. Cell Metab. 25:118–127. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|