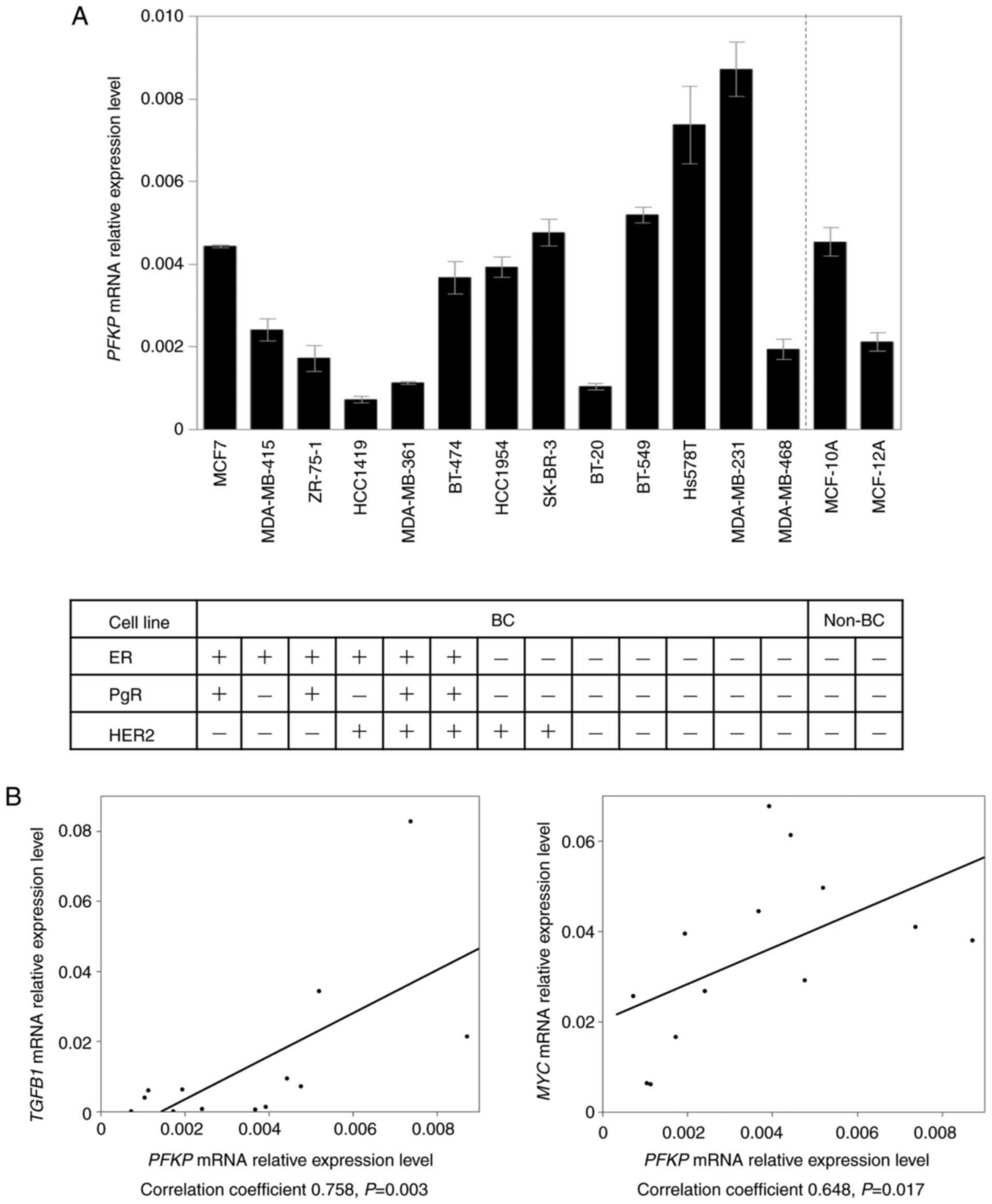
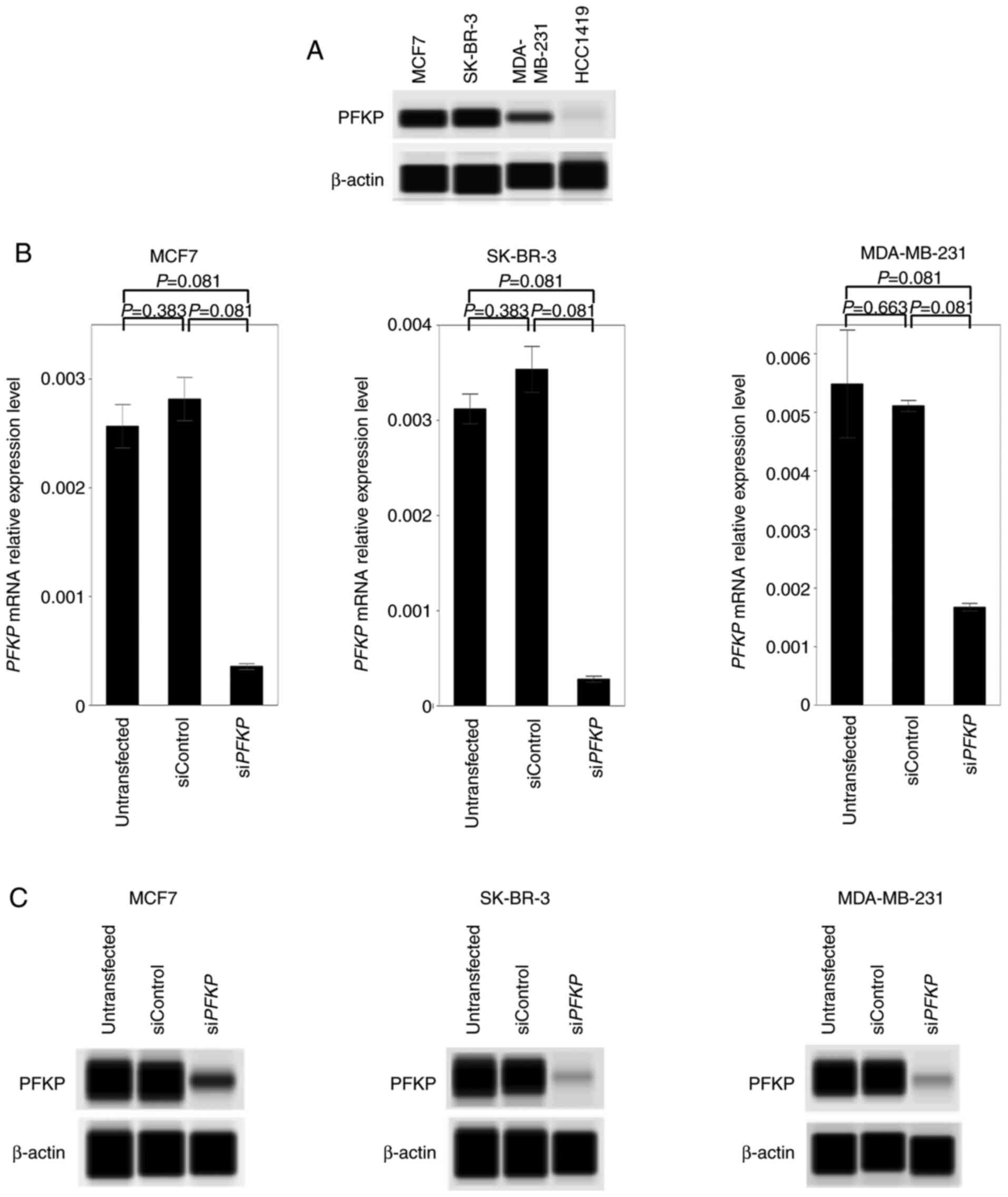
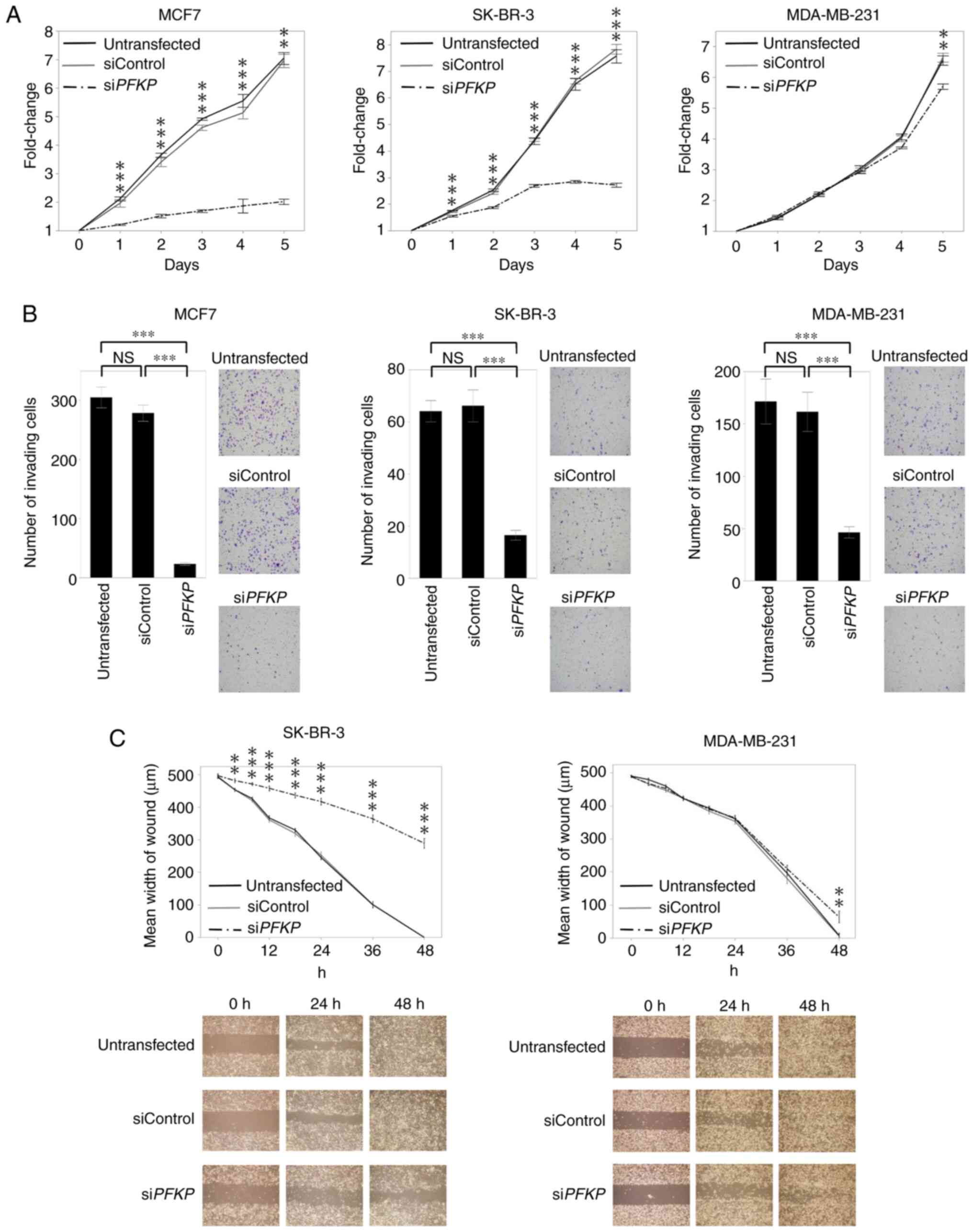
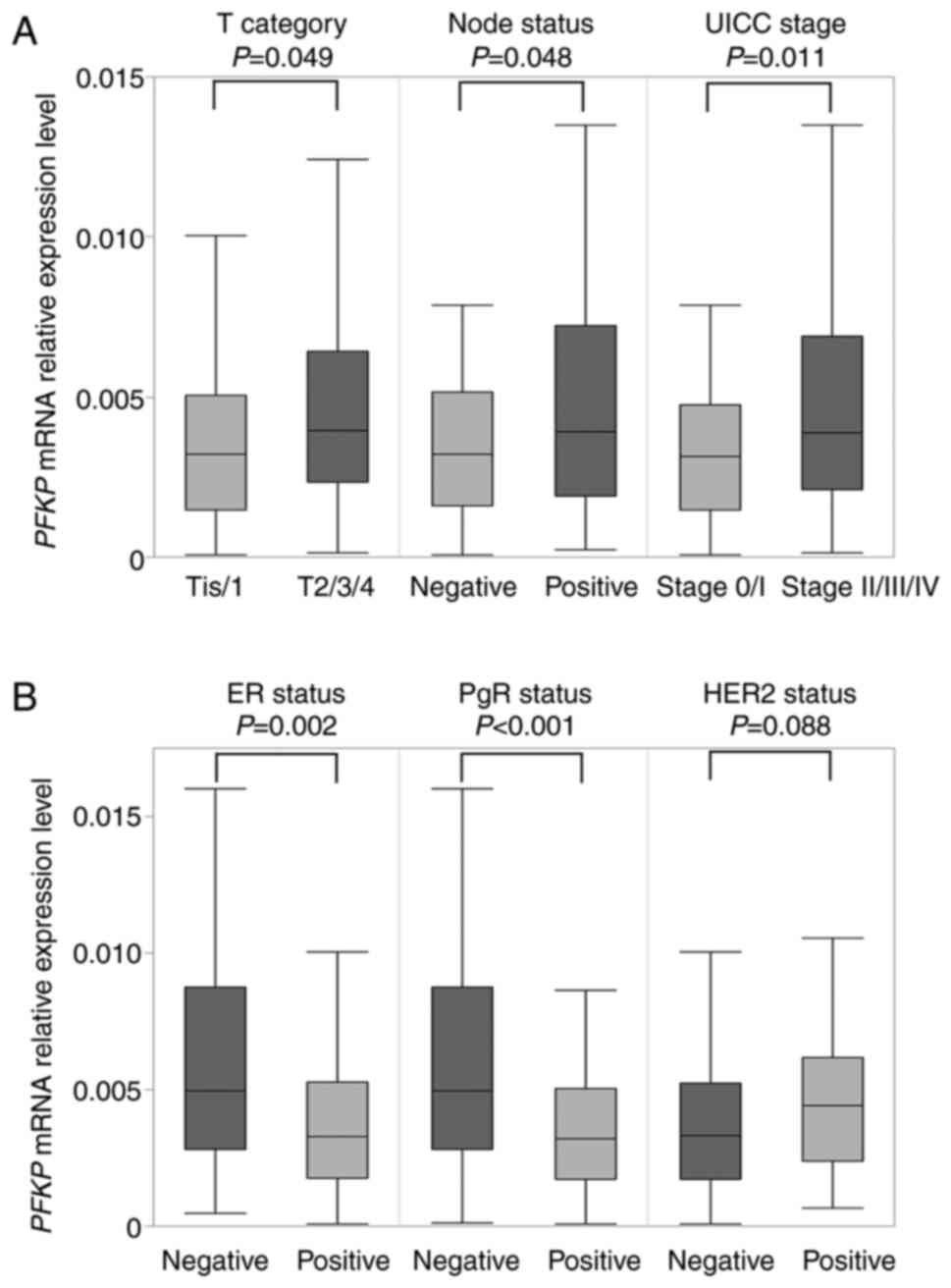
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Allemani C, Matsuda T, Di Carlo V,
Harewood R, Matz M, Nikšić M, Bonaventure A, Valkov M, Johnson CJ,
Estève J, et al: Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival
2000–14 (CONCORD-3): Analysis of individual records for 37,513,025
patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based
registries in 71 countries. Lancet. 391:1023–1075. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network, .
Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
490:61–70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Iwata H: Future treatment strategies for
metastatic breast cancer: Curable or incurable? Breast Cancer.
19:200–205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mor I, Cheung EC and Vousden KH: Control
of glycolysis through regulation of PFK1: Old friends and recent
additions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 76:211–216. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dunaway GA, Kasten TP, Sebo T and Trapp R:
Analysis of the phosphofructokinase subunits and isoenzymes in
human tissues. Biochem J. 251:677–683. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moon JS, Kim HE, Koh E, Park SH, Jin WJ,
Park BW, Park SW and Kim KS: Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) activates
the transcription of the gene for the platelet isoform of
phosphofructokinase (PFKP) in breast cancer. J Biol Chem.
286:23808–23816. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun CM, Xiong DB, Yan Y, Geng J, Liu M and
Yao XD: Genetic alteration in phosphofructokinase family promotes
growth of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Int J Biol Markers.
31:e286–e293. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee JH, Liu R, Li J, Zhang C, Wang Y, Cai
Q, Qian X, Xia Y, Zheng Y, Piao Y, et al: Stabilization of
phosphofructokinase 1 platelet isoform by AKT promotes
tumorigenesis. Nat Commun. 8:9492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang J, Zhang P, Zhong J, Tan M, Ge J, Tao
L, Li Y, Zhu Y, Wu L, Qiu J and Tong X: The platelet isoform of
phosphofructokinase contributes to metabolic reprogramming and
maintains cell proliferation in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 7:27142–27157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peng M, Yang D, Hou Y, Liu S, Zhao M, Qin
Y, Chen R, Teng Y and Liu M: Intracellular citrate accumulation by
oxidized ATM-mediated metabolism reprogramming via PFKP and CS
enhances hypoxic breast cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Cell
Death Dis. 10:2282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Umar SM, Kashyap A, Kahol S, Mathur SR,
Gogia A, Deo SVS and Prasad CP: Prognostic and therapeutic
relevance of phosphofructokinase platelet-type (PFKP) in breast
cancer. Exp Cell Res. 396:1122822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Watanabe M, Shibata M, Inaishi T, Ichikawa
T, Soeda I, Miyajima N, Takano Y, Takeuchi D, Tsunoda N, Kanda M,
et al: MZB1 expression indicates poor prognosis in estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 20:1982020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shibata M, Kanda M, Tanaka H, Umeda S,
Miwa T, Shimizu D, Hayashi M, Inaishi T, Miyajima N, Adachi Y, et
al: Overexpression of Derlin 3 is associated with malignant
phenotype of breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 38:1760–1766. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fujita M, Somasundaram V, Basudhar D,
Cheng RYS, Ridnour LA, Higuchi H, Imadome K, No JH, Bharadwaj G and
Wink DA: Role of nitric oxide in pancreatic cancer cells exhibiting
the invasive phenotype. Redox Biol. 22:1011582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Harris VM: Protein detection by Simple
Western™ analysis. Methods Mol Biol. 1312:465–468. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Györffy B, Lanczky A, Eklund AC, Denkert
C, Budczies J, Li Q and Szallasi Z: An online survival analysis
tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer
prognosis using microarray data of 1,809 patients. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 123:725–731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Riaz M, van Jaarsveld MT, Hollestelle A,
Prager-van der Smissen WJ, Heine AA, Boersma AW, Liu J, Helmijr J,
Ozturk B, Smid M, et al: MiRNA expression profiling of 51 human
breast cancer cell lines reveals subtype and driver
mutation-specific miRNAs. Breast Cancer Res. 15:R332013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Subik K, Lee JF, Baxter L, Strzepek T,
Costello D, Crowley P, Xing L, Hung MC, Bonfiglio T, Hicks DG and
Tang P: The Expression Patterns of ER, PR, HER2, CK5/6, EGFR, Ki-67
and AR by immunohistochemical analysis in breast cancer cell lines.
Breast Cancer (Auckl). 4:35–41. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Young CD and Anderson SM: Sugar and
fat-that's where it's at: Metabolic changes in tumors. Breast
Cancer Res. 10:2022008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Moreno-Sánchez R, Rodríguez-Enríquez S,
Marín-Hernández A and Saavedra E: Energy metabolism in tumor cells.
FEBS J. 274:1393–1418. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Park YY, Kim SB, Han HD, Sohn BH, Kim JH,
Liang J, Lu Y, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Lopez-Berestein G, Mills GB, et
al: Tat-activating regulatory DNA-binding protein regulates
glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the platelet
isoform of phosphofructokinase through microRNA 520. Hepatology.
58:182–191. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Z, Jiang Q and Dong C: Metabolic
reprogramming in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Biol Med.
17:44–59. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rodríguez-García A, Samsó P, Fontova P,
Simon-Molas H, Manzano A, Castaño E, Rosa JL, Martinez-Outshoorn U,
Ventura F, Navarro-Sabaté À and Bartrons R: TGF-β1 targets Smad,
p38 MAPK, and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways to induce PFKFB3 gene
expression and glycolysis in glioblastoma cells. FEBS J.
284:3437–3454. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shen L, O'Shea JM, Kaadige MR, Cunha S,
Wilde BR, Cohen AL, Welm AL and Ayer DE: Metabolic reprogramming in
triple-negative breast cancer through Myc suppression of TXNIP.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:5425–5430. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Clem BF, O'Neal J, Tapolsky G, Clem AL,
Imbert-Fernandez Y, Kerr DA II, Klarer AC, Redman R, Miller DM,
Trent JO, et al: Targeting 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase (PFKFB3) as a
therapeutic strategy against cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:1461–1470.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brand K: Aerobic glycolysis by
proliferating cells: Protection against oxidative stress at the
expense of energy yield. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 29:355–364. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gillies RJ, Robey I and Gatenby RA: Causes
and consequences of increased glucose metabolism of cancers. J Nucl
Med. 49 (Suppl 2):24S–42S. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang F, Li L and Zhang Z: Platelet isoform
of phosphofructokinase promotes aerobic glycolysis and the
progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Med Rep. 23:742021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang G, Xu Z, Wang C, Yao F, Li J, Chen C
and Sun S: Differential phosphofructokinase-1 isoenzyme patterns
associated with glycolytic efficiency in human breast cancer and
paracancer tissues. Oncol Lett. 6:1701–1706. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|