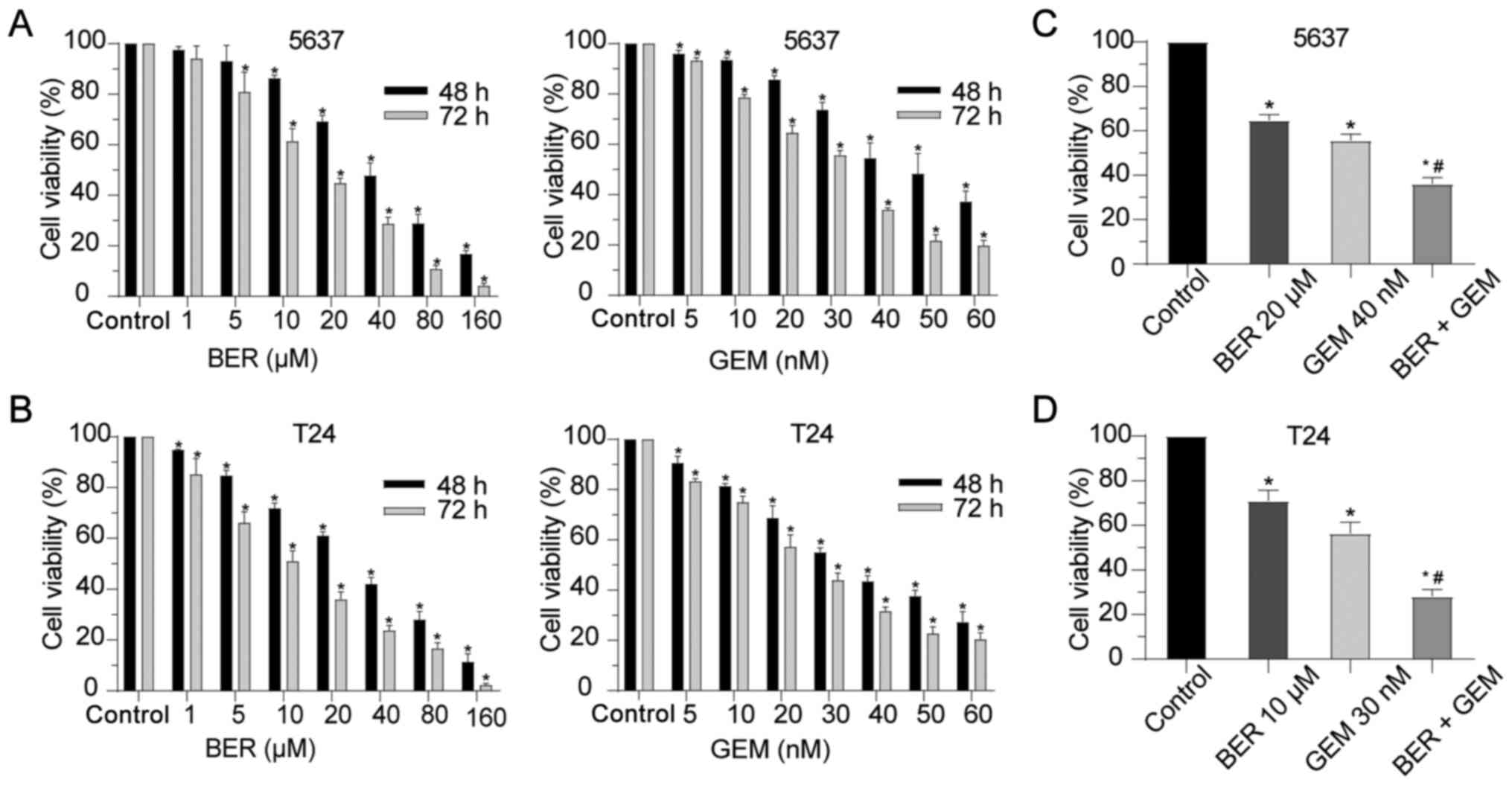
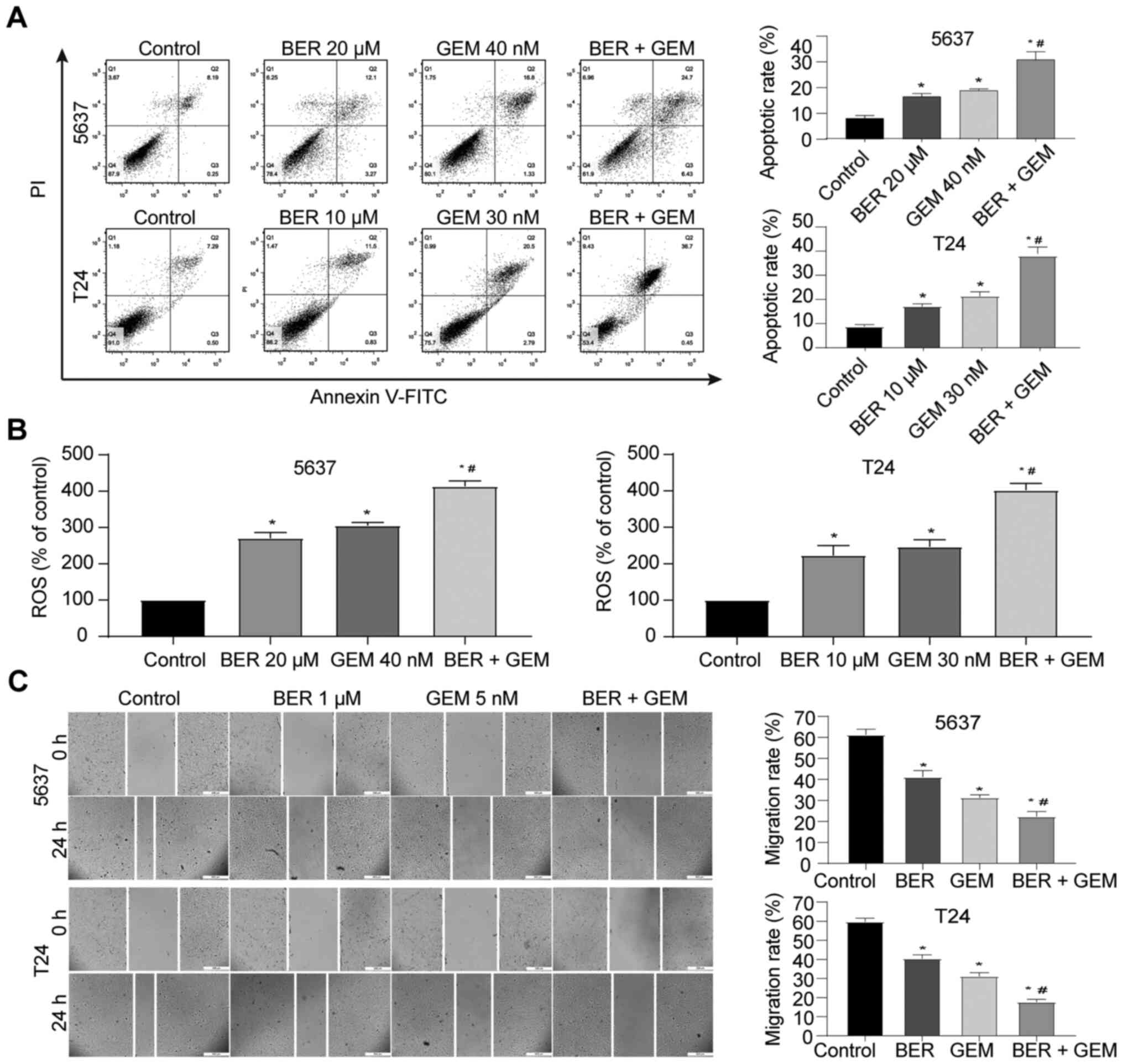
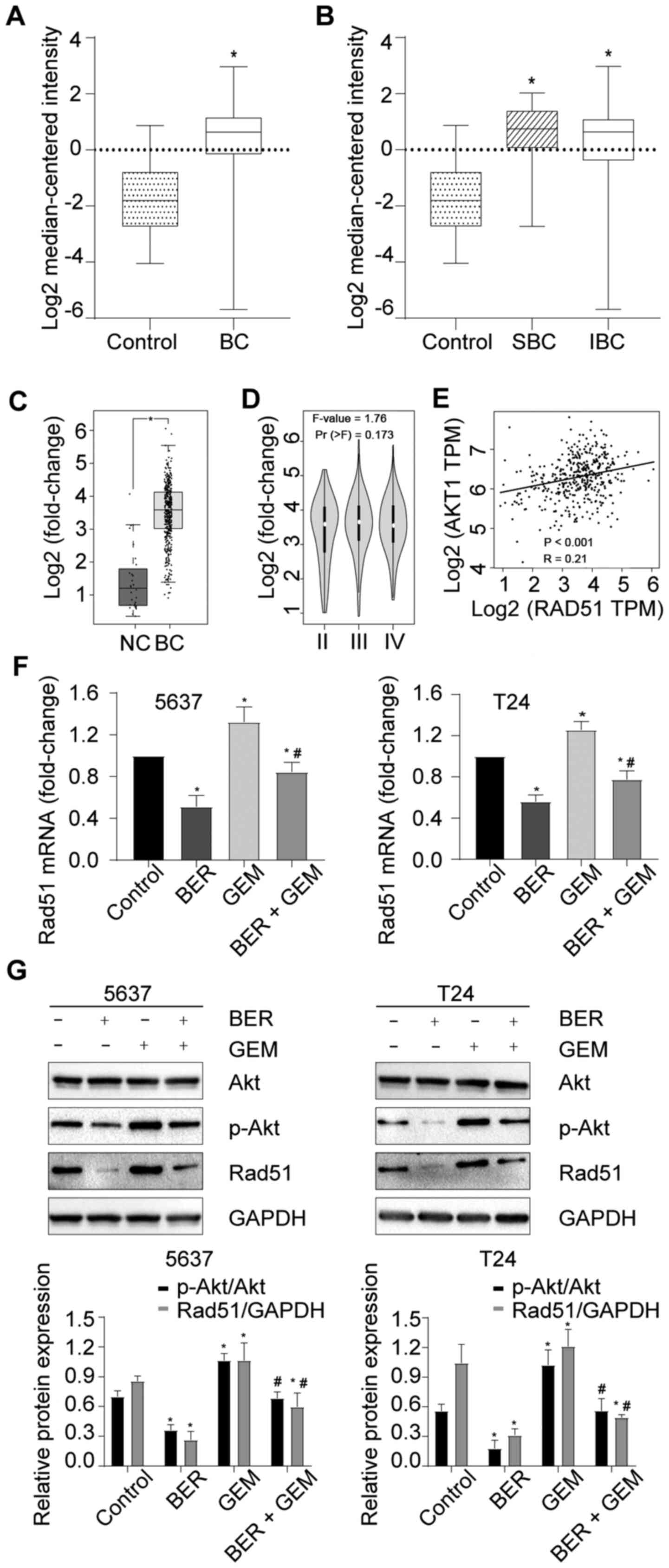
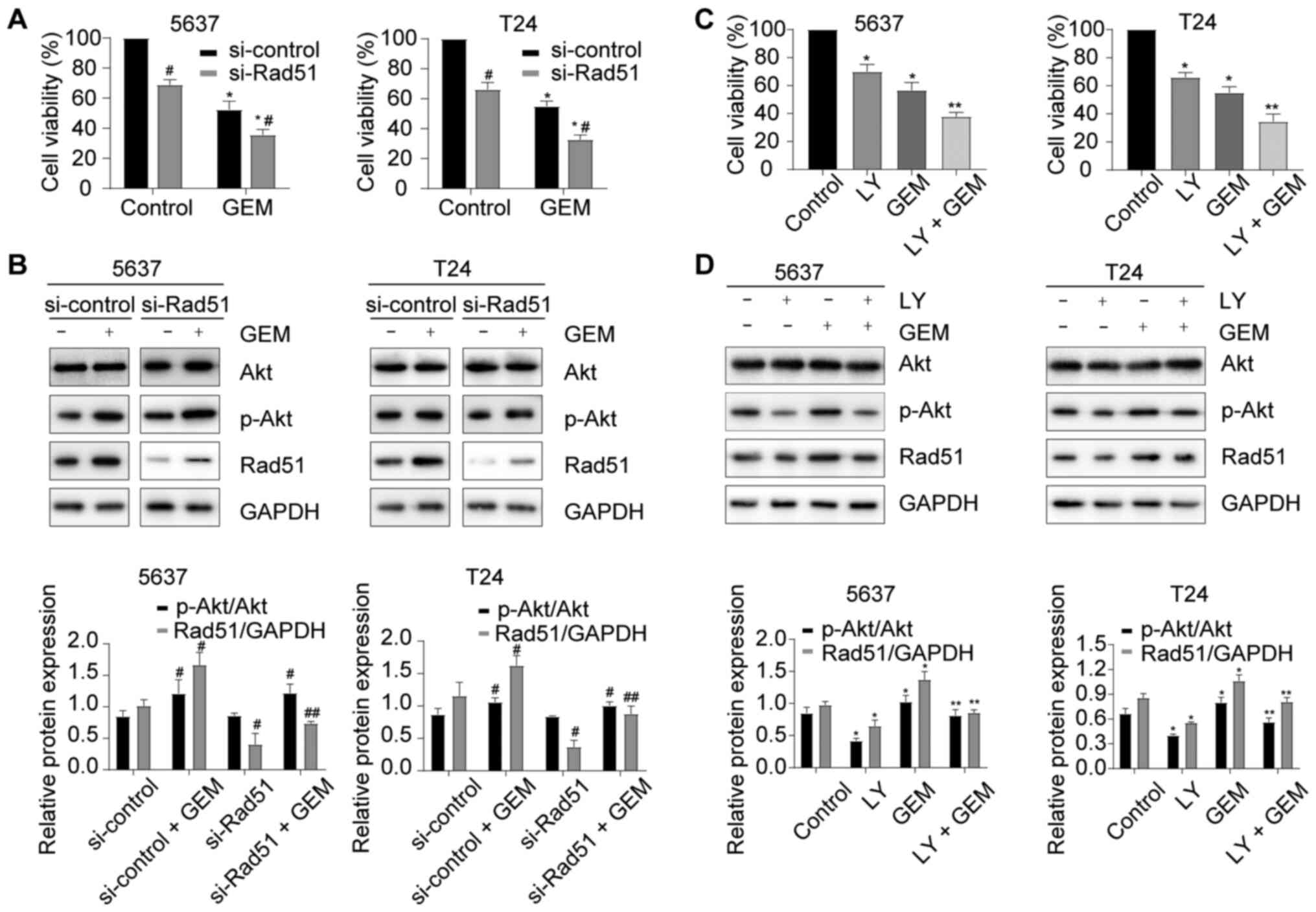
|
1
|
Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Znaor
A, Jemal A and Bray F: Bladder Cancer Incidence and Mortality: A
Global Overview and Recent Trends. Eur Urol. 71:96–108. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Babjuk M, Burger M, Compérat EM, Gontero
P, Mostafid AH, Palou J, van Rhijn BWG, Rouprêt M, Shariat SF,
Sylvester R, et al: European Association of Urology Guidelines on
Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer (TaT1 and Carcinoma In Situ) -
2019 Update. Eur Urol. 76:639–657. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gakis G: Management of Muscle-invasive
Bladder Cancer in the 2020s: Challenges and Perspectives. Eur Urol
Focus. 6:632–638. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
von der Maase H, Hansen SW, Roberts JT,
Dogliotti L, Oliver T, Moore MJ, Bodrogi I, Albers P, Knuth A,
Lippert CM, et al: Gemcitabine and cisplatin versus methotrexate,
vinblastine, doxorubicin, and cisplatin in advanced or metastatic
bladder cancer: Results of a large, randomized, multinational,
multicenter, phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 18:3068–3077. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu C, Hequn C, Jinbo C, Feng Z, Xiongbing
Z and Jian D: Gemcitabine/cisplatin versus
methotrexate/vinblastine/doxorubicin/cisplatin for muscle-invasive
bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cancer Res
Ther. 14:1260–1265. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Isono M, Hoffmann MJ, Pinkerneil M, Sato
A, Michaelis M, Cinatl J Jr, Niegisch G and Schulz WA: Checkpoint
kinase inhibitor AZD7762 strongly sensitises urothelial carcinoma
cells to gemcitabine. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:12017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xie D, Zhang H and Shang C: Long
non-coding RNA CDKN2B antisense RNA 1 gene inhibits Gemcitabine
sensitivity in bladder urothelial carcinoma. J Cancer. 9:2160–2166.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Foschini F, Formisano L, Marciano R,
Mozzillo E, Carratù A, Napolitano F, Santaniello A, De Placido P,
Cascetta P, Servetto A, et al: FOLFIRINOX after first-line
gemcitabine-based chemotherapy in metastatic pancreatic cancer: A
mono-institutional experience. Ann Oncol. 30 (Suppl 4):iv52–iv53.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhang X, Wang D, Li Z, Jiao D, Jin L, Cong
J, Zheng X and Xu L: Low-Dose Gemcitabine Treatment Enhances
Immunogenicity and Natural Killer Cell-Driven Tumor Immunity in
Lung Cancer. Front Immunol. 11:3312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kassouf W, Highshaw R, Nelkin GM, Dinney
CP and Kamat AM: Vitamins C and K3 sensitize human urothelial
tumors to gemcitabine. J Urol. 176:1642–1647. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pinto-Leite R, Arantes-Rodrigues R,
Palmeira C, Gaivão I, Cardoso ML, Colaço A, Santos L and Oliveira
P: Everolimus enhances gemcitabine-induced cytotoxicity in
bladder-cancer cell lines. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 75:788–799.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yoon CY, Lee JS, Kim BS, Jeong SJ, Hong
SK, Byun SS and Lee SE: Sunitinib malate synergistically
potentiates anti-tumor effect of gemcitabine in human bladder
cancer cells. Korean J Urol. 52:55–63. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guo Z, Hu X, Xing Z, Xing R, Lv R, Cheng
X, Su J, Zhou Z, Xu Z, Nilsson S, et al: Baicalein inhibits
prostate cancer cell growth and metastasis via the
caveolin-1/AKT/mTOR pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 406:111–119. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu Z, Liu C, Yan K, Liu J, Fang Z and Fan
Y: Huaier Extract Inhibits Prostate Cancer Growth via Targeting
AR/AR-V7 Pathway. Front Oncol. 11:6155682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tang QL, Lai ML, Zhong YF, Wang AM, Su JK
and Zhang MQ: Antinociceptive effect of berberine on visceral
hypersensitivity in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 19:4582–4589.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin X and Zhang N: Berberine: Pathways to
protect neurons. Phytother Res. 32:1501–1510. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Imenshahidi M and Hosseinzadeh H:
Berberine and barberry (Berberis vulgaris): A clinical
review. Phytother Res. 33:504–523. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mohammadinejad R, Ahmadi Z, Tavakol S and
Ashrafizadeh M: Berberine as a potential autophagy modulator. J
Cell Physiol. 234:14914–14926. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang SX, Qi B, Yao WJ, Gu CW, Wei XF,
Zhao Y, Liu YZ and Zhao BS: Berberine displays antitumor activity
in esophageal cancer cells in vitro. World J Gastroenterol.
23:2511–2518. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tian Y, Zhao L, Wang Y, Zhang H, Xu D,
Zhao X, Li Y and Li J: Berberine inhibits androgen synthesis by
interaction with aldo-keto reductase 1C3 in 22Rv1 prostate cancer
cells. Asian J Androl. 18:607–612. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hou D, Xu G, Zhang C, Li B, Qin J, Hao X,
Liu Q, Zhang X, Liu J, Wei J, et al: Berberine induces oxidative
DNA damage and impairs homologous recombination repair in ovarian
cancer cells to confer increased sensitivity to PARP inhibition.
Cell Death Dis. 8:e30702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yan K, Zhang C, Feng J, Hou L, Yan L, Zhou
Z, Liu Z, Liu C, Fan Y, Zheng B, et al: Induction of G1 cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis by berberine in bladder cancer cells. Eur J
Pharmacol. 661:1–7. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhuo Y, Chen Q, Chen B, Zhan X, Qin X,
Huang J and Lv X: Berberine promotes antiproliferative effects of
epirubicin in T24 bladder cancer cells by enhancing apoptosis and
cell cycle arrest. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 55:32–40. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Godin SK, Sullivan MR and Bernstein KA:
Novel insights into RAD51 activity and regulation during homologous
recombination and DNA replication. Biochem Cell Biol. 94:407–418.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Haber JE: DNA Repair: The Search for
Homology. BioEssays. 40:e17002292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nagathihalli NS and Nagaraju G: RAD51 as a
potential biomarker and therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1816:209–218. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cortez MA, Valdecanas D, Niknam S, Peltier
HJ, Diao L, Giri U, Komaki R, Calin GA, Gomez DR, Chang JY, et al:
In Vivo Delivery of miR-34a Sensitizes Lung Tumors to Radiation
Through RAD51 Regulation. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 4:e2702015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hong KJ, Hsu MC and Hung WC: RECK impedes
DNA repair by inhibiting the erbB/JAB1/Rad51 signaling axis and
enhances chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res.
5:2422–2430. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang B, Hou D, Liu Q, Wu T, Guo H, Zhang
X, Zou Y, Liu Z, Liu J, Wei J, et al: Artesunate sensitizes ovarian
cancer cells to cisplatin by downregulating RAD51. Cancer Biol
Ther. 16:1548–1556. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee JO, Kang MJ, Byun WS, Kim SA, Seo IH,
Han JA, Moon JW, Kim JH, Kim SJ, Lee EJ, et al: Metformin overcomes
resistance to cisplatin in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC)
cells by targeting RAD51. Breast Cancer Res. 21:1152019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tsai MS, Kuo YH, Chiu YF, Su YC and Lin
YW: Down-regulation of Rad51 expression overcomes drug resistance
to gemcitabine in human non-small-cell lung cancer cells. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 335:830–840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu Q, Jiang H, Liu Z, Wang Y, Zhao M, Hao
C, Feng S, Guo H, Xu B, Yang Q, et al: Berberine radiosensitizes
human esophageal cancer cells by downregulating homologous
recombination repair protein RAD51. PLoS One. 6:e234272011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sanchez-Carbayo M, Socci ND, Lozano J,
Saint F and Cordon-Cardo C: Defining molecular profiles of poor
outcome in patients with invasive bladder cancer using
oligonucleotide microarrays. J Clin Oncol. 24:778–789. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45((W1)):
W98–W102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals, . Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. The National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC:
2011
|
|
37
|
Tomayko MM and Reynolds CP: Determination
of subcutaneous tumor size in athymic (nude) mice. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 24:148–154. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ko JC, Chen JC, Wang TJ, Zheng HY, Chen
WC, Chang PY and Lin YW: Astaxanthin down-regulates Rad51
expression via inactivation of AKT kinase to enhance mitomycin
C-induced cytotoxicity in human non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 105:91–100. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jabbarzadeh Kaboli P, Rahmat A, Ismail P
and Ling KH: Targets and mechanisms of berberine, a natural drug
with potential to treat cancer with special focus on breast cancer.
Eur J Pharmacol. 740:584–595. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yin H, Yang X, Gu W, Liu Y, Li X, Huang X,
Zhu X, Tao Y, Gou X and He W: HMGB1-mediated autophagy attenuates
gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in bladder cancer cells involving JNK
and ERK activation. Oncotarget. 8:71642–71656. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Takeuchi H, Mmeje CO, Jinesh GG, Taoka R
and Kamat AM: Sequential gemcitabine and tamoxifen treatment
enhances apoptosis and blocks transformation in bladder cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 34:2738–2744. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Miller WH Jr, Schipper HM, Lee JS, Singer
J and Waxman S: Mechanisms of action of arsenic trioxide. Cancer
Res. 62:3893–3903. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Takeuchi H, Taoka R, Mmeje CO, Jinesh GG,
Safe S and Kamat AM: CDODA-Me decreases specificity protein
transcription factors and induces apoptosis in bladder cancer cells
through induction of reactive oxygen species. Urol Oncol.
34:337.e11–8. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang X, Bai Y, Zhang F, Yang Y, Feng D, Li
A, Yang Z, Li D, Tang Y, Wei X, et al: Targeted Inhibition of P4HB
Promotes Cell Sensitivity to Gemcitabine in Urothelial Carcinoma of
the Bladder. OncoTargets Ther. 13:9543–9558. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu Z, Liu Q, Xu B, Wu J, Guo C, Zhu F,
Yang Q, Gao G, Gong Y and Shao C: Berberine induces p53-dependent
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of human osteosarcoma cells by
inflicting DNA damage. Mutat Res. 662:75–83. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Huang J, Feng W, Li S, Tang H, Qin S, Li
W, Gong Y, Fang Y, Liu Y, Wang S, et al: Berberine Exerts
Anti-cancer Activity by Modulating Adenosine Monophosphate-
Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) and the Phosphatidylinositol
3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B (PI3K/AKT) Signaling Pathways. Curr Pharm
Des. 27:565–574. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|