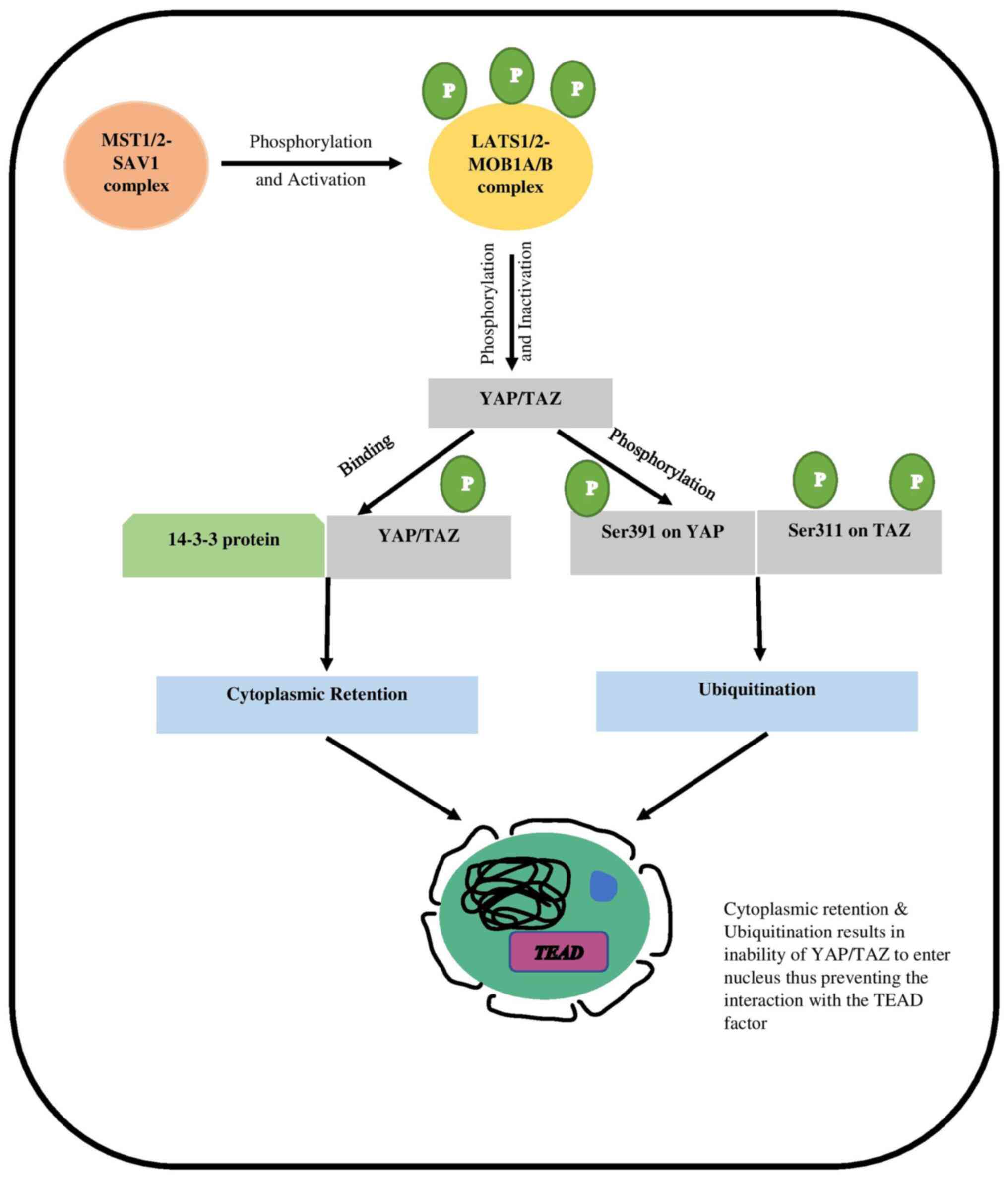
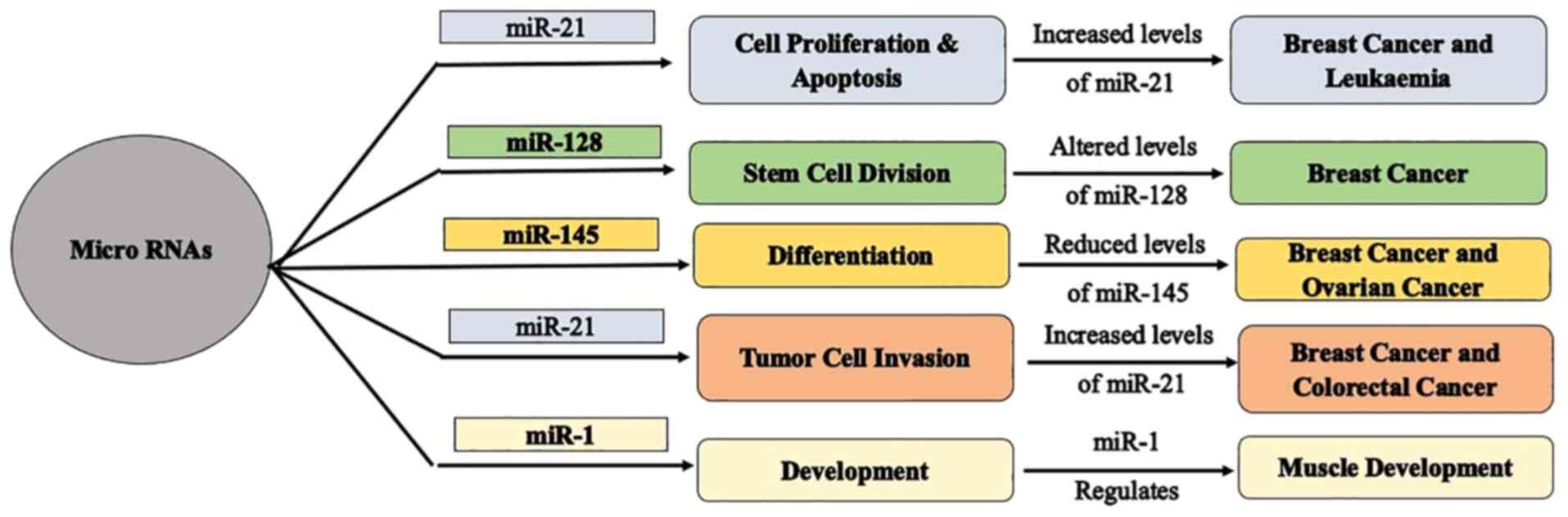
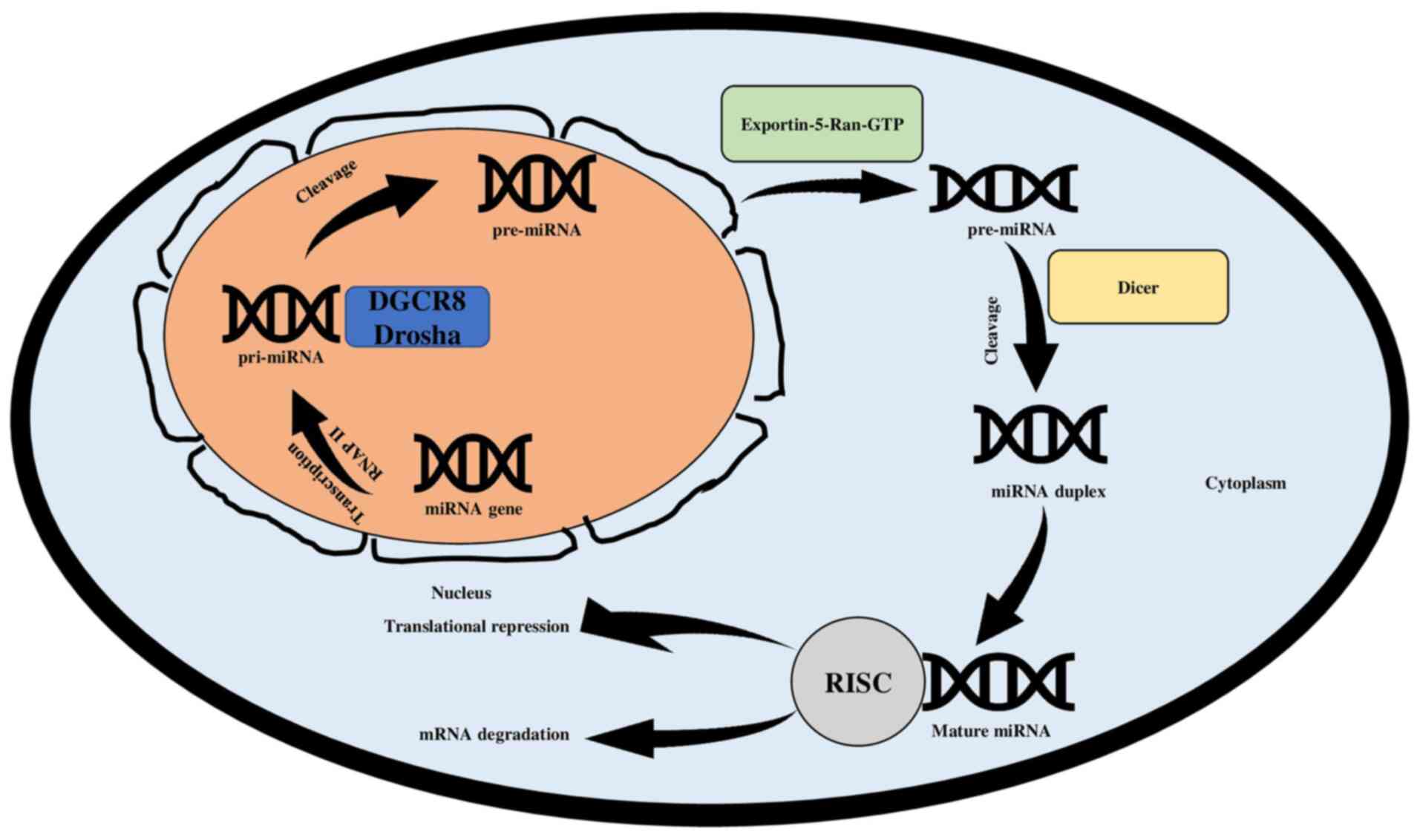
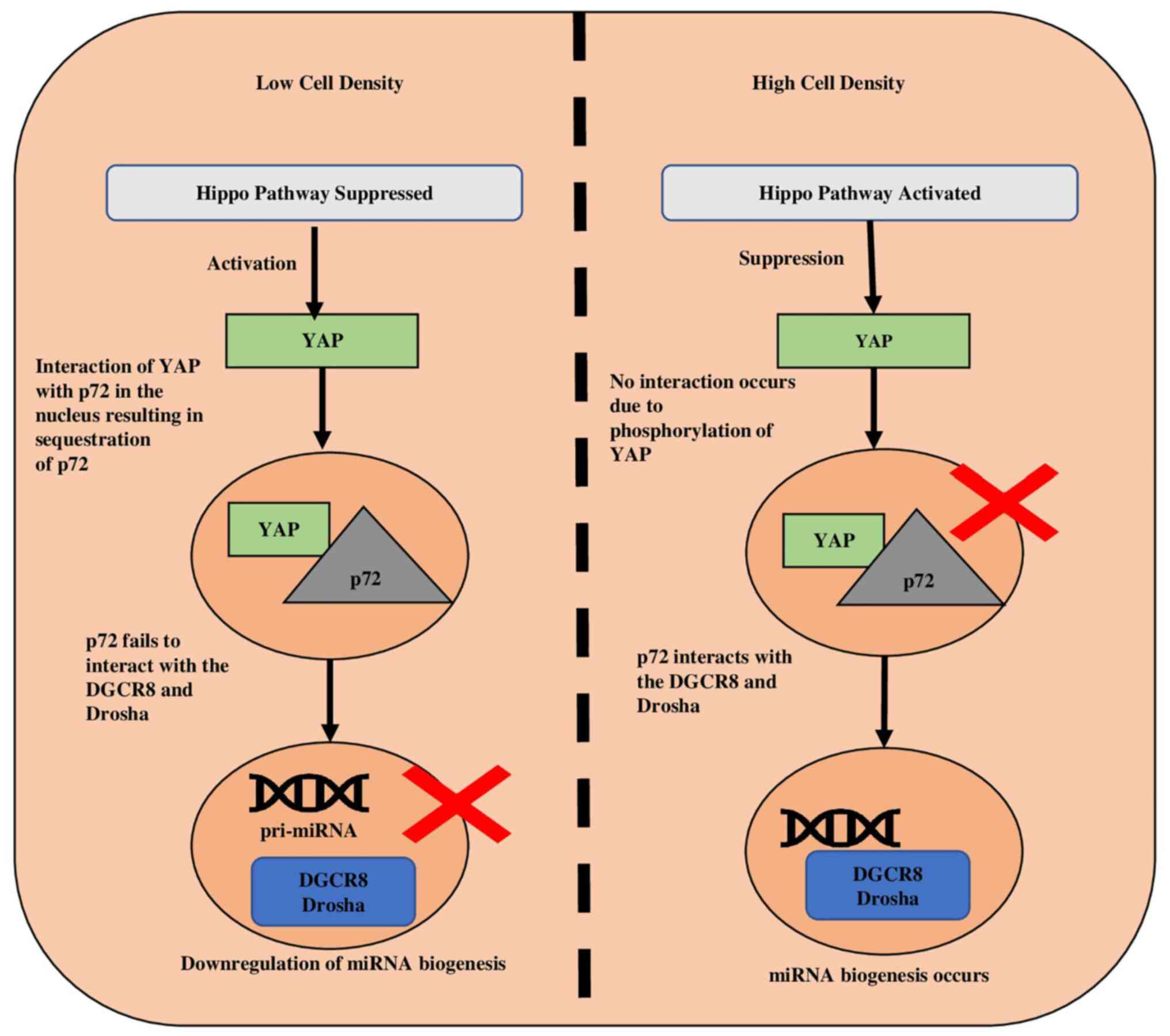
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I,
Parkin DM, Piñeros M, Znaor A and Bray F: Cancer statistics for the
year 2020: An overview. Int J Cancer. Apr 5–2021.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zygulska AL, Krzemieniecki K and
Pierzchalski P: Hippo pathway-brief overview of its relevance in
cancer. J Physiol Pharmacol. 68:311–335. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zeng R and Dong J: The Hippo signaling
pathway in drug resistance in cancer. Cancers (Basel). 13:3182021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li N, Xie C and Lu N: Crosstalk between
Hippo signaling and miRNAs in tumor progression. FEBS J.
284:1045–1055. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mori M, Triboulet R, Mohseni M,
Schlegelmilch K, Shrestha K, Camargo FD and Gregory RI: Hippo
signaling regulates microprocessor and links cell-density-dependent
miRNA biogenesis to cancer. Cell. 156:893–906. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pfleger CM: The Hippo pathway: A master
regulatory network important in development and dysregulated in
disease. Curr Top Dev Biol. 123:181–228. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dey A, Varelas X and Guan KL: Targeting
the Hippo pathway in cancer, fibrosis, wound healing and
regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 19:480–494. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kaur S, Najm MZ, Khan MA, Akhter N,
Shingatgeri VM, Sikenis M, Sadaf and Aloliqi AA: Drug-resistant
breast cancer: Dwelling the Hippo pathway to manage the treatment.
Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 13:691–700. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Praskova M, Xia F and Avruch J:
MOBKL1A/MOBKL1B phosphorylation by MST1 and MST2 inhibits cell
proliferation. Curr Biol. 18:311–321. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zheng Y and Pan D: The Hippo signaling
pathway in development and disease. Dev Cell. 50:264–282. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nguyen-Lefebvre AT, Selzner N, Wrana JL
and Bhat M: The hippo pathway: A master regulator of liver
metabolism, regeneration, and disease. FASEB J. 35:e215702021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao B, Wei X, Li W, Udan RS, Yang Q, Kim
J, Xie J, Ikenoue T, Yu J, Li L, et al: Inactivation of YAP
oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact
inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev. 21:2747–2761.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lei QY, Zhang H, Zhao B, Zha ZY, Bai F,
Pei XH, Zhao S, Xiong Y and Guan KL: TAZ promotes cell
proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and is
inhibited by the hippo pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 28:2426–2436. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Najm MZ, Sadaf, Shingatgeri VM, Saha H,
Bhattacharya H, Rath A, Verma V, Gupta A, Aloliqi AA, Kashyap P and
Parveen F: Hippo pathway in cancer: Examining its potential. J Curr
Oncol. 4:115–120. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Badouel C and McNeill H: SnapShot: The
hippo signaling pathway. Cell. 145:484.e12011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang YT, Lan Q, Lorusso G, Duffey N and
Rüegg C: The matricellular protein CYR61 promotes breast cancer
lung metastasis by facilitating tumor cell extravasation and
suppressing anoikis. Oncotarget. 8:9200–9215. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Niu J, Ma J, Guan X, Zhao X, Li P and
Zhang M: Correlation between Doppler ultrasound blood flow
parameters and angiogenesis and proliferation activity in breast
cancer. Med Sci Monit. 25:70352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu FX and Guan KL: The Hippo pathway:
Regulators and regulations. Genes Dev. 27:355–371. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Han Y: Analysis of the role of the Hippo
pathway in cancer. J Transl Med. 17:1162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mo JS: The role of extracellular
biophysical cues in modulating the Hippo-YAP pathway. BMB Rep.
50:71–78. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Varelas X, Sakuma R, Samavarchi-Tehrani P,
Peerani R, Rao BM, Dembowy J, Yaffe MB, Zandstra PW and Wrana JL:
TAZ controls Smad nucleocytoplasmic shuttling and regulates human
embryonic stem-cell self-renewal. Nat Cell Biol. 10:837–848. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Beyer TA, Weiss A, Khomchuk Y, Huang K,
Ogunjimi AA, Varelas X and Wrana JL: Switch enhancers interpret
TGF-β and Hippo signaling to control cell fate in human embryonic
stem cells. Cell Rep. 5:1611–1624. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu J, Kang R and Tang D: The KRAS-G12C
inhibitor: Activity and resistance. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021 Sep
1;(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Shen Z and Stanger BZ: YAP regulates
S-phase entry in endothelial cells. PLoS One. 10:e01175222015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Benham-Pyle BW, Pruitt BL and Nelson WJ:
Mechanical strain induces E-cadherin-dependent Yap1 and β-catenin
activation to drive cell cycle entry. Science. 348:1024–1027. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kapoor A, Yao W, Ying H, Hua S, Liewen A,
Wang Q, Zhong Y, Wu CJ, Sadanandam A, Hu B, et al: Yap1 activation
enables bypass of oncogenic Kras addiction in pancreatic cancer.
Cell. 158:185–197. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shibata M, Ham K and Hoque MO: A time for
YAP1: Tumorigenesis, immunosuppression and targeted therapy. Int J
Cancer. 143:2133–2144. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mytsyk Y, Dosenko V, Skrzypczyk MA, Borys
Y, Diychuk Y, Kucher A, Kowalskyy V, Pasichnyk S, Mytsyk O and
Manyuk L: Potential clinical applications of microRNAs as
biomarkers for renal cell carcinoma. Cent European J Urol.
71:295–303. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
O'Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y and Peng C:
Overview of microRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and
circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:4022018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bushati N and Cohen SM: MicroRNA
functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 23:175–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wightman B, Ha I and Ruvkun G:
Post-transcriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by
lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell.
75:855–862. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hong Y, Lee RC and Ambros V: Structure and
function analysis of LIN-14, a temporal regulator of postembryonic
developmental events in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Cell Biol.
20:2285–2295. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG and Bartel
DP: An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles
in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 294:858–862. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: MiRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hatfield SD, Shcherbata HR, Fischer KA,
Nakahara K, Carthew RW and Ruohola-Baker H: Stem cell division is
regulated by the microRNA pathway. Nature. 435:974–978. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Borchert GM, Lanier W and Davidson BL: RNA
polymerase III transcribes human microRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
13:1097–1101. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee Y, Kim M, Han J, Yeom KH, Lee S, Baek
SH and Kim VN: MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II.
EMBO J. 23:4051–4060. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
MacFarlane LA and R Murphy P: MicroRNA:
Biogenesis, function and role in cancer. Curr Genomics. 11:537–561.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pong SK and Gullerova M: Noncanonical
functions of microRNA pathway enzymes-Drosha, DGCR 8, Dicer and Ago
proteins. FEBS Lett. 592:2973–2986. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Han J, Lee Y, Yeom KH, Kim YK, Jin H and
Kim VN: The Drosha-DGCR8 complex in primary microRNA processing.
Genes Dev. 18:3016–3027. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wong CM, Tsang FH and Ng IO: Non-coding
RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: Molecular functions and
pathological implications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
15:137–151. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Valinezhad Orang A, Safaralizadeh R and
Kazemzadeh-Bavili M: Mechanisms of miRNA-mediated gene regulation
from common downregulation to mRNA-specific upregulation. Int J
Genomics. 2014:9706072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang HN, Xu QQ, Thakur A, Alfred MO,
Chakraborty M, Ghosh A and Yu XB: Endothelial dysfunction in
diabetes and hypertension: Role of microRNAs and long non-coding
RNAs. Life Sci. 213:258–268. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Romano G and Kwong LN: MiRNAs, melanoma
and microenvironment: An intricate network. Int J Mol Sci.
18:23542017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fukuda T, Yamagata K, Fujiyama S,
Matsumoto T, Koshida I, Yoshimura K, Mihara M, Naitou M, Endoh H,
Nakamura T, et al: DEAD-box RNA helicase subunits of the Drosha
complex are required for processing of rRNA and a subset of
microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 9:604–611. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Davis BN, Hilyard AC, Lagna G and Hata A:
SMAD proteins control DROSHA-mediated microRNA maturation. Nature.
454:56–61. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Alarcón CR, Lee H, Goodarzi H, Halberg N
and Tavazoie SF: N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for
processing. Nature. 519:482–485. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Trabucchi M, Briata P, Garcia-Mayoral M,
Haase AD, Filipowicz W, Ramos A, Gherzi R and Rosenfeld MG: The
RNA-binding protein KSRP promotes the biogenesis of a subset of
microRNAs. Nature. 459:1010–1014. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Dinami R, Ercolani C, Petti E, Piazza S,
Ciani Y, Sestito R, Sacconi A, Biagioni F, le Sage C, Agami R, et
al: MiR-155 drives telomere fragility in human breast cancer by
targeting TRF1. Cancer Res. 74:4145–4156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li L, Li C, Wang S, Wang Z, Jiang J, Wang
W, Li X, Chen J, Liu K, Li C and Zhu G: Exosomes derived from
hypoxic oral squamous cell carcinoma cells deliver miR-21 to
normoxic cells to elicit a prometastatic phenotype. Cancer Res.
76:1770–1780. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Liu C, Kelnar K, Vlassov AV, Brown D, Wang
J and Tang DG: Distinct microRNA expression profiles in prostate
cancer stem/progenitor cells and tumor-suppressive functions of
let-7. Cancer Res. 72:3393–3404. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fu V, Plouffe SW and Guan KL: The Hippo
pathway in organ development, homeostasis, and regeneration. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 49:99–107. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Harvey KF, Zhang X and Thomas DM: The
Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:246–257. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Schlegelmilch K, Mohseni M, Kirak O,
Pruszak J, Rodriguez JR, Zhou D, Kreger BT, Vasioukhin V, Avruch J,
Brummelkamp TR and Camargo FD: Yap1 acts downstream of α-catenin to
control epidermal proliferation. Cell. 144:782–795. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gregory RI, Yan KP, Amuthan G, Chendrimada
T, Doratotaj B, Cooch N and Shiekhattar R: The Microprocessor
complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature. 432:235–240.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chang TC, Yu D, Lee YS, Wentzel EA, Arking
DE, West KM, Dang CV, Thomas-Tikhonenko A and Mendell JT:
Widespread microRNA repression by Myc contributes to tumorigenesis.
Nat Genet. 40:43–50. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yu T, Ma P, Wu D, Shu Y and Gao W:
Functions and mechanisms of microRNA-31 in human cancers. Biomed
Pharmacother. 108:1162–1169. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu X, Sempere LF, Ouyang H, Memoli VA,
Andrew AS, Luo Y, Demidenko E, Korc M, Shi W, Preis M, et al:
MicroRNA-31 functions as an oncogenic microRNA in mouse and human
lung cancer cells by repressing specific tumor suppressors. J Clin
Invest. 120:1298–1309. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wu Y, Li M, Lin J and Hu C: Hippo/TEAD4
signaling pathway as a potential target for the treatment of breast
cancer. Oncol Lett. 21:3132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Egawa H, Jingushi K, Hirono T, Ueda Y,
Kitae K, Nakata W, Fujita K, Uemura M, Nonomura N and Tsujikawa K:
The miR-130 family promotes cell migration and invasion in bladder
cancer through FAK and Akt phosphorylation by regulating PTEN. Sci
Rep. 6:205742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Duan J, Zhang H, Qu Y, Deng T, Huang D,
Liu R, Zhang L, Bai M, Zhou L, Ying G and Ba Y: Onco-miR-130
promotes cell proliferation and migration by targeting TGFβR2 in
gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 7:44522–44533. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhang Y, Shen H, Withers HG, Yang N,
Denson KE, Mussell AL, Truskinovsky A, Fan Q, Gelman IH, Frangou C
and Zhang J: VGLL4 selectively represses YAP-dependent gene
induction and tumorigenic phenotypes in breast cancer. Sci Rep.
7:61902017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Cheng L, Wang H and Han S: MiR-3910
promotes the growth and migration of cancer cells in the
progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 62:2812–2820.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Liu AM, Poon RT and Luk JM: MicroRNA-375
targets Hippo-signaling effector YAP in liver cancer and inhibits
tumor properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 394:623–627. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ruan T, He X, Yu J and Hang Z:
MicroRNA-186 targets Yes-associated protein 1 to inhibit Hippo
signaling and tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol
Lett. 11:2941–2945. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Deng J, Lei W, Xiang X, Zhang L, Lei J,
Gong Y, Song M, Wang Y, Fang Z, Yu F, et al: Cullin 4A (CUL4A), a
direct target of miR-9 and miR-137, promotes gastric cancer
proliferation and invasion by regulating the Hippo signaling
pathway. Oncotarget. 7:10037–10050. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Higashi T, Hayashi H, Ishimoto T, Takeyama
H, Kaida T, Arima K, Taki K, Sakamoto K, Kuroki H, Okabe H, et al:
MiR-9-3p plays a tumour-suppressor role by targeting TAZ (WWTR1) in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 113:252–258. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Tan G, Cao X, Dai Q, Zhang B, Huang J,
Xiong S, Zhang Yy, Chen W, Yang J and Li H: A novel role for
microRNA-129-5p in inhibiting ovarian cancer cell proliferation and
survival via direct suppression of transcriptional co-activators
YAP and TAZ. Oncotarget. 6:8676–8686. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Yu S, Jing L, Yin XR, Wang MC, Chen YM,
Guo Y, Nan KJ and Han LL: MiR-195 suppresses the metastasis and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by
inhibiting YAP. Oncotarget. 8:99757–99771. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Abd-Aziz N, Kamaruzman NI and Poh CL:
Development of microRNAs as potential therapeutics against cancer.
J Oncol. 2020:80297212020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Wang V and Wu W: MicroRNA-based
therapeutics for cancer. BioDrugs. 23:15–23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ: MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Shah V and Shah J: Recent trends in
targeting miRNAs for cancer therapy. J Pharm Pharmacol.
72:1732–1749. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Lu PY, Xie F and Woodle MC: In vivo
application of RNA interference: From functional genomics to
therapeutics. Adv Genet. 54:117–142. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Abbas-Terki T, Blanco-Bose W, Deglon N,
Pralong W and Aebischer P: Lentiviral-mediated RNA interference.
Hum Gene Ther. 13:2197–2201. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Tong AW: Small RNAs and non-small cell
lung cancer. Curr Mol Med. 6:339–349. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Hanna J, Hossain GS and Kocerha J: The
potential for microRNA therapeutics and clinical research. Front
Genet. 10:4782019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Si W, Shen J, Zheng H and Fan W: The role
and mechanisms of action of microRNAs in cancer drug resistance.
Clin Epigenetics. 11:252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Samji P, Rajendran MK, Warrier VP, Ganesh
A and Devarajan K: Regulation of Hippo signaling pathway in cancer:
A MicroRNA perspective. Cell Signal. 78:1098582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Wang ZX, Lu BB, Wang H, Cheng ZX and Yin
YM: MicroRNA-21 modulates chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells
to doxorubicin by targeting PTEN. Arch Med Res. 42:281–290. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Gong C, Yao Y, Wang Y, Liu B, Wu W, Chen
J, Su F, Yao H and Song E: Up-regulation of miR-21 mediates
resistance to trastuzumab therapy for breast cancer. Biol Chem.
286:19127–19137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zhou L, Qiu T, Xu J, Wang T, Wang J, Zhou
X, Huang Z, Zhu W, Shu Y and Liu P: miR-135a/b modulate cisplatin
resistance of human lung cancer cell line by targeting MCL1. Pathol
Oncol Res. 19:677–683. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Sun C, Li N, Yang Z, Zhou B, He Y, Weng D,
Fang Y, Wu P, Chen P, Yang X, et al: miR-9 regulation of BRCA1 and
ovarian cancer sensitivity to cisplatin and PARP inhibition. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 105:1750–1758. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Xu H, Zhao L, Fang Q, Sun J, Zhang S, Zhan
C, Liu S and Zhang Y: MiR-338-3p inhibits hepatocarcinoma cells and
sensitizes these cells to sorafenib by targeting hypoxia-induced
factor 1α. PLoS One. 9:e1155652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Feng YH and Tsao CJ: Emerging role of
microRNA-21 in cancer. Biomed Rep. 5:395–402. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Thorn CF, Oshiro C, Marsh S,
Hernandez-Boussard T, McLeod H, Klein TE and Altman RB: Doxorubicin
pathways: Pharmacodynamics and adverse effects. Pharmacogenet
Genomics. 21:440–446. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Tai W, Mahato R and Cheng K: The role of
HER2 in cancer therapy and targeted drug delivery. J Control
Release. 146:264–275. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
González-Alonso P, Zazo S, Martín-Aparicio
E, Luque M, Chamizo C, Sanz-Álvarez M, Minguez P, Gómez-López G,
Cristóbal I, Caramés C, et al: The hippo pathway transducers
YAP1/TEAD induce acquired resistance to trastuzumab in
HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 12:11082020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Lin CW, Chang YL, Chang YC, Lin JC, Chen
CC, Pan SH, Wu CT, Chen HY, Yang SC, Hong TM and Yang PC:
MicroRNA-135b promotes lung cancer metastasis by regulating
multiple targets in the Hippo pathway and LZTS1. Nat Commun.
4:18772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Mandati V, Del Maestro L, Dingli F,
Lombard B, Loew D, Molinie N, Romero S, Bouvard D, Louvard D,
Gautreau AM, et al: Phosphorylation of Merlin by Aurora A kinase
appears necessary for mitotic progression. J Biol Chem.
294:12992–13005. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Dasari S and Tchounwou PB: Cisplatin in
cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol.
740:364–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Gauthier A and Ho M: Role of sorafenib in
the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: An update.
Hepatol Res. 43:147–154. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Wu XZ, Xie GR and Chen D: Hypoxia and
hepatocellular carcinoma: The therapeutic target for hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22:1178–1182. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Tak E, Lee S, Lee J, Rashid MA, Kim YW,
Park JH, Park WS, Shokat KM, Ha J and Kim SS: Human carbonyl
reductase 1 upregulated by hypoxia renders resistance to apoptosis
in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Hepatol. 54:328–339. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Trédan O, Galmarini CM, Patel K and
Tannock IF: Drug resistance and the solid tumor microenvironment. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 99:1441–1454. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|