|
1
|
Brassart-Pasco S, Brezillon S, Brassart B,
Ramont L, Oudart JB and Monboisse JC: Tumor microenvironment:
Extracellular matrix alterations influence tumor progression. Front
Oncol. 10:3972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
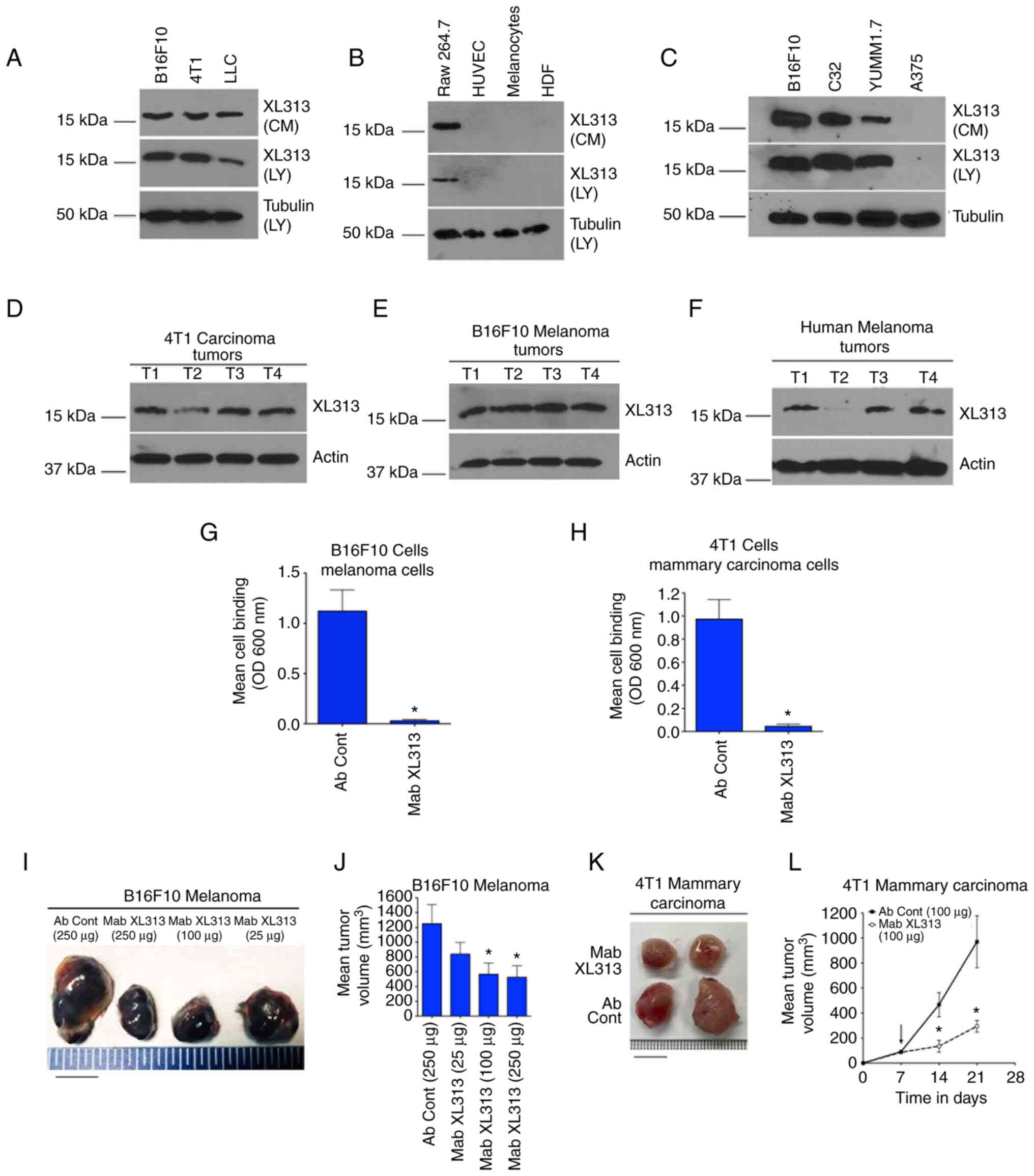
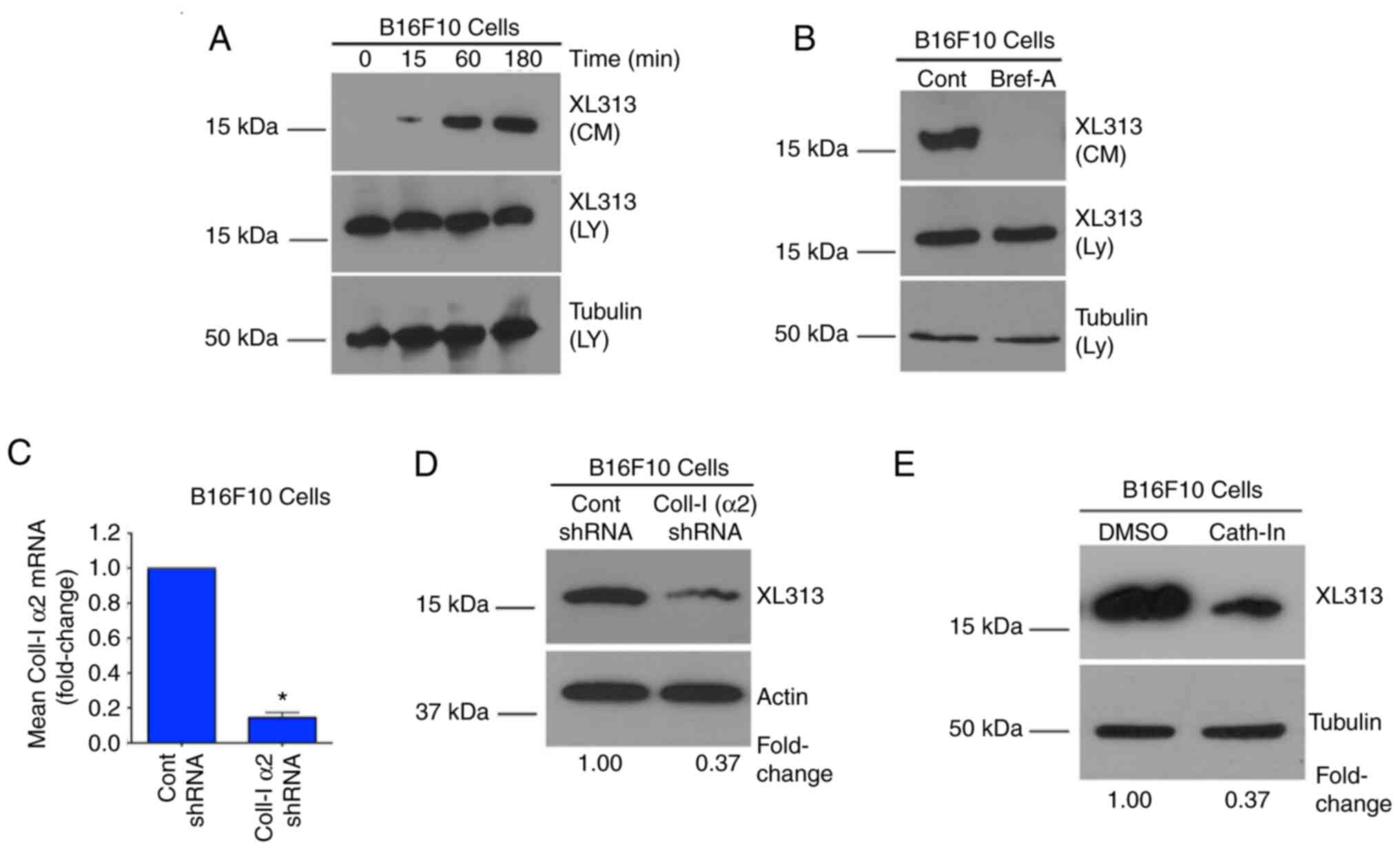
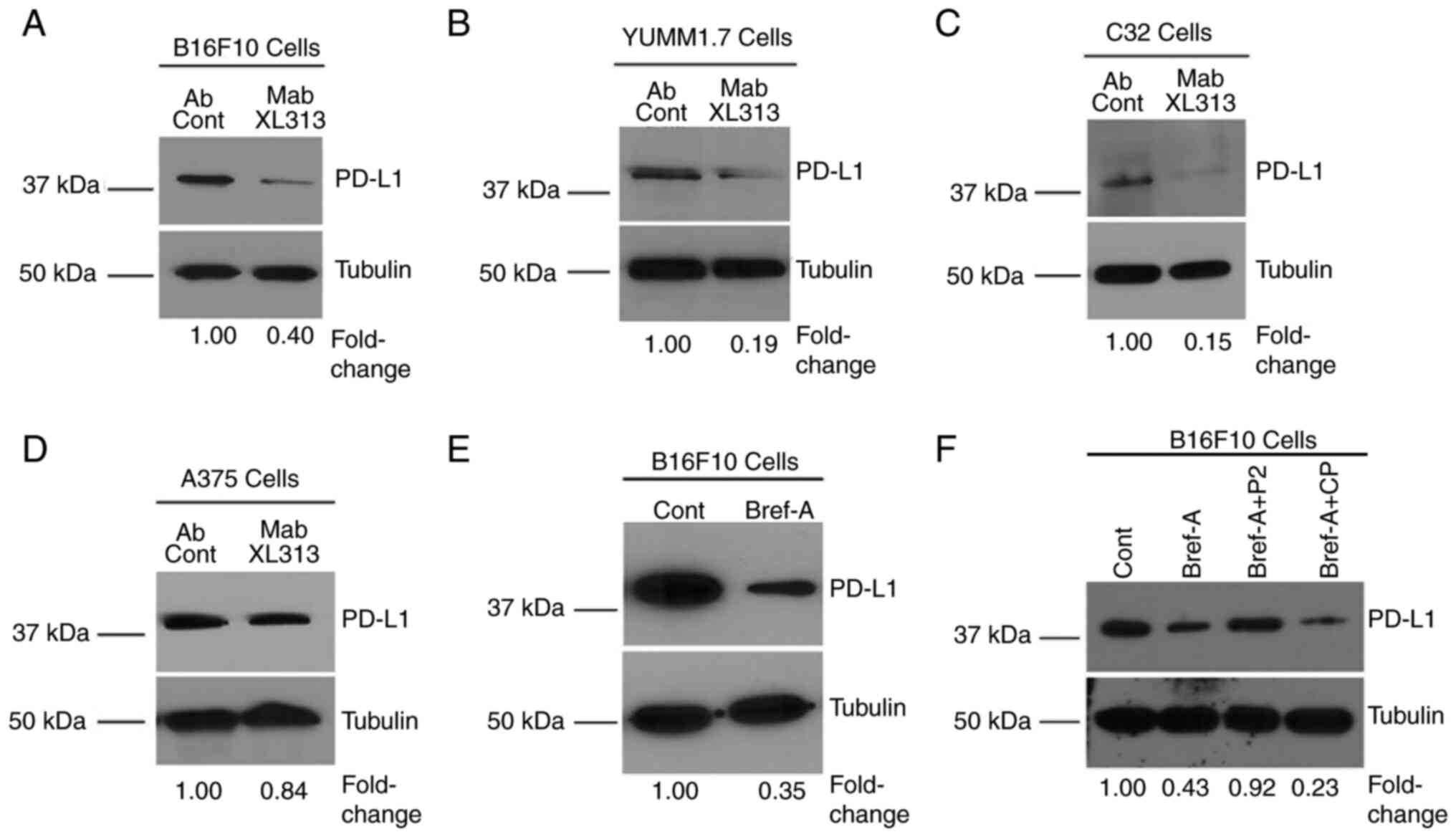
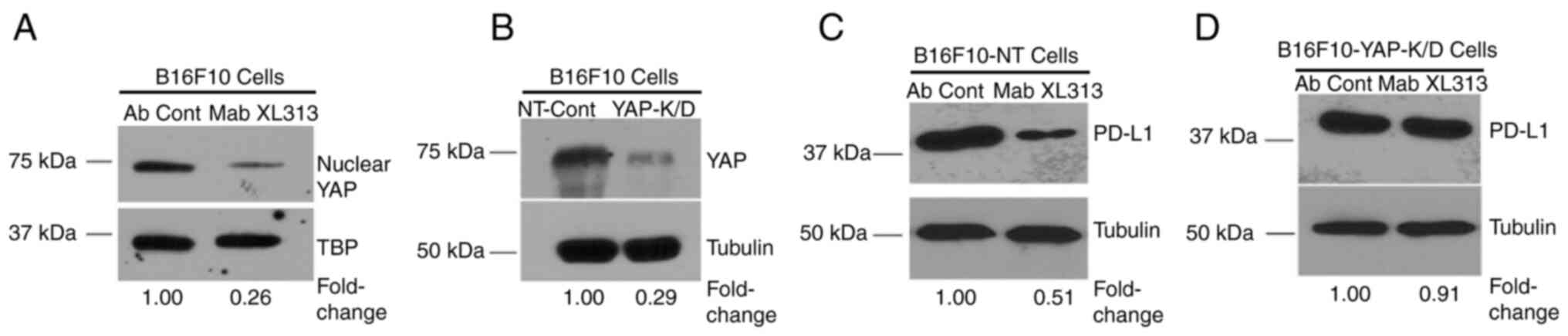
2
|
Ruiter D, Bogenrieder T, Elder D and
Herlyn M: Melanoma-stroma interactions: Structural and functional
aspects. Lancet Oncol. 3:35–43. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Han X, Caron JM and Brooks PC: Cryptic
collagen elements as signaling hubs in the regulation of tumor
growth and metastasis. J Cell Physiol. 235:9005–9020. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Contois L, Akalu A and Brooks PC:
Integrins as ‘functional hubs’ in the regulation of pathological
angiogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 19:318–328. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ricard-Blum S: The collagen family. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 3:a0049782011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zeltz C and Gullberg D: The
integrin-collagen connection-a glue for tissue repair? J Cell Sci.
129:12842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Leitinger B: Transmembrane collagen
receptors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:265–290. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bienkowski RS, Curran SF and Berg RA:
Kinetics of intracellular degradation of newly synthesized
collagen. Biochemistry. 25:2455–2459. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ames JJ, Contois L, Caron JM, Tweedie E,
Yang X, Friesel R, Vary C and Brooks PC: Identification of an
endogenously generated cryptic collagen epitope (XL313) that may
selectively regulate angiogenesis by an integrin yes-associated
protein (YAP) mechano-transduction pathway. J Biol Chem.
291:2731–2750. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Han X, Caron JM, Lary CW, Sathyanarayana
P, Vary C and Brooks PC: An RGDKGE-containing cryptic collagen
fragment regulates phosphorylation of large tumor suppressor
kinase-1 and controls ovarian tumor growth by a YAP-associated
protein-dependent mechanism. Am J Pathol. 191:527–544. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim MH, Kim CG, Kim SK, Shin SJ, Choe EA,
Park SH, Shin EC and Kim J: YAP-induced PD-L1 expression drives
immune evasion in BRAFi-resistant melanoma. Cancer Immunol Res.
6:255–266. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hsu PC, Miao J, Wang YC, Zhang WQ, Yang
YL, Wang CW, Yang CT, Huang Z, You J, Xu Z, et al: Inhibition of
yes-associated protein down-regulates PD-L1 (CD274) expression in
human malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Cell Mol Med. 22:3139–3148.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee BS, Park DI, Lee DH, Lee JE, Yeo MK,
Park YH, Lim DS, Choi W, Lee DH, Yoo G, et al: Hippo effector YAP
directly regulates the expression of PD-L1 transcripts in
EGFR-TKI-resistant lung adenocarcinoma. Biochem Biophy Res Commun.
491:493–499. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jensen C, Madsen DH, Hansen M, Schmidt H,
Svane IM, Karsdal MA and Willumsen N: Non-invasive biomarkers
derived from the extracellular matrix associate with response to
immune checkpoint blockade (anti-CTLA-4) in metastatic melanoma
patients. J Immunother Cancer. 6:1522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hurkmans DP, Jensen C, Koolen SLW, Aerts
J, Karsdal MA, Mathijssen RHJ and Willumsen N: Blood-based
extracellular matrix biomarkers are correlated with clinical
outcome after PD-1 inhibition in patients with metastatic melanoma.
J Immunother Cancer. 8:e0011932020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Abdou Y, Pandey M, Sarma M, Shah S, Baron
J and Ernstoff MS: Mechanism-based treatment of cancer with immune
checkpoint inhibitor therapies. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 86:1690–1702.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gandhi S, Pandey MR, Attwood K, Ji W,
Witkiewicz AK, Knudsen ES, Allen C, Tario JD, Wallace PK, Cedeno
CD, et al: Phase I clinical trial of combination propranolol and
pembrolizumab in locally advanced and metastatic melanoma: Safety,
tolerability, and preliminary evidence of antitumor activity. Clin
Cancer Res. 27:87–95. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Somasundaram R, Connelly T, Choi R, Choi
H, Samarkina A, Li L, Gregorio E, Chen Y, Thakur R, Abdel-Mohsen M,
et al: Tumor-infiltrating mast cells are associated with resistance
to anti-PD-1 therapy. Nat Commun. 12:3462021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cha JH, Chan LC, Li CW, Hsu JL and Hung
MC: Mechanisms controlling PD-L1 expression in cancer. Mol Cell.
76:359–370. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun C, Mezzadra R and Schumacher TN:
Regulation and function of the PD-L1 checkpoint. Immunity.
48:434–452. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gou Q, Dong C, Xu H, Khan B, Jin J, Liu Q,
Shi J and Hou Y: PD-L1 degradation pathway and immunotherapy for
cancer. Cell Death Dis. 11:9552020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li CW, Lim SO, Xia W, Lee HH, Chan LC, Kuo
CW, Khoo KH, Chang SS, Cha JH, Kim T, et al: Glycosylation and
stabilization of programmed death ligand-1 suppresses T-cell
activity. Nat Commun. 7:126322016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cha JH, Yang WH, Xia W, Wei Y, Chan LC,
Lim SO, Li CW, Kim T, Chang SS, Lee HH, et al: Metformin promotes
antitumor immunity via endoplasmic-reticulum-associated degradation
of PD-L1. Mol Cell. 71:606–620.e7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Burr ML, Sparbier CE, Chan YC, Williamson
JC, Woods K, Beavis PA, Lam EYN, Henderson MA, Bell CC, Stolzenburg
S, et al: CMTM6 maintains the expression of PD-L1 and regulates
anti-tumour immunity. Nature. 549:101–105. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang H, Yao H, Li C, Shi H, Lan J, Li Z,
Zhang Y, Liang L, Fang JY and Xu J: HIP1R targets PD-L1 to
lysosomal degradation to alter T cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Nat
Chem Biol. 15:42–50. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Coelho MA, de Carné Trécesson S, Rana S,
Zecchin D, Moore C, Molina-Arcas M, East P, Spencer-Dene B, Nye E,
Barnouin K, et al: Oncogenic RAS signaling promotes tumor
immunoresistance by stabilizing PD-L1 mRNA. Immunity.
47:1083–1099.e6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin HY, Chin YT, Nana AW, Shih YJ, Lai HY,
Tang HY, Leinung M, Mousa SA and Davis PJ: Actions of l-thyroxine
and Nano-diamino-tetrac (Nanotetrac) on PD-L1 in cancer cells.
Steroids. 114:59–67. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ren D, Zhao J, Sun Y, Li D, Meng Z, Wang
B, Fan P, Liu Z, Jin X and Wu H: Overexpressed ITGA2 promotes
malignant tumor aggression by up-regulating PD-L1 expression
through the activation of the STAT3 signaling pathway. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 38:4852019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vannini A, Leoni V, Barboni C, Sanapo M,
Zaghini A, Malatesta P, Campadelli-Fiume G and Gianni T:
αvβ3-integrin regulates PD-L1 expression and is involved in cancer
immune evasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 116:20141–20150. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Caron JM, Han X, Contois L, Vary CPH and
Brooks PC: The HU177 collagen epitope controls melanoma cell
migration and experimental metastasis by a CDK5/YAP-dependent
mechanism. Am J Pathol. 188:2356–2368. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Provenzano PP, Inman DR, Eliceiri KW,
Knittel JG, Yan L, Rueden CT, White JG and Keely PJ: Collagen
density promotes mammary tumor initiation and progression. BMC Med.
6:112008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vellinga TT, den Uil S, Rinkes IH, Marvin
D, Ponsioen B, Alvarez-Varela A, Fatrai S, Scheele C, Zwijnenburg
DA, Snippert H, et al: Collagen-rich stroma in aggressive colon
tumors induces mesenchymal gene expression and tumor cell invasion.
Oncogene. 35:5263–5271. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
van Kempen LC, Rijntjes J,
Mamor-Cornelissen I, Vincent-Naulleau S, Gerritsen MJ, Ruiter DJ,
van Dijk MC, Geffrotin C and van Muijen GN: Type I collagen
expression contributes to angiogenesis and the development of
deeply invasive cutaneous melanoma. Int J Cancer. 122:1019–1029.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Noel A, Munaut C, Boulvain A, Calberg-Bacq
CM, Lambert CA, Nusgens B, Lapiere CM and Foidart JM: Modulation of
collagen and fibronectin synthesis in fibroblasts by normal and
malignant cells. J Cell Biochem. 48:150–161. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Afik R, Zigmond E, Vugman M, Klepfish M,
Shimshoni E, Pasmanik-Chor M, Shenoy A, Bassat E, Halpern Z, Geiger
T, et al: Tumor macrophages are pivotal constructors of tumor
collagenous matrix. J Exp Med. 213:2315–2331. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gupta HB, Clark CA, Yuan B, Sareddy G,
Pandweswara S, Padron AS, Hurez V, Conejo-Garcia J, Vadlamudi R, Li
R and Curiel TJ: Tumor cell-intrinsic PD-L1 promotes
tumor-initiating cell generation and functions in melanoma and
ovarian cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 1:160302016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Clark CA, Gupta HB, Sareddy G, Pandeswara
S, Lao S, Yuan B, Drerup JM, Padron A, Conejo-Garcia J, Murthy K,
et al: Tumor-intrinsic PD-L1 signals regulate cell growth,
pathogenesis, and autophagy in ovarian cancer and melanoma. Cancer
Res. 76:6964–6974. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hudson K, Cross N, Jordan-Mahy N and
Leyland R: The extrinsic and intrinsic roles of PD-L1 and its
receptor PD-1: Implications for immunotherapy treatment. Front
Immunol. 11:5689312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xue Z, Zheng S, Linghu D, Liu B, Yang Y,
Chen MK, Huang H, Song J, Li H, Wang J, et al: PD-L1 deficiency
sensitizes tumor cells to DNA-PK inhibition and enhances cGAS-STING
activation. Am J Cancer Res. 12:2363–2375. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
VerPlank JJS, Lokireddy S, Zhao J and
Goldberg AL: 26S Proteasomes are rapidly activated by diverse
hormones and physiological states that raise cAMP and cause Rpn6
phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acd Sci USA. 116:4228–4237. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Asai M, Tsukamoto O, Minamino T, Asanuma
H, Fujita M, Asano Y, Takahama H, Sasaki H, Higo S, Asakura M, et
al: PKA rapidly enhances proteasome assembly and activity in in
vivo canine hearts. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 46:452–462. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lokireddy S, Kukushkin NV and Goldberg AL:
cAMP-induced phosphorylation of 26S proteasomes on Rpn6/PSMD11
enhances their activity and the degradation of misfolded proteins.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:E7176–E7185. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Qin XY, Zhang YL, Chi YF, Yan B, Zeng XJ,
Li HH and Liu Y: Angiotensin II regulates Th1 T cell
differentiation through angiotensin II type 1 receptor-PKA-mediated
activation of proteasome. Cell Physiol Biochem. 45:1366–1376. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kim S, Harris M and Varner JA: Regulation
of integrin alpha vbeta 3-mediated endothelial cell migration and
angiogenesis by integrin alpha5beta1 and protein kinase A. J Biol
Chem. 275:33920–33928. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Whelan MC and Senger DR: Collagen I
initiates endothelial cell morphogenesis by inducing actin
polymerization through suppression of cyclic AMP and protein kinase
A. J Biol Chem. 278:327–334. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim M, Kim M, Lee S, Kuninaka S, Saya H,
Lee H, Lee S and Lim DS: cAMP/PKA signalling reinforces the
LATS-YAP pathway to fully suppress YAP in response to actin
cytoskeletal changes. EMBO J. 32:1543–1555. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yu FX, Zhang Y, Park HW, Jewell JL, Chen
Q, Deng Y, Pan D, Taylor SS, Lai ZC and Guan KL: Protein kinase A
activates the hippo pathway to modulate cell proliferation and
differentiation. Genes Devel. 27:1223–1232. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Brooks PC, Clark RA and Cheresh DA:
Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis.
Science. 264:569–571. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Brooks PC, Montgomery AM, Rosenfeld M,
Reisfeld RA, Hu T, Klier G and Cheresh DA: Integrin alpha v beta 3
antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of
angiogenic blood vessels. Cell. 79:1157–1164. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Delbaldo C, Raymond E, Vera K,
Hammershaimb L, Kaucic K, Lozahic S, Marty M and Faivre S: Phase I
and pharmacokinetic study of etaracizumab (Abegrin), a humanized
monoclonal antibody against alphαvβeta3 integrin receptor, in
patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest New Drugs. 26:35–43.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hersey P, Sosman J, O'Day S, Richards J,
Bedikian A, Gonzalez R, Sharfman W, Weber R, Logan T, Buzoianu M,
et al: A randomized phase 2 study of etaracizumab, a monoclonal
antibody against integrin alpha(v)beta(3), + or -dacarbazine in
patients with stage IV metastatic melanoma. Cancer. 116:1526–1534.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Petitclerc E, Strömblad S, von Schalscha
TL, Mitjans F, Piulats J, Montgomery AM, Cheresh DA and Brooks PC:
Integrin alpha(v)beta3 promotes M21 melanoma growth in human skin
by regulating tumor cell survival. Cancer Res. 59:2724–2730.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Natali PG, Hamby CV, Felding-Habermann B,
Liang B, Nicotra MR, Di Filippo F, Giannarelli D, Temponi M and
Ferrone S: Clinical significance of alpha(v)beta3 integrin and
intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in cutaneous malignant
melanoma lesions. Cancer Res. 57:1554–1560. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kanamori M, Vanden Berg SR, Bergers G,
Berger MS and Pieper RO: Integrin beta3 overexpression suppresses
tumor growth in a human model of gliomagenesis: Implications for
the role of beta3 overexpression in glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer
Res. 64:2751–2758. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Jinushi M, Chiba S, Baghdadi M, Kinoshita
I, Dosaka-Akita H, Ito K, Yoshiyama H, Yagita H, Uede T and Takaoka
A: ATM-mediated DNA damage signals mediate immune escape through
integrin-αvβ3-dependent mechanisms. Cancer Res. 72:56–65. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Su X, Esser AK, Amend SR, Xiang J, Xu Y,
Ross MH, Fox GC, Kobayashi T, Steri V, Roomp K, et al: Antagonizing
integrin β3 increases immunosuppression in cancer. Cancer Res.
76:3484–3495. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Reynolds LE, Wyder L, Lively JC, Taverna
D, Robinson SD, Huang X, Sheppard D, Hynes RO and Hodivala-Dilke
KM: Enhanced pathological angiogenesis in mice lacking beta3
integrin or beta3 and beta5 integrins. Nature Med. 8:27–34. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Xi G, Guo W, Kang D, Ma J, Fu F, Qiu L,
Zheng L, He J, Fang N, Chen J, et al: Large-scale tumor-associated
collagen signatures identify high-risk breast cancer patients.
Theranostics. 11:3229–3243. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Drifka CR, Loeffler AG, Mathewson K,
Keikhosravi A, Eickhoff JC, Liu Y, Weber SM, Kao WJ and Eliceiri
KW: Highly aligned stromal collagen is a negative prognostic factor
following pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma resection. Oncotarget.
7:76197–76213. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wu PC, Hsieh TY, Tsai ZU and Liu TM: In
vivo quantification of the structural changes of collagens in a
melanoma microenvironment with second and third harmonic generation
microscopy. Sci Rep. 5:88792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Birk JW, Tadros M, Moezardalan K,
Nadyarnykh O, Forouhar F, Anderson J and Campagnola P: Second
harmonic generation imaging distinguishes both high-grade dysplasia
and cancer from normal colonic mucosa. Dig Dis Sci. 59:1529–1534.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Burke K, Smid M, Dawes RP, Timmermans MA,
Salzman P, van Deurzen CH, Beer DG, Foekens JA and Brown E: Using
second harmonic generation to predict patient outcome in solid
tumors. BMC Cancer. 15:9292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Xu J, Rodriguez D, Petitclerc E, Kim JJ,
Hangai M, Moon YS, Davis GE and Brooks PC: Proteolytic exposure of
a cryptic site within collagen type IV is required for angiogenesis
and tumor growth in vivo. J Cell Biol. 154:1069–1079. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Willumsen N, Ali SM, Leitzel K, Drabick
JJ, Yee N, Polimera HV, Nagabhairu V, Krecko L, Ali A, Maddukuri A,
et al: Collagen fragments quantified in serum as measures of
desmoplasia associate with survival outcome in patients with
advanced pancreatic cancer. Sci Rep. 9:197612019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kehlet SN, Sanz-Pamplona R, Brix S,
Leeming DJ, Karsdal MA and Moreno V: Excessive collagen turnover
products are released during colorectal cancer progression and
elevated in serum from metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Sci
Rep. 6:305992016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lipton A, Leitzel K, Ali SM, Polimera HV,
Nagabhairu V, Marks E, Richardson AE, Krecko L, Ali A, Koestler W,
et al: High turnover of extracellular matrix reflected by specific
protein fragments measured in serum is associated with poor
outcomes in two metastatic breast cancer cohorts. Int J Cancer.
143:3027–3034. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Hamilton HK, Rose AE, Christos PJ, Shapiro
RL, Berman RS, Mazumdar M, Ma MW, Krich D, Liebes L, Brooks PC and
Osman I: Increased shedding of HU177 correlates with worse
prognosis in primary melanoma. J Transl Med. 8:192010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lindsey ML, Iyer RP, Zamilpa R,
Yabluchanskiy A, DeLeon-Pennell KY, Hall ME, Kaplan A, Zouein FA,
Bratton D, Flynn ER, et al: A novel collagen matricryptin reduces
left ventricular dilation post-myocardial infarction by promoting
scar formation and angiogenesis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 66:1364–1374.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wang J and Pan W: The biological role of
the collagen alpha-3 (VI) chain and its cleaved C5 domain fragment
endotrophin in cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 13:5779–5793. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Jang JW, Kim MK and Bae SC: Reciprocal
regulation of YAP/TAZ by the hippo pathway and the small GTPase
pathway. Small GTPases. 11:280–288. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Feng X, Degese MS, Iglesias-Bartolome R,
Vaque JP, Molinolo AA, Rodrigues M, Zaidi MR, Ksander BR, Merlino
G, Sodhi A, et al: Hippo-independent activation of YAP by the GNAQ
uveal melanoma oncogene through a trio-regulated rho GTPase
signaling circuitry. Cancer Cell. 25:831–845. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Qiao Y, Chen J, Lim YB, Finch-Edmondson
ML, Seshachalam VP, Qin L, Jiang T, Low BC, Singh H, Lim CT and
Sudol M: YAP regulates actin dynamics through ARHGAP29 and promotes
metastasis. Cell Rep. 19:1495–1502. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kornepati AVR, Boyd JT, Murray CE,
Saifetiarova J, de la Peña Avalos B, Rogers CM, Bai H, Padron AS,
Liao Y, Ontiveros C, et al: Tumor intrinsic PD-L1 promotes DNA
repair in distinct cancers and suppresses PARP inhibitor-induced
synthetic lethality. Cancer Res. 82:2156–2170. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lee JJ, Kim SY, Kim SH, Choi S, Lee B and
Shin JS: STING mediates nuclear PD-L1 targeting-induced senescence
in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 13:7912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Yu J, Qin B, Moyer AM, Nowsheen S, Tu X,
Dong H, Boughey JC, Goetz MP, Weinshilboum R, Lou Z and Wang L:
Regulation of sister chromatid cohesion by nuclear PD-L1. Cell Res.
30:590–601. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Ghebeh H, Lehe C, Barhoush E, Al-Romaih K,
Tulbah A, Al-Alwan M, Hendrayani SF, Manogaran P, Alaiya A,
Al-Tweigeri T, et al: Doxorubicin downregulates cell surface B7-H1
expression and upregulates its nuclear expression in breast cancer
cells: Role of B7-H1 as an anti-apoptotic molecule. Breast Cancer
Res. 12:R482010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Ye L, Zhu Z, Chen X, Zhang H, Huang J, Gu
S and Zhao X: The importance of exosomal PD-L1 in cancer
progression and its potential as a therapeutic target. Cells.
10:32472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Gao Y, Nihira NT, Bu X, Chu C, Zhang J,
Kolodziejczyk A, Fan Y, Chan NT, Ma L, Liu J, et al:
Acetylation-dependent regulation of PD-L1 nuclear translocation
dictates the efficacy of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Nat Cell Biol.
22:1064–1075. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Gao Y, Bi D, Xie R, Li M, Gau J, Liu H,
Guo X, Fang J, Ding T, Zhu H, et al: Fusobacterium nucleatum
enhances the efficacy of PD-L1 blockade in colorectal cancer.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:3982021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wei Y, Tang X, Ren Y, Yang Y, Song F, Fu
J, Liu S, Yi M, Chen J, Wang S, et al: An RNA-RNA crosstalk network
involving HMGΒ1 and RICTOR facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma
tumorigenesis by promoting glutamine metabolism and impedes
immunotherapy by PD-L1+ exosomes activity. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 6:4212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhang JJ, Zhang QS, Li ZQ, Zhou JW and Du
J: Metformin attenuates PD-L1 expression through activating hippo
signaling pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Am J Transl Res.
11:6965–6976. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Moya IM, Castaldo SA, Van den Mooter L,
Soheily S, Sansores-Garcia L, Jacobs J, Mannaerts I, Xie J,
Verboven E, Hillen H, et al: Peritumoral activation of the hippo
pathway effectors YAP and TAZ suppresses liver cancer in mice.
Science. 366:1029–1034. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Yuan M, Tomlinson V, Lara R, Holliday D,
Chelala C, Harada T, Gangeswaran R, Manson-Bishop C, Smith P,
Danovi SA, et al: Yes-associated protein (YAP) functions as a tumor
suppressor in breast. Cell Death Differ. 15:1752–1759. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Lebid A, Chung L, Pardoll DM and Pan F:
YAP attenuates CD8 T cell-mediated anti-tumor response. Front
Immunol. 11:5802020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Stampouloglou E, Cheng N, Federico A,
Slaby E, Monti S, Szeto GL and Varelas X: Yap suppresses T-cell
function and infiltration in the tumor microenvironment. PLoS Biol.
18:e30005912020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Ni X, Tao J, Barbi J, Chen Q, Park BV, Li
Z, Zhang N, Lebid A, Ramaswamy A, Wei P, et al: YAP is essential
for Treg-mediated suppression of antitumor immunity. Cancer Discov.
8:1026–1043. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Yang W, Yang S, Zhang F, Cheng F, Wang X
and Rao J: Influence of the Hippo-YAP signalling pathway on tumor
associated macrophages (TAMs) and its implications on cancer
immunosuppressive microenvironment. Ann Transl Med. 8:3992020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wang G, Lu X, Dey P, Deng P, Wu CC, Jiang
S, Fang Z, Zhao K, Konaparthi R, Hua S, et al: Targeting
YAP-dependent MDSC infiltration impairs tumor progression. Cancer
Discov. 6:80–95. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Shibata M, Ham K and Hoque MO: A time for
YAP1: Tumorigenesis, immunosuppression and targeted therapy. Int J
Cancer. 143:2133–2144. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Lee JY, Dominguez AA, Nam S, Stowers RS,
Qi LS and Chaudhuri O: Identification of cell context-dependent
YAP-associated proteins reveals β1 and β4
integrin mediate YAP translocation independently of cell spreading.
Sci Rep. 9:171882019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Lecker SH, Goldberg AL and Mitch WE:
Protein degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in normal
and disease states. J Am Soc Nephrol. 17:1807–1819. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Bao W, Thullberg M, Zhang H, Onischenko A
and Strömblad S: Cell attachment to the extracellular matrix
induces proteasomal degradation of p21(CIP1) via Cdc42/Rac1
signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 22:4587–4597. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Sasada M, Iyoda T, Asayama T, Suenaga Y,
Sakai S, Kase N, Kodama H, Yokoi S, Isohama Y and Fukai F:
Inactivation of beta1 integrin induces proteasomal degradation of
Myc oncoproteins. Oncotarget. 10:4960–4972. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Kraman M, Bambrough PJ, Arnold JN, Roberts
EW, Magiera L, Jones JO, Gopinathan A, Tuveson DA and Fearon DT:
Suppression of antitumor immunity by stromal cells expressing
fibroblast activation protein-alpha. Science. 330:827–830. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Özdemir BC, Pentcheva-Hoang T, Carstens
JL, Zheng X, Wu CC, Simpson TR, Laklai H, Sugimoto H, Kahlert C,
Novitskiy SV, et al: Depletion of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts
and fibrosis induces immunosuppression and accelerates pancreas
cancer with reduced survival. Cancer Cell. 25:719–734. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Legler DF, Johnson-Léger C, Wiedle G, Bron
C and Imhof BA: The alpha v beta 3 integrin as a tumor homing
ligand for lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 34:1608–1616. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Larochelle C, Uphaus T, Broux B, Gowing E,
Paterka M, Michel L, Dudvarski Stankovic N, Bicker F, Lemaître F,
Prat A, et al: EGFL7 reduces CNS inflammation in mouse. Nature
Commun. 9:8192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|