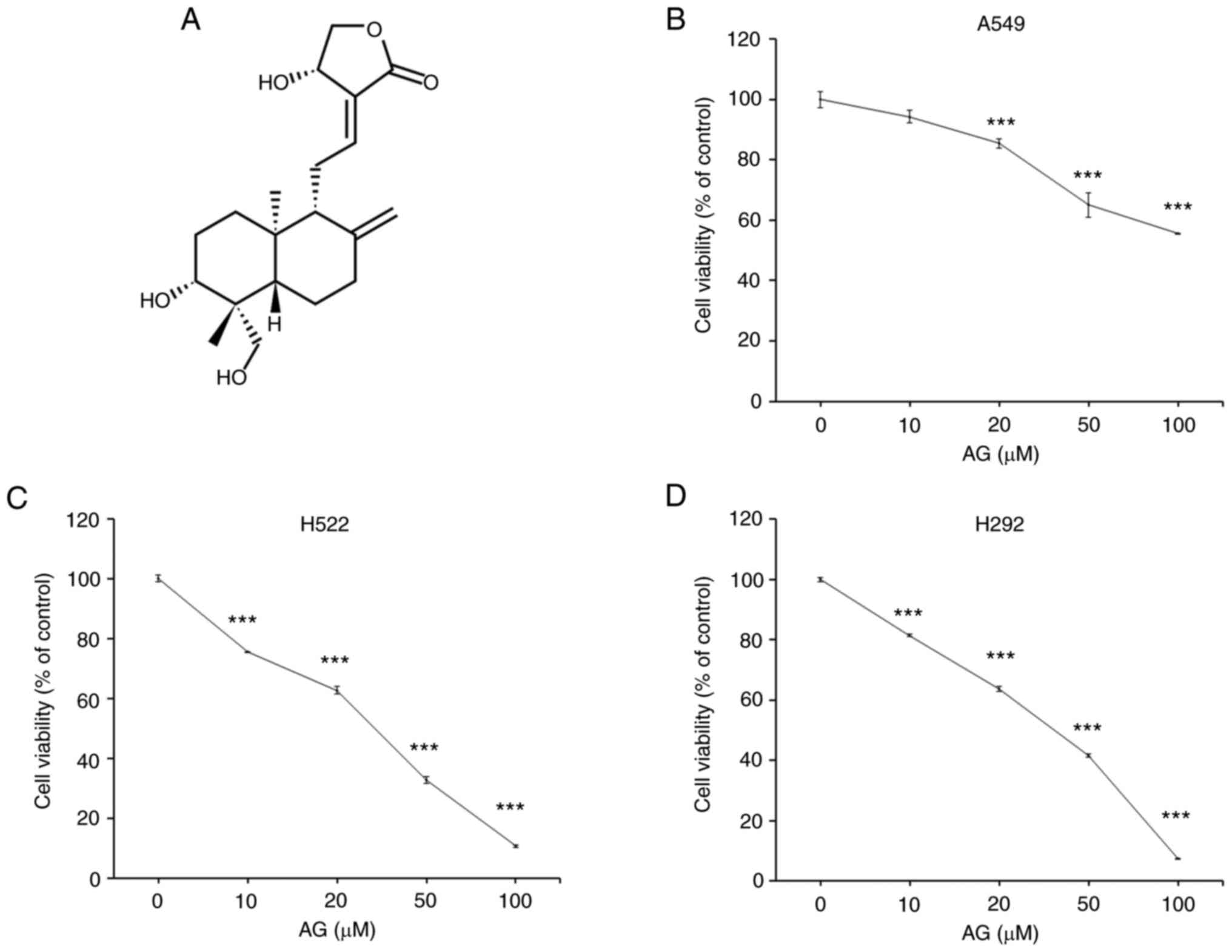
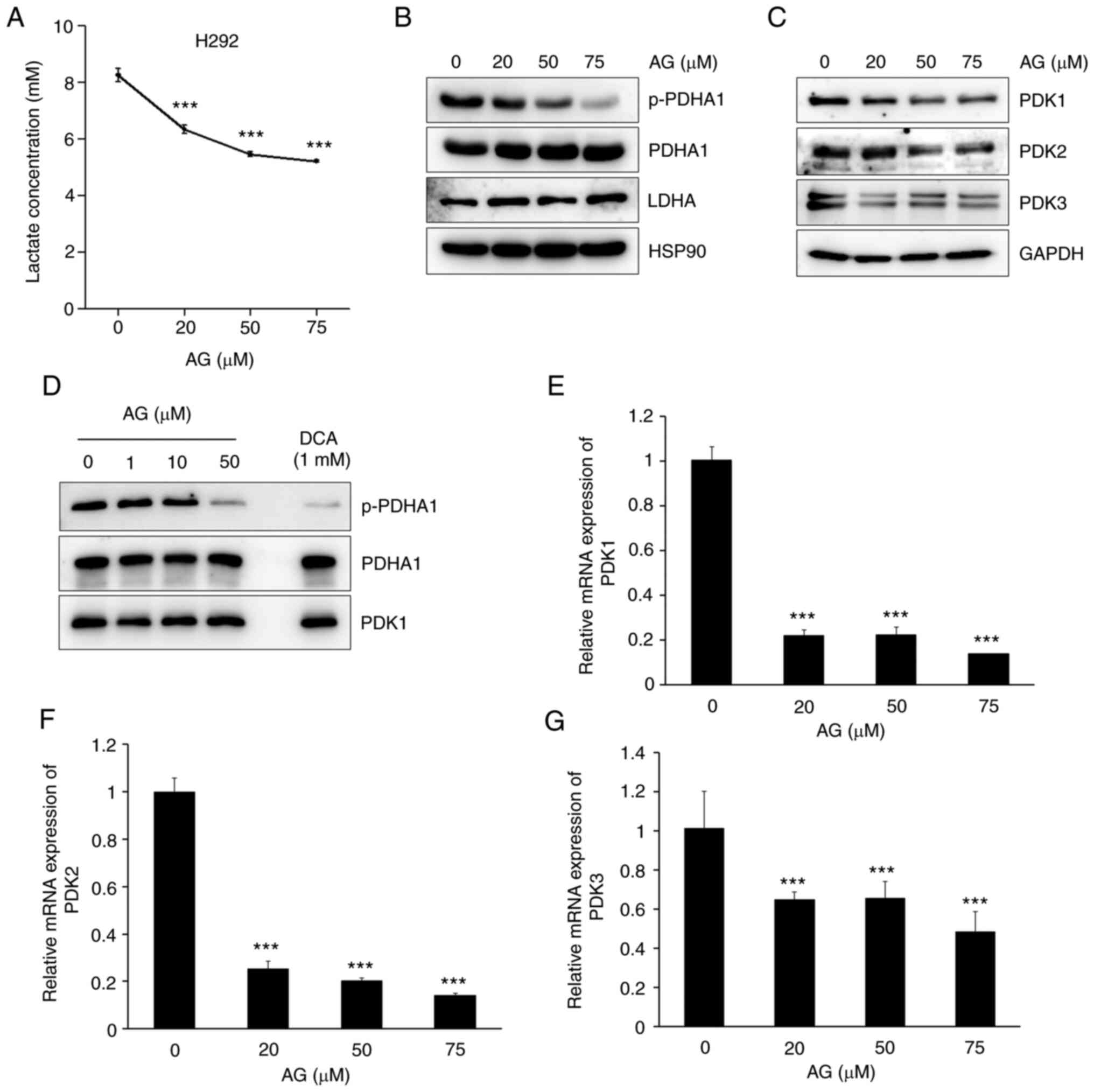
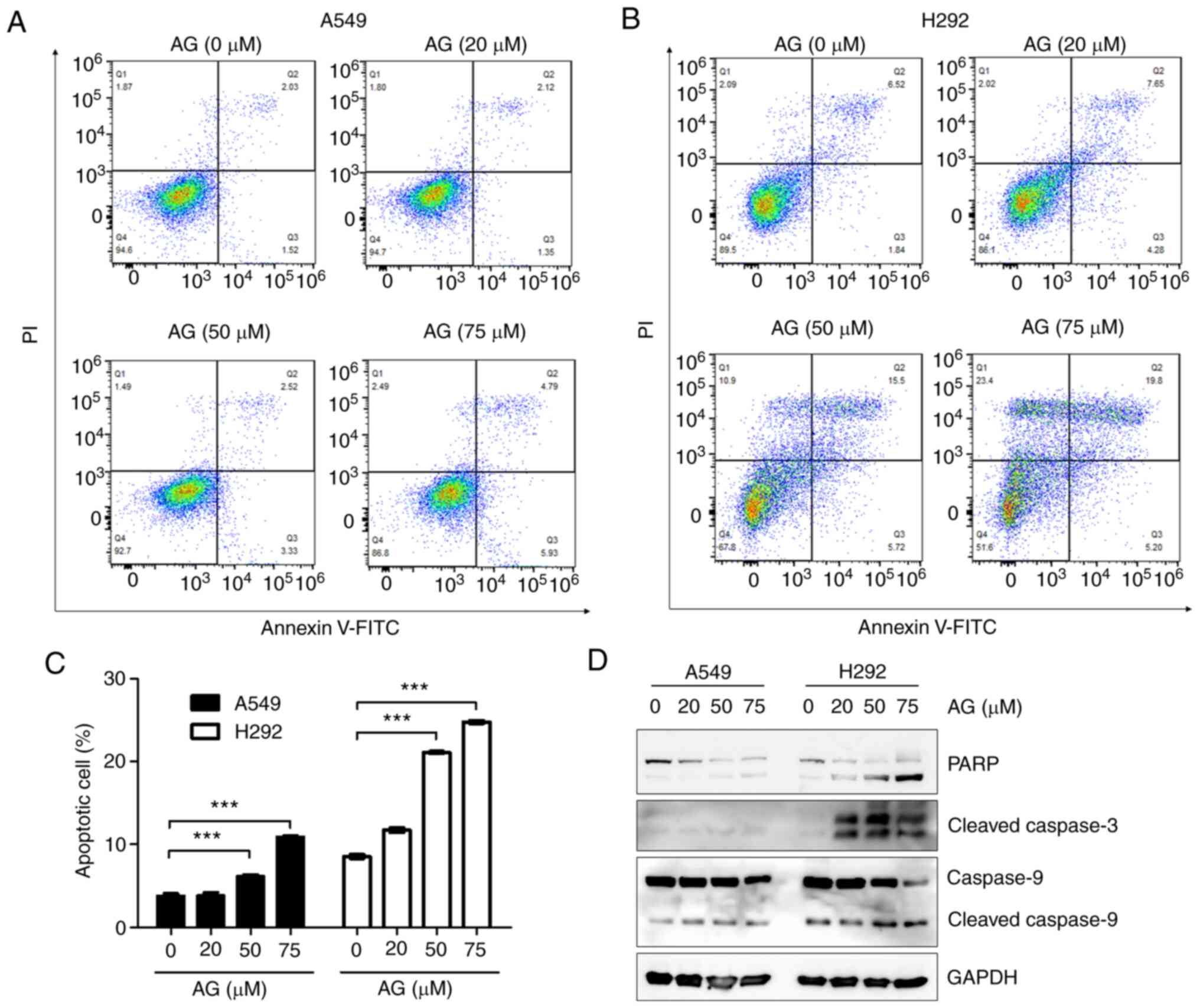
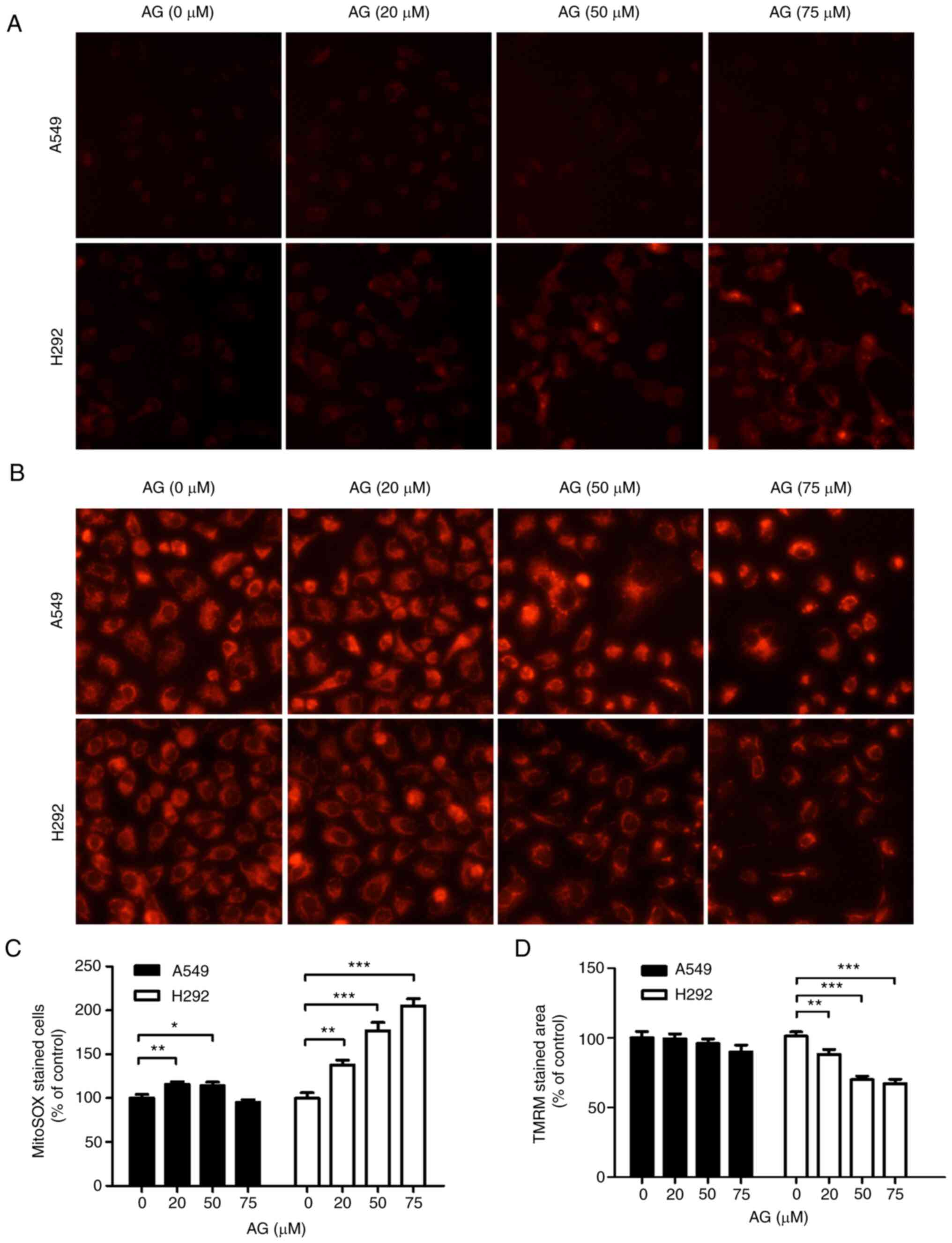
|
1
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pavlova NN, Zhu J and Thompson CB: The
hallmarks of cancer metabolism: Still emerging. Cell Metab.
34:355–377. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Altenberg B and Greulich KO: Genes of
glycolysis are ubiquitously overexpressed in 24 cancer classes.
Genomics. 84:1014–1020. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jiang B: Aerobic glycolysis and high level
of lactate in cancer metabolism and microenvironment. Genes Dis.
4:25–27. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
DeBerardinis RJ, Lum JJ, Hatzivassiliou G
and Thompson CB: The biology of cancer: Metabolic reprogramming
fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell Metab. 7:11–20. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin X, Xiao Z, Chen T, Liang SH and Guo H:
Glucose metabolism on tumor plasticity, diagnosis, and treatment.
Front Oncol. 10:3172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Woolbright BL, Rajendran G, Harris RA and
Taylor JA III: Metabolic flexibility in cancer: Targeting the
pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: Pyruvate dehydrogenase axis. Mol
Cancer Ther. 18:1673–1681. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rajani M, Shrivastava N and Ravishankara
MN: A rapid method for isolation of andrographolide from
Andrographis paniculata nees (kalmegh). Pharm Biol.
38:204–209. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Farooqi AA, Attar R, Sabitaliyevich UY,
Alaaeddine N, de Sousa DP, Xu B and Cho WC: The prowess of
andrographolide as a natural weapon in the war against cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 12:21592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Islam MT, Ali ES, Uddin SJ, Islam MA, Shaw
S, Khan IN, Saravi SSS, Ahmad S, Rehman S, Gupta VK, et al:
Andrographolide, a diterpene lactone from Andrographis
paniculata and its therapeutic promises in cancer. Cancer Lett.
420:129–145. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hocker HJ, Cho KJ, Chen CY, Rambahal N,
Sagineedu SR, Shaari K, Stanslas J, Hancock JF and Gorfe AA:
Andrographolide derivatives inhibit guanine nucleotide exchange and
abrogate oncogenic Ras function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:10201–10206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nguyen VS, Loh XY, Wijaya H, Wang J, Lin
Q, Lam Y, Wong WS and Mok YK: Specificity and inhibitory mechanism
of andrographolide and its analogues as antiasthma agents on NF-κB
p50. J Nat Prod. 78:208–217. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin HH, Tsai CW, Chou FP, Wang CJ, Hsuan
SW, Wang CK and Chen JH: Andrographolide down-regulates
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in human non-small cell lung cancer
A549 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 250:336–345. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li J, Zhang C, Jiang H and Cheng J:
Andrographolide inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1 through
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT pathway and suppresses breast
cancer growth. Onco Targets Ther. 8:427–435. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li GF, Qin YH and Du PQ: Andrographolide
inhibits the migration, invasion and matrix metalloproteinase
expression of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via
inhibition of HIF-1α signaling. Life Sci. 136:67–72. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin HC, Su SL, Lu CY, Lin AH, Lin WC, Liu
CS, Yang YC, Wang HM, Lii CK and Chen HW: Andrographolide inhibits
hypoxia-induced HIF-1α-driven endothelin 1 secretion by activating
Nrf2/HO-1 and promoting the expression of prolyl hydroxylases 2/3
in human endothelial cells. Environ Toxicol. 32:918–930. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen Z, Tang WJ, Zhou YH, Chen ZM and Liu
K: Andrographolide inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell
proliferation through the activation of the mitochondrial apoptosis
pathway and by reprogramming host glucose metabolism. Ann Transl
Med. 9:17012021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li X, Tian R, Liu L, Wang L, He D, Cao K,
Ma JK and Huang C: Andrographolide enhanced radiosensitivity by
downregulating glycolysis via the inhibition of the PI3K-Akt-mTOR
signaling pathway in HCT116 colorectal cancer cells. J Int Med Res.
48:3000605209461692020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Devkota AK, Kaoud TS, Warthaka M and Dalby
KN: Fluorescent peptide assays for protein kinases. Curr Protoc Mol
Biol. Chapter 18: Unit 18.17. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mullinax TR, Stepp LR, Brown JR and Reed
LJ: Synthetic peptide substrates for mammalian pyruvate
dehydrogenase kinase and pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 243:655–659. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Anwar S, Shamsi A, Mohammad T, Islam A and
Hassan MI: Targeting pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase signaling in the
development of effective cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev
Cancer. 1876:1885682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yadav N, Kumar S, Marlowe T, Chaudhary AK,
Kumar R, Wang J, O'Malley J, Boland PM, Jayanthi S, Kumar TK, et
al: Oxidative phosphorylation-dependent regulation of cancer cell
apoptosis in response to anticancer agents. Cell Death Dis.
6:e19692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Michelakis ED, Webster L and Mackey JR:
Dichloroacetate (DCA) as a potential metabolic-targeting therapy
for cancer. Br J Cancer. 99:989–994. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
McFate T, Mohyeldin A, Lu H, Thakar J,
Henriques J, Halim ND, Wu H, Schell MJ, Tsang TM, Teahan O, et al:
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity controls metabolic and
malignant phenotype in cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 283:22700–22708.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Shen X, Yan Y and Li H: Pyruvate
dehydrogenase kinases (PDKs): An overview toward clinical
applications. Biosci Rep. 41:BSR202044022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hur H, Xuan Y, Kim YB, Lee G, Shim W, Yun
J, Ham IH and Han SU: Expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase-1
in gastric cancer as a potential therapeutic target. Int J Oncol.
42:44–54. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fujiwara S, Kawano Y, Yuki H, Okuno Y,
Nosaka K, Mitsuya H and Hata H: PDK1 inhibition is a novel
therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. Br J Cancer. 108:170–178.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tan J, Lee PL, Li Z, Jiang X, Lim YC, Hooi
SC and Yu Q: B55β-associated PP2A complex controls PDK1-directed
myc signaling and modulates rapamycin sensitivity in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Cell. 18:459–471. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qu C, Yan C, Cao W, Li F, Qu Y, Guan K, Si
C, Yu Z and Qu Z: miR-128-3p contributes to mitochondrial
dysfunction and induces apoptosis in glioma cells via targeting
pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1. IUBMB Life. 72:465–475. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu T and Yin H: PDK1 promotes tumor cell
proliferation and migration by enhancing the Warburg effect in
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 37:193–200. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang W, Hu X, Chakravarty H, Yang Z and
Tam KY: Identification of novel pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1
(PDK1) inhibitors by kinase activity-based high-throughput
screening for anticancer therapeutics. ACS Comb Sci. 20:660–671.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Garon EB, Christofk HR, Hosmer W, Britten
CD, Bahng A, Crabtree MJ, Hong CS, Kamranpour N, Pitts S,
Kabbinavar F, et al: Dichloroacetate should be considered with
platinum-based chemotherapy in hypoxic tumors rather than as a
single agent in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 140:443–452. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang Z, Zhang SL, Hu X and Tam KY:
Inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 enhances the
anti-cancer effect of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small
cell lung cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. 838:41–52. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jin L, Kim EY, Chung TW, Han CW, Park SY,
Han JH, Bae SJ, Lee JR, Kim YW, Jang SB and Ha KT: Hemistepsin A
suppresses colorectal cancer growth through inhibiting pyruvate
dehydrogenase kinase activity. Sci Rep. 10:219402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kwak CH, Jin L, Han JH, Han CW, Kim E, Cho
M, Chung TW, Bae SJ, Jang SB and Ha KT: Ilimaquinone induces the
apoptotic cell death of cancer cells by reducing pyruvate
dehydrogenase kinase 1 activity. Int J Mol Sci. 21:60212020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kwak CH, Lee JH, Kim EY, Han CW, Kim KJ,
Lee H, Cho M, Jang SB, Kim CH, Chung TW and Ha KT: Huzhangoside A
suppresses tumor growth through inhibition of pyruvate
dehydrogenase kinase activity. Cancers (Basel). 11:7122019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Alapid AAI, Abd Majid R, Ibraheem ZO,
Mediani A, Ismail IS, Unyah NZ, Alhassan Abdullahi S, Nordin N,
Nasiru Wana M and Basir R: Investigation of andrographolide effect
on non-infected red blood cells using the 1H-NMR-based metabolomics
approach. Metabolites. 11:4862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim JW, Tchernyshyov I, Semenza GL and
Dang CV: HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase
kinase: A metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to
hypoxia. Cell Metab. 3:177–185. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Papandreou I, Cairns RA, Fontana L, Lim AL
and Denko NC: HIF-1 mediates adaptation to hypoxia by actively
downregulating mitochondrial oxygen consumption. Cell Metab.
3:187–197. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang LY, Hung CL, Chen YR, Yang JC, Wang
J, Campbell M, Izumiya Y, Chen HW, Wang WC, Ann DK and Kung HJ:
KDM4A coactivates E2F1 to regulate the PDK-dependent metabolic
switch between mitochondrial oxidation and glycolysis. Cell Rep.
16:3016–3027. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim JW, Gao P, Liu YC, Semenza GL and Dang
CV: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and dysregulated c-Myc cooperatively
induce vascular endothelial growth factor and metabolic switches
hexokinase 2 and pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1. Mol Cell Biol.
27:7381–7393. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pate KT, Stringari C, Sprowl-Tanio S, Wang
K, TeSlaa T, Hoverter NP, McQuade MM, Garner C, Digman MA, Teitell
MA, et al: Wnt signaling directs a metabolic program of glycolysis
and angiogenesis in colon cancer. EMBO J. 33:1454–1473. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Piao L, Sidhu VK, Fang YH, Ryan JJ, Parikh
KS, Hong Z, Toth PT, Morrow E, Kutty S, Lopaschuk GD and Archer SL:
FOXO1-mediated upregulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase-4
(PDK4) decreases glucose oxidation and impairs right ventricular
function in pulmonary hypertension: Therapeutic benefits of
dichloroacetate. J Mol Med (Berl). 91:333–346. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sugden MC and Holness MJ: Mechanisms
underlying regulation of the expression and activities of the
mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase kinases. Arch Physiol Biochem.
112:139–149. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Contractor T and Harris CR: p53 negatively
regulates transcription of the pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase Pdk2.
Cancer Res. 72:560–567. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gao H, Li H, Liu W, Mishra SK and Li C:
Andrographolide induces apoptosis in gastric cancer cells through
reactivation of p53 and inhibition of Mdm-2. Dokl Biochem Biophys.
500:393–401. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shi MD, Lin HH, Lee YC, Chao JK, Lin RA
and Chen JH: Inhibition of cell-cycle progression in human
colorectal carcinoma Lovo cells by andrographolide. Chem Biol
Interact. 174:201–210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Othman NS and Mohd Azman DK:
Andrographolide induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in
human glioblastoma DBTRG-05MG cell line via ERK1/2/c-Myc/p53
signaling pathway. Molecules. 27:66862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang J, Li C, Zhang L, Heng Y, Wang S,
Pan Y, Cai L, Zhang Y, Xu T, Chen X, et al: Andrographolide, a
diterpene lactone from the traditional Chinese medicine
andrographis paniculate, induces senescence in human lung
adenocarcinoma via p53/p21 and Skp2/p27. Phytomedicine.
98:1539332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jin L, Fang W, Li B, Shi G, Li X, Yang Y,
Yang J, Zhang Z and Ning G: Inhibitory effect of andrographolide in
3T3-L1 adipocytes differentiation through the PPARγ pathway. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 358:81–87. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lin HC, Lii CK, Chen HC, Lin AH, Yang YC
and Chen HW: Andrographolide inhibits oxidized LDL-induced
cholesterol accumulation and foam cell formation in macrophages. Am
J Chin Med. 46:87–106. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Shu J, Huang R, Tian Y, Liu Y, Zhu R and
Shi G: Andrographolide protects against endothelial dysfunction and
inflammatory response in rats with coronary heart disease by
regulating PPAR and NF-κB signaling pathways. Ann Palliat Med.
9:1965–1975. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tapia-Rojas C, Schuller A, Lindsay CB,
Ureta RC, Mejías-Reyes C, Hancke J, Melo F and Inestrosa NC:
Andrographolide activates the canonical Wnt signalling pathway by a
mechanism that implicates the non-ATP competitive inhibition of
GSK-3β: Autoregulation of GSK-3β in vivo. Biochem J. 466:415–430.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li G, Li M, Hu J, Lei R, Xiong H, Ji H,
Yin H, Wei Q and Hu G: The microRNA-182-PDK4 axis regulates lung
tumorigenesis by modulating pyruvate dehydrogenase and lipogenesis.
Oncogene. 36:989–998. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Atas E, Oberhuber M and Kenner L: The
implications of PDK1-4 on tumor energy metabolism, aggressiveness
and therapy resistance. Front Oncol. 10:5832172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
De Rosa V, Iommelli F, Terlizzi C,
Leggiero E, Camerlingo R, Altobelli GG, Fonti R, Pastore L and Del
Vecchio S: Non-canonical role of PDK1 as a negative regulator of
apoptosis through macromolecular complexes assembly at the
ER-mitochondria interface in oncogene-driven NSCLC. Cancers
(Basel). 13:41332021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yao S, Shang W, Huang L, Xu R, Wu M and
Wang F: The oncogenic and prognostic role of PDK1 in the
progression and metastasis of ovarian cancer. J Cancer. 12:630–643.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Peng F, Wang JH, Fan WJ, Meng YT, Li MM,
Li TT, Cui B, Wang HF, Zhao Y, An F, et al: Glycolysis gatekeeper
PDK1 reprograms breast cancer stem cells under hypoxia. Oncogene.
37:11192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lu H, Lu Y, Xie Y, Qiu S, Li X and Fan Z:
Rational combination with PDK1 inhibition overcomes cetuximab
resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. JCI Insight.
4:e1311062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Jin L, Cho M, Kim BS, Han JH, Park S, Lee
IK, Ryu D, Kim JH, Bae SJ and Ha KT: Drug evaluation based on
phosphomimetic PDHA1 reveals the complexity of activity-related
cell death in A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells. BMB Rep.
54:563–568. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kim BS, Chung TW, Choi HJ, Bae SJ, Cho HR,
Lee SO, Choi JH, Joo JK and Ha KT: Caesalpinia sappan induces
apoptotic cell death in ectopic endometrial 12Z cells through
suppressing pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 expression. Exp Ther
Med. 21:3572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zeng B, Wei A, Zhou Q, Yuan M, Lei K, Liu
Y, Song J, Guo L and Ye Q: Andrographolide: A review of its
pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, toxicity and clinical trials and
pharmaceutical researches. Phytother Res. 36:336–364. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|