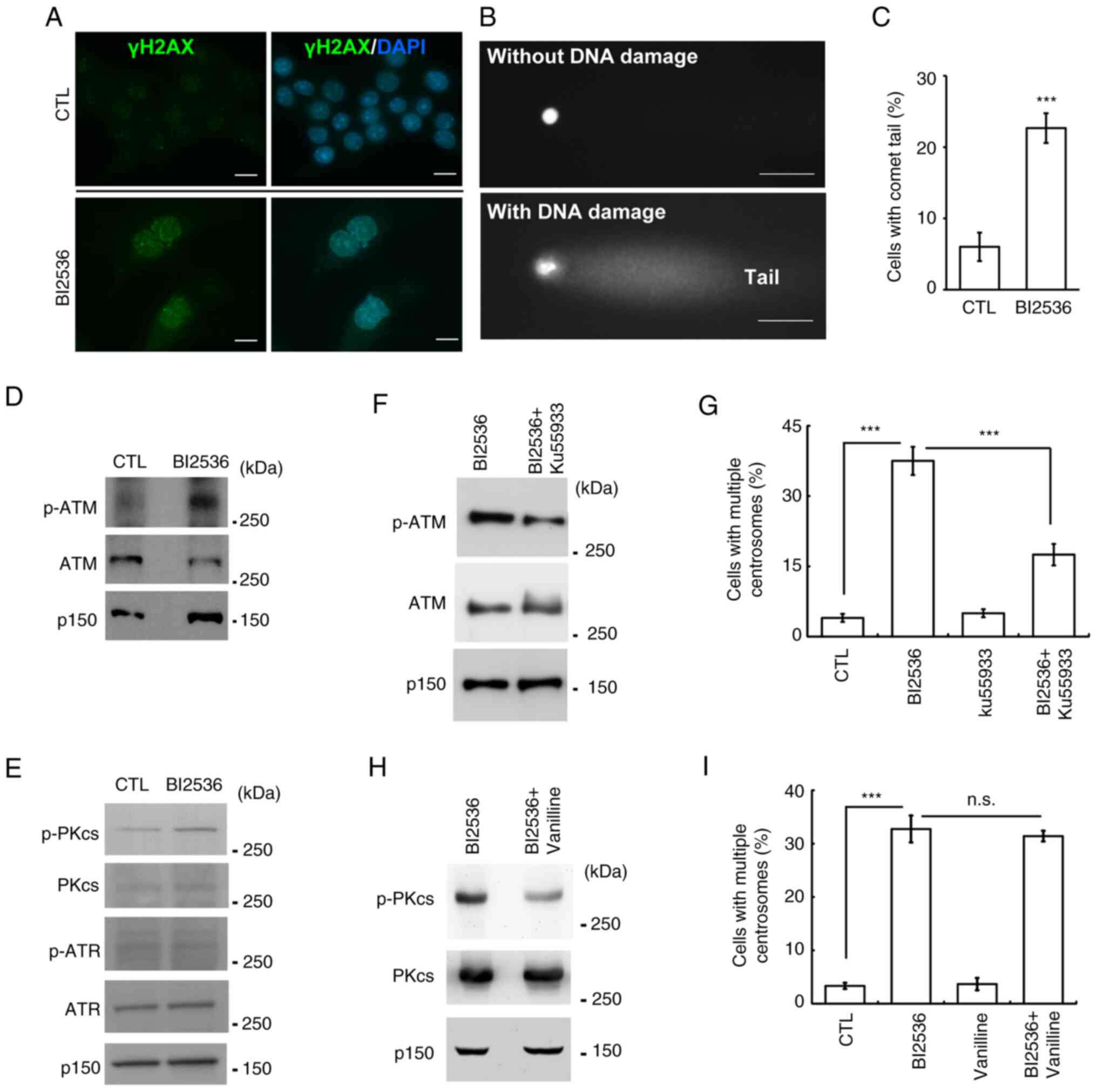
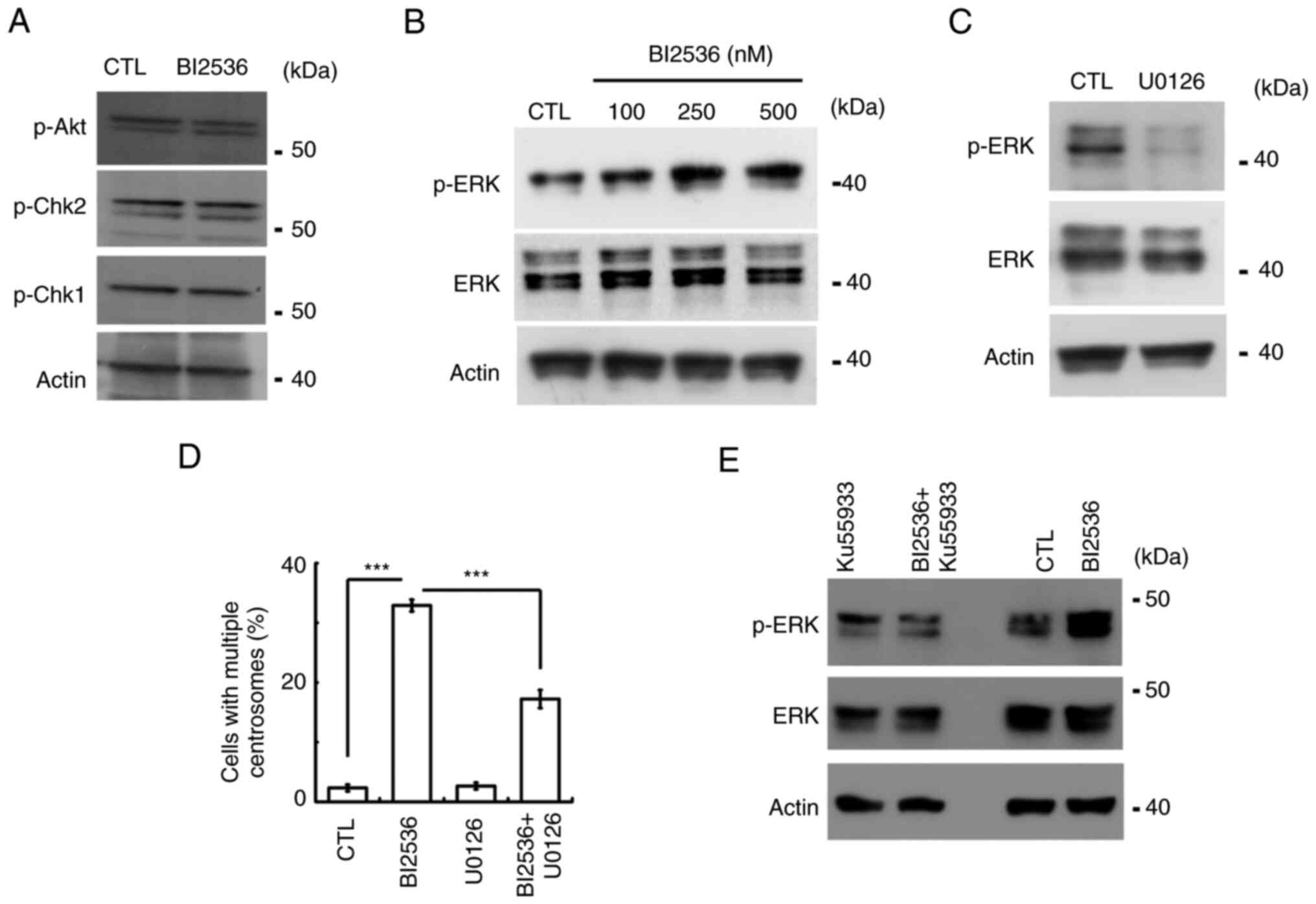
|
1
|
Long SE and Miller BS: Adrenocortical
cancer treatment. Surg Clin North Am. 99:759–771. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Abiven G, Coste J, Groussin L, Anract P,
Tissier F, Legmann P, Dousset B, Bertagna X and Bertherat J:
Clinical and biological features in the prognosis of adrenocortical
cancer: Poor outcome of cortisol-secreting tumors in a series of
202 consecutive patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 91:2650–2655.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen TY, Syu JS, Lin TC, Cheng HL, Lu FL
and Wang CY: Chloroquine alleviates etoposide-induced centrosome
amplification by inhibiting CDK2 in adrenocortical tumor cells.
Oncogenesis. 4:e1802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fassnacht M, Terzolo M, Allolio B, Baudin
E, Haak H, Berruti A, Welin S, Schade-Brittinger C, Lacroix A,
Jarzab B, et al: Combination chemotherapy in advanced
adrenocortical carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 366:2189–2197. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Libé R: Adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC):
Diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Front Cell Dev Biol. 3:452015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Steegmaier M, Hoffmann M, Baum A, Lénárt
P, Petronczki M, Krssák M, Gürtler U, Garin-Chesa P, Lieb S, Quant
J, et al: BI 2536, a potent and selective inhibitor of polo-like
kinase 1, inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Curr Biol. 17:316–322.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shin SB, Woo SU and Yim H: Differential
cellular effects of Plk1 inhibitors targeting the ATP-binding
domain or polo-box domain. J Cell Physiol. 230:3057–3067. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matthess Y, Raab M, Knecht R, Becker S and
Strebhardt K: Sequential Cdk1 and Plk1 phosphorylation of caspase-8
triggers apoptotic cell death during mitosis. Mol Oncol. 8:596–608.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen TY, Syu JS, Han TY, Cheng HL, Lu FI
and Wang CY: Cell cycle-dependent localization of dynactin subunit
p150 glued at centrosome. J Cell Biochem. 116:2049–2060. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lai PY, Wang CY, Chen WY, Kao YH, Tsai HM,
Tachibana T, Chang WC and Chung BC: Steroidogenic factor 1 (NR5A1)
resides in centrosomes and maintains genomic stability by
controlling centrosome homeostasis. Cell Death Differ.
18:1836–1844. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang CY, Kao YH, Lai PY, Chen WY and Chung
BC: Steroidogenic factor 1 (NR5A1) maintains centrosome homeostasis
in steroidogenic cells by restricting centrosomal DNA-dependent
protein kinase activation. Mol Cell Biol. 33:476–484. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Su S, Chhabra G, Singh CK, Ndiaye MA and
Ahmad N: PLK1 inhibition-based combination therapies for cancer
management. Transl Oncol. 16:1013322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lian G, Li L, Shi Y, Jing C, Liu J, Guo X,
Zhang Q, Dai T, Ye F, Wang Y and Chen M: BI2536, a potent and
selective inhibitor of polo-like kinase 1, in combination with
cisplatin exerts synergistic effects on gastric cancer cells. Int J
Oncol. 52:804–814. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Choi M, Kim W, Cheon MG, Lee CW and Kim
JE: Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor BI2536 causes mitotic catastrophe
following activation of the spindle assembly checkpoint in
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 357:591–601. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang CY, Huang EY, Huang SC and Chung BC:
DNA-PK/Chk2 induces centrosome amplification during prolonged
replication stress. Oncogene. 34:1263–1269. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen TY, Huang BM, Tang TK, Chao YY, Xiao
XY, Lee PR, Yang LY and Wang CY: Genotoxic stress-activated
DNA-PK-p53 cascade and autophagy cooperatively induce ciliogenesis
to maintain the DNA damage response. Cell Death Differ.
28:1865–1879. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang CY, Tsai HL, Syu JS, Chen TY and Su
MT: Primary cilium-regulated EG-VEGF signaling facilitates
trophoblast invasion. J Cell Physiol. 232:1467–1477. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Teng YN, Chang HC, Chao YY, Cheng HL, Lien
WC and Wang CY: Etoposide triggers cellular senescence by inducing
multiple centrosomes and primary cilia in adrenocortical tumor
cells. Cells. 10:14662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chao YY, Huang BM, Peng IC, Lee PR, Lai
YS, Chiu WT, Lin YS, Lin SC, Chang JH, Chen PS, et al: ATM- and
ATR-induced primary ciliogenesis promotes cisplatin resistance in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 237:4487–4503.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang CY, Chen WY, Lai PY and Chung BC:
Distinct functions of steroidogenic factor-1 (NR5A1) in the nucleus
and the centrosome. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 371:148–153. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ferguson RL and Maller JL: Centrosomal
localization of cyclin E-Cdk2 is required for initiation of DNA
synthesis. Curr Biol. 20:856–860. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ferguson RL, Pascreau G and Maller JL: The
cyclin A centrosomal localization sequence recruits MCM5 and Orc1
to regulate centrosome reduplication. J Cell Sci. 123:2743–2749.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bailey LJ, Teague R, Kolesar P, Bainbridge
LJ, Lindsay HD and Doherty AJ: PLK1 regulates the PrimPol damage
tolerance pathway during the cell cycle. Sci Adv. 7:eabh10042021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nakamura K, Kustatscher G, Alabert C, Hödl
M, Forne I, Völker-Albert M, Satpathy S, Beyer TE, Mailand N,
Choudhary C, et al: Proteome dynamics at broken replication forks
reveal a distinct ATM-directed repair response suppressing DNA
double-strand break ubiquitination. Mol Cell. 81:1084–1099.e6.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee M, Daniels MJ and Venkitaraman AR:
Phosphorylation of BRCA2 by the Polo-like kinase Plk1 is regulated
by DNA damage and mitotic progression. Oncogene. 23:865–872. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Z, Li J, Kong Y, Yan S, Ahmad N and Liu
X: Plk1 phosphorylation of Mre11 antagonizes the DNA damage
response. Cancer Res. 77:3169–3180. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Combes G, Alharbi I, Braga LG and Elowe S:
Playing polo during mitosis: PLK1 takes the lead. Oncogene.
36:4819–4827. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Johnson N, Cai D, Kennedy RD, Pathania S,
Arora M, Li YC, D'Andrea AD, Parvin JD and Shapiro GI: Cdk1
participates in BRCA1-dependent S phase checkpoint control in
response to DNA damage. Mol Cell. 35:327–339. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ira G, Pellicioli A, Balijja A, Wang X,
Fiorani S, Carotenuto W, Liberi G, Bressan D, Wan L, Hollingsworth
NM, et al: DNA end resection, homologous recombination and DNA
damage checkpoint activation require CDK1. Nature. 431:1011–1017.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|