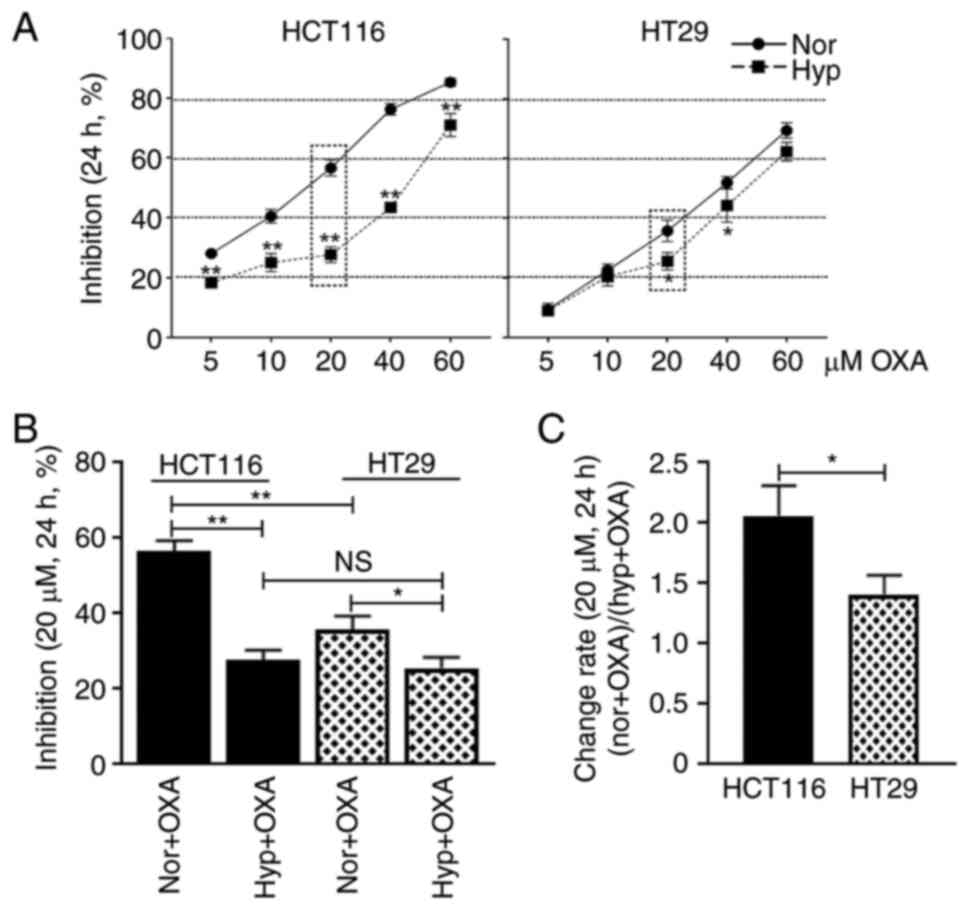
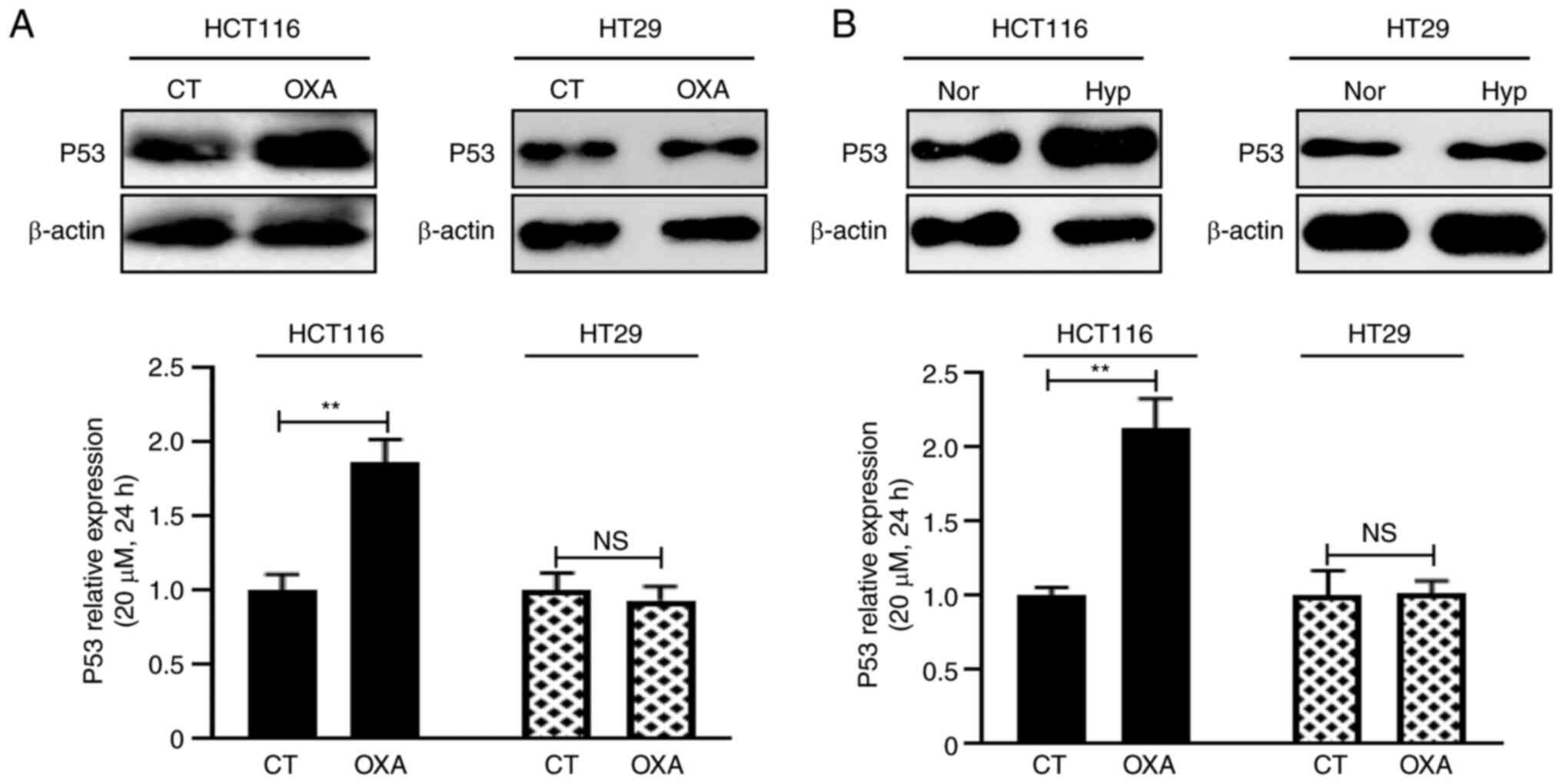
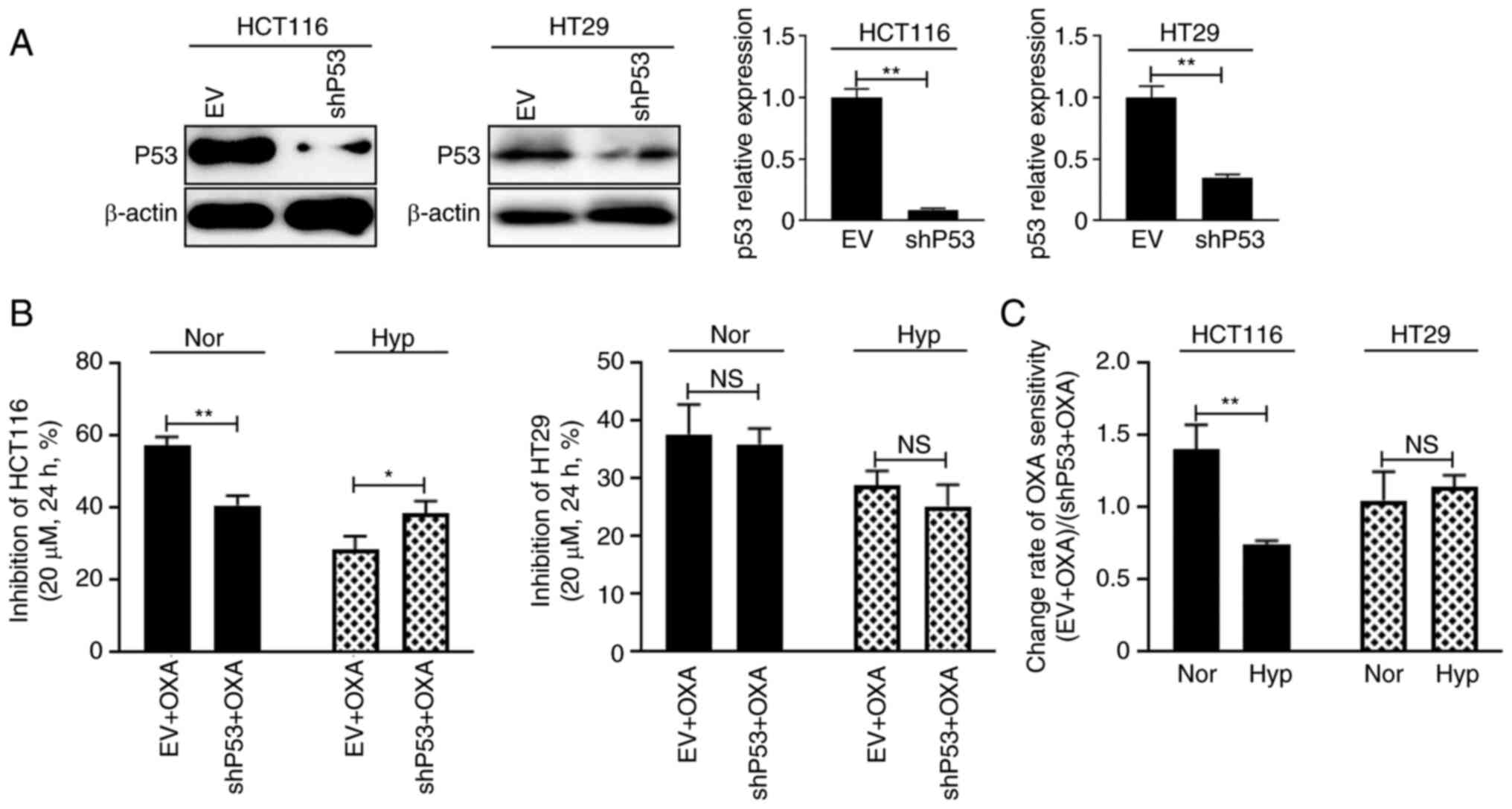
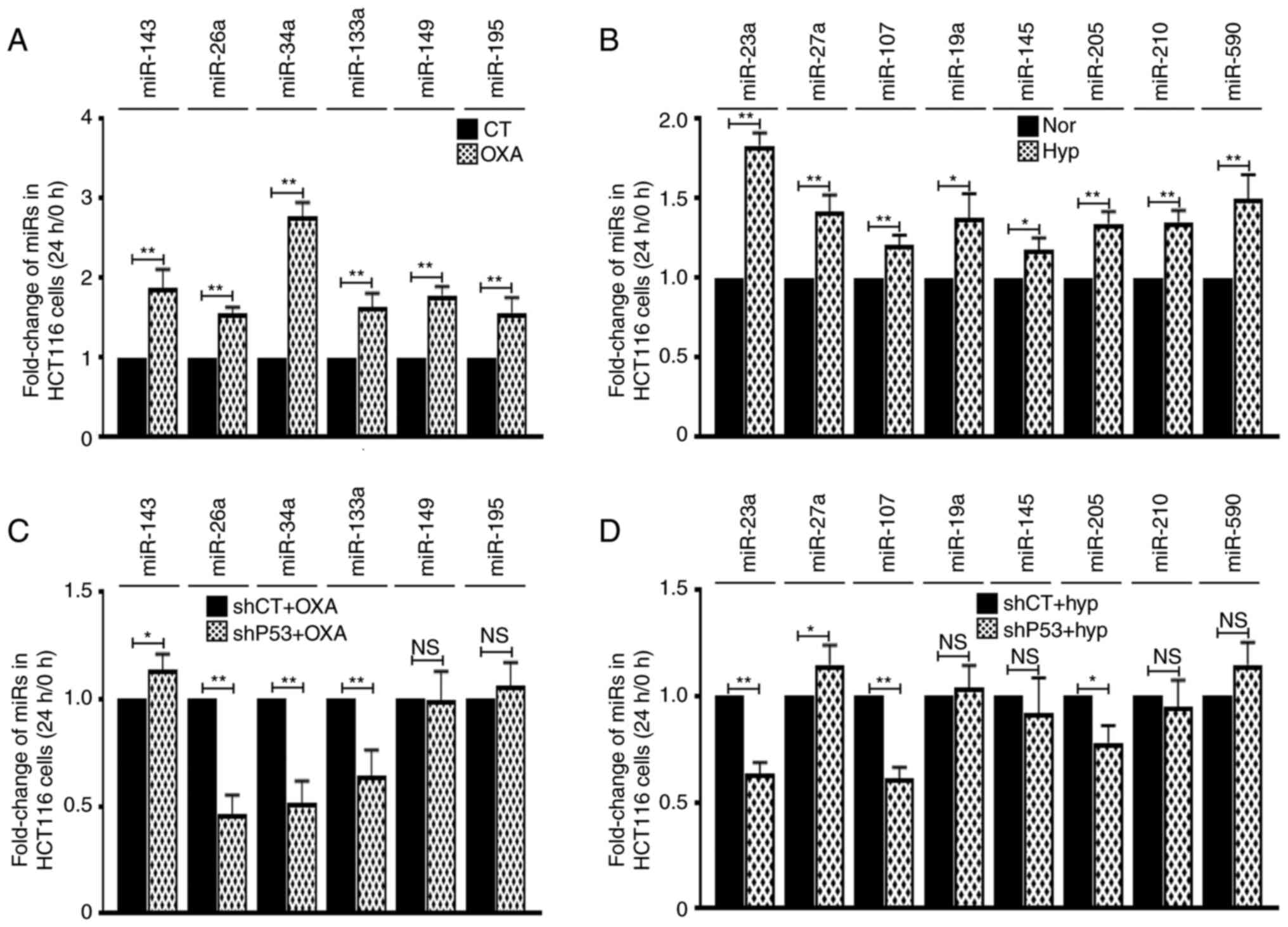
|
1
|
Cai J and Wang L: Looking back
2018-focused on colorectal cancer. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za
Zhi. 22:9–16. 2019.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Quirke P, Durdey P, Dixon MF and Williams
NS: Local recurrence of rectal adenocarcinoma due to inadequate
surgical resection. Histopathological study of lateral tumour
spread and surgical excision. Lancet. 2:996–999. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hsu HH, Chen MC, Baskaran R, Lin YM, Day
CH, Lin YJ, Tu CC, Vijaya Padma V, Kuo WW and Huang CY: Oxaliplatin
resistance in colorectal cancer cells is mediated via activation of
ABCG2 to alleviate ER stress induced apoptosis. J Cell Physiol.
233:5458–5467. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang C, Zhou Q, Li M, Tong X, Sun J, Qing
Y, Sun L, Yang X, Hu X, Jiang J, et al: Upregulation of CYP2S1 by
oxaliplatin is associated with p53 status in colorectal cancer cell
lines. Sci Rep. 6:330782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Meads MB, Gatenby RA and Dalton WS:
Environment-mediated drug resistance: A major contributor to
minimal residual disease. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:665–674. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Martinez-Balibrea E, Martínez-Cardús A,
Ginés A, Ruiz de Porras V, Moutinho C, Layos L, Manzano JL, Bugés
C, Bystrup S, Esteller M and Abad A: Tumor-related molecular
mechanisms of oxaliplatin resistance. Mol Cancer Ther.
14:1767–1776. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Plasencia C, Martinez-Balibrea E,
Martinez-Cardús A, Quinn DI, Abad A and Neamati N: Expression
analysis of genes involved in oxaliplatin response and development
of oxaliplatin-resistant HT29 colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
29:225–235. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pedraz-Cuesta E, Christensen S, Jensen AA,
Jensen NF, Bunch L, Romer MU, Brünner N, Stenvang J and Pedersen
SF: The glutamate transport inhibitor DL-Threo-β-Benzyloxyaspartic
acid (DL-TBOA) differentially affects SN38- and oxaliplatin-induced
death of drug-resistant colorectal cancer cells. BMC Cancer.
15:4112015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liao X, Song G, Xu Z, Bu Y, Chang F, Jia
F, Xiao X, Ren X, Zhang M and Jia Q: Oxaliplatin resistance is
enhanced by saracatinib via upregulation Wnt-ABCG1 signaling in
hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 20:312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hubbi ME and Semenza GL: Regulation of
cell proliferation by hypoxia-inducible factors. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 309:C775–C782. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pugh CW and Ratcliffe PJ: Regulation of
angiogenesis by hypoxia: Role of the HIF system. Nat Med.
9:677–684. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gilkes DM, Semenza GL and Wirtz D: Hypoxia
and the extracellular matrix: Drivers of tumour metastasis. Nat Rev
Cancer. 14:430–439. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang YA, Chen YF, Bao Y, Mahara S, Yatim
SMJM, Oguz G, Lee PL, Feng M, Cai Y, Tan EY, et al: Hypoxic tumor
microenvironment activates GLI2 via HIF-1α and TGF-β2 to promote
chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
115:E5990–E5999. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Roberts DL, Williams KJ, Cowen RL,
Barathova M, Eustace AJ, Brittain-Dissont S, Tilby MJ, Pearson DG,
Ottley CJ, Stratford IJ and Dive C: Contribution of HIF-1 and drug
penetrance to oxaliplatin resistance in hypoxic colorectal cancer
cells. Br J Cancer. 101:1290–1297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gariboldi MB, Taiana E, Bonzi MC,
Craparotta I, Giovannardi S, Mancini M and Monti E: The BH3-mimetic
obatoclax reduces HIF-1α levels and HIF-1 transcriptional activity
and sensitizes hypoxic colon adenocarcinoma cells to
5-fluorouracil. Cancer Lett. 364:156–164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nijhuis A, Thompson H, Adam J, Parker A,
Gammon L, Lewis A, Bundy JG, Soga T, Jalaly A, Propper D, et al:
Remodelling of microRNAs in colorectal cancer by hypoxia alters
metabolism profiles and 5-fluorouracil resistance. Hum Mol Genet.
26:1552–1564. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu K, Zhan Y, Yuan Z, Qiu Y, Wang H, Fan
G, Wang J, Li W, Cao Y, Shen X, et al: Hypoxia induces drug
resistance in colorectal cancer through the HIF-1α/miR-338-5p/IL-6
feedback loop. Mol Ther. 27:1810–1824. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Therachiyil L, Haroon J, Sahir F, Siveen
KS, Uddin S, Kulinski M, Buddenkotte J, Steinhoff M and
Krishnankutty R: Dysregulated phosphorylation of p53, autophagy and
stemness attributes the mutant p53 harboring colon cancer cells
impaired sensitivity to oxaliplatin. Front Oncol. 10:17442020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shang L and Wei M: Inhibition of SMYD2
sensitized cisplatin to resistant cells in NSCLC through activating
p53 pathway. Front Oncol. 9:3062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Takayama T, Miyanishi K, Hayashi T, Sato Y
and Niitsu Y: Colorectal cancer: Genetics of development and
metastasis. J Gastroenterol. 41:185–192. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang D, Sun W, Zhou Y, Li P, Chen F, Chen
H, Xia D, Xu E, Lai M, Wu Y and Zhang H: Mutations of key driver
genes in colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 37:173–187. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sui X, Kong N, Wang X, Fang Y, Hu X, Xu Y,
Chen W, Wang K, Li D, Jin W, et al: JNK confers 5-fluorouracil
resistance in p53-deficient and mutant p53-expressing colon cancer
cells by inducing survival autophagy. Sci Rep. 4:46942014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ikediobi ON, Davies H, Bignell G, Edkins
S, Stevens C, O'Meara S, Santarius T, Avis T, Barthorpe S,
Brackenbury L, et al: Mutation analysis of 24 known cancer genes in
the NCI-60 cell line set. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:2606–2612. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park JY, Park SJ, Shim KY, Lee KJ, Kim YB,
Kim YH and Kim SK: Echinomycin and a novel analogue induce
apoptosis of HT-29 cells via the activation of MAP kinases pathway.
Pharmacol Res. 50:201–207. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim JS, Lee C, Bonifant CL, Ressom H and
Waldman T: Activation of p53-dependent growth suppression in human
cells by mutations in PTEN or PIK3CA. Mol Cell Biol. 27:662–677.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Meng X, Sun W, Yu J, Zhou Y, Gu Y, Han J,
Zhou L, Jiang X and Wang C: LINC00460-miR-149-5p/miR-150-5p-mutant
p53 feedback loop promotes oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal
cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 22:1004–1015. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maqbool R, Lone SN and Ul Hussain M:
Post-transcriptional regulation of the tumor suppressor p53 by a
novel miR-27a, with implications during hypoxia and tumorigenesis.
Biochem J. 473:3597–3610. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li H, Rokavec M, Jiang L, Horst D and
Hermeking H: Antagonistic effects of p53 and HIF1A on microRNA-34a
regulation of PPP1R11 and STAT3 and hypoxia-induced epithelial to
mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer cells.
Gastroenterology. 153:505–520. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kiyonari S, Iimori M, Matsuoka K, Watanabe
S, Morikawa-Ichinose T, Miura D, Niimi S, Saeki H, Tokunaga E, Oki
E, et al: The 1,2-diaminocyclohexane carrier ligand in oxaliplatin
induces p53-dependent transcriptional repression of factors
involved in thymidylate biosynthesis. Mol Cancer Ther.
14:2332–2342. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Moradi Marjaneh R, Khazaei M, Ferns GA,
Avan A and Aghaee-Bakhtiari SH: MicroRNAs as potential therapeutic
targets to predict responses to oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer:
From basic evidence to therapeutic implication. IUBMB Life.
71:1428–1441. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Islam SU, Ahmed MB, Sonn JK, Jin EJ and
Lee YS: PRP4 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and drug
resistance in colon cancer cells via activation of p53. Int J Mol
Sci. 23:30922022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Du Y, Wei N, Ma R, Jiang S and Song D: A
miR-210-3p regulon that controls the Warburg effect by modulating
HIF-1α and p53 activity in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell
Death Dis. 11:7312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nersisyan S, Galatenko A, Chekova M and
Tonevitsky A: Hypoxia-induced miR-148a downregulation contributes
to poor survival in colorectal cancer. Front Genet. 12:6624682021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ullmann P, Qureshi-Baig K, Rodriguez F,
Ginolhac A, Nonnenmacher Y, Ternes D, Weiler J, Gäbler K, Bahlawane
C, Hiller K, et al: Hypoxia-responsive miR-210 promotes
self-renewal capacity of colon tumor-initiating cells by repressing
ISCU and by inducing lactate production. Oncotarget. 7:65454–65470.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Evert J, Pathak S, Sun XF and Zhang H: A
study on effect of oxaliplatin in MicroRNA expression in human
colon cancer. J Cancer. 9:2046–2053. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yamakuchi M, Lotterman CD, Bao C, Hruban
RH, Karim B, Mendell JT, Huso D and Lowenstein CJ: P53-induced
microRNA-107 inhibits HIF-1 and tumor angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 107:6334–6339. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang X, Yu M, Zhao K, He M, Ge W, Sun Y,
Wang Y, Sun H and Hu Y: Upregulation of MiR-205 under hypoxia
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting ASPP2. Cell
Death Dis. 7:e25172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jin F, Yang R, Wei Y, Wang D, Zhu Y, Wang
X, Lu Y, Wang Y, Zen K and Li L: HIF-1α-induced miR-23a~27a~24
cluster promotes colorectal cancer progression via reprogramming
metabolism. Cancer Lett. 440–441. 211–222. 2019.
|
|
40
|
Qian X, Yu J, Yin Y, He J, Wang L, Li Q,
Zhang LQ, Li CY, Shi ZM, Xu Q, et al: MicroRNA-143 inhibits tumor
growth and angiogenesis and sensitizes chemosensitivity to
oxaliplatin in colorectal cancers. Cell Cycle. 12:1385–1394. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
He C, Wang L, Zhang J and Xu H:
Hypoxia-inducible microRNA-224 promotes the cell growth, migration
and invasion by directly targeting RASSF8 in gastric cancer. Mol
Cancer. 16:352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen HY, Lin YM, Chung HC, Lang YD, Lin
CJ, Huang J, Wang WC, Lin FM, Chen Z, Huang HD, et al: miR-103/107
promote metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting the metastasis
suppressors DAPK and KLF4. Cancer Res. 72:3631–3641. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sun Z, Zhang Q, Yuan W, Li X, Chen C, Guo
Y, Shao B, Dang Q, Zhou Q, Wang Q, et al: MiR-103a-3p promotes
tumour glycolysis in colorectal cancer via hippo/YAP1/HIF1A axis. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:2502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tang Y, Weng X, Liu C, Li X and Chen C:
Hypoxia enhances activity and malignant behaviors of colorectal
cancer cells through the STAT3/MicroRNA-19a/PTEN/PI3K/AKT axis.
Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2021:41324882021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kim CW, Oh ET, Kim JM, Park JS, Lee DH,
Lee JS, Kim KK and Park HJ: Hypoxia-induced microRNA-590-5p
promotes colorectal cancer progression by modulating matrix
metalloproteinase activity. Cancer Lett. 416:31–41. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xu K, Chen G, Qiu Y, Yuan Z, Li H, Yuan X,
Sun J, Xu J, Liang X and Yin P: miR-503-5p confers drug resistance
by targeting PUMA in colorectal carcinoma. Oncotarget.
8:21719–21732. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Saieva L, Barreca MM, Zichittella C, Prado
MG, Tripodi M, Alessandro R and Conigliaro A: Hypoxia-induced
miR-675-5p supports β-catenin nuclear localization by regulating
GSK3-β activity in colorectal cancer cell lines. Int J Mol Sci.
21:38322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Costa V, Lo Dico A, Rizzo A, Rajata F,
Tripodi M, Alessandro R and Conigliaro A: MiR-675-5p supports
hypoxia induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colon
cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:24292–24302. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Poel D, Boyd LNC, Beekhof R, Schelfhorst
T, Pham TV, Piersma SR, Knol JC, Jimenez CR, Verheul HMW and
Buffart TE: Proteomic analysis of miR-195 and miR-497 replacement
reveals potential candidates that increase sensitivity to
oxaliplatin in MSI/P53wt colorectal cancer cells. Cells.
8:11112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Dong Y, Zhao J, Wu CW, Zhang L, Liu X,
Kang W, Leung WW, Zhang N, Chan FK, Sung JJ, et al: Tumor
suppressor functions of miR-133a in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer
Res. 11:1051–1060. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Moriondo G, Scioscia G, Soccio P, Tondo P,
De Pace CC, Sabato R, Foschino Barbaro MP and Lacedonia D: Effect
of hypoxia-induced micro-RNAs expression on oncogenesis. Int J Mol
Sci. 23:62942022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang X, Lan Z, He J, Lai Q, Yao X, Li Q,
Liu Y, Lai H, Gu C, Yan Q, et al: LncRNA SNHG6 promotes
chemoresistance through ULK1-induced autophagy by sponging
miR-26a-5p in colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 19:2342019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu J, Ke F, Chen T, Zhou Q, Weng L, Tan
J, Shen W, Li L, Zhou J, Xu C, et al: MicroRNAs that regulate PTEN
as potential biomarkers in colorectal cancer: A systematic review.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 146:809–820. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xu M, Chen X, Lin K, Zeng K, Liu X, Xu X,
Pan B, Xu T, Sun L, He B, et al: lncRNA SNHG6 regulates EZH2
expression by sponging miR-26a/b and miR-214 in colorectal cancer.
J Hematol Oncol. 12:32019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gao J, Li L, Wu M, Liu M and Xie X, Guo J,
Tang H and Xie X: MiR-26a inhibits proliferation and migration of
breast cancer through repression of MCL-1. PLoS One. 8:e651382013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yang Y, Zhang P, Zhao Y, Yang J, Jiang G
and Fan J: Decreased MicroRNA-26a expression causes cisplatin
resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol Ther.
17:515–525. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Rokavec M, Öner MG, Li H, Jackstadt R,
Jiang L, Lodygin D, Kaller M, Horst D, Ziegler PK, Schwitalla S, et
al: IL-6R/STAT3/miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated
colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J Clin Invest.
124:1853–1867. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Werner TV, Hart M, Nickels R, Kim YJ,
Menger MD, Bohle RM, Keller A, Ludwig N and Meese E: MiR-34a-3p
alters proliferation and apoptosis of meningioma cells in vitro and
is directly targeting SMAD4, FRAT1 and BCL2. Aging (Albany NY).
9:932–954. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Velaei K, Samadi N, Barazvan B and
Soleimani Rad J: Tumor microenvironment-mediated chemoresistance in
breast cancer. Breast. 30:92–100. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Scholten DJ II, Timmer CM, Peacock JD,
Pelle DW, Williams BO and Steensma MR: Down regulation of Wnt
signaling mitigates hypoxia-induced chemoresistance in human
osteosarcoma cells. PLoS One. 9:e1114312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Muz B, Kusdono HD, Azab F, de la Puente P,
Federico C, Fiala M, Vij R, Salama NN and Azab AK: Tariquidar
sensitizes multiple myeloma cells to proteasome inhibitors via
reduction of hypoxia-induced P-gp-mediated drug resistance. Leuk
Lymphoma. 58:2916–2925. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Mirnezami AH, Pickard K, Zhang L, Primrose
JN and Packham G: MicroRNAs: Key players in carcinogenesis and
novel therapeutic targets. Eur J Surg Oncol. 35:339–347. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Munk R, Panda AC, Grammatikakis I, Gorospe
M and Abdelmohsen K: Senescence-associated MicroRNAs. Int Rev Cell
Mol Biol. 334:177–205. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Vienberg S, Geiger J, Madsen S and
Dalgaard LT: MicroRNAs in metabolism. Acta Physiol (Oxf).
219:346–361. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Si W, Shen J, Zheng H and Fan W: The role
and mechanisms of action of microRNAs in cancer drug resistance.
Clin Epigenetics. 11:252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Tiwari A, Mukherjee B and Dixit M:
MicroRNA key to angiogenesis regulation: MiRNA biology and therapy.
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 18:266–277. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Oikawa T, Otsuka Y and Sabe H:
p53-dependent and -independent epithelial integrity: beyond miRNAs
and metabolic fluctuations. Cancers (Basel). 10:1622018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Blume CJ, Hotz-Wagenblatt A, Hüllein J,
Sellner L, Jethwa A, Stolz T, Slabicki M, Lee K, Sharathchandra A,
Benner A, et al: p53-dependent non-coding RNA networks in chronic
lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 29:2015–2023. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ueno T, Toyooka S, Fukazawa T, Kubo T, Soh
J, Asano H, Muraoka T, Tanaka N, Maki Y, Shien K, et al:
Preclinical evaluation of microRNA-34b/c delivery for malignant
pleural mesothelioma. Acta Med Okayama. 68:23–26. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Suh SO, Chen Y, Zaman MS, Hirata H,
Yamamura S, Shahryari V, Liu J, Tabatabai ZL, Kakar S, Deng G, et
al: MicroRNA-145 is regulated by DNA methylation and p53 gene
mutation in prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis. 32:772–778. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Huang Y, Kesselman D, Kizub D,
Guerrero-Preston R and Ratovitski EA: Phospho-ΔNp63α/microRNA
feedback regulation in squamous carcinoma cells upon cisplatin
exposure. Cell Cycle. 12:684–697. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Bisio A, De Sanctis V, Del Vescovo V,
Denti MA, Jegga AG, Inga A and Ciribilli Y: Identification of new
p53 target microRNAs by bioinformatics and functional analysis. BMC
Cancer. 13:5522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Suzuki HI, Yamagata K, Sugimoto K, Iwamoto
T, Kato S and Miyazono K: Modulation of microRNA processing by p53.
Nature. 460:529–533. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kulshreshtha R, Ferracin M, Wojcik SE,
Garzon R, Alder H, Agosto-Perez FJ, Davuluri R, Liu CG, Croce CM,
Negrini M, et al: A microRNA signature of hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol.
27:1859–1867. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Liao JM, Cao B, Zhou X and Lu H: New
insights into p53 functions through its target microRNAs. J Mol
Cell Biol. 6:206–213. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Rokavec M, Li H, Jiang L and Hermeking H:
The p53/microRNA connection in gastrointestinal cancer. Clin Exp
Gastroenterol. 7:395–413. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Du R, Sun W, Xia L, Zhao A, Yu Y, Zhao L,
Wang H, Huang C and Sun S: Hypoxia-induced down-regulation of
microRNA-34a promotes EMT by targeting the Notch signaling pathway
in tubular epithelial cells. PLoS One. 7:e307712012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhou B, Wei E, Shi H, Huang J, Gao L,
Zhang T, Wei Y and Ge B: MiR-26a inhibits cell proliferation and
induces apoptosis in human bladder cancer through regulating EZH2
bioactivity. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 10:11234–11241. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Li P, Zhang X, Wang H, Wang L, Liu T, Du
L, Yang Y and Wang C: MALAT1 is associated with poor response to
oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in colorectal cancer patients and
promotes chemoresistance through EZH2. Mol Cancer Ther. 16:739–751.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Sun C, Wang FJ, Zhang HG, Xu XZ, Jia RC,
Yao L and Qiao PF: miR-34a mediates oxaliplatin resistance of
colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting macroautophagy via
transforming growth factor-β/Smad4 pathway. World J Gastroenterol.
23:1816–1827. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Shi X, Kaller M, Rokavec M, Kirchner T,
Horst D and Hermeking H: Characterization of a
p53/miR-34a/CSF1R/STAT3 feedback loop in colorectal cancer. Cell
Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:391–418. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wu T, Wang Z, Liu Y, Mei Z, Wang G, Liang
Z, Cui A, Hu X, Cui L, Yang Y and Liu CY: Interleukin 22 protects
colorectal cancer cells from chemotherapy by activating the STAT3
pathway and inducing autocrine expression of interleukin 8. Clin
Immunol. 154:116–126. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Jahid S, Sun J, Edwards RA, Dizon D,
Panarelli NC, Milsom JW, Sikandar SS, Gümüs ZH and Lipkin SM:
miR-23a promotes the transition from indolent to invasive
colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov. 2:540–553. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Huang S, He X, Ding J, Liang L, Zhao Y,
Zhang Z, Yao X, Pan Z, Zhang P, Li J, et al: Upregulation of
miR-23a approximately 27a approximately 24 decreases transforming
growth factor-beta-induced tumor-suppressive activities in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 123:972–978. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Li X, Li X, Liao D, Wang X, Wu Z, Nie J,
Bai M, Fu X, Mei Q and Han W: Elevated microRNA-23a expression
enhances the chemoresistance of colorectal cancer cells with
microsatellite instability to 5-fluorouracil by directly targeting
ABCF1. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 16:301–309. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Peng F, Zhang H, Du Y and Tan P: miR-23a
promotes cisplatin chemoresistance and protects against
cisplatin-induced apoptosis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells
through twist. Oncol Rep. 33:942–950. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Xu F, Li Q, Wang Z and Cao X: Sinomenine
inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and promotes apoptosis
of prostate cancer cells by regulation of miR-23a. Biomed
Pharmacother. 112:1085922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Zhang YS, Wang MY, Zhang WL and Tang CH:
Proliferation, migration and apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia
cells regulated by mir-23a-3p targeting SMC1A and the mechanism.
Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 41:753–759. 2019.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|