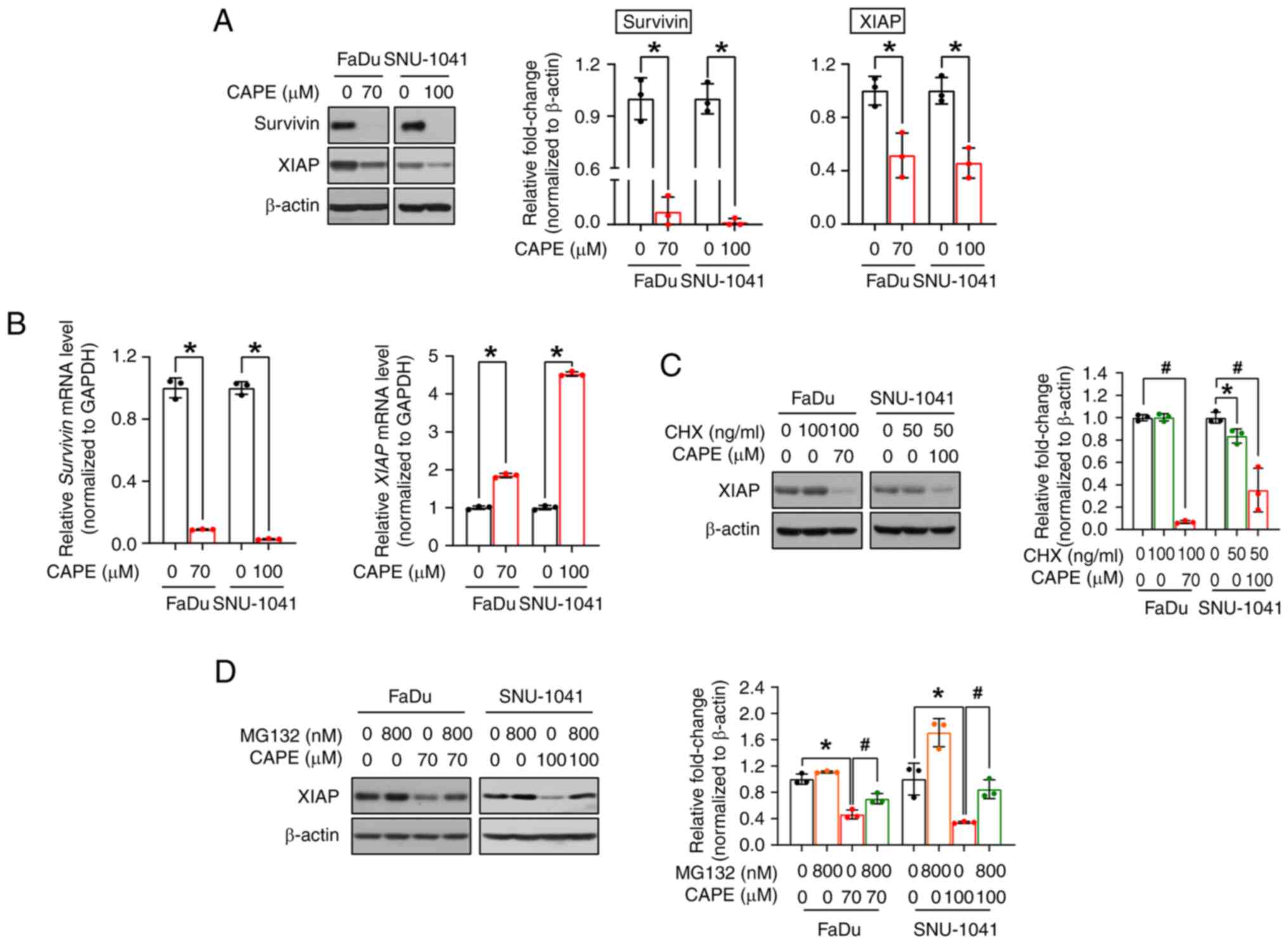
|
1
|
Newman JR, Connolly TM, Illing EA, Kilgore
ML, Locher JL and Carroll WR: Survival trends in hypopharyngeal
cancer: A population-based review. Laryngoscope. 125:624–629. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Eckel HE and Bradley PJ: Treatment options
for hypopharyngeal cancer. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 83:47–53.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mura F, Bertino G, Occhini A and Benazzo
M: Surgical treatment of hypopharyngeal cancer: A review of the
literature and proposal for a decisional flow-chart. Acta
Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 33:299–306. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pandey P, Khan F, Upadhyay TK and Giri PP:
Therapeutic efficacy of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in cancer
therapy: An updated review. Chem Biol Drug Des. 102:201–216. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Murtaza G, Karim S, Akram MR, Khan SA,
Azhar S, Mumtaz A and Bin Asad MH: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester and
therapeutic potentials. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1453422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Patel S: Emerging adjuvant therapy for
cancer: Propolis and its constituents. J Diet Suppl. 13:245–268.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kuo YY, Su LC, Chung CJ, Lin CY, Huo C,
Tseng JC, Huang SH, Lai CJ, Chen BC, Wang BJ, et al: Caffeic Acid
phenethyl ester is a potential therapeutic agent for oral cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 16:10748–1066. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu HJ, Shin JA and Cho SD: Inhibition of
focal adhesion kinase/paxillin axis by caffeic acid phenethyl ester
restrains aggressive behaviors of head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma in vitro. Arch Oral Biol. 146:1056112023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chung LC, Chiang KC, Feng TH, Chang KS,
Chuang ST, Chen YJ, Tsui KH, Lee JC and Juang HH: Caffeic acid
phenethyl ester upregulates N-myc downstream regulated gene 1 via
ERK pathway to inhibit human oral cancer cell growth in vitro and
in vivo. Mol Nutr Food Res. 612017.doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201600842.
|
|
10
|
Frassanito MA, Saltarella I, Vinella A,
Muzio LL, Pannone G, Fumarulo R, Vacca A and Mariggiò MA: Survivin
overexpression in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas as a new
therapeutic target (Review). Oncol Rep. 41:2615–2624.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tu H and Costa M: XIAP's profile in human
cancer. Biomolecules. 10:14932020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jaiswal PK, Goel A and Mittal RD:
Survivin: A molecular biomarker in cancer. Indian J Med Res.
141:389–397. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou LQ, Hu Y and Xiao HJ: The prognostic
significance of survivin expression in patients with HNSCC: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 21:4242021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Khan SA, Burke M, Zhu F, Yang DH, Dubyk C,
Mehra R, Lango MJ, Ridge JA, Sher DJ and Burtness B: Survivin
expression and impact on head and neck cancer outcomes. Oral Oncol.
112:1050492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Obexer P and Ausserlechner MJ: X-linked
inhibitor of apoptosis protein-a critical death resistance
regulator and therapeutic target for personalized cancer therapy.
Front Oncol. 4:1972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nagi C, Xiao GQ, Li G, Genden E and
Burstein DE: Immunohistochemical detection of X-linked inhibitor of
apoptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Diagn
Pathol. 11:402–406. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li X, Ma X, Lu X, Cui L and Dong W:
Expression of inhibitor of apoptosis protein XIAP in laryngeal
carcinoma and its clinicopathological significance. Lin Chung Er Bi
Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 21:973–975. 2007.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dohi T, Okada K, Xia F, Wilford CE, Samuel
T, Welsh K, Marusawa H, Zou H, Armstrong R, Matsuzawa S, et al: An
IAP-IAP complex inhibits apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 279:34087–34090.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singh R, Letai A and Sarosiek K:
Regulation of apoptosis in health and disease: The balancing act of
BCL-2 family proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:175–193. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Y, Park JS, Deng JH and Bai Y:
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV is essential for assembly and
respiratory function of the enzyme complex. J Bioenerg Biomembr.
38:283–291. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schwarzerová K, Bellinvia E, Martinek J,
Sikorová L, Dostál V, Libusová L, Bokvaj P, Fischer L, Schmit AC
and Nick P: Tubulin is actively exported from the nucleus through
the Exportin1/CRM1 pathway. Sci Rep. 9:57252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang YL and Li XM: The IAP family:
Endogenous caspase inhibitors with multiple biological activities.
Cell Res. 10:169–177. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jo MJ, Jeong S, Yun HK, Kim DY, Kim BR,
Kim JL, Na YJ, Park SH, Jeong YA, Kim BG, et al: Genipin induces
mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis via downregulation of
Stat3/mcl-1 pathway in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 19:7392019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen M, Tong C, Wu Q, Zhong Z, He Q, Zeng
L and Xiao L: 6-Shogaol inhibits the cell migration of colon cancer
by suppressing the EMT process through the IKKβ/NF-κB/Snail
pathway. Integr Cancer Ther. 22:153473542311727322023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li X, Wei Y and Wei X: Napabucasin, a
novel inhibitor of STAT3, inhibits growth and synergises with
doxorubicin in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Lett.
491:146–161. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dong H, Hu L, Li W, Shi M, He L, Wang C,
Hu Y, Wang H, Wen C, Liu H and Yang X: Pyrimethamine inhibits cell
growth by inducing cell senescence and boosting CD8+
T-cell mediated cytotoxicity in colorectal cancer. Mol Biol Rep.
49:4281–4292. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Murugesan A, Lassalle-Claux G, Hogan L,
Vaillancourt E, Selka A, Luiker K, Kim MJ, Touaibia M and Reiman T:
Antimyeloma potential of caffeic acid phenethyl ester and its
analogues through Sp1 mediated downregulation of IKZF1-IRF4-MYC
axis. J Nat Prod. 83:3526–3535. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sari C, SÜmer C and Celep EyÜpoĞlu F:
Celep EyÜpoĞlu, Caffeic acid phenethyl ester induces apoptosis in
colorectal cancer cells via inhibition of survivin. Turk J Biol.
4:264–274. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kleczka A, Kubina R, Dzik R, Jasik K,
Stojko J, Cholewa K and Kabała-Dzik A: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester
(CAPE) induced apoptosis in serous ovarian cancer OV7 cells by
deregulation of BCL2/BAX genes. Molecules. 25:35142020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Colombo D, Gatti L, Sjöstrand L, Carenini
N, Costantino M, Corna E, Arrighetti N, Zuccolo M, De Cesare M,
Linder S, et al: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester targets
ubiquitin-specific protease 8 and synergizes with cisplatin in
endometrioid ovarian carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol.
197:1149002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Marin EH, Paek H, Li M, Ban Y, Karaga MK,
Shashidharamurthy R and Wang X: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester exerts
apoptotic and oxidative stress on human multiple myeloma cells.
Invest New Drugs. 37:837–848. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pfeffer CM and Singh ATK: Apoptosis: A
target for anticancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 19:4482018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Koff JL, Ramachandiran S and
Bernal-Mizrachi L: A time to kill: Targeting apoptosis in cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 16:2942–2955. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fulda S and Debatin KM: Extrinsic versus
intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene.
25:4798–811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Choi SJ, Ahn CH, Hong KO, Kim JH, Hong SD,
Shin JA and Cho SD: Molecular mechanism underlying the apoptotic
modulation by ethanol extract of Pseudolarix kaempferi in
mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the salivary glands. Cancer Cell Int.
21:4272021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chung TW, Choi H, Lee JM, Ha SH, Kwak CH,
Abekura F, Park JY, Chang YC, Ha KT, Cho SH, et al: Oldenlandia
diffusa suppresses metastatic potential through inhibiting matrix
metalloproteinase-9 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1
expression via p38 and ERK1/2 MAPK pathways and induces apoptosis
in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 195:309–317.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cheng AC, Jian CB, Huang YT, Lai CS, Hsu
PC and Pan MH: Induction of apoptosis by Uncaria tomentosa through
reactive oxygen species production, cytochrome c release, and
caspases activation in human leukemia cells. Food Chem Toxicol.
45:2206–2218. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Roy S and Nicholson DW: Cross-talk in cell
death signaling. J Exp Med. 192:F21–F25. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gavrilescu LC and Denkers EY: Apoptosis
and the balance of homeostatic and pathologic responses to
protozoan infection. Infect Immun. 71:6109–6115. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Suzuki S, Yamamoto M, Sanomachi T, Togashi
K, Sugai A, Seino S, Yoshioka T, Kitanaka C and Okada M:
Brexpiprazole, a serotonin-dopamine activity modulator, can
sensitize glioma stem cells to osimertinib, a third-generation
EGFR-TKI, via survivin reduction. Cancers. 11:9472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sakoguchi-Okada N, Takahashi-Yanaga F,
Fukada K, Shiraishi F, Taba Y, Miwa Y, Morimoto S, Iida M and
Sasaguri T: Celecoxib inhibits the expression of survivin via the
suppression of promoter activity in human colon cancer cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 73:1318–1329. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dean E, Jodrell D, Connolly K, Danson S,
Jolivet J, Durkin J, Morris S, Jowle D, Ward T, Cummings J, et al:
Phase I trial of AEG35156 administered as a 7-day and 3-day
continuous intravenous infusion in patients with advanced
refractory cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:1660–1666. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yue C, Li RH, Chen C and Liu H: Study on
the relationship between XIAP gene and resistance of taxol in
ovarian cancer. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 49:337–341.
2018.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hehlgans S, Petraki C, Reichert S, Cordes
N, Rödel C and Rödel F: Double targeting of Survivin and XIAP
radiosensitizes 3D grown human colorectal tumor cells and decreases
migration. Radiother Oncol. 108:32–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Werner TA, Dizdar L, Nolten I, Riemer JC,
Mersch S, Schütte SC, Driemel C, Verde PE, Raba K, Topp SA, et al:
Survivin and XIAP-two potential biological targets in follicular
thyroid carcinoma. Sci Rep. 7:113832017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li Y, Gao W, Ma Y, Zhu G, Chen F and Qu H:
Dual targeting of survivin and X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis
protein suppresses the growth and promotes the apoptosis of gastric
cancer HGC-27 cells. Oncol Lett. 16:3489–3498. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fang W, Che X, Li G, Wang A, Wang Y, Shi
X, Hou K, Zhang X, Qu X and Liu Y: Sur-X, a novel peptide, kills
colorectal cancer cells by targeting survivin-XIAP complex. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 39:822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu TT, Yang H, Zhuo FF, Yang Z, Zhao MM,
Guo Q, Liu Y, Liu D, Zeng KW and Tu PF: Atypical E3 ligase ZFP91
promotes small-molecule-induced E2F2 transcription factor
degradation for cancer therapy. EBioMedicine. 86:1043532022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Dohi T, Xia F and Altieri DC: Altieri,
Compartmentalized phosphorylation of IAP by protein kinase A
regulates cytoprotection. Mol Cell. 27:17–28. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Arora V, Cheung HH, Plenchette S, Micali
OC, Liston P and Korneluk RG: Degradation of survivin by the
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP)-XAF1 complex. J Biol Chem.
282:26202–26209. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hoffman WH, Biade S, Zilfou JT, Chen J and
Murphy M: Transcriptional repression of the anti-apoptotic survivin
gene by wild type p53. J Biol Chem. 277:3247–3257. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mirza A, McGuirk M, Hockenberry TN, Wu Q,
Ashar H, Black S, Wen SF, Wang L, Kirschmeier P, Bishop WR, et al:
Human survivin is negatively regulated by wild-type p53 and
participates in p53-dependent apoptotic pathway. Oncogene.
21:2613–2622. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Baek HS, Kwon YJ, Ye DJ, Cho E, Kwon TU
and Chun YJ: CYP1B1 prevents proteasome-mediated XIAP degradation
by inducing PKCε activation and phosphorylation of XIAP. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1866:1185532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hong SW, Shin JS, Moon JH, Jung SA, Koh
DI, Ryu Y, Park YS, Kim DY, Park SS, Hong JK, et al:
Chemosensitivity to HM90822, a novel synthetic IAP antagonist, is
determined by p-AKT-inducible XIAP phosphorylation in human
pancreatic cancer cells. Invest New Drugs. 38:1696–1706. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chung TW, Moon SK, Chang YC, Ko JH, Lee
YC, Cho G, Kim SH, Kim JG and Kim CH: Novel and therapeutic effect
of caffeic acid and caffeic acid phenyl ester on hepatocarcinoma
cells: Complete regression of hepatoma growth and metastasis by
dual mechanism. FASEB J. 18:1670–1681. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Tang H, Yao X, Yao C, Zhao X, Zuo H and Li
Z: Anti-colon cancer effect of caffeic acid p-nitro-phenethyl ester
in vitro and in vivo and detection of its metabolites. Sci Rep.
7:75992017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kapałczyńska M, Kolenda T, Przybyła W,
Zajączkowska M, Teresiak A, Filas V, Ibbs M, Bliźniak R, Łuczewski
Ł and Lamperska K: 2D and 3D cell cultures-a comparison of
different types of cancer cell cultures. Arch Med Sci. 14:910–919.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mañós M, Giralt J, Rueda A, Cabrera J,
Martinez-Trufero J, Marruecos J, Lopez-Pousa A, Rodrigo JP, Castelo
B, Martínez-Galán J, et al: Multidisciplinary management of head
and neck cancer: First expert consensus using Delphi methodology
from the Spanish Society for Head and Neck Cancer (part 1). Oral
Oncol. 70:58–64. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kuo YY, Lin HP, Huo C, Su LC, Yang J,
Hsiao PH, Chiang HC, Chung CJ, Wang HD, Chang JY, et al: Caffeic
acid phenethyl ester suppresses proliferation and survival of TW2.6
human oral cancer cells via inhibition of Akt signaling. Int J Mol
Sci. 14:8801–8817. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Peng CY, Yang HW, Chu YH, Chang YC, Hsieh
MJ, Chou MY, Yeh KT, Lin YM, Yang SF and Lin CW: Caffeic Acid
phenethyl ester inhibits oral cancer cell metastasis by regulating
matrix metalloproteinase-2 and the mitogen-activated protein kinase
pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:7325782012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Machiels JP, René Leemans C, Golusinski W,
Grau C, Licitra L and Gregoire V; EHNS Executive Board, ESMO
Guidelines Committee, : ESTRO Executive Board: Reprint of ‘Squamous
cell carcinoma of the oral cavity, larynx, oropharynx and
hypopharynx: EHNS-ESMO-ESTRO Clinical Practice Guidelines for
diagnosis, treatment and follow-up’. Ann Oncol. 31:1462–1475. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|