|
1
|
Hussen BM, Hidayat HJ, Salihi A, Sabir DK,
Taheri M and Ghafouri-Fard S: MicroRNA: A signature for cancer
progression. Biomed Pharmacother. 138:1115282021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Soifer HS, Rossi JJ and Saetrom P:
MicroRNAs in disease and potential therapeutic applications. Mol
Ther. 15:2070–2079. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Budakoti M, Panwar AS, Molpa D, Singh RK,
Büsselberg D, Mishra AP, Coutinho HDM and Nigam M: Micro-RNA: The
darkhorse of cancer. Cell Signal. 83:1099952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Douvris A, Viñas J and Burns KD:
miRNA-486-5p: Signaling targets and role in non-malignant disease.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 79:3762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu Z, Yang Y, Ju J, Zhang G, Zhang P, Ji
P, Jin Q, Cao G, Zuo R, Wang H, et al: miR-100-5p promotes
epidermal stem cell proliferation through targeting MTMR3 to
activate PIP3/AKT and ERK signaling pathways. Stem Cells Int.
2022:14742732022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang K, Liufu S, Yu Z, Xu X, Ai N, Li X,
Liu X, Chen B, Zhang Y, Ma H and Yin Y: miR-100-5p regulates
skeletal muscle myogenesis through the Trib2/mTOR/S6K signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 24:89062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eniafe J and Jiang S: MicroRNA-99 family
in cancer and immunity. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 12:e16352021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Belles X: MicroRNAs and the evolution of
insect metamorphosis. Annu Rev Entomol. 62:111–125. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Heimberg AM, Sempere LF, Moy VN, Donoghue
PC and Peterson KJ: MicroRNAs and the advent of vertebrate
morphological complexity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:2946–2950.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu Y, Wang Z, Yu S, Liu D and Sun L:
LncmiRHG-MIR100HG: A new budding star in cancer. Front Oncol.
12:9975322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen JF, Wu P, Xia R, Yang J, Huo XY, Gu
DY, Tang CJ, De W and Yang F: STAT3-induced lncRNA HAGLROS
overexpression contributes to the malignant progression of gastric
cancer cells via mTOR signal-mediated inhibition of autophagy. Mol
Cancer. 17:62018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Peng CW, Yue LX, Zhou YQ, Tang S, Kan C,
Xia LM, Yang F and Wang SY: miR-100-3p inhibits cell proliferation
and induces apoptosis in human gastric cancer through targeting to
BMPR2. Cancer Cell Int. 19:3542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang R, Zhang M, Hu Y, He J, Lin Q and
Peng N: MiR-100-5p inhibits osteogenic differentiation of human
bone mesenchymal stromal cells by targeting TMEM135. Hum Cell.
35:1671–1683. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ai L, Yi W, Chen L, Wang H and Huang Q:
Xian-Ling-Gu-Bao protects osteoporosis through promoting osteoblast
differentiation by targeting miR-100-5p/KDM6B/RUNX2 axis. In Vitro
Cell Dev Biol Anim. 57:3–9. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ding W, Ding S, Li J, Peng Z, Hu P, Zhang
T and Pan L: Aberrant expression of miR-100 in plasma of patients
with osteoporosis and its potential diagnostic value. Clin Lab.
65:1903272019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen R, Liao X, Chen F, Wang B, Huang J,
Jian G, Huang Z, Yin G, Liu H and Jin D: Circulating microRNAs,
miR-10b-5p, miR-328-3p, miR-100 and let-7, are associated with
osteoblast differentiation in osteoporosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
11:1383–1390. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu J, Kuang L, Chen C, Yang J, Zeng WN, Li
T, Chen H, Huang S, Fu Z, Li J, et al: miR-100-5p-abundant exosomes
derived from infrapatellar fat pad MSCs protect articular cartilage
and ameliorate gait abnormalities via inhibition of mTOR in
osteoarthritis. Biomaterials. 206:87–100. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lai Z and Cao Y: Plasma miR-200c-3p,
miR-100-5p, and miR-1826 serve as potential diagnostic biomarkers
for knee osteoarthritis: Randomized controlled trials. Medicine
(Baltimore). 98:e181102019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang W, Zhu W, Yang Y, Guo M, Qian H,
Jiang W, Chen Y, Lian C, Xu Z, Bai H, et al: Exosomal miR-100-5p
inhibits osteogenesis of hBMSCs and angiogenesis of HUVECs by
suppressing the BMPR2/Smad1/5/9 signalling pathway. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 12:3902021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chamorro Á, Dirnagl U, Urra X and Planas
AM: Neuroprotection in acute stroke: Targeting excitotoxicity,
oxidative and nitrosative stress, and inflammation. Lancet Neurol.
15:869–881. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xia X, Chen J, Ren H, Zhou C, Zhang Q,
Cheng H and Wang X: Gypenoside pretreatment alleviates the cerebral
ischemia injury via inhibiting the microglia-mediated
neuroinflammation. Mol Neurobiol. 61:1140–1156. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xin D, Li T, Zhao Y, Guo X, Gai C, Jiang
Z, Yu S, Cheng J, Song Y, Cheng Y, et al: MiR-100-5p-rich small
extracellular vesicles from activated neuron to aggravate
microglial activation and neuronal activity after stroke. J
Nanobiotechnology. 22:5342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cao X, Zhang X, Chen J, Sun Q, Sun Y, Lin
N and Liu X: miR-100-5p activation of the autophagy response
through inhibiting the mTOR pathway and suppression of cerebral
infarction progression in mice. Aging (Albany NY). 15:8315–8324.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He S, Wang Q, Chen L, He YJ, Wang X and Qu
S: miR-100a-5p-enriched exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem
cells enhance the anti-oxidant effect in a Parkinson's disease
model via regulation of Nox4/ROS/Nrf2 signaling. J Transl Med.
21:7472023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Feng N, Huang X and Jia Y: Small
extracellular vesicles from adipose derived stem cells alleviate
microglia activation and improve motor deficit of Parkinson's
disease via miR-100-5p/DTX3L/STAT1 signaling axis. Exp Neurol.
389:1152502025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li XH, Fu NS and Xing ZM: MiR-100
suppresses inflammatory activation of microglia and neuronal
apoptosis following spinal cord injury via TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:8713–8720. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Marx C, Novotny J, Salbeck D, Zellner KR,
Nicolai L, Pekayvaz K, Kilani B, Stockhausen S, Bürgener N, Kupka
D, et al: Eosinophil-platelet interactions promote atherosclerosis
and stabilize thrombosis with eosinophil extracellular traps.
Blood. 134:1859–1872. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gao H, Yu Z, Li Y and Wang X: miR-100-5p
in human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes
mediates eosinophilic inflammation to alleviate atherosclerosis via
the FZD5/Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 53:1166–1176. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ji P, Song X and Lv Z: Knockdown of
circ_0004104 alleviates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced
vascular endothelial cell injury by regulating miR-100/TNFAIP8
axis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 78:269–279. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zeng J, Wang L, Zhao J, Zheng Z, Peng J,
Zhang W, Wen T, Nie J, Ding L and Yi D: MiR-100-5p regulates
cardiac hypertrophy through activation of autophagy by targeting
mTOR. Hum Cell. 34:1388–1397. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhong Z, Tian Y, Luo X, Zou J, Wu L and
Tia J: Extracellular vesicles derived from human umbilical cord
mesenchymal stem cells protect against DOX-induced heart failure
through the miR-100-5p/NOX4 pathway. Front Bioeng Biotechnol.
9:7032412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu H, Chen Y, Huang Y, Wei L, Ran J, Li
Q, Tian Y, Luo Z, Yang L, Liu H, et al: Macrophage-derived
mir-100-5p orchestrates synovial proliferation and inflammation in
rheumatoid arthritis through mTOR signaling. J Nanobiotechnology.
22:1972024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li N, Gao Z, Zhao L, Du B, Ma B, Nian H
and Wei R: MSC-derived small extracellular vesicles attenuate
autoimmune dacryoadenitis by promoting M2 macrophage polarization
and inducing tregs via miR-100-5p. Front Immunol. 13:8889492022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen G, Li X, Zhou X, Li Y, Yu H, Peng X,
Bai X, Zhang C, Feng Z, Mei Y, et al: Extracellular vesicles
secreted from mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate renal ischemia
reperfusion injury by delivering miR-100-5p targeting FKBP5/AKT
axis. Sci Rep. 14:67202024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu Z, He L, Yan L, Tan B, Ma L, He G, Dai
Z, Sun R and Li C: Hydrogels treat atopic dermatitis by
transporting marine-derived miR-100-5p-abundant extracellular
vesicles. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 10:7667–7682. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang F, Li F and Lu J: microRNA-100
shuttled by human umbilical cord MSC-secreted extracellular
vesicles induces endometriosis by inhibiting HS3ST2. Cell Signal.
102:1105322023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Smolka C, Schlosser D, Hohnloser C,
Bemtgen X, Jänich C, Schneider L, Martin J, Pfeifer D, Moser M,
Hasselblatt P, et al: MiR-100 overexpression attenuates high fat
diet induced weight gain, liver steatosis, hypertriglyceridemia and
development of metabolic syndrome in mice. Mol Med. 27:1012021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ge Y, Shu J, Shi G, Yan F, Li Y and Ding
H: miR-100 suppresses the proliferation, invasion, and migration of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells via targeting CXCR7. J Immunol Res.
2021:99207862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cao Y, Song J, Ge J, Song Z, Chen J and Wu
C: MicroRNA-100 suppresses human gastric cancer cell proliferation
by targeting CXCR7. Oncol Lett. 15:453–458. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhou SM, Zhang F, Chen XB, Jun CM, Jing X,
Wei DX, Xia Y, Zhou YB, Xiao XQ, Jia RQ, et al: miR-100 suppresses
the proliferation and tumor growth of esophageal squamous cancer
cells via targeting CXCR7. Oncol Rep. 35:3453–3459. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xie H, Xiao R, He Y, He L, Xie C, Chen J
and Hong Y: MicroRNA-100 inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation,
invasion and migration by targeting FOXA1. Oncol Lett. 22:8162021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li X, Ren Y, Liu D, Yu X and Chen K: Role
of miR-100-5p and CDC25A in breast carcinoma cells. PeerJ.
9:e122632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
He W, Huang Y, Jiang CC, Zhu Y, Wang L,
Zhang W, Huang W, Zhou T and Tang S: miR-100 inhibits cell growth
and proliferation by targeting HOXA1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Onco Targets Ther. 13:593–602. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sun X, Liu X, Wang Y, Yang S, Chen Y and
Yuan T: miR-100 inhibits the migration and invasion of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting IGF1R. Oncol Lett.
15:8333–8338. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang H, Yang K, Ren T, Huang Y, Liang X,
Yu Y, Wang W, Niu J, Lou J, Tang X and Guo W: miR-100-5p inhibits
malignant behavior of chordoma cells by targeting IGF1R. Cancer
Manag Res. 12:4129–4137. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Han W, Ren X, Yang Y, Li H, Zhao L and Lin
Z: microRNA-100 functions as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell
lung cancer via regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
Wnt/β-catenin by targeting HOXA1. Thorac Cancer. 11:1679–1688.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fu B, Zhou F, Zhang J, Kong X, Ni B, Bu J,
Xu S and He C: Sevoflurane attenuates proliferative and migratory
activity of lung cancer cells via mediating the
microRNA-100-3p/sterol O-Acyltransferase 1 axis. Chin J Physiol.
66:456–465. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lin L, Huang Y, Zhuang W, Lin P and Ma X:
miR-100 inhibits cell proliferation in mantle cell lymphoma by
targeting mTOR. Exp Hematol Oncol. 9:252020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sun Y, Wang H and Luo C: MiR-100 regulates
cell viability and apoptosis by targeting ATM in pediatric acute
myeloid leukemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 522:855–861. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wei X, Feng Y, Fu Y, Liu F, Chen Q, Zhang
W, Zhao Y, Huang X, Chen Y, Li Q and Zhang Q: miR-100-5p is
upregulated in multiple myeloma and involves in the pathogenesis of
multiple myeloma through targeting MTMR3. Hematology.
28:21968572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhou B, Yi F, Chen Y, Li CH, Cheng YS and
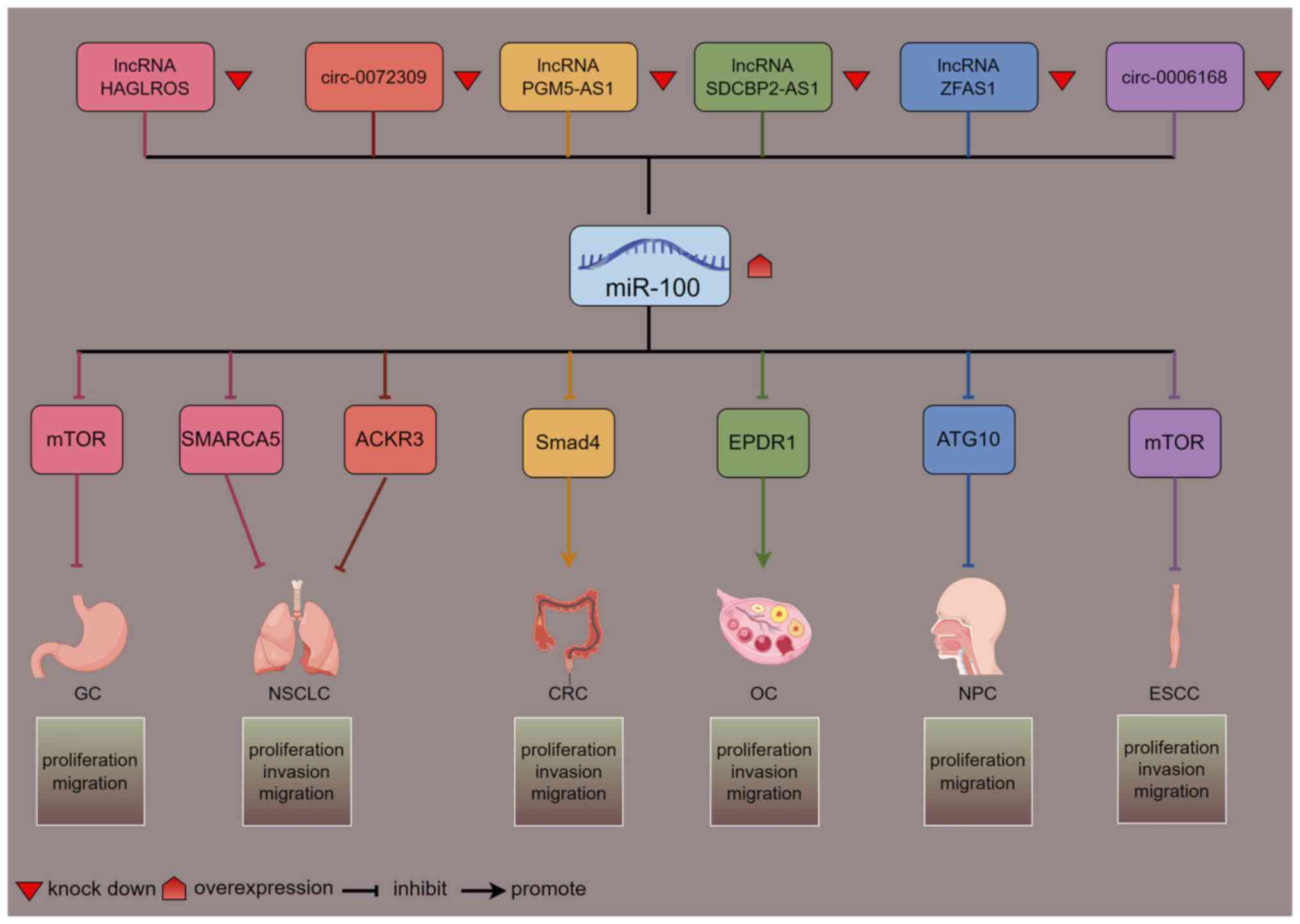
Yang K: Reduced long noncoding RNA PGM5-AS1 facilitated
proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer through sponging
miR-100-5p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:7972–7981.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu X, Liu C, Zhang A, Wang Q, Ge J, Li Q
and Xiao J: Long non-coding RNA SDCBP2-AS1 delays the progression
of ovarian cancer via microRNA-100-5p-targeted EPDR1. World J Surg
Oncol. 19:1992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Peng J, Zheng H, Liu F, Wu Q and Liu S:
The m6A methyltransferase METTL3 affects autophagy and progression
of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating the stability of lncRNA
ZFAS1. Infect Agent Cancer. 17:12022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li L, Zhu H, Li X, Ke Y, Yang S and Cheng
Q: Long non-coding RNA HAGLROS facilitates the malignant phenotypes
of NSCLC cells via repressing miR-100 and up-regulating SMARCA5.
Biomed J. 44 (6 Suppl 2):S305–S315. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Shu L, Guo K, Lin ZH and Liu H: Long
non-coding RNA HAGLROS promotes the development of diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma via suppressing miR-100. J Clin Lab Anal.
36:e241682022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Shi Y, Guo Z, Fang N and Liu H:
hsa_circ_0006168 sponges miR-100 and regulates mTOR to promote the
proliferation, migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 117:1091512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang XQ, Song Q and Zeng LX: Circulating
hsa_circ_0072309, acting via the miR-100/ACKR3 pathway, maybe a
potential biomarker for the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of
brain metastasis from non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Med.
12:18005–18019. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Seol HS, Akiyama Y, Lee SE, Shimada S and
Jang SJ: Loss of miR-100 and miR-125b results in cancer stem cell
properties through IGF2 upregulation in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Sci Rep. 10:214122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
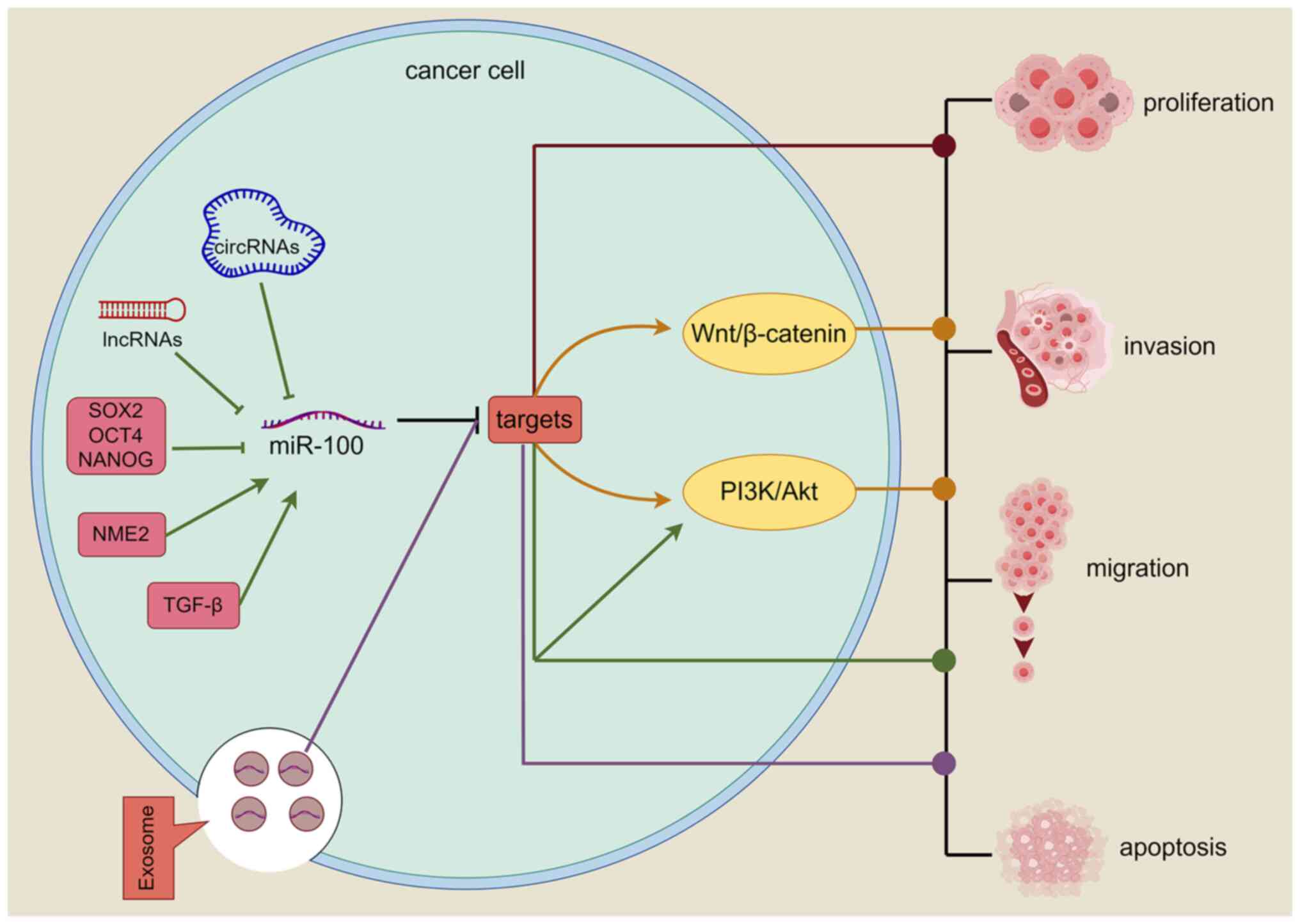
Gong Y, Yang G, Wang Q, Wang Y and Zhang
X: NME2 is a master suppressor of apoptosis in gastric cancer cells
via transcriptional regulation of miR-100 and other survival
factors. Mol Cancer Res. 18:287–299. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ottaviani S, Stebbing J, Frampton AE,
Zagorac S, Krell J, de Giorgio A, Trabulo SM, Nguyen VTM, Magnani
L, Feng H, et al: TGF-β induces miR-100 and miR-125b but blocks
let-7a through LIN28B controlling PDAC progression. Nat Commun.
9:18452018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Peng Q, Zhang L, Li J, Wang W, Cai J, Ban
Y, Zhou Y, Hu M, Mei Y, Zeng Z, et al: FOXA1 suppresses the growth,
migration, and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through
repressing miR-100-5p and miR-125b-5p. J Cancer. 11:2485–2495.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang L, Chen X, Meng F, Huang T, Wang S,
Zheng Z, Zheng G, Li W, Zhang J and Liu Y: α2,6-Sialylation
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cells migration and invasion via
enhancement of nSmase2-mediated exosomal miRNA sorting. J Physiol
Biochem. 79:19–34. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chen C, Yang C, Tian X, Liang Y, Wang S,
Wang X, Shou Y, Li H, Xiao Q, Shu J, et al: Downregulation of
miR-100-5p in cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomes
facilitates lymphangiogenesis in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Med. 12:14468–14483. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Jiang Q, He M, Guan S, Ma M, Wu H, Yu Z,
Jiang L, Wang Y, Zong X, Jin F and Wei M: MicroRNA-100 suppresses
the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by targeting
FZD-8 and inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Tumour Biol.
37:5001–5011. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Huang C, Qin X, Zhao N, Jin H, Zhang S and
Yang H: MicroRNA-100 functions as a tumor suppressor in cervical
cancer via downregulating the SATB1 expression and regulating
AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Oncol Lett. 20:1336–1344. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ma P and Han J: Overexpression of
miR-100-5p inhibits papillary thyroid cancer progression via
targeting FZD8. Open Med (Wars). 17:1172–1182. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Adamo A, Dal Collo G, Bazzoni R and
Krampera M: Role of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular
vesicles in tumour microenvironment. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev
Cancer. 1871:192–198. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Mathieu M, Martin-Jaular L, Lavieu G and
Théry C: Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and
other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat
Cell Biol. 21:9–17. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Shojaei S, Hashemi SM, Ghanbarian H,
Salehi M and Mohammadi-Yeganeh S: Effect of mesenchymal stem
cells-derived exosomes on tumor microenvironment: Tumor progression
versus tumor suppression. J Cell Physiol. 234:3394–3409. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Jahangiri B, Khalaj-Kondori M, Asadollahi
E, Dizaj LP and Sadeghizadeh M: MSC-Derived exosomes suppress
colorectal cancer cell proliferation and metastasis via
miR-100/mTOR/miR-143 pathway. Int J Pharm. 627:1222142022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ding Y, Mei W, Zheng Z, Cao F, Liang K,
Jia Y, Wang Y, Liu D, Li J and Li F: Exosomes secreted from human
umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promote pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma growth by transferring miR-100-5p. Tissue Cell.
73:1016232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Pakravan K, Babashah S, Sadeghizadeh M,
Mowla SJ, Mossahebi-Mohammadi M, Ataei F, Dana N and Javan M:
MicroRNA-100 shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes
suppresses in vitro angiogenesis through modulating the
mTOR/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling axis in breast cancer cells. Cell Oncol
(Dordr). 40:457–470. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhou HC, Fang JH, Shang LR, Zhang ZJ, Sang
Y, Xu L, Yuan Y, Chen MS, Zheng L, Zhang Y and Zhuang SM: MicroRNAs
miR-125b and miR-100 suppress metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma by disrupting the formation of vessels that encapsulate
tumour clusters. J Pathol. 240:450–460. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Chelakkot C, Chelakkot VS, Shin Y and Song
K: Modulating glycolysis to improve cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
24:26062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhou Y, Huang Y, Hu K, Zhang Z, Yang J and
Wang Z: HIF1A activates the transcription of lncRNA RAET1K to
modulate hypoxia-induced glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells via miR-100-5p. Cell Death Dis. 11:1762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Schmitt AM and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 29:452–463. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Wang Y, Zhang W, Liu W, Huang L, Wang Y,
Li D, Wang G, Zhao Z, Chi X, Xue Y, et al: Long noncoding RNA
VESTAR regulates lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by enhancing VEGFC mRNA
stability. Cancer Res. 81:3187–3199. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Ishii G, Ochiai A and Neri S: Phenotypic
and functional heterogeneity of cancer-associated fibroblast within
the tumor microenvironment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 99:186–196. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Fujino Y, Takeishi S, Nishida K, Okamoto
K, Muguruma N, Kimura T, Kitamura S, Miyamoto H, Fujimoto A,
Higashijima J, et al: Downregulation of microRNA-100/microRNA-125b
is associated with lymph node metastasis in early colorectal cancer
with submucosal invasion. Cancer Sci. 108:390–397. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Liu J, Xiao Q, Xiao J, Niu C, Li Y, Zhang
X, Zhou Z, Shu G and Yin G: Wnt/β-catenin signalling: function,
biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 7:32022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Yu F, Yu C, Li F, Zuo Y, Wang Y, Yao L, Wu
C, Wang C and Ye L: Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cancers and targeted
therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:3072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Chen W, Liu Z, Mai W, Xiao Y, You X and
Qin L: FZD8 indicates a poor prognosis and promotes gastric cancer
invasion and metastasis via B-catenin signaling pathway. Ann Clin
Lab Sci. 50:13–23. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Wang W, Liu Y, Guo J, He H, Mi X, Chen C,
Xie J, Wang S, Wu P, Cao F, et al: miR-100 maintains phenotype of
tumor-associated macrophages by targeting mTOR to promote tumor
metastasis via Stat5a/IL-1ra pathway in mouse breast cancer.
Oncogenesis. 7:972018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Debnath J, Gammoh N and Ryan KM: Autophagy
and autophagy-related pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
248:560–575. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A,
Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, a
mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome
membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Pattingre S, Espert L, Biard-Piechaczyk M
and Codogno P: Regulation of macroautophagy by mTOR and Beclin 1
complexes. Biochimie. 90:313–323. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Cai J, Zhang Y, Huang S, Yan M, Li J, Jin
T and Bao S: MiR-100-5p, miR-199a-3p and miR-199b-5p induce
autophagic death of endometrial carcinoma cell through targeting
mTOR. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 10:9262–9272. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Deng X, Su R, Weng H, Li Z and Chen J: RNA
N(6)-methyladenosine modification in cancers: Current status and
perspectives. Cell Res. 28:507–517. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Yang Y, Hsu PJ, Chen YS and Yang YG:
Dynamic transcriptomic m(6)A decoration: Writers, erasers, readers
and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res. 28:616–624. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Zaccara S, Ries RJ and Jaffrey SR:
Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 20:608–624. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zheng ZQ, Li ZX, Zhou GQ, Lin L, Zhang LL,
Lv JW, Huang XD, Liu RQ, Chen F, He XJ, et al: Long noncoding RNA
FAM225A promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumorigenesis and
metastasis by acting as ceRNA to sponge miR-590-3p/miR-1275 and
upregulate ITGB3. Cancer Res. 79:4612–4626. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Katheder NS, Khezri R, O'farrell F,
Schultz SW, Jain A, Rahman MM, Schink KO, Theodossiou TA, Johansen
T, Juhász G, et al: Microenvironmental autophagy promotes tumour
growth. Nature. 541:417–420. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Cirillo LA, Lin FR, Cuesta I, Friedman D,
Jarnik M and Zaret KS: Opening of compacted chromatin by early
developmental transcription factors HNF3 (FoxA) and GATA-4. Mol
Cell. 9:279–289. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Ye Y, Li SL and Wang JJ: miR-100-5p
downregulates mTOR to suppress the proliferation, migration, and
invasion of prostate cancer cells. Front Oncol. 10:5789482020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Liu X, Zhong L, Li P and Zhao P:
MicroRNA-100 enhances autophagy and suppresses migration and
invasion of renal cell carcinoma cells via disruption of
NOX4-dependent mTOR pathway. Clin Transl Sci. 15:567–575. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Raji S, Sahranavard M, Mottaghi M and
Sahebkar A: MiR-212 value in prognosis and diagnosis of cancer and
its association with patient characteristics: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 22:1632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Qian Y, Shi L and Luo Z: Long non-coding
RNAs in cancer: Implications for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy.
Front Med (Lausanne). 7:6123932020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Cheng G: Circulating miRNAs: Roles in
cancer diagnosis, prognosis and therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
81:75–93. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Wnuk J, Strzelczyk JK and Gisterek I:
Clinical value of circulating miRNA in diagnosis, prognosis,
screening and monitoring therapy of pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma-a review of the literature. Int J Mol Sci.
24:51132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Damodaran M, Dandapani MC, Simondurairaj,
SandhyaSundaram, VenkatRamanan S, Ramachandran I and Venkatesan V:
Differentially expressed miR-20, miR-21, miR-100, miR-125a and
miR-146a as a potential biomarker for prostate cancer. Mol Biol
Rep. 48:3349–3356. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Wang S, Li L, Yang M, Wang X, Zhang H, Wu
N, Jia K, Wang J, Li M, Wei L and Liu J: Identification of three
circulating MicroRNAs in plasma as clinical biomarkers for breast
cancer detection. J Clin Med. 12:3222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Ludwig N, Nourkami-Tutdibi N, Backes C,
Lenhof HP, Graf N, Keller A and Meese E: Circulating serum miRNAs
as potential biomarkers for nephroblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer.
62:1360–1367. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Motawi TK, Rizk SM, Ibrahim TM and Ibrahim
IA: Circulating microRNAs, miR-92a, miR-100 and miR-143, as
non-invasive biomarkers for bladder cancer diagnosis. Cell Biochem
Funct. 34:142–148. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Yamanaka Z, Sasaki T, Yamanaka A, Kato K
and Nishi H: Circulating and tissue miR-100 acts as a potential
diagnostic biomarker for cervical cancer. Cancer Biomark.
32:551–558. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Hassan NM, Refaat LA, Ismail GN,
Abdellateif M, Fadel SA and AbdelAziz RS: Diagnostic, prognostic
and predictive values of miR-100 and miR-210 in pediatric acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematology. 25:405–413. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Liao Z, Zhang Q, Yang L, Li H, Mo W, Song
Z, Huang X, Wen S, Cheng X and He M: Increased hsa-miR-100-5p
expression improves hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis in the asian
population with PLK1 variant rs27770A>G. Cancers (Basel).
16:1292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
He QL, Qin SY, Tao L, Ning HJ and Jiang
HX: Prognostic value and prospective molecular mechanism of
miR-100-5p in hepatocellular carcinoma: A comprehensive study based
on 1,258 samples. Oncol Lett. 18:6126–6142. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Song SK, Jung WY, Park SK, Chung CW and
Park Y: Significantly different expression levels of microRNAs
associated with vascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma and
their prognostic significance after surgical resection. PLoS One.
14:e02168472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Fuso P, Di Salvatore M, Santonocito C,
Guarino D, Autilio C, Mulè A, Arciuolo D, Rinninella A, Mignone F,
Ramundo M, et al: Let-7a-5p, miR-100-5p, miR-101-3p, and
miR-199a-3p hyperexpression as potential predictive biomarkers in
early breast cancer patients. J Pers Med. 11:8162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Zhang HC and Tang KF: Clinical value of
integrated-signature miRNAs in esophageal cancer. Cancer Med.
6:1893–1903. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Wang J, Tao Y and Bian Q: miRNA and mRNA
expression profiling reveals potential biomarkers for metastatic
cutaneous melanoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 21:557–567. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Jakob M, Mattes LM, Küffer S, Unger K,
Hess J, Bertlich M, Haubner F, Ihler F, Canis M, Weiss BG and Kitz
J: MicroRNA expression patterns in oral squamous cell carcinoma:
Hsa-mir-99b-3p and hsa-mir-100-5p as novel prognostic markers for
oral cancer. Head Neck. 41:3499–3515. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Chen Z, Wu L, Lin Q, Shi J, Lin X and Shi
L: Evaluation of miR-182/miR-100 ratio for diagnosis and survival
prediction in bladder cancer. Arch Iran Med. 19:645–651.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Azizmohammadi S, Azizmohammadi S, Safari
A, Kosari N, Kaghazian M, Yahaghi E and Seifoleslami M: The role
and expression of miR-100 and miR-203 profile as prognostic markers
in epithelial ovarian cancer. Am J Transl Res. 8:2403–2410.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zhang H, Wang J, Wang Z, Ruan C, Wang L
and Guo H: Serum miR-100 is a potential biomarker for detection and
outcome prediction of glioblastoma patients. Cancer Biomark.
24:43–49. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Wang G, Yang L, Hu M, Hu R, Wang Y, Chen
B, Jiang X and Cui R: Comprehensive analysis of the prognostic
significance of Hsa-miR-100-5p and its related gene signature in
stomach adenocarcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7362742021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Hu XY, Song Z, Yang ZW, Li JJ, Liu J and
Wang HS: Cancer drug resistance related microRNAs: recent advances
in detection methods. Analyst. 147:2615–2632. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Lai Y, Kacal M, Kanony M, Stukan I, Jatta
K, Kis L, Norberg E, Vakifahmetoglu-Norberg H, Lewensohn R,
Hydbring P and Ekman S: miR-100-5p confers resistance to ALK
tyrosine kinase inhibitors Crizotinib and Lorlatinib in EML4-ALK
positive NSCLC. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 511:260–265. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Qin X, Yu S, Zhou L, Shi M, Hu Y, Xu X,
Shen B, Liu S, Yan D and Feng J: Cisplatin-resistant lung cancer
cell-derived exosomes increase cisplatin resistance of recipient
cells in exosomal miR-100-5p-dependent manner. Int J Nanomedicine.
12:3721–3733. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Nabavi N, Saidy NRN, Venalainen E, Haegert
A, Parolia A, Xue H, Wang Y, Wu R, Dong X, Collins C, et al:
miR-100-5p inhibition induces apoptosis in dormant prostate cancer
cells and prevents the emergence of castration-resistant prostate
cancer. Sci Rep. 7:40792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Samli H, Samli M, Vatansever B, Ardicli S,
Aztopal N, Dincel D, Sahin A and Balci F: Paclitaxel resistance and
the role of miRNAs in prostate cancer cell lines. World J Urol.
37:1117–1126. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Nishi H, Ono M, Ohno S, Yamanaka Z, Sasaki
T, Ohyashiki K, Ohyashiki JH and Kuroda M: Hypoxia-induced
paclitaxel resistance in cervical cancer modulated by miR-100
targeting of USP15. Gynecol Oncol Rep. 45:1011382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|