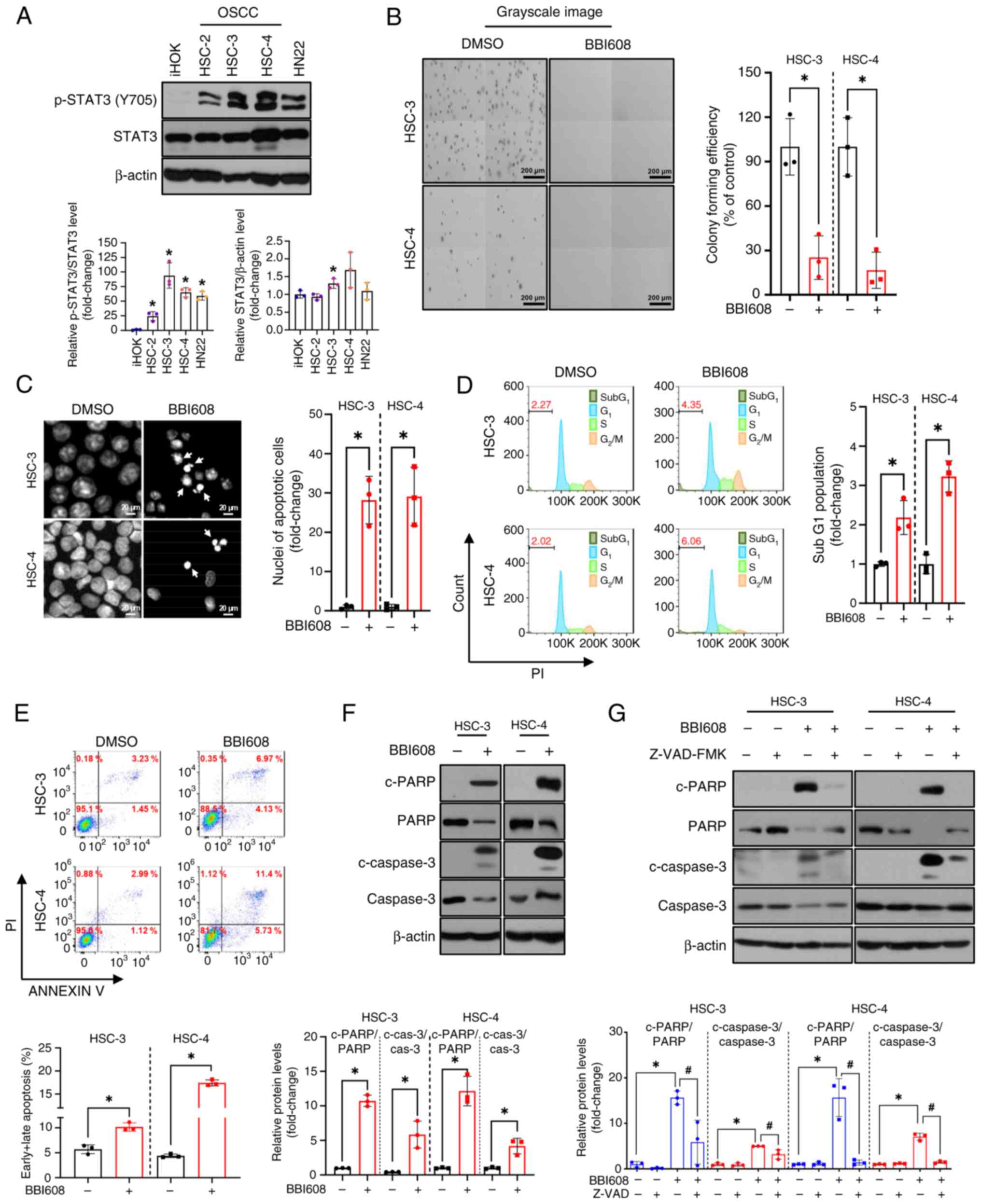
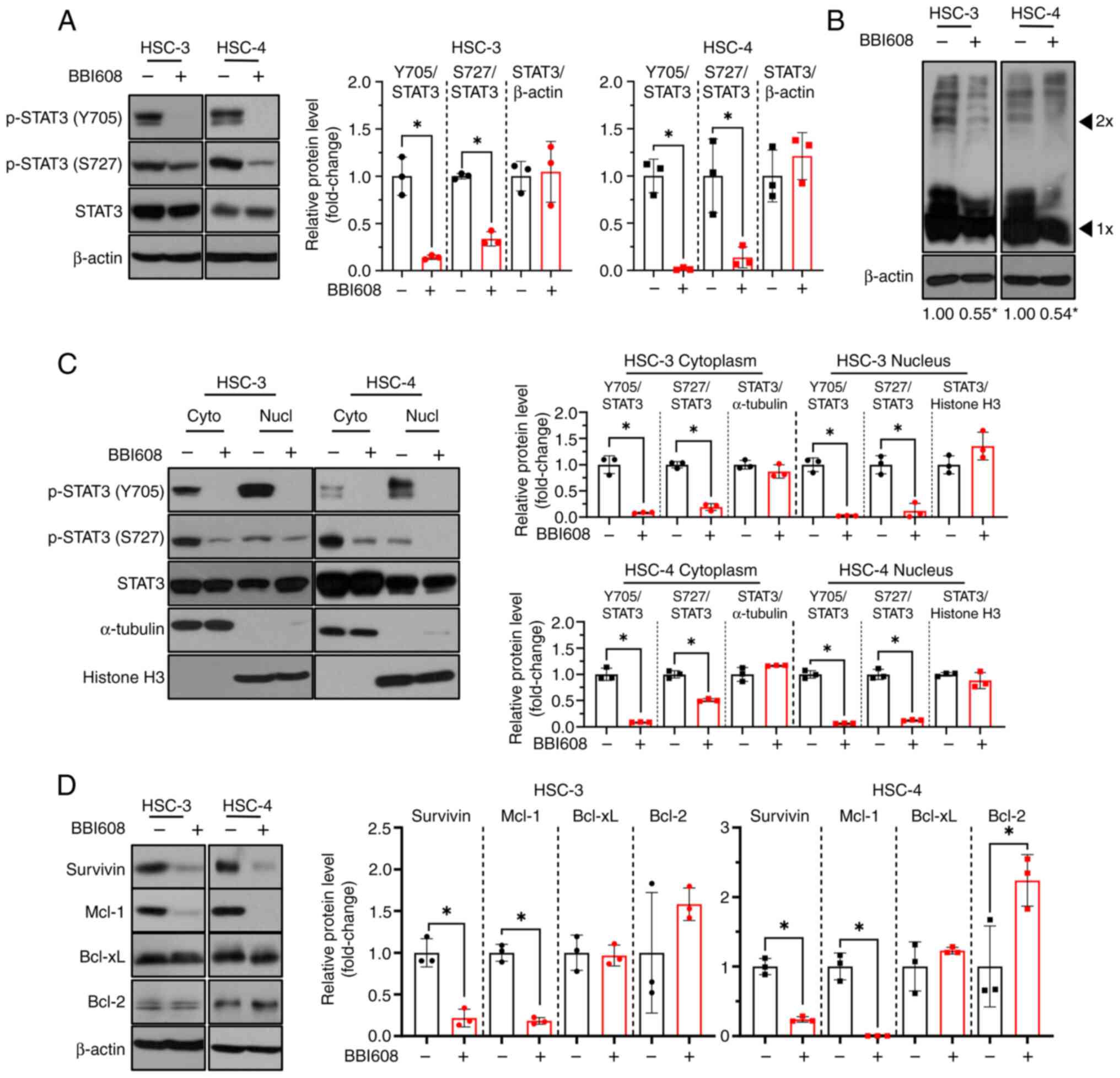
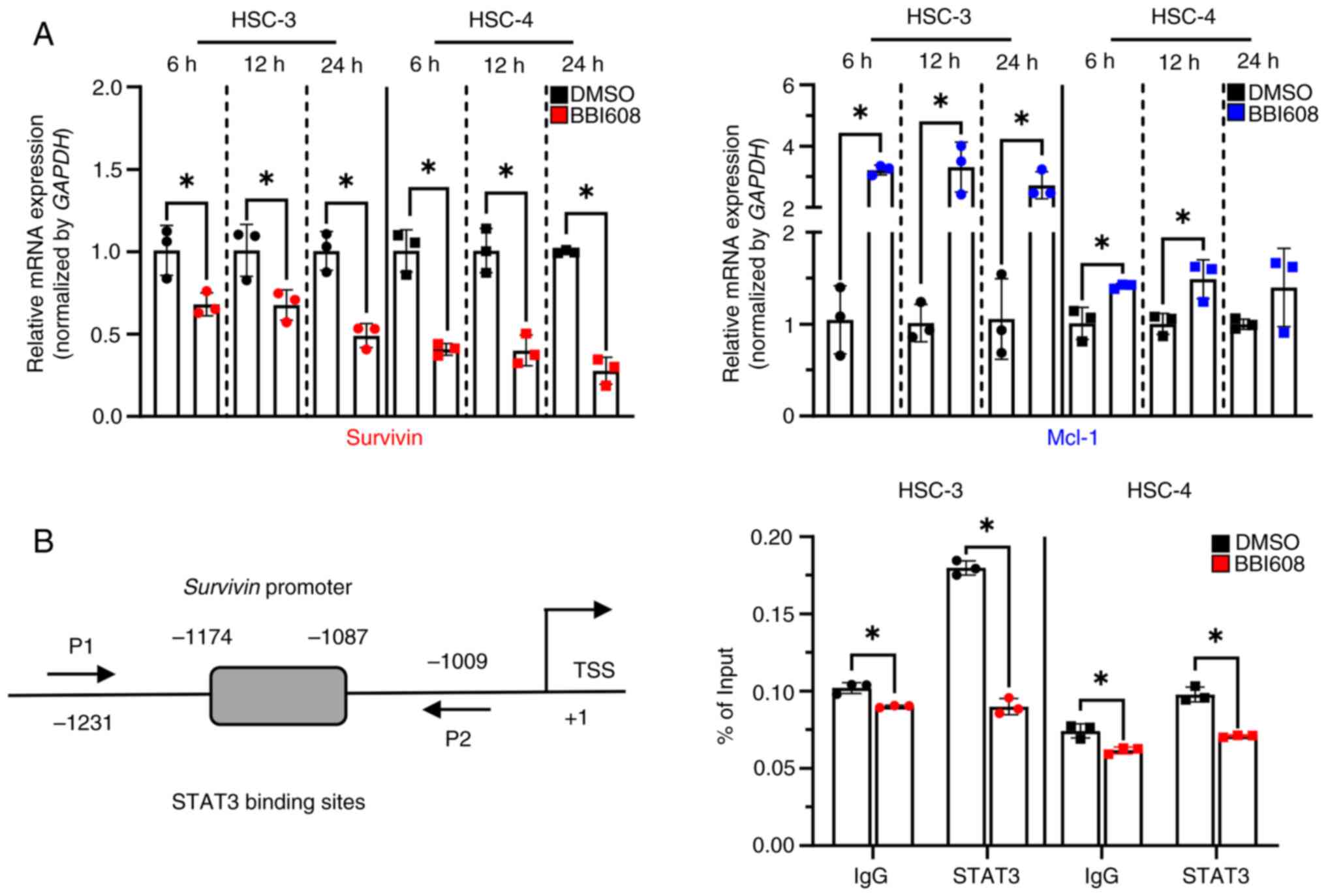
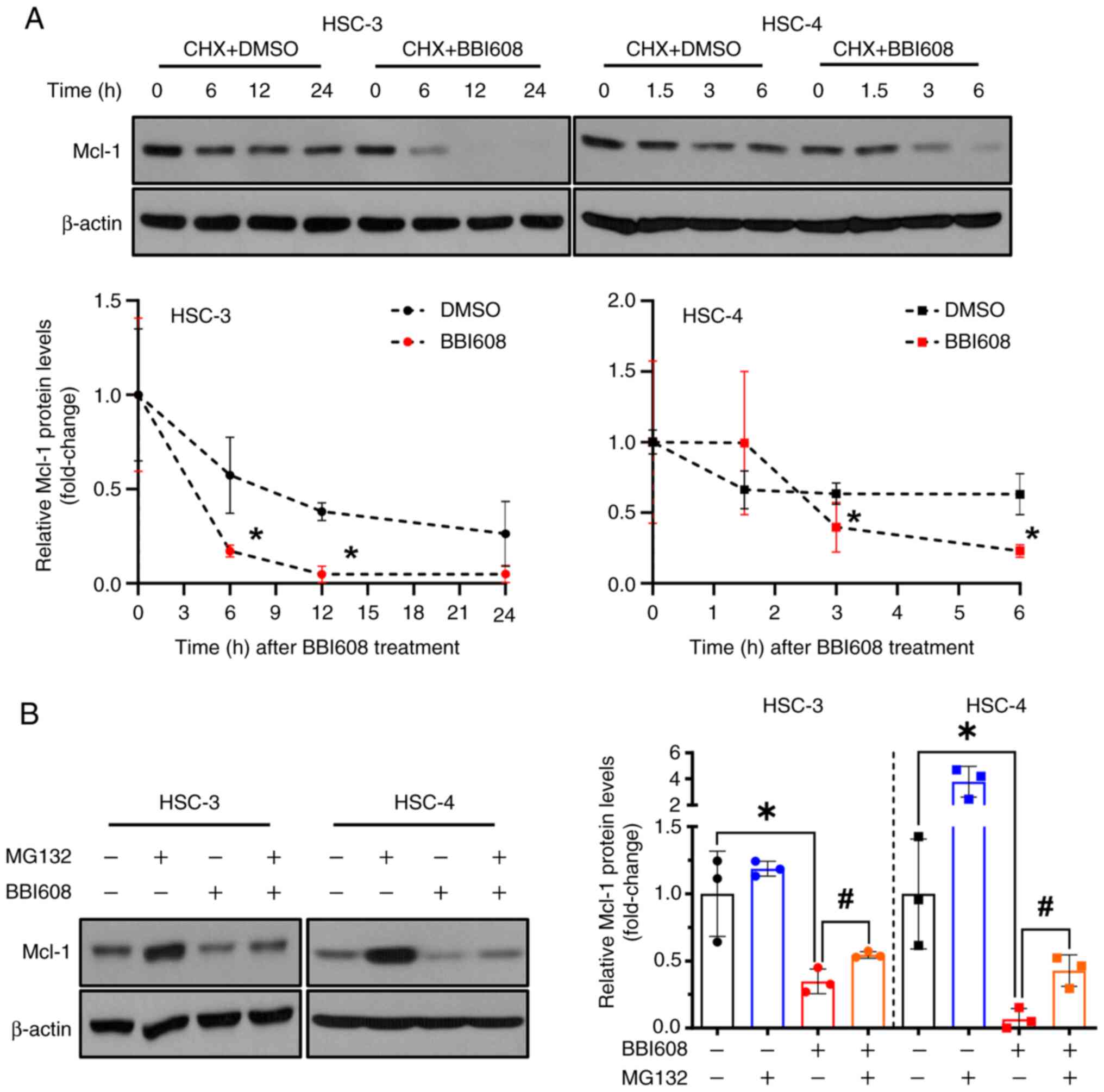
|
1
|
Pushpakom S, Iorio F, Eyers PA, Escott KJ,
Hopper S, Wells A, Doig A, Guilliams T, Latimer J, McNamee C, et
al: Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 18:41–58. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Abdelsayed M, Kort EJ, Jovinge S and
Mercola M: Repurposing drugs to treat cardiovascular disease in the
era of precision medicine. Nat Rev Cardiol. 19:751–764. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xia Y, Sun M, Huang H and Jin WL: Drug
repurposing for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Tar. 9:922024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hanahan D: Hallmarks of Cancer: New
dimensions. Cancer Discov. 12:31–46. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hu YM, Dong ZG and Liu KD: Unraveling the
complexity of STAT3 in cancer: Molecular understanding and drug
discovery. J Exp Clin Canc Res. 43:232024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yu H and Jove R: The stats of cancer - New
molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:97–105. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Macha MA, Matta A, Kaur J, Chauhan SS,
Thakar A, Shukla NK, Gupta SD and Ralhan R: Prognostic significance
of nuclear pSTAT3 in oral cancer. Head Neck-J Sci Spec. 33:482–489.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wei LY, Lin HC, Tsai FC, Ko JY, Kok SH,
Cheng SJ, Lee JJ and Chia JS: Effects of interleukin-6 on
STAT3-regulated signaling in oral cancer and as a prognosticator of
patient survival. Oral Oncol. 124:1056652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim LH, Khadka S, Shin JA, Jung JY, Ryu
MH, Yu HJ, Lee HN, Jang B, Yang IH, Won DH, et al: Nitidine
chloride acts as an apoptosis inducer in human oral cancer cells
and a nude mouse xenograft model via inhibition of STAT3.
Oncotarget. 8:91306–91315. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Rogoff HA, Keates S, Gao Y,
Murikipudi S, Mikule K, Leggett D, Li W, Pardee AB and Li CJ:
Suppression of cancer relapse and metastasis by inhibiting cancer
stemness. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:1839–1844. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Froeling FEM, Swamynathan MM, Deschenes A,
Chio IIC, Brosnan E, Yao MA, Alagesan P, Lucito M, Li J, Chang AY,
et al: Bioactivation of napabucasin triggers reactive oxygen
species-mediated cancer cell death. Clin Cancer Res. 25:7162–7174.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bendell JC, Hubbard JM, O'Neil BH, Jonker
DJ, Starodub A, Peyton JD, Pitot HC, Halfdanarson TR, Nadeau BR,
Zubkus JD, et al: Phase 1b/II study of cancer stemness inhibitor
napabucasin (BBI-608) in combination with FOLFIRI+/-bevacizumab
(bev) in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients (pts). J Clin
Oncol. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bekaii-Saab TS, Starodub A, El-Rayes BF,
Shahda S, O'Neil BH, Noonan AM, Shaib WL, Hanna WT, Mikhail S, Neki
AS, et al: Phase 1b/2 trial of cancer stemness inhibitor
napabucasin (NAPA)+ nab-paclitaxel (nPTX) and gemcitabine (Gem) in
metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma (mPDAC). J Clin Oncol. 36
(Suppl 15):41102018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shao Z, Wang H, Ren H, Sun Y and Chen X:
The anticancer effect of napabucasin (BBI608), a natural
naphthoquinone. Molecules. 28:56782023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ware MJ, Colbert K, Keshishian V, Ho J,
Corr SJ, Curley SA and Godin B: Generation of homogenous
three-dimensional pancreatic cancer cell spheroids using an
improved hanging drop technique. Tissue Eng Part C-Me. 22:312–321.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oner E, Gray SG and Finn SP: Cell
viability assay with 3d prostate tumor spheroids. Methods Mol Biol.
2645:263–275. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu HJ, Park C, Kim SJ, Cho NP and Cho SD:
Signal transducer and activators of transcription 3 regulates
cryptotanshinone-induced apoptosis in human mucoepidermoid
carcinoma cells. Pharmacogn Mag. 10:622–629. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gritsko T, Williams A, Turkson J, Kaneko
S, Bowman T, Huang M, Nam S, Eweis I, Diaz N, Sullivan D, et al:
Persistent activation of STAT3 signaling induces survivin gene
expression and confers resistance to apoptosis in human breast
cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 12:11–19. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Riccardi C and Nicoletti I: Analysis of
apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. Nat
Protoc. 1:1458–1461. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim HJ, Shin JA, Lee YG, Jin B, Lee WW,
Lee Y, Choi SJ, Han JM, Ahn MH, Kim JH, et al: Zingiber officinale
promotes autophagy and apoptosis in human oral cancer through the
C/EBP homologous protein. Cancer Sci. 115:2701–2717. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Won DH, Kim LH, Jang B, Yang IH, Kwon HJ,
Jin B, Oh SH, Kang JH, Hong SD, Shin JA and Cho SD: In vitro and in
vivo anti-cancer activity of silymarin on oral cancer. Tumour Biol.
40:10104283187761702018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang IH, Hong SH, Jung M, Ahn CH, Yoon HJ,
Hong SD, Cho SD and Shin JA: Cryptotanshinone chemosensitivity
potentiation by TW-37 in human oral cancer cell lines by targeting
STAT3-Mcl-1 signaling. Cancer Cell Int. 20:4052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Johnson DE, O'Keefe RA and Grandis JR:
Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 15:234–248. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hsieh FC, Cheng G and Lin J: Evaluation of
potential Stat3-regulated genes in human breast cancer. Biochem
Bioph Res Co. 335:292–299. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zou SL, Tong QY, Liu BW, Huang W, Tian Y
and Fu XH: Targeting STAT3 in cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer.
19:1452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang H, Guo M, Wei H and Chen Y: Targeting
MCL-1 in cancer: Current status and perspectives. J Hematol Oncol.
14:672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Breslin S and O'Driscoll L:
Three-dimensional cell culture: The missing link in drug discovery.
Drug Discov Today. 18:240–249. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Geiger JL, Grandis JR and Bauman JE: The
STAT3 pathway as a therapeutic target in head and neck cancer:
Barriers and innovations. Oral Oncol. 56:84–92. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Levy DE and Lee CK: What does Stat3 do? J
Clin Invest. 109:1143–1148. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Becerra C, Stephenson J, Jonker DJ, Cohn
AL, Asmis TR, Bekaii-Saab TS, Conkling PR, Garbo LE, Lenz HJ, et
al: Phase Ib/II study of cancer stem cell (CSC) inhibitor BBI608
combined with paclitaxel in advanced gastric and gastroesophageal
junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 33 (Suppl
15):40692015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Senichkin VV, Streletskaia AY, Gorbunova
AS, Zhivotovsky B and Kopeina GS: Saga of Mcl-1: Regulation from
transcription to degradation. Cell Death Differ. 27:405–419. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li X, Wei YQ and Wei XW: Napabucasin, a
novel inhibitor of STAT3, inhibits growth and synergises with
doxorubicin in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Lett.
491:146–161. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Han D, Yu T, Dong N, Wang B, Sun F and
Jiang D: Napabucasin, a novel STAT3 inhibitor suppresses
proliferation, invasion and stemness of glioblastoma cells. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 38:2892019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zajączkowska M, Teresiak A, Filas V, Ibbs
M, Bliźniak R, Łuczewski Ł and Lamperska K: 2D and 3D cell cultures
- A comparison of different types of cancer cell cultures. Arch Med
Sci. 14:910–919. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Edmondson R, Broglie JJ, Adcock AF and
Yang LJ: Three-dimensional cell culture systems and their
applications in drug discovery and cell-based biosensors. Assay
Drug Dev Techn. 12:207–218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tung YC, Hsiao AY, Allen SG, Torisawa YS,
Ho M and Takayama S: High-throughput 3D spheroid culture and drug
testing using a 384 hanging drop array. Analyst. 136:473–478. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zuo D, Shogren KL, Zang J, Jewison DE,
Waletzki BE, Miller AL II, Okuno SH, Cai Z and Yaszemski MJ:
Inhibition of STAT3 blocks protein synthesis and tumor metastasis
in osteosarcoma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:2442018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim J, Park A, Hwang J, Zhao X, Kwak J,
Kim HW, Ku M, Yang J, Kim TI, Jeong KS, et al: KS10076, a chelator
for redox-active metal ions, induces ROS-mediated STAT3 degradation
in autophagic cell death and eliminates ALDH1 stem cells. Cell Rep.
40:1110772022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jonker DJ, Nott L, Yoshino T, Gill S,
Shapiro J, Ohtsu A, Zalcberg J, Vickers MM, Wei AC, Gao Y, et al:
Napabucasin versus placebo in refractory advanced colorectal
cancer: A randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol.
3:263–270. 2018.
|
|
41
|
Chang AY, Hsu E, Patel J, Li Y, Zhang M,
Iguchi H and Rogoff HA: Evaluation of tumor cell-tumor
microenvironment component interactions as potential predictors of
patient response to napabucasin. Mol Cancer Res. 17:1429–1434.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Petsri K, Thongsom S, Racha S, Chamni S,
Jindapol S, Kaekratoke N, Zou H and Chanvorachote P: Novel
mechanism of napabucasin, a naturally derived furanonaphthoquinone:
Apoptosis and autophagy induction in lung cancer cells through
direct targeting on Akt/mTOR proteins. Bmc Complement Med.
22:2502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|