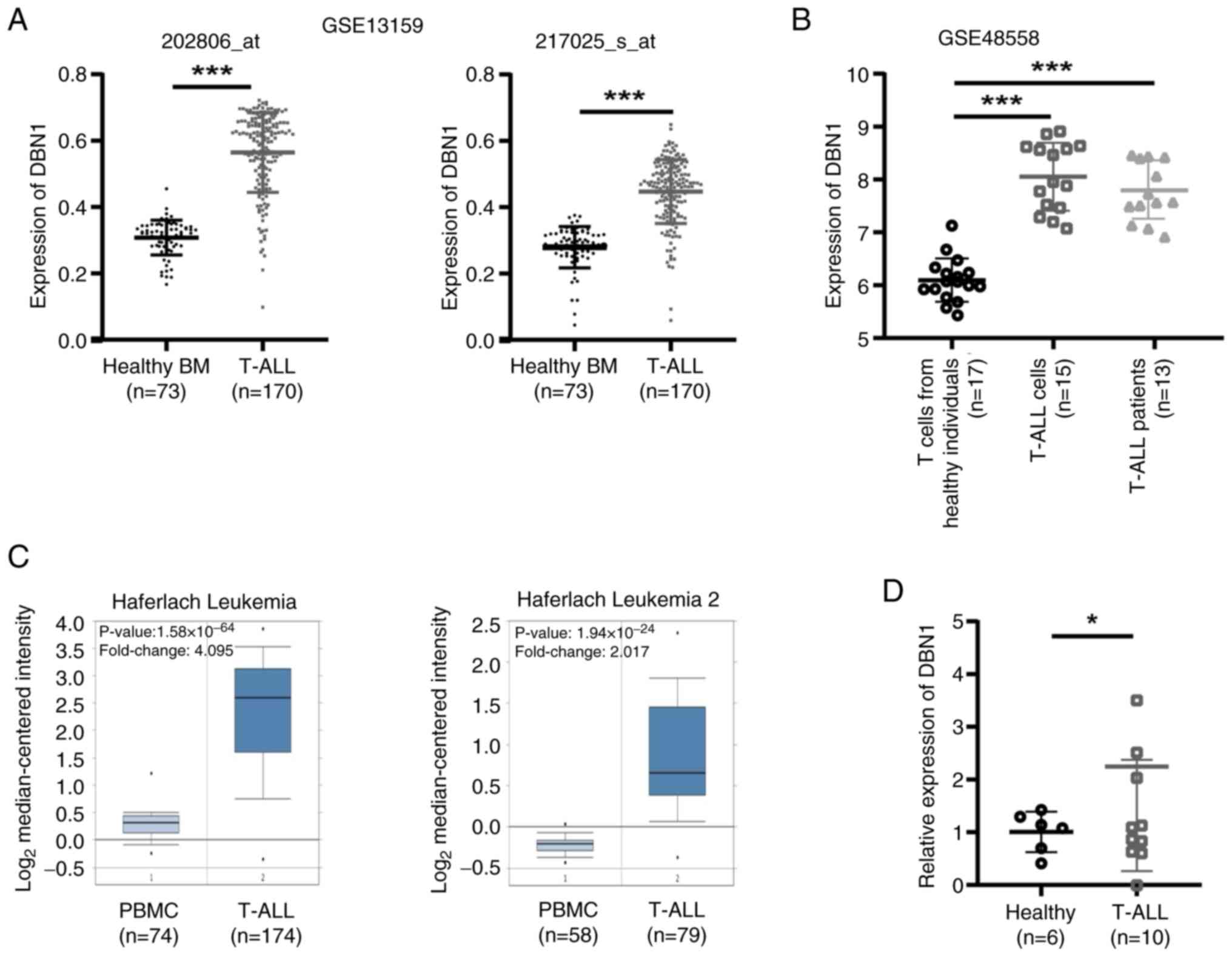
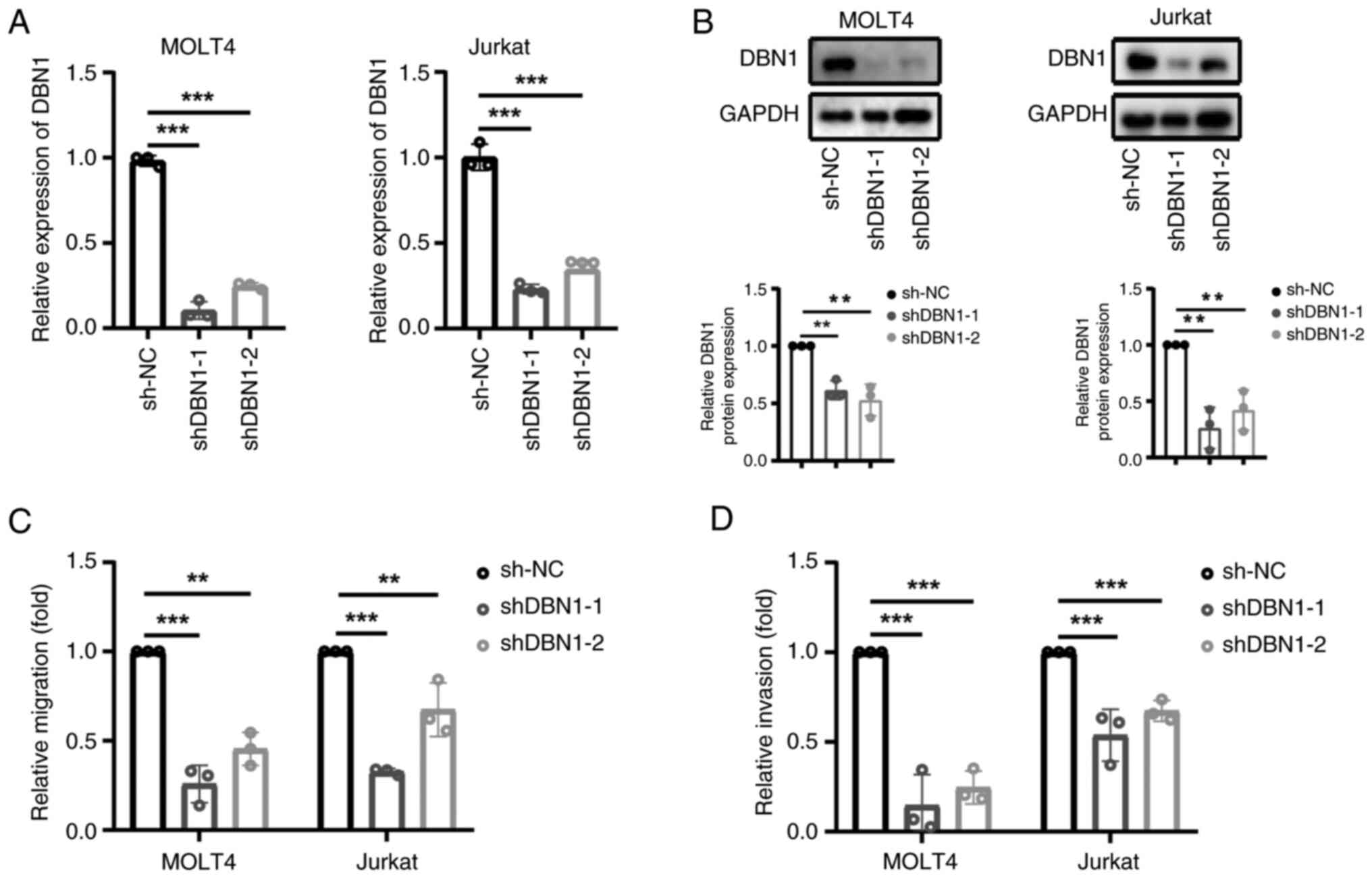
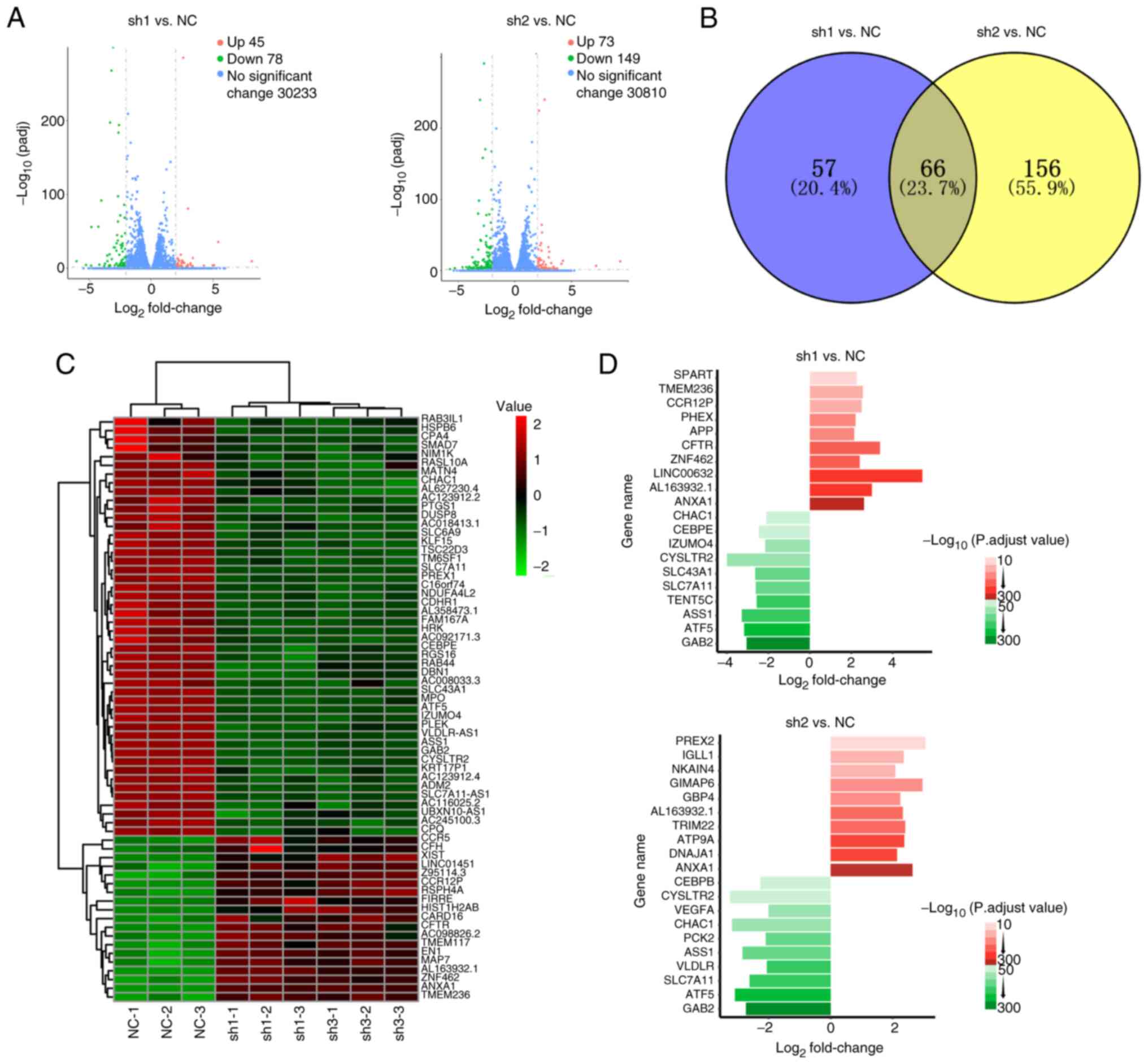
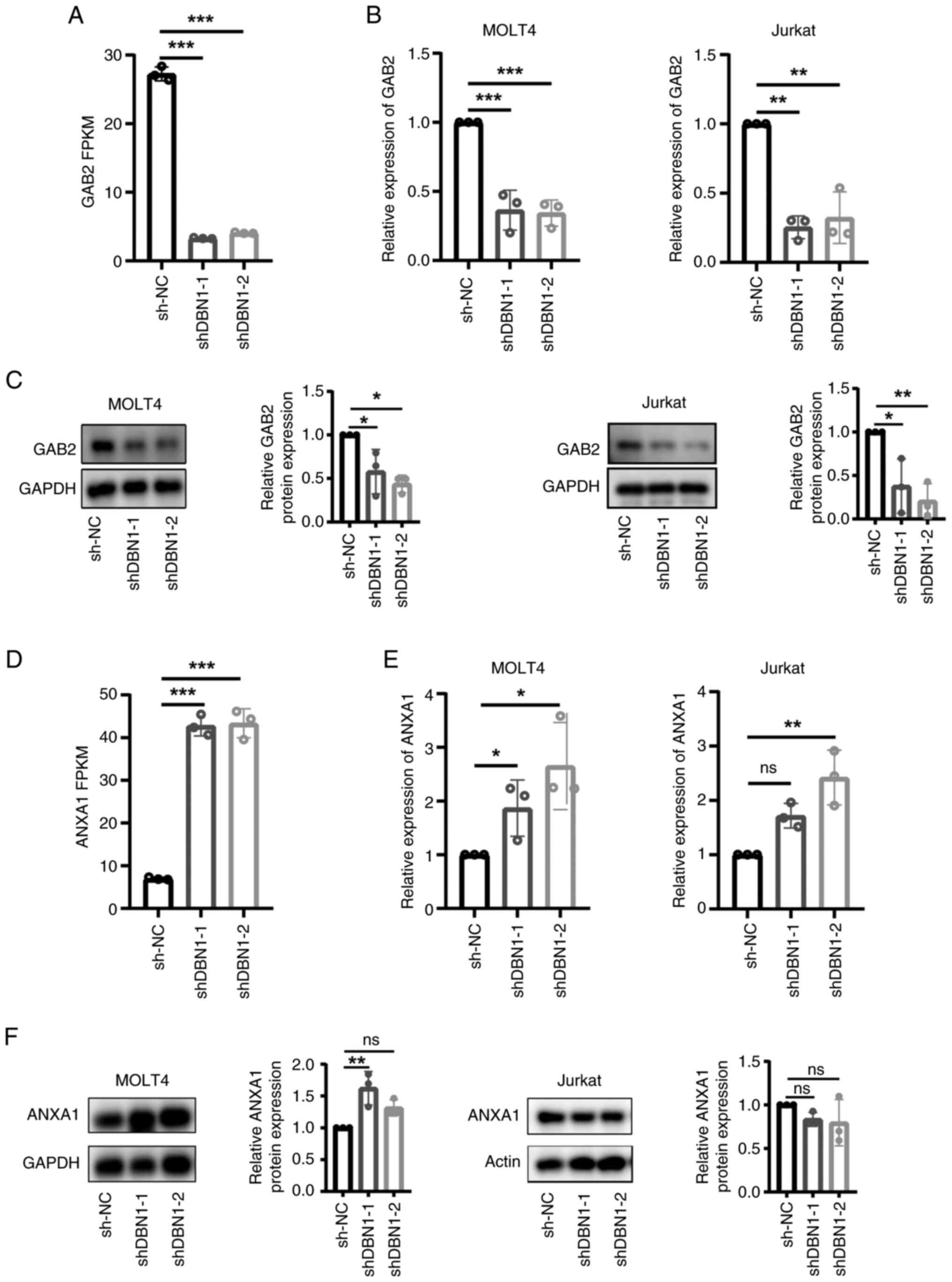
|
1
|
Raetz EA and Teachey DT: T-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program.
2016:580–588. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sanchez-Martin M and Ferrando A: The
NOTCH1-MYC highway toward T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Blood. 129:1124–1133. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Passaro D, Quang CT and Ghysdael J:
Microenvironmental cues for T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
development. Immunol Rev. 271:156–172. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Terwilliger T and Abdul-Hay M: Acute
lymphoblastic leukemia: A comprehensive review and 2017 update.
Blood Cancer J. 7:e5772017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marks DI and Rowntree C: Management of
adults with T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 129:1134–1142.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vadillo E, Dorantes-Acosta E, Pelayo R and
Schnoor M: T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL): New
insights into the cellular origins and infiltration mechanisms
common and unique among hematologic malignancies. Blood Rev.
32:36–51. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shirao T, Hanamura K, Koganezawa N,
Ishizuka Y, Yamazaki H and Sekino Y: The role of drebrin in
neurons. J Neurochem. 141:819–834. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ishikawa R, Hayashi K, Shirao T, Xue Y,
Takagi T, Sasaki Y and Kohama K: Drebrin, a development-associated
brain protein from rat embryo, causes the dissociation of
tropomyosin from actin filaments. J Biol Chem. 269:29928–29933.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shirao T and Sekino Y: General
introduction to drebrin. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1006:3–22. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rocha-Perugini V, Gordon-Alonso M and
Sanchez-Madrid F: Role of drebrin at the immunological synapse. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 1006:271–280. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shan Y, Farmer SM and Wray S: Drebrin
regulates cytoskeleton dynamics in migrating neurons through
interaction with CXCR4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
118:e20094931182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shirao T, Hayashi K, Ishikawa R, Isa K,
Asada H, Ikeda K and Uyemura K: Formation of thick, curving bundles
of actin by drebrin A expressed in fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res.
215:145–153. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peitsch WK, Hofmann I, Prätzel S, Grund C,
Kuhn C, Moll I, Langbein L and Franke WW: Drebrin particles:
Components in the ensemble of proteins regulating actin dynamics of
lamellipodia and filopodia. Eur J Cell Biol. 80:567–579. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ridley AJ, Schwartz MA, Burridge K, Firtel
RA, Ginsberg MH, Borisy G, Parsons JT and Horwitz AR: Cell
migration: Integrating signals from front to back. Science.
302:1704–1709. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dart AE, Worth DC, Muir G, Chandra A,
Morris JD, McKee C, Verrill C, Bryant RJ and Gordon-Weeks PR: The
drebrin/EB3 pathway drives invasive activity in prostate cancer.
Oncogene. 36:4111–4123. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Terakawa Y, Agnihotri S, Golbourn B, Nadi
M, Sabha N, Smith CA, Croul SE and Rutka JT: The role of drebrin in
glioma migration and invasion. Exp Cell Res. 319:517–528. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Alfarsi LH, El Ansari R, Masisi BK, Parks
R, Mohammed OJ, Ellis IO, Rakha EA and Green AR: Integrated
analysis of key differentially expressed genes identifies DBN1 as a
predictive marker of response to endocrine therapy in luminal
breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 12:15492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Horst B, Gruvberger-Saal SK, Hopkins BD,
Bordone L, Yang Y, Chernoff KA, Uzoma I, Schwipper V, Liebau J,
Nowak NJ, et al: Gab2-mediated signaling promotes melanoma
metastasis. Am J Pathol. 174:1524–1533. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bentires-Alj M, Gil SG, Chan R, Wang ZC,
Wang Y, Imanaka N, Harris LN, Richardson A, Neel BG and Gu H: A
role for the scaffolding adapter GAB2 in breast cancer. Nat Med.
12:114–121. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Adams SJ, Aydin IT and Celebi JT: GAB2-a
scaffolding protein in cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 10:1265–1270. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wöhrle FU, Daly RJ and Brummer T:
Function, regulation and pathological roles of the Gab/DOS docking
proteins. Cell Commun Signal. 7:222009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang C, Gu C, Jeong KJ, Zhang D, Guo W, Lu
Y, Ju Z, Panupinthu N, Yang JY, Gagea MM, et al: YAP/TAZ-mediated
upregulation of GAB2 leads to increased sensitivity to growth
factor-induced activation of the PI3K pathway. Cancer Res.
77:1637–1648. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cheng J, Zhong Y, Chen S, Sun Y, Huang L,
Kang Y, Chen B, Chen G, Wang F, Tian Y, et al: Gab2 mediates
hepatocellular carcinogenesis by integrating multiple signaling
pathways. FASEB J. 31:5530–5542. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shi X, Gong L, Liu Y, Hou K, Fan Y, Li C,
Wen T, Qu X and Che X: 4-Phenylbutyric acid promotes migration of
gastric cancer cells by histone deacetylase inhibition-mediated
IL-8 upregulation. Epigenetics. 15:632–645. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gu S, Sayad A, Chan G, Yang W, Lu Z,
Virtanen C, Van Etten RA and Neel BG: SHP2 is required for
BCR-ABL1-induced hematologic neoplasia. Leukemia. 32:203–213. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Spohr C, Poggio T, Andrieux G, Schönberger
K, Cabezas-Wallscheid N, Boerries M, Halbach S, Illert AL and
Brummer T: Gab2 deficiency prevents Flt3-ITD driven acute myeloid
leukemia in vivo. Leukemia. 36:970–982. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sies K, Spohr C, Gründer A, Todorova R,
Uhl FM, Huber J, Zeiser R, Pahl HL, Becker H, Aumann K, et al: Gab2
is essential for transformation by FLT3-ITD in acute myeloid
leukemia. Hemasphere. 3:e1842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gong R, Li H, Liu Y, Wang Y, Ge L, Shi L,
Wu G, Lyu J, Gu H and He L: Gab2 promotes acute myeloid leukemia
growth and migration through the SHP2-Erk-CREB signaling pathway. J
Leukoc Biol. 112:669–677. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Haferlach T, Kohlmann A, Wieczorek L,
Basso G, Kronnie GT, Béné MC, De Vos J, Hernandez JM, Hofmann WK,
Mills KI, et al: Clinical utility of microarray-based gene
expression profiling in the diagnosis and subclassification of
leukemia: report from the International microarray innovations in
leukemia study group. J Clin Oncol. 28:2529–2537. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cramer-Morales K, Nieborowska-Skorska M,
Scheibner K, Padget M, Irvine DA, Sliwinski T, Haas K, Lee J, Geng
H and Roy D: Personalized synthetic lethality induced by targeting
RAD52 in leukemias identified by gene mutation and expression
profile. Blood. 122:1293–1304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ng OH, Erbilgin Y, Firtina S, Celkan T,
Karakas Z, Aydogan G, Turkkan E, Yildirmak Y, Timur C, Zengin E, et
al: Deregulated WNT signaling in childhood T-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 4:e1922014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Homminga I, Pieters R, Langerak AW, de
Rooi JJ, Stubbs A, Verstegen M, Vuerhard M, Buijs-Gladdines J, Kooi
C, Klous P, et al: Integrated transcript and genome analyses reveal
NKX2-1 and MEF2C as potential oncogenes in T cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell. 19:484–497. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kohlmann A, Kipps TJ, Rassenti LZ, Downing
JR, Shurtleff SA, Mills KI, Gilkes AF, Hofmann WK, Basso G,
Dell'orto MC, et al: An international standardization programme
towards the application of gene expression profiling in routine
leukaemia diagnostics: The microarray innovations in leukemia study
prephase. Br J Haematol. 142:802–807. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zeng X, Lei Y, Pan S, Sun J, He H, Xiao D,
Jamal M, Shen H, Zhou F, Shao L and Zhang Q: LncRNA15691 promotes
T-ALL infiltration by upregulating CCR9 via increased MATR3
stability. J Leukoc Biol. 113:203–215. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jamal M, Lei Y, He H, Zeng X, Bangash HI,
Xiao D, Shao L, Zhou F and Zhang Q: CCR9 overexpression promotes
T-ALL progression by enhancing cholesterol biosynthesis. Front
Pharmacol. 14:12572892023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li G, Gao L, Zhao J, Liu D, Li H and Hu M:
LncRNA ANRIL/miR-7-5p/TCF4 axis contributes to the progression of T
cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell Int. 20:3352020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Guoren Z, Zhaohui F, Wei Z, Mei W, Yuan W,
Lin S, Xiaoyue X, Xiaomei Z and Bo S: TFAP2A induced ITPKA serves
as an oncogene and interacts with DBN1 in lung adenocarcinoma. Int
J Biol Sci. 16:504–514. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ding C, Luo J, Li L, Li S, Yang L, Pan H,
Liu Q, Qin H, Chen C and Feng J: Gab2 facilitates
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the MEK/ERK/MMP signaling
in colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:52016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bhojwani D and Pui CH: Relapsed childhood
acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet Oncol. 14:e205–e217. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Stock W, Johnson JL, Stone RM, Kolitz JE,
Powell BL, Wetzler M, Westervelt P, Marcucci G, DeAngelo DJ,
Vardiman JW, et al: Dose intensification of daunorubicin and
cytarabine during treatment of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia:
Results of cancer and leukemia group B study 19802. Cancer.
119:90–98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wei M, Haney MG, Rivas DR and Blackburn
JS: Protein tyrosine phosphatase 4A3 (PTP4A3/PRL-3) drives
migration and progression of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in
vitro and in vivo. Oncogenesis. 9:62020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nourshargh S, Hordijk PL and Sixt M:
Breaching multiple barriers: Leukocyte motility through venular
walls and the interstitium. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 11:366–378.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Krummel MF, Friedman RS and Jacobelli J:
Modes and mechanisms of T cell motility: Roles for confinement and
Myosin-IIA. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 30:9–16. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dun XP and Chilton JK: Control of cell
shape and plasticity during development and disease by the
actin-binding protein Drebrin. Histol Histopathol. 25:533–540.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Dang E, Yang S, Song C, Jiang D, Li Z, Fan
W, Sun Y, Tao L, Wang J, Liu T, et al: BAP31, a newly defined
cancer/testis antigen, regulates proliferation, migration, and
invasion to promote cervical cancer progression. Cell Death Dis.
9:7912018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Iyama S, Ono M, Kawai-Nakahara H, Husni
RE, Dai T, Shiozawa T, Sakata A, Kohrogi H and Noguchi M: Drebrin:
A new oncofetal biomarker associated with prognosis of lung
adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 102:74–81. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Peitsch WK, Hofmann I, Bulkescher J, Hergt
M, Spring H, Bleyl U, Goerdt S and Franke WW: Drebrin, an
actin-binding, cell-type characteristic protein: Induction and
localization in epithelial skin tumors and cultured keratinocytes.
J Invest Dermatol. 125:761–774. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lin Q, Tan HT, Lim TK, Khoo A, Lim KH and
Chung MCM: iTRAQ analysis of colorectal cancer cell lines suggests
Drebrin (DBN1) is overexpressed during liver metastasis.
Proteomics. 14:1434–1443. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Jasek-Gajda E, Jurkowska H, Jasińska M and
Lis GJ: Targeting the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways
affects NRF2, Trx and GSH antioxidant systems in leukemia cells.
Antioxidants (Basel). 9:6332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Guo JR, Li W, Wu Y, Wu LQ, Li X, Guo YF,
Zheng XH, Lian XL, Huang HF and Chen YZ: Hepatocyte growth factor
promotes proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of myeloid
leukemia cells through PI3K-AKT and MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Am
J Transl Res. 8:3630–3644. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jiang H, Tang J, Qiu L, Zhang Z, Shi S,
Xue L, Kui L, Huang T, Nan W, Zhou B, et al: Semaphorin 4D is a
potential biomarker in pediatric leukemia and promotes
leukemogenesis by activating PI3K/AKT and ERK signaling pathways.
Oncol Rep. 45:12021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chiang YJ, Liao WT, Ho KC, Wang SH, Chen
YG, Ho CL, Huang SF, Shih LY, Yang-Yen HFY and Yen JJY: CBAP
modulates Akt-dependent TSC2 phosphorylation to promote Rheb-mTORC1
signaling and growth of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Oncogene. 38:1432–1447. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR,
Soleymani Fard S and Ghaffari SH: An overview of microRNAs:
Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell
Physiol. 234:5451–5465. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bartel DP and Chen CZ: Micromanagers of
gene expression: The potentially widespread influence of metazoan
microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 5:396–400. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Huang W, Wang WT, Fang K, Chen ZH, Sun YM,
Han C, Sun LY, Luo XQ and Chen YQ: MIR-708 promotes phagocytosis to
eradicate T-ALL cells by targeting CD47. Mol Cancer. 17:122018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Deng M, Zeng C, Lu X, He X, Zhang R, Qiu
Q, Zheng G, Jia X, Liu H and He Z: miR-218 suppresses gastric
cancer cell cycle progression through the CDK6/Cyclin D1/E2F1 axis
in a feedback loop. Cancer Lett. 403:175–185. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li Y, Shi B, Dong F, Zhu X, Liu B and Liu
Y: LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 facilitates the progression of bladder cancer by
targeting MiR-218-5p/HS3ST3B1. Cancer Gene Ther. 28:212–220. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Liu Z, Mao L, Wang L, Zhang H and Hu X:
miR-218 functions as a tumor suppressor gene in cervical cancer.
Mol Med Rep. 21:209–219. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|