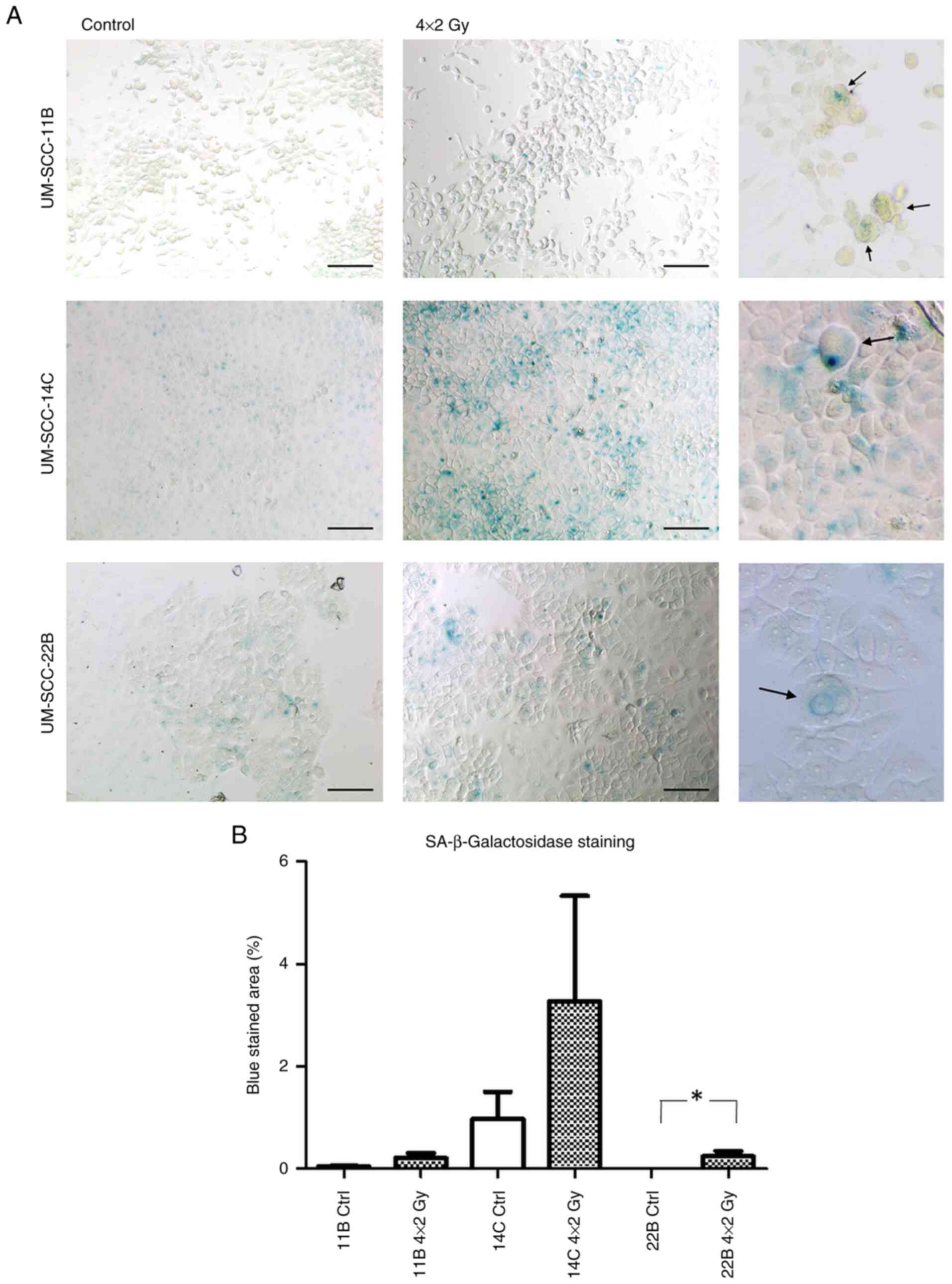
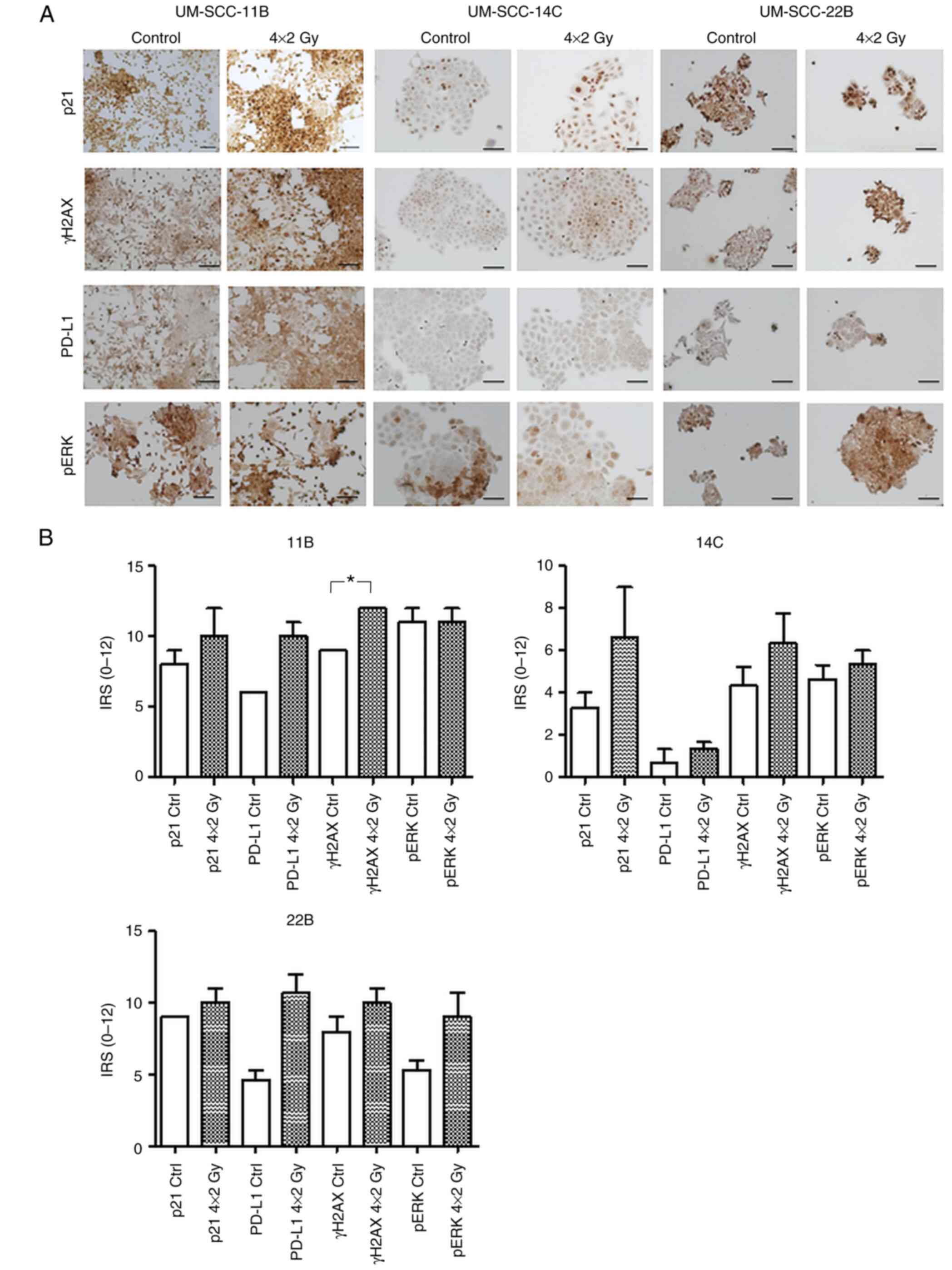
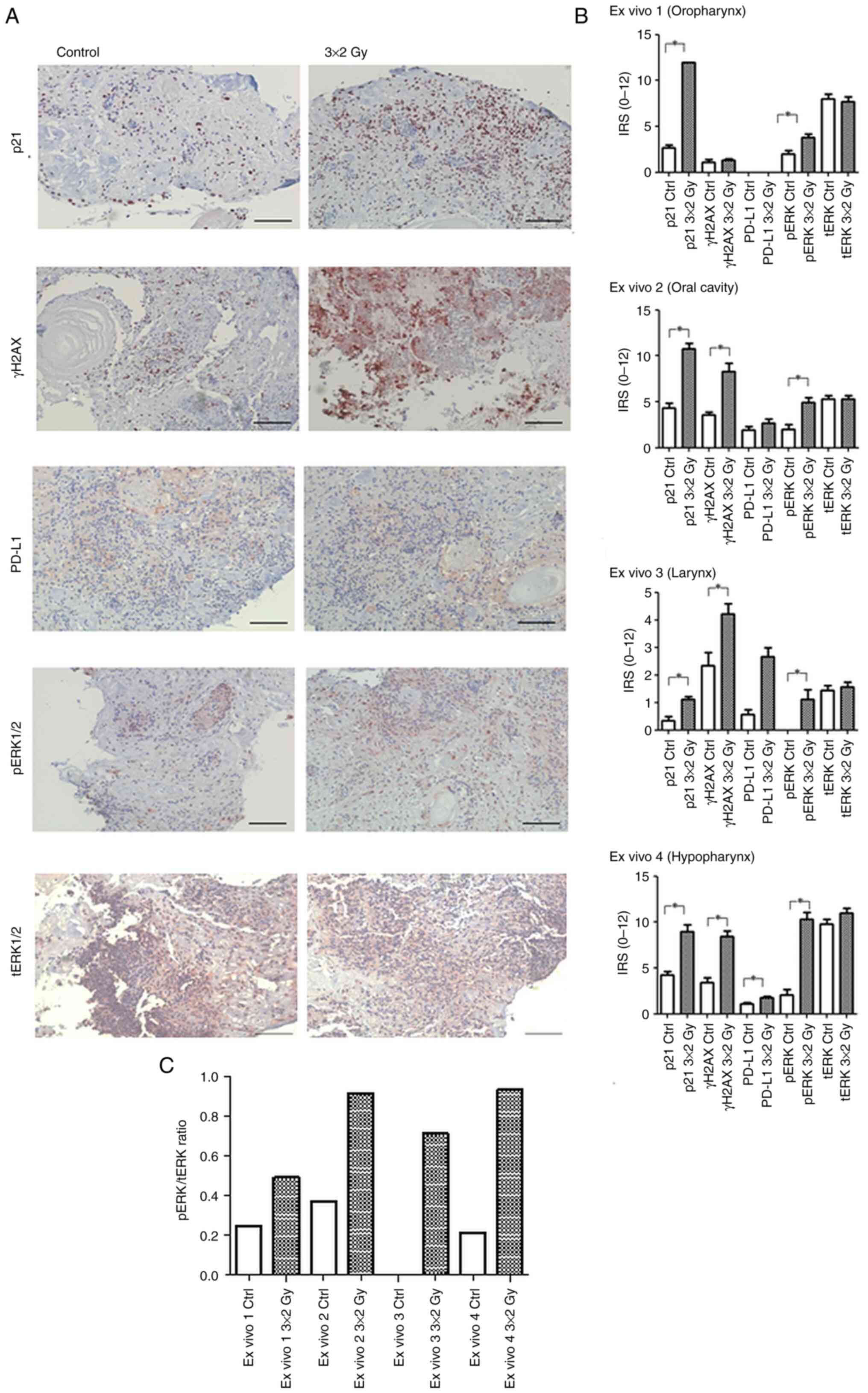
|
1
|
Herranz N and Gil J: Mechanisms and
functions of cellular senescence. J Clin Invest. 128:1238–1246.
2018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim HS, Song MC, Kwak IH, Park TJ and Lim
IK: Constitutive induction of p-Erk1/2 accompanied by reduced
activities of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A and MKP3 due to
reactive oxygen species during cellular senescence. J Biol Chem.
278:37497–37510. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
White RR and Vijg J: Do DNA double-strand
breaks drive aging? Mol Cell. 63:729–738. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Si F, Liu X, Tao Y, Zhang Y, Ma F, Hsueh
EC, Puram SV and Peng G: Blocking senescence and tolerogenic
function of dendritic cells induced by γδ Treg cells enhances
tumor-specific immunity for cancer immunotherapy. J Immunother
Cancer. 12:e0082192024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ruhland MK and Alspach E: Senescence and
immunoregulation in the tumor microenvironment. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 9:7540692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Toso A, Revandkar A, Di Mitri D, Guccini
I, Proietti M, Sarti M, Pinton S, Zhang J, Kalathur M, Civenni G,
et al: Enhancing chemotherapy efficacy in Pten-deficient prostate
tumors by activating the senescence-associated antitumor immunity.
Cell Rep. 9:75–89. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang J, Zhou CC, Sun HC, Li Q, Hu JD,
Jiang T and Zhou S: Identification of several senescence-associated
genes signature in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin
Lab Anal. 36:e245552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ostrowska K, Niewinski P, Piotrowski I,
Ostapowicz J, Koczot S, Suchorska WM, Golusiński P, Masternak MM
and Golusiński W: Senescence in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma: relationship between senescence-associated secretory
phenotype (SASP) mRNA expression level and clinicopathological
features. Clin Transl Oncol. 26:1022–1032. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schoetz U, Klein D, Hess J, Shnayien S,
Spoerl S, Orth M, Mutlu S, Hennel R, Sieber A, Ganswindt U, et al:
Early senescence and production of senescence-associated cytokines
are major determinants of radioresistance in head-and-neck squamous
cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 12:11622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee YC, Nam Y, Kim M, Kim SI, Lee JW, Eun
YG and Kim D: Prognostic significance of senescence-related tumor
microenvironment genes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Aging (Albany NY). 16:985–1001. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH,
Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M,
Tafuri A, et al: Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth,
malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1773:1263–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Golding SE, Morgan RN, Adams BR, Hawkins
AJ, Povirk LF and Valerie K: Pro-survival AKT and ERK signaling
from EGFR and mutant EGFRvIII enhances DNA double-strand break
repair in human glioma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:730–738. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hein AL, Ouellette MM and Yan Y:
Radiation-induced signaling pathways that promote cancer cell
survival (review). Int J Oncol. 45:1813–1819. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chung EJ, Brown AP, Asano H, Mandler M,
Burgan WE, Carter D, Camphausen K and Citrin D: In vitro and in
vivo radiosensitization with AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), an inhibitor of
mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated
kinase 1/2 kinase. Clin Cancer Res. 15:3050–3057. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Leiker AJ, DeGraff W, Choudhuri R, Sowers
AL, Thetford A, Cook JA, Van Waes C and Mitchell JB: Radiation
enhancement of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by the Dual
PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor PF-05212384. Clin Cancer Res. 21:2792–2801.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Affolter A, Drigotas M, Fruth K,
Schmidtmann I, Brochhausen C, Mann WJ and Brieger J: Increased
radioresistance via G12S K-Ras by compensatory upregulation of MAPK
and PI3K pathways in epithelial cancer. Head Neck. 35:220–228.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Affolter A, Fruth K, Brochhausen C,
Schmidtmann I, Mann WJ and Brieger J: Activation of
mitogen-activated protein kinase extracellular signal-related
kinase in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas after irradiation
as part of a rescue mechanism. Head Neck. 33:1448–1457. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Affolter A and Hess J: Preclinical models
in head and neck tumors: Evaluation of cellular and molecular
resistance mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment. HNO.
64:860–869. 2016.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Affolter A, Samosny G, Heimes AS,
Schneider J, Weichert W, Stenzinger A, Sommer K, Jensen A, Mayer A,
Brenner W, et al: Multikinase inhibitors sorafenib and sunitinib as
radiosensitizers in head and neck cancer cell lines. Head Neck.
39:623–632. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Perri F, Pacelli R, Della Vittoria
Scarpati G, Cella L, Giuliano M, Caponigro F and Pepe S:
Radioresistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma:
Biological bases and therapeutic implications. Head Neck.
37:763–770. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sharon S and Bell RB: Immunotherapy in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A narrative review. Front
Oral Maxillofac Med. 4:282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen Z, Wong PY, Ng CWK, Lan L, Fung S, Li
JW, Cai L, Lei P, Mou Q, Wong SH, et al: The intersection between
oral microbiota, host gene methylation and patient outcomes in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 12:34252020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Affolter A, Kern J, Bieback K, Scherl C,
Rotter N and Lammert A: Biomarkers and 3D models predicting
response to immune checkpoint blockade in head and neck cancer
(Review). Int J Oncol. 61:882022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang TW, Johmura Y, Suzuki N, Omori S,
Migita T, Yamaguchi K, Hatakeyama S, Yamazaki S, Shimizu E, Imoto
S, et al: Blocking PD-L1-PD-1 improves senescence surveillance and
ageing phenotypes. Nature. 611:358–364. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Onorati A, Havas AP, Lin B, Rajagopal J,
Sen P, Adams PD and Dou Z: Upregulation of PD-L1 in Senescence and
Aging. Mol Cell Biol. 42:e00171222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Brenner E, Schörg BF, Ahmetlić F, Wieder
T, Hilke FJ, Simon N, Schroeder C, Demidov G, Riedel T,
Fehrenbacher B, et al: Cancer immune control needs senescence
induction by interferon-dependent cell cycle regulator pathways in
tumours. Nat Commun. 11:13352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen Z, Hu K, Feng L, Su R, Lai N, Yang Z
and Kang S: Senescent cells re-engineered to express soluble
programmed death receptor-1 for inhibiting programmed death
receptor-1/programmed death ligand-1 as a vaccination approach
against breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 109:1753–1763. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang J, Bu X, Wang H, Zhu Y, Geng Y,
Nihira NT, Tan Y, Ci Y, Wu F, Dai X, et al: Cyclin D-CDK4 kinase
destabilizes PD-L1 via cullin 3-SPOP to control cancer immune
surveillance. Nature. 553:91–95. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee JJ, Kim SY, Kim SH, Choi S, Lee B and
Shin JS: STING mediates nuclear PD-L1 targeting-induced senescence
in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 13:7912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Moreira A, Gross S, Kirchberger MC,
Erdmann M, Schuler G and Heinzerling L: Senescence markers:
Predictive for response to checkpoint inhibitors. Int J Cancer.
144:1147–1150. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Abdel-Naby R, Wang K, Song D, Bozentka J,
LaFonte M, Ou P, Stanek A, Mueller C, Alfonso A and Huan C:
Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK)-dependent p21
(WAF1/Cip1) Expression Is Associated with Gemcitabine Resistance in
Pancreatic Cancer Cells. J Am Coll Surg. 219:S272014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Affolter A, Liebel K, Tengler L, Seiz E,
Tiedtke M, Azhakesan A, Schütz J, Theodoraki MN, Kern J, Ruder AM,
et al: Modulation of PD-L1 expression by standard therapy in head
and neck cancer cell lines and exosomes. Int J Oncol. 63:1022023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Welters MJ, Fichtinger-Schepman AM, Baan
RA, Hermsen MA, van der Vijgh WJ, Cloos J and Braakhuis BJ:
Relationship between the parameters cellular differentiation,
doubling time and platinum accumulation and cisplatin sensitivity
in a panel of head and neck cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer.
71:410–415. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Engelmann L, Thierauf J, Koerich Laureano
N, Stark HJ, Prigge ES, Horn D, Freier K, Grabe N, Rong C,
Federspil P, et al: Organotypic co-cultures as a novel 3D model for
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancers (Basel).
12:23302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Affolter A, Muller MF, Sommer K,
Stenzinger A, Zaoui K, Lorenz K, Wolf T, Sharma S, Wolf J, Perner
S, et al: Targeting irradiation-induced mitogen-activated protein
kinase activation in vitro and in an ex vivo model for human head
and neck cancer. Head Neck. 38 (Suppl 1):E2049–E2061. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Remmele W and Stegner HE: Recommendation
for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for
immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast
cancer tissue. Pathologe. 8:138–140. 1987.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Muñoz-Espín D and Serrano M: Cellular
senescence: From physiology to pathology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:482–496. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Demaria M: Senescent cells: New target for
an old treatment? Mol Cell Oncol. 4:e12996662017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bernadotte A, Mikhelson VM and Spivak IM:
Markers of cellular senescence. Telomere shortening as a marker of
cellular senescence. Aging (Albany NY). 8:3–11. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Matuschek C, Haussmann J, Bölke E, Gripp
S, Schuler PJ, Tamaskovics B, Gerber PA, Djiepmo-Njanang FJ,
Kammers K, Plettenberg C, et al: Accelerated vs. conventionally
fractionated adjuvant radiotherapy in high-risk head and neck
cancer: A meta-analysis. Radiat Oncol. 13:1952018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qin S, Schulte BA and Wang GY: Role of
senescence induction in cancer treatment. World J Clin Oncol.
9:180–187. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Milanovic M, Fan DNY, Belenki D, Däbritz
JHM, Zhao Z, Yu Y, Dörr JR, Dimitrova L, Lenze D, Monteiro Barbosa
IA, et al: Senescence-associated reprogramming promotes cancer
stemness. Nature. 553:96–100. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nicolas AM, Pesic M, Engel E, Ziegler PK,
Diefenhardt M, Kennel KB, Buettner F, Conche C, Petrocelli V,
Elwakeel E, et al: Inflammatory fibroblasts mediate resistance to
neoadjuvant therapy in rectal cancer. Cancer Cell. 40:168–184.e13.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Demaria M, O'Leary MN, Chang J, Shao L,
Liu S, Alimirah F, Koenig K, Le C, Mitin N, Deal AM, et al:
Cellular senescence promotes adverse effects of chemotherapy and
cancer relapse. Cancer Discov. 7:165–176. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gu L and Kitamura M: Sensitive detection
and monitoring of senescence-associated secretory phenotype by
SASP-RAP assay. PLoS One. 7:e523052012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Redon CE, Nakamura AJ, Sordet O, Dickey
JS, Gouliaeva K, Tabb B, Lawrence S, Kinders RJ, Bonner WM and
Sedelnikova OA: γ-H2AX detection in peripheral blood lymphocytes,
splenocytes, bone marrow, xenografts, and skin. Methods Mol Biol.
682:249–270. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sedelnikova OA, Horikawa I, Zimonjic DB,
Popescu NC, Bonner WM and Barrett JC: Senescing human cells and
ageing mice accumulate DNA lesions with unrepairable double-strand
breaks. Nat Cell Biol. 6:168–170. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Golomb L, Sagiv A, Pateras IS, Maly A,
Krizhanovsky V, Gorgoulis VG, Oren M and Ben-Yehuda A:
Age-associated inflammation connects RAS-induced senescence to stem
cell dysfunction and epidermal malignancy. Cell Death Differ.
22:1764–1774. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Krtolica A, Parrinello S, Lockett S,
Desprez PY and Campisi J: Senescent fibroblasts promote epithelial
cell growth and tumorigenesis: A link between cancer and aging.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:12072–12077. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Halazonetis TD, Gorgoulis VG and Bartek J:
An oncogene-induced DNA damage model for cancer development.
Science. 319:1352–1355. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Serrano M, Lin AW, McCurrach ME, Beach D
and Lowe SW: Oncogenic ras provokes premature cell senescence
associated with accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a. Cell. 88:593–602.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang B, Kohli J and Demaria M: Senescent
cells in cancer therapy: Friends or Foes? Trends Cancer. 6:838–857.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gordon RR and Nelson PS: Cellular
senescence and cancer chemotherapy resistance. Drug Resist Updat.
15:123–131. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
D'Ambrosio M and Gil J: Reshaping of the
tumor microenvironment by cellular senescence: An opportunity for
senotherapies. Dev Cell. 58:1007–1021. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Domen A, Deben C, Verswyvel J, Flieswasser
T, Prenen H, Peeters M, Lardon F and Wouters A: Cellular senescence
in cancer: Clinical detection and prognostic implications. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 41:3602022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
George B, Horn D, Bayo P, Zaoui K,
Flechtenmacher C, Grabe N, Plinkert P, Krizhanovsky V and Hess J:
Regulation and function of Myb-binding protein 1A (MYBBP1A) in
cellular senescence and pathogenesis of head and neck cancer.
Cancer Lett. 358:191–199. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Mosieniak G, Sliwinska M, Alster O,
Strzeszewska A, Sunderland P, Piechota M, Was H and Sikora E:
Polyploidy formation in doxorubicin-treated cancer cells can favor
escape from senescence. Neoplasia. 17:882–893. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wang Q, Wu PC, Dong DZ, Ivanova I, Chu E,
Zeliadt S, Vesselle H and Wu DY: Polyploidy road to therapy-induced
cellular senescence and escape. Int J Cancer. 132:1505–1515. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhai J, Han J, Li C, Lv D, Ma F and Xu B:
Tumor senescence leads to poor survival and therapeutic resistance
in human breast cancer. Front Oncol. 13:10975132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Stivala LA, Cazzalini O and Prosperi E:
The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21CDKN1A as a target of
anti-cancer drugs. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 12:85–96. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Xu Y, Li N, Xiang R and Sun P: Emerging
roles of the p38 MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways in
oncogene-induced senescence. Trends Biochem Sci. 39:268–276. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Anerillas C, Abdelmohsen K and Gorospe M:
Regulation of senescence traits by MAPKs. Geroscience. 42:397–408.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chambard JC, Lefloch R, Pouysségur J and
Lenormand P: ERK implication in cell cycle regulation. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1773:1299–1310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Patel PL, Suram A, Mirani N, Bischof O and
Herbig U: Derepression of hTERT gene expression promotes escape
from oncogene-induced cellular senescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:E5024–E5033. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Schmitt CA, Wang B and Demaria M:
Senescence and cancer-role and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 19:619–636. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Woo SH, Yang LP, Chuang HC, Fitzgerald A,
Lee HY, Pickering C, Myers JN and Skinner HD: Down-regulation of
malic enzyme 1 and 2: Sensitizing head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma cells to therapy-induced senescence. Head Neck. 38 (Suppl
1):E934–E940. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
McConkey DJ, Choi W, Marquis L, Martin F,
Williams MB, Shah J, Svatek R, Das A, Adam L, Kamat A, et al: Role
of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in drug sensitivity
and metastasis in bladder cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
28:335–344. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Khalaf K, Hana D, Chou JT, Singh C,
Mackiewicz A and Kaczmarek M: Aspects of the tumor microenvironment
involved in immune resistance and drug resistance. Front Immunol.
12:6563642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Eckers JC, Kalen AL, Sarsour EH, Tompkins
VS, Janz S, Son JM, Doskey CM, Buettner GR and Goswami PC: Forkhead
box M1 regulates quiescence-associated radioresistance of human
head and neck squamous carcinoma cells. Radiat Res. 182:420–429.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Cahu J, Bustany S and Sola B:
Senescence-associated secretory phenotype favors the emergence of
cancer stem-like cells. Cell Death Dis. 3:e4462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Özcan S, Alessio N, Acar MB, Mert E,
Omerli F, Peluso G and Galderisi U: Unbiased analysis of senescence
associated secretory phenotype (SASP) to identify common components
following different genotoxic stresses. Aging (Albany NY).
8:1316–1329. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Fares CM, Van Allen EM, Drake CG, Allison
JP and Hu-Lieskovan S: Mechanisms of resistance to immune
checkpoint blockade: Why does checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy
not work for all patients? Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 39:147–164.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Nowicki TS, Hu-Lieskovan S and Ribas A:
Mechanisms of resistance to PD-1 and PD-L1 blockade. Cancer J.
24:47–53. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Saleh R and Elkord E: Acquired resistance
to cancer immunotherapy: Role of tumor-mediated immunosuppression.
Semin Cancer Biol. 65:13–27. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Haratani K, Yonesaka K, Takamura S,
Maenishi O, Kato R, Takegawa N, Kawakami H, Tanaka K, Hayashi H,
Takeda M, et al: U3-1402 sensitizes HER3-expressing tumors to PD-1
blockade by immune activation. J Clin Invest. 130:374–388. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Arasanz H, Zuazo M, Bocanegra A, Gato M,
Martínez-Aguillo M, Morilla I, Fernández G, Hernández B, López P,
Alberdi N, et al: Early detection of hyperprogressive disease in
non-small cell lung cancer by monitoring of systemic T cell
dynamics. Cancers (Basel). 12:3442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Hirsch L, Zitvogel L, Eggermont A and
Marabelle A: PD-Loma: A cancer entity with a shared sensitivity to
the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway blockade. Br J Cancer. 120:3–5. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kim HAJ, Zeng PYF, Shaikh MH, Mundi N,
Ghasemi F, Di Gravio E, Khan H, MacNeil D, Khan MI, Patel K, et al:
All HPV-negative head and neck cancers are not the same: Analysis
of the TCGA dataset reveals that anatomical sites have distinct
mutation, transcriptome, hypoxia, and tumor microenvironment
profiles. Oral Oncol. 116:1052602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ahmadinejad F, Bos T, Hu B, Britt E,
Koblinski J, Souers AJ, Leverson JD, Faber AC, Gewirtz DA and
Harada H: Senolytic-mediated elimination of head and neck tumor
cells induced into senescence by cisplatin. Mol Pharmacol.
101:168–180. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|