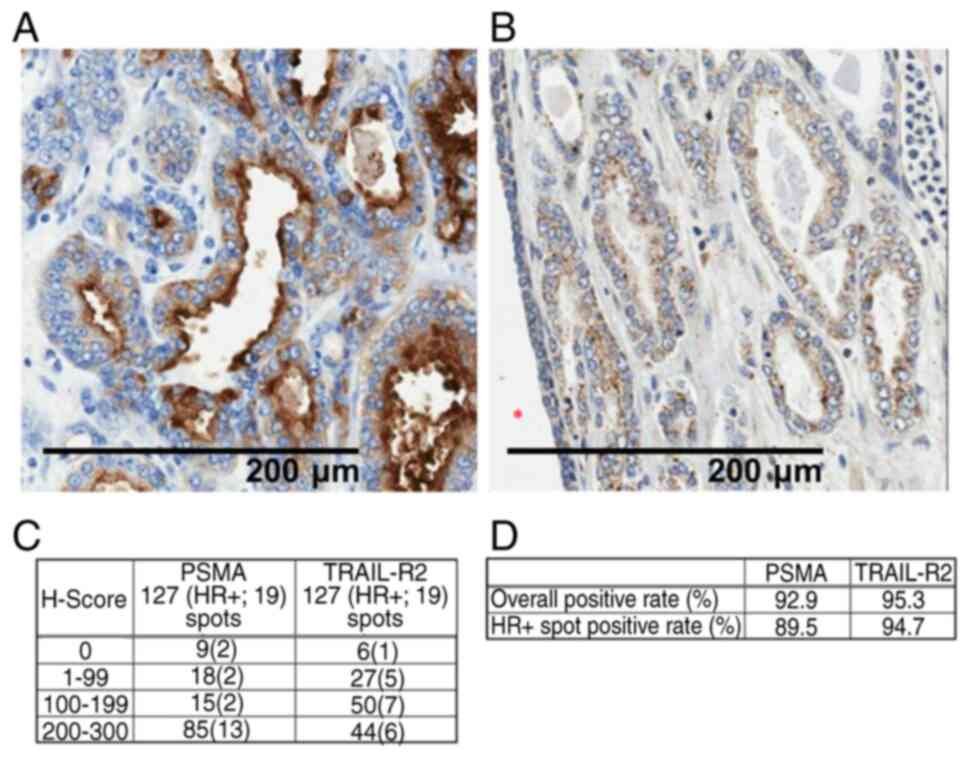
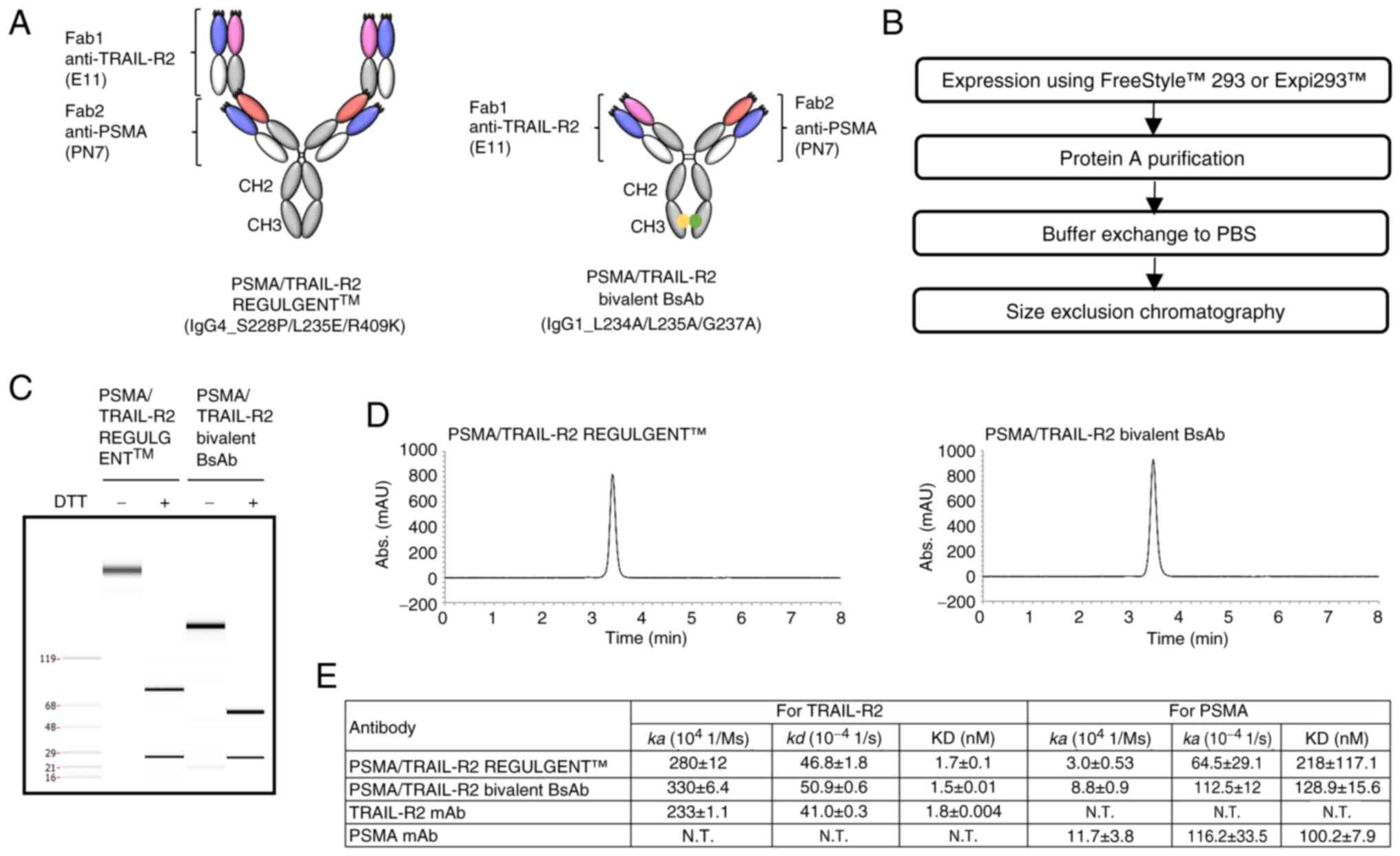
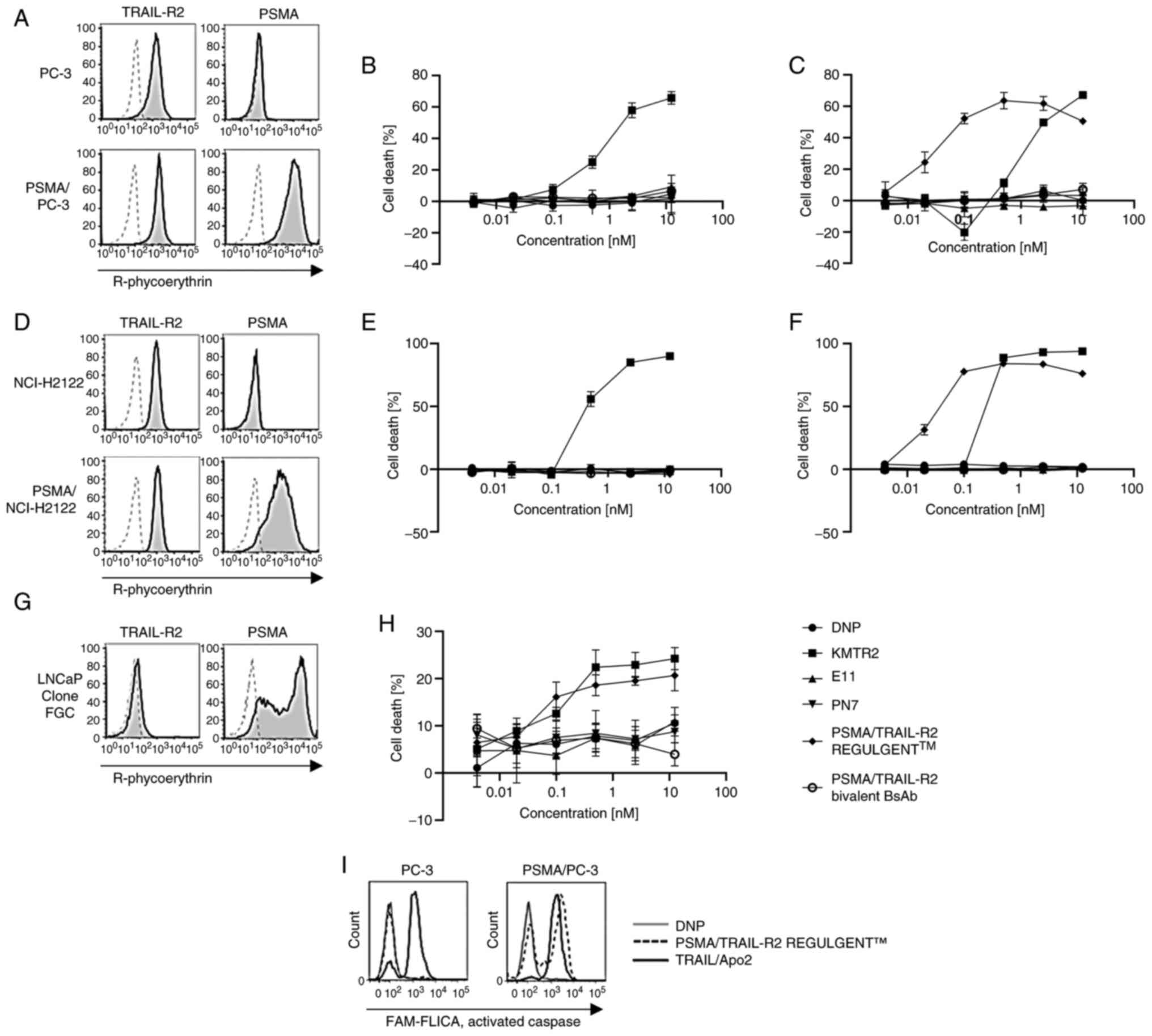
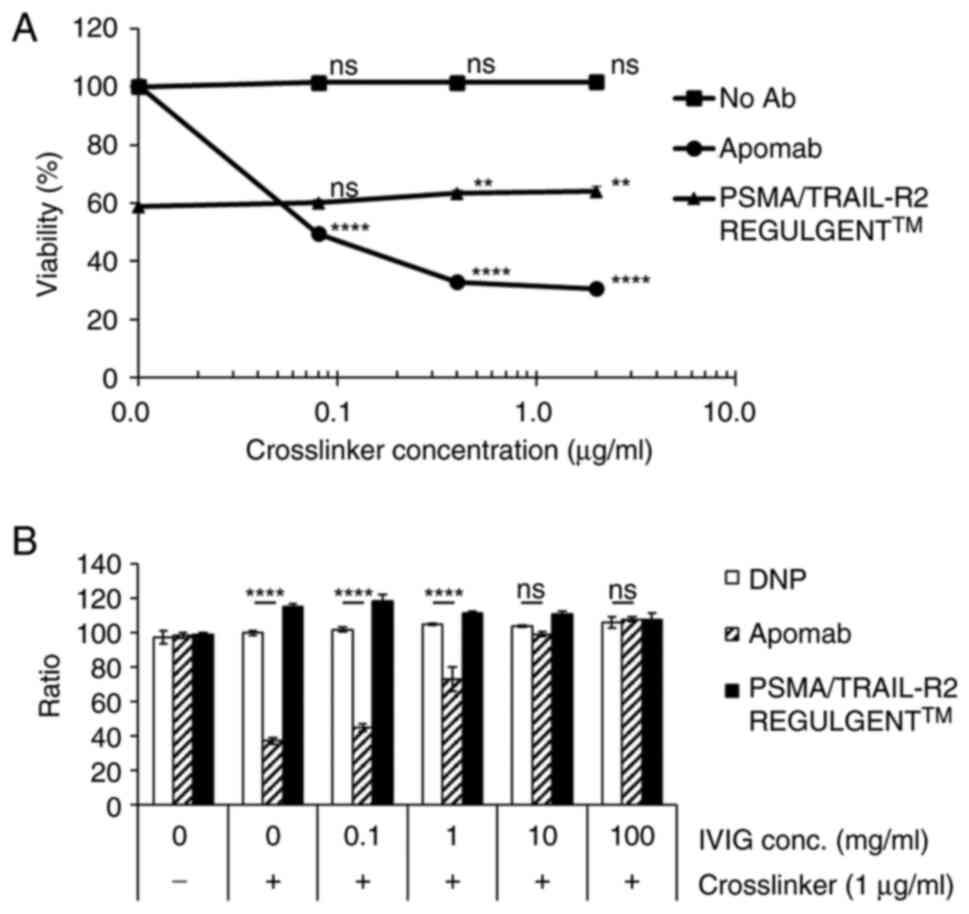
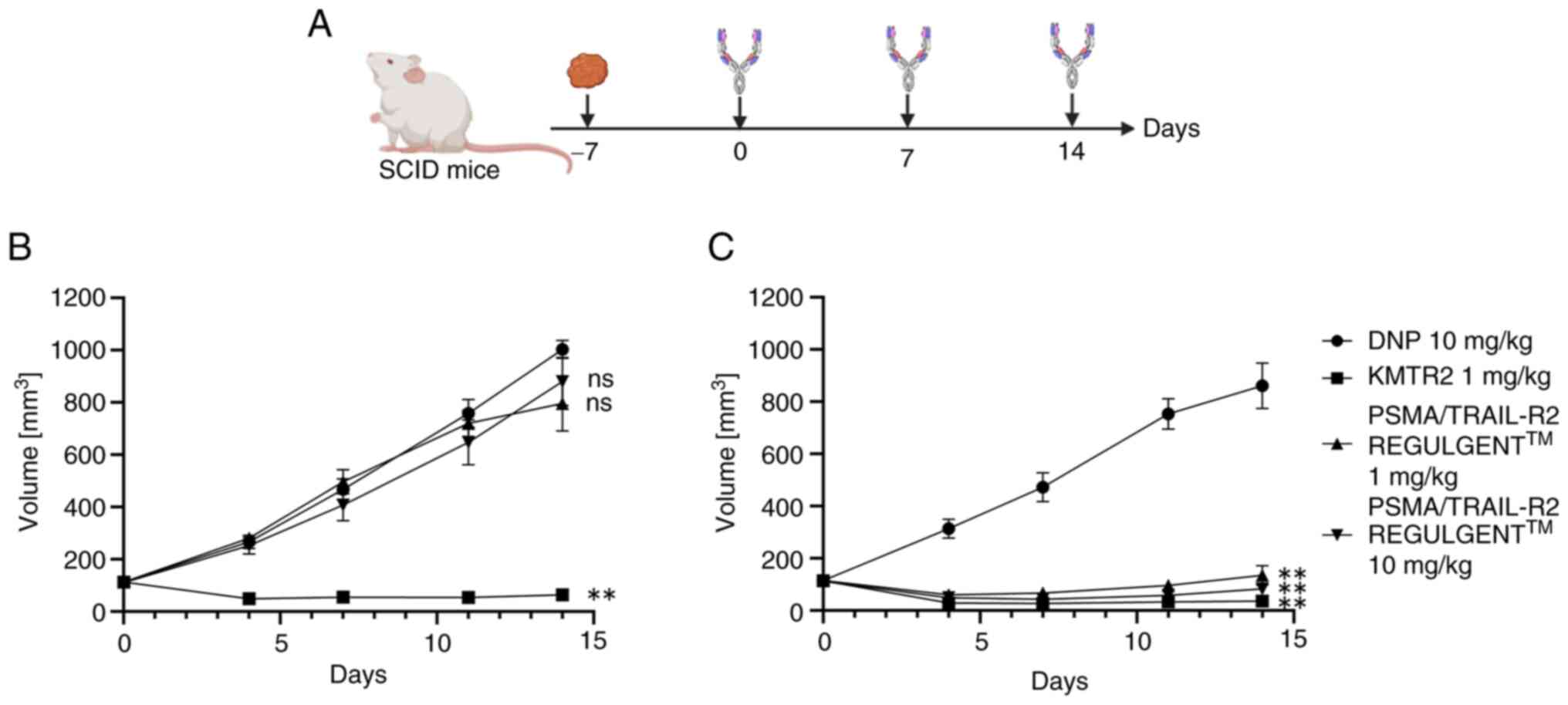
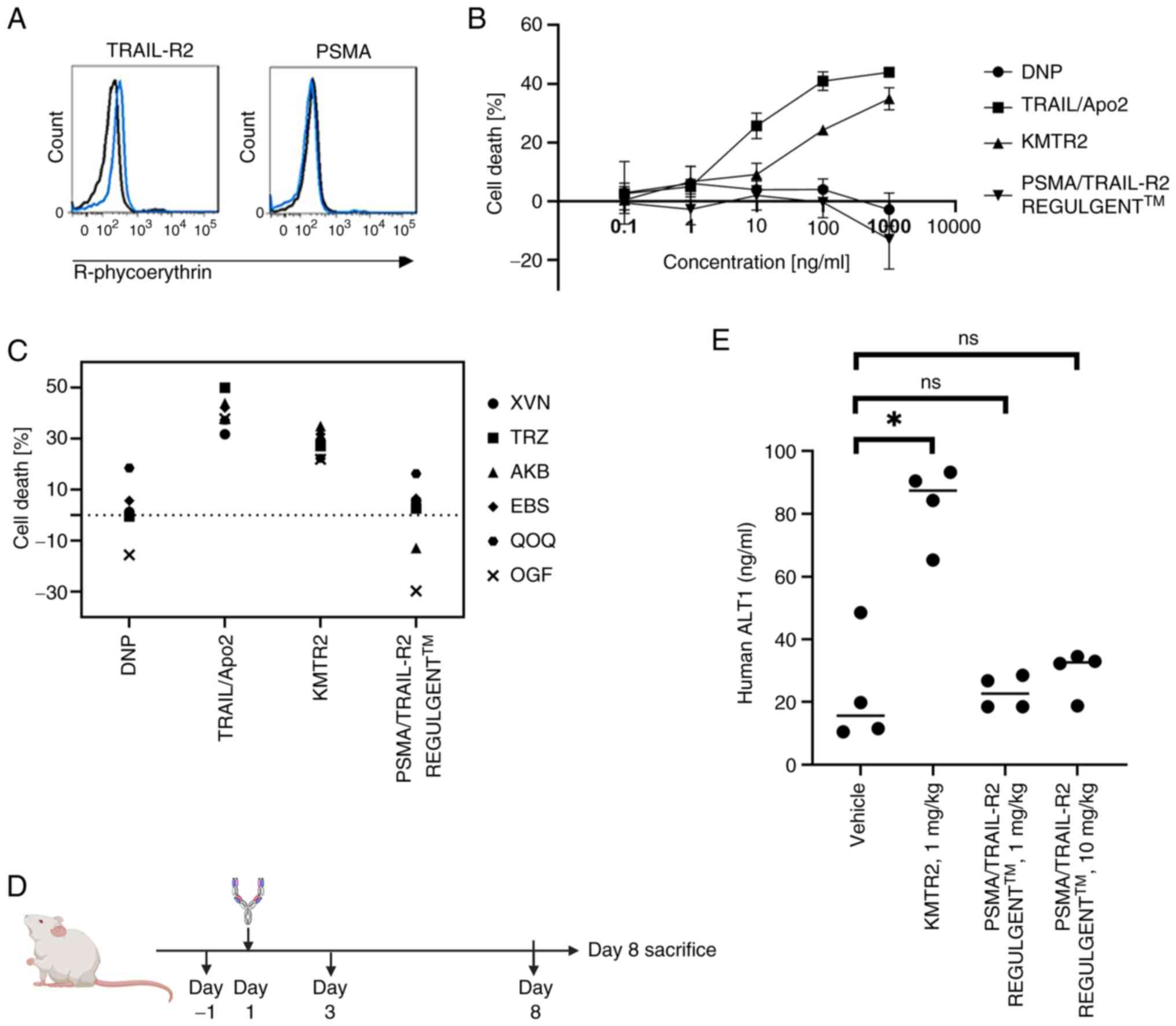
|
1
|
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S,
Lawrence DA, Marsters SA, Blackie C, Chang L, McMurtrey AE, Hebert
A, et al: Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2
ligand. J Clin Invest. 104:155–162. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Snajdauf M, Havlova K, Vachtenheim J Jr,
Ozaniak A, Lischke R, Bartunkova J, Smrz D and Strizova Z: The
TRAIL in the treatment of human cancer: An update on clinical
trials. Front Mol Biosci. 8:6283322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yada A, Yazawa M, Ishida S, Yoshida H,
Ichikawa K, Kurakata S and Fujiwara K: A novel humanized anti-human
death receptor 5 antibody CS-1008 induces apoptosis in tumor cells
without toxicity in hepatocytes. Ann Oncol. 19:1060–1067. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fuchs CS, Fakih M, Schwartzberg L, Cohn
AL, Yee L, Dreisbach L, Kozloff MF, Hei YJ, Galimi F, Pan Y, et al:
TRAIL receptor agonist conatumumab with modified FOLFOX6 plus
bevacizumab for first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal
cancer: A randomized phase 1b/2 trial. Cancer. 119:4290–4298. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Motoki K, Mori E, Matsumoto A, Thomas M,
Tomura T, Humphreys R, Albert V, Muto M, Yoshida H Aoki, et al:
Enhanced apoptosis and tumor regression induced by a direct agonist
antibody to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
receptor 2. Clin Cancer Res. 11:3126–3135. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nihira K, Nan-Ya KI, Kakuni M, Ono Y,
Yoshikawa Y, Ota T, Hiura M and Yoshinari K: Chimeric mice with
humanized livers demonstrate human-specific hepatotoxicity caused
by a therapeutic antibody against TRAIL-receptor 2/death receptor
5. Toxicol Sci. 167:190–201. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Papadopoulos KP, Isaacs R, Bilic S,
Kentsch K, Huet HA, Hofmann M, Rasco D, Kundamal N, Tang Z, Cooksey
J and Mahipal A: Unexpected hepatotoxicity in a phase I study of
TAS266, a novel tetravalent agonistic Nanobody®
targeting the DR5 receptor. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 75:887–895.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hutt M, Fellermeier-Kopf S, Seifert O,
Schmitt LC, Pfizenmaier K and Kontermann RE: Targeting
scFv-Fc-scTRAIL fusion proteins to tumor cells. Oncotarget.
9:11322–11335. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu Y, Bassoff N, Reinshagen C, Bhere D,
Nowicki MO, Lawler SE, Roux J and Shah K: Bi-specific molecule
against EGFR and death receptors simultaneously targets
proliferation and death pathways in tumors. Sci Rep. 7:26022017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brünker P, Wartha K, Friess T,
Grau-Richards S, Waldhauer I, Koller CF, Weiser B, Majety M, Runza
V, Niu H, et al: RG7386, a novel tetravalent FAP-DR5 antibody,
effectively triggers FAP-dependent, avidity-driven DR5
hyperclustering and tumor cell apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther.
15:946–957. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shivange G, Urbanek K, Przanowski P, Perry
JSA, Jones J, Haggart R, Kostka C, Patki T, Stelow E, Petrova Y, et
al: A single-agent dual-specificity targeting of FOLR1 and DR5 as
an effective strategy for ovarian cancer. Cancer Cell.
34:331–345.e311. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
García-Martínez JM, Wang S, Weishaeupl C,
Wernitznig A, Chetta P, Pinto C, Ho J, Dutcher D, Gorman PN,
Kroe-Barrett R, et al: Selective tumor cell apoptosis and tumor
regression in CDH17-positive colorectal cancer models using BI
905711, a novel liver-sparing TRAILR2 agonist. Mol Cancer Ther.
20:96–108. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Goldmacher VS, Gershteyn I, Chari R and
Kovtun Y: A bispecific anti-MUC16/anti-death receptor 5 antibody
achieves effective and tumor-selective death receptor 5-mediated
tumor regression. Sci Rep. 15:99092025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Minner S, Wittmer C, Graefen M, Salomon G,
Steuber T, Haese A, Huland H, Bokemeyer C, Yekebas E, Dierlamm J,
et al: High level PSMA expression is associated with early PSA
recurrence in surgically treated prostate cancer. Prostate.
71:281–288. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang HL, Wang SS, Song WH, Pan Y, Yu HP,
Si TG, Liu Y, Cui XN and Guo Z: Expression of prostate-specific
membrane antigen in lung cancer cells and tumor neovasculature
endothelial cells and its clinical significance. PLoS One.
10:e01259242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tolkach Y, Gevensleben H, Bundschuh R,
Koyun A, Huber D, Kehrer C, Hecking T, Keyver-Paik MD, Kaiser C,
Ahmadzadehfar H, et al: Prostate-specific membrane antigen in
breast cancer: A comprehensive evaluation of expression and a case
report of radionuclide therapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
169:447–455. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Andryszak N, Kurzawa P, Krzyżaniak M,
Nowicki M, Ruchała M, Iżycki D and Czepczyński R: Evaluation of
prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) immunohistochemical
expression in early-stage breast cancer ubtypes. Int J Mol Sci.
25:65192024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Milowsky MI, Nanus DM, Kostakoglu L,
Sheehan CE, Vallabhajosula S, Goldsmith SJ, Ross JS and Bander NH:
Vascular targeted therapy with anti-prostate-specific membrane
antigen monoclonal antibody J591 in advanced solid tumors. J Clin
Oncol. 25:540–547. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tolmachev V, Malmberg J, Estrada S,
Eriksson O and Orlova A: Development of a 124I-labeled version of
the anti-PSMA monoclonal antibody capromab for immunoPET staging of
prostate cancer: Aspects of labeling chemistry and biodistribution.
Int J Oncol. 44:1998–2008. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang Z, Guo J, Hu L, Yang S, Meng B and
Tang Q; Diagnostic performance of (18)F-DCFPyL PET vs. (68)Ga-PSMA
PET/CT in patients with suspected prostate cancer, : A systemic
review and meta-analysis. Oncol Lett. 2024.27:188 View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Simon H, Henkel D, Chiron P and Helissey
C: New perspectives on metabolic imaging in the management of
prostate cancer in 2022: A focus on radiolabeled PSMA-PET/CT
(Review). Mol Clin Oncol. 19:512023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Petrylak DP, Vogelzang NJ, Chatta K,
Fleming MT, Smith DC, Appleman LJ, Hussain A, Modiano M, Singh P,
Tagawa ST, et al: PSMA ADC monotherapy in patients with progressive
metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer following
abiraterone and/or enzalutamide: efficacy and safety in open-label
single-arm phase 2 study. Prostate. 80:99–108. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Saga T, Nakamoto Y, Ishimori T, Inoue T,
Shimizu Y, Kimura H, Akamatsu S, Goto T, Watanabe H, Kitaguchi K,
et al: Initial evaluation of PET/CT with (18) F-FSU-880 targeting
prostate-specific membrane antigen in prostate cancer patients.
Cancer Sci. 110:742–750. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hou H, Lin Y, Pan Y, Ma Y, Hou G, Sun X
and Gao F: Synthesis and preclinical evaluation of (68)Ga-labeled
PSMA tracers with improved pharmacological properties. Eur J Med
Chem. 274:1165452024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Droghetti M, Bianchi L, Presutti M,
Vetrone L, Farolfi A, Mei R, Giunchi F, Degiovanni A, Mottaran A,
Piazza P, et al: Immunohistochemistry analysis of PSMA expression
at prostatic biopsy in high-risk prostate cancer: Potential
implications for PSMA-PET patient selection. Front Oncol.
14:13246312024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mori E, Thomas M, Motoki K, Nakazawa K,
Tahara T, Tomizuka K, Ishida I and Kataoka S: Human normal
hepatocytes are susceptible to apoptosis signal mediated by both
TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2. Cell Death Differ. 11:203–207. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Krah S, Schröter C, Eller C, Rhiel L,
Rasche N, Beck J, Sellmann C, Günther R, Toleikis L, Hock B, et al:
Generation of human bispecific common light chain antibodies by
combining animal immunization and yeast display. Protein Eng Des
Sel. 30:291–301. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ishida I, Tomizuka K, Yoshida H, Tahara T,
Takahashi N, Ohguma A, Tanaka S, Umehashi M, Maeda H, Nozaki C, et
al: Production of human monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies in
TransChromo animals. Cloning Stem Cells. 4:91–102. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Namisaki H, Saito S, Hiraishi K, Haba T,
Tanaka Y, Yoshida H, Iida S and Takahashi N: R409K mutation
prevents acid-induced aggregation of human IgG4. PLoS One.
15:e02290272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Merchant AM, Zhu Z, Yuan JQ, Goddard A,
Adams CW, Presta LG and Carter P: An efficient route to human
bispecific IgG. Nat Biotechnol. 16:677–681. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hezareh M, Hessell AJ, Jensen RC, van de
Winkel JG and Parren PW: Effector function activities of a panel of
mutants of a broadly neutralizing antibody against human
immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 75:12161–12168. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Camidge DR: Apomab: An agonist monoclonal
antibody directed against death receptor 5/TRAIL-receptor 2 for use
in the treatment of solid tumors. Expert Opin Biol Ther.
8:1167–1176. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zinonos I, Labrinidis A, Lee M, Liapis V,
Hay S, Ponomarev V, Diamond P, Zannettino AC, Findlay DM and
Evdokiou A: Apomab, a fully human agonistic antibody to DR5,
exhibits potent antitumor activity against primary and metastatic
breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:2969–2980. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tateno C, Iwanari H, Shimada T, Kimura T,
Iwasaki Y, Yamasaki C, Kakuni M and Ishida Y: Detection of human
hepatic toxicity in chimeric mice with humanized liver by human
ALT1 ELISA system. The 53rd Annual Meeting of the Society of
Toxicology Phoenix, AZ: 2014
|
|
35
|
Mori E, Thomas M, Motoki K and Kataika S:
Distinct function of monoclonal antibody to TRAIL-R2 as potentiator
or inhibitor of the ligand TRAIL-induced apoptosis. FEBS Lett.
579:5379–5384. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Saito S, Nakayama M, Yamazaki K, Miyamoto
Y, Hiraishi K, Tomioka D, Takagi-Maeda S, Usami K, Takahashi N,
Nara S and Imai E: Engineering and physicochemical characterization
of a novel, stable, symmetric bispecific antibody with dual
target-binding using a common light chain. Protein Sci.
33:e51212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cieślewicz M, Andryszak N, Pełka K,
Szczepanek-Parulska E, Ruchała M, Kunikowska J and Czepczyński R:
Evaluation of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)
immunohistochemical expression in early-stage breast cancer
subtype. Int J Mol Sci. 25:65192024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Harding JJ, Hofheinz RD, Elez E, Kuboki Y,
Rasco DW, Cecchini M, Shen L, He M, Archuadze S, Chhaya N and Pant
S: A phase Ia/b first-in-human, open-label, multicenter study of BI
905711, a bispecific TRAILR2 agonist, in patients with advanced
gastrointestinal cancers. J Clin Oncol. 41:115. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P,
Hofmann K, Steiner V, Bodmer JL, Schröter M, Burns K, Mattmann C,
et al: Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP.
Nature. 388:190–195. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shankar S, Chen X and Srivastava RK:
Effects of sequential treatments with chemotherapeutic drugs
followed by TRAIL on prostate cancer in vitro and in vivo.
Prostate. 62:165–186. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nazim UM, Yin H and Park SY: Neferine
treatment enhances the TRAIL-induced apoptosis of human prostate
cancer cells via autophagic flux and the JNK pathway. Int J Oncol.
56:1152–1161. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Koschny R, Ganten TM, Sykora J, Haas TL,
Sprick MR, Kolb A, Stremmel W and Walczak H: TRAIL/bortezomib
cotreatment is potentially hepatotoxic but induces cancer-specific
apoptosis within a therapeutic window. Hepatology. 45:649–658.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang J, Xiu M, Wang J, Gao Y and Li Y:
Proteasome inhibition sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells,
but not human hepatocytes, to TRAIL. Hepatology. 42:588–597. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Koschny R, Holland H, Sykora J, Erdal H,
Krupp W, Bauer M, Bockmuehl U, Ahnert P, Meixensberger J, Stremmel
W, et al: Bortezomib sensitizes primary human esthesioneuroblastoma
cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. J Neurooncol. 97:171–185. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang FJ, Steeg PS, Price JE, Chiu WT,
Chou PC, Xie K, Sawaya R and Huang S: Molecular basis for the
critical role of suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 in melanoma
brain metastasis. Cancer Res. 68:9634–9642. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cristofanon S and Fulda S: ABT-737
promotes tBid mitochondrial accumulation to enhance TRAIL-induced
apoptosis in glioblastoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 3:e4322012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lemke J, von Karstedt S, Zinngrebe J and
Walczak H: Getting TRAIL back on track for cancer therapy. Cell
Death Differ. 21:1350–1364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Montinaro A, Areso Zubiaur I, Saggau J,
Kretz AL, Ferreira RMM, Hassan O, Kitzig E, Müller I, El-Bahrawy
MA, von Karstedt S, et al: Potent pro-apoptotic combination therapy
is highly effective in a broad range of cancers. Cell Death Differ.
29:492–503. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Xiuhan S, Xiangyu H and Bao TZ: Role of
mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in chemically-induced
ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 223:473–492. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Suzuki-Karasaki M, Ochiai T and
Suzuki-Karasaki Y: Crosstalk between mitochondrial ROS and
depolarization in the potentiation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis in
human tumor cells. Int J Oncol. 44:616–628. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kaur M, Rüger K, Chen EC, Rangaswamy US,
Davison LM, Arteaga SM, Smith I, Chu R, Chattopadhyay S, Rickert M,
et al: Potency-optimized CD28-activating bispecific antibody for
the targeted treatment of Nectin-4 positive cancers. J Immunother
Cancer. 13:e0113232025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|